Land–Sea Interactions and Ecosystem Services: Research Gaps and Future Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
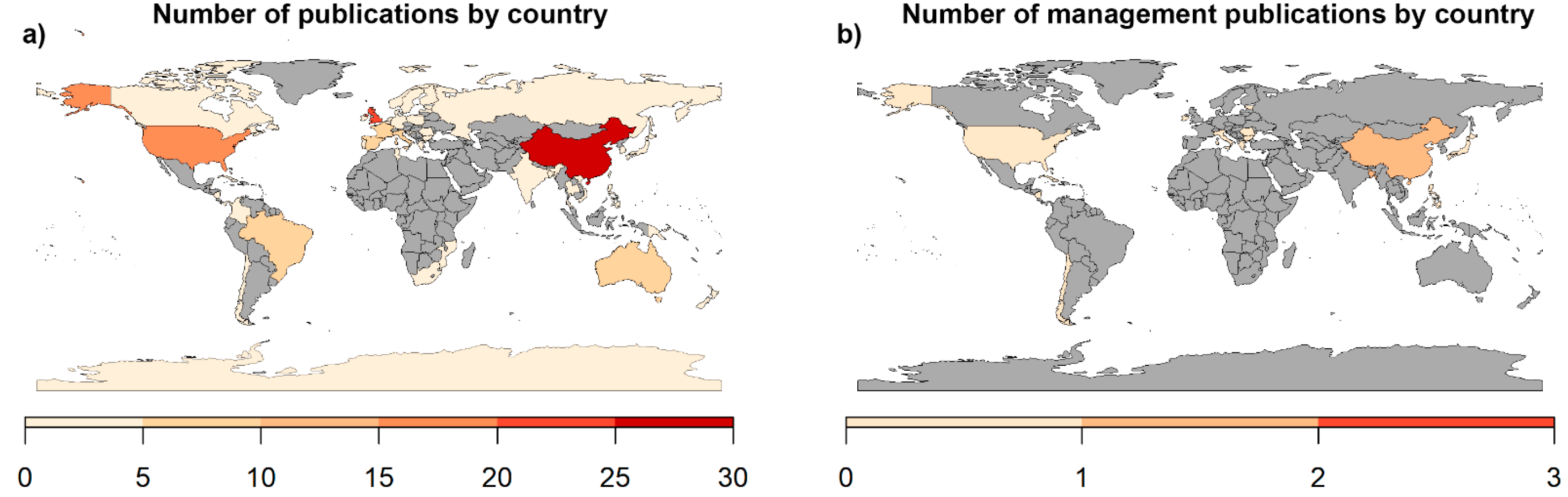
3.1. Location of Study and Years of Publication
3.2. Discipline and Focus of Research
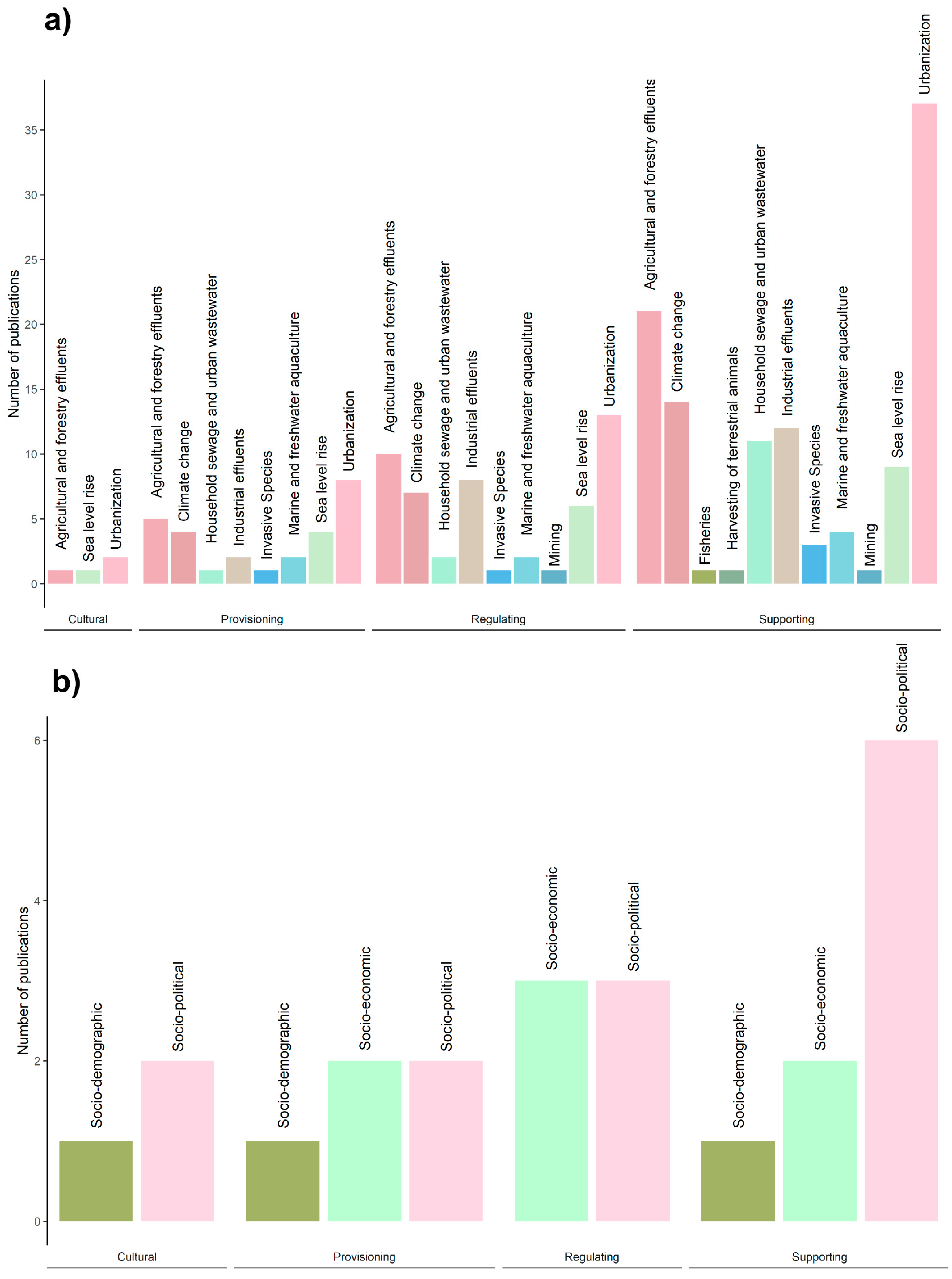
3.3. Ecosystem Services
3.4. Drivers of Change
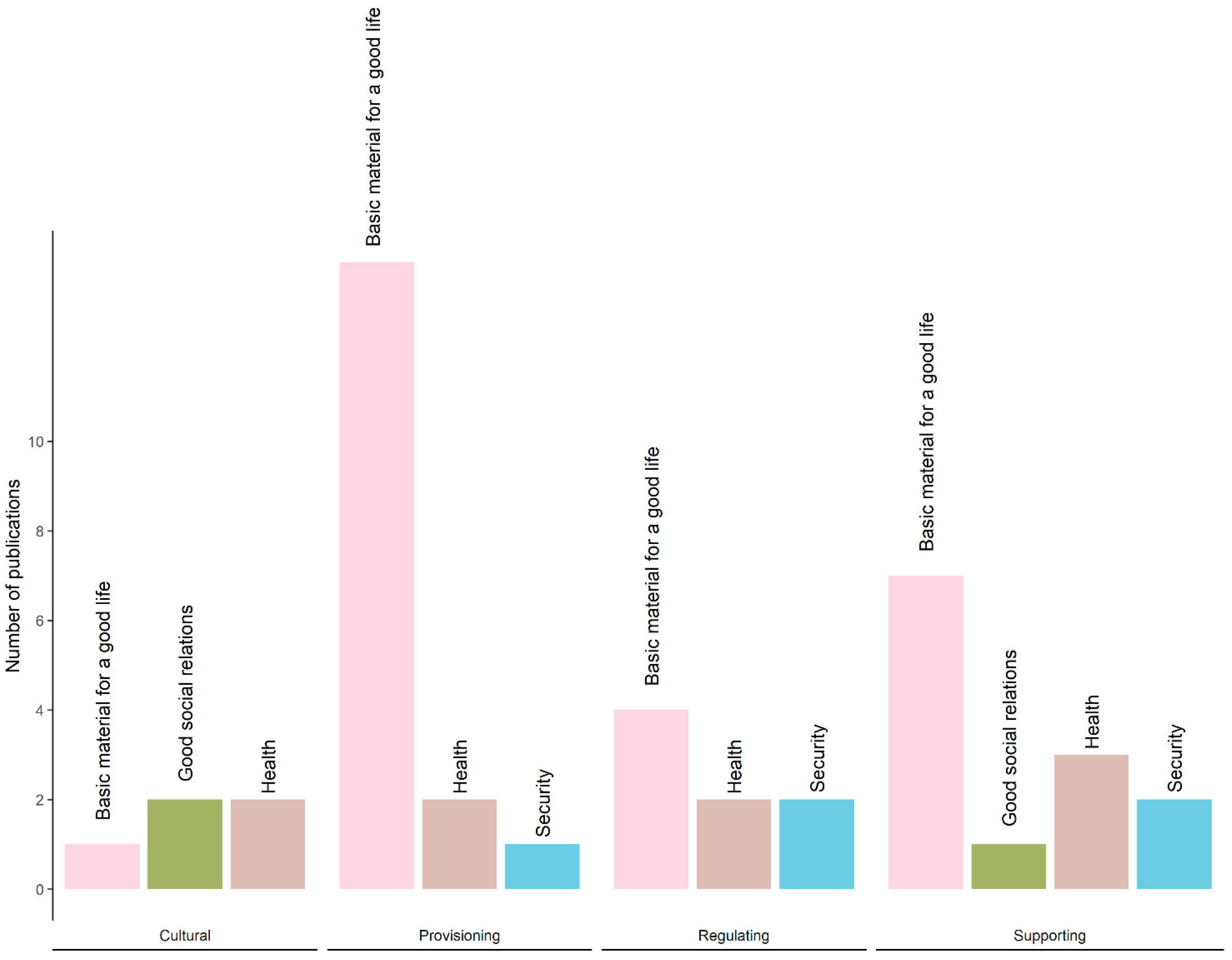
3.5. Human Well-Being
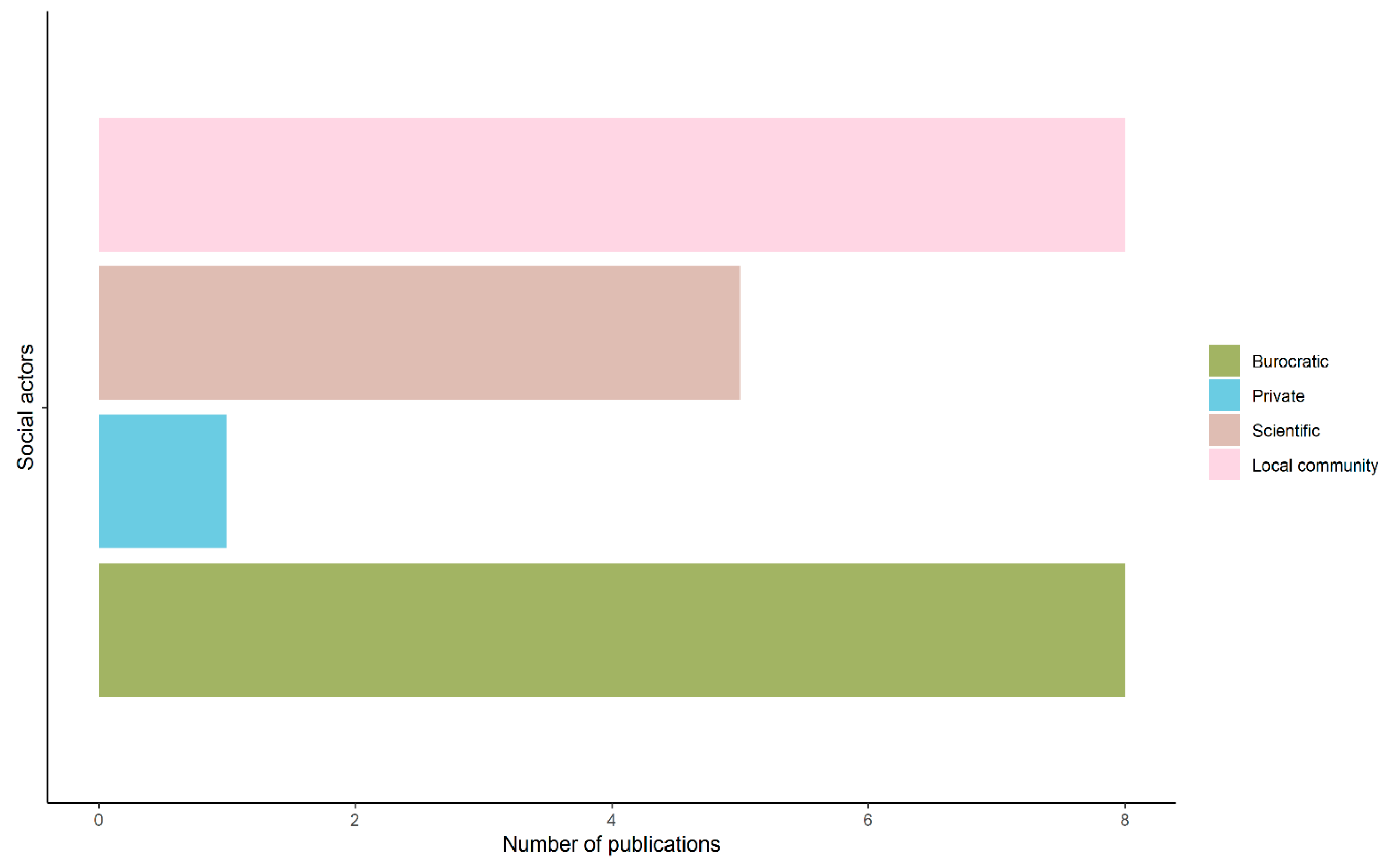
3.6. Social–Ecological Perspective
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations of the Study
4.2. Future Challenges
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Webb, T.J. Marine and Terrestrial Ecology: Unifying Concepts, Revealing Differences. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Romero, J.G.; Pressey, R.L.; Ban, N.C.; Vance-Borland, K.; Willer, C.; Klein, C.J.; Gaines, S.D. Integrated Land-Sea Conservation Planning: The Missing Links. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2011, 42, 381–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoms, D.M.; Davis, F.W.; Andelman, S.J.; Carr, M.H.; Gaines, S.D.; Halpern, B.S.; Hoenicke, R.; Leibowitz, S.G.; Leydecker, A.; Madin, E.M.P.; et al. Integrated Coastal Reserve Planning: Making the Land—Sea Connection in a Nutshell. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 3, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beger, M.; Grantham, H.S.; Pressey, R.L.; Wilson, K.A.; Peterson, E.L.; Dorfman, D.; Mumby, P.J.; Lourival, R.; Brumbaugh, D.R.; Possingham, H.P. Conservation Planning for Connectivity across Marine, Freshwater, and Terrestrial Realms. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Hou, X.; Li, X.; Hou, W.; Nakaoka, M.; Yu, X. Ecological Connectivity between Land and Sea: A Review. Ecol. Res. 2018, 33, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, E.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Galloway, J.N.; Dentener, F.J.; Green, P.A.; Vörösmarty, C.J. Riverine Nitrogen Export from the Continents to the Coasts. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2006, 20, GB1S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, T.S. The Role of Terrestrially Derived Organic Carbon in the Coastal Ocean: A Changing Paradigm and the Priming Effect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19473–19481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, J.E.; Raimbault, P.; Garcia, N.; Lansard, B.; Babin, M.; Gagnon, J. Impact of River Discharge, Upwelling and Vertical Mixing on the Nutrient Loading and Productivity of the Canadian Beaufort Shelf. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 4853–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, C.A.; Contreras, P.Y.; Pérez, C.A.; Sobarzo, M.; Saldías, G.S.; Salisbury, J. Influences of Riverine and Upwelling Waters on the Coastal Carbonate System off Central Chile and Their Ocean Acidification Implications. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 1468–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masotti, I.; Aparicio-Rizzo, P.; Yevenes, M.A.; Garreaud, R.; Belmar, L.; Farías, L. The Influence of River Discharge on Nutrient Export and Phytoplankton Biomass off the Central Chile Coast (33°–37°S): Seasonal Cycle and Interannual Variability. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczuciński, W.; Jagodziński, R.; Hanebuth, T.J.J.; Stattegger, K.; Wetzel, A.; Mitrega, M.; Unverricht, D.; Van Phach, P. Modern Sedimentation and Sediment Dispersal Pattern on the Continental Shelf off the Mekong River Delta, South China Sea. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 110, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagherazzi, S.; Edmonds, D.A.; Nardin, W.; Leonardi, N.; Canestrelli, A.; Falcini, F.; Jerolmack, D.J.; Mariotti, G.; Rowland, J.C.; Slingerland, R.L. Dynamics of River Mouth Deposits. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 642–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallis, H.; Ferdaña, Z.; Gray, E. Linking Terrestrial and Marine Conservation Planning and Threats Analysis. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Holt, T.; Crona, B.; Johnson, J.C.; Gelcich, S. The Consequences of Landscape Change on Fishing Strategies. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 579, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottrell, R.S.; Fleming, A.; Fulton, E.A.; Nash, K.L.; Watson, R.A.; Blanchard, J.L. Considering Land–Sea Interactions and Trade-Offs for Food and Biodiversity. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 580–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyong, A.; Adesina, F.; Osman Elasha, B. The Value of Indigenous Knowledge in Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies in the African Sahel. Mitig. Adapt. Strat. Glob. Chang. 2007, 12, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, L.G.; Pereira, L.M.; Ravera, F.; Jiménez-Aceituno, A. Flipping the Tortilla: Social-Ecological Innovations and Traditional Ecological Knowledge for More Sustainable Agri-Food Systems in Spain. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA). Ecosystems and Human Well-Being; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Blythe, J.; Armitage, D.; Alonso, G.; Campbell, D.; Esteves Dias, A.C.; Epstein, G.; Marschke, M.; Nayak, P. Frontiers in Coastal Well-Being and Ecosystem Services Research: A Systematic Review. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2020, 185, 105028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R Package and Shiny App for Producing PRISMA 2020-compliant Flow Diagrams, with Interactivity for Optimised Digital Transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Naudin, J.J.; Cauwet, G.; Chrétiennot-Dinet, M.J.; Deniaux, B.; Devenon, J.L.; Pauc, H. River Discharge and Wind Influence upon Particulate Transfer at the Land-Ocean Interaction: Case Study of the Rhone River Plume. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 45, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wass, P.D.; Marks, S.D.; Finch, J.W.; Leeks, G.J.L.; Ingram, J.K. Monitoring and preliminary interpretation of in-river turbidity and remote sensed imagery for suspended sediment transport studies in the humber catchment. Sci. Total. Environ. 1997, 194–195, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, A.; Fonseca, A. Coupled Effects of Anthropogenic Nutrient Sources and Meteo-Oceanographic Events in the Trophic State of a Subtropical Estuarine System. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 225, 106228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.B.; Wei, X.; Mostafiz, C.; Yang, Y.J.; Weiss, J.; Belavel, M. Reconstruction of Sea-Land Interactions between Terrestrial Vegetation Cover and Water Quality Constituents in the Mattapoisett Harbor Area during the 1991 Hurricane Bob Event. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 83, 101929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, A.; Wang, K.; Chen, M.T.; Khokiattiwong, S.; Kornkanitnan, N.; Shi, X. Distribution of Rare Earth Elements in Surface Sediments of the Western Gulf of Thailand: Constraints from Sedimentology and Mineralogy. Quat. Int. 2019, 527, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, N.E.; Landry, C.E.; Alexander, C.R.; Samples, K.; Bledsoe, B.P. Socioeconomic and Environmental Predictors of Estuarine Shoreline Hard Armoring. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncles, R.J.; Stephens, J.A. Suspended Sediment Fluxes in the Tidal Ouse, UK. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncles, R.J.; Easton, A.E.; Griffiths, M.L.; Harris, C.; Howland, R.J.M.; King, R.S.; Morris, A.W.; Plummer, D.H. Seasonality of the Turbidity Maximum in the Humber-Ouse Estuary, UK. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1998, 37, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncles, R.J.; Howland, R.J.M.; Easton, A.E.; Griffiths, M.L.; Harris, C.; King, R.S.; Morris, A.W.; Plummer, D.H.; Woodward, E.M.S. Seasonal Variability of Dissolved Nutrients in the Humber-Ouse Estuary, UK. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 37, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantasano, N.; Pellicone, G. Marine and River Environments: A Pattern of Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) in Calabria (Southern Italy). Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2014, 89, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohel, M.S.I.; Ullah, M.H. Ecohydrology: A Framework for Overcoming the Environmental Impacts of Shrimp Aquaculture on the Coastal Zone of Bangladesh. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2012, 63, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhai, L.; Deng, Q.; Pan, D.; Gao, S.; Zou, C. Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of Soil Chloride Distribution in a Coastal Saline Plain: Implication for Ocean and Climate Influences. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros, T.E.A.L.; Croll, D.; Tershy, B.; Fortes, M.D.; Raimondi, P. Land Use Is a Better Predictor of Tropical Seagrass Condition than Marine Protection. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 209, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ge, Y.U. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Vegetation Index and Its Infl Uencing Factors—A Case Study of the Jiaozhou Bay, China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2017, 35, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Zhu, Q.; Hong, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Synchronous Response of Sedimentary Organic Carbon Accumulation on the Inner Shelf of the East China Sea to the Water Impoundment of Three Gorges and Gezhouba Dams. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, M.; Kong, F.; Li, Y.; Kong, F. Temporal-Spatial Variation of DOC Concentration, UV Absorbance and the Flux Estimation in the Lower Dagu River, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 11, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeaton, C.; Austin, W.E.N. Sources, Sinks, and Subsidies: Terrestrial Carbon Storage in Mid-Latitude Fjords. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 2754–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, O.; Marquet, P.A.; Bacigalupe, L.D.; Christie, D.A.; del-Val, E.; Gutierrez, A.G.; Jones, C.G.; Weathers, K.C.; Armesto, J.J. Interactions among Patch Area, Forest Structure and Water Fluxes in a Fog-Inundated Forest Ecosystem in Semi-Arid Chile. Funct. Ecol. 2010, 24, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamito, R.; Vinagre, C.; Teixeira, C.M.; Costa, M.J.; Cabral, H.N. Are Portuguese Coastal Fisheries Affected by River Drainage? Aquat. Living Resour. 2016, 29, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A. Impact of Human Activities on Depositional Process of Tidal Flat in Quanzhou Bay of China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2007, 17, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, J.; Ji, T.; Wen, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J. An Estimation of Nutrient Fluxes via Submarine Groundwater Discharge into the Sanggou Bay—A Typical Multi-Species Culture Ecosystem in China. Mar. Chem. 2014, 167, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Printsmann, A.; Pikner, T. The Role of Culture in the Self-Organisation of Coastal Fishers Sustaining Coastal Landscapes: A Case Study in Estonia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenhardt, P.; Stelzenmüller, V.; Pascal, N.; Probst, W.N.; Aubanel, A.; Bambridge, T.; Charles, M.; Clua, E.; Féral, F.; Quinquis, B.; et al. Exploring Social-Ecological Dynamics of a Coral Reef Resource System Using Participatory Modeling and Empirical Data. Mar. Policy 2017, 78, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, O.; Kokubu, H. Recent Coastal Environmental Management Based on New Concept of Satoumi Which Promotes Land-Ocean Interaction: A Case Study in Japan. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 183, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanchev, H.; Stancheva, M.; Young, R.; Palazov, A. Analysis of Shoreline Changes and Cliff Retreat to Support Marine Spatial Planning in Shabla Municipality, Northeast Bulgaria. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2018, 156, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.; Jeong, H.; Sangwan, N.; Yu, D.J. Effects of Flood Control Strategies on Flood Resilience Under Sociohydrological Disturbances. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 2661–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Z. From Natural Driving to Artificial Intervention: Changes of the Yellow River Estuary and Delta Development. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 174, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coverdale, T.C.; Herrmann, N.C.; Altieri, A.H.; Bertness, M.D. Latent Impacts: The Role of Historical Human Activity in Coastal Habitat Loss. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubayashi, J.; Morimoto, J.O.; Tayasu, I.; Mano, T.; Nakajima, M.; Takahashi, O.; Kobayashi, K.; Nakamura, F. Major Decline in Marine and Terrestrial Animal Consumption by Brown Bears (Ursus arctos). Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luczak, C.; Beaugrand, G.; Lindley, J.A.; Dewarumez, J.; Dubois, P.J.; Kirby, R.R. North Sea Ecosystem Change from Swimming Crabs to Seagulls. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Huang, Q.; Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Lin, G. Restoration of Native Mangrove Wetlands Can Reverse Diet Shifts of Benthic Macrofauna Caused by Invasive Cordgrass. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, X.; Shi, P.; Yu, L. Detecting Shoreline Changes in Typical Coastal Wetlands of Bohai Rim in North China. Wetlands 2013, 33, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Beiras, R.; Ovejero, A.; Méndez, G. Coexistence of Urban Uses and Shellfish Production in an Upwelling-Driven, Highly Productive Marine Environment: The Case of the Ría de Vigo (Galicia, Spain). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 8, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, J.; Armitage, D. How Does Network Governance Affect Social-Ecological Fit across the Land—Sea Interface? An Empirical Assessment from the Lesser Antilles. Ecol. Soc. 2017, 22, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, D.B.; Stevens, K.; Williams, N.E.; Sistla, S.A.; Roddy, A.B.; Urquhart, G.R. Coastal Livelihood Transitions under Globalization with Implications for Trans-Ecosystem Interactions. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, F.; Komiyama, E. A Challenge to Dam Improvement for the Protection of Both Salmon and Human Livelihood in Shiretoko, Japan’s Third Natural Heritage Site. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 6, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, C.; Gasparotti, C.; Anton, I.; Rusu, E. Implementation of a Coastal Management Model at Kinvara Bay in the North Atlantic Ocean. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, C.M.; Pereira, C.I.; Botero, C.M. Improving a Decree Law about Coastal Zone Management in a Small Island Developing State: The Case of Cuba. Mar. Policy 2019, 101, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, R.B.; Mamauag, S.S.; Aliño, P.M. Designing a Marine Protected Areas Network in a Data-Limited Situation. Mar. Policy 2015, 59, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Văidianu, N.; Tătui, F.; Ristea, M.; Stănică, A. Managing Coastal Protection through Multi-Scale Governance Structures in Romania. Mar. Policy 2020, 112, 103567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeks, G.J.L.; Jarvie, H.P. Introduction to the Land–Ocean Interaction Study (LOIS): Rationale and International Context. Sci. Total. Environ. 1998, 210, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.; Skeffington, R.; Neal, M.; Wyatt, R.; Wickham, H.; Hill, L.; Hewitt, N. Rainfall and Runoff Water Quality of the Pang and Lambourn, Tributaries of the River Thames, South-Eastern England. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 8, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Tu, C.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Soils of the Yellow River Delta: Concentrations in Different Soil Horizons and Source Identification. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, J.; Armitage, D. Governance across the Land-Sea Interface: A Systematic Review. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 64, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelcich, S.; Martínez-Harms, M.J.; Tapia-Lewin, S.; Vasquez-Lavin, F.; Ruano-Chamorro, C. Comanagement of Small-Scale Fisheries and Ecosystem Services. Conserv. Lett. 2019, 12, e12637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.D.; Hicks, C.C.; Gurney, G.G.; Cinner, J.E. What Matters to Whom and Why? Understanding the Importance of Coastal Ecosystem Services in Developing Coastal Communities. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 35, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowell, M.; Edelman, S.; Coulton, K.; McAfee, S. How Many People Live in Coastal Areas? J. Coast. Res. 2007, 23, iii–vi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Gatica, M.; Mujica, M.I.; Barceló, M.; Vio-Garay, M.F.; Gelcich, S.; Armesto, J.J. Traditional and Local Knowledge in Chile: Review of Experiences and Insights for Management and Sustainability. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiller, D.A.; Piovia-Scott, J.; Wright, A.N.; Yang, L.H.; Takimoto, G.; Schoener, T.W.; Iwata, T. Marine Subsidies Have Multiple Effects on Coastal Food Webs. Ecology 2010, 91, 1424–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polis, G.A.; Strong, D.R. Food Web Complexity and Community Dynamics. Am. Nat. 1996, 147, 813–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polis, G.A.; Hurd, S.D. Linking Marine and Terrestrial Food Webs: Allochthonous Input from the Ocean Supports High Secondary Productivity on Small Islands and Coastal Land Communities. Am. Nat. 1996, 147, 396–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, P.J.; Barlow, C.; Agostinho, A.A.; Baran, E.; Cada, G.F.; Chen, D.; Cowx, I.G.; Ferguson, J.W.; Jutagate, T.; Mallen-Cooper, M.; et al. Fish Migration, Dams, and Loss of Ecosystem Services in the Mekong Basin. Ambio 2010, 39, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polis, G.A.; Anderson, W.B.; Holt, R.D. Toward an Integration of Landscape and Food Web Ecology: The Dynamics of Spatially Subsidized Food Webs. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1997, 28, 289–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arismendi, I.; Soto, D. Are Salmon-Derived Nutrients Being Incorporated in Food Webs of Invaded Streams? Evidence from Southern Chile. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2012, 405, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, G.; Wüest, A. Disrupting Biogeochemical Cycles-Consequences of Damming. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 64, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.C.; Pringle, C.M.; Greathouse, E.A.; Freeman, B.J. Ecosystem-Level Consequences of Migratory Faunal Depletion Caused by Dams. In American Fisheries Society Symposium; Citeseer: State College, PA, USA, 2003; Volume 35, pp. 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, R.M. Environmental Effects of Dams and Impoundments. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1977, 8, 255–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heatwole, H. Marine-Dependent Terrestrial Biotic Communities on Some Cays in the Coral Sea. Ecology 1971, 52, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, L.; Carney Almroth, B.M.; Collins, C.D.; Cornell, S.; de Wit, C.A.; Diamond, M.L.; Fantke, P.; Hassellöv, M.; MacLeod, M.; Ryberg, M.W.; et al. Outside the Safe Operating Space of the Planetary Boundary for Novel Entities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 1510–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarrubia-Gómez, P.; Cornell, S.E.; Fabres, J. Marine Plastic Pollution as a Planetary Boundary Threat—The Drifting Piece in the Sustainability Puzzle. Mar. Policy 2018, 96, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Criteria of Classification | Definition | Categories |
|---|---|---|
| Year of publication | Year when study was published | 1975–2020 |
| Country of study | Country where study was carried out | |
| Discipline of research | Area or branch of knowledge of how research might be studied | Biogeochemistry Ecology Geochemistry Geography Microbiology Management Oceanography |
| Focus of research | Main focus of research of articles based on the objectives of the investigation | Climate Change Fisheries Food web Land-cover change Nutrient flux Social Ecology Water quality Sea-level rise … |
| Problem identification | If publication addresses and provides explicit management recommendations | Yes No |
| Management Approach | Provides an explicit approach to address the management strategies | Ecosystem-based management Integrated management Land–sea conservation planning |
| Participation of social actors and type of knowledge | Types of social actors who were involved in the research | Local community Bureaucratic Scientific Private Sector |
| Criteria of Classification | Definition | Categories |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Drivers of Change | Factors that directly cause a change in the ecosystem | Agricultural and forestry effluents Marine and freshwater aquaculture Industrial and military effluents Urban wastewater Fisheries Harvesting of terrestrial animals Invasive species Introduced material genetic Climate Change Sea-level rise |
| Indirect Drivers of Change | Factors that indirectly cause a change in the ecosystem | Socio-economic Socio-demographic Socio-political Scientific and technological |
| Ecosystem Services | If the research addresses effects on ecosystem services that can influence human well-being | Cultural (e.g., recreation, spiritual) Provisioning (e.g., food, water) Regulating (e.g., climate, water quality) Supporting (e.g., primary production, pollination) |
| Human well-being | If the research addresses effects on aspects of human well-being. | Security Basic material for good life Health Good basic relations Freedom of choice and action |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barceló, M.; Vargas, C.A.; Gelcich, S. Land–Sea Interactions and Ecosystem Services: Research Gaps and Future Challenges. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8068. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108068
Barceló M, Vargas CA, Gelcich S. Land–Sea Interactions and Ecosystem Services: Research Gaps and Future Challenges. Sustainability. 2023; 15(10):8068. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108068
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarceló, Matías, Cristian A. Vargas, and Stefan Gelcich. 2023. "Land–Sea Interactions and Ecosystem Services: Research Gaps and Future Challenges" Sustainability 15, no. 10: 8068. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108068
APA StyleBarceló, M., Vargas, C. A., & Gelcich, S. (2023). Land–Sea Interactions and Ecosystem Services: Research Gaps and Future Challenges. Sustainability, 15(10), 8068. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108068







