A Methodological Review on Development of Crack Healing Technologies of Asphalt Pavement
Abstract
1. Background
2. Crack Healing Theories
3. Evaluation Methods of Crack Healing
4. Crack Healing Technologies
4.1. Hot Pouring
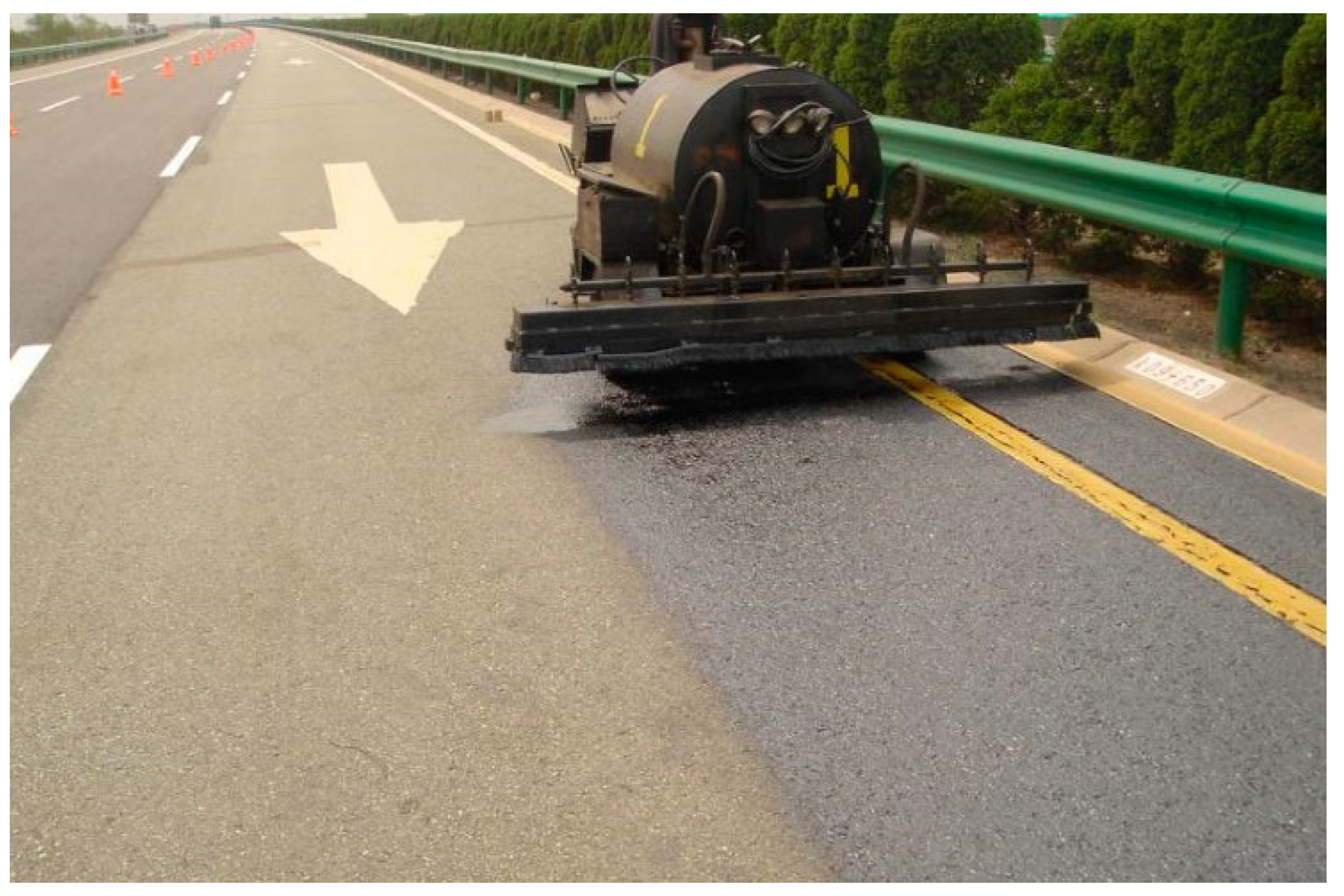
4.2. Fog Sealing
4.3. Heating Technologies
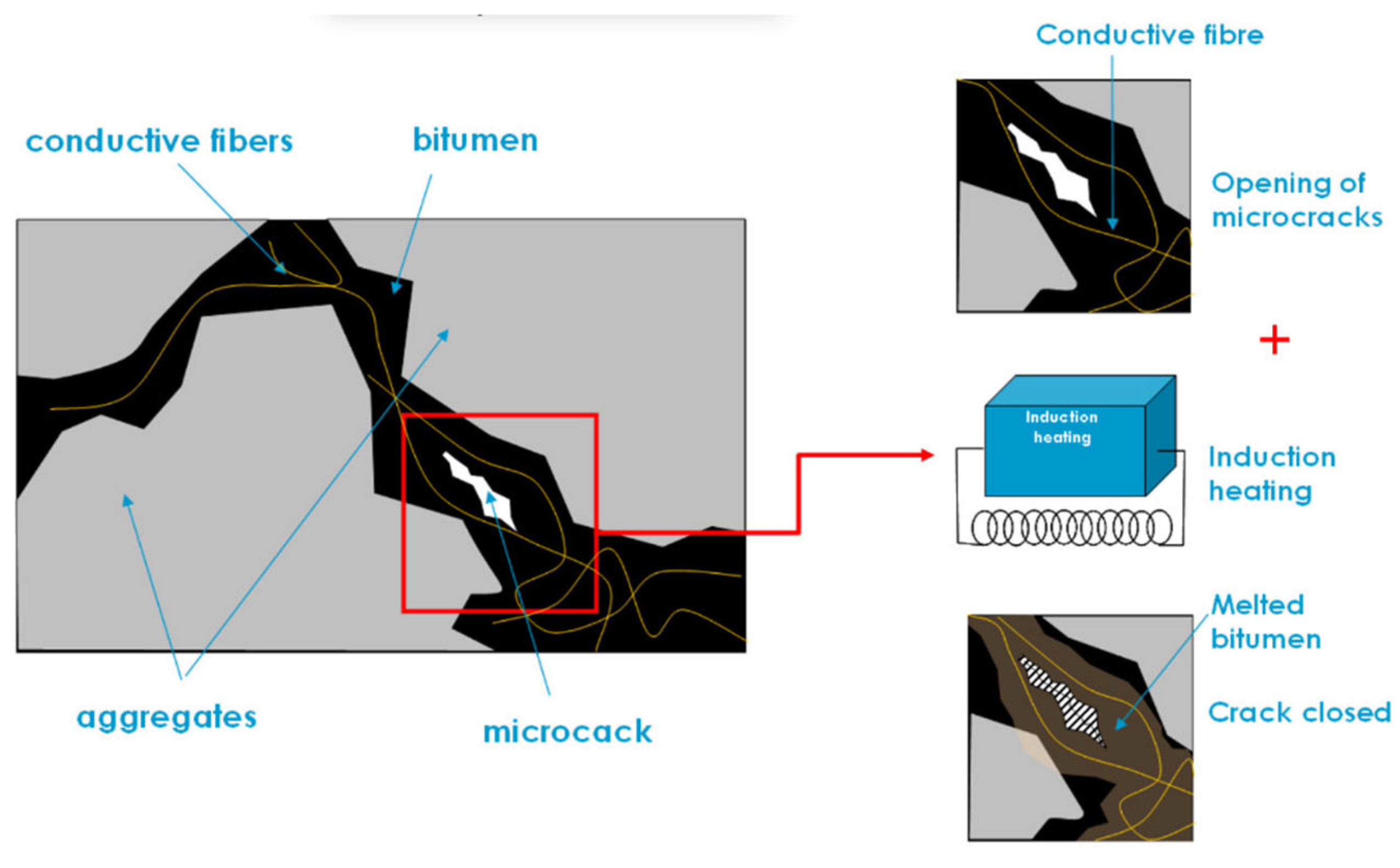
4.3.1. Induction Heating
4.3.2. Microwave Heating
4.4. Agents Encapsulated Technology
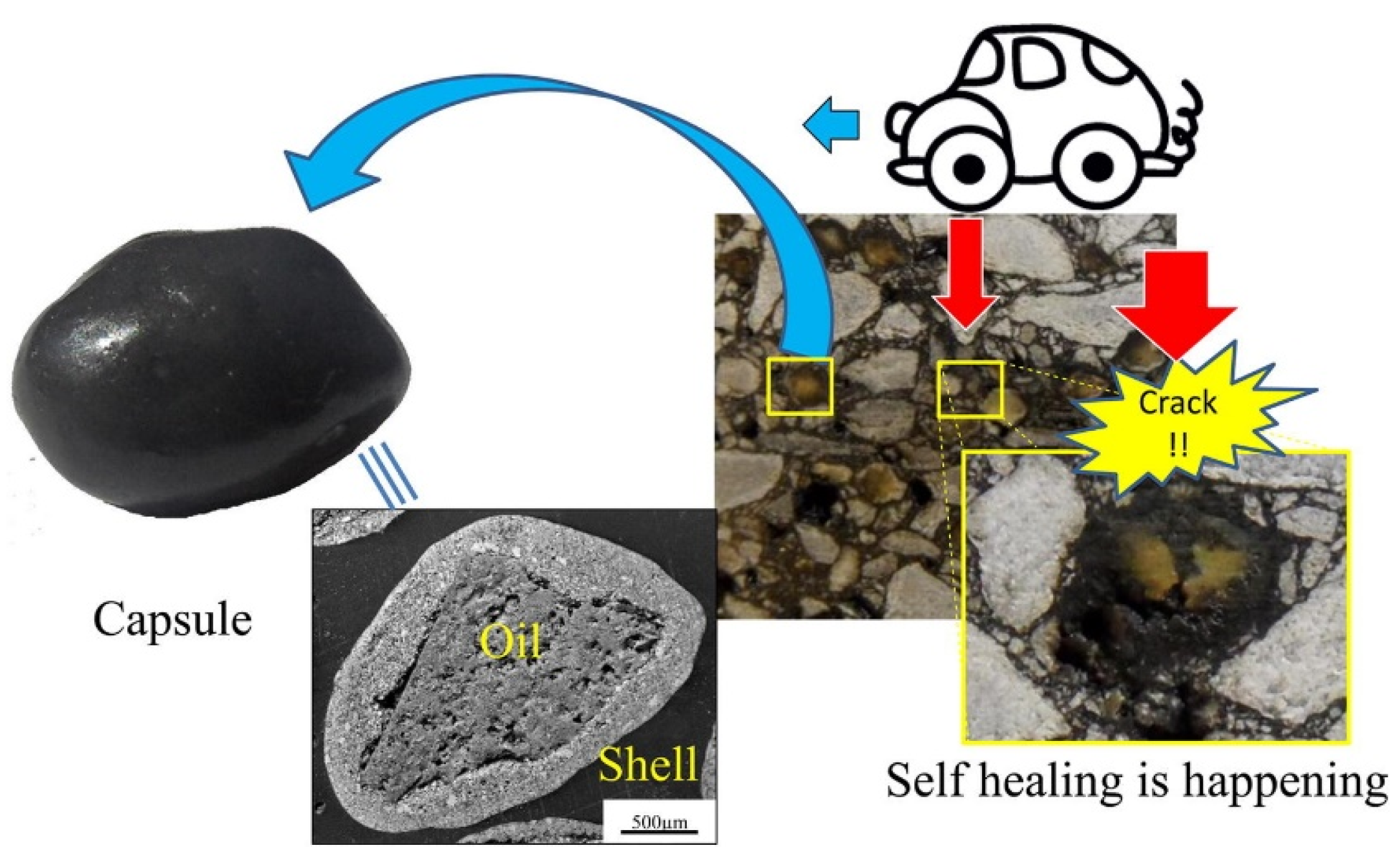
4.4.1. Saturated Porous Aggregates Encapsulate Rejuvenators
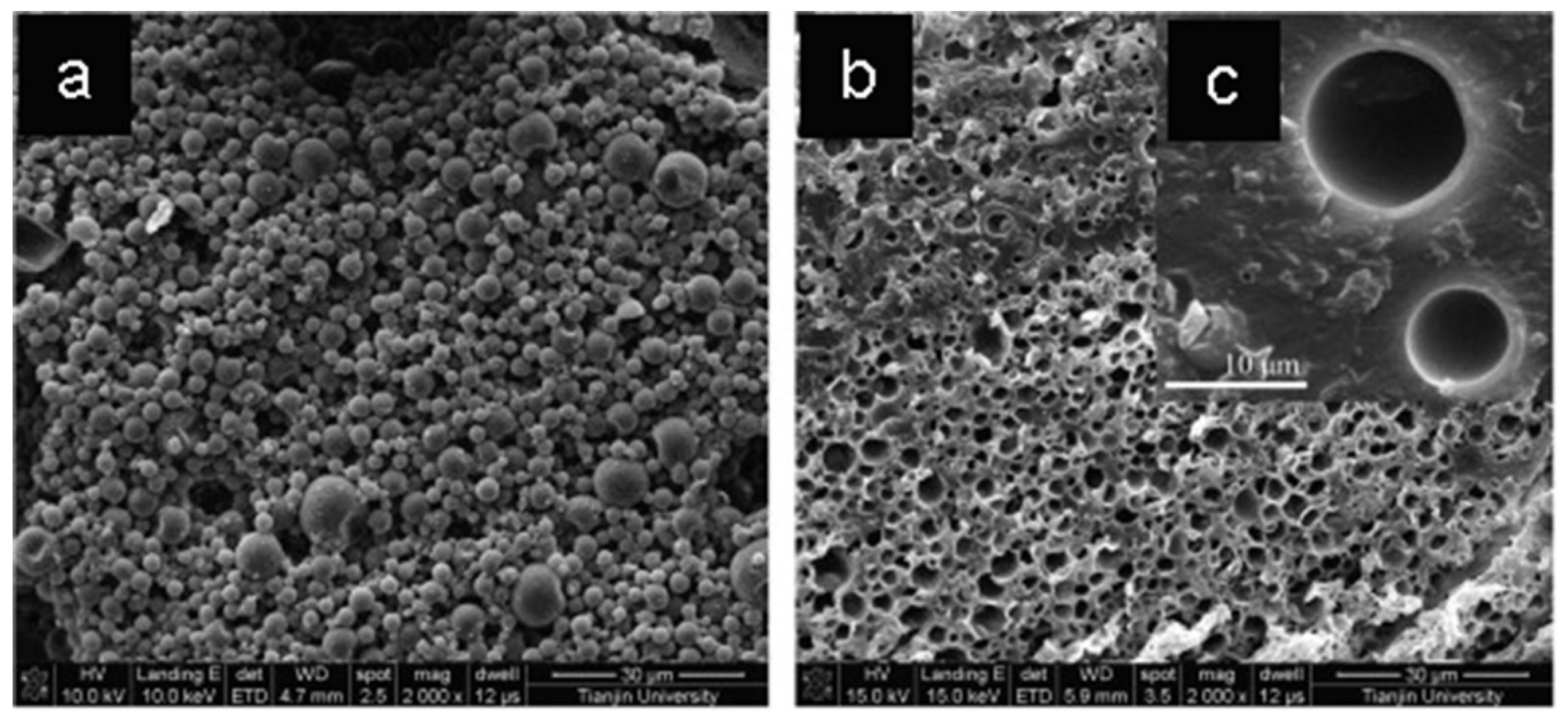
4.4.2. Core-Shell Polymeric Microcapsules
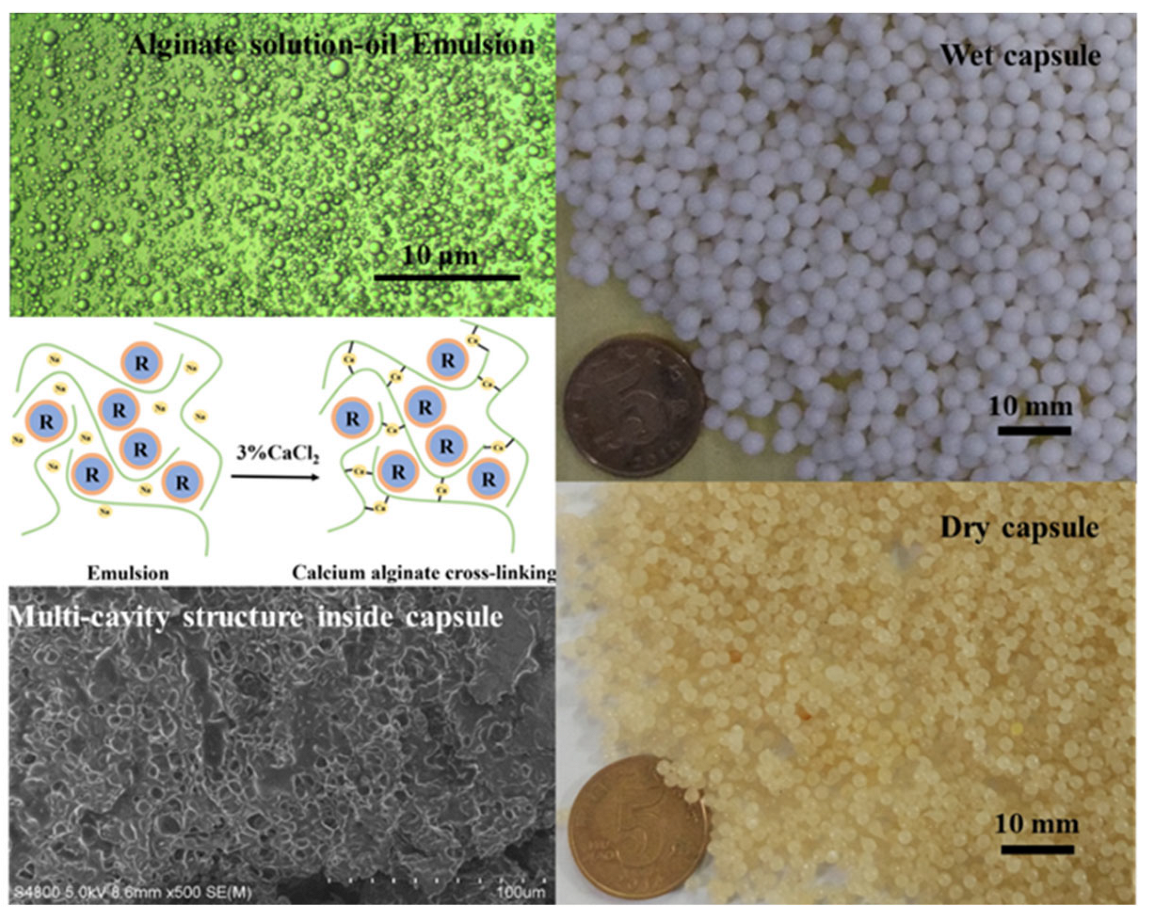
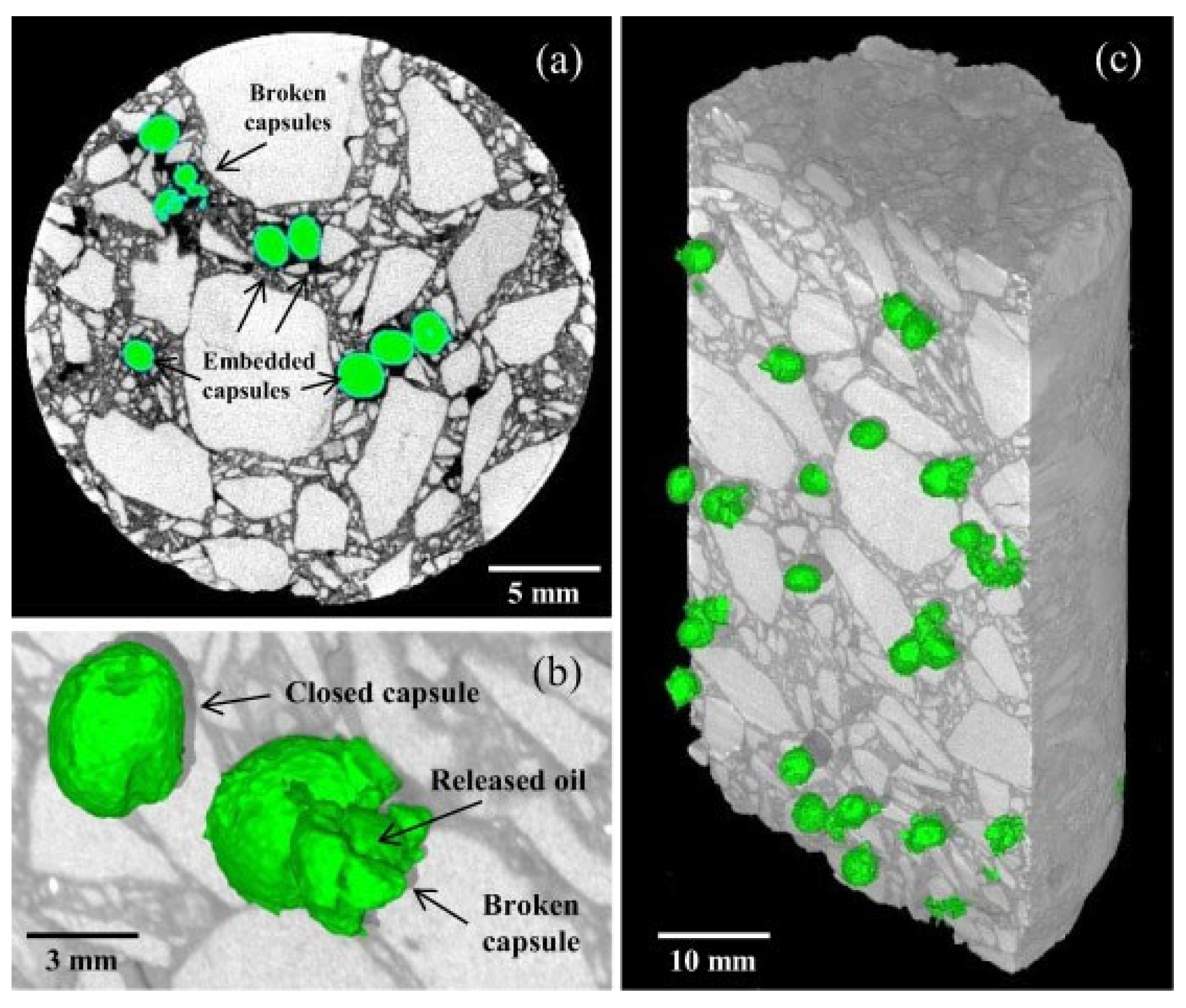
4.4.3. Ca-Alginate Capsule
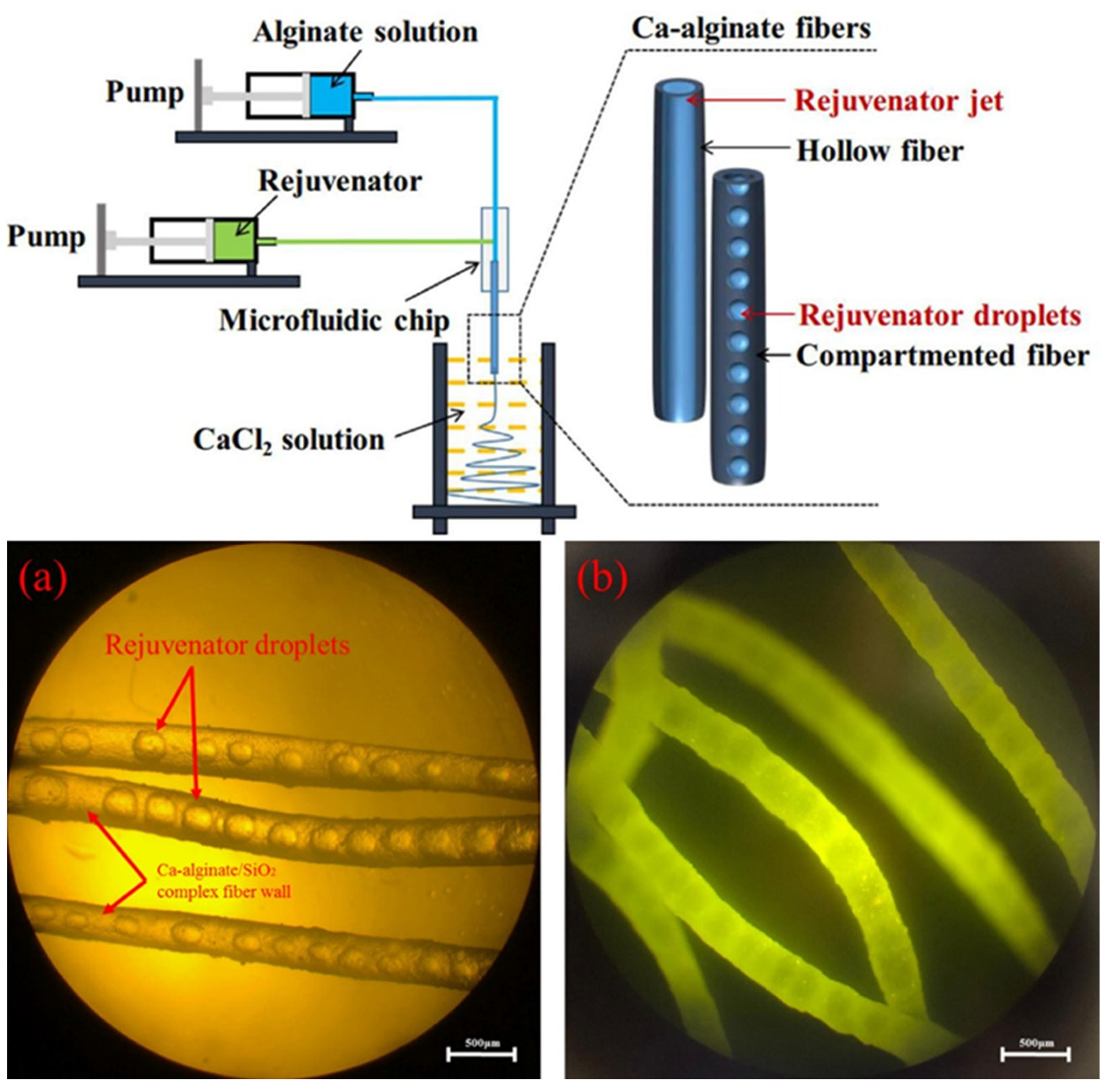
4.4.4. Hollow Fibers
4.4.5. Compartment Fibers
4.5. Other Technologies
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.H. Pavement Analysis and Design; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Hicks, R.G. Moisture Damage in Asphalt Concrete; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Xie, J.; Wu, S.; Li, J.; Barbieri, D.M.; Zhang, L. Life cycle energy consumption by roads and associated interpretative analysis of sustainable policies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 141, 110823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, Q.; Xie, J.; Wu, S. Energy Consumption and Environment Performance Analysis of Induction-Healed Asphalt Pavement by Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). Materials 2021, 14, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondi, G.; Pettinari, M.; Sangiorgi, C.; Wu, R. Designing long life pavements including eco-friendly ACs by means of the Mechanistic-Empirical approach. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 53, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santero, N.J.; Harvey, J.; Horvath, A. Environmental policy for long-life pavements. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2011, 16, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Dong, W.; Fu, Z.; Wang, R.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J. Life cycle assessment of greenhouse gas emissions from asphalt pavement maintenance: A case study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, H.; Nejad, F.M.; Fahimifar, A. Image based techniques for crack detection, classification and quantification in asphalt pavement: A review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2017, 24, 935–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Hossiney, N.; Ma, Z.; Wang, H. Insight into the effects of waste vegetable oil on self-healing behavior of bitumen binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 363, 129888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Sun, G.; Zhu, X.; Guarin, A.; Li, B.; Dai, Z.; Ling, J. A comprehensive review on self-healing of asphalt materials: Mechanism, model, characterization and enhancement. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 256, 65–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office, J.E.; Chen, J.; Dan, H.; Ding, Y.; Gao, Y.; Guo, M.; Guo, S.; Han, B.; Hong, B.; Hou, Y.; et al. New innovations in pavement materials and engineering: A review on pavement engineering research 2021. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2021, 8, 815–999. [Google Scholar]
- Anupam, B.; Sahoo, U.C.; Chandrappa, A.K. A methodological review on self-healing asphalt pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 321, 126395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Garcia, A. Self-healing of asphalt mixture by microwave and induction heating. Mater. Des. 2016, 106, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hao, P.; Zhang, M. Fabrication, characterization and assessment of the capsules containing rejuvenator for improving the self-healing performance of asphalt materials: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wool, R.; O’Connor, K. A theory crack healing in polymers. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 5953–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-R.; Little, D.; Lytton, R. Fatigue and healing characterization of asphalt mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2003, 15, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. Self Healing of Asphalt Mixtures: Towards a Better Understanding of the Mechanism. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- De Gennes, P.-G. Reptation of a polymer chain in the presence of fixed obstacles. J. Chem. Phys. 1971, 55, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Lin, T.; Zhu, X.; Cao, L. Calculation and evaluation of activation energy as a self-healing indication of asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 95, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Rao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xie, J.; Pan, P. Investigation of the flow and self-healing properties of UV aged asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Pauli, T.; Sun, W. Investigation of the asphalt self-healing mechanism using a phase-field model. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04014118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kringos, N.; Scarpas, A.; Pauli, T.; Robertson, R. Advanced Testing and Characterization of Bituminous Materials; Two Volume Set; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Nahar, S. Phase-Separation Characteristics of Bitumen and Their Relation to Damage-Healing. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lytton, R.L.; Uzan, J.; Fernando, E.G.; Roque, R.; Hiltunen, D.; Stoffels, S.M. Development and Validation of Performance Prediction Models and Specifications for Asphalt Binders and Paving Mixes; Strategic Highway Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 357. [Google Scholar]
- Schapery, R. On the mechanics of crack closing and bonding in linear viscoelastic media. Int. J. Fract. 1989, 39, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Little, D.N.; Lytton, R.L. Characterization of Microdamage and Healing of Asphalt Concrete Mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2002, 14, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Bueno, M.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Partl, M.N. Induction healing of dense asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Van de Ven, M.; Wu, S.; Yu, J.; Molenaar, A. Investigating the self healing capability of bituminous binders. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2009, 10, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Shan, L.; Kim, Y.R.; Underwood, B.S. Healing characteristics of asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 27, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Tan, Y.; Kim, Y.R. Establishment of a universal healing evaluation index for asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Zhou, S. Generating adversarial examples with input significance indicator. Neurocomputing 2020, 394, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Komacka, J.; Gu, X. Influence of the chemical composition and the morphology of crumb rubbers on the rheological and self-healing properties of bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 210, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Simms, R.; Koh, C.; Lopp, G.; Roque, R. Development of a test method for evaluation and quantification of healing in asphalt mixture. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2013, 14, 901–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riara, M.; Tang, P.; Mo, L.; Javilla, B.; Chen, M.; Wu, S. Systematic evaluation of fracture-based healing indexes of asphalt mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, P.; He, Z. Fatigue–healing performance evaluation of asphalt mixture using four-point bending test. Mater. Struct. 2020, 53, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, W.; Wu, S.; Schlangen, E.; Pan, P. A comparative study of the induction healing behaviors of hot and warm mix asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P. Discussion on the Maintenance and Repair Technology of Asphalt Pavement Crack and Pit. J. Guangdong Commun. Polytech. 2016, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Z.; Ping, Y. Crack mechanism and prevention measures of concrete in the initial pouring based on field temperature gradient experiment. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 153, 052021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praticò, F.G.; Vaiana, R.; Iuele, T. Macrotexture modeling and experimental validation for pavement surface treatments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 95, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.H.; Kim, Y.R. Methods for fog seal field test with polymer-modified emulsions: Development and performance evaluation. Transp. Res. Rec. 2013, 2361, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Yuan, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xiao, F. Cracking investigation on fog seal technology with waterborne acrylate and polyurethane as a clean modification approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.M.; Arafat, S.; Wasiuddin, N.M. Quantification of reduction in hydraulic conductivity and skid resistance caused by fog seal in low-volume roads. Transp. Res. Rec. 2017, 2657, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Xiao, F.; Guo, R.; Xiang, Q.; Wang, T.; Wang, J. Application of spectrophotometry on detecting asphalt content of emulsified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zheng, M.; Liu, X.; Ding, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q. Performance evaluation of waterborne epoxy resin-SBR composite modified emulsified asphalt fog seal. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, H.; Hui, B.; Jelagin, D.; You, Z.; Feng, P. Optimal design of fresh sand fog seal mortar using response surface methodology (RSM): Towards to its workability and rheological properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 340, 127638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Hasan, M.R.M.; Gao, J.; Irfan, M. Traffic open time prediction of fog seal with sand using image processing technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, M.D.; Greil, P.; Leyens, C.; van der Zwaag, S.; Schubert, U.S. Self-healing materials. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 5424–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Ye, Q.; Sun, Y.; Schlangen, E. Investigation of the optimal self-healing temperatures and healing time of asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Hu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Ye, Q. Snow and ice melting properties of self-healing asphalt mixtures with induction heating and microwave heating. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 129, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.-Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, D.; Shin, H.-O. Self-healing capability of asphalt concrete with carbon-based materials. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Cortavitarte, M.; Jato-Espino, D.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Calzada-Pérez, M.Á. Self-healing capacity of asphalt mixtures including by-products both as aggregates and heating inductors. Materials 2018, 11, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, Á.; Schlangen, E.; van de Ven, M.; Liu, Q. Electrical conductivity of asphalt mortar containing conductive fibers and fillers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3175–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Partl, M.N. Experimental evaluation of dense asphalt concrete properties for induction heating purposes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 46, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Schlangen, E.; van de Ven, M.; Poot, M. Optimization of Steel Fiber Used for Induction Heating in Porous Asphalt Concrete. Traffic Transp. Stud. 2010, 2010, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Schlangen, E. Induction heating of asphalt mastic for crack control. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 41, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Induction Healing of Porous Asphalt Concrete. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, A.; Schlangen, E.; Van de Ven, M. Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 573–576. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Schlangen, E.; van de Ven, M. Induction healing of porous asphalt concrete beams on an elastic foundation. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Schlangen, E.; van de Ven, M.; van Bochove, G.; van Montfort, J. Evaluation of the induction healing effect of porous asphalt concrete through four point bending fatigue test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; García, Á.; Schlangen, E.; van de Ven, M. Induction healing of asphalt mastic and porous asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 3746–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Schlangen, E.; van de Ven, M. Induction Healing of Porous Asphalt. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2012, 2305, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wu, S.; Xie, J.; Amirkhanian, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, N.; et al. Enhanced induction heating and self-healing performance of recycled asphalt mixtures by incorporating steel slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 366, 132999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xie, J.; Wu, S.; Amirkhanian, S.; Wang, Z.; Song, J.; Zou, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L. Enhancement mechanism of induction heating on blending efficiency of RAP-virgin asphalt in steel slag recycled asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; García, A.; Su, J.; Liu, Q.; Tabaković, A.; Schlangen, E. Self-Healing Asphalt Review: From Idea to Practice. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1800536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bochove, G. Self Healing Asphalt-extending the service life by induction heating of asphalt. In Proceedings of the 6th Eurasphalt & Eurobitume Congress, Prague, Czech Republic, 1–3 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, H.; Shu, B.; Li, Y.; Gu, D.; Gao, Y.; Li, C. Microwave heating mechanism and self-healing performance of asphalt mixture with basalt and limestone aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Sha, A.; Barbieri, D.M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Hoff, I. Evaluation of microwave aging impact on asphalt mixtures. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2023, 24, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Gonzalez-Torre, I. Influence of the microwave heating time on the self-healing properties of asphalt mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, J.; del Val, M.A.; Contreras, V.; Páez, A. Heating asphalt mixtures with microwaves to promote self-healing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 42, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; Tao, G.; Xiao, Y. Improved microwave heating and healing properties of bitumen by using nanometer microwave-absorbers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 189, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, S.; Shu, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Microwave absorption and anti-aging properties of modified bitumen contained SiC attached layered double hydroxides. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, W.; Chen, Z.; Ye, Q.; Pan, P. Self-healing performance of asphalt mixtures through heating fibers or aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 150, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Sha, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Cui, X. Effect of metallic-waste aggregates on microwave self-healing performances of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Sha, A.; Barbieri, D.M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, W. Improved microwave heating uniformity and self-healing properties of steel slag asphalt containing ferrite filler. Mater. Struct. 2021, 54, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franesqui, M.A.; Yepes, J.; García-González, C. Top-down cracking self-healing of asphalt pavements with steel filler from industrial waste applying microwaves. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atakan, M.; Yıldız, K. Improving Microwave Heating Characteristic of Asphalt Binder by Using Fly Ash. In Proceedings of the ISBS 2019—4th International Sustainable Buildings Symposium, Dallas, TX, USA, 18–20 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jahanbakhsh, H.; Karimi, M.M.; Jahangiri, B.; Nejad, F.M. Induction heating and healing of carbon black modified asphalt concrete under microwave radiation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Gu, D.; Gao, Y.; Feng, J.; Xu, Z. Microwave heating mechanism and Self-healing performance of scrap tire pyrolysis carbon black modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 341, 127873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yuan, H.; Liu, Y.; Fan, S.; Ding, Y. Evaluation of self-healing performance of asphalt concrete for macrocracks via microwave heating. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Storey, L.; Schlangen, E. Effect of RAP and fibers addition on asphalt mixtures with self-healing properties gained by microwave radiation heating. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 159, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulisano, F.; Gallego, J. Microwave heating of asphalt paving materials: Principles, current status and next steps. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 121993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Xu, G.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Wan, Y.; Chen, H. An overview of utilization of steel slag. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hoff, I.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C. Investigation of the self-healing and rejuvenating properties of aged asphalt mixture containing multi-cavity Ca-alginate capsules. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 129685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, Á.; Schlangen, E.; van de Ven, M.; Sierra-Beltrán, G. Preparation of capsules containing rejuvenators for their use in asphalt concrete. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, Á.; Schlangen, E.; Van de Ven, M. Properties of capsules containing rejuvenators for their use in asphalt concrete. Fuel 2011, 90, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Austin, C.J.; Jelfs, J. Mechanical properties of asphalt mixture containing sunflower oil capsules. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 118, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Jelfs, J.; Austin, C.J. Internal asphalt mixture rejuvenation using capsules. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, N.V.N.; Prasanna, P.M.; Sakarkar, S.N.; Prabha, K.S.; Ramaiah, P.S.; Srawan, G.Y. Microencapsulation techniques, factors influencing encapsulation efficiency. J. Microencapsul. 2010, 27, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelehan, M.; Marison, I.W. Microencapsulation using vibrating technology. J. Microencapsul. 2011, 28, 669–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, B.; Tian, Y.; Lu, T.; Zhu, X.; Sun, G.; Gilabert, F. Aided regeneration system of aged asphalt binder based on microcapsule technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-F.; Qiu, J.; Schlangen, E.; Wang, Y.-Y. Investigation the possibility of a new approach of using microcapsules containing waste cooking oil: In situ rejuvenation for aged bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 74, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-F.; Schlangen, E. Synthesis and physicochemical properties of high compact microcapsules containing rejuvenator applied in asphalt. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Hu, J.; Zhu, X. Size optimization and self-healing evaluation of microcapsules in asphalt binder. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 3505–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, B.; Ye, F.; Zhu, X.; Lu, T.; Tian, Y. Fatigue behavior of microcapsule-induced self-healing asphalt concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, P.; Han, S.; Han, N.; Li, W. Evaluating and modeling the internal diffusion behaviors of microencapsulated rejuvenator in aged bitumen by FTIR-ATR tests. Materials 2016, 9, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Su, J.; Schlangen, E.; Han, N.; Han, S.; Li, W. Fabrication and characterization of self-healing microcapsules containing bituminous rejuvenator by a nano-inorganic/organic hybrid method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 121, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-F.; Schlangen, E.; Qiu, J. Design and construction of microcapsules containing rejuvenator for asphalt. Powder Technol. 2013, 235, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Wu, S.; Bao, S.; Shu, B. Synthesis and characterization of multi-cavity Ca-alginate capsules used for self-healing in asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Liu, Q.; Yu, X.; Wan, P.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Ye, Q. Efficient preparation and characterization of calcium alginate-attapulgite composite capsules for asphalt self-healing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Yalcin, E.; Garcia, A. Influence of encapsulated sunflower oil on the mechanical and self-healing properties of dense-graded asphalt mixtures. Mater. Struct. 2019, 52, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micaelo, R.; Al-Mansoori, T.; Garcia, A. Study of the mechanical properties and self-healing ability of asphalt mixture containing calcium-alginate capsules. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Tabaković, A.; Liu, X.; Schlangen, E. Calcium alginate capsules encapsulating rejuvenator as healing system for asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S. Recent advances in calcium alginate hydrogels encapsulating rejuvenator for asphalt self-healing. J. Road Eng. 2022, 2, 181–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Yalcin, E.; Garcia, A.; Al-Mansoori, T.; Yilmaz, M.; Hudson-Griffiths, R. Effect of mixing and ageing on the mechanical and self-healing properties of asphalt mixtures containing polymeric capsules. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Liu, Q.; Rao, W.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L. Synthesis and characterization of calcium alginate-attapulgite composite capsules for long term asphalt self-healing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, T.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Garcia, A. Effect of capsule addition and healing temperature on the self-healing potential of asphalt mixtures. Mater. Struct. 2018, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Yalcin, E.; Hudson-Griffiths, R.; García, A. Mechanical and self-healing properties of stone mastic asphalt containing encapsulated rejuvenators. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S.; Zou, Y.; Yu, X. A novel microwave induced oil release pattern of calcium alginate/nano-Fe3O4 composite capsules for asphalt self-healing. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micaelo, R.; Freire, A.; Pereira, G. Asphalt self-healing with encapsulated rejuvenators: Effect of calcium-alginate capsules on stiffness, fatigue and rutting properties. Mater. Struct. 2020, 53, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Tabaković, A.; Schlangen, E. Investigation of the potential use of calcium alginate capsules for self-healing in porous asphalt concrete. Materials 2019, 12, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Hernández, A.; Salih, S.; Ruiz-Riancho, I.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Hudson-Griffiths, R.; Gomez-Meijide, B. Self-healing of reflective cracks in asphalt mixtures by the action of encapsulated agents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 118929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Concha, J.L.; Arteaga-Pérez, L.E.; Gonzalez-Torre, I. Synthesis and Characterisation of Alginate-Based Capsules Containing Waste Cooking Oil for Asphalt Self-Healing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toohey, K.S.; Sottos, N.R.; Lewis, J.A.; Moore, J.S.; White, S.R. Self-healing materials with microvascular networks. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.-F.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Fang, Y.; Han, N. Experimental observation of the vascular self-healing hollow fibers containing rejuvenator states in bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-L.; Su, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Han, N. Novel vascular self-nourishing and self-healing hollow fibers containing oily rejuvenator for bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 183, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-D.; Xie, X.; Su, J.; Mu, R.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Fang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Lv, L.; Han, N. Mechanical experiment evaluation of the microvascular self-healing capability of bitumen using hollow fibers containing oily rejuvenator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaković, A.; Post, W.; Cantero, D.; Copuroglu, O.; Garcia, S.J.; Schlangen, E. The reinforcement and healing of asphalt mastic mixtures by rejuvenator encapsulation in alginate compartmented fibres. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 084003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, B.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Dong, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Q. Synthesis and characterization of compartmented Ca-alginate/silica self-healing fibers containing bituminous rejuvenator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, B.; Bao, S.; Wu, S.; Dong, L.; Li, C.; Yang, X.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Q. Synthesis and effect of encapsulating rejuvenator fiber on the performance of asphalt mixture. Materials 2019, 12, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Tabaković, A.; Schlangen, E. A novel self-healing system: Towards a sustainable porous asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, H.; Niu, Y.; Ye, Q. Dual responsive self-healing system based on calcium alginate/Fe3O4 capsules for asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 360, 129585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Peng, Z.; Rao, W.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S. Self-healing properties of asphalt concrete containing responsive calcium alginate/nano-Fe3O4 composite capsules via microwave irradiation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 310, 125258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, M.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, G. A conductive self-healing hybrid gel enabled by metal–ligand supramolecule and nanostructured conductive polymer. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6276–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.A.; Boydston, A.J.; Bielawski, C.W. Towards electrically conductive, self-healing materials. J. R. Soc. Interface 2007, 4, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, F.; Cheng, X.; Fang, B.; Cheng, C.; Liu, Y.; You, Z. Prospect of 3D printing technologies in maintenance of asphalt pavement cracks and potholes. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 397, 136551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.J.; Wojcik, A.; Miodownik, M. 3D printing of asphalt and its effect on mechanical properties. Mater. Des. 2018, 160, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Huang, W.; Xiao, F. Laboratory evaluation of self-healing properties of various modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Q.; Yan, C.; Jiao, Y. Evaluation of the adhesion and healing properties of modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 119026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Lv, Q.; Xiao, F. Investigation of using binder bond strength test to evaluate adhesion and self-healing properties of modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaee, N.; Shafiee, M.H. 7th RILEM International Conference on Cracking in Pavements: Mechanisms, Modeling, Testing, Detection and Prevention Case Histories; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 869–878. [Google Scholar]
- Ganjei, M.A.; Aflaki, E. Application of nano-silica and styrene-butadiene-styrene to improve asphalt mixture self healing. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2019, 20, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Seo, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Hong, Y.-K. Self-Healing Asphalt Prepared by using Ionic Epoxy Resin. Elastomers Compos. 2015, 50, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ma, B.; Wei, K.; Wang, X. Deformation recovery properties of asphalt mixtures with shape memory epoxy resin. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Materials Types | Test Method | Healing Parameter | Healing Indicator | Notes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binders | Ductility | Ductility value | HI = | and are ductility test result before and after break-healing | Qiu, J. et al. [28] |
| DSR sweep test | Complex modulus and number of cycles | HI = 100· | Ginitial and Gterminal are the dynamic modulus before and after loading test; Nbefore and Nafter are the numbers of cycles before and after rest period; | Tan, Y. et al. [29] | |
| Fatigue-rest-fatigue test using DSR sweep test | Area under the curve | HI = | Abefore and Ad is the area between the curves of the modulus versus the number of load cycles and the line of ½ modulus before and after rest; | Shan, L. et al. [30] | |
| Fatigue-rest-fatigue test | Complex shear modulus | HI = | G*0 and G*h0 are the complex shear modulus before and after healing; | Qiu, X. et al. [31] | |
| Fatigue-rest-fatigue test | Dissipated energy | HI = | Wbefore and Wafter are the initial dissipative energy before and after healing | Qiu, X. et al. [31] | |
| Fatigue-rest-fatigue test | Fatigue life | HI = | and are the fatigue life after and before rest | Liu, G. et al. [32] | |
| Asphalt mixture | IDT | Resilient modulus | HI = | MR(t) is the normalised resilient modulus at time t; MR0 is the normalised resilient modulus at t = 0; and MRundamaged is the undamaged normalised resilient modulus | Chen, Y. et al. [33] |
| SCB test or 3-point bending test | Strength | HI = | Fafter and Fbefore are fracture peak load after and before healing | Riara, M. et al. [34] | |
| SCB test or 3-point bending test | Stiffness | HI = | Safter and Sbefore are stiffness after and before healing | Riara, M.et al. [34] | |
| SCB test or 3-point bending test | Fracture energy | HI = | Eafter and Ebefore are fracture energy after and before healing | Riara, M. et al. [34] | |
| Four-point bending fatigue-healing-fatigue test | Stiffness modulus | HI = | S1 and S2 are the initial stiffness modulus before and after rest; SS is stiffness modulus when beam reaches fatigue condition | Xiang, H. et al. [35] | |
| Four-point bending fatigue-healing-fatigue test | Fatigue life | HI = | Nf-after and Nf-initial are fatigue life after and before resting | Liu, Q. et al. [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Hoff, I.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, F. A Methodological Review on Development of Crack Healing Technologies of Asphalt Pavement. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129659
Zhang L, Hoff I, Zhang X, Liu J, Yang C, Wang F. A Methodological Review on Development of Crack Healing Technologies of Asphalt Pavement. Sustainability. 2023; 15(12):9659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129659
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lei, Inge Hoff, Xuemei Zhang, Jianan Liu, Chao Yang, and Fusong Wang. 2023. "A Methodological Review on Development of Crack Healing Technologies of Asphalt Pavement" Sustainability 15, no. 12: 9659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129659
APA StyleZhang, L., Hoff, I., Zhang, X., Liu, J., Yang, C., & Wang, F. (2023). A Methodological Review on Development of Crack Healing Technologies of Asphalt Pavement. Sustainability, 15(12), 9659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129659










