Sustainable Supplier’s Equilibrium Discount Strategy under Random Demand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
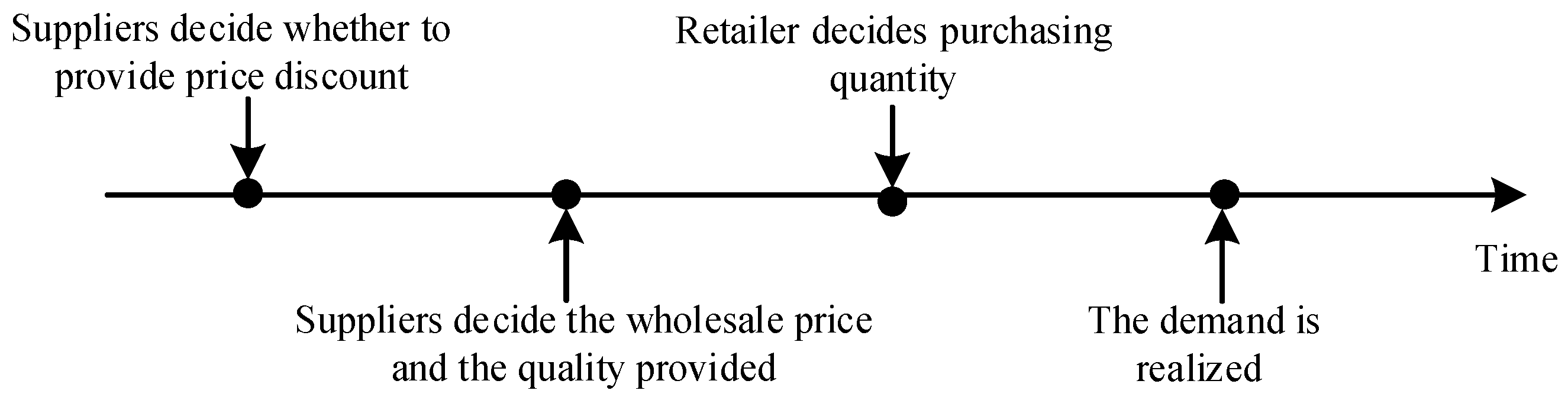
3. Model Description
4. Analysis
4.1. The Equilibrium Quantity Strategy
4.2. The Equilibrium Price Discount Strategy
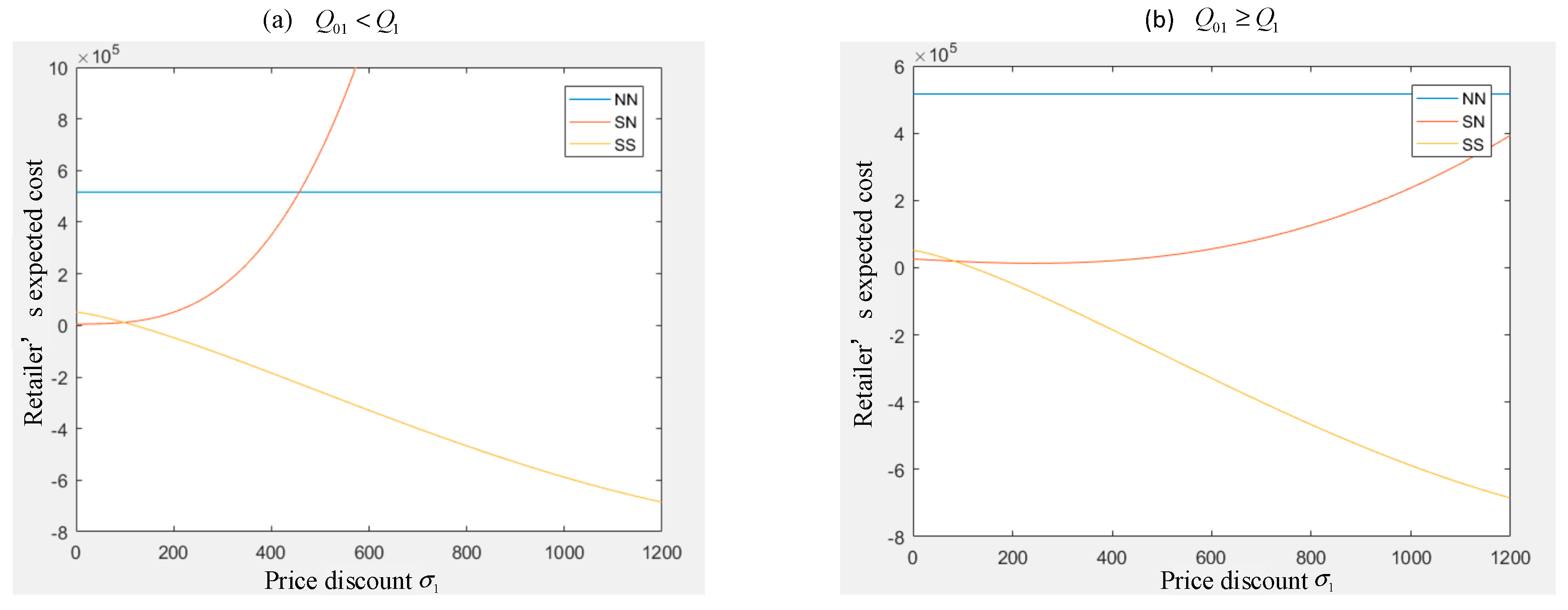
4.3. The Impact on the Retailer
5. Numerical Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, A.; Mishra, H. The Influence of Price Discount versus Bonus Pack on the Preference for Virtue and Vice Foods. J. Mark. Res. 2011, 48, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Biswas, A.; Grewal, D.; Verma, S.; Banerjee, S.; Nordfält, J. Reframing the discount as a comparison against the sale price: Does it make the discount more attractive? J. Mark. Res. 2018, 55, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.; Wang, Q. Discount pricing decisions in distribution channels with price-sensitive demand. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 149, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, J.-S. Effects of Price Discounts and Bonus Packs on Online Impulse Buying. Soc. Behav. Pers. Int. J. 2014, 42, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKechnie, S.; Devlin, J.; Ennew, C.; Smith, A. Effects of discount framing in comparative price advertising. Eur. J. Mark. 2012, 46, 1501–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Leng, M.; Huang, J.; Liang, L. Supply chain analysis under a price-discount incentive scheme for electric vehicles. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 235, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.E.; Choi, J.; Sedatole, K.L. The effect of supplier industry competition on pay-for-performance incentive intensity. J. Account. Econ. 2021, 71, 101389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, A. Excessive Competition and Supplier Non-Performance Risk: Trade-offs in Reverse Auctions. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2021, 30, 3073–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, E. Outsourcing through competition: What is the best competition parameter? Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 144, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, Y. Supplier Competition in Decentralized Assembly Systems with Price-Sensitive and Uncertain Demand. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2010, 12, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wan, Z. Supplier Competition and Cost Improvement. Manag. Sci. 2017, 63, 2460–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Guan, X.; Chen, Y.-J. Retailer Information Sharing with Supplier Encroachment. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2018, 27, 1133–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, O.; Nishi, T.; Zhang, G. Analysis of quantity discounts for multi-period production planning for single supplier and retailer under uncertain demands. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, Selangor, Malaysia, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 882–886. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Shin, H.; Zhou, Q. The optimal investment decision for an innovative supplier in a supply chain. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 292, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugh, L.J. Defining and redefining. Advert. Age 1983, 14, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Monahan, J.P. A Quantity Discount Pricing Model to Increase Vendor Profits. Manag. Sci. 1984, 30, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Stecke, K.E.; Zhao, X. Advance Selling by a Newsvendor Retailer. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2011, 20, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Zhai, X. Risk hedging in a supply chain: Option vs. price discount. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 151, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Returns with wholesale-price-discount contract in a newsvendor problem. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 130, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan-Demirag, O.; Chen, Y.; Li, J. Channel coordination under fairness concerns and nonlinear demand. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 207, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Chen-Yu, J.H. Effects of price discount on consumers’ perceptions of savings, quality, and value for apparel products: Mediating effect of price discount affect. Fash. Text. 2018, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Lobschat, L.; Verhoef, P.C.; Zhao, H. The effect of permanent product discounts and order coupons on purchase incidence, purchase quantity, and spending. J. Retail. 2021, 97, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aust, G.; Buscher, U. Vertical cooperative advertising and pricing decisions in a manufacturer–retailer supply chain: A game-theoretic approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 223, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.-W.; Wan, J.-Y. Price discount, inventories and the distortion of WTI benchmark. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lou, W.; Tian, Y. Bullwhip effect and complexity analysis in a multi-channel supply chain considering price game with discount sensitivity. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 5432–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Notations | Description |
|---|---|
| The supplier, where when the supplier is the sustainable supplier and when the supplier is the competitive supplier The total amount that the retailer sends to the two suppliers | |
| The ordering cost for each order | |
| The inventory cost of the unit product | |
| The wholesale price from before provides a price discount | |
| The quantity of product provided by The market demand rate | |
| The degree of wholesale price discount of | |
| , , | The supplier ’s optimal profit, where superscript denotes none of the suppliers provide a price discount; denotes that only provides a price discount; denotes both of the suppliers provide a price discount |
| The actual order quantity that is purchased by the retailer from the supplier | |
| The critical value of the order quantity at which the retailer can enjoy a discounted price | |
| The difference between the two suppliers |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhou, J. Sustainable Supplier’s Equilibrium Discount Strategy under Random Demand. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084802
Li Y, Zhou J. Sustainable Supplier’s Equilibrium Discount Strategy under Random Demand. Sustainability. 2022; 14(8):4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084802
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yingxiao, and Jianheng Zhou. 2022. "Sustainable Supplier’s Equilibrium Discount Strategy under Random Demand" Sustainability 14, no. 8: 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084802
APA StyleLi, Y., & Zhou, J. (2022). Sustainable Supplier’s Equilibrium Discount Strategy under Random Demand. Sustainability, 14(8), 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084802






