The Characteristics and Seepage Stability Analysis of Toppling-Sliding Failure under Rainfall
Abstract
1. Introduction
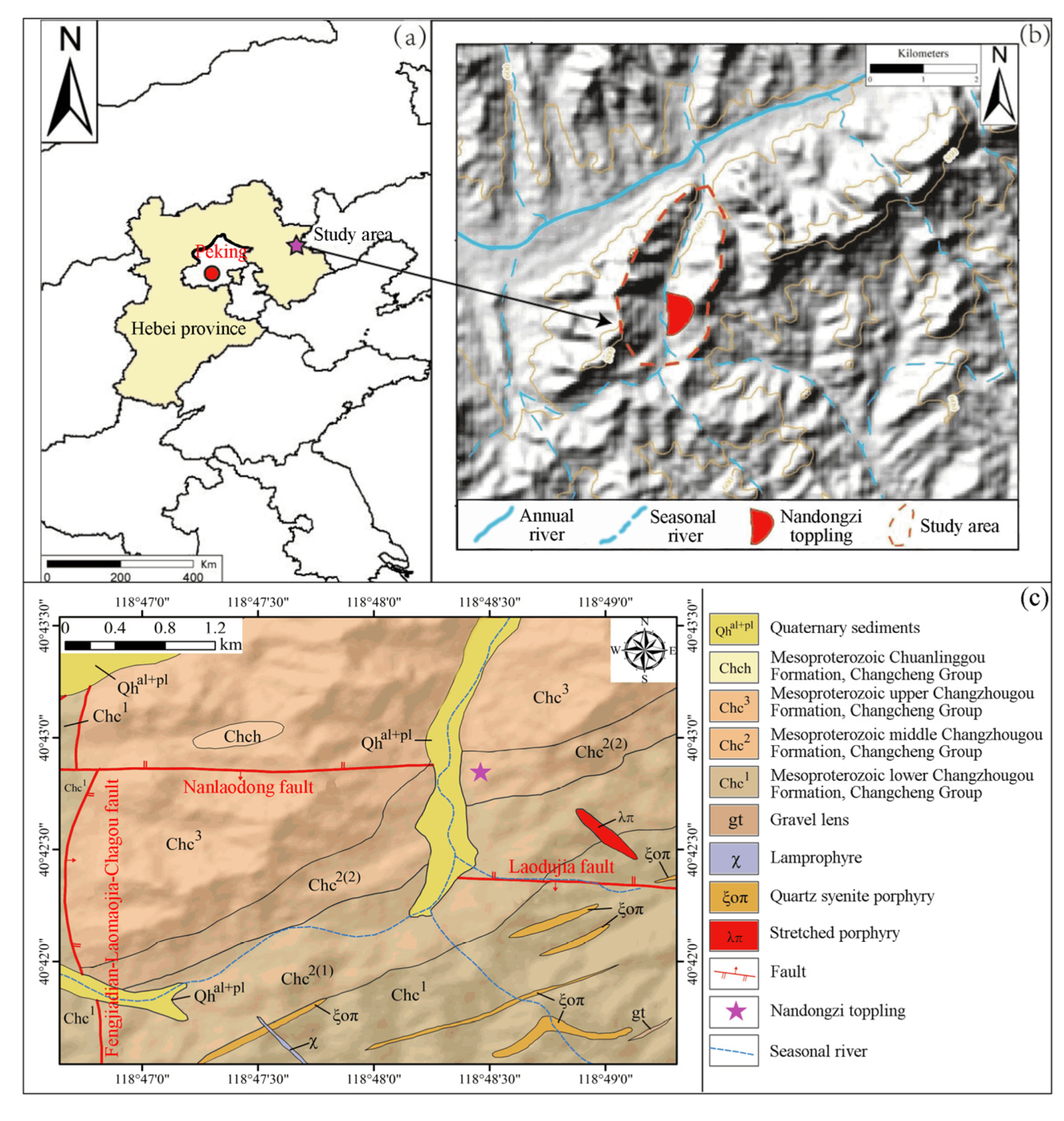
2. Geological Setting of the Study Area
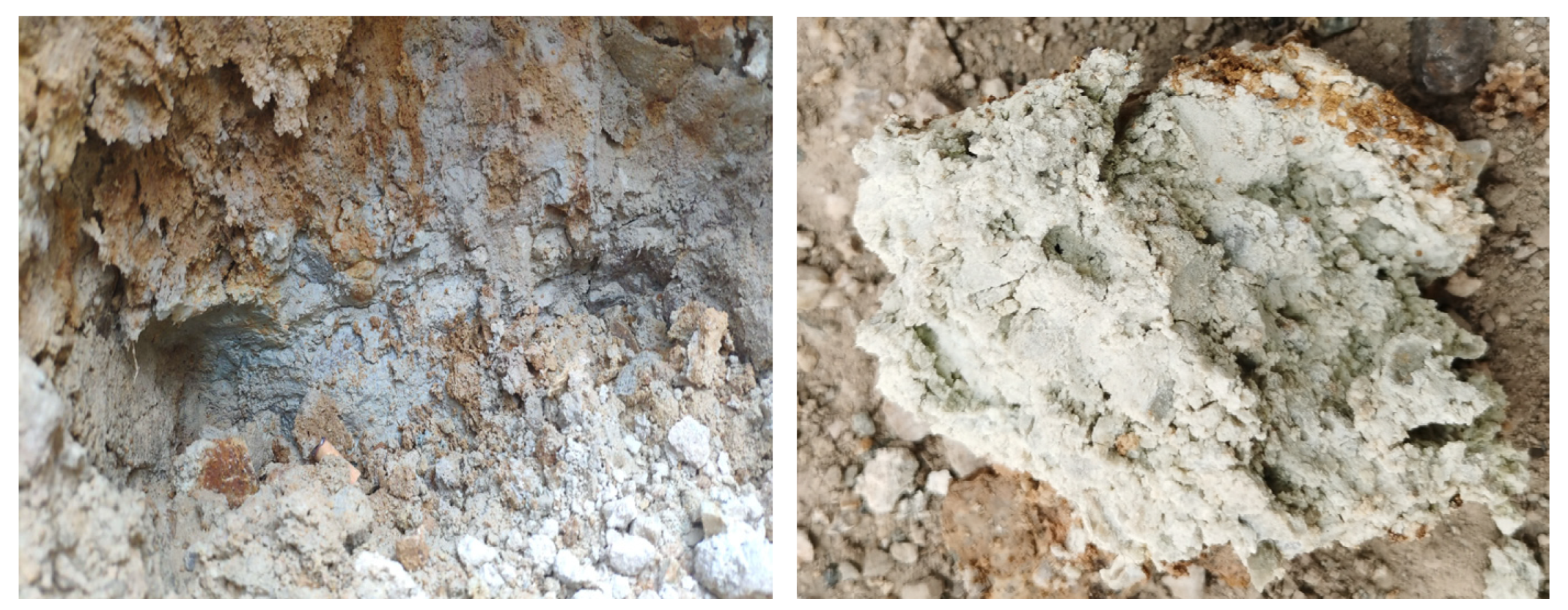
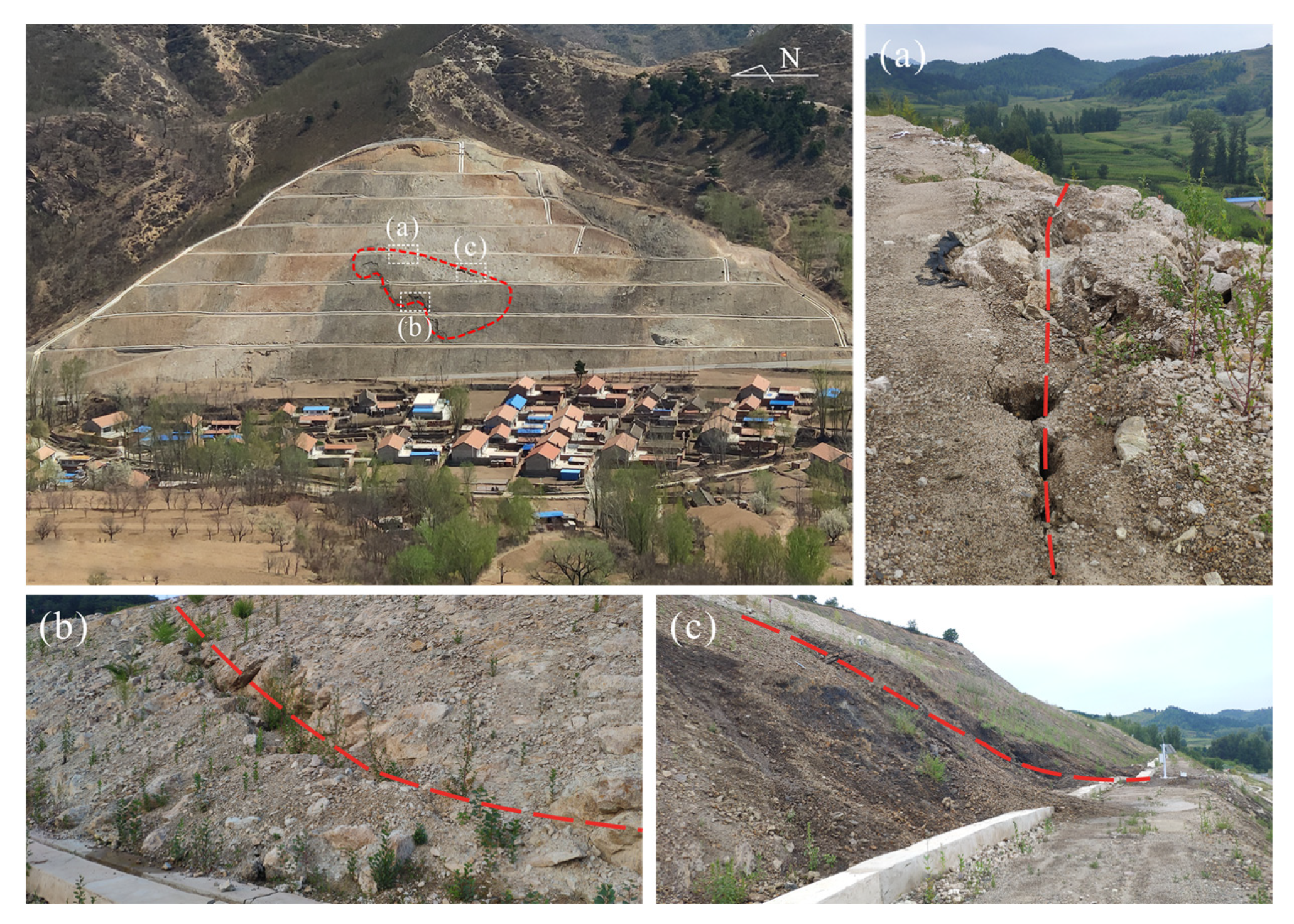
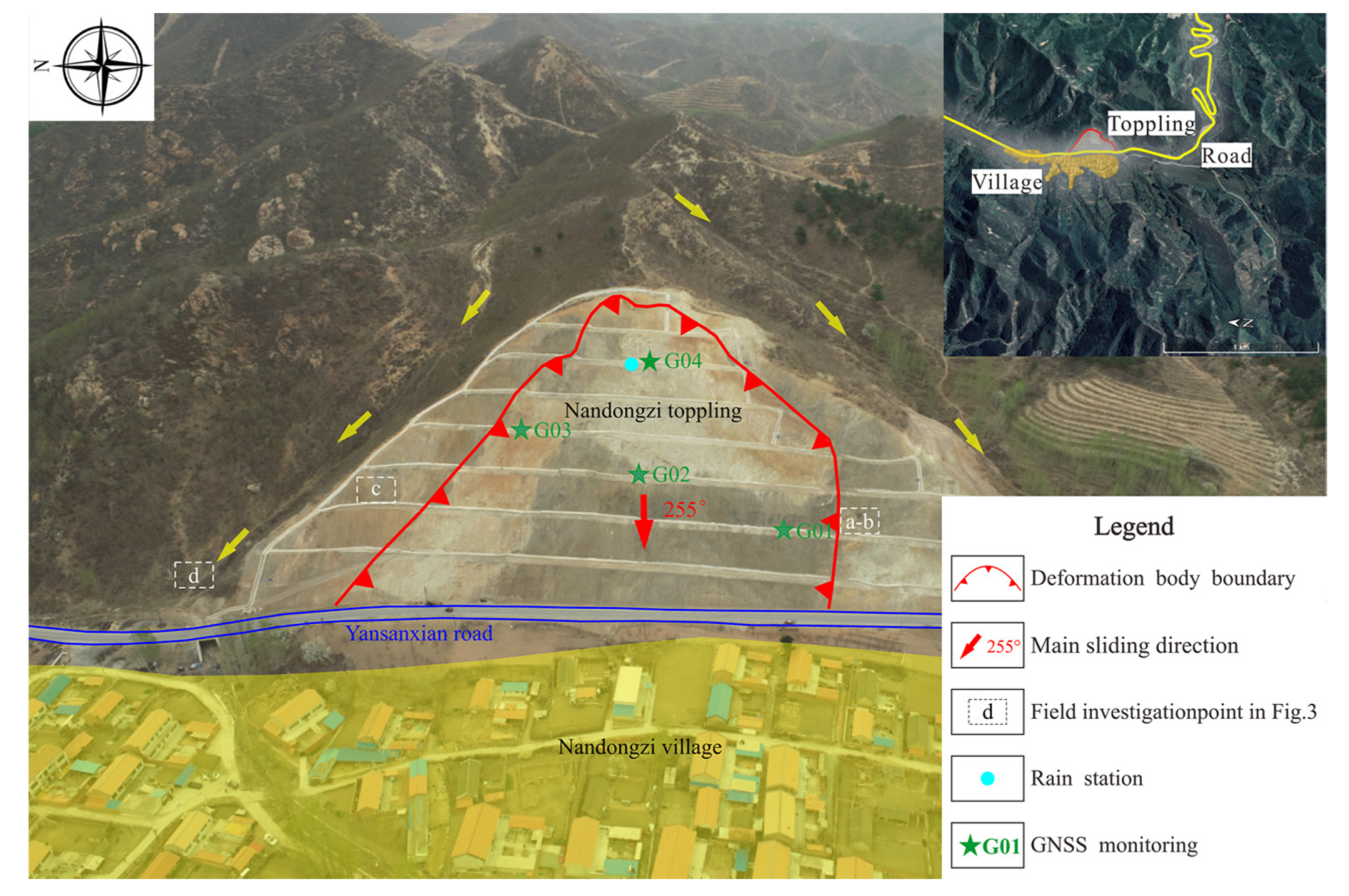
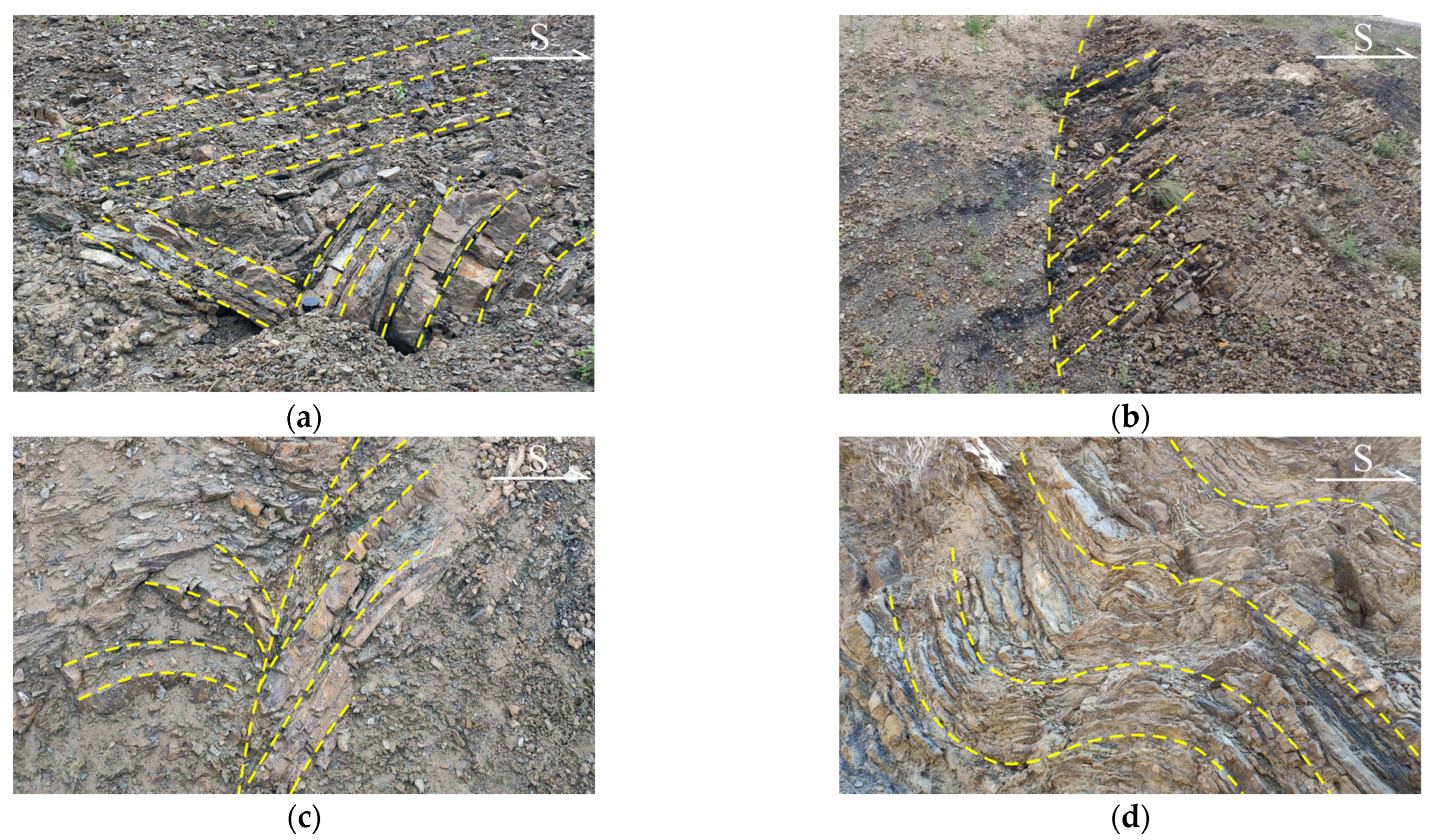
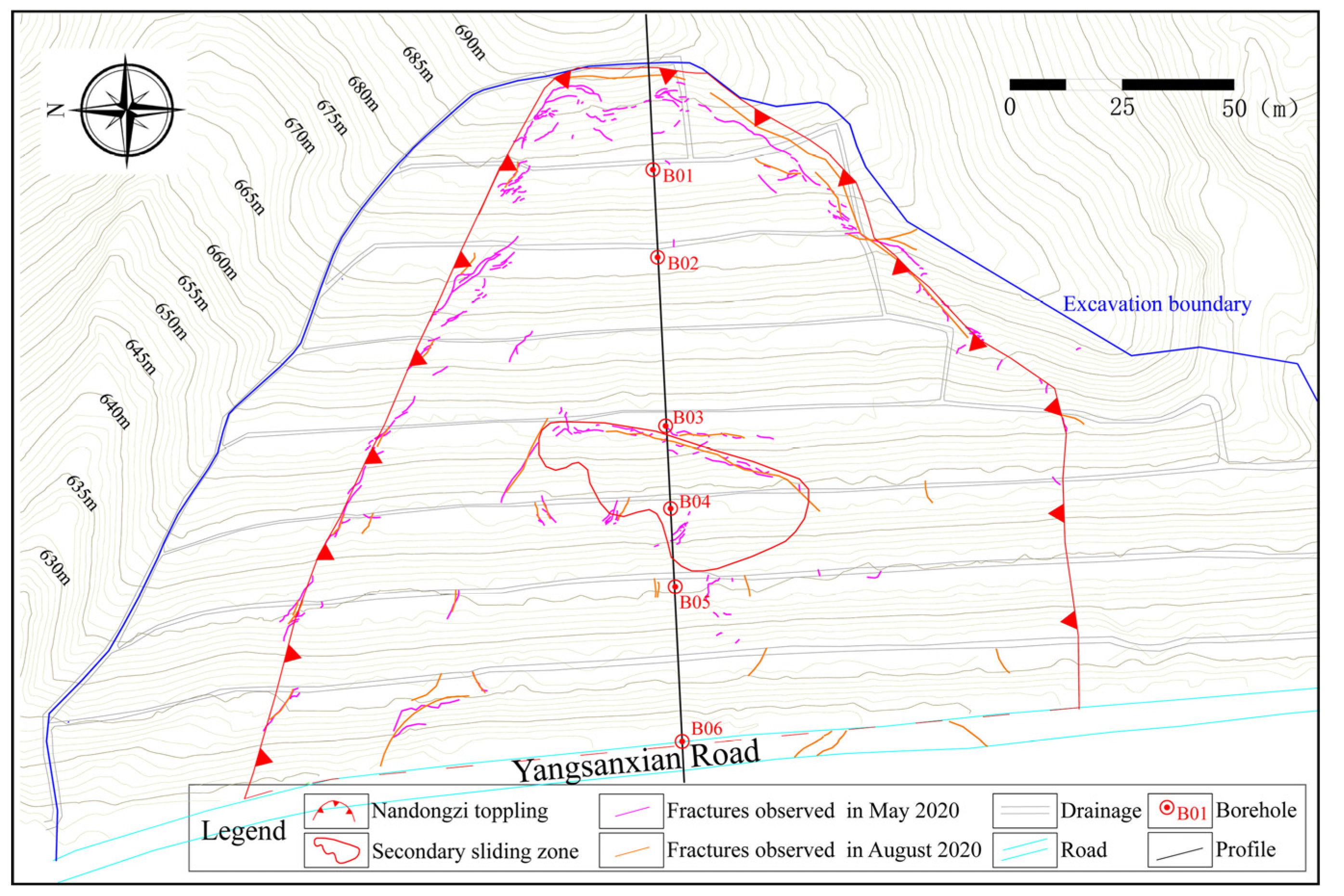
3. Characterization of the Nandongzi Toppling
4. Seepage Stability Analysis Using Geo–Studio
4.1. Model Setup
4.2. The Properties of Rock and Soil Materials
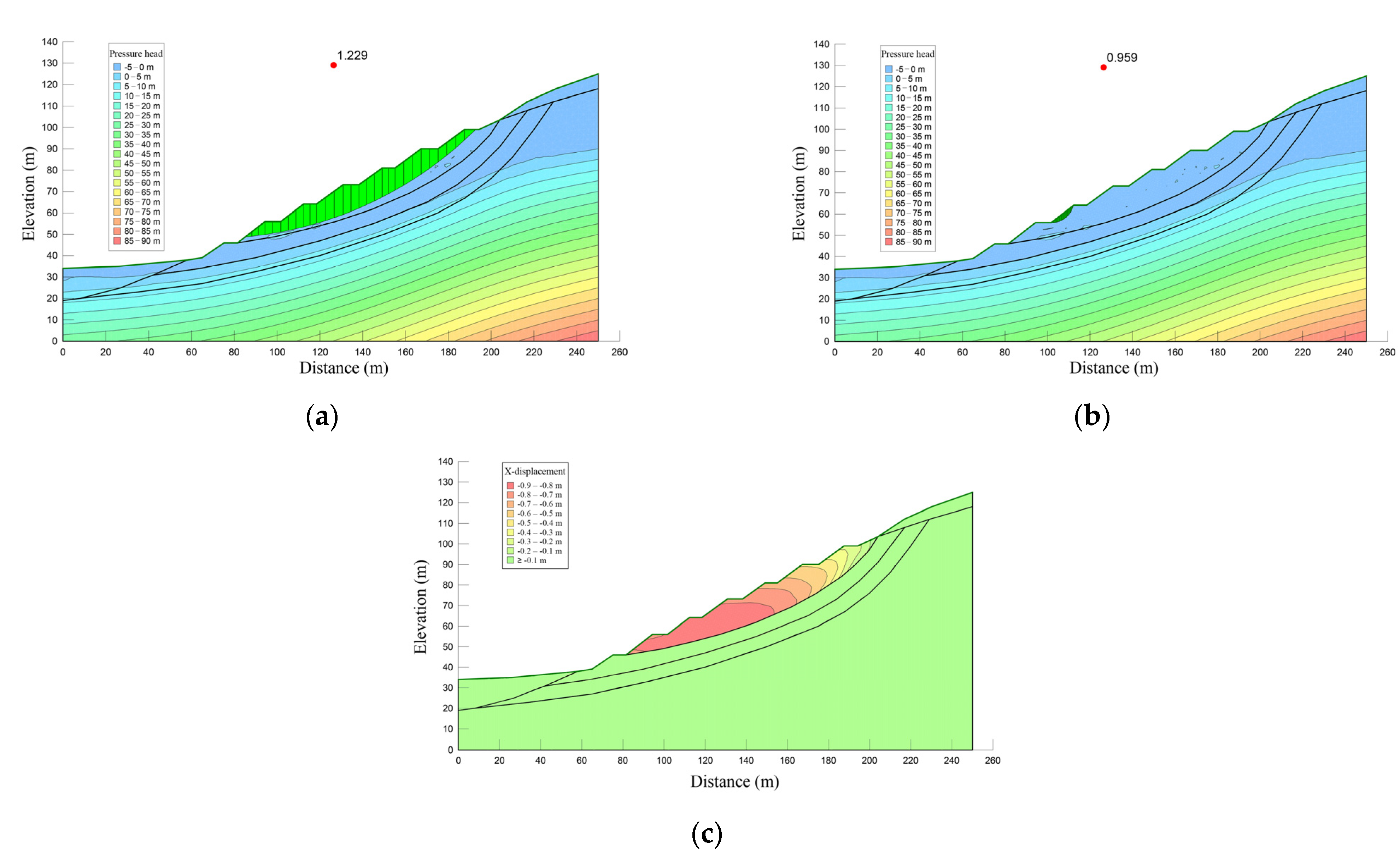
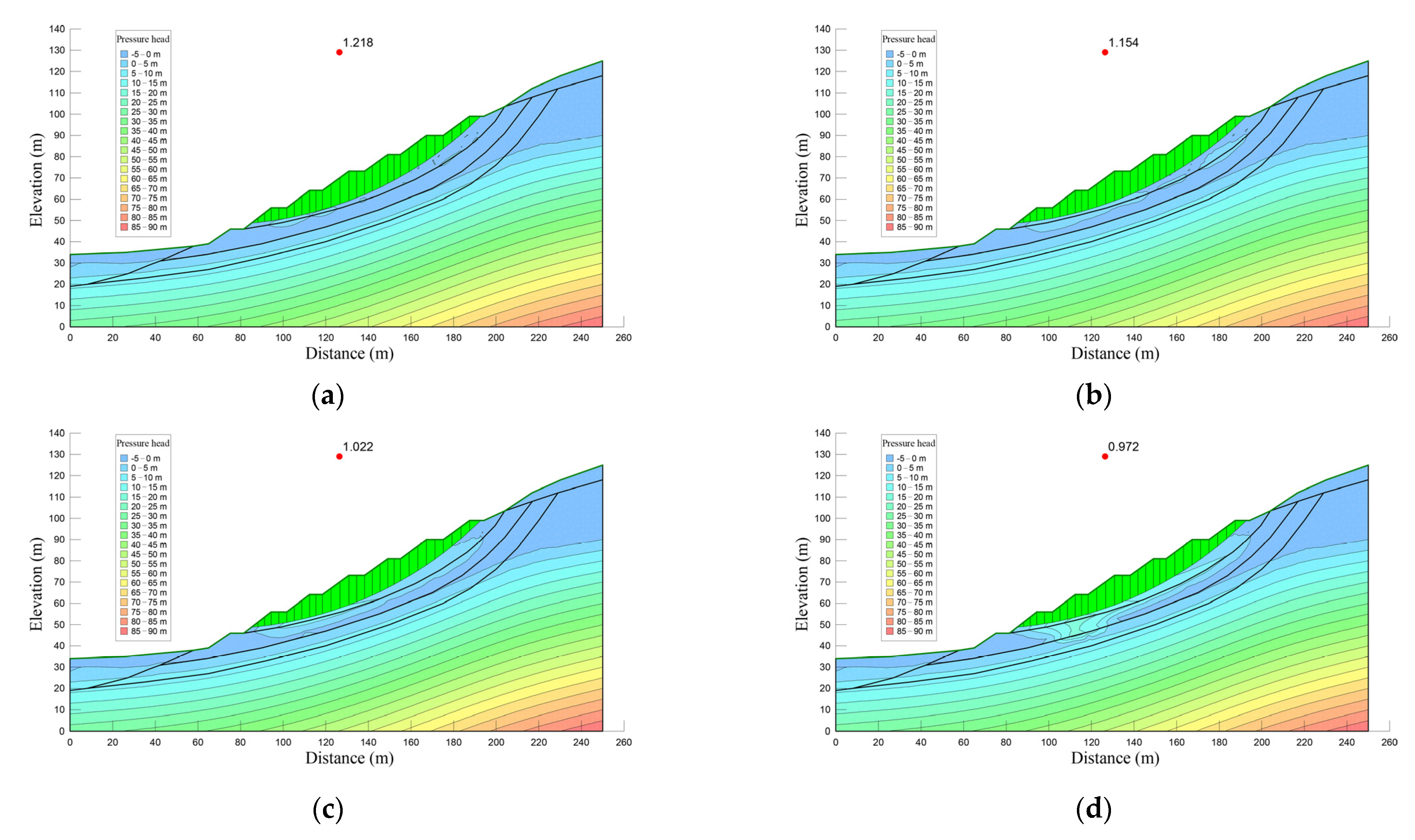
4.3. Numerical Modeling Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- 1.
- From surface to interior, the Nandongzi slope can be divided into toppling-falling zone, strong toppling zone, slight toppling zone, and non-deformation zone.
- 2.
- The geological structure that consists of an upper strong slab and an underlying weak rock layer controls the early deformation. The deformation and failure mode is compressing-bending-toppling. In the later deformation stage, excavation and rainfall induce sliding movements along planar rupture planes in the toppling-falling zone of the slope, with the failure mode switching to creeping-cracking.
- 3.
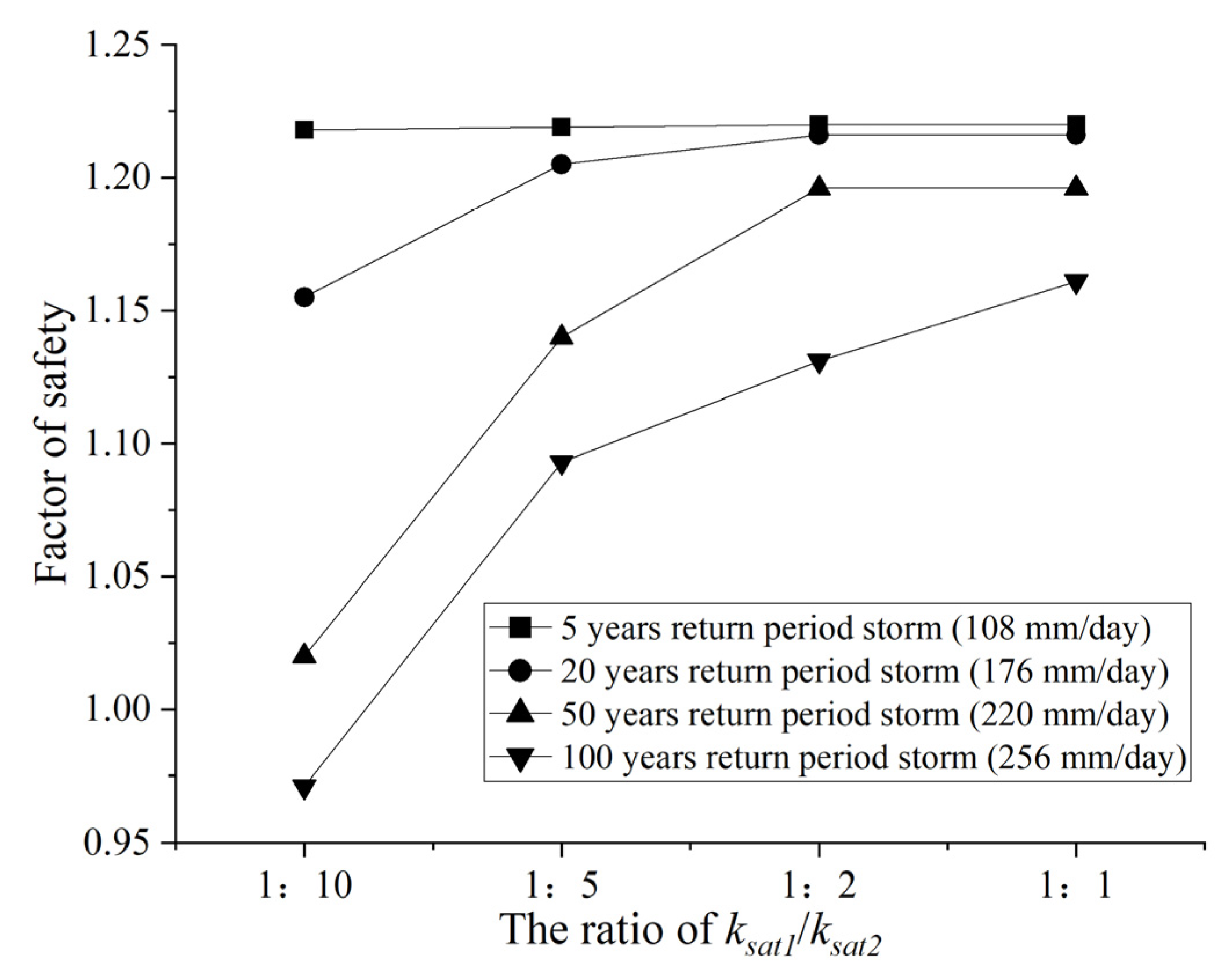
- The ratio of ksat1/ksat2 and rainfall intensity control the pore-water pressure developed in the boundary between the toppling-falling zone and strong toppling zone. The pore-water pressure further influences the safety factor of toppling-sliding slopes. The higher the ratio of ksat1/ksat2, the higher the safety factor.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Görüm, T.; Fidan, S. Spatiotemporal variations of fatal landslides in Turkey. Landslides 2021, 18, 1691–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Pei, X.J.; Evans, S.G.; Huang, R.Q. Mechanics of the earthquake–induced Hongshiyan landslide in the 2014 Mw 6.2 Ludian earthquake, Yunnan, China. Eng. Geol. 2019, 251, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.N.; Densmore, A.L.; Rosser, N.J.; De Michele, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, R.; Whadcoat, S.; Petley, D.N. Mass wasting triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake is greater than orogenic growth. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.M. Advance and prospects of major landslides prediction and forecasting. Bull. Geol. Sci. Tech. 2022, 41, 1–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, D. Vulnerability to landslides. In Landslide Hazard and Risk; Glade, T., Anderson, M., Crozier, M.J., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 175–198. [Google Scholar]
- Lacasse, S.; Nadim, F.; Kalsnes, B. Living with landslide risk. Geotech. Eng. J. Seags Agssea 2010, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Nadim, F.; Kalsnes, B.; Solheim, A. Plenary: Progress of living with landslide risk in Europe. In Landslide Science for a Safer Geoenvironment; Sassa, K., Canuti, P., Yin, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, R.E.; Bray, J.W. Toppling of Rock Slopes. In Proceedings of the Specialty Conference on Rock Engineering for Foundations and Slopes, Boulder, CO, USA, 15–18 August 1976; Volume 2, pp. 201–234. [Google Scholar]
- Nichol, S.L.; Hungr, O.; Evans, S.G. Large–scale brittle and ductile toppling of rock slopes. Can. Geotech. J. 2002, 39, 773–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Q.; Li, Y.S.; Yan, M. The implication and evaluation of Toppling Failure in Engineering Geology Practice. J. Eng. Geol. 2017, 25, 1165–1181. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Ma, H.; Huang, R.Q. Deep–seated toppling deformations of rock slopes in western China. Landslides 2022, 19, 809–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, G.B. Landslide, spreading, deep seated gravitational deformation: Analysis, examples, problems and proposals. Geogr. Fis. Dinam. Quat. 1996, 19, 297–313. [Google Scholar]
- Crosta, G.B.; Frattini, P.; Agliardi, F. Deep seated gravitational slope deformations in the European Alps. Tectonophysics 2013, 605, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glueer, F.; Loew, S.; Manconi, A.; Aaron, J. From toppling to sliding: Progressive evolution of the Moosfluh Landslide, Switzerland. J. Geophy. Res. Earth Surf. 2019, 124, 2899–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, A.; Gong, Y. Deformation and Failure Mechanism of a Massive Ancient Anti–Dip River–Damming Landslide in the Upper Jinsha River. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.B.; Tang, H.M.; Zhang, G.C.; Smith, J.V.; Zhang, B.C.; Shen, P.W.; Chen, H.J. A complex rockslide developed from a deep–seated toppling failure in the upper Lancang River, Southwest China. Eng. Geol. 2021, 293, 106329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tang, H.M. Mechanism and evolotion of toppling in interbedded slopes at upstream of Yalong river. J. Eng. Geol. 2017, 25, 1501–1508. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.M.; Xia, M.; Zeng, Q.; Jia, Y.; Lu, S.D.; Lu, D.L.; Liu, R.Q.; Zhao, H.Y.; Gou, F.M. Characteristics and formation mechanism of typical sliding–toppling landslides in Bailong River truck stream of Gansu, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Tech. (Sci. Tech. Ed.) 2015, 42, 18–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Nguyen, V.; Han, W. The critical curve for shallow saturated zone in soil slope under rainfall and its prediction for landslide characteristics. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 1927–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Lee, S.R.; Cho, S.E. Slope Stability Analysis of unsaturated soil slopes based on the site–specific characteristics: A case study of Hwangryeong Mountain, Busan, Korea. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qiu, C.; Huang, J.; Guo, X.; Hu, Y.; Mugahed, A.S.Q.; Tan, J. Stability Analysis of a High–Steep Dump Slope under Different Rainfall Conditions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Ling, C.; Hu, B.X.; Ran, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Q.; Tong, J. Characterizing groundwater flow in a translational rock landslide of southwestern China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 1989–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, C.; Onda, Y.; Iida, T.; Takahashi, S.; Uchida, T. Characterization of the groundwater response to rainfall on a hillslope with fractured bedrock by creep deformation and its implication for the generation of deep–seated landslides on Mt. Wanitsuka, Kyushu Island. Geomorphology 2014, 204, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, R.; Marino, P.; Santonastaso, G.F.; Damiano, E. Interaction between perched epikarst aquifer and unsaturated soil cover in the initiation of shallow landslides in pyroclastic soils. Water 2018, 10, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, P.; Santonastaso, G.F.; Fan, X.; Greco, R. Prediction of shallow landslides in pyroclastic–covered slopes by coupled modeling of unsaturated and saturated groundwater flow. Landslides 2021, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Shi, Q. A numerical investigation of the stability of unsaturated soil slopes subjected to transient seepage. Comput. Geotech. 1998, 22, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Fredlund, D.G.; Zhang, L.M.; Tang, W.H. Numerical study of soil conditions under which matric suction can be maintained. Can. Geotech. J. 2004, 41, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.Y.; Zou, L.F.; Sun, H.K. Analysis of seepage stability of large–scale landslide under rainfall condition. Rock Soil Mech. 2013, 34, 833–841. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Alejano, L.R.; Gómez–Márquez, I.; Martínez–Alegría, R. Analysis of a complex toppling–circular slope failure. Eng. Geol. 2010, 114, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.M.; Gofar, N.; Rahardjo, H. A simple model for preliminary evaluation of rainfall–induced slope instability. Eng. Geol. 2009, 108, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Jiang, X.Y.; Zou, N.N.; Luo, B.J. Numerical analysis of colluvial landslide stability under the effect of rainfall infiltration: Taking Darong landslide of Guizhou Province for an example. Sci. Tech. Eng. 2019, 19, 338–344. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Childs, E.C.; Collis–George, N. The permeability of porous material. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1950, 201, 392–405. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed–form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyas, E.L.; Radhakrishna, H.S. Volume change characteristics of partially saturated soils. Geotechnique 1968, 18, 432–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Morgenstern, N.R.; Widger, R.A. The shear strength of unsaturated soils. Can. Geotech. J. 1978, 15, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Rahardjo, H. Soil Mechanics for Unsaturated Soils; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
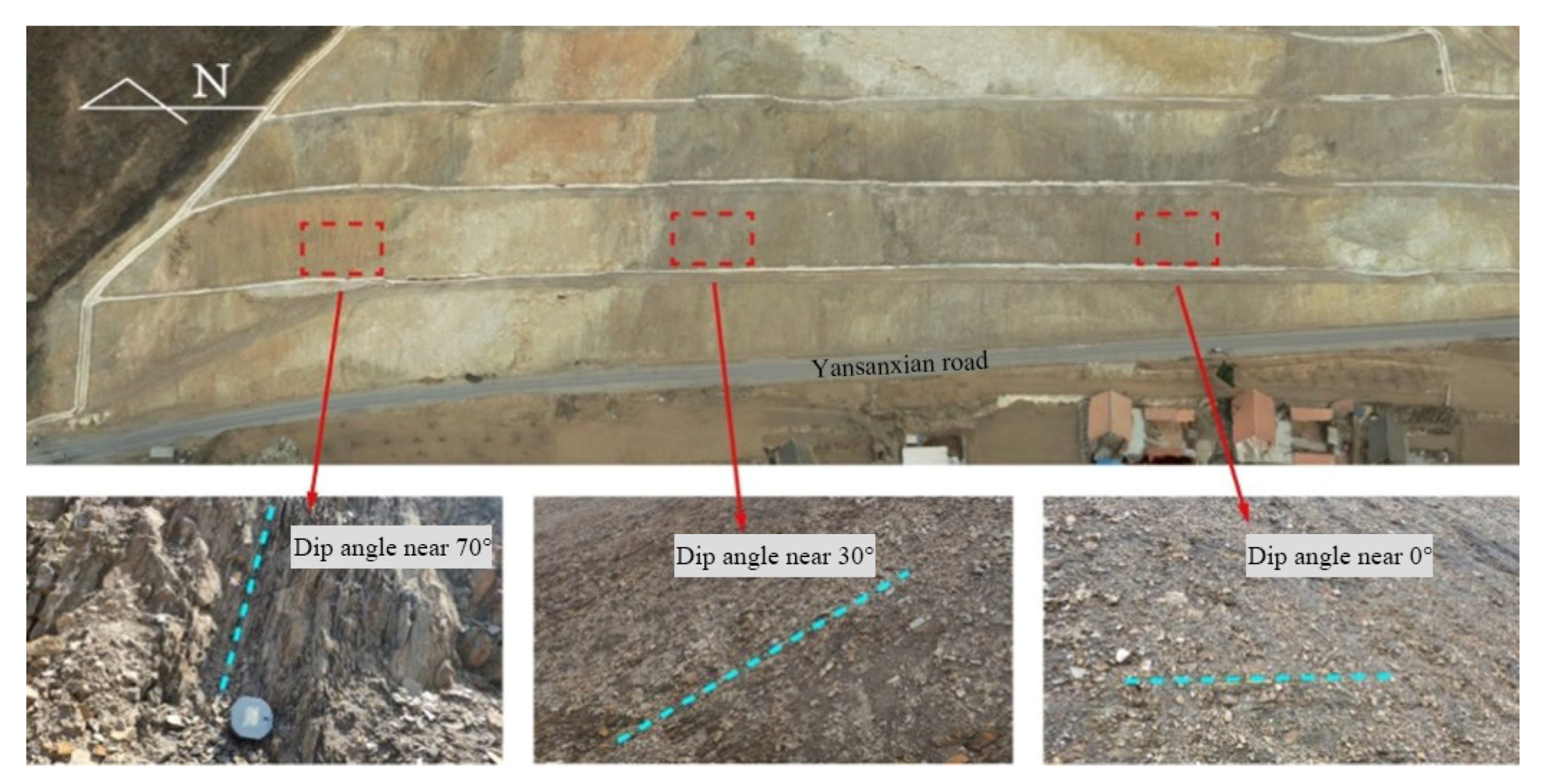



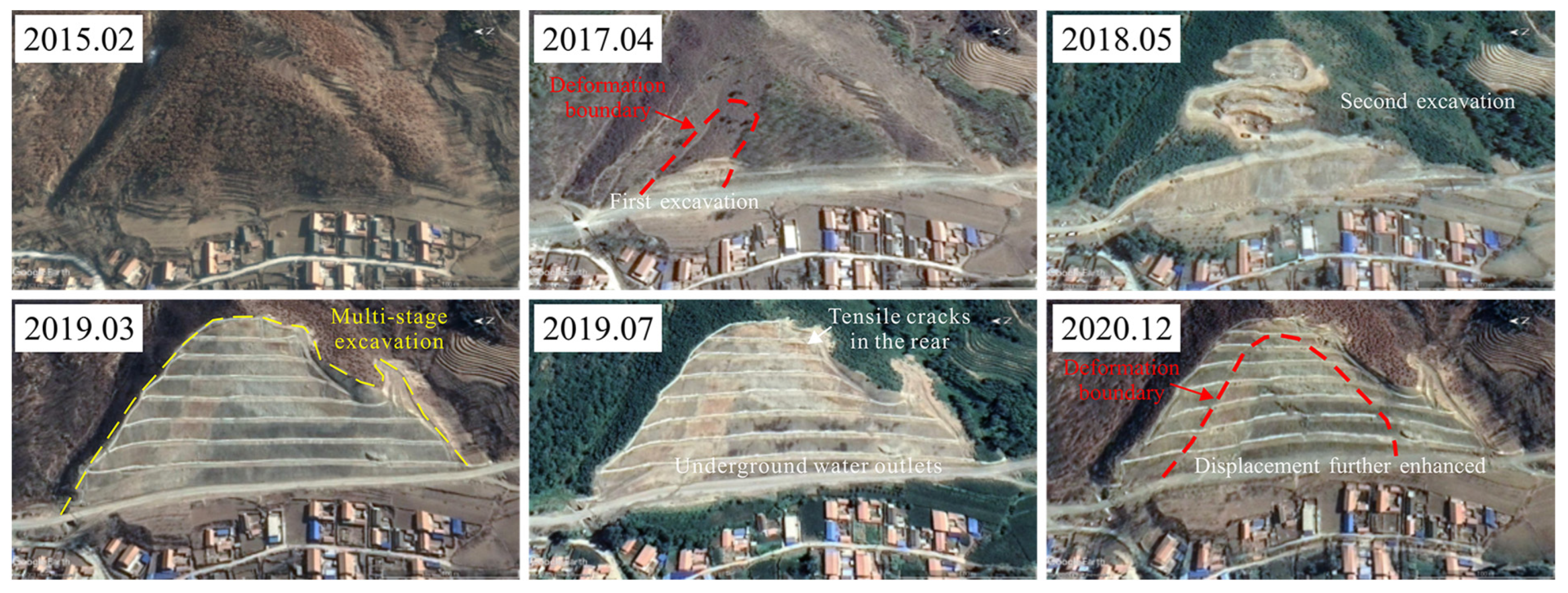
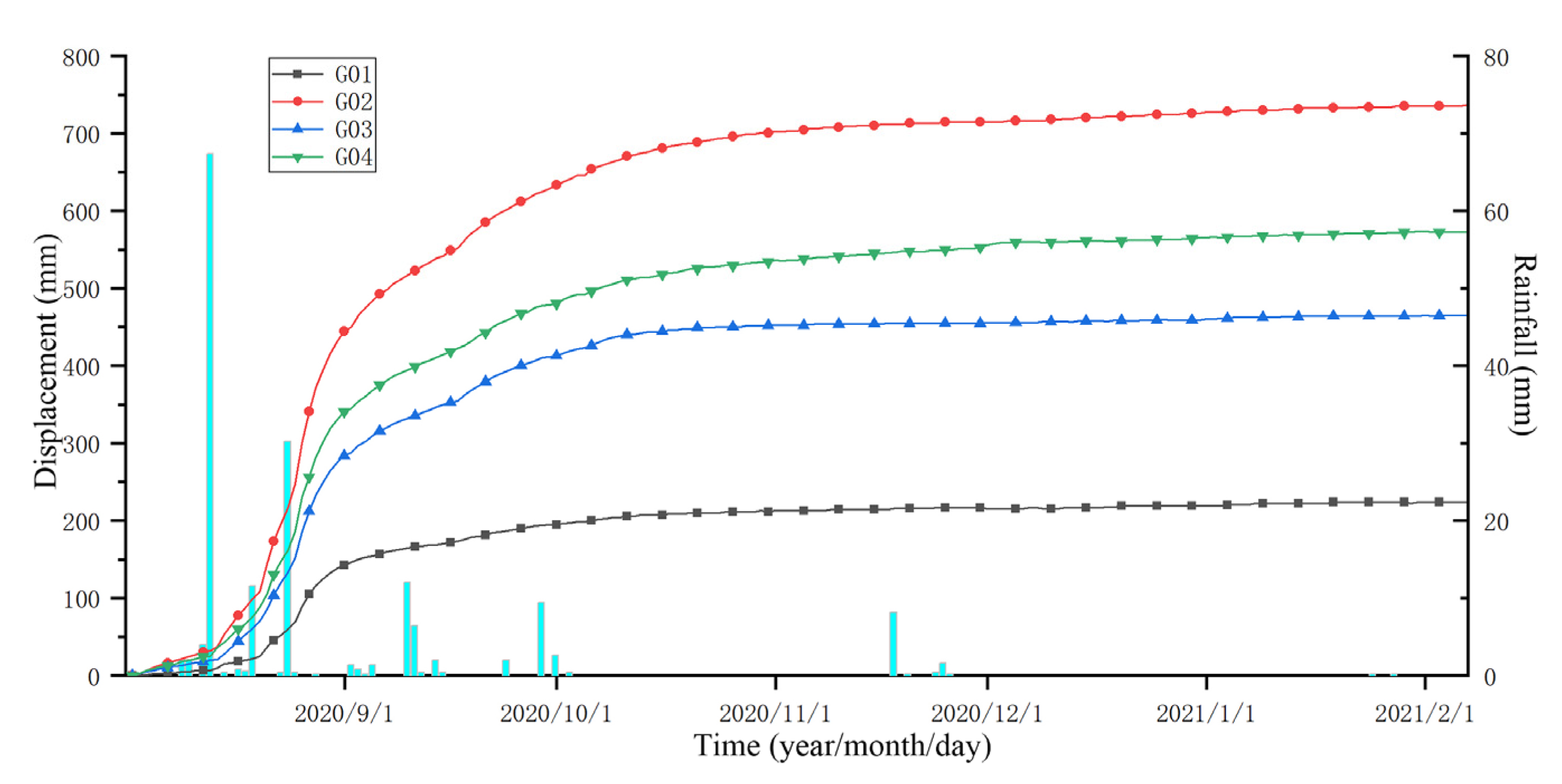

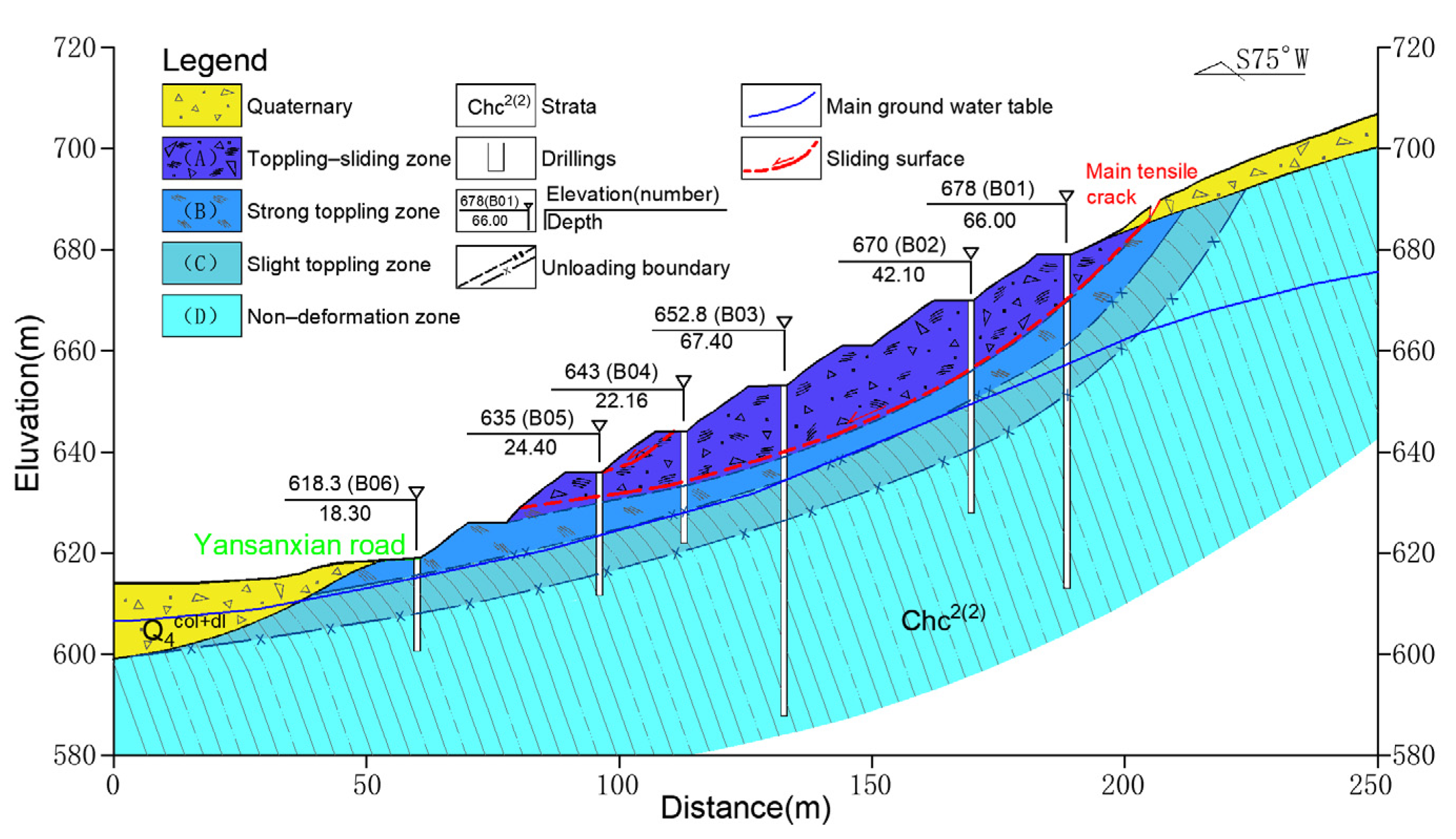
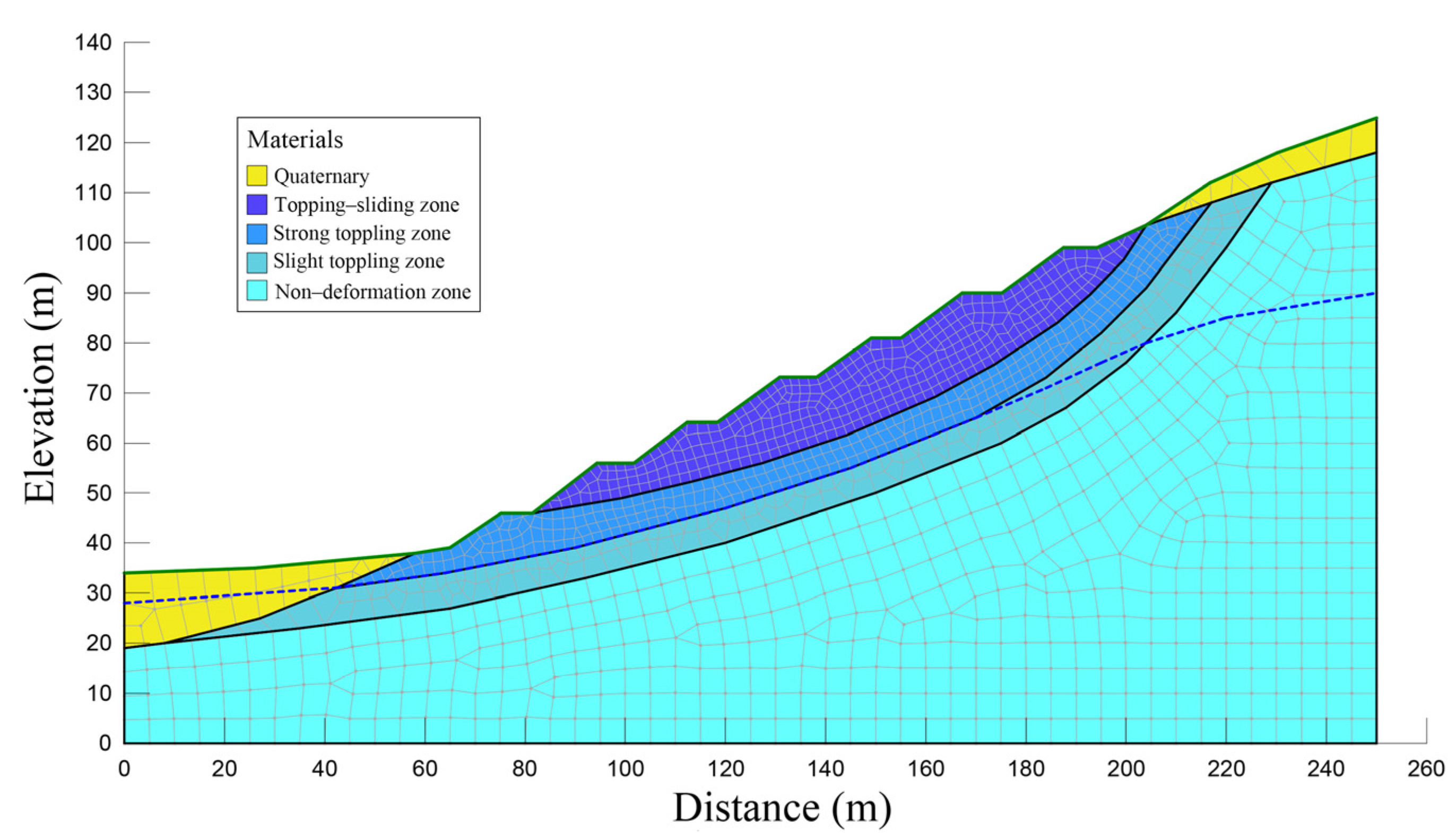
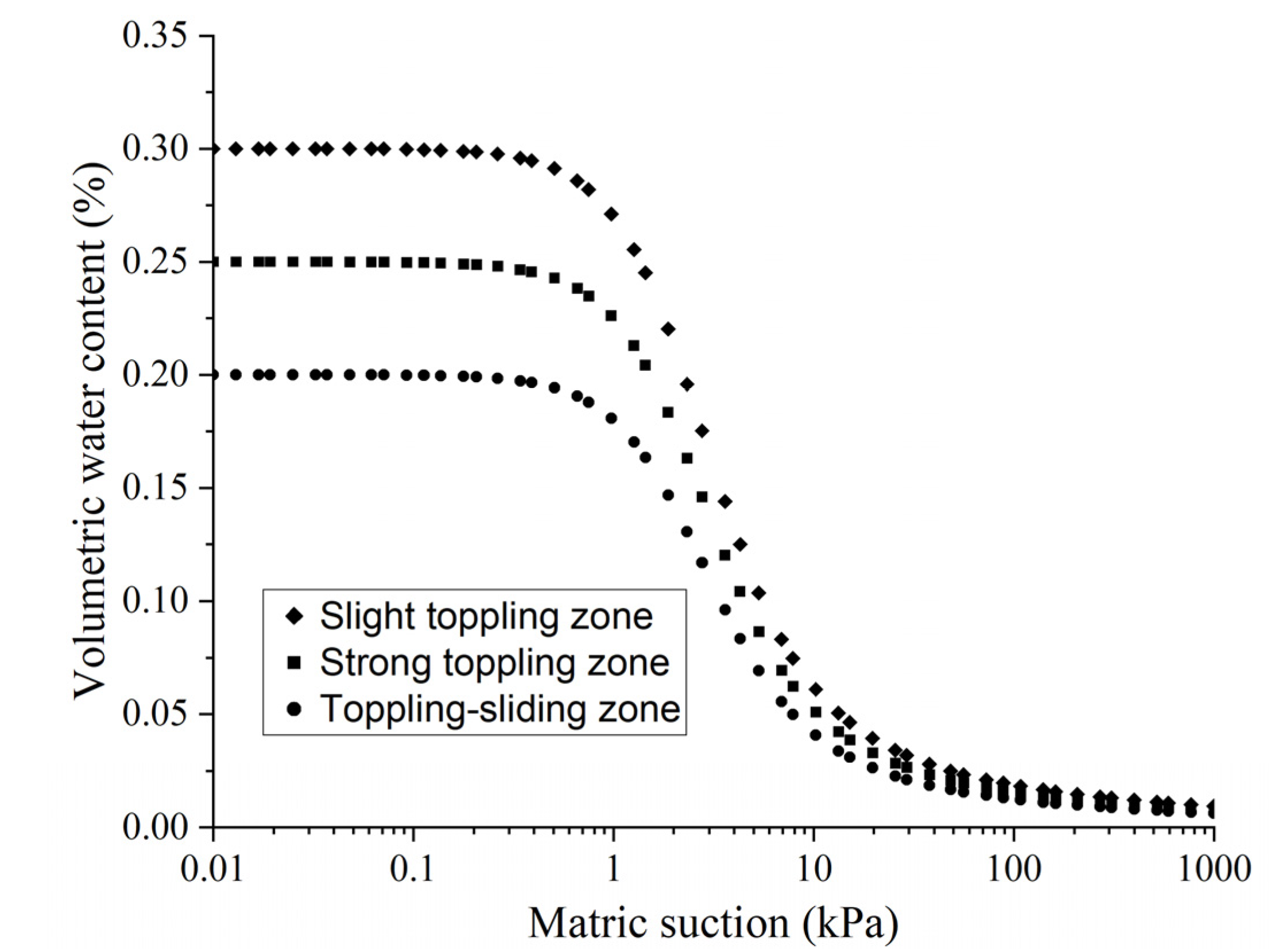
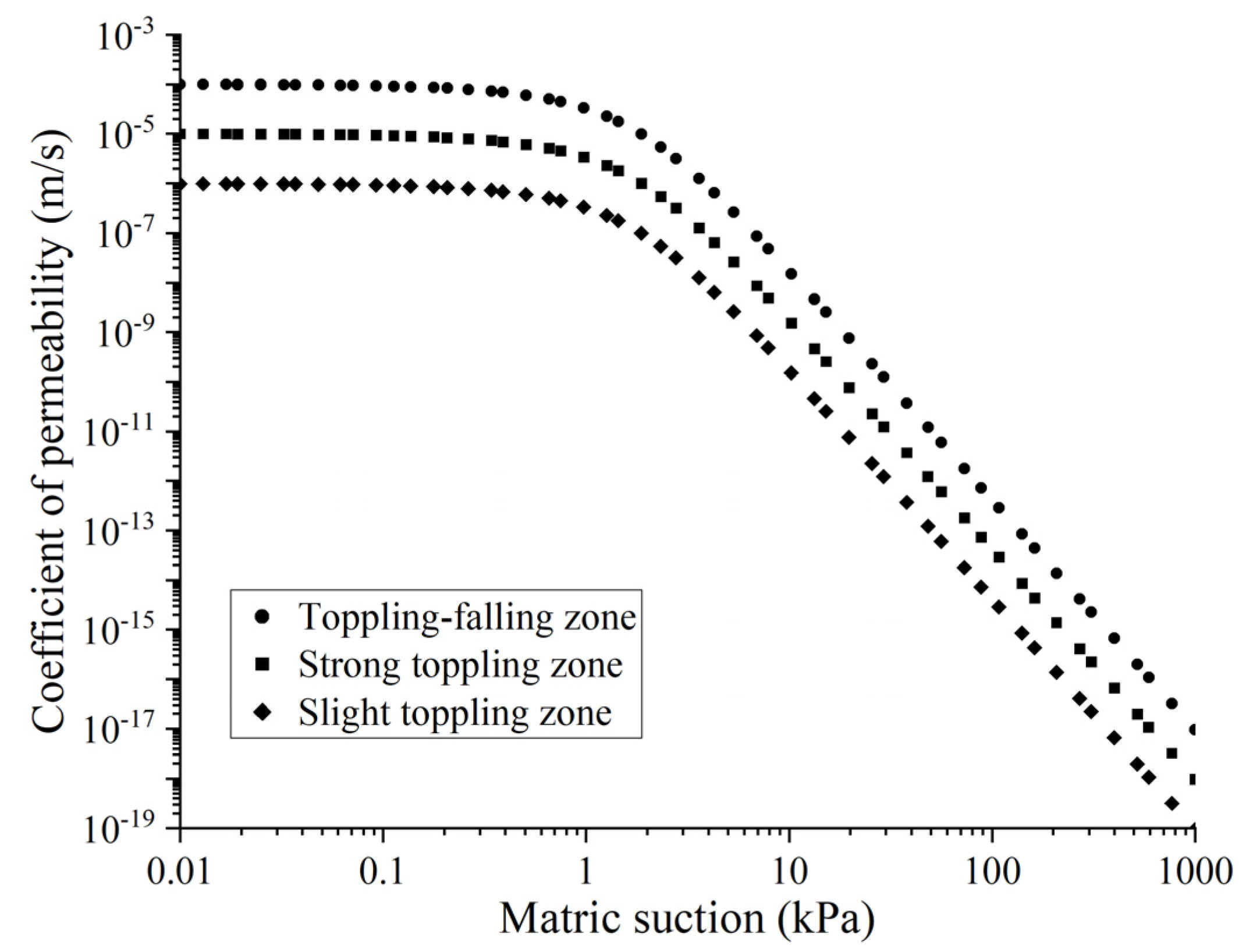

| Index | Toppling-Falling Zone (A) | Strong Toppling Zone (B) | Slight Toppling Zone (C) | Non-Deformation Zone (D) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fracture mechanism | Complete block detachment | Tensile-shear fracture | Tensile fracture | / |
| Deflection angle (°) | / | 15–35° | 0–15° | 0° |
| Unloading degree | / | Large | Medium | Small |
| Weathering degree | / | Intense | Moderate | Mild |
| Return Period of 100 Years | Return Period of 50 Years | Return Period of 20 Years | Return Period of 5 Years |
|---|---|---|---|
| 256 mm/day | 220 mm/day | 176 mm/day | 108 mm/day |
| Unit Weight/(kN/m3) | Cohesion/kPa | Angle of Friction/° | Saturated Volumetric Water Content/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toppling-falling zone | 21.00 | 2.00 | 28.00 | 0.20 |
| Strong toppling zone | 22.00 | 5.00 | 32.00 | 0.25 |
| Slight toppling zone | 23.00 | 10.00 | 35.00 | 0.30 |
| Non-deformation zone | 24.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 0.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.; Pei, X.; Jiang, R.; Li, T.; Sun, H.; Jin, B.; Li, Q. The Characteristics and Seepage Stability Analysis of Toppling-Sliding Failure under Rainfall. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7736. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15107736
Luo J, Pei X, Jiang R, Li T, Sun H, Jin B, Li Q. The Characteristics and Seepage Stability Analysis of Toppling-Sliding Failure under Rainfall. Sustainability. 2023; 15(10):7736. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15107736
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jing, Xiangjun Pei, Ronghao Jiang, Tiantao Li, Hao Sun, Bo Jin, and Qian Li. 2023. "The Characteristics and Seepage Stability Analysis of Toppling-Sliding Failure under Rainfall" Sustainability 15, no. 10: 7736. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15107736
APA StyleLuo, J., Pei, X., Jiang, R., Li, T., Sun, H., Jin, B., & Li, Q. (2023). The Characteristics and Seepage Stability Analysis of Toppling-Sliding Failure under Rainfall. Sustainability, 15(10), 7736. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15107736






