Impact of Combined Exposure to Glyphosate and Diquat on Microbial Community Structure and Diversity in Lateritic Paddy Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Database Construction
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis of Microbial 16S rRNA and ITS
2.4. Data Analysis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Combined Exposure of GP and DQ on the Composition and Diversity of Soil Bacterial Community
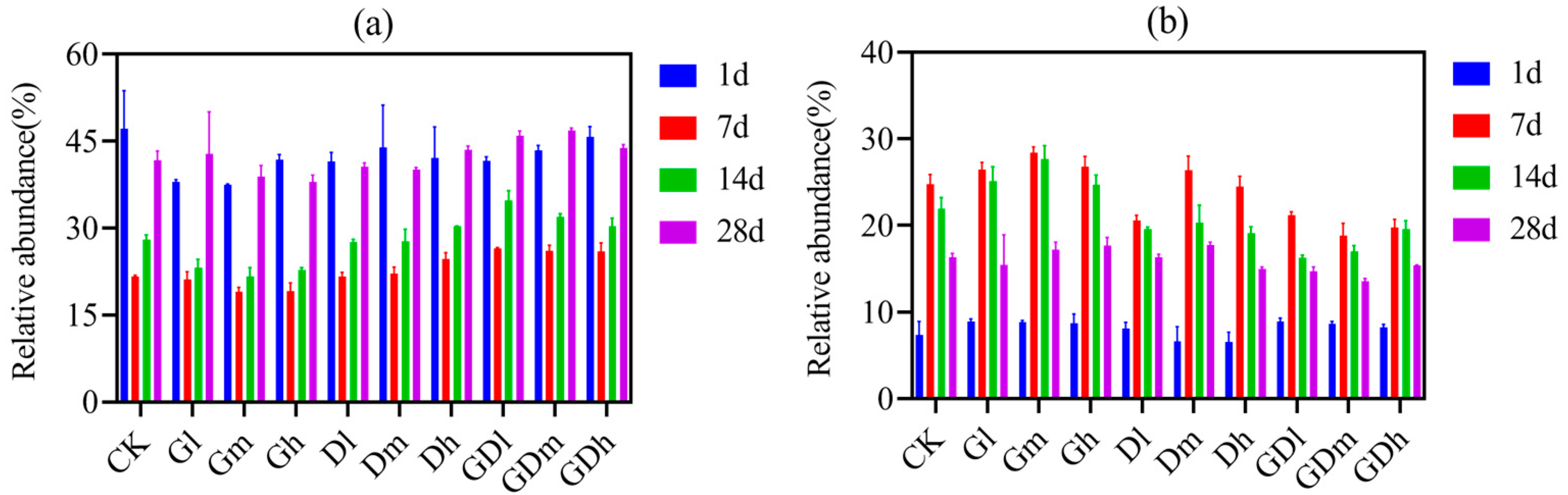
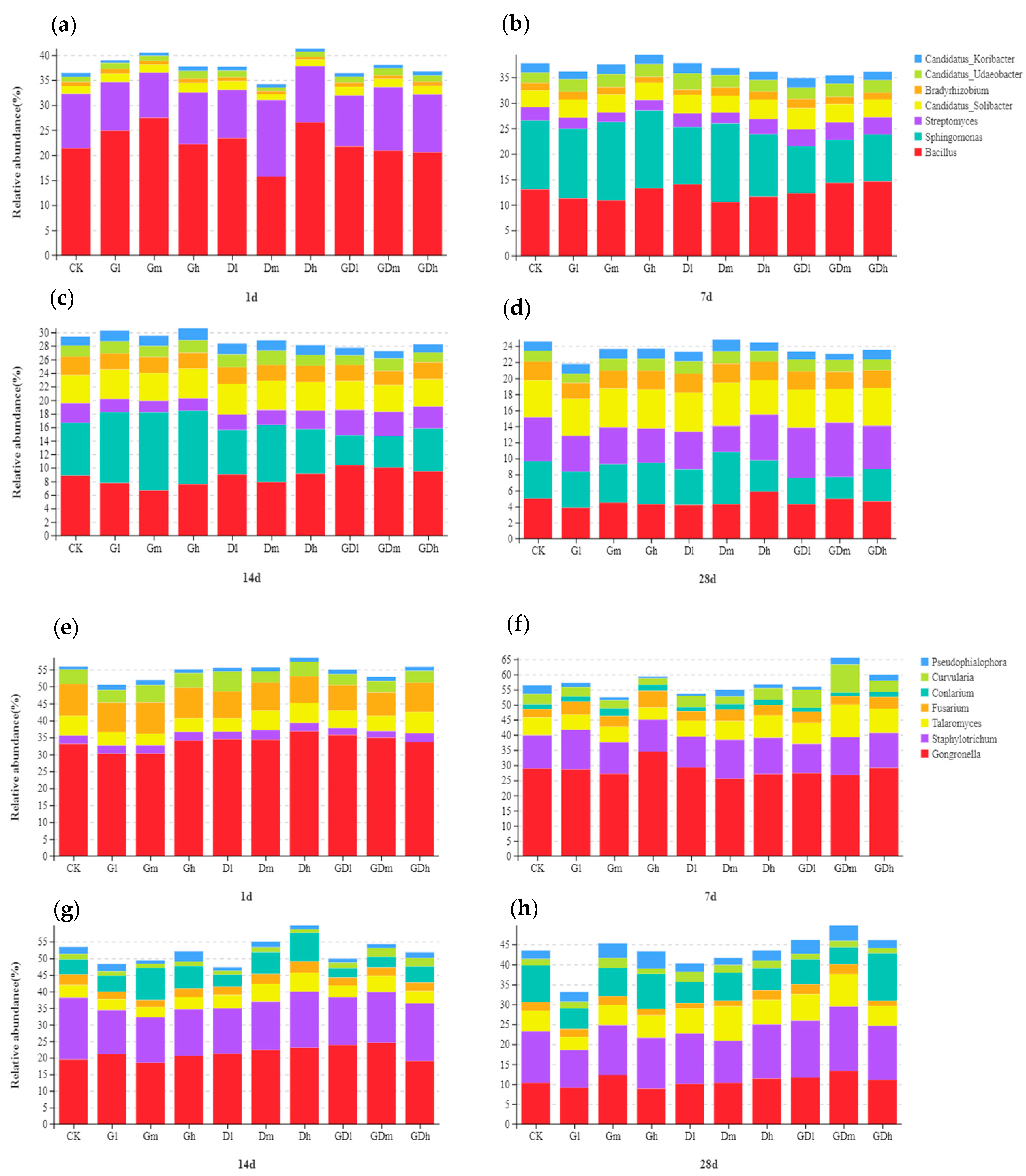
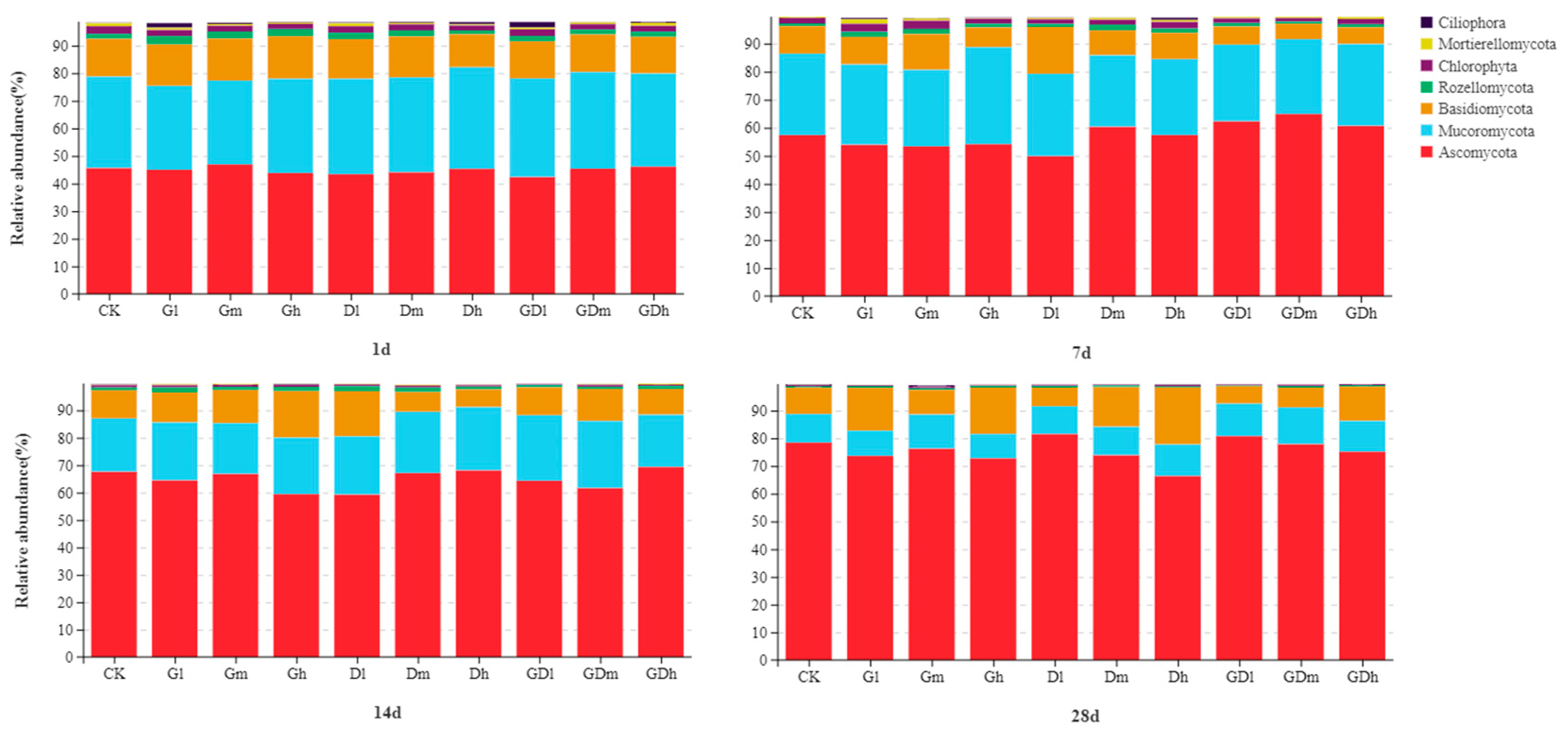
3.1.1. Bacterial Community Composition
3.1.2. Alpha Diversity of the Bacterial Community
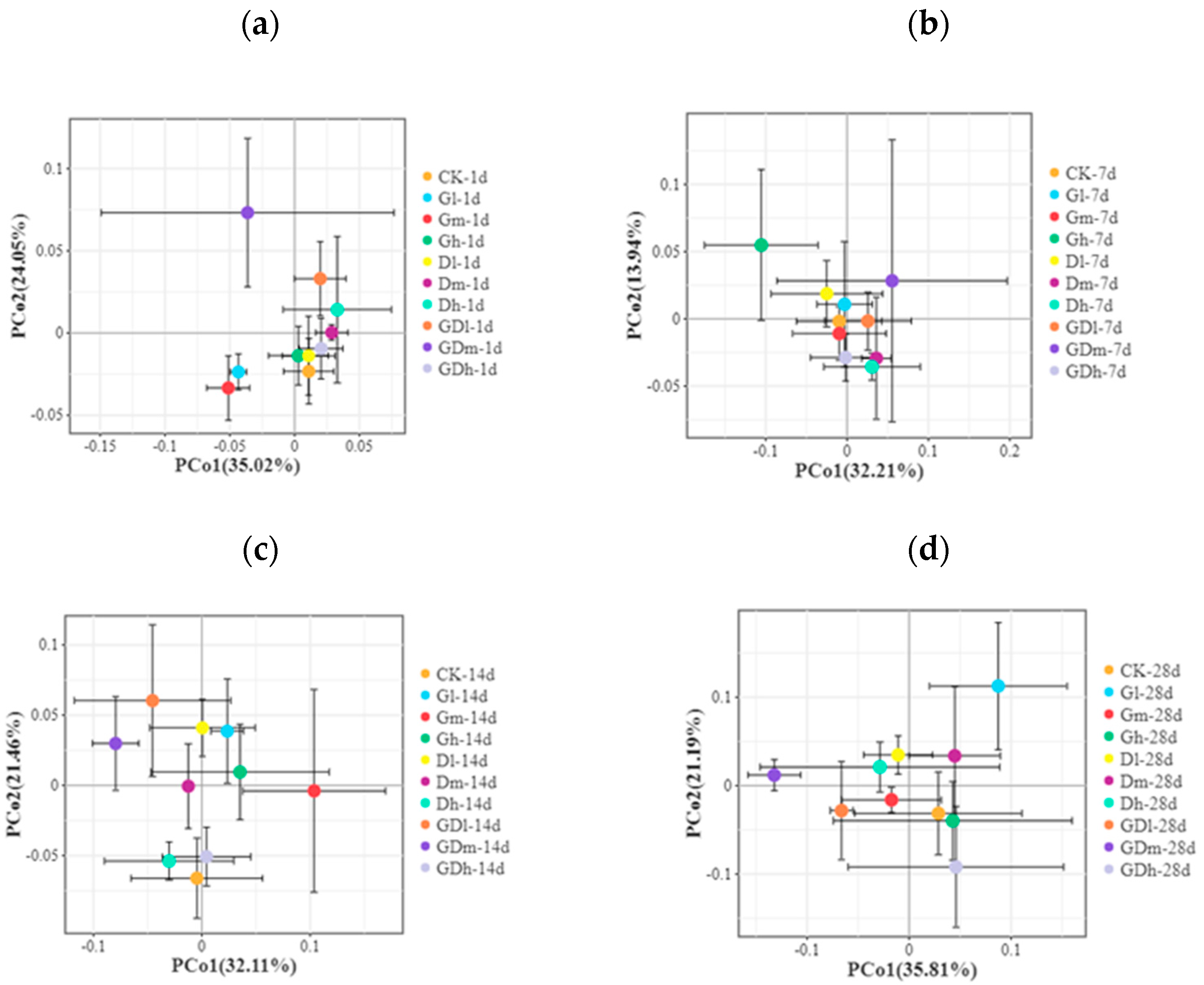
3.1.3. Beta Diversity of the Bacterial Community
3.1.4. LEfSe Analysis of the Bacterial Community
3.2. Effects of Combined Exposure of GP and DQ on the Composition and Diversity of the Soil Fungal Community
3.2.1. Fungal Community Composition
3.2.2. Alpha Diversity of Fungal Community
3.2.3. Beta Diversity of the Fungal Community
3.2.4. LEfSe Analysis of the Fungal Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grube, A.; Donaldson, D.; Kiely, T.; Wu, L. Pesticides Industry Sales and Usage; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Pesticide Use Data; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, S.O. The history and current status of glyphosate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, M.T.; Poulsen, H.D.; Katholm, C.L.; Højberg, O. Review: Feed residues of glyphosate—Potential consequences for livestock health and productivity. Animal 2021, 15, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, G.; Atreya, K.; Scheepers, P.T.J.; Geissen, V. Concentration and distribution of pesticide residues in soil: Non-dietary human health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horth, H.; Blackmore, K. Survey of glyphosate and AMPA in groundwaters and surface waters in Europe. In WRC Report; WRC: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; p. UC8073,2. [Google Scholar]
- Demonte, L.D.; Michlg, N.; Gaggiotti, M. Determination of glyphosate, AMPA and glufosinate in dairy farm water from Argentina using a simplified UHPLC-MS/MS method. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, D. Glyphosate, aminomethyl-phosphonic acid, and glufosinate ammonium in agricultural groundwater and surface water in China from 2017 to 2018: Occurrence, main drivers, and environmental risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, V.C.; De Gerónimo, E.; Marino, D.; Primost, J.; Carriquiriborde, P.; Costa, J.L. Environmental fate of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters and soil of agricultural basins. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, J. Monitoring and risk assessment of pesticide residue in plant soil-groundwater system about medlar planting in Golmud. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 26413–26426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Rosee, M.; Van Zwieten, L. Direct determination of glyphosate and its metabolite AMPA in soil using mixed-mode solid-phase purification and LC-MS/MS determination on a hypercarb column. J AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.Y.; Peng, Z.R.; He, W.H.; Feng, M.J.; Dai, X.L. Assessment of glyphosate residues and ecological risk in P. rosii cultured ponds. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 2021, 5, 821–827. [Google Scholar]
- Botero-coy, A.M.; Ibáñez, M.; Sancho, J.V.; Hernandez, F. Improvements in the analytical methodology for the residue determination of the herbicide glyphosate in soils by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1292, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primost, J.E.; Marino, D.J.; Aparicio, V.C.; Costa, J.L.; Carriquiriborde, P. Glyphosate and AMPA, “pseudo-persistent” pollutants under real-world agricultural management practices in the mesopotamic pampas agroecosystem, Argentina. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunarathna, S.; Gunawardana, B.; Jayaweera, M. Glyphosate and AMPA of agricultural soil, surface water, groundwater and sediments in areas prevalent with chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology, Sri Lanka. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2018, 53, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasali, H.; Pavlidis, G.; Marousopoulou, A. Investigation of the presence of glyphosate and its major metabolite AMPA in Greek soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 36308–36321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateiro, M.M.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Simal-Gándara, J. Critical Review on the Environmental Fate of Quaternary Ammonium Herbicides in Soils Devoted to Vineyards. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4984–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roede, J.R.; Miller, G.W. Diquat. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimsing, A.L.; Borggaard, O.K.; Bang, M. Influence of soil composition on adsorption of glyphosate and phosphate by contrasting Danish surface soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 55, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamy, L.; Barriuso, E. Glyphosate adsorption in soils compared to herbicides replaced with the introduction of glyphosate resistant crops. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Mol, H.G.J.; Zomer, P.; Tienstra, M.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Pesticide residues in European agricultural soils—A hidden reality unfolded. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 653, 1532–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Heijden, M.G.; Bardgett, R.D.; Van Straalen, N.M. The unseen majority: Soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagg, C.; Bender, S.F.; Widmer, F.; van der Heijden, M.G. Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5266–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Lydon, J.; Koskinen, W.C.; Moorman, T.B.; Chaney, R.L.; Hammerschmidt, R. Glyphosate effects on plant mineral nutrition, crop rhizosphere microbiota, and plant disease in glyphosate-resistant crops. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10375–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.B.; Rose, M.T.; Rose, T.J.; Morris, S.G.; Zwieten, L.V. Impact of glyphosate on soil microbial biomass and respiration: A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 92, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, J.T.; Selim, H.M. Environmental behavior of Glyphosate in soils. Adv. Agron. 2020, 159, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bruggen, A.H.C.; Finckh, M.R.; He, M.; Ritsema, C.J.; Harkes, P.; Knuth, D.; Geissen, V. Indirect effects of the herbicide glyphosate on plant, animal and human health through its effects on microbial communities. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 763917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, M.A.; Krutz, L.J.; Zablotowicz, R.M.; Reddy, K.N. Effects of glyphosate on soil microbial communities and its mineralization in a Mississippi soil. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kepler, R.M.; Schmidt, D.J.E.; Yarwood, S.A.; Cavigelli, M.A.; Reddy, K.N.; Duke, S.O.; Bradley, C.A.; Williams, M.M., Jr.; Buyer, J.S.; Maul, J.E. Soil v to the herbicide glyphosate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01744-19. [Google Scholar]
- Lupwayi, N.Z.; Fernandez, M.R.; Kanashiro, D.A.; Petri, R.M. Profiles of wheat rhizobacterial communities in response to repeated glyphosate applications, crop rotation, and tillage. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 101, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accinelli, C.; Koskinen, W.C.; Seebinger, J.D.; Vicari, A.; Sadowsky, M.J. Effects of incorporated corn residues on Glyphosate mineralization and sorption in soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4110–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, E.; Ferreras, L.; Lovotti, L.; Fernández, E. Impact of Glyphosate application on microbial biomass and metabolic activity in a Vertic Argiudoll from Argentina. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2009, 45, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accinelli, C.; Koskinen, W.C.; Becker, J.M.; Sadowsky, M.J. Environmental fate of two sulfonamide antimicrobial agents in soil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 2677–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, S.H.; Hollister, E.B.; Senseman, S.A.; Gentry, T.J. Effects of repeated glyphosate applications on soil microbial community composition and the mineralization of glyphosate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, T.I.; Warner, D.J.; Davies, K.G.; Edmonds-Brown, V. Tillage, glyphosate and beneficial arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: Optimising crop management for plantfungal symbiosis. Agric. For. 2020, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch’avez-Ortiz, P.; Tapia-Torres, Y.; Larsen, J.; García-Oliva, F. Glyphosate-based herbicides alter soil carbon and phosphorus dynamics and microbial activity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 169, 104256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobiole, L.; Kremer, R.; Oliveira, R.; Constantin, J. Glyphosate affects microorganisms in rhizospheres of glyphosate-resistant soybeans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carles, L.; Artigas, J. Interaction between glyphosate and dissolved phosphorus on bacterial and eukaryotic communities from river biofilms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.M.; Hoilett, N.; Lorenz, N.; Dick, R.P.; Liles, M.R.; Ramsier, C.; Kloepper, J.W. Glyphosate effects on soil rhizosphere-associated bacterial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegrini, M.; Gomez, E.; Zabaloy, M.C. Repeated glyphosate exposure induces shifts in nitrifying communities and metabolism of phenylpropanoids. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 105, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druille, M.; Omacini, M.; Golluscio, R.A.; Cabello, M.N. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are directly and indirectly affected by glyphosate application. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 72, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.; Fernandes, B.; Paiva, C.; Nogueira, V.; Cachada, A.; Fidalgo, F.; Pereira, R. Ecotoxicological relevance of glyphosate and flazasulfuron to soil habitat and retention functions—Single vs combined exposures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.H. The Toxic Effects of Glyphosate and Cadmium on E. coli. Master’s Thesis, Hunan University of Science and Technology, Xiangtan, China, 16 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.C. Response of Lead, Cadmium and Glyphosate to Pollution Stress and HSPs in C. elegans. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 16 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.F. Ecological Toxicicology of Heavy Metals and Glyphosate. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 16 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.F.; Luo, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Tian, M. Microbial ecological effects of soil contaminated with Zn, Pb and glyphosate. J. Southwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2010, 32, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.B.; Li, R.Q.; Deng, M.C.; Li, Z.H.; Xu, J.B. Combined toxicity of arsenic with the pesticide glyphosate, and dichlorvos against C. elegans. J. Ecol. Toxicol. 2013, 8, 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.J.; Rao, C.Y.; Yuan, R.J.; Sun, D.D.; Guo, S.Q.; Li, L.L.; Yang, S.; Qian, D.D.; Lu, R.H.; Cao, X.L. Long-term exposure to polyethylene microplastics and glyphosate interferes with the behavior, intestinal microbial homeostasis, and metabolites of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millet, M. A method to assess glyphosate, glufosinate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in soil and earthworms. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1651, 462339. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzutti, I.R.; Vela, G.M.E.; De Kok, A.; Scholten, J.M.; Dias, J.V.; Cardoso, C.D.; Vivian, R. Determination of paraquat and diquat: LC-MS method optimization and validation. Food Chem. 2016, 209, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Soil survey manual. In Soil Survey Division Staff; Soil Conservation Service Volume Handbook 18; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- China Pesticide Information Network. Available online: http://www.chinapesticide.org.cn/ (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Wang, Q. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNAsequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruesse, E. SILVA: A comprehensive online resource for quality checked andaligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.H.; TaylorAF, S. The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi: Handling dark taxa and parallel taxonomic classifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D259–D264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankenbrand, M.J.; Keller, A.; Wolf, M. ITS2 database V: Twice as much. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 3030–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R. Vegan: Community ecology package. R Proj. Stat. Comput. 2010, 23, 2010. Available online: http://cran.r-project.org (accessed on 21 April 2023).
- Wołejko, E.; Jabłonska-Trypuc, A.; Wydro, U.; Butarewicz, A.; Łozowicka, B. Soil biological activity as an indicator of soil pollution with pesticides—A review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 147, 103356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widenfalk, A.; Bertilsson, S.; Sundh, I.; Goedkoop, W. Effects of pesticides on community composition and activity of sediment microbes–responses at various levels of microbial community organization. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro, H.; Vera, M.S.; Vinocur, A.; P’erez, G.; Ferraro, M.; Helman, R.M.; Dos Santos Afonso, M. Glyphosate input modifies microbial community structure in clear and turbid freshwater systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5143–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, M.; Lorenz, N.; Saxena, J.; Ramsier, C.; Dick, R.P. The effect of glyphosate on soil microbial activity, microbial community structure, and soil potassium. Pedobiologia 2012, 55, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grube, M.; Kalnenieks, U.; Muter, O. Metabolic response of bacteria to elevated concentrations of glyphosate-based herbicide. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, R.L.; Pieterse, C.M.; Bakker, P.A. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Ka, J.O.; Cho, J.C. Members of the phylum Acidobacteria are dominant and metabolically active in rhizosphere soil. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 285, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Lemanceau, P.; van der Putten, W.H. Going back to the roots: The microbial ecology of the rhizosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Long, M.X.; Yin, Y.J.; Si, M.R.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.Q.; Shen, X.H. Physiological roles of mycothiol in detoxification and tolerance to multiple poisonous chemicals in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Arch. Microbiol. 2013, 195, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, M.B.; Moreno, M.V.; Amodeo, M.R.; Bianchinotti, M.V. Effects of Glyphosate on soil fungal communities: A field study. Rev. Argent. De Microbiol. 2021, 53, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhane, S.; Devers-Lamrani, M.; Beguet, J.; Bertrand, C.; Calvayrac, C.; Salvia, M.V.; Jrad, A.B.; Dayan, F.E.; Spor, A.; Barthelmebs, L.; et al. Assessment of the ecotoxicological impact of natural and synthetic β-triketone herbicides on the diversity and activity of the soil bacterial community using omic approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashar, P.; Shah, S. Impact of fertilizers and pesticides on soil microflora in agriculture. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 331–361. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, E.; Bushnell, B.; Coleman-Derr, D.; Bowman, B.; Bowers, R.M.; Levy, A.; Gies, E.A.; Cheng, J.F.; Copeland, A.; Klenk, H.P.; et al. High-resolution phylogenetic microbial community profiling. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2020–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parada, A.E.; Needham, D.M.; Fuhrman, J.A. Every base matters: Assessing small subunit rRNA primers for marine microbiomes with mock communities, time series and global field samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apprill, A.; McNally, S.; Parsons, R.; Weber, L. Minor revision to V4 region SSU rRNA 806R gene primer greatly increases detection of SAR11 bacterioplankton. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 75, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wu, F.; Hao, G.; Qi, Q.; Li, R.; Li, N.; Wei, L.M.; Chai, T.J. Bacillus subtilis improves immunity and disease resistance in rabbits. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzini, R.A.B.; Levican, G.; Parada, P. Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans secretome containing a newly described lipoprotein Licanantase enhances chalcopyrite bioleaching rate. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2011, 89, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, B.; Op De Beeck, M.; Thijs, S.; Truyens, S.; Weyens, N.; Boerjan, W.; Vangronsveld, J. Performance of 16s rDNA Primer Pairs in the Study of Rhizosphere and Endosphere Bacterial Microbiomes in Metabarcoding Studies. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teske, A.; Sørensen, K.B. Uncultured archaea in deep marine subsurface sediments: Have we caught them all? ISME J. 2008, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.K.; Au, C.H.; Chu, K.H.; Kwan, H.S.; Wong, C.K. Composition and genetic diversity of picoeukaryotes in subtropical coastal waters as revealed by 454 pyrosequencing. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scibetta, S.; Schena, L.; Abdelfattah, A.; Pangallo, S.; Cacciola, S.O. Selection and experimental evaluation of universal primers to study the fungal microbiome of higher plants. Phytobiomes J. 2018, 2, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toju, H.; Tanabe, A.S.; Yamamoto, S.; Sato, H. High-coverage ITS primers for the DNA-based identification of ascomycetes and basidiomycetes in environmental samples. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Treatment | Concentration (mg kg−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (l) | Middle (m) | High (h) | |
| Blank (CK) | 0 | ||
| Glyphosate (G) | 0.6 (Gl) | 6 (Gm) | 60 (Gh) |
| Diquat (D) | 0.4 (Dl) | 4 (Dm) | 40 (Dh) |
| Glyphosate + diquat (GD) | 0.6 + 0.4 (GDl) | 6 + 4 (GDm) | 60 + 40 (GDh) |
| Index | Treatment | Days after Application | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 14 | 28 | ||
| Shannon | CK | 5.918 ± 0.311 ab | 7.264 ± 0.027 bc | 7.556 ± 0.023 cd | 7.315 ± 0.093 abc |
| Gl | 6.390 ± 0.071 a | 7.458 ± 0.009 a | 7.650 ± 0.017 abc | 7.254 ± 0.320 bc | |
| Gm | 6.249 ± 0.063 a | 7.405 ± 0.032 ab | 7.736 ± 0.022 a | 7.497 ± 0.090 ab | |
| Gh | 6.266 ± 0.161 a | 7.145 ± 0.051 c | 7.671 ± 0.018 ab | 7.453 ± 0.067 abc | |
| Dl | 6.131 ± 0.140 a | 7.407 ± 0.033 ab | 7.583 ± 0.015 bcd | 7.416 ± 0.027 abc | |
| Dm | 5.382 ± 0.379 b | 7.485 ± 0.044 a | 7.669 ± 0.030 ab | 7.629 ± 0.006 a | |
| Dh | 5.770 ± 0.256 ab | 7.416 ± 0.038 ab | 7.404 ± 0.011 e | 7.152 ± 0.014 bc | |
| GDl | 6.298 ± 0.046 a | 7.381 ± 0.029 ab | 7.284 ± 0.078 f | 7.100 ± 0.034 c | |
| GDm | 6.409 ± 0.001 a | 7.414 ± 0.090 ab | 7.505 ± 0.015 d | 7.090 ± 0.023 c | |
| GDh | 6.092 ± 0.104 a | 7.370 ± 0.106 ab | 7.499 ± 0.038 de | 7.238 ± 0.039 bc | |
| Chao1 | CK | 2188.649 ± 150.191 bcd | 2263.584 ± 36.558 ab | 2369.947 ± 39.031 a | 2303.254 ± 45.996 ab |
| Gl | 2536.324 ± 75.475 ab | 2377.208 ± 3.108 a | 2352.648 ± 36.608 a | 2219.027 ± 135.281 b | |
| Gm | 2602.062 ± 60.436 a | 2338.966 ± 56.674 a | 2386.601 ± 49.563 a | 2450.166 ± 44.036 aA | |
| Gh | 2508.073 ± 91.128 abc | 2184.617 ± 30.267 b | 2417.438 ± 28.661 a | 2285.848 ± 30.396 ab | |
| Dl | 2229.911 ± 153.341 bcd | 2406.547 ± 28.774 a | 2334.005 ± 44.040 a | 2352.122 ± 40.203 ab | |
| Dm | 1993.626 ± 203.891 d | 2417.230 ± 8.741 a | 2351.966 ± 34.642 a | 2254.606 ± 47.180 b | |
| Dh | 2154.460 ± 98.706 cd | 2329.326 ± 48.987 ab | 2249.354 ± 70.180 a | 2297.709 ± 26.360 ab | |
| GDl | 2372.901 ± 44.448 abc | 2332.078 ± 103.682 ab | 2305.535 ± 69.564 a | 2309.014 ± 8.035 ab | |
| GDm | 2488.896 ± 9.119 abc | 2363.224 ± 52.350 a | 2358.002 ± 63.922 a | 2366.971 ± 23.944 ab | |
| GDh | 2250.869 ± 64.077 abcd | 2380.824 ± 14.352 a | 2332.714 ± 39.074 a | 2250.471 ± 9.346 b | |
| Index | Treatment | Days after Application | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 14 | 28 | ||
| Shannon | CK | 4.780 ± 0.083 abc | 4.368 ± 0.046 cd | 4.614 ± 0.015 a | 4.727 ± 0.044 abc |
| Gl | 4.882 ± 0.054 a | 4.634 ± 0.023 ab | 4.363 ± 0.029 ab | 4.783 ± 0.039 ab | |
| Gm | 4.765 ± 0.011 ab | 4.635 ± 0.086 bc | 4.259 ± 0.135 ab | 4.980 ± 0.057 a | |
| Gh | 4.544 ± 0.129 d | 4.231 ± 0.043 d | 4.388 ± 0.121 ab | 4.684 ± 0.023 cd | |
| Dl | 4.686 ± 0.072 bcd | 4.371 ± 0.020 cd | 4.259 ± 0.076 ab | 4.708 ± 0.007 bcd | |
| Dm | 4.683 ± 0.018 abc | 4.652 ± 0.044 ab | 4.516 ± 0.052 ab | 4.661 ± 0.028 bcd | |
| Dh | 4.509 ± 0.014 cd | 4.800 ± 0.053 a | 4.488 ± 0.043 ab | 4.598 ± 0.053 cd | |
| GDl | 4.688 ± 0.033 abc | 4.405 ± 0.049 cd | 4.128 ± 0.111 b | 4.867 ± 0.076 bcd | |
| GDm | 4.452 ± 0.014 d | 4.325 ± 0.028 cd | 4.376 ± 0.097 ab | 4.821 ± 0.134 abcd | |
| GDh | 4.763 ± 0.060 abc | 4.490 ± 0.069 cd | 4.369 ± 0.010 ab | 4.547 ± 0.053 d | |
| Chao1 | CK | 673.214 ± 21.296 ab | 543.470 ± 18.721 bc | 462.809 ± 3.810 b | 455.377 ± 60.937 a |
| Gl | 773.434 ± 39.275 ab | 579.153 ± 19.726 abc | 464.205 ± 2.574 b | 479.181 ± 56.792 a | |
| Gm | 772.912 ± 28.255 a | 626.580 ± 29.634 a | 465.700 ± 4.486 b | 469.934 ± 53.990 a | |
| Gh | 717.335 ± 44.500 ab | 510.983 ± 12.810 c | 452.857 ± 1.069 b | 438.914 ± 55.892 a | |
| Dl | 733.530 ± 38.877 ab | 546.209 ± 15.359 bc | 461.212 ± 6.469 b | 438.962 ± 53.068 a | |
| Dm | 706.838 ± 26.245 ab | 595.042 ± 19.484 ab | 477.764 ± 9.637 b | 425.494 ± 44.871 a | |
| Dh | 641.645 ± 17.447 b | 578.217 ± 19.415 ab | 468.624 ± 8.868 b | 437.094 ± 48.999 a | |
| GDl | 697.382 ± 28.165 ab | 540.641 ± 15.796 bc | 452.803 ± 0.858 b | 455.715 ± 39.099 a | |
| GDm | 666.482 ± 30.530 b | 500.521 ± 2.086 bc | 496.728 ± 3.212 a | 491.149 ± 35.763 a | |
| GDh | 679.040 ± 27.961 ab | 541.952 ± 8.107 abc | 499.915 ± 16.673 b | 426.687 ± 6.304 a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Wu, C.; Tan, H.; Deng, X.; Li, Y. Impact of Combined Exposure to Glyphosate and Diquat on Microbial Community Structure and Diversity in Lateritic Paddy Soil. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8497. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118497
He X, Wu C, Tan H, Deng X, Li Y. Impact of Combined Exposure to Glyphosate and Diquat on Microbial Community Structure and Diversity in Lateritic Paddy Soil. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):8497. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118497
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xiaoyu, Chunyuan Wu, Huadong Tan, Xiao Deng, and Yi Li. 2023. "Impact of Combined Exposure to Glyphosate and Diquat on Microbial Community Structure and Diversity in Lateritic Paddy Soil" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 8497. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118497
APA StyleHe, X., Wu, C., Tan, H., Deng, X., & Li, Y. (2023). Impact of Combined Exposure to Glyphosate and Diquat on Microbial Community Structure and Diversity in Lateritic Paddy Soil. Sustainability, 15(11), 8497. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118497





