Displacement Field Calculation of Large-Scale Structures Using Computer Vision with Physical Constraints: An Experimental Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structural Displacement Field Calculation Framework
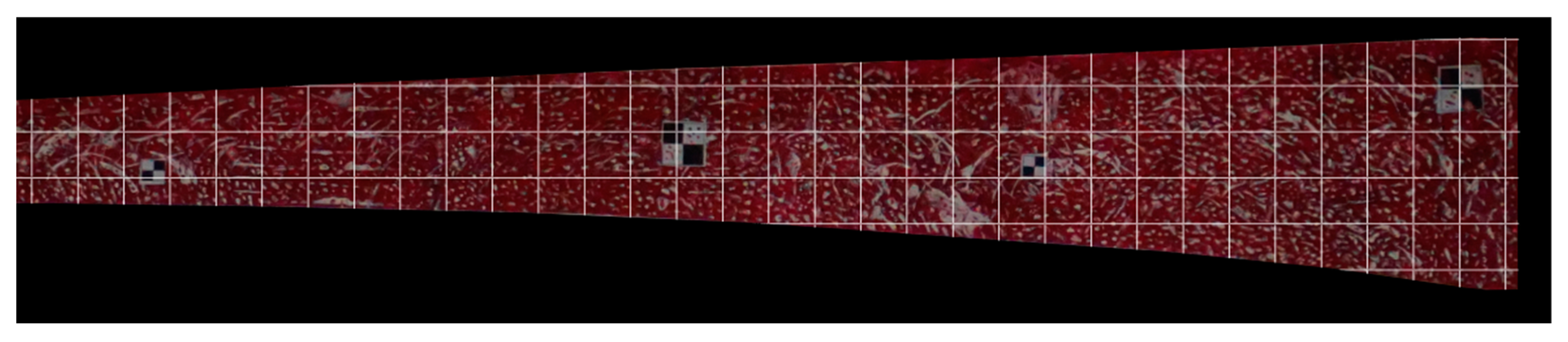
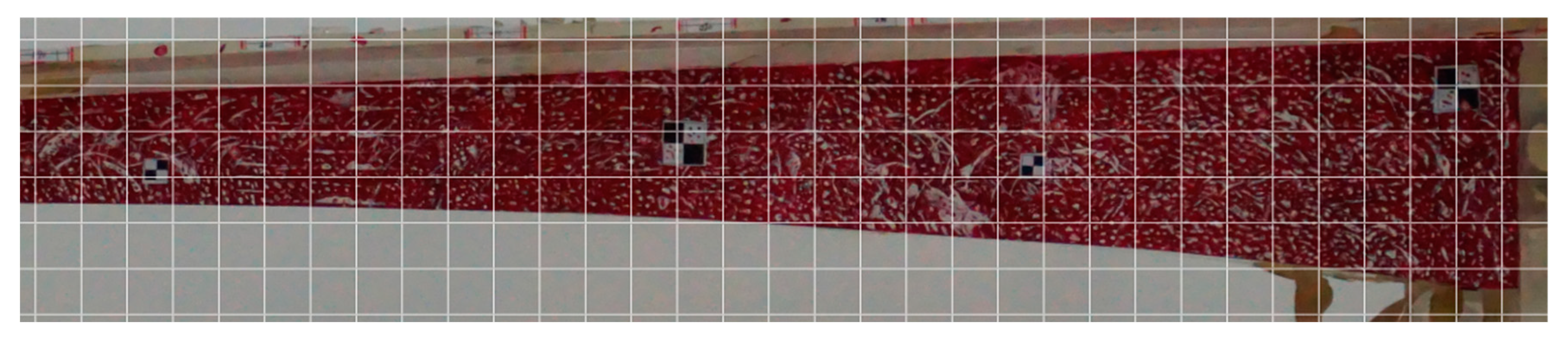
2.1. Large-Scale Structure Full-Field Image Generation Using Image Stitching
2.1.1. Image Preprocessing
2.1.2. Image Registration
2.1.3. Structure Foreground Segmentation
2.2. Structure Image Discretization and Displacement Field Calculation
2.2.1. Image Preprocessing
2.2.2. Node Displacement Calculation Using Template Matching
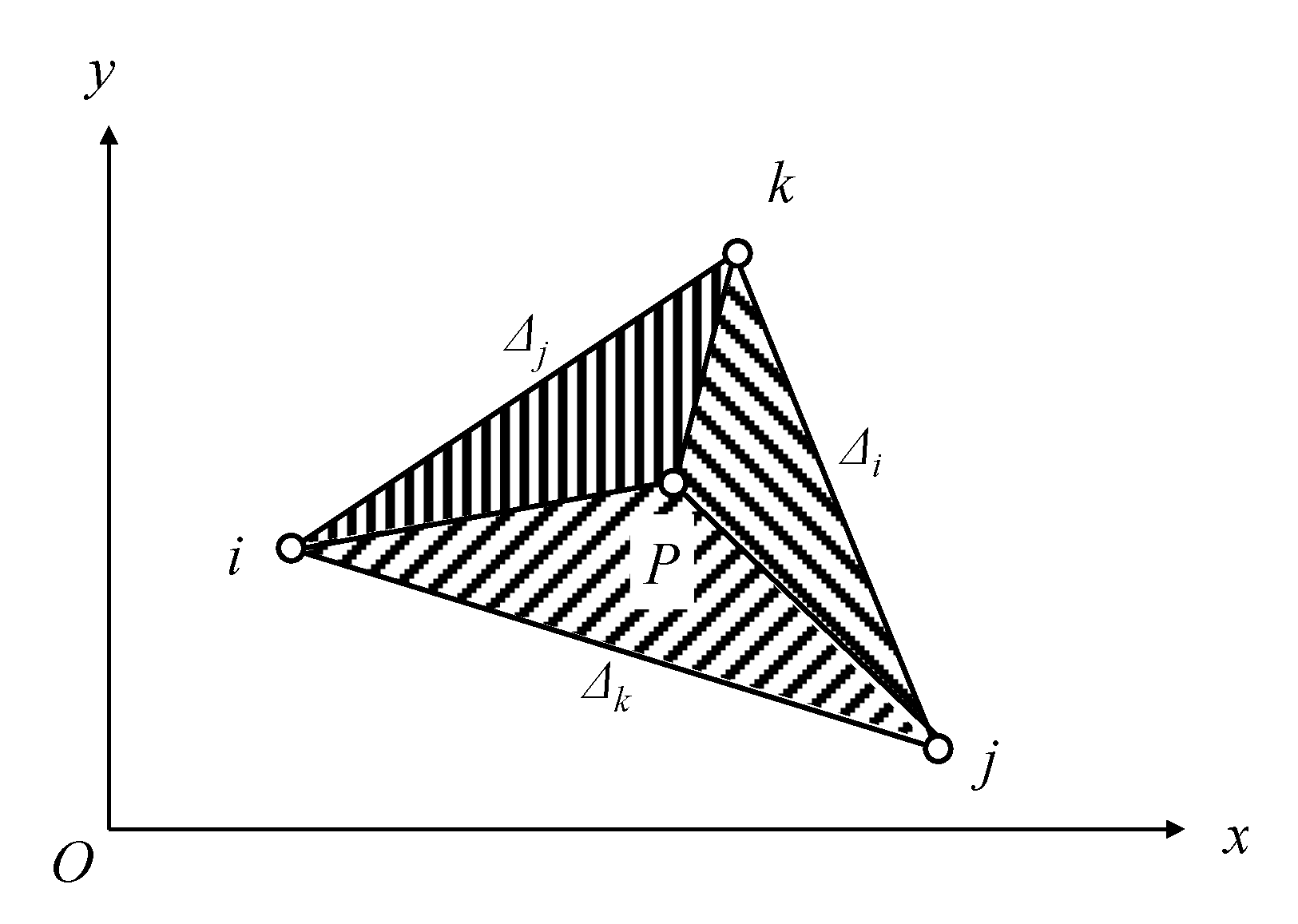
2.2.3. Non-Node Displacement Calculation Using Shape Function
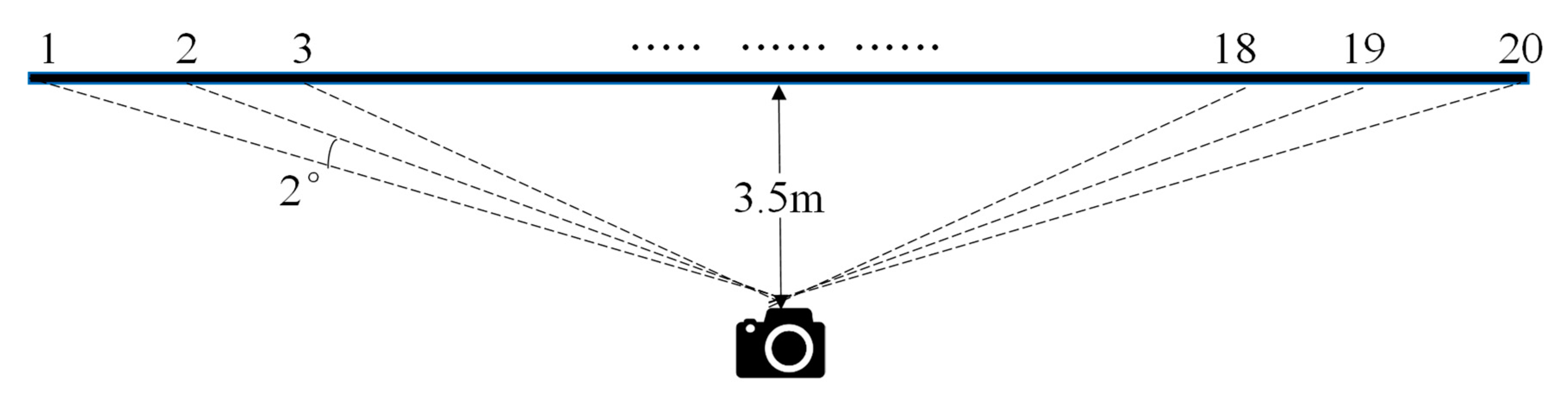
3. Validation Results and Discussion
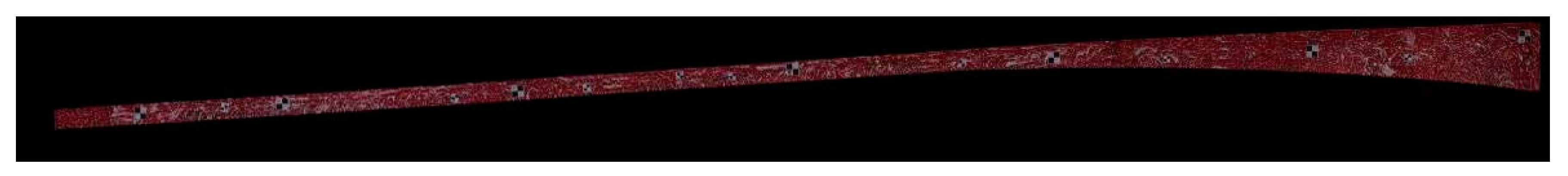
3.1. Full-Field Image Generation Results
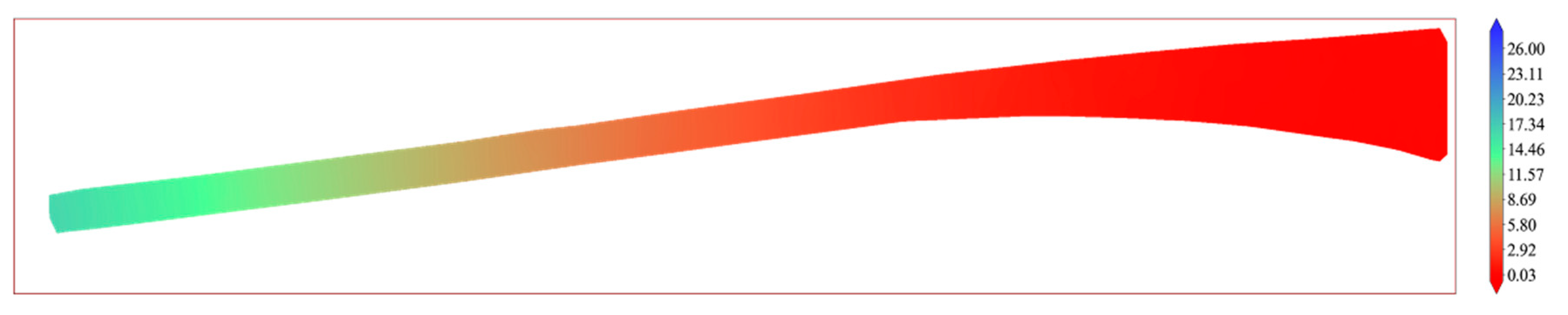
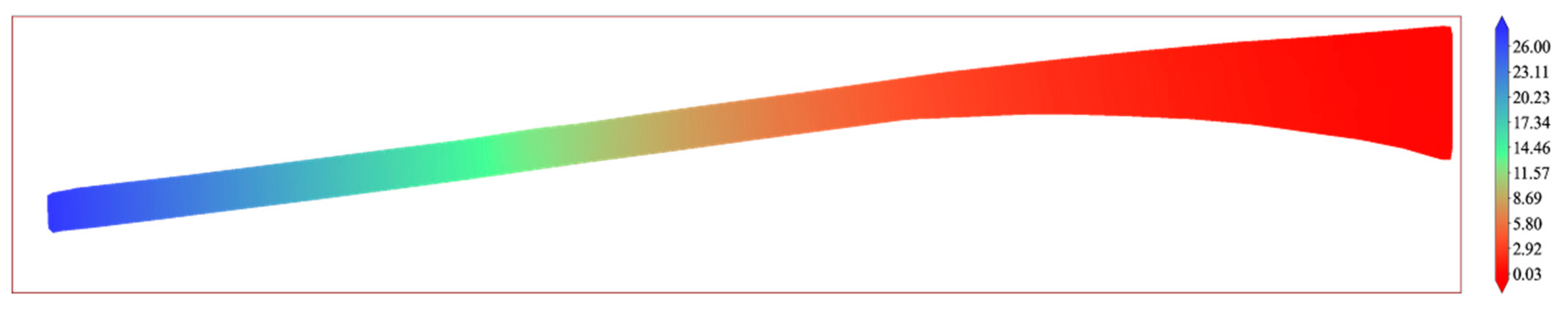
3.2. Displacement Field Calculation Results
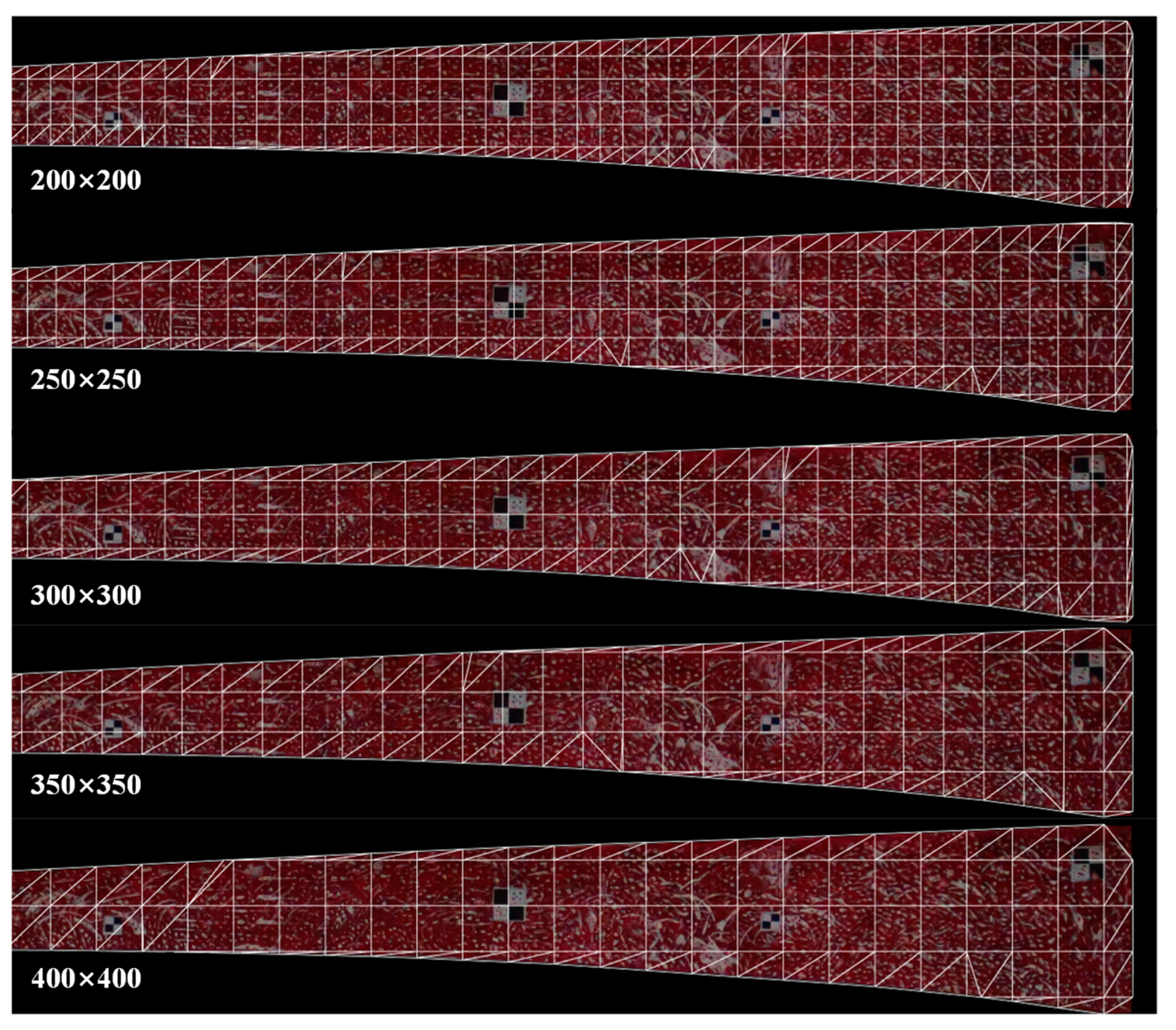
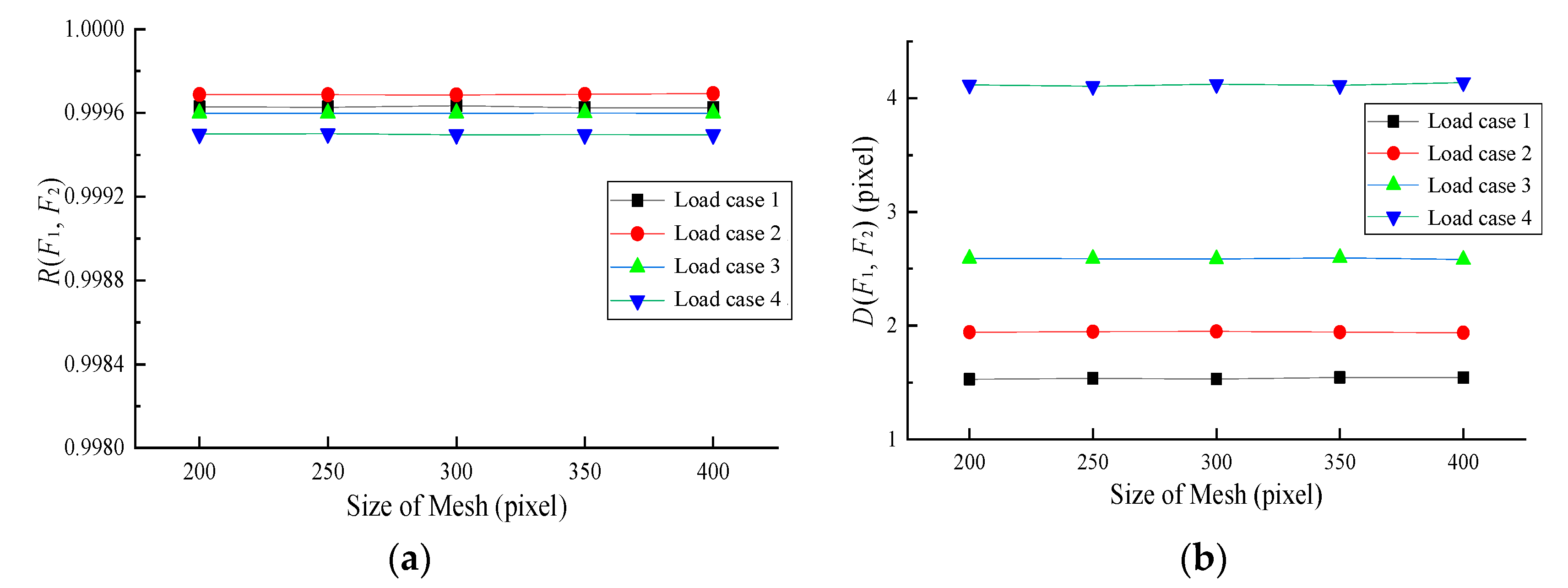
3.3. The Influence of Different Mesh Sizes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, C.-Z.; Catbas, F.N. A review of computer vision–based structural health monitoring at local and global levels. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 20, 692–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Feng, M.Q. Experimental validation of cost-effective vision-based structural health monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 88, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S. Model Updating of Complex Structures Using the Combination of Component Mode Synthesis and Kriging Predictor. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 476219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Damage Localization of Beam Bridges Using Quasi-Static Strain Influence Lines Based on the BOTDA Technique. Sensors 2018, 18, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, Y.J.; Choi, W.; Büyüköztürk, O. Deep learning-based crack damage detection using convolutional neural networks. Comput. -Aided Civil. Infrastruct. Eng. 2017, 32, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Li, J. Vision-based fatigue crack detection of steel structures using video feature tracking. Comput. -Aided Civil. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 33, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, L.; Choi, W.; Cha, Y.-J. Fully automated vision-based loosened bolt detection using the Viola–Jones algorithm. Struct. Health Monit. 2018, 18, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, D.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, N.; Li, H. Identification framework for cracks on a steel structure surface by a restricted Boltzmann machines algorithm based on consumer-grade camera images. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2018, 25, e2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Beck, J.L.; Li, H.; Hou, T.Y. Identification of time-varying cable tension forces based on adaptive sparse time-frequency analysis of cable vibrations. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2017, 24, e1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Beck, J.L.; Li, H. Bayesian system identification based on hierarchical sparse Bayesian learning and Gibbs sampling with application to structural damage assessment. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 318, 382–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lan, C.M.; Ju, Y.; Li, D.S. Experimental and Numerical Study of the Fatigue Properties of Corroded Parallel Wire Cables. J. Bridge Eng. 2012, 17, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mao, C.-X.; Ou, J.-P. Experimental and theoretical study on two types of shape memory alloy devices. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2008, 37, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wei, S.; Bao, Y.; Li, H. Condition assessment of cables by pattern recognition of vehicle-induced cable tension ratio. Eng. Struct. 2018, 155, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, S.; Xu, Y.-L.; Chen, Z.-W.; Li, H. Long-term condition assessment of suspenders under traffic loads based on structural monitoring system: Application to the Tsing Ma Bridge. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2012, 19, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sony, S.; Laventure, S.; Sadhu, A. A literature review of next-generation smart sensing technology in structural health monitoring. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, B.F.; Hoskere, V.; Narazaki, Y. Advances in Computer Vision-Based Civil Infrastructure Inspection and Monitoring. Engineering 2019, 5, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, A.; Carboni, M.; Comolli, L.; Galeazzi, R.; Gianneo, A.; Kharshiduzzaman, M. Fatigue Crack Growth Monitoring in Composite Bonded Lap Joints by a Distributed Fibre Optic Sensing System and Comparison with Ultrasonic Testing. J. Adhes. 2016, 92, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, P.; Jaamialahmadi, A.; da Silva, L.F.M.; Farhangdoost, K. An investigation on fatigue life evaluation and crack initiation of Al-GFRP bonded lap joints under four-point bending. Compos. Struct. 2019, 229, 111433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, A.; Shariati, M.; Zamani, P.; Karimi, R. Experimental and numerical analysis of ratcheting behavior of A234 WPB steel elbow joints including corrosion defects. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2022, 237, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, P.; Fm da Silva, L.; Masoudi Nejad, R.; Ghahremani Moghaddam, D.; Soltannia, B. Experimental study on mixing ratio effect of hybrid graphene nanoplatelet/nano-silica reinforcement on the static and fatigue life of aluminum-to-GFRP bonded joints under four-point bending. Compos. Struct. 2022, 300, 116108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djabali, A.; Toubal, L.; Zitoune, R.; Rechak, S. Fatigue damage evolution in thick composite laminates: Combination of X-ray tomography, acoustic emission and digital image correlation. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 183, 107815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Feng, M.Q. Computer vision for SHM of civil infrastructure: From dynamic response measurement to damage detection—A review. Eng. Struct. 2018, 156, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Brownjohn, J.M.W. Review of machine-vision based methodologies for displacement measurement in civil structures. J. Civil. Struct. Health Monit. 2018, 8, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Feng, M.Q. Vision-based multipoint displacement measurement for structural health monitoring. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2016, 23, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, T.; Li, L.; Jiang, M.; Takaki, T.; Ishii, I.; Yang, H.; Umemoto, C.; Matsuda, H.; Chikaraishi, M.; Fujiwara, A. Vision-Based Modal Analysis Using Multiple Vibration Distribution Synthesis to Inspect Large-Scale Structures. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 2018, 141, 031007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Feng, M.Q.; Wu, Z.Y. Robust vision sensor for multi-point displacement monitoring of bridges in the field. Eng. Struct. 2018, 163, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydon, D.; Lydon, M.; Rincón, J.M.d.; Taylor, S.E.; Robinson, D.; O’Brien, E.; Catbas, F.N. Development and Field Testing of a Time-Synchronized System for Multi-Point Displacement Calculation Using Low-Cost Wireless Vision-Based Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 9744–9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Brownjohn, J.; Kong, D. A non-contact vision-based system for multipoint displacement monitoring in a cable-stayed footbridge. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2018, 25, e2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.S.; Wu, J.R.; Wang, H.L.; An, Y.S.; Tang, G.W. Computer vision-based illumination-robust and multi-point simultaneous structural displacement measuring method. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 2022, 170, 108822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Alzugaray, I.; Chli, M.; Chatzi, E. Full-field structural monitoring using event cameras and physics-informed sparse identification. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 2020, 145, 106905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Shen, Z. Multi-point vibration measurement and mode magnification of civil structures using video-based motion processing. Autom. Constr. 2018, 93, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dorn, C.; Farrar, C.; Mascarenas, D. Blind, simultaneous identification of full-field vibration modes and large rigid-body motion of output-only structures from digital video measurements. Eng. Struct. 2020, 207, 110183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sanchez, L.; Zhang, H.; Roeder, A.; Bowlan, J.; Crochet, J.; Farrar, C.; Mascarenas, D. Estimation of full-field, full-order experimental modal model of cable vibration from digital video measurements with physics-guided unsupervised machine learning and computer vision. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narazaki, Y.; Gomez, F.; Hoskere, V.; Smith, M.D.; Spencer, B.F. Efficient development of vision-based dense three-dimensional displacement measurement algorithms using physics-based graphics models. Struct. Health Monit. Int. J. 2021, 20, 1841–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narazaki, Y.; Hoskere, V.; Eick, B.A.; Smith, M.D.; Spencer, B.F. Vision-based dense displacement and strain estimation of miter gates with the performance evaluation using physics-based graphics models. Smart Struct. Syst. 2019, 24, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Nagarajaiah, S. Identification of full-field dynamic modes using continuous displacement response estimated from vibrating edge video. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 489, 115657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Nagarajaiah, S. Spatiotemporal compressive sensing of full-field Lagrangian continuous displacement response from optical flow of edge: Identification of full-field dynamic modes. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 2022, 164, 108232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Nagarajaiah, S.; Lai, Z. Measurement of full-field displacement time history of a vibrating continuous edge from video. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 2020, 144, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, L.; Zheng, J.; Wang, M.L.; Yang, Y.; Rizzo, P.; Sun, H. Extracting full-field subpixel structural displacements from videos via deep learning. J. Sound. Vib. 2021, 505, 116142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.; Hamarneh, G. n-SIFT: N-dimensional scale invariant feature transform. Trans. Img. Proc. 2009, 18, 2012–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, C.; Kolmogorov, V.; Blake, A. “GrabCut”: Interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts. In Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH 2004: 31st Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 8–12 August 2004; pp. 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente, S.; Kolmogorov, V.; Rother, C. Graph cut based image segmentation with connectivity priors. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, R. Optimality of a Standard Adaptive Finite Element Method. Found. Comput. Math. 2007, 7, 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











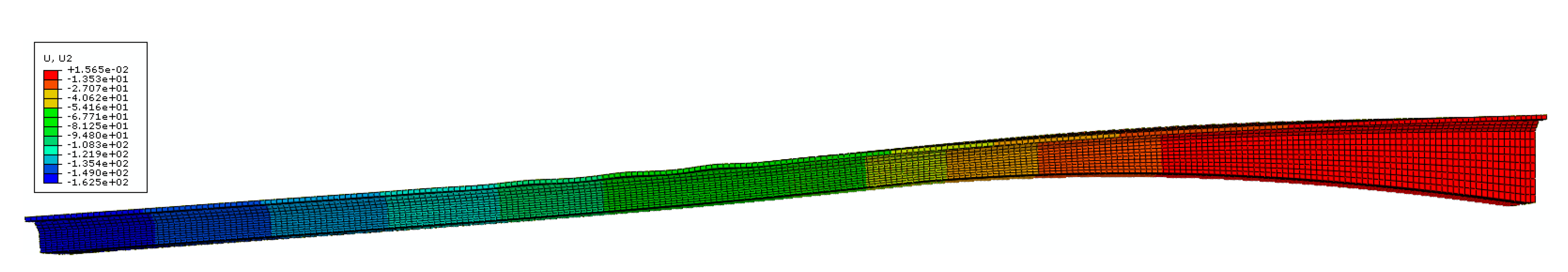
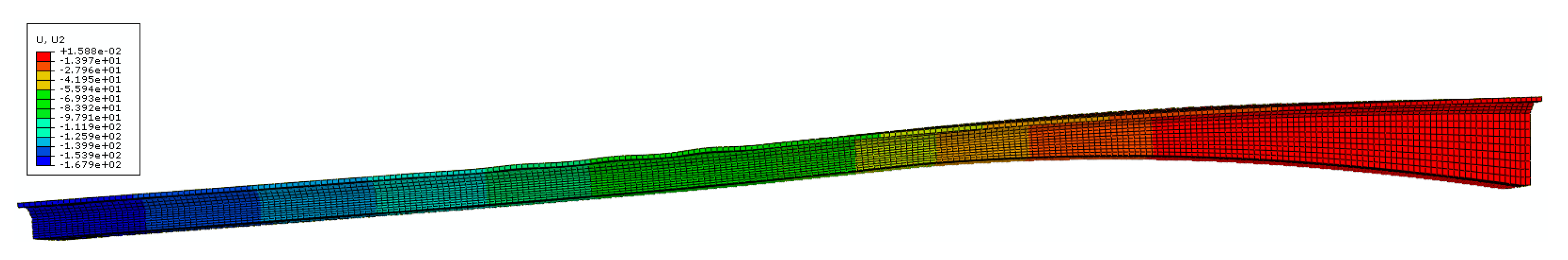
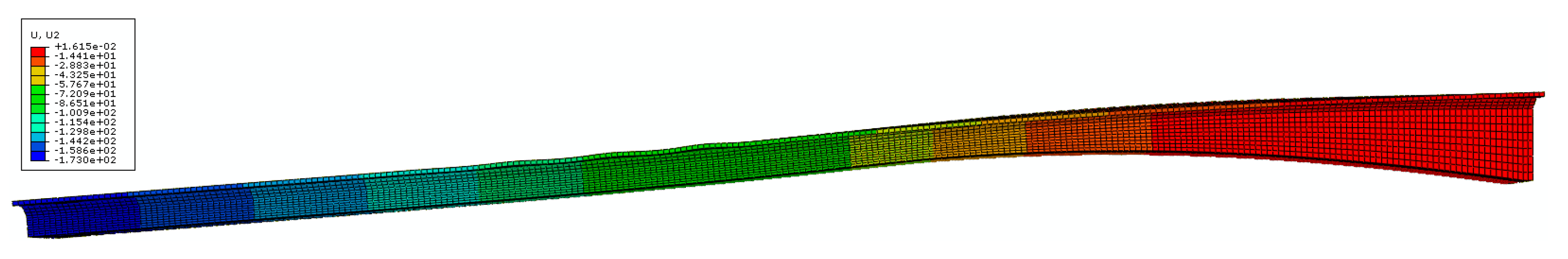
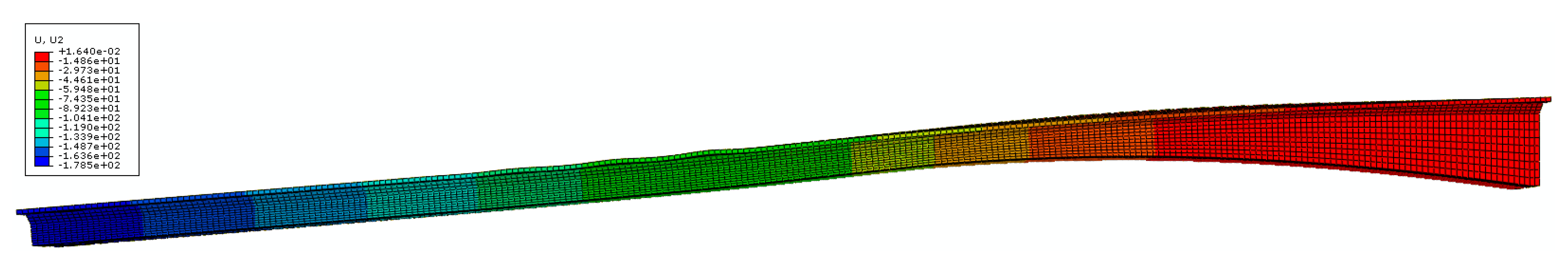

| Loading Case | 400 mm (mm) | 1300 mm (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVDT | Proposed | Error | Error (%) | LVDT | Proposed | Error | Error (%) | |
| 1 | 8.356 | 8.455 | 0.099 | 1.2 | 2.901 | 2.895 | 0.006 | 0.2 |
| 2 | 12.381 | 12.454 | 0.073 | 0.6 | 4.229 | 4.002 | 0.227 | 5.4 |
| 3 | 16.354 | 16.574 | 0.220 | 1.3 | 5.662 | 5.485 | 0.177 | 3.1 |
| 4 | 20.466 | 20.504 | 0.038 | 0.2 | 7.048 | 6.877 | 0.171 | 2.4 |
| Average | - | - | - | 0.826 | - | - | - | 2.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Zhong, P.; Zhuo, Y.; Meng, F.; Di, H.; Li, S. Displacement Field Calculation of Large-Scale Structures Using Computer Vision with Physical Constraints: An Experimental Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118683
Guo Y, Zhong P, Zhuo Y, Meng F, Di H, Li S. Displacement Field Calculation of Large-Scale Structures Using Computer Vision with Physical Constraints: An Experimental Study. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):8683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118683
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yapeng, Peng Zhong, Yi Zhuo, Fanzeng Meng, Hao Di, and Shunlong Li. 2023. "Displacement Field Calculation of Large-Scale Structures Using Computer Vision with Physical Constraints: An Experimental Study" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 8683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118683
APA StyleGuo, Y., Zhong, P., Zhuo, Y., Meng, F., Di, H., & Li, S. (2023). Displacement Field Calculation of Large-Scale Structures Using Computer Vision with Physical Constraints: An Experimental Study. Sustainability, 15(11), 8683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118683






