Enhancing Green Electronic Word-of-Mouth in the Saudi Tourism Industry: An Integration of the Ability, Motivation, and Opportunity and Planned Behaviour Theories
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Examine the effect of green AMO on tourists’ green intentions and on GeWOM in the Saudi tourism industry.
- Examine the effect of green attitude on tourists’ green intentions and on GeWOM in the Saudi tourism industry.
- Test the mediating effect of green intention on the relationship between green AMO, green attitude, and GeWOM in the Saudi tourism industry.
- Establish a conclusion and a set of theoretical and practical implications for stimulating green purchase intention, and hence, the GeWOM for the Saudi tourism industry.
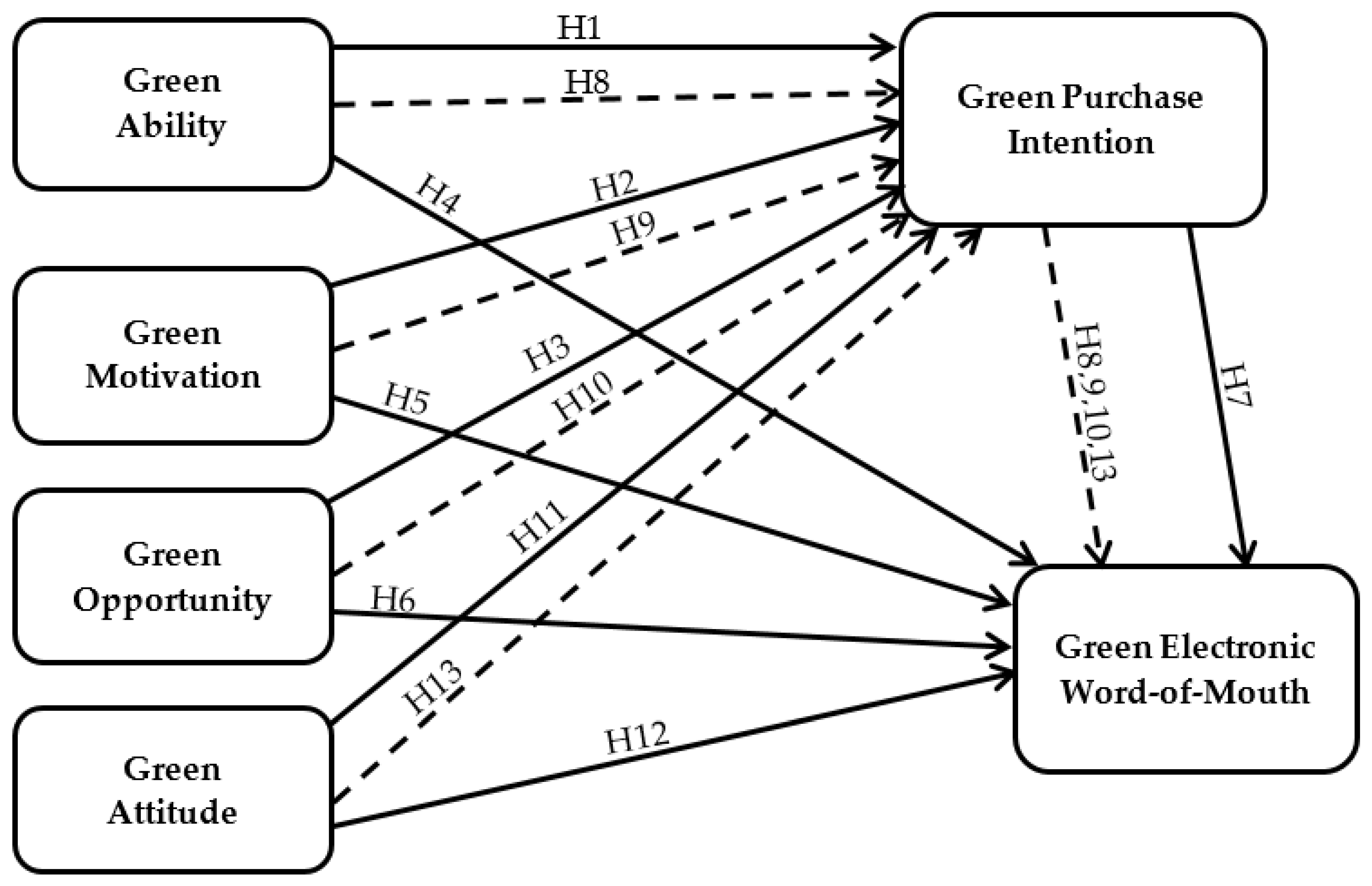
2. Conceptual Framework
2.1. The Relationship between Green Ability–Motivation–Opportunity, Green Purchase Intention, and GeWOM
2.2. The Relationship between Green Attitude, Green Intention, and GeWOM
3. Methodology
3.1. Study Measures
3.2. Participants and Data Collection
3.3. Data Analysis Methods
4. The Study Results
4.1. Outer Model Evaluation
Convergent and Discriminant Validity Evaluation
4.2. Inner Model Hypotheses Testing
5. Discussions
6. Implications of the Research
7. Conclusions, Limitations, and Future Research Opportunities
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Straughan, R.D.; Roberts, J.A. Environmental Segmentation Alternatives: A Look at Green Consumer Behavior in the New Millennium. J. Consum. Mark. 1999, 16, 558–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobaih, A.E.E.; Hasanein, A.; Gharbi, H.; Abu Elnasr, A.E. Going Green Together: Effects of Green Transformational Leadership on Employee Green Behaviour and Environmental Performance in the Saudi Food Industry. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobaih, A.E.E.; Gharbi, H.; Hasanein, A.M.; Elnasr, A.E.A. The Mediating Effects of Green Innovation and Corporate Social Responsibility on the Link between Transformational Leadership and Performance: An Examination Using SEM Analysis. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, I.A.; Azazz, A.M.S.; Ameen, F.A.; Fayyad, S. Agritourism and Peer-to-Peer Accommodation: A Moderated Mediation Model. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, I.A.; AboAlkhair, A.M.; Fayyad, S.; Azazz, A.M.S. Post-COVID-19 Family Micro-Business Resources and Agritourism Performance: A Two-Mediated Moderated Quantitative-Based Model with a PLS-SEM Data Analysis Method. Mathematics 2023, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H. Consumer Behavior and Environmental Sustainability in Tourism and Hospitality: A Review of Theories, Concepts, and Latest Research. J. Sustain. Tour. 2021, 29, 1021–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Swanson, S.R.; Hsu, M.; Chen, X. How Does Perceived Corporate Social Responsibility Contribute to Green Consumer Behavior of Chinese Tourists: A Hotel Context. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2017, 29, 3157–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, I.A.; Azazz, A.M.S.; Fayyad, S. Green Management and Sustainable Performance of Small- and Medium-Sized Hospitality Businesses: Moderating the Role of an Employee’s Pro-Environmental Behaviour. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, I.A.; Azazz, A.M.S.; Fayyad, S. Green Human Resources and Innovative Performance in Small- and Medium-Sized Tourism Enterprises: A Mediation Model Using PLS-SEM Data Analysis. Mathematics 2023, 11, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, I.A.; Azazz, A.M.S.; Ameen, F.A.; Fayyad, S. Sustainable Horticulture Practices to Predict Consumer Attitudes towards Green Hotel Visit Intention: Moderating the Role of an Environmental Gardening Identity. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-L.; Chang, C.-H. The Influence of Greenwash on Green Word-of-Mouth (Green WOM): The Mediation Effects of Green Perceived Quality and Green Satisfaction. Qual. Quant. 2014, 48, 2411–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, L.V.; Phan, Q.P.T.; Phan, H.L.; Pham, N.T.; Nguyen, N. Improving Tourists’ Green Electronic Word-of-Mouth: A Mediation and Moderation Analysis. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2022, 27, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclnnis, D.J.; Jaworski, B.J. Enhancing and Measuring Consumers’ Motivation, Opportunity, and Ability to Process Brand Information from Ads. J. Mark. 1991, 55, 32–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruen, T.W.; Osmonbekov, T.; Czaplewski, A.J. EWOM: The Impact of Customer-to-Customer Online Know-How Exchange on Customer Value and Loyalty. J. Bus. Res. 2006, 59, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigné, E.; Ruiz, C.; Andreu, L.; Hernandez, B. The Role of Social Motivations, Ability, and Opportunity in Online Know-How Exchanges: Evidence from the Airline Services Industry. Serv. Bus. 2015, 9, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. From Intentions to Actions: A Theory of Planned Behavior; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ajzen, I. The Theory of Planned Behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balance, F. Appendix A: Vision Realization Programs; Atlantic Council: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sadi, M.A.; Henderson, J.C. Tourism in Saudi Arabia and Its Future Development. J. Bus. Econ. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliedan, M.M.; Sobaih, A.E.E.; Elshaer, I.A. Influence of Cities-Based Entertainment on Tourist Satisfaction: Mediating Roles of Destination Image and Experience Quality. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grand, S.; Wolff, K. Assessing Saudi Vision 2030: A 2020 Review; Atlantic Council: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Raju, V.; Phung, S.P. Economic Dimensions of Blockchain Technology: In the Context of Extention of Cryptocurrencies. Int. J. Psychosoc. Rehabil. 2020, 24, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, V. Implementing Flexible Systems in Doctoral Viva Defense through Virtual Mechanism. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2021, 22, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, N.T.; Thanh, T.V.; Tučková, Z.; Thuy, V.T.N. The Role of Green Human Resource Management in Driving Hotel’s Environmental Performance: Interaction and Mediation Analysis. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 88, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, N.T.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Usman, M.; Ali, M.; Phan, H.-L. How Does Training Boost Employees’ Intention to Implement Environmental Activities? An Empirical Study in Vietnam. Int. J. Manpow. 2022, 43, 1761–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig-Thurau, T.; Gwinner, K.P.; Walsh, G.; Gremler, D.D. Electronic Word-of-Mouth via Consumer-Opinion Platforms: What Motivates Consumers to Articulate Themselves on the Internet? J. Interact. Mark. 2004, 18, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.; Khan, K.U.; Atlas, F.; Irfan, M. Stimulating Student’s Pro-Environmental Behavior in Higher Education Institutions: An Ability–Motivation–Opportunity Perspective. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 4128–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabian, A.; Russell, J.A. An Approach to Environmental Psychology; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Fine, M.B.; Gironda, J.; Petrescu, M. Prosumer Motivations for Electronic Word-of-Mouth Communication Behaviors. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2017, 8, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.W.; Sanders, G.L.; Moon, J. Exploring the Effect of E-WOM Participation on e-Loyalty in e-Commerce. Decis. Support Syst. 2013, 55, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.W.-J.; Ekinci, Y.; Occhiocupo, N.; Whyatt, G. Antecedents of Travellers’ Electronic Word-of-Mouth Communication. J. Mark. Manag. 2013, 29, 584–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.; Lai, K.; Cheng, T.E. Informational and Relational Influences on Electronic Word of Mouth: An Empirical Study of an Online Consumer Discussion Forum. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2013, 17, 137–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobaih, A.E.E.; Abdelaziz, A.S. The Impact of Nutrition Labelling on Customer Buying Intention and Behaviours in Fast Food Operations: Some Implications for Public Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellithorpe, M.E. MODE Model. In The International Encyclopedia of Media Psychology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ibnou-Laaroussi, S.; Rjoub, H.; Wong, W.-K. Sustainability of Green Tourism among International Tourists and Its Influence on the Achievement of Green Environment: Evidence from North Cyprus. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, S. The Effects of Sponsor Relevance on Consumer Reactions to Internet Sponsorships. J. Advert. 2003, 32, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, F. Website Attributes in Urging Online Impulse Purchase: An Empirical Investigation on Consumer Perceptions. Decis. Support Syst. 2013, 55, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, P.E.; Sigala, P.M.; Gretzel, P.U. Social Media in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality: Theory, Practice and Cases; Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.: Farnham, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4094-8514-8. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.E.; Srinivasan, S.S. E-Satisfaction and e-Loyalty: A Contingency Framework. Psychol. Mark. 2003, 20, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-K. Understanding Relationship Quality and Online Purchase Intention in E-Tourism: A Qualitative Application. Qual. Quant. 2009, 43, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lennon, S. The Effects of Visual and Verbal Information on Attitudes and Purchase Intentions in Internet Shopping. Psychol. Mark. 2008, 25, 146–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common Method Biases in Behavioral Research: A Critical Review of the Literature and Recommended Remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; Organ, D.W. Self-Reports in Organizational Research: Problems and Prospects. J. Manag. 1986, 12, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibeh, K.; Brock, J.K.-U.; Zhou, Y.J. The Drop and Collect Survey among Industrial Populations: Theory and Empirical Evidence. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2004, 33, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S.; Ullman, J.B. Using Multivariate Statistics, 7th ed.; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-13-479054-1. [Google Scholar]
- Nunnally, J.C. Psychometric Theory 3E; Tata McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sinkovics, R.R. The Use of Partial Least Squares Path Modeling in International Marketing. In New Challenges to International Marketing; Emerald Group Publishing Ltd.: Bingley, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzels, M.; Odekerken-Schröder, G.; Van Oppen, C. Using PLS Path Modeling for Assessing Hierarchical Construct Models: Guidelines and Empirical Illustration. MIS Q. 2009, 33, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM); SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Leguina, A. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM); Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error: Algebra and Statistics. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.W. The Partial Least Squares Approach for Structural Equation Modeling. In Modern Methods for Business Research; Methodology for Business and Management; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 295–336. ISBN 978-0-8058-2677-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Academic Press: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]

| Category | Group (N = 625) | Frequency | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 288 | 46 |
| Female | 337 | 54 | |
| Age group | 20–24 | 125 | 20 |
| 25–34 | 250 | 40 | |
| 35–40 | 188 | 30 | |
| 41 and above | 62 | 10 | |
| Education | High school certificate | 94 | 15 |
| Bachelor’s degree | 469 | 75 | |
| Graduate degree | 62 | 10 | |
| Region | Eastern Europe | 344 | 55 |
| Middle East | 138 | 22 | |
| Western Europe | 106 | 17 | |
| Africa | 37 | 6 |
| Dimensions and Related Variables | Load. | α | C.R | AVE | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green electronic word-of-mouth (GeWOM) | 0.907 | 0.909 | 0.787 | ||
| In the coming days, I plan to regularly utilize SM platforms to communicate my own experiences of the eco-friendly destination. | 0.947 | 1.280 | |||
| I intend to make frequent use of SM platforms to share my own experiences of the green destination in the near future. | 0.929 | 3.672 | |||
| I will urge other friends to use SM platforms to share their own experiences of the green destination. | 0.909 | 4.078 | |||
| Through SM platforms, I aim to inspire others to visit environmentally friendly green destinations. | 0.750 | 1.573 | |||
| Green Ability | 0.952 | 0.954 | 0.839 | ||
| I usually have no trouble talking about environmental concerns with others on social media. | 0.903 | 3.513 | |||
| I have the ability to effectively convey environmental issues through social media platforms. | 0.936 | 4.024 | |||
| I am adept at handling environmental topics on social media platforms. | 0.932 | 3.381 | |||
| I view myself as highly proficient in using social media to address environmental issues. | 0.912 | 1.909 | |||
| I do not require an excessive amount of personal effort or time to locate environment-related content on social media platforms. | 0.897 | 1.136 | |||
| Green Attitude | 0.876 | 0.884 | 0.730 | ||
| Using social media platforms is a beneficial action. | 0.804 | 1.996 | |||
| Utilizing social media platforms is a prudent action. | 0.896 | 2.828 | |||
| Making use of social media platforms is an enjoyable action. | 0.857 | 2.168 | |||
| Using social media platforms is an appealing action. | 0.857 | 2.371 | |||
| Green Motivation | 0.887 | 0.888 | 0.818 | ||
| The environmental concerns discussed on SM platforms are usually pertinent to me. | 0.917 | 4.594 | |||
| I consistently find the environmental topics being discussed on SM platforms to be engaging. | 0.949 | 4.499 | |||
| Engaging in conversations about environmental issues on SM platforms invigorates me. | 0.844 | 1.880 | |||
| Green Opportunity | 0.816 | 0.831 | 0.726 | ||
| Social media provides me with access to information pertaining to environmental conservation and enables me to stay informed. | 0.882 | 3.941 | |||
| Expressing my thoughts and ideas related to the environment is effortless on social media platforms. | 0.863 | 3.730 | |||
| With my computer, laptop, mobile phone, and internet connection, I can easily access environmental information on social media platforms | 0.809 | 1.319 | |||
| Green Purchase Intention | 0.934 | 0.937 | 0.753 | ||
| It is probable that I will buy the product(s) offered on the website. | 0.865 | 1.957 | |||
| I am inclined to suggest the website to my acquaintances. | 0.888 | 1.953 | |||
| If I require a travel package that is available on the website, I am likely to make another purchase from it. | 0.810 | 1.059 | |||
| I intend to utilize the online channel for purchasing travel items in the future. | 0.920 | 1.862 | |||
| The website will be my primary preference for purchasing travel items. | 0.911 | 1.619 | |||
| I will contact the website to obtain more information regarding my future purchase. | 0.805 | 1.393 | |||
| GeWOM | G_Ability | G_Attitude | G_Motivation | G_Opportunity | G_Purchase Intention | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ablty_1 | 0.504 | 0.903 | 0.379 | 0.461 | 0.368 | 0.524 |
| Ablty_2 | 0.453 | 0.936 | 0.386 | 0.513 | 0.337 | 0.472 |
| Ablty_3 | 0.444 | 0.932 | 0.381 | 0.499 | 0.330 | 0.464 |
| Ablty_4 | 0.522 | 0.912 | 0.403 | 0.487 | 0.375 | 0.532 |
| Ablty_5 | 0.473 | 0.897 | 0.377 | 0.457 | 0.340 | 0.513 |
| Attitde_1 | 0.448 | 0.377 | 0.804 | 0.370 | 0.439 | 0.453 |
| Attitde_2 | 0.558 | 0.337 | 0.896 | 0.342 | 0.383 | 0.521 |
| Attitde_3 | 0.547 | 0.388 | 0.857 | 0.406 | 0.394 | 0.572 |
| Attitde_4 | 0.478 | 0.337 | 0.857 | 0.344 | 0.396 | 0.466 |
| GeWOM_1 | 0.947 | 0.460 | 0.566 | 0.519 | 0.434 | 0.679 |
| GeWOM_2 | 0.929 | 0.448 | 0.536 | 0.514 | 0.418 | 0.679 |
| GeWOM_3 | 0.909 | 0.462 | 0.558 | 0.480 | 0.445 | 0.696 |
| GeWOM_4 | 0.750 | 0.492 | 0.455 | 0.507 | 0.394 | 0.658 |
| Intntion_1 | 0.639 | 0.472 | 0.544 | 0.587 | 0.434 | 0.865 |
| Intntion_2 | 0.652 | 0.488 | 0.537 | 0.585 | 0.436 | 0.888 |
| Intntion_3 | 0.642 | 0.434 | 0.455 | 0.529 | 0.375 | 0.810 |
| Intntion_4 | 0.718 | 0.532 | 0.523 | 0.596 | 0.465 | 0.920 |
| Intntion_5 | 0.693 | 0.509 | 0.560 | 0.650 | 0.432 | 0.911 |
| Intntion_6 | 0.641 | 0.416 | 0.460 | 0.540 | 0.351 | 0.805 |
| Motvn_1 | 0.527 | 0.462 | 0.388 | 0.917 | 0.367 | 0.574 |
| Motvn_2 | 0.528 | 0.490 | 0.380 | 0.949 | 0.408 | 0.623 |
| Motvn_3 | 0.490 | 0.476 | 0.392 | 0.844 | 0.328 | 0.621 |
| Oportnty_1 | 0.340 | 0.321 | 0.336 | 0.302 | 0.882 | 0.332 |
| Oportnty_2 | 0.354 | 0.305 | 0.305 | 0.296 | 0.863 | 0.370 |
| Oportnty_3 | 0.487 | 0.342 | 0.508 | 0.409 | 0.809 | 0.485 |
| Fornell–Larcker Values | HTMT | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 0.887 | |||||||||||
| 0.525 | 0.916 | 0.564 | |||||||||
| 0.598 | 0.421 | 0.854 | 0.667 | 0.461 | |||||||
| 0.570 | 0.527 | 0.428 | 0.904 | 0.637 | 0.574 | 0.485 | |||||
| 0.478 | 0.384 | 0.469 | 0.407 | 0.852 | 0.536 | 0.427 | 0.534 | 0.462 | |||
| 0.766 | 0.549 | 0.593 | 0.671 | 0.480 | 0.868 | 0.834 | 0.579 | 0.650 | 0.736 | 0.529 | |
| Hypotheses | Beta (β) | (t-Value) | p Values | Results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Green Ability -> Green Purchase Intention | 0.165 | 4.287 | 0.000 | Accepted |
| H2 | Green Motivation -> Green Purchase Intention | 0.413 | 9.523 | 0.000 | Accepted |
| H3 | Green Opportunity -> Green Purchase Intention | 0.111 | 2.879 | 0.004 | Accepted |
| H4 | Green Ability -> GeWOM | 0.100 | 2.527 | 0.012 | Accepted |
| H5 | Green Motivation -> GeWOM | 0.051 | 1.080 | 0.280 | Not Acceped |
| H6 | Green Opportunity -> GeWOM | 0.078 | 1.930 | 0.054 | Not Acceped |
| H7 | Green Attitude -> Green Purchase Intention | 0.295 | 6.257 | 0.000 | Accepted |
| H8 | Green Attitude -> GeWOM | 0.183 | 4.465 | 0.000 | Accepted |
| H9 | Green Purchase Intention -> GeWOM | 0.531 | 8.973 | 0.000 | Accepted |
| Specific indirect effects | |||||
| Green Ability -> Green Purchase Intention -> GeWOM | 0.088 | 3.690 | 0.000 | Accepted | |
| Green Motivation -> Green Purchase Intention -> GeWOM | 0.219 | 6.495 | 0.000 | Accepted | |
| Green Opportunity -> Green Purchase Intention -> GeWOM | 0.059 | 2.574 | 0.010 | Accepted | |
| Green Attitude -> Green Purchase Intention -> GeWOM | 0.157 | 5.444 | 0.000 | Accepted | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Naim, A.F.; Sobaih, A.E.E.; Elshaer, I.A. Enhancing Green Electronic Word-of-Mouth in the Saudi Tourism Industry: An Integration of the Ability, Motivation, and Opportunity and Planned Behaviour Theories. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9085. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119085
Al Naim AF, Sobaih AEE, Elshaer IA. Enhancing Green Electronic Word-of-Mouth in the Saudi Tourism Industry: An Integration of the Ability, Motivation, and Opportunity and Planned Behaviour Theories. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):9085. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119085
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Naim, Abdullah F., Abu Elnasr E. Sobaih, and Ibrahim A. Elshaer. 2023. "Enhancing Green Electronic Word-of-Mouth in the Saudi Tourism Industry: An Integration of the Ability, Motivation, and Opportunity and Planned Behaviour Theories" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 9085. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119085
APA StyleAl Naim, A. F., Sobaih, A. E. E., & Elshaer, I. A. (2023). Enhancing Green Electronic Word-of-Mouth in the Saudi Tourism Industry: An Integration of the Ability, Motivation, and Opportunity and Planned Behaviour Theories. Sustainability, 15(11), 9085. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119085




_Li.png)




