Study on the Coupling Development of Industry, City and Population in the Yellow River Basin from the Perspective of Green Economy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Indicator System and Research Methodology
2.1. Indicator System
2.2. Research Methodology
2.2.1. Comprehensive Evaluation Method
2.2.2. Coupling Model
2.2.3. Kernel Density Estimation
2.2.4. Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis
3. Evaluation of the Coupled Development of Industry, City and Population in the Yellow River Basin
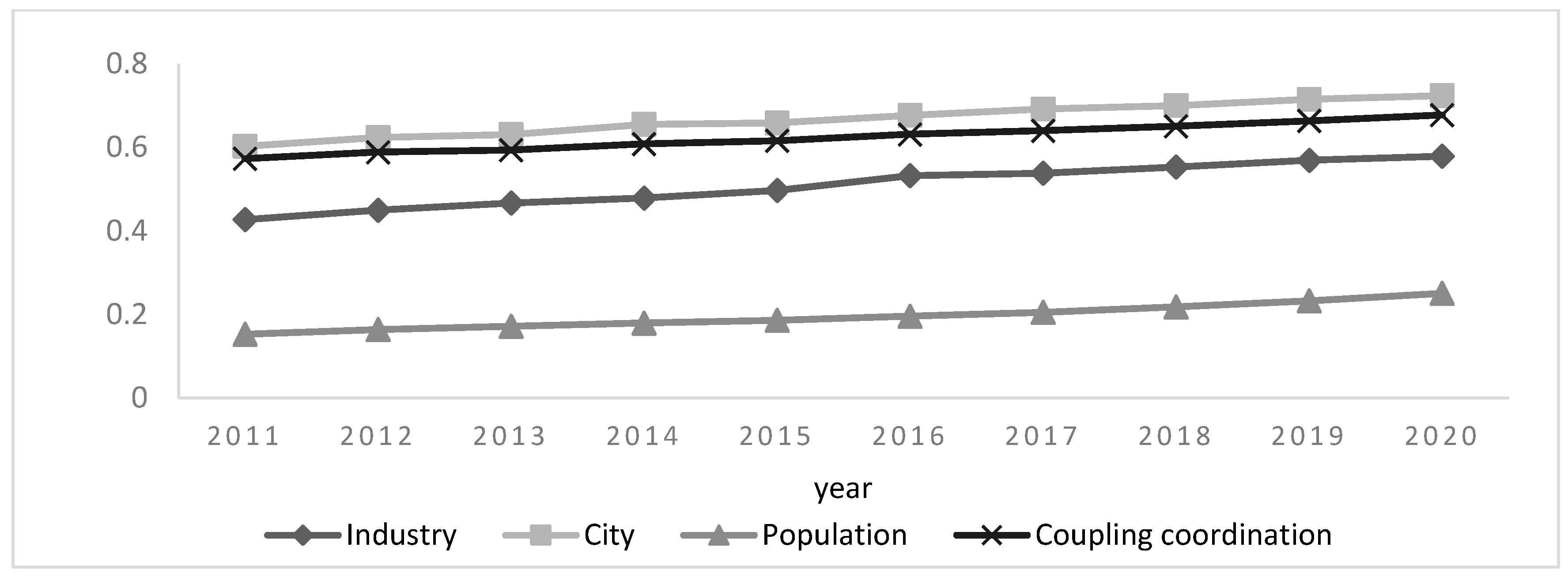
3.1. Evaluation of Industry, City and Population System in the Yellow River Basin
3.2. Evaluation of the Coupled Development of Industry, City and Population in the Yellow River Basin
4. Analysis of the Spatial and Temporal Characteristics
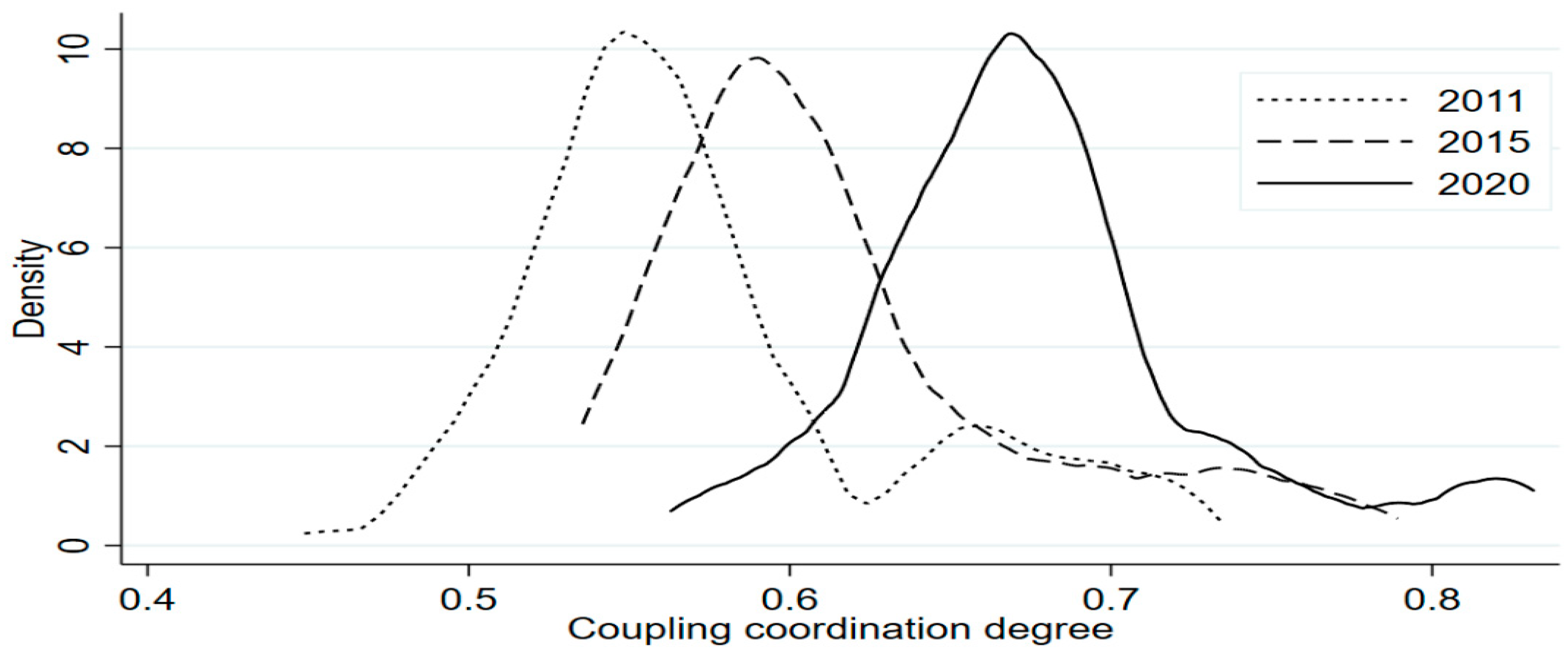
4.1. Spatio-Temporal Evolution Analysis
4.2. Spatial Correlation Analysis
4.2.1. Global Spatial Correlation
4.2.2. Local Spatial Correlation
5. Analysis of the Influence Factors
5.1. Model Construction
5.2. Analysis of Influencing Factors
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, H.; Lee, C.C.; Zhou, F. Green credit policy, credit allocation efficiency and upgrade of energy-intensive enterprises. Energy Econ. 2021, 94, 105099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, L.; Sheng, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Qiu, D.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Q.; et al. Evaluation of regional sustainability through emergy analysis: A case study of nine cities in the Yellow River Basin of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 40213–40225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.C.; Ye, Q.; Sun, Y.P. Financial Innovation. Information Screening and Industries’ Green Innovation—Industry-Level Evidence from the OECD. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 17, 120998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.Q.; Yang, D.W.; Yang, F.; Luken, R.; Saieed, A.; Wang, K. Green Industry Development in China:An Index Based Assessment from Perspectives of both Current Performance and Historical Effort. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artmann, M.; Kohler, M.; Meinel, G.; Gan, J.; Ioja, I.C. How Smart Growth and Green Infrastructure can Mutually Support each Other—A Conceptual Framework for Compact and Green Cities. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.J.; Dong, X.; Zhao, X.M.; Zhu, A. Evaluation of Urban Green Development Transformation Process for Chinese Cities during 2005–2016. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, M.; Ma, S.J. The Effect of the Spatial Heterogeneity of Human Capital Structure on Regional Green Total Factor Productivity. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2021, 59, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.L.; Li, H.Z.; Ghosal, V. Firm-Level Human Capital and Innovation: Evidence from China. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 59, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Ivanovski, K.; Inekwe, J.; Smyth, R. Human Capital and Energy Consumption: Evidence from OECD Countries. Energy Econ. 2019, 84, 104534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Hossain, M.R.; Badeeb, R.A.; Zhang, C. Aggregate and Disaggregate Impact of Natural Resources on Economic Performance: Role of Green Growth and Human Capital. Resour. Policy 2023, 80, 103103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Godil, D.I.; Bibi, M.; Khan, M.K.; Sarwat, S.; Anser, M.K. Caring for the Environment: How Human Capital, Natural Resources, and Economic Growth Interact with Environmental Degradation in Pakistan? A Dynamic ARDL Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, G.; D’Alessandro, S. Systems-Dynamic Analysis of Employment and Inequality Impacts of Low-Carbon Investments. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2016, 21, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.F.; Zhang, X.X. Analysis on the Influence of Urban Living Environment on Healthy Human Capital Based on Health Production Function. In Proceedings of the 2020 Management Science Informatization and Economic Innovation Development Conference (MSIEID), Guangzhou, China, 18–20 December 2020; pp. 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Heblich, S.; Trew, A.; Zylberberg, Y. East-Side Story: Historical Pollution and Persistent Neighborhood Sorting. J. Political Econ. 2021, 129, 1508–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yue, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, M. Air Pollution, Human Capital, and Urban Innovation in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 38031–38051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Shi, H.; Hu, Y.; Lev, B.; Lan, H. Coupling Coordination Degree for Urbanization City-Industry Integration Level: Sichuan Case. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 58, 102136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Xiao, J. The Urban City-Industry Integration Degree Evaluation Based on Ordinal Logistic Regression. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th Annual International Conference on Network and Information Systems for Computers (ICNISC), Guiyang, China, 23–25 July 2021; pp. 582–588. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.L. Research on the Planning and Design of Sports Characteristic Town Based on the Integration of “Human Culture in Industry City”, IOP Conference Series. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 525, 12120. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Fan, M.; Yang, L.; Shao, S. Heterogeneous Green Innovations and Carbon Emission Performance: Evidence at China’s City Level. Energy Econ. 2021, 99, 105269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.Z.; Liang, L. Regional Environmental Efficiency in China: An Empirical Analysis Based on Entropy Weight Method and Non-Parametric Models. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y. China’s Multi-Dimensional Ecological Well-being Performance Evaluation: A New Method Based on Coupling Coordination Model. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzen, E. On Estimation of a Probability Density Function and Mode. Ann. Math. Stat. 1962, 33, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Yang, J. Total-Factor Industrial Eco-Efficiency and its Influencing Factors in China: A Spatial Panel Data Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Wang, Q. Research on the Impact of Green Finance on the Upgrading of China’s Regional Industrial Structure from the Perspective of Sustainable Development. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, R.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, D.; Xia, Y. Can Green Financial Development Promote Renewable Energy Investment Efficiency? A Consideration of Bank Credit. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecklin, D.R.; Sepulveda, C. The Diverse Properties of Private Land Conservation in Chile: Growth and Barriers to Private Protected Areas in a Market-friendly Context. Conserv. Soc. 2014, 12, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, D.C. Accounting for Loss of Variety and Factor Reallocations in the Welfare Cost of Regulations. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 88, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, P.M. Environmental regulation and green investments: The role of green finance. Int. J. Green Econ. 2020, 14, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Industry | City | Population |
|---|---|---|
| Tertiary sector share | Greening coverage rate of built-up areas | Per capita expenditure on science and technology |
| Energy consumption intensity * | Public green space per capita | Per capita expenditure on education |
| Per capita gross regional product | Harmless treatment rate of domestic waste | Percentage of students in general primary and secondary schools |
| Comprehensive utilization rate of general industrial solid waste | Sewage treatment rate | Number of science and technology personnel per 10,000 people |
| Industrial wastewater emission intensity * | Per capita domestic electricity consumption * | Urbanization rate |
| Industrial SO2 emission intensity * | Number of buses per 10,000 people | Number of books in public libraries per 100 people |
| Industrial smoke (dust) emission intensity * | Per capita domestic water consumption * | Percentage of college students in school |
| Industrial CO2 emission intensity * | Annual average concentration of pm 2.5 * | Number of patents granted to 10,000 people |
| Index | Year | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| I | 0.378 | 0.256 | 0.239 | 0.206 | 0.214 | 0.423 | 0.293 | 0.202 | 0.293 | 0.284 |
| Z | 5.685 | 4.146 | 3.881 | 3.077 | 3.192 | 6.342 | 4.315 | 3.031 | 4.127 | 4.043 |
| P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Influencing Factors | Industry | City | Population | Coupling Coordination |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Regulation | 0.028 * | 0.045 *** | −0.009 | 0.017 ** |
| (0.015) | (0.012) | (0.011) | (0.008) | |
| Government Regulation | 0.305 *** | 0.442 *** | 0.217 *** | 0.301 *** |
| (0.052) | (0.047) | (0.044) | (0.035) | |
| External Opening | 0.046 *** | 0.016 *** | 0.013 *** | 0.016 *** |
| (0.006) | (0.004) | (0.004) | (0.003) | |
| Green Finance | 0.871 *** | 0.614 *** | 0.534 *** | 0.574 *** |
| (0.052) | (0.045) | (0.04) | (0.032) | |
| _cons | −0.01 | 0.309 *** | −0.057 ** | 0.319 *** |
| (0.03) | (0.026) | (0.025) | (0.019) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, X.; Ci, F. Study on the Coupling Development of Industry, City and Population in the Yellow River Basin from the Perspective of Green Economy. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10029. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310029
Cao X, Ci F. Study on the Coupling Development of Industry, City and Population in the Yellow River Basin from the Perspective of Green Economy. Sustainability. 2023; 15(13):10029. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310029
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Xiangdong, and Fuyi Ci. 2023. "Study on the Coupling Development of Industry, City and Population in the Yellow River Basin from the Perspective of Green Economy" Sustainability 15, no. 13: 10029. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310029
APA StyleCao, X., & Ci, F. (2023). Study on the Coupling Development of Industry, City and Population in the Yellow River Basin from the Perspective of Green Economy. Sustainability, 15(13), 10029. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310029







