Soil Water Erosion and Its Hydrodynamic Characteristics in Degraded Bald Patches of Alpine Meadows in the Yellow River Source Area, Western China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
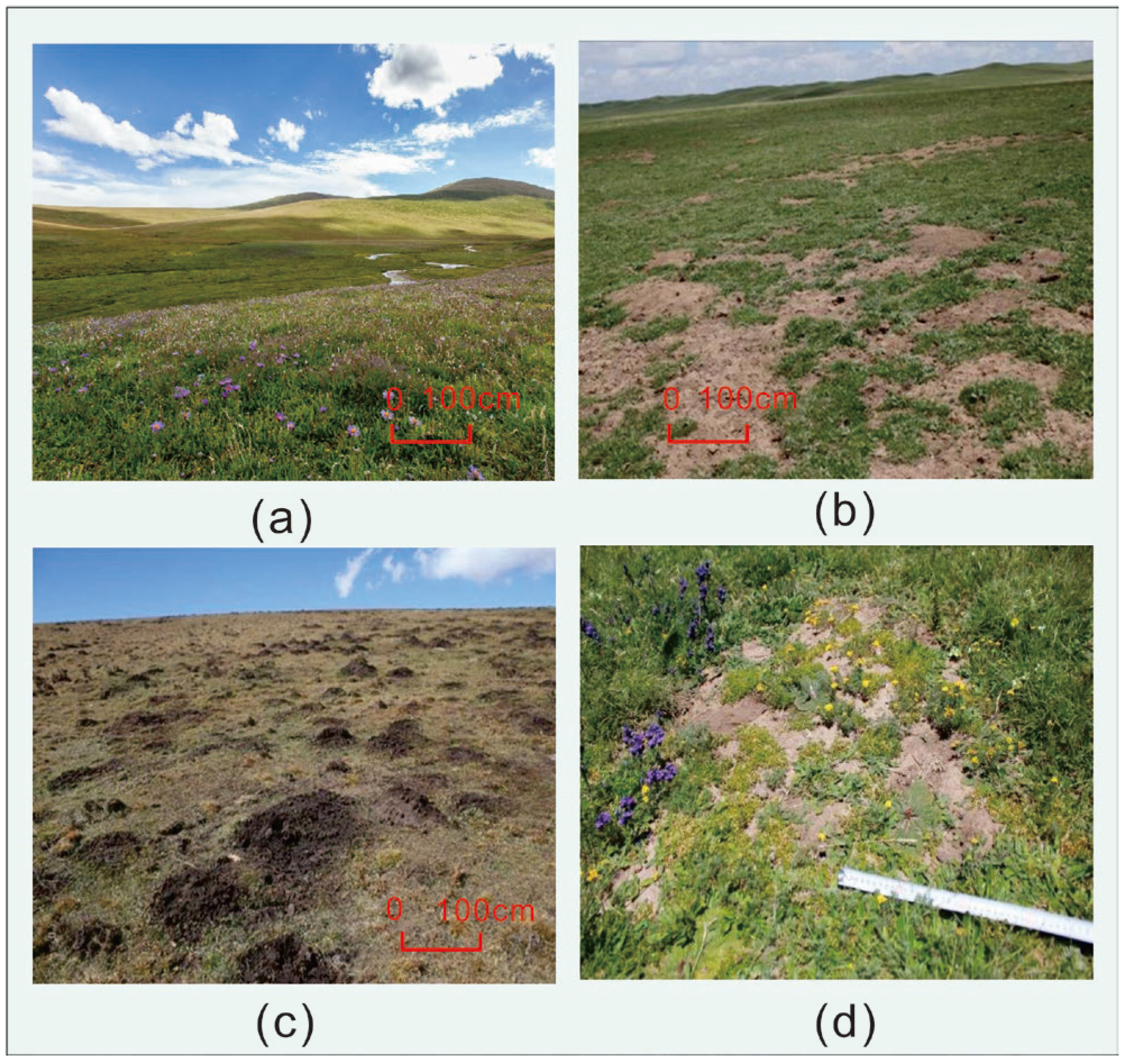
2.1. Study Area
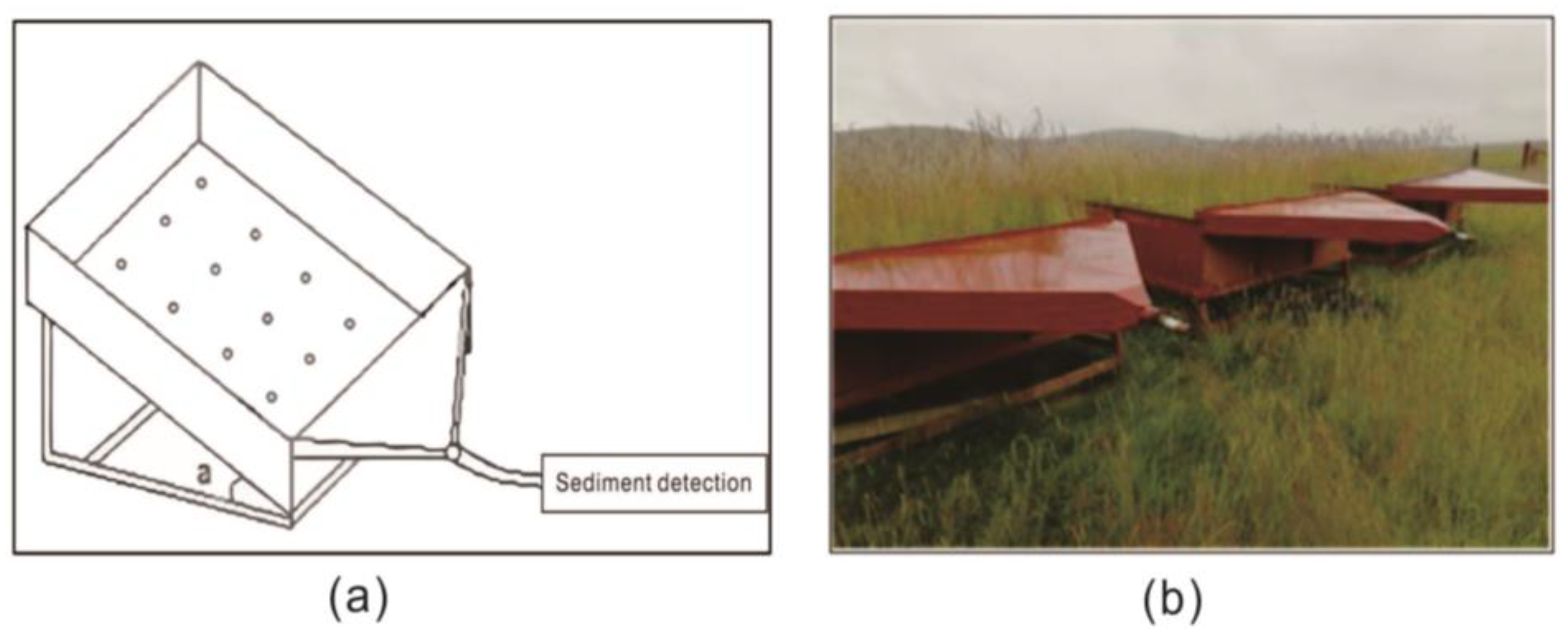
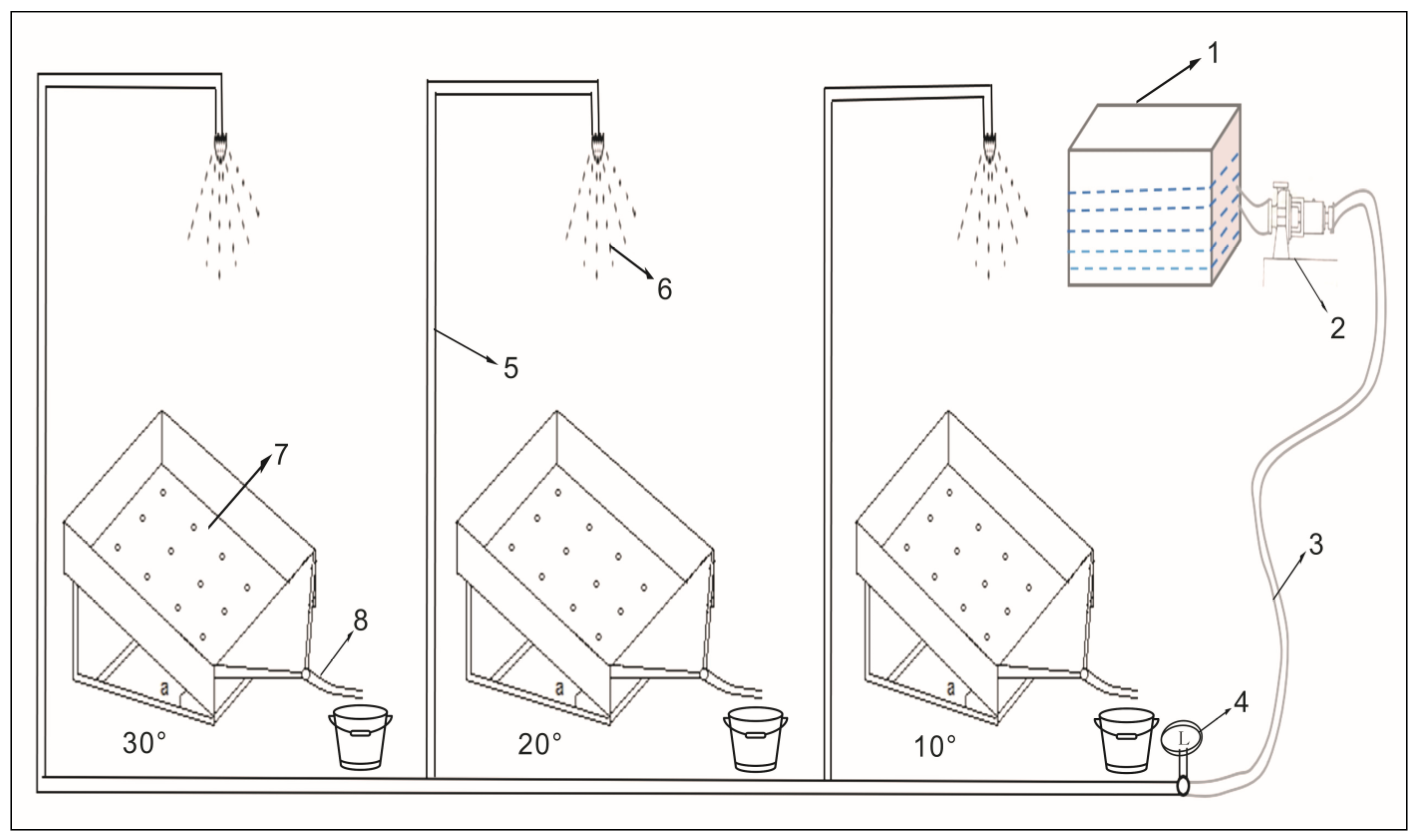
2.2. Experimental Design and Methods
2.3. Data Testing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Water Erosion Patterns in Different Degraded Bald Patches
3.1.1. Soil Loss Status of Different Degraded Bald Patches
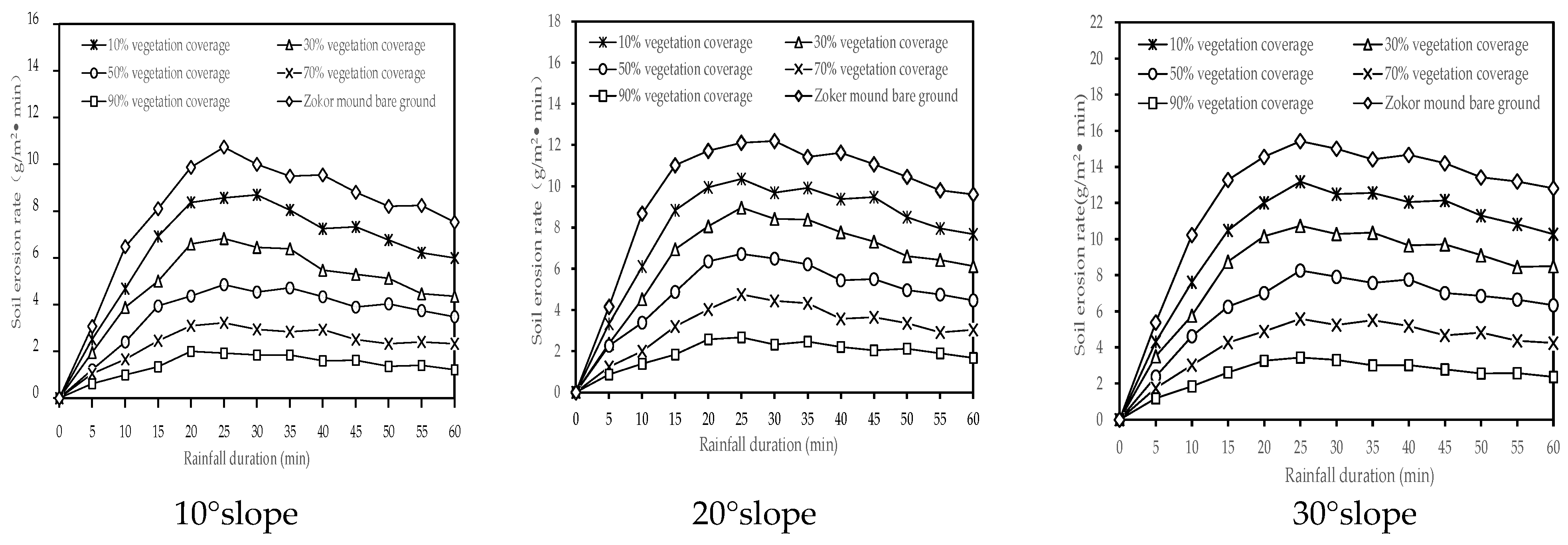
3.1.2. Soil Erosion Processes on Different Degraded Bald Patches
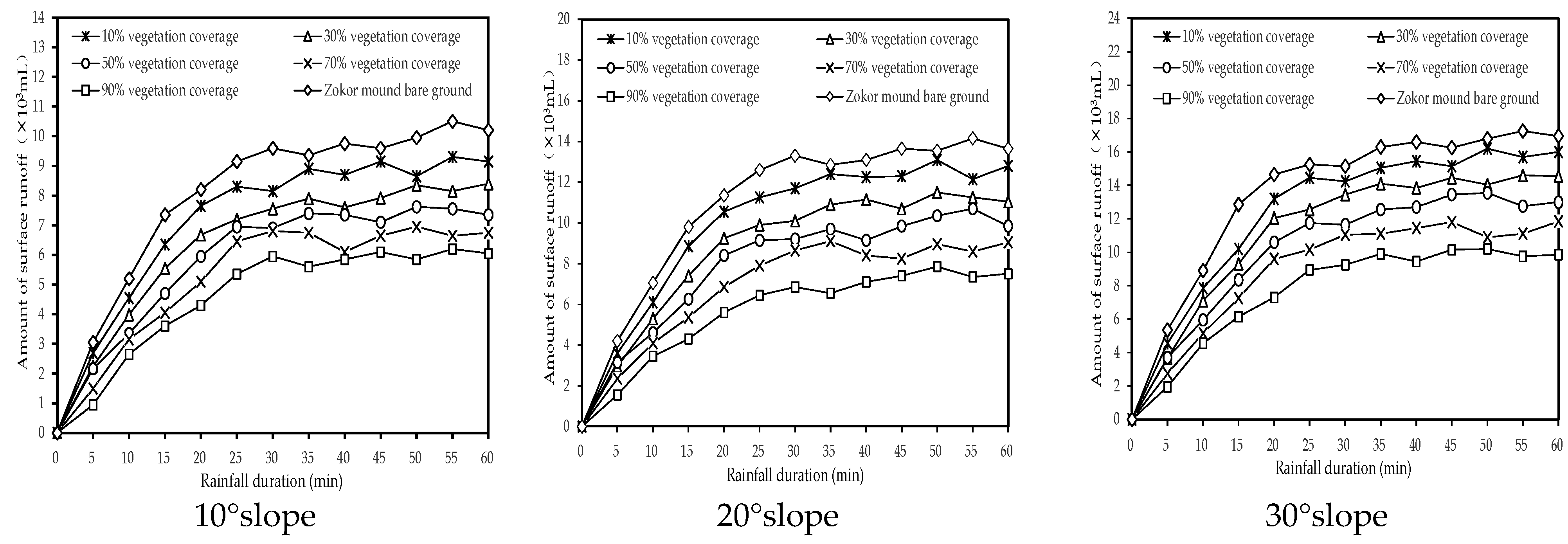
3.1.3. Surface Runoff Characteristics of Different Degraded Bald Patches
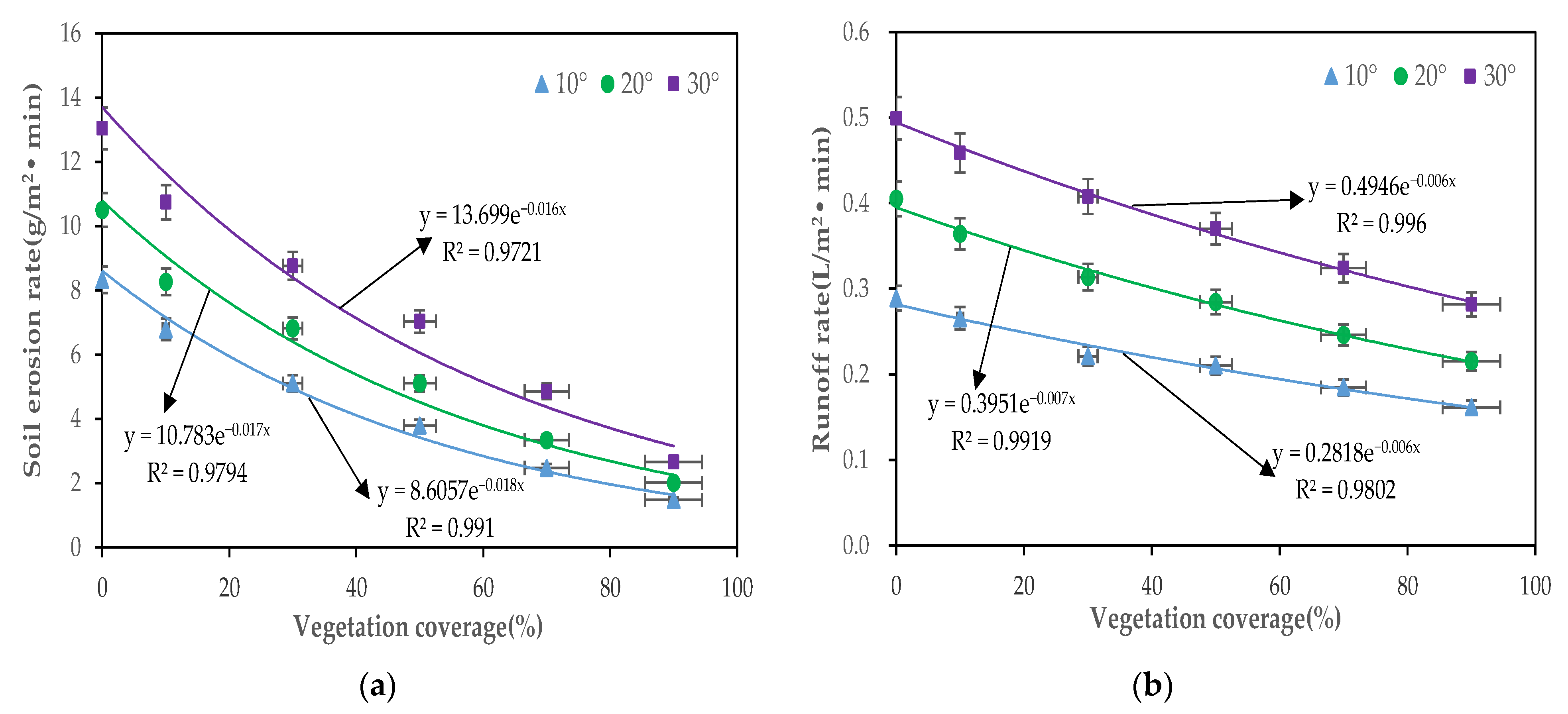
3.1.4. Relationship between Soil Erosion and the Degree of Meadow Degradation
3.2. Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Different Degraded Bald Patches
3.2.1. Flow Regime
3.2.2. Runoff Resistance
3.2.3. Runoff Shear Stress
3.3. Relationship between Soil Erosion and Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Bald Patches with Different Degrees of Degradation
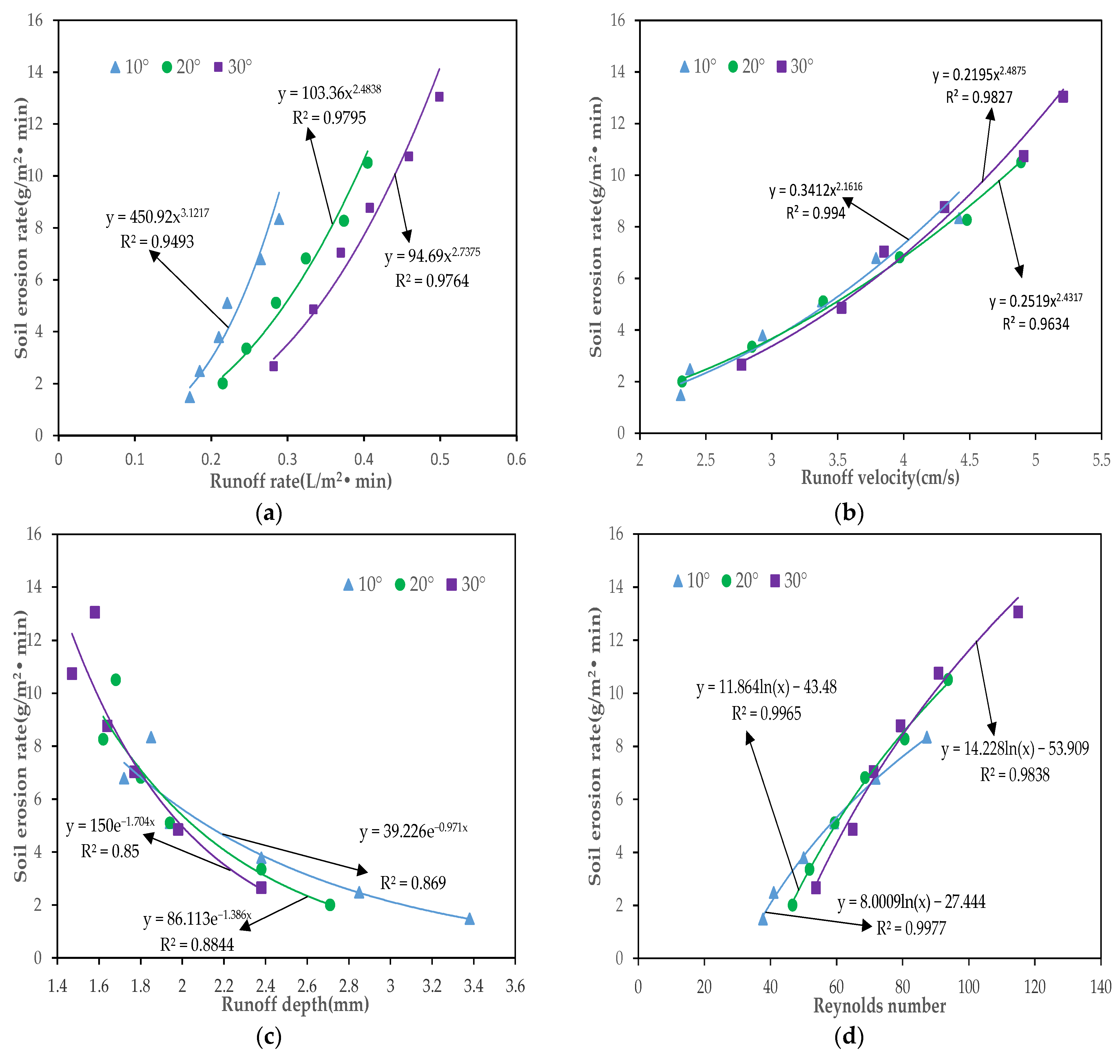
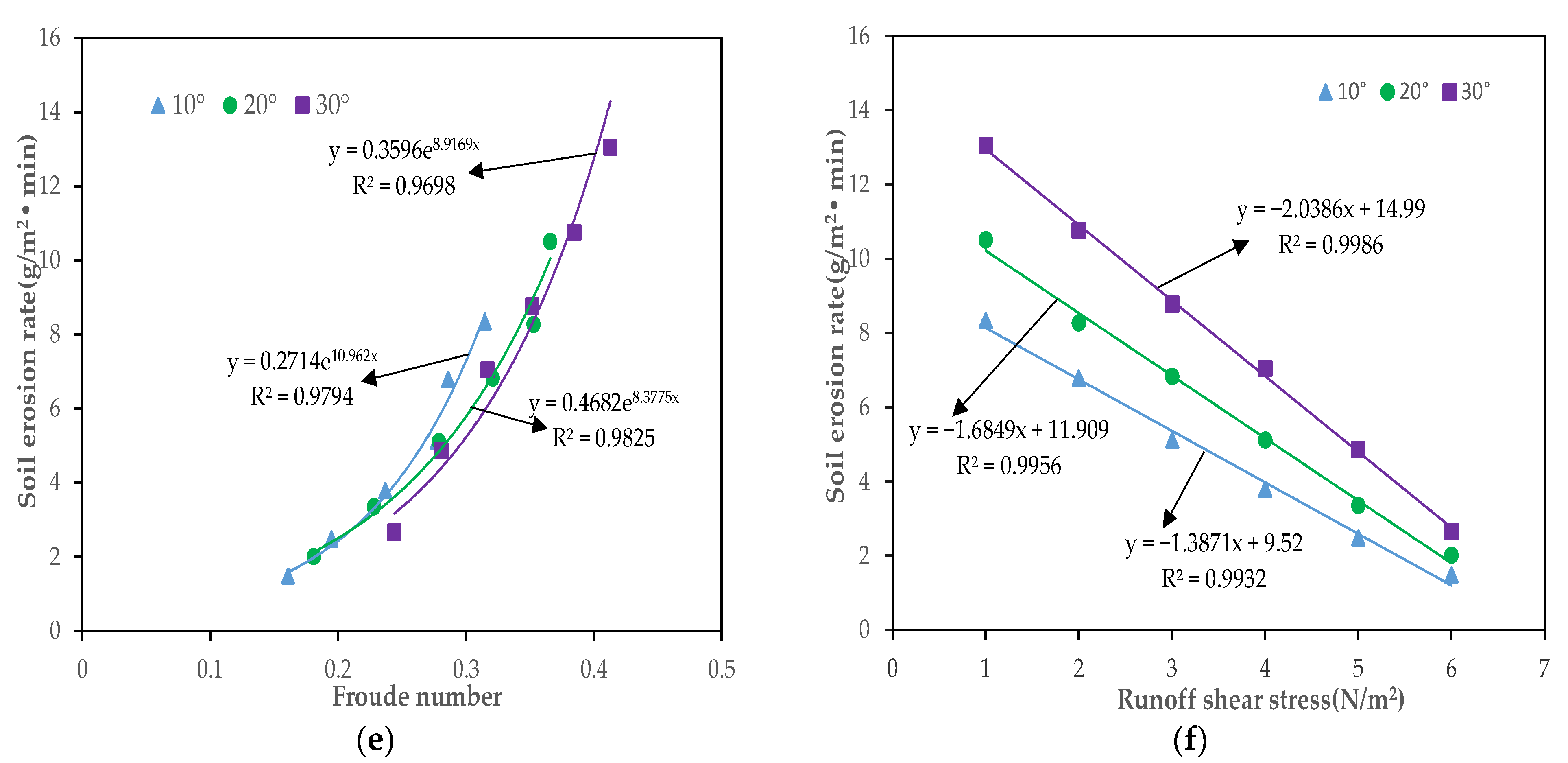
3.3.1. Regression Equation of the Soil Erosion Rate and Hydrodynamic Parameters
3.3.2. Correlation Analysis of Soil Erosion Rate and Hydrodynamic Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Existing Similar Studies
4.2. Effect of Vegetation Coverage and Slope on Hydrodynamic Characteristics
4.3. Implications of This Study for Sustainable Management of Meadow Ecosystems
5. Conclusions
- Vegetation coverage and slope are significant factors affecting soil erosion in degraded bald patches, and soil erosion and runoff rates increase exponentially as a result of meadow degradation (p < 0.01). Rodent activity can increase soil erosion compared to vegetated slopes;
- All slope flows are laminar, with Reynolds and Froude numbers decreasing exponentially and linearly, respectively, as a function of vegetation coverage (p < 0.01), both of which are positively correlated with slope gradients. The Darcy–Weisbach resistance and Manning roughness coefficients were found to be larger on densely vegetated and gently sloping surfaces and significantly affected by vegetation coverage and slope; (p < 0.05). Runoff shear stress is positively correlated with vegetation coverage and slope, with a greater effect on the slope than vegetation coverage (p < 0.05);
- The relationship between soil erosion rate and flow velocity, Reynolds number, Froude number, and runoff shear stress can be described by power, logarithmic, exponential and linear functions, respectively (p < 0.01). Based on the Pearson correlation and grey correlation analysis results, we tentatively determined that the Reynolds number is the most suitable hydrodynamic parameter to describe the soil erosion process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flanagan, D.C.; Ascough, J.C., II; Nieber, J.L.; Misra, D.; Douglas-Mankin, K.R. Advances in Soil Erosion Research: Processes, Measurement, and Modeling. Trans. ASABE 2013, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, M.X.; Wan, G.N.; Wang, X.J. Spatial and temporal precipitation variability in the source region of the Yellow River. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Yang, T.; Yong, B.; Valentina, K.; Shi, P.F.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhou, X.D. Impacts of climate change on flow regime and sequential threats to riverine ecosystem in the source region of the Yellow River. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.B.; Song, Q.; Zhao, J.Y.; Wang, S.R. Prediction and Evaluation of Ecosystem Service Value Based on Land Use of the Yellow River Source Area. Sustainability 2022, 15, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.L.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yang, Q.L.; Liu, C.S.; Liu, Y.L.; Bao, Z.X.; He, R.M. Impacts of climate change on hydrology in the Yellow River source region, China. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2020, 11, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, Q.S.; Gao, Z.Q. Changes in Herdsmen’s Pastoral Behaviour Triggered by Rangeland Degradation in the Source Region of the Yellow River, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Outlook Agric. 2015, 44, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.S.; Li, G.S.; Yin, Y.Y. The impacts of grassland vegetation degradation on soil hydrological and ecological effects in the source region of the Yellow River—A case study in Junmuchang region of Maqin country. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Zhang, Y.P.; Yan, H.R.; Salahou, M.K. Watershed-level spatial pattern of degraded alpine meadow and its key influencing factors in the Yellow River Source Zone of West China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, G.; Li, X.L.; Fryirs, K.; Gao, J.; Shi, Y.; Preey, G.L.W.; Cullum, C. Degradation and recovery of alpine meadow catenas in the source zone of the Yellow River, Western China. J. Mt. Sci. 2022, 19, 2487–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.J.; Steven, A.K.; Huang, Z.G.; Yu, H.Q.; Zhang, Q.W. Livestock grazing significantly accelerates soil erosion more than climate change in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Evidenced from 137Cs and 210Pbex measurements. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 285, 106643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.J.; Jing, J.; Shen, Y.; Liu, H.X.; Gao, Y.H. Short-term grazing exclusion improved topsoil conditions and plant characteristics in degraded alpine grasslands. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 108, 105680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J. Natural and anthropogenic influences on the spatiotemporal change of degraded meadows in southern Qinghai Province, West China:1976–2015. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 97, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ganjurjav, H.; Dong, S.K.; Gao, Q.Z. Excessive plant compensatory growth: A potential endogenous driver of meadow degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2020, 6, 1816500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.R.; Li, X.L.; Li, J.F.; Chen, W.T.; Zhu, H.L.; Hu, X.S.; Zhou, H.K.; Sun, H.Q. Effects of degradation severity on the physical, chemical and mechanical properties of topsoil in alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, west China. Catena 2019, 187, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, R.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Li, K.X.; Xu, Z.H.; Hu, J.M.; Wang, F.; Rui, Y.C.; Li, L.F.; Pang, Z.; Cui, X.Y. Degraded patch formation significantly changed microbial community composition in alpine meadow soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 195, 104426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.X.; Li, X.B.; Dang, D.L.; Dou, H.S.; Wang, K.; Gong, J.R.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.L. A Perspective on the Impact of Grassland Degradation on Ecosystem Services for the Purpose of Sustainable Management. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Cheng, F.Y.; Hou, X.Y.; Zhao, S. Response of Grassland Degradation to Drought at Different Time-Scales in Qinghai Province: Spatio-Temporal Characteristics, Correlation, and Implications. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yao, Z.S.; Zheng, X.H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, K.; Zhu, B.; Wang, R.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.Y. Increasing grassland degradation stimulates the non-growing season CO2 emissions from an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 26576–26591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.P.; Guo, Z.G. Plateau pika disturbances alter plant productivity and soil nutrients in alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Rangel. J. 2017, 39, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.X.; Chai, Q.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhong, M.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Wei, X.T.; Pan, D.; Shao, X.Q. Impacts of burrows and mounds formed by plateau rodents on plant species diversity on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Rangel. J. 2015, 37, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Li, X.L.; Gao, J.; Shi, Y.; Ma, G.L.; Ka, Z.C.R. Influences of pika and simulated grazing disturbances on bare patches of alpine meadow in the Yellow River Source Zone. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, H.; Bao, G.S.; Pang, X.P.; Guo, Z.G. Effect of the presence of plateau pikas on the ecosystem services of alpine meadows. Biogeosciences 2022, 19, 4521–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.X.; Guo, Z.G. Effect of Plateau Pika Disturbance on Plant Aboveground Biomass of Alpine Meadows at Two Different Scales. Plants 2022, 11, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.L.; Fan, J.W.; Li, Y.Z.; Shi, W.J. Effects of Myospalax baileyi disturbance on plant community at alpine meadow in Three Rivers Headwater Region, China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.R.; Li, X.L.; Li, J.F.; Chen, W.T.; Zhu, H.L.; Zhao, J.Y.; Hu, X.S. Influences of Plateau Zokor Burrowing on Soil Erosion and Nutrient Loss in Alpine Meadows in the Yellow River Source Zone of West China. Water 2019, 11, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y. Evaluation of Soil and Water Conservation Function in Dingxi City, Upper Yellow River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.J.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Li, X.G.; Liu, W.J.; Zakari, S. Lateral flow between bald and vegetation patches induces the degradation of alpine meadow in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 142338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.G.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, W.B.; Fu, S.; Yin, S.Q.; Wei, X.; Zhang, K.L.; Wang, Z.Q.; et al. The assessment of soil loss by water erosion in China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, A.F.; Zhang, H.X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.N.; Sun, H.L.; Zhao, C. Soil Erosion in Relation to Climate Change and Vegetation Coverage over the Past 2000 years as inferred from the Tianchi lake in the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 180, 103850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, I.; Bogunovic, I.; Pereira, P. Soil management and seasonality impact on soil properties and soil erosion in steep vineyards of north-western Croatia. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2023, 71, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Alabbadi, A.M.; Jabbar, F.K.; Alzahrani, H.; Hamad, S. Predicting Soil Erosion Rate at Transboundary Sub-Watersheds in Ali Al-Gharbi, Southern Iraq, Using RUSLE-Based GIS Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Ran, L.S.; Fang, N.F.; Shi, Z.H. Aggregate stability and associated organic carbon and nitrogen as affected by soil erosion and vegetation rehabilitation on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2018, 167, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.J.; Wang, W.G.; Shao, Q.X.; Yu, Z.B.; Hao, Z.C.; Xing, W.Q.; Yong, B.; Li, J.X. Hydrological projections of future climate change over the source region of Yellow River and Yangtze River in the Tibetan Plateau: A comprehensive assessment by coupling RegCM4 and VIC model. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2096–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Lai, Z.H.; Ji, G.X. Using Budyko-Type Equations for Separating the Impacts of Climate and Vegetation Change on Runoff in the Source Area of the Yellow River. Water 2020, 12, 3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.P.; Chen, Z.T.; Xiao, H. Projection in Extreme Climate Events and uncertainty analysis in the Source Area of the Yellow River for the Next Three Decades. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 199, 022024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Wen, J.; Wang, S.P.; Tian, H.; Adnan, M. Variations of precipitation characteristics during the period 1960–2014 in the Source Region of the Yellow River, China. J. Arid Land 2018, 10, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.Q.; Wang, X.K.; Wang, Z.F.; Lin, H.; Xie, H.L.; Shi, Z.Y.; Hu, X.T.; Liu, X.Z. Influence of Landscape Pattern Evolution on Soil Conservation in a Red Soil Hilly Watershed of Southern China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.W.; Du, Y.G.; Li, Q.; Guo, X.W.; Fan, B.; Cao, G.M. Impacts of alpine shrub-meadow degradation on its ecosystem services and spatial patterns in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarin, M.; Zweifel, L.; Roth, V.; Alewell, C. Identifying Soil Erosion Processes in Alpine Grasslands on Aerial Imagery with a U-Net Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Ma, L.; Shao, M.A.; Wei, X.R.; Jia, Y.H.; Sun, S.C.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Li, T.C.; Yang, X.; Gan, M. Chinese zokor (Myospalax fontanierii) excavating activities lessen runoff but facilitate soil erosion—A simulation experiment. Catena 2021, 202, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.M.; Xiao, P.Q.; Yu, X.X.; Hao, S.L.; Jia, G.D.; Yang, C.X. A Field Study for the Effects of Grass Coverage, Rainfall Intensity and Slope Length on Soil Erosion in the Loess Plateau, China. Water 2022, 14, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.O.; Ma, R.M.; Ye, Q.; Feng, J.; Wang, J.H. Impacts of Corn Straw Coverage and Slope Gradient on Soil Erosion and Sediment Size Distributions in the Mollisol Region, NE China. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2021, 54, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Ji, X.D.; Strauss, P.; Zhang, Z.Q. Effects of shrub-grass coverage on the hillslope overland flow and soil erosion under simulated rainfall. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.M.; Fan, D.X.; Yu, X.X.; Li, H.Z. Hydraulic characteristics of varying slope gradients, rainfall intensities and litter coverage on vegetated slopes. Hydrol. Res. 2018, 49, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Yu, Z.B.; Yuan, F.F.; Acharya, K. The Multi-Scale Temporal Variability of Extreme Precipitation in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Water 2019, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, D.; Zhuo, M.; Guo, T.; Liao, Y.; Xie, Z.J.S.E.R.; Assessment, R. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on erosion characteristics of the red soil slope. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Zheng, F.; Lu, J.; Li, G. Investigating the Role of Raindrop Impact on Hydrodynamic Mechanism of Soil Erosion Under Simulated Rainfall Conditions. Soil Sci. 2012, 177, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.R.; Bi, H.X.; Huo, Y.M.; Wei, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wang, X.X.; Liao, W.C. Determining the optimal vegetation coverage for controlling soil erosion in Cynodon dactylon grassland in North China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Cui, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.H.; Yin, R.; Kardol, P. Trade-off between vegetation type, soil erosion control and surface water in global semi-arid regions: A meta-analysis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.X.; Ma, L.; Zhang, S.H.; Yu, Y.; Shen, M.S.; Zhang, H.B.; Wang, D.S.; Yang, Y.B.; Zhang, J.A.; Zhang, Y.Z.; et al. Study on Landscape Patches Influencing Hillslope Erosion Processes and Flow Hydrodynamics in the Loess Plateau of Western Shanxi Province, China. Water 2020, 12, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.D.; Xin, Z.B.; Jiang, Q.L.; Yu, X.X.; Fan, D.X. Slope erosion and its hydrodynamic characteristic of Cinnamon soil under continuous rainfull. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 34, 14–20+30. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Kang, H.L.; Wang, W.L.; Su, H.; Li, J.M.; Ma, C.Y. Characteristics of gully topography and sediment on the platform-steep slope system of spoil dump. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, C.Z.; Shangguan, Z.P. Runoff hydraulic characteristics and sediment generation in sloped grassplots under simulated rainfall conditions. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xu, S.S.; Ji, X.Y.; Wang, S.Q.; Ding, S.Y. Relationships between Riparian Vegetation Pattern and the Hydraulic Characteristics of Upslope Runoff. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Liang, Z.Q.; Xie, Z.Y.; Zhuo, M.N.; Liao, Y.S.; Guo, T.L.; Li, D.Q. Mechanisms of grass in slope erosion control in red soil region of southern China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 30, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.D.; Dong, S.K.; Shen, H.; Xiao, J.N.; Li, S.; Gao, X.X.; Wu, S.N. Degradation significantly decreased the ecosystem multifunctionality of three alpine grasslands: Evidences from a large-scale survey on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Cheng, X.N.; Wu, Y.F.; Hu, C.W.; Jemin, R.S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.M.; Cai, Q.F.; Geng, X.D.; Guo, X.M.; et al. Evaluation of soil and water conservation function in the Wugong mountain meadow based on the comprehensive index method. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Wei, C.; Shao, Q.Q.; Huang, L.; He, T. Characteristics of Land Use/Cover and Macroscopic Ecological Changes in the Headwaters of the Yangtze River and of the Yellow River over the Past 30 Years. Sustainability 2016, 8, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.Y.; Jia, Z.R.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wu, D.S.; Li, J.P. Research on Dynamic Rotational Grazing Assignment Model based on Grass Resource Leveling. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 162, 696–703. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.F.; Li, M. Effects of grass coverage and distribution patterns on erosion and overland flow hydraulic characteristics. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Pan, C.Z. Overland runoff erosion dynamics on steep slopes with forages under field simulated rainfall and inflow. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 1794–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Gao, Z.L.; Li, Y.H.; Niu, Y.B.; Su, Y.; Wang, K. Erosion control of hedgerows under soils affected by disturbed soil accumulation in the slopes of loess plateau, China. Catena 2019, 181, 104079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Degraded Meadow Types | Moisture Content | Density | Porosity | Firmness | Cohesion | Less Than a Certain Soil Particle Size (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (g m−3) | (%) | (kPa) | (kPa) | d < 2 mm | d < 0.5 mm | d < 0.075 mm | |
| Degraded bald patches | 15.16 ± 2.08 | 1.51 ± 0.15 | 11.38 ± 0.14 | 25.6 ± 2.38 | 26.61 ± 3.24 | 75.26 | 48.97 | 8.15 |
| Zokor mound bare ground | 9.35 ± 1.75 | 1.43 ± 0.11 | 14.34 ± 0.16 | 10.21 ± 2.15 | 12.56 ± 1.12 | 88.79 | 59.72 | 8.88 |
| Slope (°) | Vegetation Coverage (%) | Flow Velocity (v, cm s−1) | Runoff Depth (h, mm) | Reynolds Number (Re) | Froude Number (Fr) | Darcy–Weisbach Resistance (f) | Manning Roughness (n) | Flow Shear Stress (τ, N m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10° | 0 | 4.42 ± 0.17 Ca | 1.85 ± 0.21 Ade | 87.29 ± 29.83 BCa | 0.315 ± 0.060 Ca | 25.27 ± 6.58 Ae | 0.211 ± 0.046 Ade | 1.71 ± 1.07 Cf |
| 10% | 3.79 ± 0.20 Cb | 1.72 ± 0.12 Ae | 71.82 ± 24.27 Cb | 0.286 ± 0.054 Cb | 29.52 ± 8.28 Ae | 0.196 ± 0.039 Ae | 2.32 ± 0.98 Ce | |
| 30% | 3.38 ± 0.22 Cc | 1.94 ± 0.22 Ad | 59.23 ± 22.60 Cc | 0.277 ± 0.053 Cbc | 44.78 ± 13.95 Ac | 0.233 ± 0.056 Ad | 2.67 ± 0.99 Cd | |
| 50% | 2.93 ± 0.18 Cd | 2.38 ± 0.23 Ac | 50.01 ± 19.80 Cd | 0.237 ± 0.050 Cd | 36.24 ± 11.09 Ad | 0.258 ± 0.063 Ac | 3.56 ± 1.04 Cc | |
| 70% | 2.38 ± 0.22 Ce | 2.85 ± 0.31 Ab | 40.96 ± 17.48 Ce | 0.195 ± 0.040 Ce | 56.77 ± 17.44 Ab | 0.292 ± 0.071 Ab | 3.92 ± 1.05 Cab | |
| 90% | 2.31 ± 0.20 BCf | 3.38 ± 0.25 Aa | 37.70 ± 16.53 Ce | 0.161 ± 0.032 BCf | 77.43 ± 26.35 Aa | 0.337 ± 0.090 Aa | 4.05 ± 1.11 Ca | |
| 20° | 0 | 4.89 ± 0.24 Ba | 1.68 ± 0.15 Be | 93.73 ± 32.78 Ba | 0.366 ± 0.078 Ba | 23.25 ± 5.40 ABde | 0.187 ± 0.038 Be | 2.34 ± 2.07 Bf |
| 10% | 4.48 ± 0.28 Bb | 1.62 ± 0.17 Ade | 80.60 ± 29.50 Bb | 0.353 ± 0.063 Bab | 22.17 ± 5.90 Be | 0.188 ± 0.034 ABe | 2.98 ± 1.82 Be | |
| 30% | 3.97 ± 0.25 Bc | 1.80 ± 0.19 ABd | 68.53 ± 26.11 Bc | 0.321 ± 0.065 Bc | 28.72 ± 7.61 Bd | 0.208 ± 0.043 Bd | 3.42 ± 1.95 Bd | |
| 50% | 3.39 ± 0.24 Bd | 1.94 ± 0.18 Bc | 59.35 ± 24.57 Bd | 0.279 ± 0.060 Bd | 39.32 ± 10.49 ABc | 0.239 ± 0.051 Bc | 4.08 ± 1.96 Bc | |
| 70% | 2.85 ± 0.24 Be | 2.38 ± 0.24 Bb | 51.78 ± 20.33 Bde | 0.228 ± 0.054 Be | 51.08 ± 17.17 ABb | 0.297 ± 0.068 Ab | 4.48 ± 2.23 Bb | |
| 90% | 2.32 ± 0.28 Bf | 2.71 ± 0.12 Ba | 46.63 ± 19.93 ABef | 0.181 ± 0.040 Bf | 63.05 ± 25.36 Ba | 0.313 ± 0.080 Ba | 4.74 ± 2.23 Ba | |
| 30° | 0 | 5.21 ± 0.24 Aa | 1.58 ± 0.10 Bd | 114.89 ± 34.60 Aa | 0.413 ± 0.084 Aa | 20.81 ± 3.70 Bcd | 0.171 ± 0.029 BCd | 2.61 ± 2.73 Af |
| 10% | 4.81 ± 0.23 Ab | 1.47 ± 0.18 ABd | 90.80 ± 30.06 Ab | 0.385 ± 0.087 Ab | 18.97 ± 4.3 BCd | 0.156 ± 0.031 Ce | 3.24 ± 2.92 Ae | |
| 30% | 4.31 ± 0.23 Ac | 1.64 ± 0.15 Bcd | 79.36 ± 29.42 Ac | 0.352 ± 0.091 Ac | 21.02 ± 5.28 Ccd | 0.168 ± 0.035 Cde | 3.77 ± 3.16 Ad | |
| 50% | 3.85 ± 0.23 Ad | 1.77 ± 0.14 Cc | 71.16 ± 27.35 Acd | 0.317 ± 0.081 Ad | 26.86 ± 7.64 Cc | 0.201 ± 0.044 Cc | 4.34 ± 3.19 Ac | |
| 70% | 3.53 ± 0.25 Ae | 1.98 ± 0.20 Cb | 64.84 ± 23.96 Ad | 0.281 ± 0.073 Ae | 39.74 ± 11.11 Cb | 0.243 ± 0.052 Bb | 4.68 ± 3.33 Ab | |
| 90% | 2.77 ± 0.21 Af | 2.38 ± 0.26 Ca | 53.69 ± 31.78 Ae | 0.244 ± 0.068 Af | 54.05 ± 15.48 Ca | 0.296 ± 0.063 Ca | 5.27 ± 3.45 Aa |
| Hydrodynamic Parameters | Vegetation Coverage (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10° | 20° | 30° | |
| Flow velocity (v, m s−1) | y = 4.2189e−0.007x (R2 = 0.9726) | y = 4.9502e−0.008x (R2 = 0.9938) | y = 5.2721e−0.007x (R2 = 0.9833) |
| Reynolds number(Re) | y = 81.165e−0.009x (R2 = 0.9709) | y = 88.789e−0.008x (R2 = 0.9778) | y = 104.66e−0.007x (R2 = 0.9278) |
| Froude number(Fr) | y = −0.0017x + 0.3146 (R2 = 0.9796) | y = −0.0018x + 0.4081 (R2 = 0.9976) | y = −0.0021x + 0.3746 (R2 = 0.9900) |
| Darcy–Weisbach resistance coefficient(n) | y = 26.143e0.0113x (R2 = 0.9021) | y = 21.158e0.0122x (R2 = 0.9911) | y = 17.387e0.0114x (R2 = 0.9396) |
| Manning roughness coefficient(n) | y = 0.1972e0.0057x (R2 = 0.9695) | y = 0.1742e0.0077x (R2 = 0.9608) | y = 0.1514e0.0067x (R2 = 0.9236) |
| Runoff shear stress(τ, N m−2) | y = 0.0264x + 1.9382 (R2 = 0.9447) | y = 0.026x + 2.5893 (R2 = 0.9628) | y = 0.0276x + 2.8333 (R2 = 0.9781) |
| Slope(°) | SD | VC | RR | v | h | Re | Fr | f | n | τ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10° | Grey correlation | 0.497 | 0.776 | 0.812 | 0.615 | 0.844 | 0.796 | 0.640 | 0.638 | 0.599 |
| Pearson correlation | −0.998 ** | 0.993 ** | 0.994 ** | −0.914 * | 0.993 ** | 0.971 ** | −0.895 * | −0.931 ** | −0.987 ** | |
| Sig.(2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.011 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.016 | 0.007 | 0 | |
| 20° | Grey correlation | 0.508 | 0.830 | 0.848 | 0.658 | 0.842 | 0.84 | 0.590 | 0.638 | 0.636 |
| Pearson correlation | −0.989 ** | 0.997 ** | 0.994 ** | −0.916 * | 0.993 ** | 0.974 ** | −0.946 ** | −0.917 * | −0.996 ** | |
| Sig.(2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.01 | 0 | |
| 30° | Grey correlation | 0.509 | 0.819 | 0.828 | 0.673 | 0.845 | 0.816 | 0.612 | 0.646 | 0.647 |
| Pearson correlation | −0.994 ** | 0.998 ** | 0.992 ** | −0.910 * | 0.974 ** | 0.998 ** | −0.901 * | −0.905 * | −0.997 ** | |
| Sig.(2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.012 | 0.001 | 0 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, S.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhai, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, X. Soil Water Erosion and Its Hydrodynamic Characteristics in Degraded Bald Patches of Alpine Meadows in the Yellow River Source Area, Western China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8165. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108165
Tong S, Li G, Li X, Li J, Zhai H, Zhao J, Zhu H, Liu Y, Chen W, Hu X. Soil Water Erosion and Its Hydrodynamic Characteristics in Degraded Bald Patches of Alpine Meadows in the Yellow River Source Area, Western China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(10):8165. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108165
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Shengchun, Guorong Li, Xilai Li, Jinfang Li, Hui Zhai, Jianyun Zhao, Haili Zhu, Yabin Liu, Wenting Chen, and Xiasong Hu. 2023. "Soil Water Erosion and Its Hydrodynamic Characteristics in Degraded Bald Patches of Alpine Meadows in the Yellow River Source Area, Western China" Sustainability 15, no. 10: 8165. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108165
APA StyleTong, S., Li, G., Li, X., Li, J., Zhai, H., Zhao, J., Zhu, H., Liu, Y., Chen, W., & Hu, X. (2023). Soil Water Erosion and Its Hydrodynamic Characteristics in Degraded Bald Patches of Alpine Meadows in the Yellow River Source Area, Western China. Sustainability, 15(10), 8165. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108165








