Investigating the Moderating Role of Political Factors on Internal Success Factors and Project Success: Empirical Evidence from Pakistan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Theoretical Foundation
2.2. Categorization of Critical Success Factors
- Communication factors;
- Team factors;
- Technical factors;
- Organizational factors;
- Environmental factors.
2.3. Political Factors
2.4. Project Success
3. Hypothesis Development
3.1. Communication Factors
3.2. Organizational Factors
3.3. External Environmental Factors and Project Success
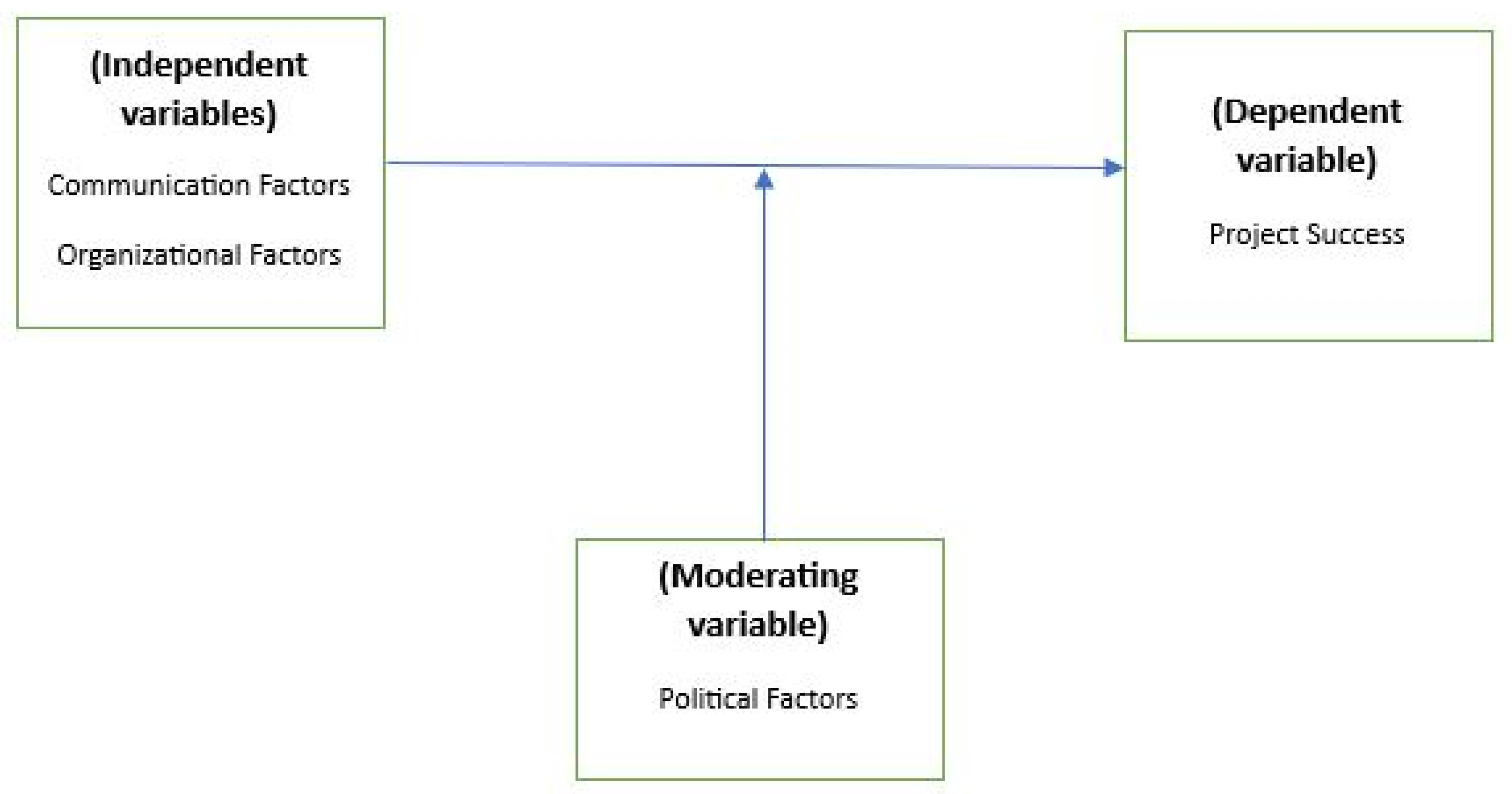
3.4. Conceptual Framework
4. Methodology
4.1. Research Approach
4.2. Instrument Development
4.3. Variables and Measures
4.4. Sample and Data Collection
5. Data Analysis and Results
5.1. Reliability and Validity Testing
5.2. Descriptive Analysis
5.3. Hypothesis Testing
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
7.1. Theoretical Findings
7.2. Practical Implications of the Study
7.3. Limitations and Avenues for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNEP. Emissions Gap Report 2022. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/emissions-gap-report-2022#:~:text=Yet%20the%20Emissions%20Gap%20Report,transformation%20can%20avoid%20climate%20disaster (accessed on 24 December 2022).
- IEA. Renewables 2022. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/renewables-2022/executive-summary (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- The World Bank. Solar Photovoltaic Power Potential by Country. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/energy/publication/solar-photovoltaic-power-potential-by-country (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- NEPRA. State of Industry Report 2021–22. Available online: https://nepra.org.pk/publications/State%20of%20Industry%20Reports.php (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Mirjat, N.H.; Uqaili, M.A.; Harijan, K.; Das Valasai, G.; Shaikh, F.; Waris, M. A Review of Energy and Power Planning and Policies of Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GoP. Energy projects under CPEC. Available online: https://cpec.gov.pk/energy (accessed on 7 October 2022).
- NTDC. Available online: https://ntdc.gov.pk/ntdc/public/uploads/downloads/NTDC.PSP.IGCEP.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Berman, N. What’s at Stake in Pakistan’s Power Crisis. Available online: https://www.cfr.org/in-brief/whats-stake-pakistans-power-crisis (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- AEDB. Current Status. Available online: https://www.aedb.org/ae-technologies/solar-power/solar-current-status (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Ghimire, L.P.; Kim, Y. An Analysis on Barriers to Renewable Energy Development in the Context of Nepal Using AHP. Renew. Energy 2018, 129, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yang, P. Risk Management in Distributed Wind Energy Implementing Analytic Hierarchy Process. Renew. Energy 2020, 150, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambodo, M.T.; Yuliana, C.I.; Hidayat, S.; Novandra, R.; Handoyo, F.W.; Farandy, A.R.; Inayah, I.; Yuniarti, P.I. Breaking Barriers to Low-Carbon Development in Indonesia: Deployment of Renewable Energy. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudha, S.W.; Tjahjono, B. Stakeholder Mapping and Analysis of the Renewable Energy Industry in Indonesia. Energies 2019, 12, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.A.; Shendrikova, D.; Crevani, G.; Silinto, B.; Colombo, E. Enabling Factors for the Development of Mini-Grid Solutions in Mozambique: A PESTLE-Based Analysis. Energy Strateg. Rev. 2023, 45, 101040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalengera, C.; Blanchard, R.E.; Eames, P.C.; Juma, A.M.; Chitawo, M.L.; Gondwe, K.T. Overview of the Malawi Energy Situation and A PESTLE Analysis for Sustainable Development of Renewable Energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohunakin, O.S.; Adaramola, M.S.; Oyewola, O.M.; Fagbenle, R.O. Solar Energy Applications and Development in Nigeria: Drivers and Barriers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasiri, B.; Dissanayake, P. Barriers to Implementing Waste-to-Energy Projects in Sri Lanka: A PESTEL Analysis. Built Environ. Proj. Asset Manag. 2021, 11, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, E.K.; Kilias, V.; Goumas, A.; Rigopoulos, A.; Karakatsani, E.; Damasiotis, M.; Papastefanakis, D.; Marini, N. Renewable Energy Sources (RES) Projects and Their Barriers on a Regional Scale: The Case Study of Wind Parks in the Dodecanese Islands, Greece. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 4874–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirov, S.; Silva, C.; Agostini, C.A. Investors’ Perspectives on Barriers to the Deployment of Renewable Energy Sources in Chile. Energies 2015, 8, 3794–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donastorg, A.; Renukappa, S.; Suresh, S. Evaluating Critical Success Factors for Implementing Renewable Energy Strategies in the Dominican Republic. Renew. Energy 2020, 149, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, R.; Sudong, Y. Critical Success Factors for Renewable Energy Projects; Empirical Evidence from Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, R. Efficiency and Effectiveness of Factors Affecting Renewable Energy Projects; an Empirical Perspective. Energy 2018, 158, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, S.; Chin, T.; Wang, M.; Asghar, A.; Khan, A. Exploring the Role of Organizational Support, and Critical Success Factors on Renewable Energy Projects of Pakistan. Energy 2022, 243, 12276. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Rasool, S.F.; Zhao, Y.; Samma, M.; Iqbal, J. Investigating the nexus between critical success factors, despotic leadership, and success of renewable energy projects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 10388–10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqbool, R.; Rashid, Y.; Ashfaq, S. Renewable energy project success: Internal versus external stakeholders’ satisfaction and influences of power-interest matrix. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 30, 1542–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, R.; Deng, X.; Rashid, Y. Stakeholders’ Satisfaction as a Key Determinant of Critical Success Factors in Renewable Energy Projects. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2020, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, W.G. Organizational Theory An Overview and an Appraisal. J. Acad. Manag. 1961, 4, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafritz, J.M.; Ott, J.S.; Jang, Y.S. Classics of Organization Theory, 8th ed.; Cengage Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-285-87027-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hatch, J.M.; Cunliffe, A.L. Theory Organization: Modern, Symbolic and Postmodern Perspectives, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; ISBN 9780199640379. [Google Scholar]
- Helms, M.M. Encyclopedia of Management, 5th ed.; Thomson Gale: Detroit, MI, USA, 2006; ISBN 8007624058. [Google Scholar]
- Leeman, J.; Wangen, M.; Kegler, M.; Lee, M.; Leary, M.C.O.; Ko, L.K.; Fernández, M.E.; Birken, S.A. Applying Theory to Explain the Influence of Factors External to an Organization on the Implementation of an Evidence-Based Intervention. Front. Heal. Serv. 2022, 2, 889786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, T.; Stalker, G.M. The Management of Innovation, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Tavistock, UK, 1994; ISBN 9780191684630. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, D.R. Management Information Crisis. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1961, 39, 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, J.K.; Slevin, D.P. Project Success: Definitions and Measurement Techniques. Proj. Manag. J. 1988, 19, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Leidecker, J.K.; Bruno, A.V. Identifying and Using Success Factors. Long Range Plann. 1984, 17, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, Y.P. Critical Success Factors. Planin. Rev. 2006, 16, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.K.; Slevin, D.P. Critical Success Factors in Effective Project Implementatio. In Project Management Handbook, 2nd ed.; Cleland, D.I., King, W.R., Eds.; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 902–909. [Google Scholar]
- Baccarini, D.; Collins, A. Critical Success Factors for Projects. In Proceedings of the 17th ANZAM Conference, Fremantle, Australia, 2–5 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Y.; Zuo, J.; Zillante, G. Factors Influencing the Success of BOT Power Plant Projects in China: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 22, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Y.; Zuo, J.; Zillante, G.; Wang, X.W. Critical Success Factors for BOT Electric Power Projects in China: Thermal Power versus Wind Power. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ika, L.A.; Diallo, A.; Thuillier, D. Critical Success Factors for World Bank Projects: An Empirical Investigation. JPMA 2012, 30, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, H.H.; Lee, S.W.; Chua, Q.S.; Goh, K.C.; Kok, B.C.; Teo, K.T.K. Renewable Energy Project: Project Management, Challenges and Risk. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 917–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, K.; Khallaf, R. Identification of the Barriers and Key Success Factors for Renewable Energy Public-Private Partnership Projects: A Continental Analysis. Buildings 2022, 12, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belassi, W.; Tukel, O.I. A New Framework for Determining Critical Success / Failure Factors in Projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 1996, 14, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarini, D. The Logical Framework Method for Defining Project Success. Proj. Manag. J. 1999, 30, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R. Project Management: Cost, Time and Quality, Two Best Guesses and a Phenomenon, Its Time to Accept Other Success Criteria. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 1999, 17, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.; Turner, R. The Influence of Project Managers on Project Success Criteria and Project Success by Type of Project. Eur. Manag. J. 2007, 25, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.N.; Murphy, D.C.; Fisher, D. Factors Affecting Project Success. In Project Management Handbook, 2nd ed.; Cleland, I.P., King, R.W., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 902–919. [Google Scholar]
- Jugdev, K.; Müller, R. A Retrospective Look at Our Evolving Understanding of Project Success. Proj. Manag. J. 2005, 36, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervone, H.F. Effective Communication for Project Success. OCLC Systmes Serv. Int. Digit. Libr. Perspect. 2014, 30, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsing, L. Project Communication in a Strategic Internal Perspective. Corp. Commun. An Int. J. 2009, 14, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegari, C.; Szklo, A.; Schaeffer, R. Cost Overruns and Delays in Energy Megaprojects: How Big Is Big Enough? Energy Policy 2018, 114, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arditi, D.; Nayak, S.; Damci, A. Effect of Organizational Culture on Delay in Construction. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwikael, O. Top Management Involvement in Project Management Exclusive Support Practices for Different. Int. J. Manag. Proj. Bus. 2014, 1, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.; Jordan, E. Top Management Support: Mantra or Necessity? Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2008, 26, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, G.P. A Model of Critical Success Factors for Software Projects. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2012, 25, 537–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khang, D.B.; Moe, T.L. Success Criteria and Factors for International Development Projects: A Life Cycle Based Framework. Proj. Manag. J. 2008, 39, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, G.; Sambasivan, M.; Viswanathan, K. Does Size of Construction Firms Matter ? Impact of Project-Factors and Organization-Factors on Project Performance. Built Environ. Proj. Asset Manag. 2020, 11, 174–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, A. Measurement of Project Success. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 1988, 6, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.P.C.; Scott, D.; Chan, A.P.L. Factors Affecting the Success of a Construction Project. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2004, 130, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Jamil, M.; Farooq, M.U.; Asim, M.; Rafique, M.Z.; Pruncu, C.I. Project Managers ’ Personality and Project Success: Moderating Role of External Environmental Factors. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, M.; Kock, A. Impact of Relationship Value on Project Portfolio Success—Investigating the Moderating Effects of Portfolio Characteristics and External Turbulence. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2013, 31, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, D.B.; Bonner, J.J. Political Risks in International Construction. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 1987, 113, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.M.; Amirudin, R.B.; Sofield, T. Influence of External Environmental Factors on the Success of Public Housing Projects in Developing Countries. Constr. Econ. Build. 2015, 15, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balnaves, M.; Caputi, P. Introduction to Quantitative Research Methods: An Investigative Approach, 1st ed.Sage Publications: London, UK, 2001; ISBN 0-7619-6803-2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, E.Y. Perceived Importance of Information System Success Factors: A Meta Analysis of Group Differences. Inf. Manag. 1997, 32, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, G.P. What Is Project Success: A Literature Review. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2008, 3, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Sarstedt, M.; Hopkins, L.; Kuppelwieser, V.G. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) An Emerging Tool in Business Research. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2014, 26, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, R.; Sudong, Y.; Manzoor, N.; Rashid, Y. The Impact of Emotional Intelligence, Project Managers’ Competencies, and Transformational Leadership on Project Success: An Empirical Perspective. Proj. Manag. J. 2017, 48, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S. Using Multivariate Statistics, 5th ed.; Pearson Education: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; ISBN 0-205-45938-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), 2nd ed.; Sage Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to Use and How to Report the Results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2018, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemy, M.; Teeroovengadum, V.; Becker, J.M.; Ringle, C.M. This Fast Car Can Move Faster: A Review of PLS-SEM Application in Higher Education Research. High. Educ. 2020, 80, 1121–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, U.; Rashid, T.U.; Khosa, A.A.; Khalil, M.S.; Rashid, M. An Overview of Implemented Renewable Energy Policy of Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittha, M. Renewable Energy Policy in Pakistan: A Critique. Available online: https://courtingthelaw.com/2021/04/19/commentary/renewable-energy-policy-in-pakistan-a-critique/ (accessed on 6 December 2022).
| Critical Success Factors | References |
|---|---|
| Communication Factors | |
| A key area of project management. Whole project | [29,32,33] |
| aspects are reliant on the effectiveness of communication. | |
| Its effectiveness and brevity provide an environment | |
| that delivers project success. | |
| Organizational Factors | |
| This refers to the best processes, methods, and techniques | [35,38,39] |
| devised to achieve project success. | |
| External Environmental Factors | |
| Environmental factors refer to the factors that | [16,23,25,40,42] |
| are not under the control of the project team. | |
| Domains include political, economic, social, | |
| technological, and natural disasters. | |
| Country | Source | Political Environment | RE Policy | Fiscal Subsidies/Incentives | Taxation | Transparency in Decision-Making | Corruption | Approval Process | Land Acquisition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | [11] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Indonesia | [13] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Indonesia | [12] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Nigeria | [16] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Sri Lanka | [17] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Malawi | [15] | ✓ | |||||||
| Chile | [19] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Nepal | [10] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Mozambique | [14] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Greece | [18] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Dominican Republic | [20] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Hypotheses | Theoretical Support | References |
|---|---|---|
| H1: Communication factors positively affect a project’s success. | Modern Organizational Theory | [27,29,30] |
| H2: Organizational factors positively affect a project’s success. | Modern Organizational Theory | |
| H3: The relation between communication factors and project success weakens when political factors increase. | Environmental Contingency Theory | [29,30,31] |
| H4: The relation between organizational factors and project success weakens when political factors increase. | Environmental Contingency Theory | [29,30,31] |
| Variables | Dimensions | Items | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication Factors (CFs) | Communication, leadership, relationship between client and project leadership, reduce ambiguity, maximize stability, cooperation, and balance between flexibility and rigidity. | 10 | [56,66,67] |
| Organizational Factors (OFs) | Top management support, realistic expectations, organizational politics, financial support, power, market intelligence, personal recruitment, business process re-engineering, reducing a cost base, increasing efficiency, and attrition. | 7 | [56] |
| Project Success (PS) | Within stipulated time, cost, quality, and stakeholder satisfaction. | 9 | [47,69] |
| Political Factors (PFs) | Stability of political environment, government support, government guarantees to developers, supporting legal framework, provision of secured land by the government, and sufficient funding by the government. | 6 | [40,64] |
| Characteristics | Category | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 204 | 85.71 |
| Female | 34 | 14.28 | |
| Working Experience | 5–10 years | 150 | 63.02 |
| 10–15 years | 61 | 25.63 | |
| Above 15 years | 27 | 11.34 | |
| Positions | Project directors | 32 | 13.44 |
| Managers | 91 | 38.23 | |
| Functional manager | 42 | 17.64 | |
| Leaders of the team | 34 | 14.28 | |
| Project site engineers | 24 | 10.08 | |
| Other staff | 15 | 6.30 | |
| Education | Post-graduate | 53 | 22.26 |
| Graduate | 110 | 46.21 | |
| Others | 75 | 31.51 |
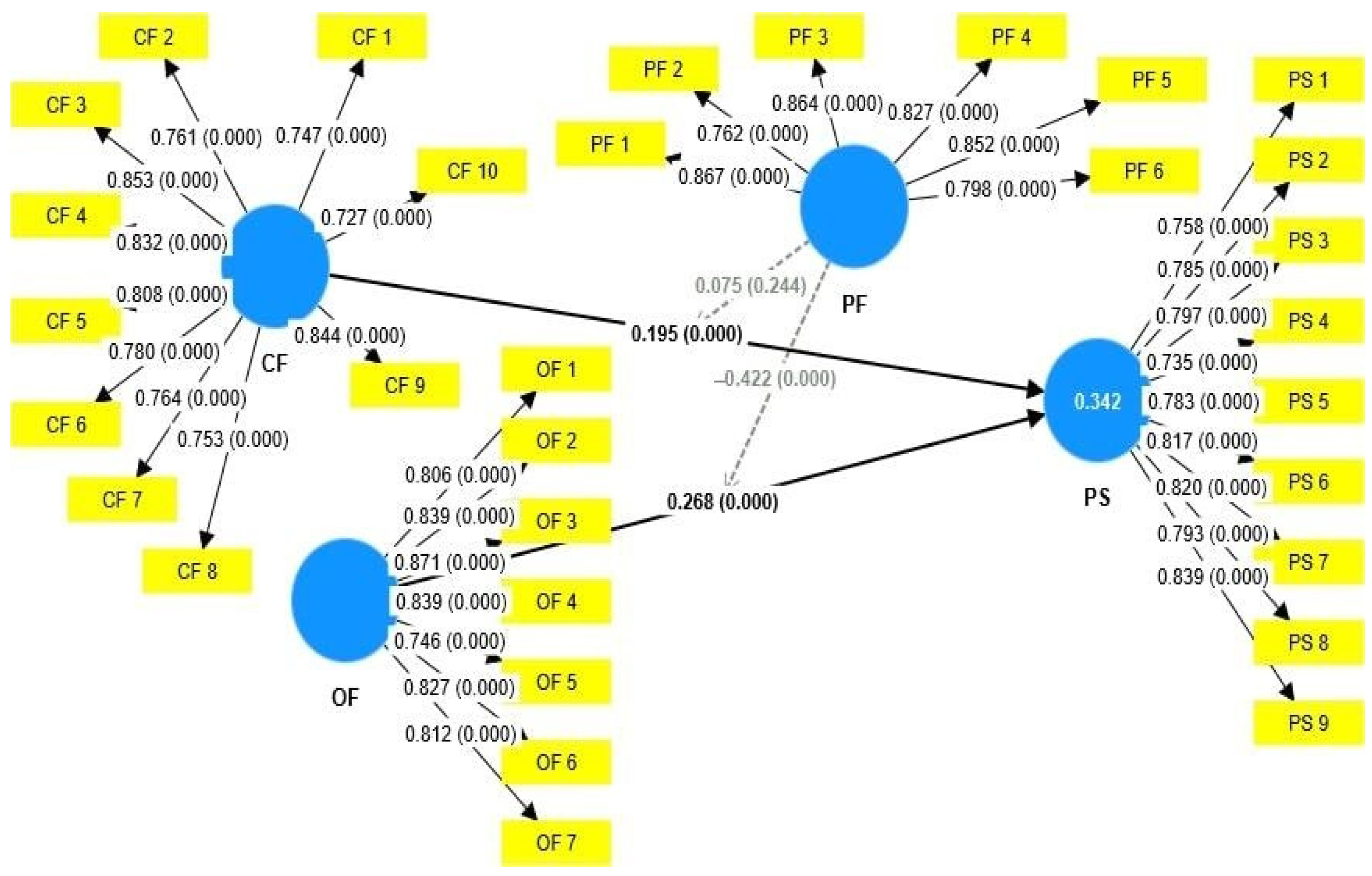
| Indicators | Loading | CA | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Communication factors | 0.933 | 0.942 | 0.621 | |
| CF1 | 0.747 | |||
| CF2 | 0.761 | |||
| CF3 | 0.853 | |||
| CF4 | 0.832 | |||
| CF5 | 0.808 | |||
| CF6 | 0.780 | |||
| CF7 | 0.764 | |||
| CF8 | 0.753 | |||
| CF9 | 0.844 | |||
| CF10 | 0.727 | |||
| Organizational factors | 0.920 | 0.935 | 0.674 | |
| OF1 | 0.806 | |||
| OF2 | 0.839 | |||
| OF3 | 0.871 | |||
| OF4 | 0.839 | |||
| OF5 | 0.746 | |||
| OF6 | 0.827 | |||
| OF7 | 0.812 | |||
| Political factors | 0.911 | 0.930 | 0.688 | |
| PF1 | 0.867 | |||
| PF2 | 0.762 | |||
| PF3 | 0.864 | |||
| PF4 | 0.827 | |||
| PF5 | 0.852 | |||
| PF6 | 0.798 | |||
| Project success | 0.926 | 0.938 | 0.628 | |
| PS1 | 0.758 | |||
| PS2 | 0.785 | |||
| PS3 | 0.797 | |||
| PS4 | 0.735 | |||
| PS5 | 0.783 | |||
| PS6 | 0.817 | |||
| PS7 | 0.820 | |||
| PS8 | 0.793 | |||
| PS9 | 0.839 | |||
| No. | Factors | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CF | |||||
| 2 | OF | 0.149 | ||||
| 3 | PF | 0.083 | 0.063 | |||
| 4 | PS | 0.180 | 0.274 | 0.167 | ||
| 5 | PF × OF | 0.049 | 0.072 | 0.023 | 0.485 | |
| 6 | PF × CF | 0.045 | 0.061 | 0.051 | 0.128 | 0.149 |
| Dimension Correlation | VIF |
|---|---|
| CF and PS | 1.028 |
| OF and PS | 1.026 |
| PF and PS | 1.007 |
| PF × OF and PS | 1.033 |
| PF × CF and PS | 1.033 |
| Constructs | R2 | Adjusted R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Project Success | 0.342 | 0.328 |
| No. | Coding | Items | Min | Max | Mean | Std. Dev |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CF1 | I believe communication creates an atmosphere for achieving project success. | 1 | 5 | 3.886 | 0.914 |
| 2 | CF2 | I believe there should be realistic expectations from management, user, and client to increase project success. | 1 | 5 | 3.873 | 0.914 |
| 3 | CF3 | I believe funder involvement is necessary to make a project successful. | 1 | 5 | 3.831 | 1.009 |
| 4 | CF4 | I believe customer involvement is necessary to make a project successful. | 1 | 5 | 3.768 | 0.990 |
| 5 | CF5 | I believe vendor partnership is necessary to make a project successful. | 1 | 5 | 3.819 | 1.038 |
| 6 | CF6 | I consider client acceptance influences project success. | 1 | 5 | 3.831 | 0.996 |
| 7 | CF7 | I believe availability of on-time information increases the probability of project success. | 1 | 5 | 3.852 | 0.985 |
| 8 | CF8 | I believe effective communication among project stakeholders helps to reduce any ambiguity. | 1 | 5 | 3.928 | 0.885 |
| 9 | CF9 | I believe maximum stability and cooperation could be attained by effective communication between project participants. | 1 | 5 | 3.852 | 1.031 |
| 10 | CF10 | I believe effective communication helps to create a balance between flexibility and rigidity during decision-making by project parties. | 1 | 5 | 3.810 | 1.016 |
| 11 | OF1 | The nature of my relationship with clients, as a member of a construction/engineering organization, affects project success. | 1 | 5 | 3.785 | 1.051 |
| 12 | OF2 | I believe management support is necessary for the people working on project sites to use their capabilities. | 1 | 5 | 3.907 | 0.994 |
| 13 | OF3 | I believe financial support can have a constructive influence on project performance. | 1 | 5 | 3.920 | 0.927 |
| 14 | OF4 | I believe documentation of systems and procedures should be followed. | 1 | 5 | 3.899 | 1.034 |
| 15 | OF5 | I believe an organization should have realistic expectations regarding the work performance of project employees. | 1 | 5 | 3.941 | 0.855 |
| 16 | OF6 | I believe market intelligence is necessary for project organizations to judge ongoing trends in the current market. | 1 | 5 | 3.907 | 0.937 |
| 17 | OF7 | I believe project organizations should go for business process re-engineering according to the requirements of the business situation. | 1 | 5 | 3.937 | 0.905 |
| 18 | PF1 | I believe stability in the political situation of a country affects project success. | 1 | 5 | 3.241 | 1.161 |
| 19 | PF2 | I believe government support of renewable projects affects project success. | 1 | 5 | 3.203 | 1.080 |
| 20 | PF3 | I believe government guarantees play a significant role in timely implementation of a project. | 1 | 5 | 3.190 | 1.209 |
| 21 | PF4 | I believe the legal system is important for project stakeholders. | 1 | 5 | 3.190 | 1.107 |
| 22 | PF5 | I believe the provision of land helps to decide about investment in a project. | 1 | 5 | 3.270 | 1.156 |
| 23 | PF6 | I believe that adequate funding by government plays a significant role in timely achievement of project milestones. | 1 | 5 | 3.241 | 1.066 |
| 24 | PS1 | I always complete my assigned projects within the given timeframe. | 1 | 5 | 4.131 | 0.798 |
| 25 | PS2 | I always complete my projects within the assigned budget. | 2 | 5 | 4.135 | 0.745 |
| 26 | PS3 | I always fulfill the quality demands of the customers. | 1 | 5 | 4.110 | 0.799 |
| 27 | PS4 | I always satisfy my team associates. | 2 | 5 | 4.105 | 0.775 |
| 28 | PS5 | I always manage to get stakeholders’ satisfaction with the project deliverables. | 1 | 5 | 4.127 | 0.801 |
| 29 | PS6 | I always achieve project owners’ satisfaction with project deliverables. | 1 | 5 | 4.135 | 0.773 |
| 30 | PS7 | I always ensure suppliers’ satisfaction. | 1 | 5 | 4.122 | 0.825 |
| 31 | PS8 | I always achieve a project’s purpose. | 1 | 5 | 4.114 | 0.811 |
| 32 | PS9 | I am assured that projects assigned to me have reached their self-defined success measures. | 1 | 5 | 4.118 | 0.863 |
| Hypothesis Relationship | Coefficient | Mean | SD | T Statistic | p Value | Confidence Interval | Findings | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit Upper Limit | |||||||||
| H1 | CF-PS | 0.195 | 0.217 | 0.049 | 4.002 | 0.000 | 0.146 | 0.295 | Significant |
| H2 | OF-PS | 0.268 | 0.272 | 0.057 | 4.685 | 0.000 | 0.185 | 0.359 | Significant |
| H3 | PF-CF and PS | 0.075 | 0.078 | 0.064 | 1.165 | 0.244 | −0.027 | 0.183 | Insignificant |
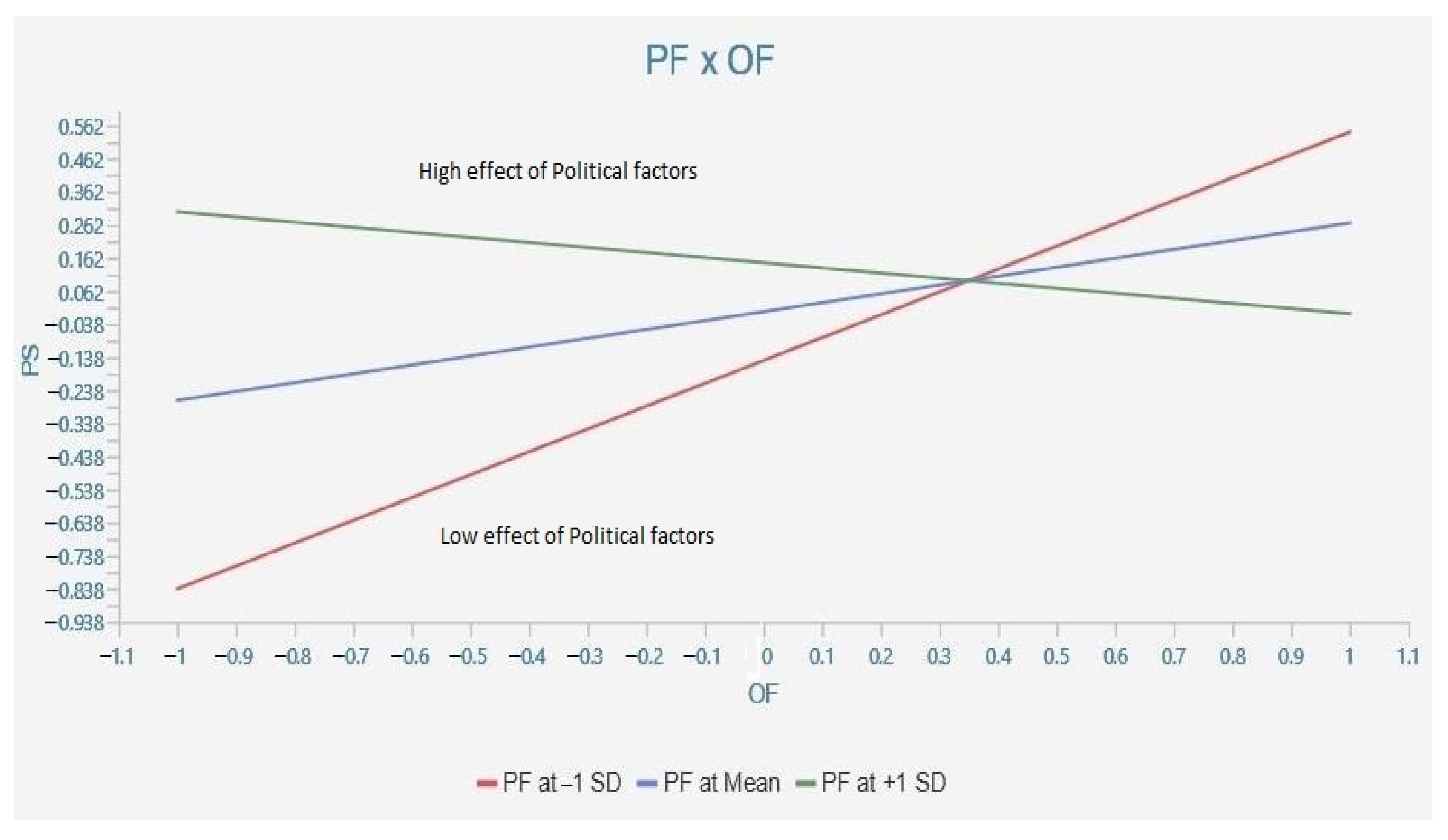
| H4 | PF-OF and PS | −0.422 | −0.404 | 0.071 | 5.977 | 0.000 | −0.494 | −0.294 | Significant |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haris, M.; Yang, Q. Investigating the Moderating Role of Political Factors on Internal Success Factors and Project Success: Empirical Evidence from Pakistan. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8910. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118910
Haris M, Yang Q. Investigating the Moderating Role of Political Factors on Internal Success Factors and Project Success: Empirical Evidence from Pakistan. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):8910. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118910
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaris, Muhammad, and Qing Yang. 2023. "Investigating the Moderating Role of Political Factors on Internal Success Factors and Project Success: Empirical Evidence from Pakistan" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 8910. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118910
APA StyleHaris, M., & Yang, Q. (2023). Investigating the Moderating Role of Political Factors on Internal Success Factors and Project Success: Empirical Evidence from Pakistan. Sustainability, 15(11), 8910. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118910






