Dissolved Iron from Steel Slag with Its Chelating Agent Promotes Seaweed Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Seaweed Collection and Analysis
2.2. Element Elution and Analysis
2.3. Analysis of the Photosynthetic Pigment
2.4. Pelletization of the Slag and DTPA
2.5. Growth Measurement in the Sea
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fe-DTPA Elutes the Soluble Iron in the Range of Oceanic pH
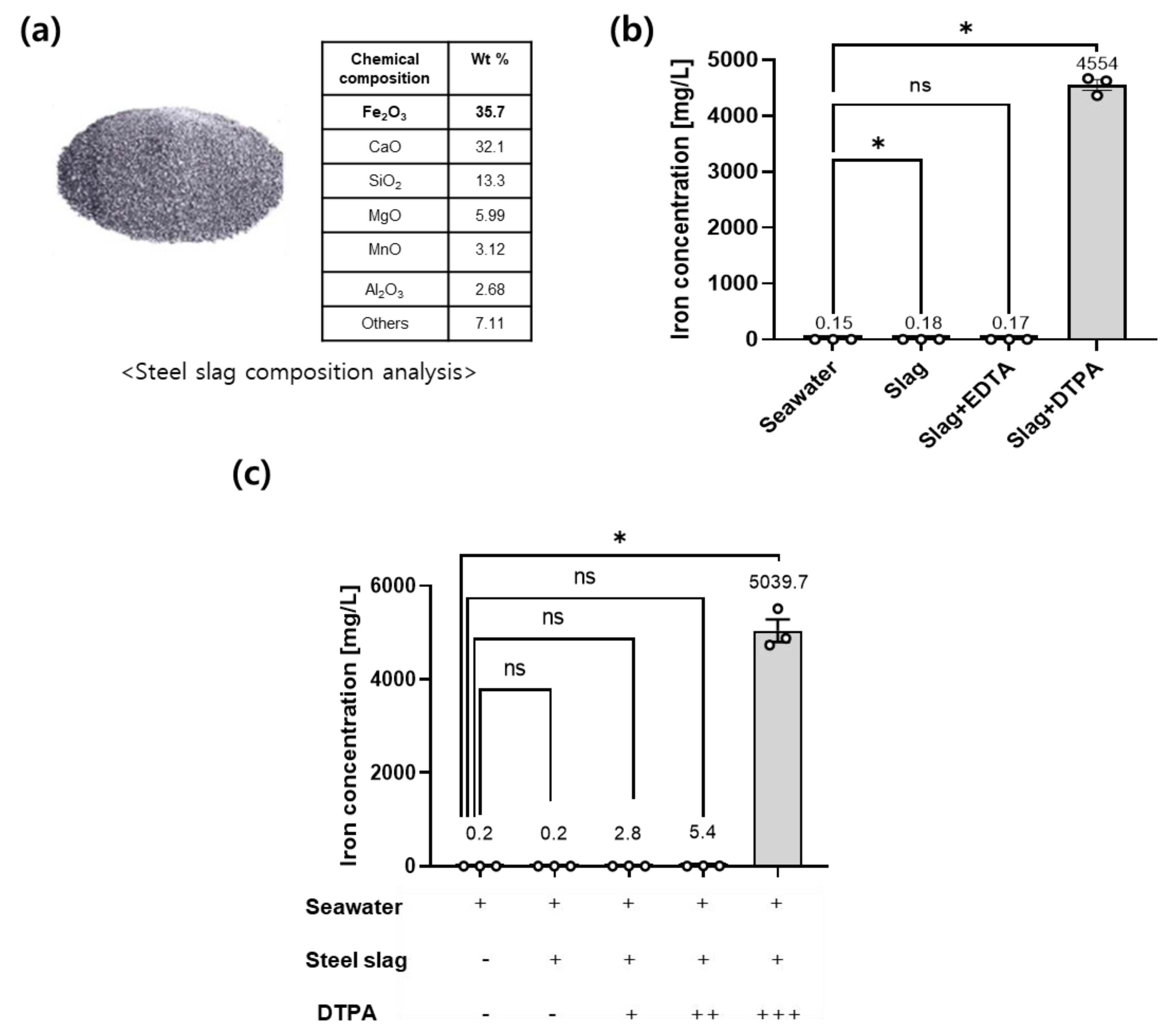
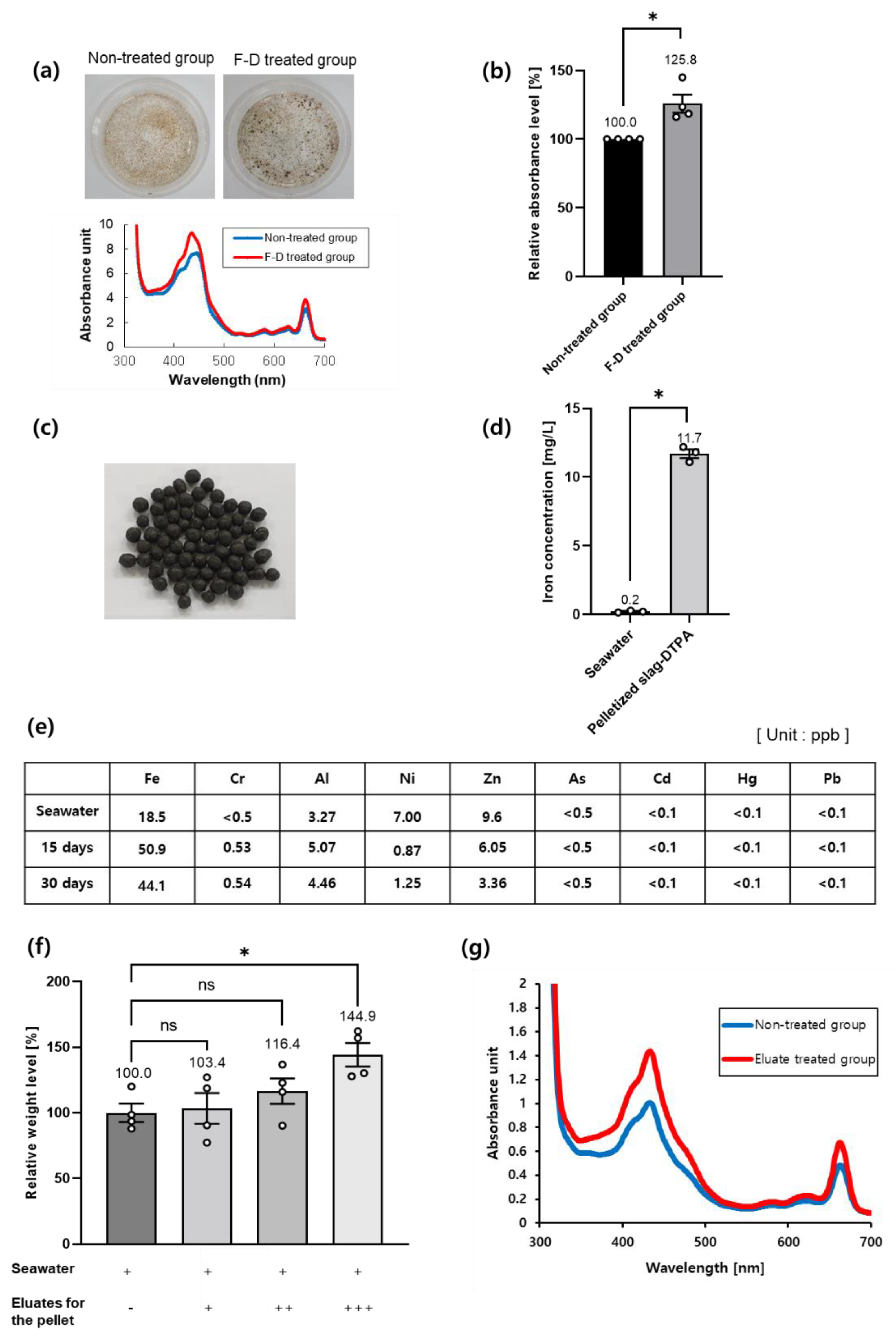
3.2. Slag-DTPA Promotes Growth of Seaweed
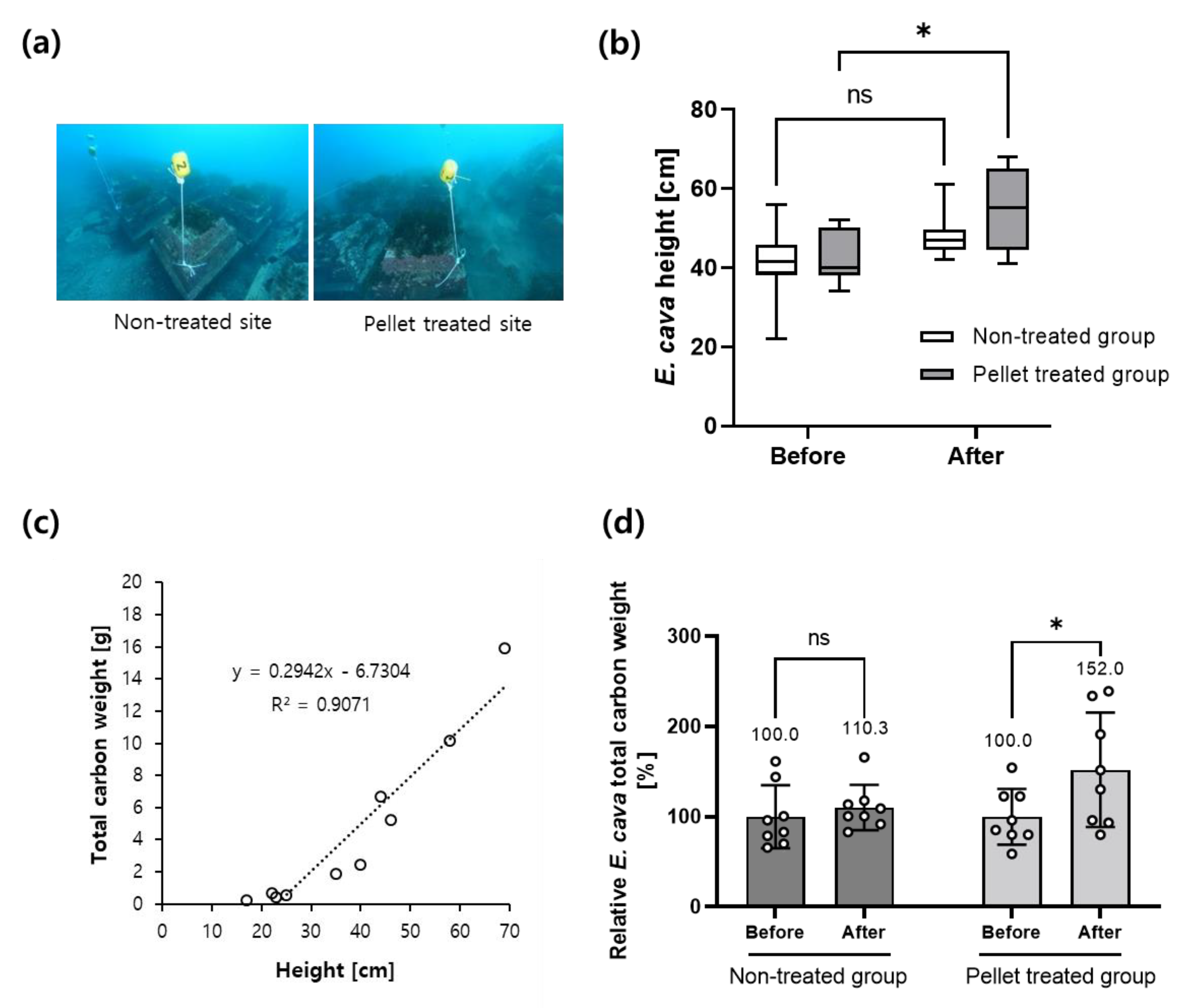
3.3. Pelletized Slag-DTPA Promotes a Sea Forest and Enhances Carbon Sequestration
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filbee-Dexter, K.; Wernberg, T. Substantial blue carbon in overlooked Australian kelp forests. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, C. Exploring new blue carbon plants for sustainable ecosystems. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause-Jensen, D.; Duarte, C.M. Substantial role of macroalgae in marine carbon sequestration. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondak, C.F.A.; Chung, I.K. Potential blue carbon from coastal ecosystems in the Republic of Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2015, 50, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.K.; Oak, J.H.; Lee, J.A.; Shin, J.A.; Kim, J.G.; Park, K.-S. Installing kelp forests/seaweed beds for mitigation and adaptation against global warming: Korean Project Overview. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 70, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filbee-Dexter, K.; Feehan, C.J.; Scheibling, R.E. Large-scale degradation of a kelp ecosystem in an ocean warming hotspot. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 543, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernberg, T.; Bennett, S.; Babcock, R.C.; Bettignies, T.D.; Cure, K.; Depczynski, M.; Dufois, F.; Fromont, J.; Fulton, C.J.; Hovey, R.K.; et al. Climate-driven regime shift of a temperate marine ecosystem. Science 2016, 353, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-I.; Kim, D.-K.; Sung, B.-J.; Jun, S.-K.; Bae, J.-I.; Jeon, B.-H. Effects of climate change on whitening event proliferation the coast of jeju. Korean J. Environ. Ecol. 2017, 31, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, O.; Nagai, T.; Marzuki, M.; Okumura, C.; Kosugi, C.; Kato, T. Effects of Fe fertilizer eluate on the growth of Sargassum horneri at the germling and immature stages. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krumhansl, K.A.; Okamoto, D.K.; Rassweiler, A.; Novak, M.; Bolton, J.J.; Cavanaugh, K.C.; Connell, S.D.; Johnson, C.R.; Konar, B.; Ling, S.D.; et al. Global patterns of kelp forest change over the past half-century. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13785–13790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, X.; Ma, S. Responses of the macroalga Gracilaria tenuistipitata var. liui (Rhodophyta) to iron stress. J. Appl. Phycol. 2004, 12, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.A.; Carell, E.F. Control by iron of chlorophyll formation and growth in euglena gracilis. Plant Physiol. 1964, 39, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, J.; LaRoche, J. Iron uptake proteins in algae and the role of iron starvation-induced proteins (ISIPs). Eur. J. Phycol. 2020, 55, 339–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Miki, O.; Okumura, C. Effects of chelated iron on the growth of sargassaceae species at the germling and immature stages. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2014, 12, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anton, A.; Hendriks, I.E.; Marba, N.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Garcias-Bonet, N.; Duarte, C.M. Iron deficiency in seagrasses and macroalgae in the Red Sea is unrelated to latitude and physiological performance. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Ni, W. On the use of blast furnace slag and steel slag in the preparation of green artificial reef concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Kang, C.; Yu, J. Marine life and coastal restoration by utilizing steel slag to create sea forest on sandy coast of Southwest Taiwan. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2019, Marseille, France, 17–20 June 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, N.T.; Sadhu, S.; Murthy, K.N.V.V.; Pilli, S.R.; Ramesh, S.; Kumar, S.V.S.P.; Dharani, G.; Atmanand, M.A.; Rao, M.B.V.; Dey, T.K.; et al. Carbon-dioxide fixation by artificial reef development in marine environment using carbonated slag material from steel plant. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2014, Taipei, Taiwan, 7–10 April 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-T.; Kim, M.-K.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.-B. Analysis of Fe-deficient inducing enzyme and required time for recovery of nutritional disorder by Fe-DTPA treatment in the Fe-deficient induced tomato cultivars. Korean Soc. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2011, 44, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, H.I.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Ha, D.S.; Hwang, E.K. Regeneration and the maturation induction of free-living gametophytes of a kelp, saccharina sculpera (phaeophyceae). Environ. Biol. Res. 2018, 36, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provasoli, L. Media and prospects for the cultivation of marine algae. In Proceedings of the US-Japan Conference, Hakone, Japan, 12–15 September 1966; pp. 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Tanaka, A.; Tanaka, R. Simple extraction methods that prevent the artifactual conversion of chlorophyll to chlorophyllide during pigment isolation from leaf samples. Plant Methods 2013, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, S.L.; Wangpraseurt, D.; Kühl, M. Optical properties of living corals determined with diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kang, Y.H.; Kim, T.-H.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.R. Use of morphological characteristics for calculating individual biomass in the kelp Ecklonia cava. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 2587–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, P.K.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, B.; Yi, H.; Ku, H.O.; Roh, T.Y.; Kim, K.T. The Poly(C) motif in the proximal promoter region of the D site-binding protein gene (Dbp) drives its high-amplitude oscillation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 39, e00101-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, P.K.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Tae, S.; Ham, S.; Jeong, Y.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, B.; Kim, H.M.; Choi, J.H.; et al. hnRNP K supports high-amplitude D site-Binding protein mRNA (Dbp mRNA) oscillation to sustain circadian rhythms. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 40, e00537-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, P.K.; Kim, H.M.; Kang, B.; Kim, S.W.; Hwang, S.M.; Im, S.H.; Roh, T.Y.; Kim, K.T. hnRNP K supports the maintenance of RORγ circadian rhythm through ERK signaling. Faseb J. 2021, 35, e21507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, P.K.; Kim, S.W.; De, R.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, K.T. Isoprocurcumenol supports keratinocyte growth and survival through epidermal growth factor receptor activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.-B.; Kim, B.-J.; Ryu, K.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Shin, H.-J.; Hwang, T.-K.; Choi, H.-Y.; Lee, Y.-W.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-J. Relationships between micronutrient contents in soils and crops of plastic film house. Korean Soc. Environ. Agric. 2006, 25, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Welch, R.M.; Allaway, W.H.; House, W.A.; Kubota, J. Geographic distribution of trace element problems. In Micronutrients in Agriculture; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1991; pp. 31–57. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.-Q.; Carter, B.R.; Feely, R.A.; Lauvset, S.K.; Olsen, A. surface ocean pH and buffer capacity: Past, present and future. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.F.P.; Pino, C.G. Leaching of heavy metals from steelmaking slags. Rev. Metal. 2006, 42, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Anton, A.; Raven, J.A.; Beaumont, N.; Connolly, R.M.; Friess, D.A.; Kelleway, J.J.; Kennedy, H.; Kuwae, T.; Lavery, P.S.; et al. The future of blue carbon science. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause-Jensen, D.; Lavery, P.; Serrano, O.; Marba, N.; Masque, P.; Duarte, C.M. Sequestration of macroalgal carbon: The elephant in the blue carbon room. Biol. Lett. 2018, 14, 20180236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.; Sutton-Grier, A.; Herr, D.; Kleypas, J.; Landis, E.; Mcleod, E.; Pidgeon, E.; Simpson, S. Clarifying the role of coastal and marine systems in climate mitigation. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 15, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Losada, I.J.; Hendriks, I.E.; Mazarrasa, I.; Marbà, N. The role of coastal plant communities for climate change mitigation and adaptation. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, P.K.; Kim, H.-S.; Jeong, S.W. Dissolved Iron from Steel Slag with Its Chelating Agent Promotes Seaweed Growth. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095498
Kwon PK, Kim H-S, Jeong SW. Dissolved Iron from Steel Slag with Its Chelating Agent Promotes Seaweed Growth. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095498
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Paul Kwangho, Hyung-Suek Kim, and Sung Woo Jeong. 2022. "Dissolved Iron from Steel Slag with Its Chelating Agent Promotes Seaweed Growth" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095498
APA StyleKwon, P. K., Kim, H.-S., & Jeong, S. W. (2022). Dissolved Iron from Steel Slag with Its Chelating Agent Promotes Seaweed Growth. Sustainability, 14(9), 5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095498




