Land-Use Change Effects on Soil Erosion: The Case of Roman “Via Herculia” (Southern Italy)—Combining Historical Maps, Aerial Images and Soil Erosion Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
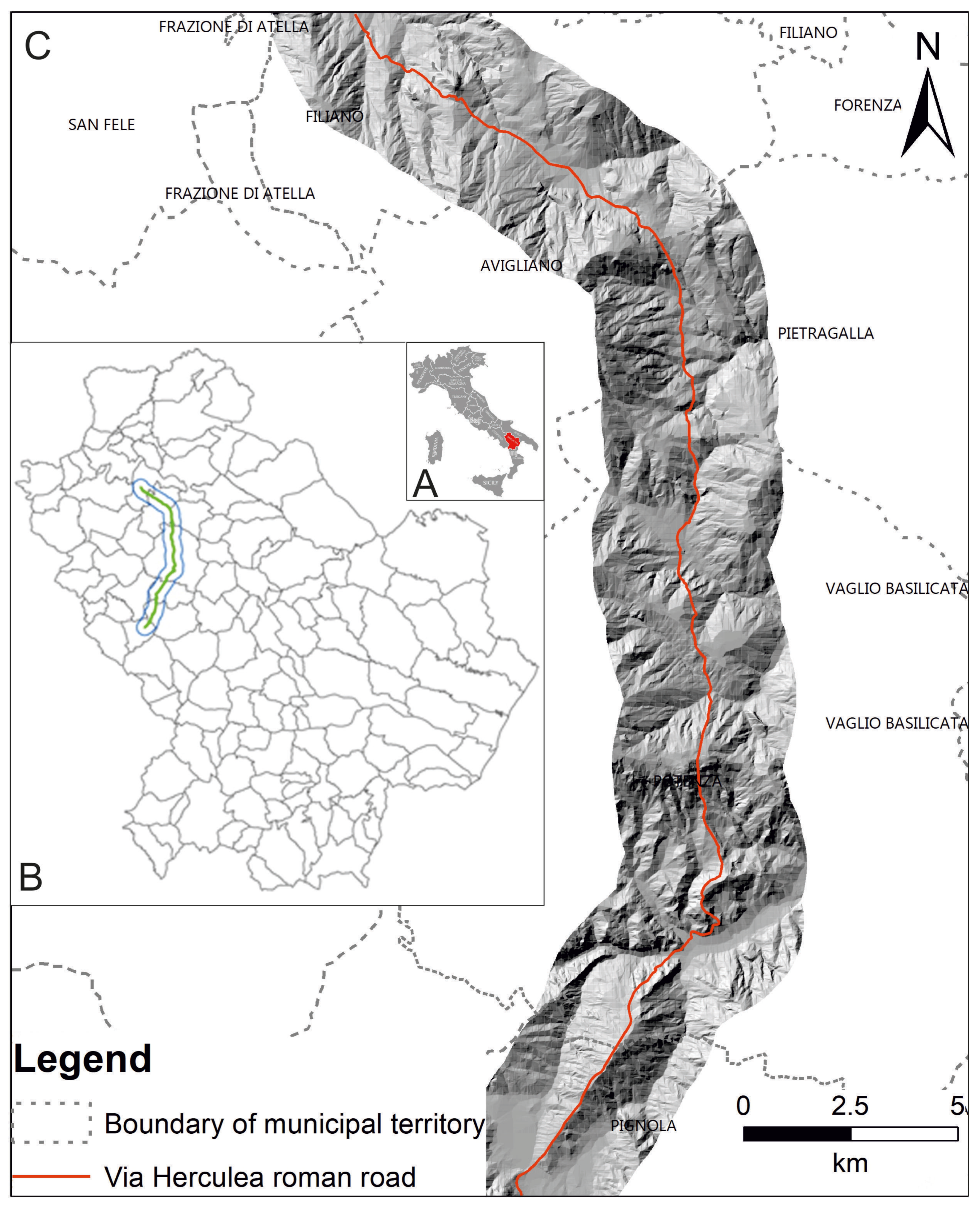
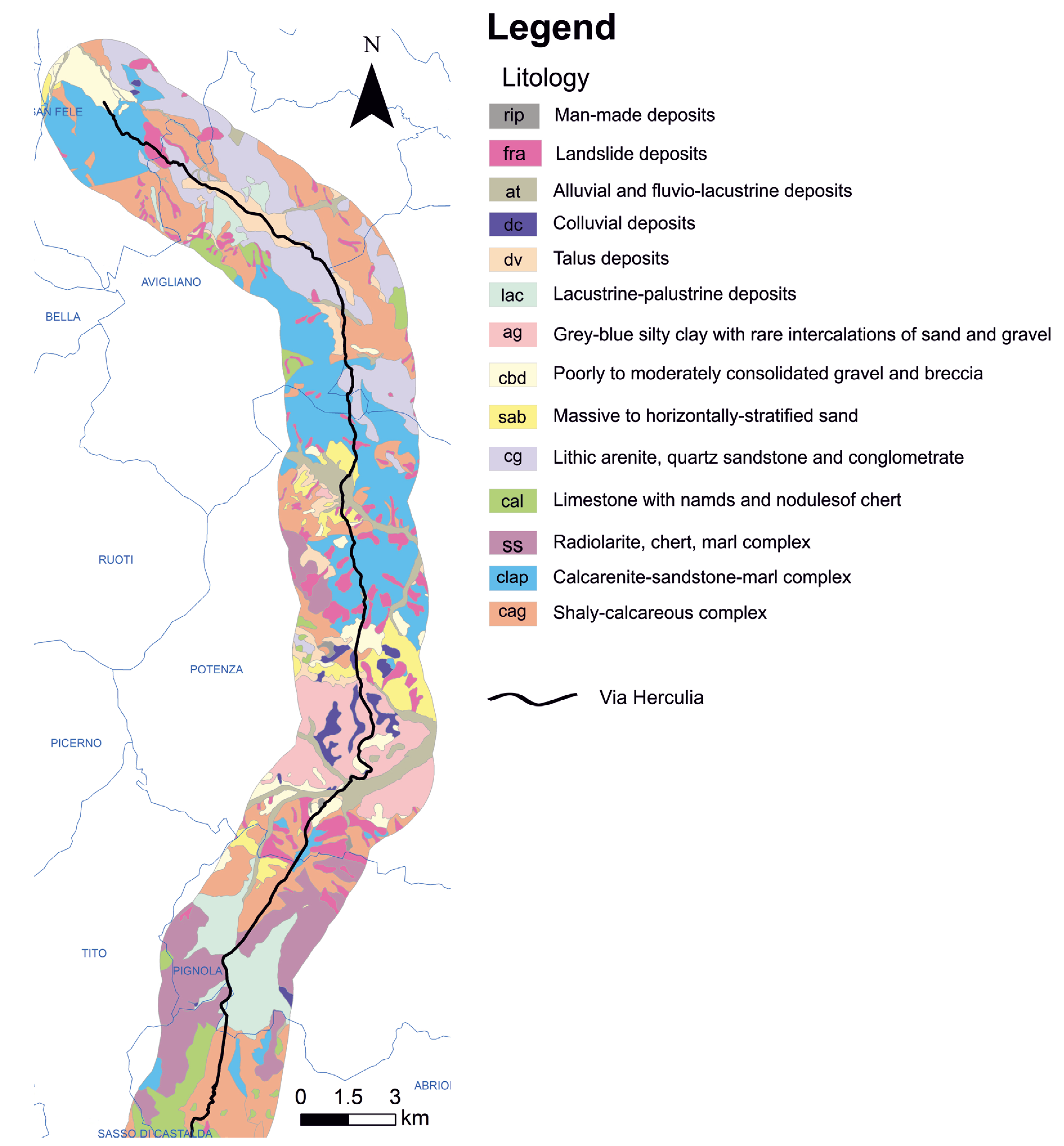
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Historical Map, Aerial Image and Orthophoto
2.3. USPED Model
3. Results
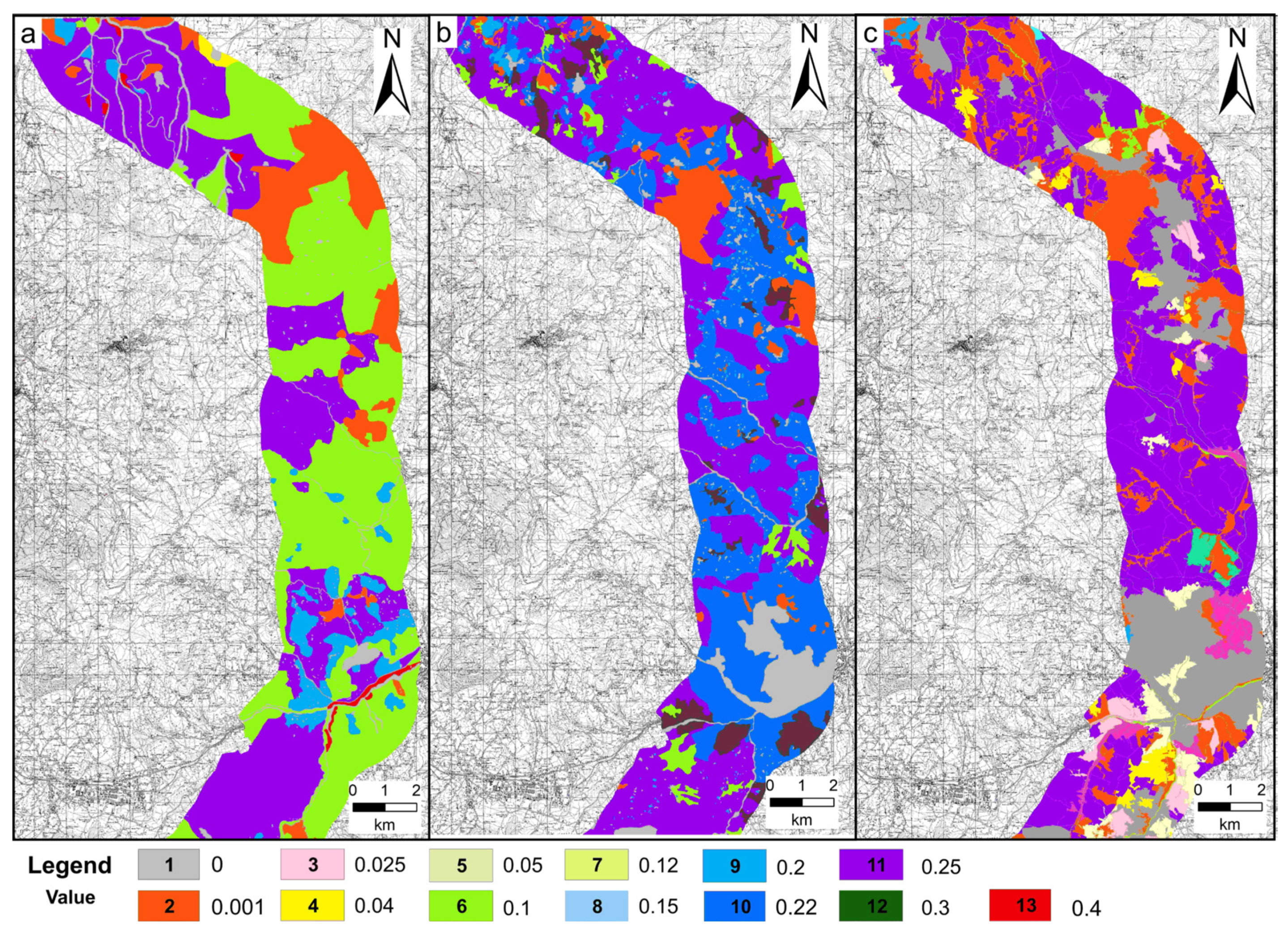
3.1. Land-Use Change (1870–2013)
3.2. USPED Model
- Extreme erosion (<−40 Mg ha−1 yr−1);
- High erosion (−40/−20 Mg ha−1 yr−1);
- Moderate erosion (−20/−10 Mg ha−1 yr−1);
- Low erosion (−10/−5 Mg ha−1 yr−1);
- Very low erosion (−5/−2 Mg ha−1 yr−1);
- Stable (−2/2 Mg ha−1 yr−1);
- Very low deposition (2/5 Mg ha−1 yr−1);
- Low deposition (5/10 Mg ha−1 yr−1);
- Moderate deposition (10/20 Mg ha−1 yr−1);
- High deposition (20/40 Mg ha−1 yr−1);
- Extreme deposition (>40 Mg ha−1 yr−1).
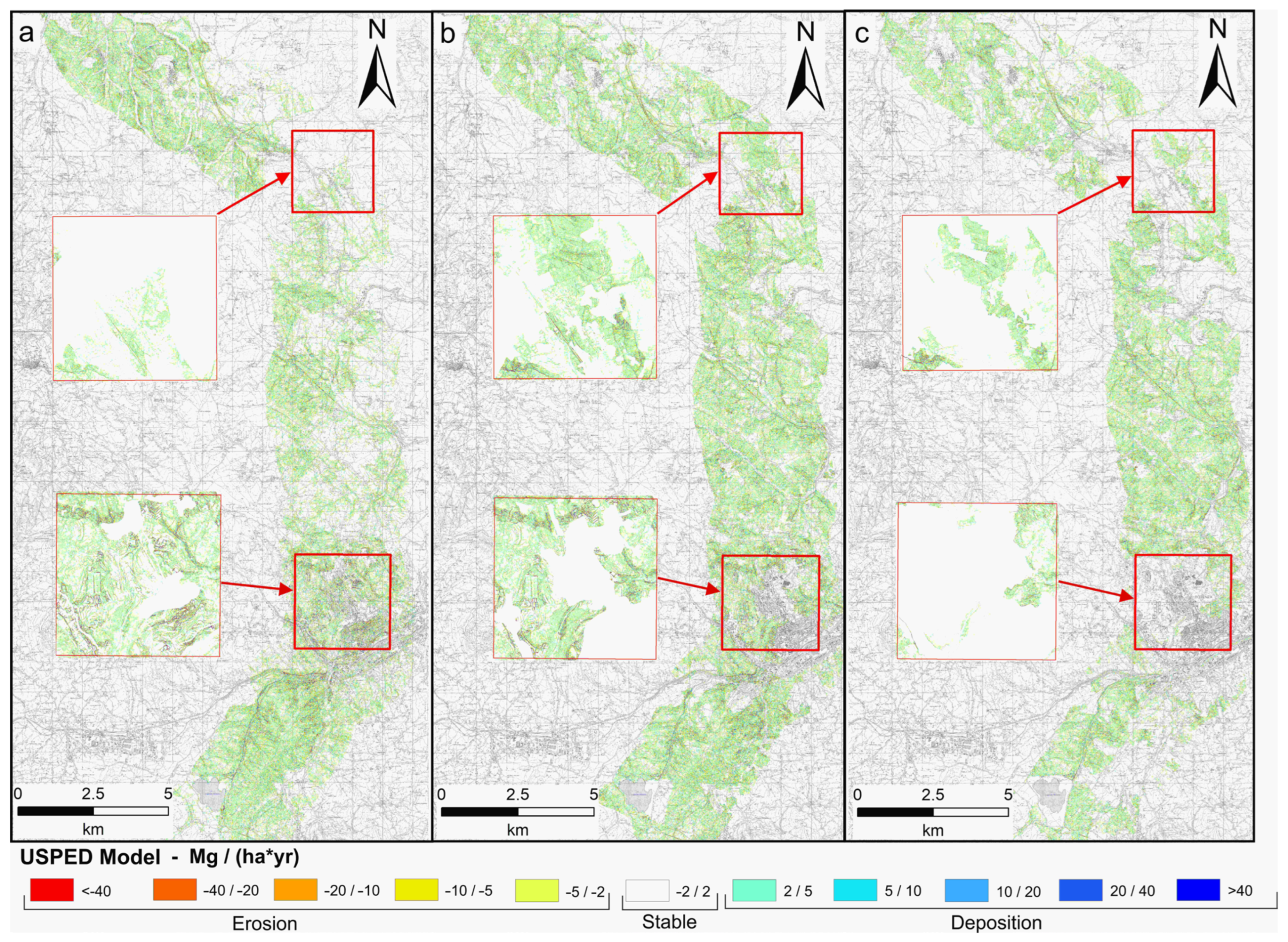
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohammadi, M.; Darvishan, A.K.; Spalevic, V.; Dudic, B.; Billi, P. Analysis of the impact of land use changes on soil erosion intensity and sediment yield using the intero model in the talar watershed of iran. Water 2021, 13, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, M.; Mirchooli, F.; Motevalli, A.; Khaledi Darvishan, A.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Zakeri, M.A.; Sadighi, F. Spatial modelling of gully erosion in Mazandaran Province, northern Iran. Catena 2018, 161, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishan, A.K.; Homayounfar, V.; Sadeghi, S.H. The impact of standard preparation practice on the runoff and soil erosion rates under laboratory conditions. Solid Earth 2016, 7, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buraka, T.; Elias, E.; Suryabhagavan, K.V.; Lelago, A. Assessment of soil erosion risks in response to land-use and land-cover changes in Coka watershed, Southern Ethiopia. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, E.; Ekpenyong, R.; Offiong, N.A.; Udotong, U.; Benjamin, M.; William, N. Climate variability, land cover change and soil erosion risk implications for water quality of a humid tropical river basin in sub-Saharan Africa. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiu, J.; Wu, H.; Li, S. The implication of land-use/land-cover change for the declining soil erosion risk in the three gorges reservoir region, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, K.; Matin, M.A.; Maharjan, S. Assessment of land cover change and its impact on changes in soil erosion risk in Nepal. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrastina, P.; Hronček, P.; Gregorová, B.; Žoncová, M. Land-use changes of historical rural landscape-heritage, protection, and sustainable ecotourism: Case study of Slovak Exclave Čív (Piliscsév) in Komárom-Esztergom County (Hungary). Sustainability 2020, 12, 6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, C. The Earth as Transformed by Human Action Conversations in the Round: The Forum’s Aims and Ambitions. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1994, 84, 710–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner Ii, B.L.; Clark, W.C.; Kates, R.W.; Richards, J.F.; Mathews, J.T.; Meyer, W.B. The Earth as transformed by human action: Global change and regional changes in the biosphere over the past 300 years. In The Earth as Transformed by Human Action: Global Change and Regional Changes in the Biosphere over the Past 300 Years; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Dabral, P.P.; Baithuri, N.; Pandey, A. Soil erosion assessment in a hilly catchment of North Eastern India using USLE, GIS and remote sensing. Water Resour. Manag. 2008, 22, 1783–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri, H.; Annabi, M.; Cheikh M’Hamed, H.; Frija, A. Assessing the long-term impact of conservation agriculture on wheat-based systems in Tunisia using APSIM simulations under a climate change context. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavian, A.; Gholami, L.; Mohammadi, M.; Spalevic, V.; Soraki, M.F. Impact of wheat residue on soil erosion processes. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2018, 46, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.; Panagopoulos, T.; Cakula, A.; Andrade, R.; Arvela, A. Predicting Soil Erosion After Land Use Changes for Irrigating Agriculture in a Large Reservoir of Southern Portugal. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 4, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Yu, J.; Jiang, H.; Sun, W.; Li, Z. Roles of soil erodibility, rainfall erosivity and land use in affecting soil erosion at the basin scale. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 174, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, B. Soil erosion evaluation in a rapidly urbanizing city (Shenzhen, China) and implementation of spatial land-use optimization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4475–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J. Landscape sustainability science: Ecosystem services and human well-being in changing landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 999–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Toman, E.; Fuller, Z.; Chen, G.; Londo, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, K. Integration of historical map and aerial imagery to characterize long-term land-use change and landscape dynamics: An object-based analysis via Random Forests. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olah, B. Historical maps and their application in landscape ecological research. Ekol. Bratisl. 2009, 28, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, J.T.T.R.; Coops, N.C.; Daniels, L.D.; Falls, R.W. Detecting forest damage after a low-severity fire using remote sensing at multiple scales. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 35, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitas, I.Z.; San-Miguel-Ayanz, J.; Chuvieco, E.; Camia, A. Advances in remote sensing and GIS applications in support of forest fire management. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2014, 23, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.; Tateishi, R. Remote sensing and GIS for mapping and monitoring land cover and land-use changes in the Northwestern coastal zone of Egypt. Appl. Geogr. 2007, 27, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; García, M.; Liu, S.; Guo, Q.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X. Terrestrial lidar remote sensing of forests: Maximum likelihood estimates of canopy profile, leaf area index, and leaf angle distribution. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 209–210, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, D.; Schiattarella, M. Modeling Short-Term Landscape Modification and Sedimentary Budget Induced by Dam Removal: Insights from LEM Application. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbold, T.; Hudson, L.N.; Hill, S.L.L.; Contu, S.; Lysenko, I.; Senior, R.A.; Börger, L.; Bennett, D.J.; Choimes, A.; Collen, B.; et al. Global effects of land use on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature 2015, 520, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; et al. High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fu, H.; Yu, L.; Gong, P.; Feng, D.; Li, C.; Clinton, N. Stacked Autoencoder-based deep learning for remote-sensing image classification: A case study of African land-cover mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 5632–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelková, R.; Frajer, J.; Havlíček, M.; Netopil, P.; Rozkošný, M.; David, V.; Dzuráková, M.; Šarapatka, B. Historical ponds of the Czech Republic: An example of the interpretation of historic maps. J. Maps 2016, 12, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, D.; Dellungo, S.; Sannazzaro, A.; Lazzari, M. Geological and geomorphological controls on the path of an intermountain roman road: The case of the via herculia, southern Italy. Geosciences 2019, 9, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitasova, H.; Hofierka, J.; Zlocha, M.; Iverson, L.R. Modelling topographic potential for erosion and deposition using GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1996, 10, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, B.A.; Mitasova, H.; Petrasova, A.; Petras, V. r.sim.terrain 1.0: A landscape evolution model with dynamic hydrology. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 2837–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolongo, D.; Diodato, N.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Piccarreta, M.; Strobl, R.O. Analyzing temporal changes in climate erosivity using a simplified rainfall erosivity model in Basilicata (southern Italy). J. Hydrol. 2008, 356, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, D.; Amodio, A.M.; Maggio, A.; Sabia, C.A. Impact of land use changes on the erosion processes of a degraded rural landscape: An analysis based on high-resolution DEMs, historical images, and soil erosion models. Land 2021, 10, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Capolongo, D.; Pennetta, L.; Piccarreta, M.; Fallacara, G.; Boenzi, F. Spatial and temporal variations in soil erosion and deposition due to land-levelling in a semi-arid area of Basilicata (Southern Italy). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 364–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Phillips, C.P. Crust development in relation to vegetation and agricultural practice on erosion susceptible, dispersive clay soils from central and southern Italy. Soil Tillage Res. 2001, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; 58p. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R. Soil Conservation: Principles of Erosion by Water; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Alewell, C.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L. Estimating the soil erosion cover-management factor at the European scale. Land Use Policy 2015, 48, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabia, C.A. Strade e percorsi storici. Esempi di rapporto di causa ed effetto con i territori che attraversano. In Antiche vie in Basilicata. Percorsi, Ipotesi, Osservazioni, Note e Curiosità; IGM Edizioni: Lagonegro, Italy, 2019; pp. 141–168. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, G.; Mandarino, A.; Raso, E.; Scarpellini, P.; Brandolini, P.; Cevasco, A. Investigation on farmland abandonment of terraced slopes using multitemporal data sources comparison and its implication on hydro-geomorphological processes. Water 2019, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandolini, P.; Pepe, G.; Capolongo, D.; Cappadonia, C.; Cevasco, A.; Conoscenti, C.; Marsico, A.; Vergari, F.; Del Monte, M. Hillslope degradation in representative Italian areas: Just soil erosion risk or opportunity for development? Land Degrad Dev 2018, 29, 3050–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Knijff, J.M.; Jones, R.J.A.; Montanarella, L. Soil Erosion Risk in Italy; EUR19022 EN; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 1999; 54p. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, R.P.C. Soil Erosion and Conservation, 2nd ed.; Longman: Essex, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
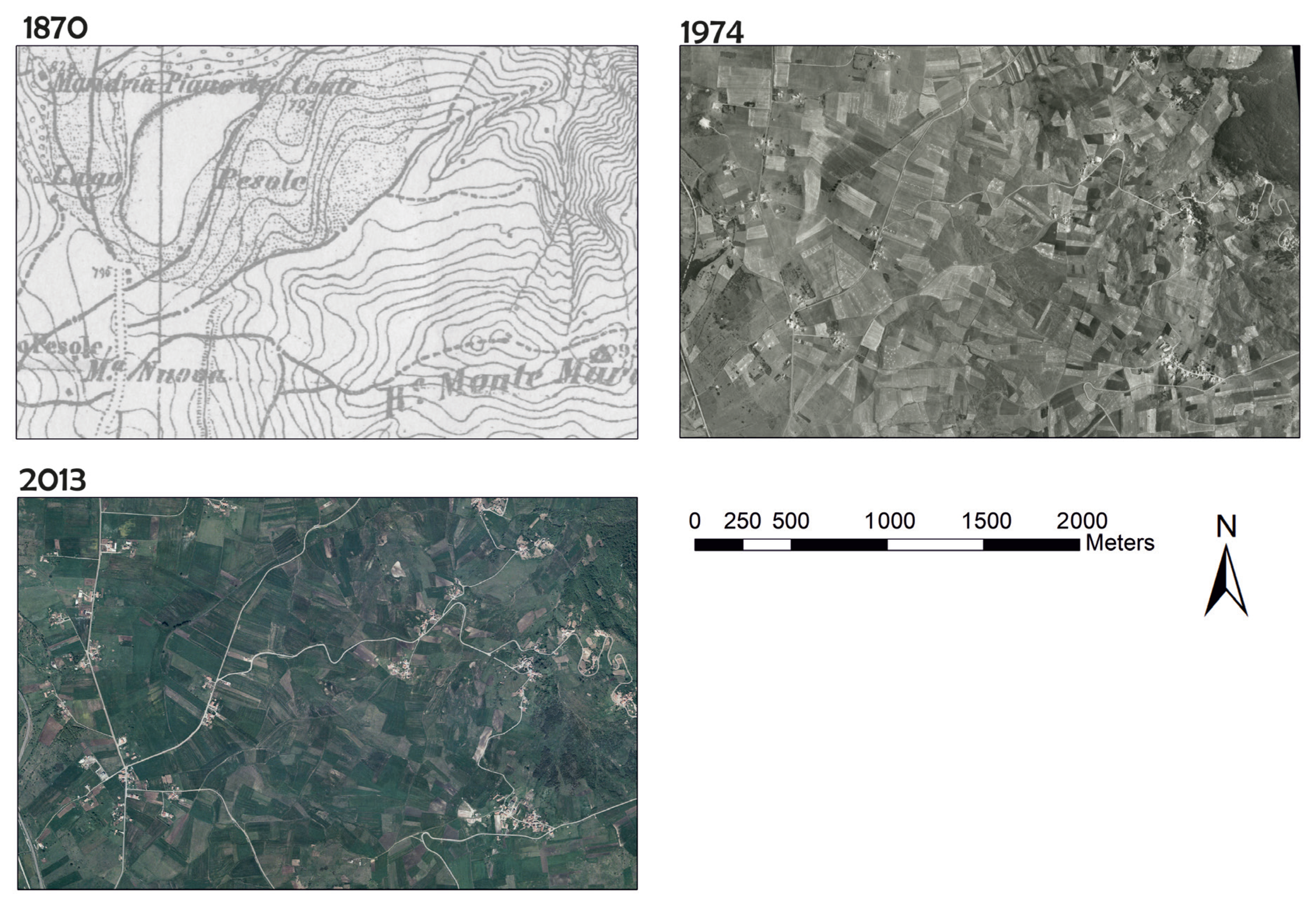



| Land-Use Type | Land Use 1870 | Land Use 1974 | Land Use 2013 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (ha) | Percent | Area (ha) | Percent | Area (ha) | Percent | |
| Urban, industrial, and commercial area | 286.0 | 2.1 | 796.8 | 5.9 | 2517.5 | 18.5 |
| Arable land | 5000.4 | 36.8 | 9806.3 | 72.7 | 6987.7 | 51.5 |
| Fruit trees, vineyards, and olive groves | 752.1 | 5.5 | 179.6 | 1.3 | 44.5 | 0.3 |
| Pastures and natural grasslands | 5700.2 | 42.0 | 1337.8 | 9.9 | 1434.6 | 10.6 |
| Forest area | 1525.4 | 11.2 | 1070.0 | 7.9 | 2357.6 | 17.4 |
| Water | 322.6 | 2.4 | 300.8 | 2.2 | 235.3 | 1.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minervino Amodio, A.; Gioia, D.; Danese, M.; Masini, N.; Sabia, C.A. Land-Use Change Effects on Soil Erosion: The Case of Roman “Via Herculia” (Southern Italy)—Combining Historical Maps, Aerial Images and Soil Erosion Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129479
Minervino Amodio A, Gioia D, Danese M, Masini N, Sabia CA. Land-Use Change Effects on Soil Erosion: The Case of Roman “Via Herculia” (Southern Italy)—Combining Historical Maps, Aerial Images and Soil Erosion Model. Sustainability. 2023; 15(12):9479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129479
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinervino Amodio, Antonio, Dario Gioia, Maria Danese, Nicola Masini, and Canio Alfieri Sabia. 2023. "Land-Use Change Effects on Soil Erosion: The Case of Roman “Via Herculia” (Southern Italy)—Combining Historical Maps, Aerial Images and Soil Erosion Model" Sustainability 15, no. 12: 9479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129479
APA StyleMinervino Amodio, A., Gioia, D., Danese, M., Masini, N., & Sabia, C. A. (2023). Land-Use Change Effects on Soil Erosion: The Case of Roman “Via Herculia” (Southern Italy)—Combining Historical Maps, Aerial Images and Soil Erosion Model. Sustainability, 15(12), 9479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129479









