Quantifying the Potential Co-Benefit of Air Quality Improvement on Cultural Heritage in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
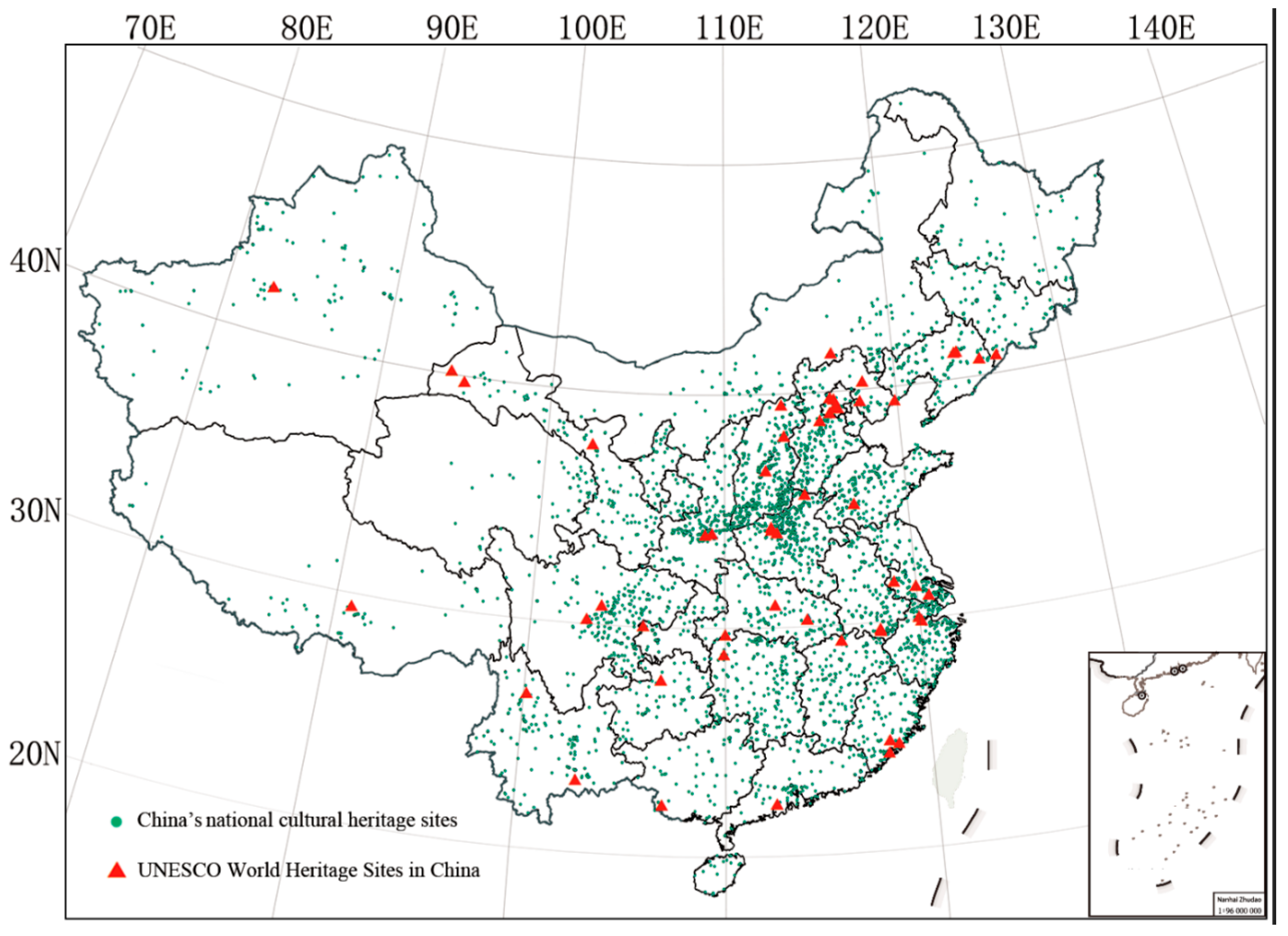
2.1. Scope
2.2. Methods
- R = surface recession or corrosion depth, μm;
- Rh = annual average relative humidity, %;
- Rh60 = Rh–60 when Rh > 60, and 0 otherwise;
- Rain = annual amount of precipitation (mm year−1);
- T = annual average temperature, °C;
- [SO2] = annual average SO2 concentration, μg m−3;
- [HNO3] = annual average HNO3 concentration, μg m−3;
- [O3] = annual average O3 concentration, μg m−3;
- [PM10] = annual average PM10 concentration, μg m−3;
- [H+] = annual average H+ concentration in rain, mg L−1.
2.3. Data
3. Results
3.1. The Pollutant Emissions in 2006–2020
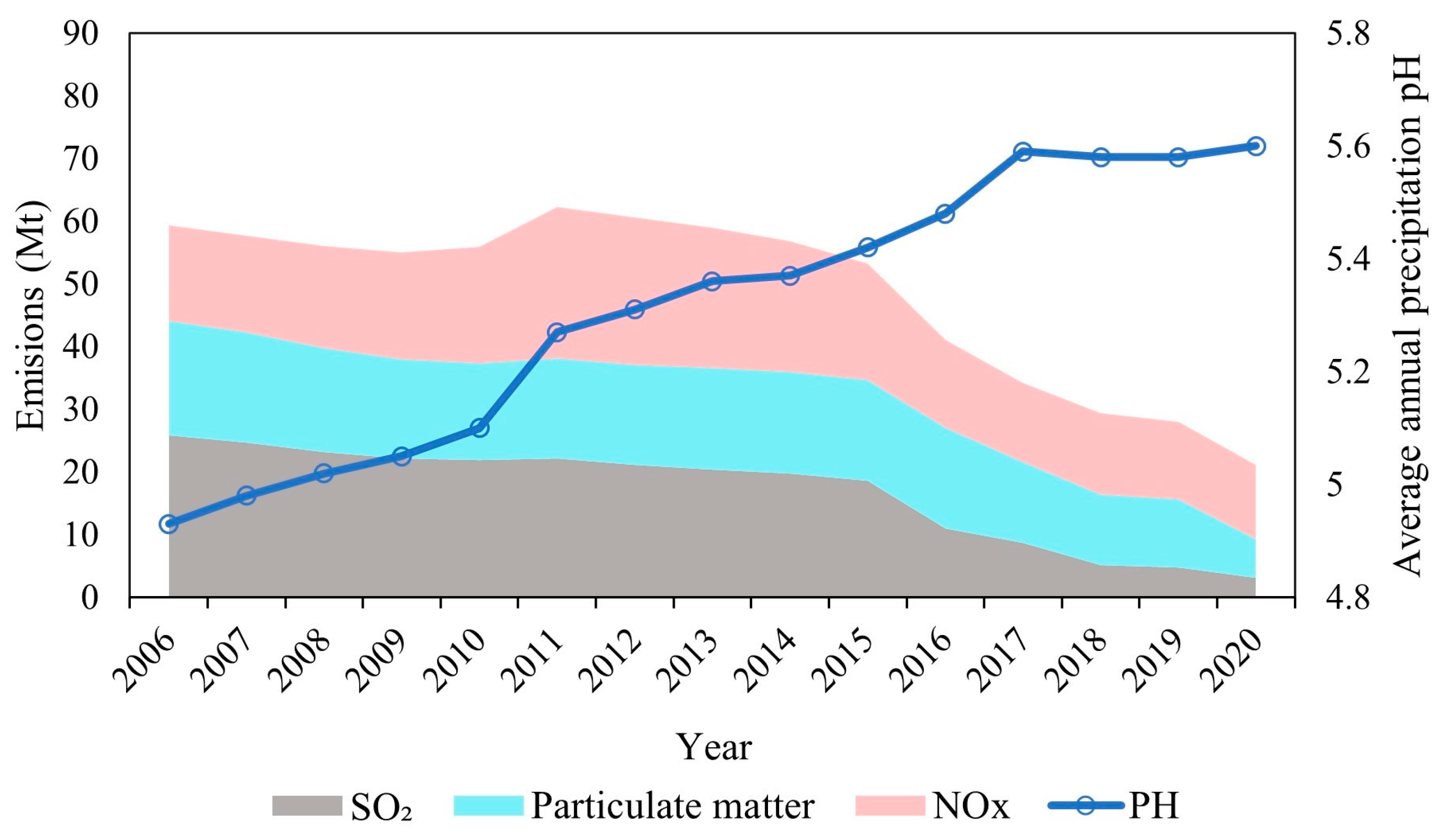
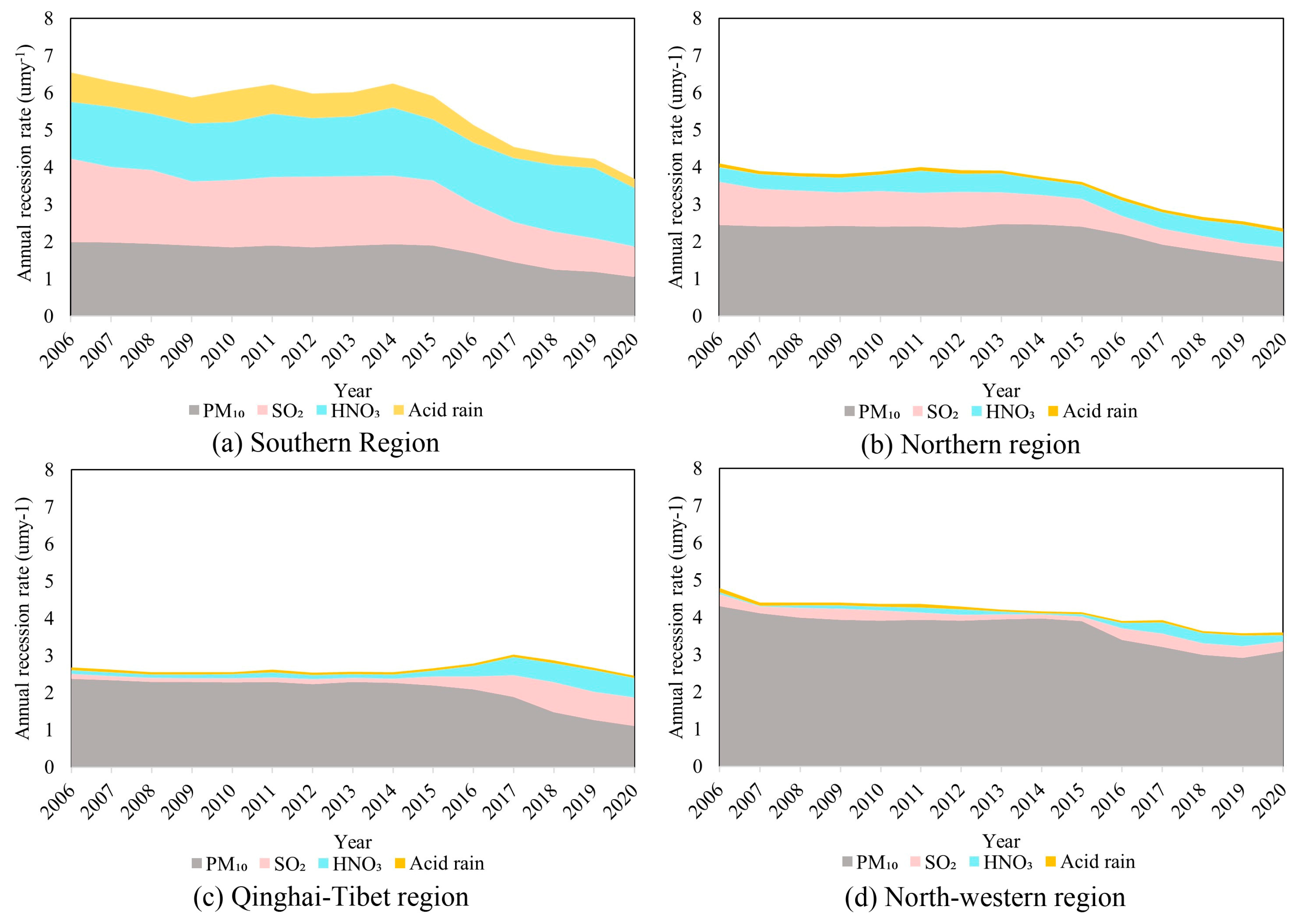
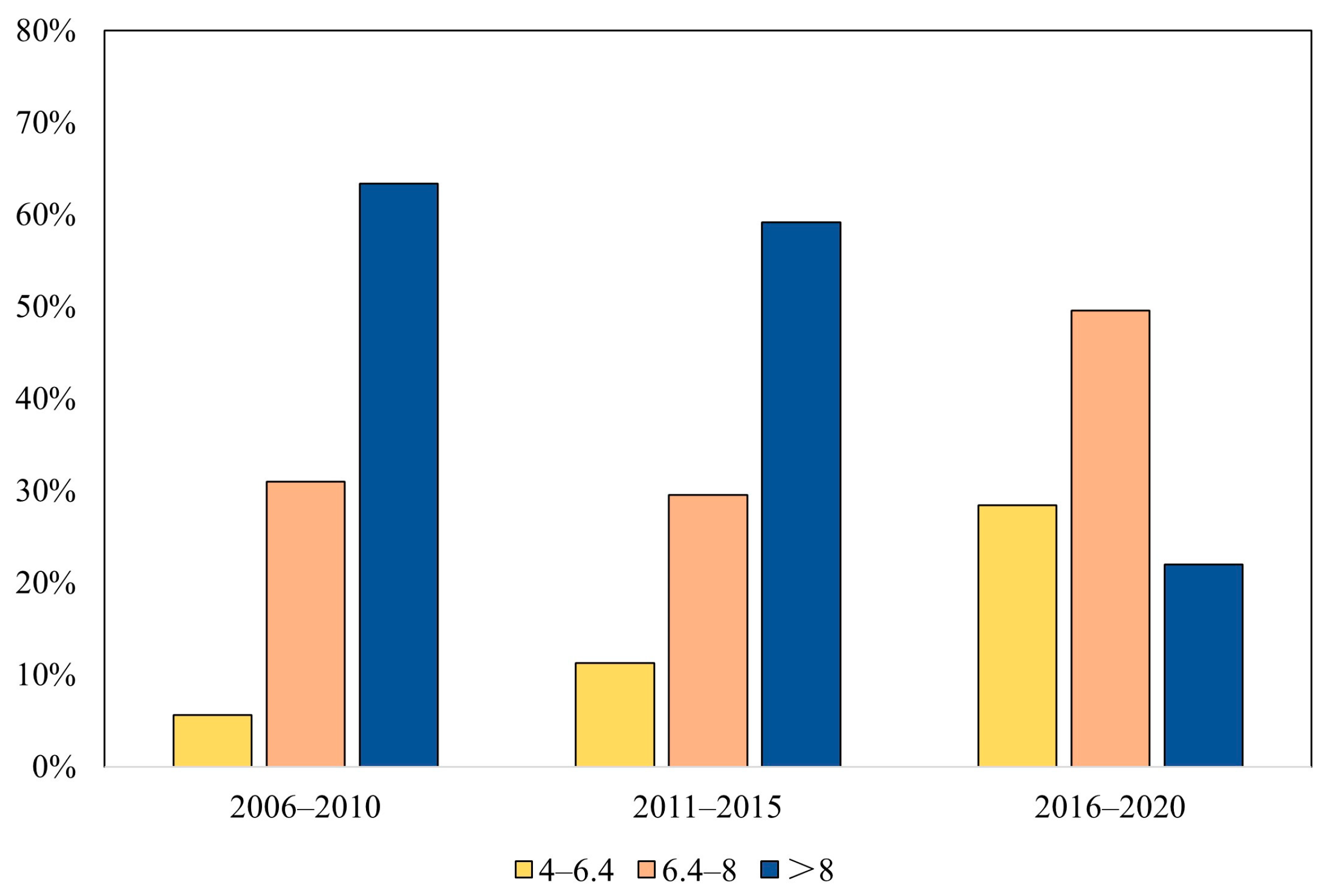
3.2. The Recession Depths of Heritage
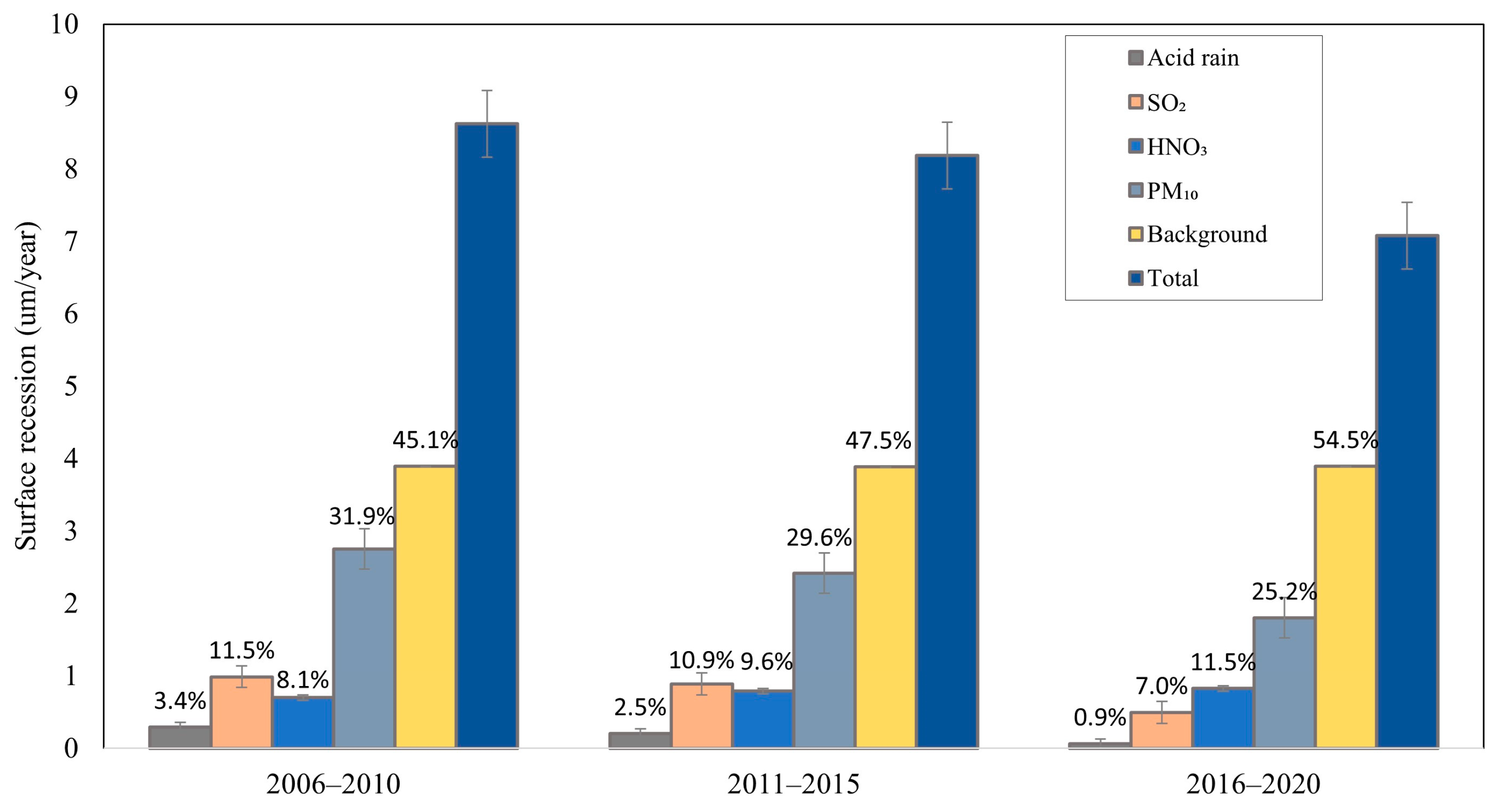
3.3. Contribution of Different Pollutants to Heritage Recession
3.4. The Risk Level of Limestone Heritage
4. Discussion
4.1. The Losses Avoided from Air Quality Improvement
4.2. Policy Implications for Heritage Conservation
4.2.1. Paying Attention to the Degradation Risk of Heritage
4.2.2. Promoting Heritage Conservation through Social Sustainability
4.2.3. Implementing Differentiated Conservation Tactics
4.3. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marta, D.L.T. Values and Heritage Conservation. Herit. Soc. 2013, 6, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Andreu, M. Heritage Values and the Public. J. Community Archaeol. Herit. 2017, 4, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spennemann, D.H.R. Beyond “Preserving the Past for the Future”: Contemporary Relevance and Historic Preservation. CRM J. Herit. Steward 2011, 8, 7–22. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, J.D. Stone Patina. A Controversial Concept of Relevant Importance in Conservation, International Seminar Theory and Practice in Conservation. A Tribute to Cesare Brandi, Lisbon, Portugal. 2006. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261611730_Stone_patina_A_controversial_concept_of_relevant_importance_in_conservation (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Silva, C.; Vélez, G.; Colorado, H.A. Patina in the construction of the poetic bronze image: Science of materials, art and philosophy. Herit. Sci. 2017, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, F.; Vicente, R.; Silva, J.M. Review of environmental and air pollution impacts on built heritage:10 questions on corrosion and soiling effects for urban intervention. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 23, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO Policy Document on the Impacts of Climate Change on World Heritage Properties, The 16th General Assembly of States Parties to the World Heritage Convention, Paris. 2008. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/sessions/16GA/documents/ (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- Vidović, K.; Hočevar, S.; Menart, E.; Drventić, I. Impact of air pollution on outdoor cultural heritage objects and decoding the role of particulate matter: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 46405–46437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimblecombe, P.; Lefèvre, R.-A. Weathering of materials at Notre-Dame from changes in air pollution and climate in Paris, 1325–2090. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 50, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonazza, A.; Sardella, A.; Kaiser, A.; Cacciotti, R.; Nuntiis, P.D.; Hanus, C.; Maxwell, I.; Drdácký, T.; Drdácký, M. Safeguarding cultural heritage from climate change related hydrometeorological hazards in Central Europe. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 63, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doehne, E.; Price, C.A. Stone Conservation: An Overview of Current Research, 2nd ed.; Getty Conservation Institute: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2010; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Rabl, A. Air pollution and buildings: An estimation of damage costs in france. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 1999, 19, 361–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, R.; Kucera, V.; Tidblad, J.; Watt, J. The Effects of Air Pollution on Cultural Heritage; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 312. [Google Scholar]
- Butlin, R.N. Effects of air pollutants on buildings and materials. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. B Biol. Sci. 1990, 97, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabl, A.; Spadaro, J.V.; Holland, M. Impacts of air pollution on building materials. In How Much Is Clean Air Worth?: Calculating the Benefits of Pollution Control; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 131–159. [Google Scholar]
- Kucera, V.; Fitz, S. Direct and indirect air pollution effects on materials including cultural monuments. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995, 85, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozga, I.; Bonazza, A.; Bernardi, E.; Tittarelli, F.; Favoni, O.; Ghedini, N.; Morselli, L.; Sabbioni, C. Diagnosis of surface damage induced by air pollution on 20th-century concrete buildings. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4986–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesch, S.; Faller, M. Environmental effects on materials: The effect of the air pollutants SO2, NO2, NO and O3 on the corrosion of copper, zinc and aluminium. A short literature survey and results of laboratory exposures. Corros. Sci. 1997, 39, 1505–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getty Conservation Institute. Stone Conservation: The International Course on Stone Conservation. Available online: https://www.getty.edu/conservation/publications_resources/teaching/intl_course_stone.html (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Přikryl, R.; Smith, B.J. Building Stone Decay: From Diagnosis to Conservation; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grøntoft, T.; Verney-Carron, A.; Tidblad, J. Cleaning Costs for European Sheltered White Painted Steel and Modern Glass Surfaces Due to Air Pollution Since the Year 2000. Atmosphere 2015, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieken, R.V.; Delalieux, F.; Gysels, K. Cultural heritage and the environment. In Proceedings of the XI CHEMRAWN Meeting on Environmental Chemistry: Latin American Symposium on Environmental Analytical Chemistry, Montevideo, Uruguay, 15–20 March 1998; IUPAC: Antwerpen, Belgium, 1998; pp. 2327–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaskova, M.; Kotes, P.; Brodnan, M. Air Pollution as an Important Factor in Construction Materials Deterioration in Slovak Republic. Procedia Eng. 2015, 108, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, S.W. The effects of ozone and NOx on the deterioration of calcareous stone. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 227, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baedecker, P.A.; Reddy, M.M. The erosion of carbonate stone by acid rain: Laboratory and field investigations. J. Chem. Educ. 1993, 70, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidorni, G.; Sardella, A.; Nuntiis, P.D.; Volpi, F. Air pollution impact on carbonate building stones in Italian urban sites. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2019, 134, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, S.; Pedersoli, J.L., Jr. The ABC Method: A Risk Management Approach to the Preservation of Cultural Heritage. Canadian Conservation Institute 1030 Innes Road. 2016. Available online: https://www.iccrom.org/publication/abc-method-risk-management-approach-preservation-cultural-heritage (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- Samie, F.; Tidblad, J.; Kucera, V.; Leygraf, C. Atmospheric corrosion effects of HNO3—Comparison of laboratory-exposed copper, zinc and carbon steel. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4888–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidblad, J.; Kucera, V.; Ferm, M.; Kreislova, K. Effects of Air Pollution on Materials and Cultural Heritage: ICP Materials Celebrates 25 Years of Research. Atmos. Corros. 2013, 2012, 496321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, D.; Vega, J.M.; Viejo, F. Mapping air pollution effects on atmospheric degradation of cultural heritage. J. Cult. Herit. 2012, 14, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paola, F.; Comite, V.; Ciantelli, C.; Sardella, A.; Bonazza, A. A multi-analytical approach to study the chemical composition of total suspended particulate matter (TSP) to assess the impact on urban monumental heritage in Florence. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D. Historical Documents as Proxy Data in Venice and Its Marine Environment; Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Climate Science: Venice, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, C.M.; Brimblecombe, P. Effect of long-term changes in air pollution and climate on the decay and blackening of European stone buildings. Build. Stone Decay Diagn. Conserv. 2007, 271, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screpanti, A.; Marco, A.D. Corrosion on cultural heritage buildings in Italy: A role for ozone. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontozova-Deutsch, V.; Deutsch, F.; Godoi, R.H.M. Urban air pollutants and their micro effects on medieval stained glass windows. Microchem. J. 2011, 99, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonazza, A.; Messina, P.; Sabbioni, C.; Grossi, C.M.; Brimblecombe, P. Mapping the impact of climate change on surface recession of carbonate buildings in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, C.M.; Murray, M.; Butlin, R.N. Response of porous building stones to acid deposition. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995, 85, 2713–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalagli, N.; Kita, A.; Castaldo, V.L.; Pisello, A.L.; Ubertini, F. Hierarchical environmental risk mapping of material degradation in historic masonry buildings: An integrated approach considering climate change and structural damage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 215, 998–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, F.; Vicente, R.; Bastos, A.C.; Rocha, A.M.F.; Silva, J.M. Atmospheric corrosion in two different urban environments in Portugal: Results of one-year exposure. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, C.M.; Murray, M. Characteristics of carbonate building stones that influence the dry deposition of acidic gases. Constr. Build. Mater. 1999, 133, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omari, A.; Brunetaud, X.; Beck, K.; Al-Mukhtar, M. Thermal stress and damage risk in the stones of Al-Ziggurat in Al-Nimrud city, Iraq. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 37, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.-G. Synergistic effects of air pollutants on the atmospheric corrosion of metals and calcareous stones. Mar. Chem. 1990, 30, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baedecker, P.A.; Reddy, M.M.; Reimann, K.J.; Sciammarella, C.A. Effects of acidic deposition on the erosion of carbonate stone—Experimental results from the U.S. National Acid Precipitation Assessment Program (NAPAP). Atmos Environ. Part B Urban Atmos 1992, 26, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, R.A. Graphical methods for examining the effects of acid rain and sulfur dioxide on carbonate stones. In Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Deterioration and Conservation of Stone, Lisbon, Portugal, 15–18 June 1992; pp. 375–386. [Google Scholar]
- Lipfert, F.W. Atmospheric damage to calcareous stones: Comparison and reconciliation of recent experimental findings. Atmos. Environ. 1989, 23, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.H.; Bawden, R.J.; Busby, A.K.; Hopkins, J.N. Studies on the effects of air pollution on limestone degradation in Great Britain. Atmos. Environ. 1992, 26, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, V. Model for Multi-Pollutant Impact and Assessment of Threshold Levels for Cultural Heritage. EU 5FP RTD Project: 2005. Available online: https://www.ri.se/sites/default/files/2021-04/ICP-MULTI-ASSESS-Publishable-final-report.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- Tidblad, J.; Kucera, V.; Mikhailov, A.A.; Henriksen, J.; Kreislova, K. UN ECE ICP Materials: Dose-Response Functions on Dry and Wet Acid Deposition Effects After 8 Years of Exposure. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 130, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, V.; Tidblad, J.; Kreislova, K.; Knotkova, D.; Faller, M. UN/ECE ICP Materials Dose-response Functions for the Multi-pollutant Situation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 7, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, F. Mapping the corrosion impact of air pollution on the historical peninsula of Istanbul. J. Cult. Herit. 2012, 14, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-S.; Hsieh, C.-M.; Hsu, M.-F. Using heritage risk maps as an approach to estimating the threat to materials of traditional buildings in Tainan (Taiwan). J. Cult. Herit. 2014, 15, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spezzano, P. Mapping the susceptibility of UNESCO World Cultural Heritage sites in Europe to ambient (outdoor) air pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRC People’s Commentary: The Protection and USE of cultural Relics to Move forward to a Strong Country. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-11/22/content_5652399.htm (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- Li, H. Physicochemical Analysis of Atmospheric Pollutants in Terracotta Pits and Their Effects on Deterioration of Cultural Relics. Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences 2015. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CDFDLAST2015&filename=1015986095.nh (accessed on 26 October 2022). (In Chinese).
- Xiao, B.; Ning, L.; Lin, Z.; Wang, S.; Zang, H. The Impact of Air Pollution on the Protection of World Cultural Heritage in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Tong, D.; Hao, J. Drivers of improved PM2.5 air quality in China from 2013 to 2017. Environ. Sci. 2019, 116, 24463–24469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEE. Bulletin on the State of China’s Ecological Environment 2013–2020. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China; 2021. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/ (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- China State Council, Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan. 2013. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2013-09/12/content_ (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Spatiotemporal distribution of ground-level ozone in China at a city level. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The NPC Standing Committee. The Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Protection of Cultural Relics in Beijing; 2007. Available online: http://www.ncha.gov.cn/art/2007/10/29/art_2301_42894.html (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- National Cultural Heritage Administration of China. Cultural Relics at the National Level. Available online: http://www.ncha.gov.cn/col/col2262/index.html (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- World Heritage Convention. UNESCO World Heritage List in China. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/statesparties/cn (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- CLRTAP. Mapping of Effects on Materials, Chapter IV of Manual on Methodologies and Criteria for Modelling and Mapping Critical Loads and Levels and Air Pollution Effects, Risks and Trends. UNECE Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution. 2014. Available online: www.icpmapping.org (accessed on 11 March 2023).
- ChinaHighO3: Big Data Full-Coverage Ground-Level MDA8 O3 L2 Daily 0.1 Deg Product. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/5765588#.ZGLh8BFBztU (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- ChinaHighPM10: Big Data Seamless 1 km Ground-Level PM10 Dataset for China. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/6449937#.ZGI-CBFBztV (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. Regional 1 km Resolution Monthly Average Relative Humidity Dataset for China (2000–2020). Available online: http://www.geodata.cn/data/datadetails.html?dataguid=5361255&docId=5738 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. Monthly Average Temperature Dataset at 1 km Resolution for China, 1901–2021. Available online: http://www.geodata.cn/data/datadetails.html?dataguid=164304785536614&docId=1975 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. Annual Precipitation Data at 1 km Resolution in China (2001–2020). Available online: http://www.geodata.cn/data/datadetails.html?dataguid=113786088533256&docId=5697 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. The 10 km High-Resolution High-Quality Year-by-Year Near-Surface NO2 Dataset in China (2013–2018). Available online: http://www.geodata.cn/data/datadetails.html?dataguid=184194340398183&docId=1251 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. 0.1° Global Year-by-Year SO2 Surface Emissions Dataset (1970–2012). Available online: http://www.geodata.cn/data/datadetails.html?dataguid=227961991712104&docId=26236 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. 0.1° Global Year-by-Year NOx Surface Emissions Dataset (1970–2012). Available online: http://www.geodata.cn/data/datadetails.html?dataguid=140001060837618&docId=14385 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. 10 km High-Resolution, High-Quality, Year-by-Year Near-Surface SO2 Dataset for China (2013–2020). Available online: http://www.geodata.cn/data/datadetails.html?dataguid=232572854729661&docid=1254 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China. 1 km High-Resolution High-Quality Year-by-Year near-Surface NO2 Dataset for China (2019–2020). Available online: http://www.geodata.cn/data/datadetails.html?dataguid=234756137240935&docId=2315 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Ecological and Environmental Status Bulletin. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- MEE. Notice on Printing and Distributing the “Eleventh Five-Year Plan for the Prevention and Control of National Acid Rain and Sulfur Dioxide Pollution”; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- MEE. Emission Standard of Air Pollutants for Sintering and Pelletizing of Iron and Steel Industry; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- MEE. The Work Plan for the Full Implementation of Ultra-Low Emission and Energy Conservation Transformation of Coal-fired Power Plants; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chai, F.; Ren, Q.; Wang, X. Process, achievements and experience of air ollution control in China since the founding of People’s Republic of China 70 years ago. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Teng, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, M. Economic transition and industrial sulfur dioxide emissions in the Chinese economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; He, K.; Wang, Y.; Richter, A. NOx emission trends for China, 1995–2004: The view from the ground and the view from space. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, H.; Geng, G.; Hong, C.; Liu, F. Corrigendum to Anthropogenic emission inventories in China: A review. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. Statistical Yearbook of China. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.I.; Woo, J.H.; He, K.; Lu, Z.; Ohara, T.; Song, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; et al. MIX: A mosaic Asian anthropogenic emission inventory under the international collaboration framework of the MICS-Asia and HTAP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 935–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-M.; Wang, X.-C.; Zhao, X.-F.; Qi, Y. Understanding systemic risk induced by climate change. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 12, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broomandi, P.; Jahanbakhshi, A.; Fathian, A.; Darynova, Z.; Janatian, N.; Nikfal, A.; Kim, J.R.; Karaca, F. Impacts of ambient air pollution on UNESCO world cultural heritage sites in Eastern Asia: Dose-response calculations for material corrosions. Urban Clim. 2022, 46, 101275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D. Microclimate for Cultural Heritage: Conservation, Restoration, and Maintenance of Indoor and Outdoor Monuments, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, P.A. Fundamentals of Corrosion Mechanisms, Causes, and Preventative Methods; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2009; pp. 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.D.; Zhang, L.; Huang, C.L. Future Climate Projection in Northwest China with RegCM4.6. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2019EA000819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University: Cambridge, UK, 2022; Available online: https://report.ipcc.ch/ar6wg2/pdf/IPCC_AR6_WGII_SummaryForPolicymakers.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. Assessing climate risk related to precipitation on cultural heritage at the provincial level in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halofsky, J.E.; Peterson, D.L.; Ho, J.J.; Little, N.; Joyce, L.A. Climate change vulnerability and adaptation in the Intermountain Region [Part 2]; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: West Prospect Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development, New York. 2015. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Magno, F.; Cassia, F. Effects of agritourism businesses’ strategies to cope with the COVID-19 crisis: The key role of corporate social responsibility (CSR) behaviours. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 325, 129292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiwumi, F.A. Strangers and Sierra Leone mining: Cultural heritage and sustainable development challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 84, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hribar, M.Š.; Bole, D.; Pipan, P. Sustainable Heritage Management: Social, Economic and Other Potentials of Culture in Local Development. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 188, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. International Policy and Action for Adaptation to Climate Change in Heritage Sector and Its Implications to China. Environ. Prot. 2022, 50, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-X.; Lu, W.-M.; Hung, S.-W. You gain when you give: Constructing a sustainable development model for world heritage sites. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 328, 129547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro-Reyes, L.; Díaz-Lazcano, V.; Zumelzu, A.; Prieto, A.J. Resilience and sustainability assessment of cultural heritage and built environment: The Libertad pedestrian walkway in Valdivia, Chile. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 53, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.S.; Ciantelli, C.; Cassar, J.; Hughes, J.J. Climate change impacts on cultural heritage: A literature review. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, Q.B.; Morel, J.C.; Hans, S.; Walker, P. Effect of moisture content on the mechanical characteristics of rammed earth. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 54, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omari, A.; Brunetaud, X.; Beck, K. Freezing-Thawing Action in the Deterioration of the Stones of Chambord Castle. EGU General Assembly 2013 at: Vienna 2013. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279532086_Freezing-thawing_action_in_the_deterioration_of_the_stones_of_Chambord_Castle (accessed on 5 November 2022).
- Barbara, L.; Hees, R.P.J.V.; Groot, C. The role of sea salts in the occurrence of different damage mechanisms and decay patterns on brick masonry. Constr. Build. Mater. 2004, 18, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lūsis, R.; Vītiņa, I.; Krāģe, L. Corrosion of Porous Stone Materials Caused by Salts. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2009, 205, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Site | The Annul Recession Rate of Limestone (μmy−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006–2010 | 2011–2015 | 2016–2020 | ||
| The Great Wall | Badaling Great Wall | 6.9 | 6.7 | 5.8 |
| Shanhaiguan Great Wall | 7.9 | 10.0 | 6.6 | |
| Jiayuguan Great Wall | 7.1 | 7.0 | 6.1 | |
| Mogao Caves | 8.4 | 8.4 | 7.3 | |
| Imperial Palaces of the Ming and Qing Dynasties in Beijing and Shenyang | Imperial Palaces of the Ming and Qing Dynasties in Beijing | 7.8 | 7.5 | 6.5 |
| Imperial Palaces of the Ming and Qing Dynasties in Shenyang | 10.1 | 8.4 | 6.1 | |
| Mausoleum of the First Qin Emperor | 9.3 | 8.7 | 7.1 | |
| Peking Man Site at Zhoukoudian | 7.7 | 7.4 | 6.3 | |
| Ancient Building Complex in the Wudang Mountains | 13.2 | 14.1 | 7.3 | |
| Historic Ensemble of the Potala Palace, Lhasa | 5.9 | 6.0 | 5.1 | |
| Mountain Resort and its Outlying Temples, Chengde | 6.6 | 6.5 | 5.7 | |
| Temple and Cemetery of Confucius and the Kong Family Mansion in Qufu | 12.1 | 12.2 | 7.4 | |
| Lushan National Park | 9.9 | 11.0 | 8.7 | |
| Ancient City of Ping Yao | 7.2 | 7.2 | 6.4 | |
| Classical Gardens of Suzhou | 12.3 | 12.1 | 7.0 | |
| Old Town of Lijiang | 5.4 | 5.1 | 6.1 | |
| Summer Palace, an Imperial Garden in Beijing | 7.7 | 7.4 | 6.9 | |
| Temple of Heaven: An Imperial Sacrificial Altar in Beijing | 7.8 | 7.5 | 6.4 | |
| Dazu Rock Carvings | 7.8 | 8.0 | 8.9 | |
| Ancient Villages in Southern Anhui—Xidi and Hongcun | 10.0 | 9.2 | 8.2 | |
| Longmen Grottoes | 8.4 | 8.3 | 6.9 | |
| Imperial Tombs of the Ming and Qing Dynasties | Eastern and Western Qing Tombs | 7.7 | 7.5 | 6.4 |
| Ming Xiaoling Tombs | 11.6 | 11.4 | 7.8 | |
| Ming Tombs | 7.1 | 7.0 | 6.1 | |
| Three Tombs of Shengjing | 9.4 | 8.0 | 6.2 | |
| Xianling Tombs | 11.5 | 11.0 | 7.9 | |
| Mount Qingcheng and the Dujiangyan Irrigation System | 9.7 | 9.1 | 7.4 | |
| Yungang Grottoes | 6.7 | 6.5 | 6.0 | |
| Capital Cities and Tombs of the Ancient Koguryo Kingdom | Jilin Province section | 8.5 | 7.9 | 7.1 |
| Liaoning Province section | 8.9 | 7.8 | 6.7 | |
| Yin Xu | 10.4 | 8.7 | 7.2 | |
| Fujian Tulou | 8.4 | 9.2 | 6.9 | |
| Kaiping Diaolou and Villages | 10.5 | 11.8 | 9.0 | |
| Mount Wutai | 6.6 | 6.7 | 6.0 | |
| Historic Monuments of Dengfeng in “The Centre of Heaven and Earth” | 8.7 | 8.4 | 6.6 | |
| Cultural Landscape of Honghe Hani Rice Terraces | 9.6 | 9.5 | 7.6 | |
| West Lake Cultural Landscape of Hangzhou | 12.0 | 12.1 | 9.4 | |
| Site of Xanadu | 6.3 | 6.2 | 5.5 | |
| Tusi Sites | Sites of Laosicheng | 11.0 | 9.4 | 7.2 |
| Sites of Hailongtun | 11.4 | 10.6 | 6.9 | |
| Sites of Tangya | 10.4 | 8.8 | 7.1 | |
| Zuojiang Huashan Rock Art Cultural Landscape | 8.7 | 9.9 | 8.9 | |
| Kulangsu, a Historic International Settlement | 7.9 | 7.9 | 8.1 | |
| Archaeological Ruins of Liangzhu City | 12.5 | 12.3 | 8.2 | |
| Quanzhou: Emporium of the World in Song-Yuan China | 9.3 | 11.6 | 6.0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. Quantifying the Potential Co-Benefit of Air Quality Improvement on Cultural Heritage in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8709. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118709
Wang X, Li H, Wang Y, Zhao X. Quantifying the Potential Co-Benefit of Air Quality Improvement on Cultural Heritage in China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):8709. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118709
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ximo, Huimin Li, Yufei Wang, and Xiaofan Zhao. 2023. "Quantifying the Potential Co-Benefit of Air Quality Improvement on Cultural Heritage in China" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 8709. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118709
APA StyleWang, X., Li, H., Wang, Y., & Zhao, X. (2023). Quantifying the Potential Co-Benefit of Air Quality Improvement on Cultural Heritage in China. Sustainability, 15(11), 8709. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118709







