Leverage of Local State-Owned Enterprises, Implicit Contingent Liabilities of Government and Economic Growth
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Theoretical Framework
3.1. The Measurement Index of the Implicit Contingent Liabilities
3.2. Theoretical Framework of Emipirical Study
3.2.1. The Formation of Local Governments’ Implicit Contingent Liabilities
3.2.2. The Local Governments’ Implicit Contingent Liabilities and Economic Growth
3.2.3. How to Balance between Implicit Contingent Liabilities and Economic Growth
4. Empirical Model and Variable Specification
4.1. Data Sources and Data Processing
4.2. Variable Description
4.3. Model Specification and Data Statistics
5. Empirical Research Results
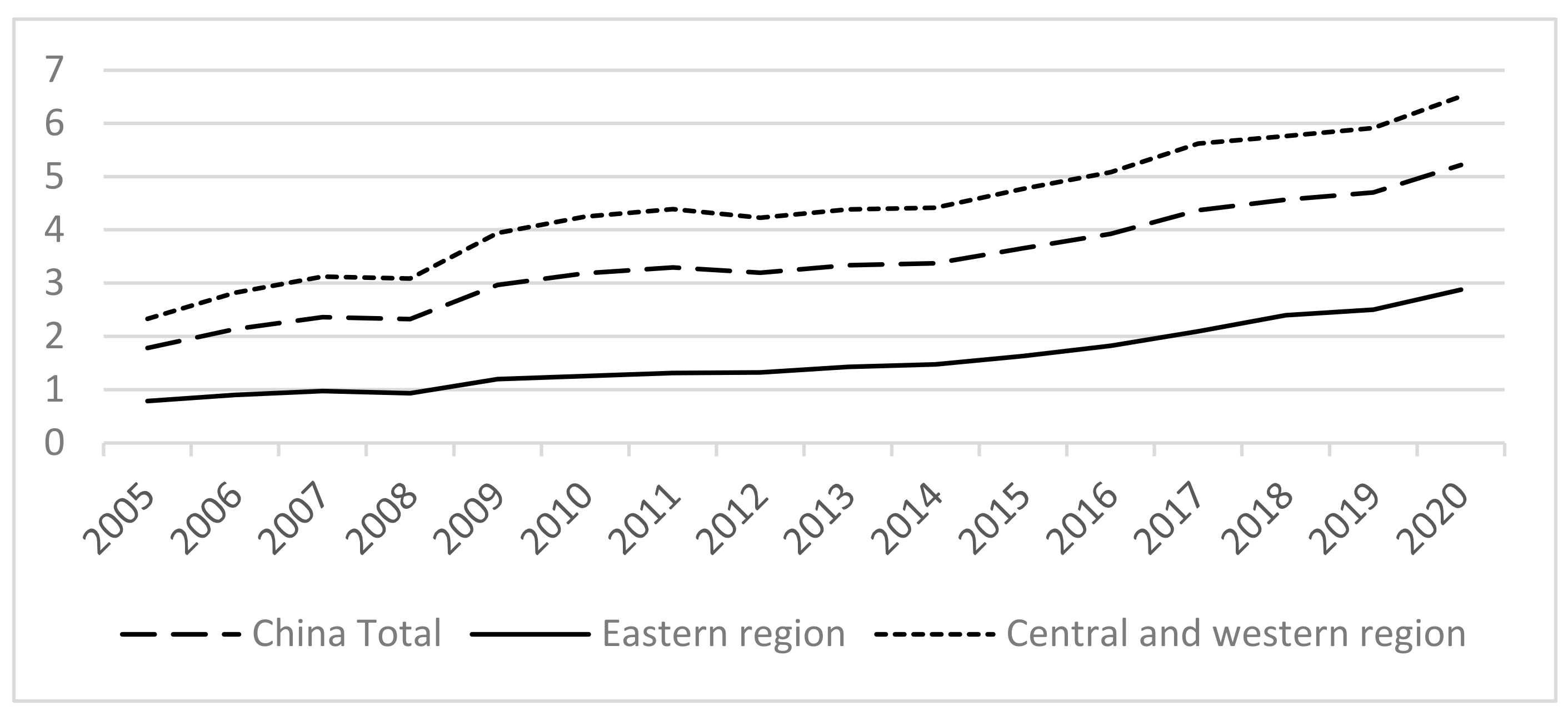
5.1. The Implicit Contingent Liabilities and the Economic Fluctuations
5.2. The Implicit Contingent Liabilities and the Economic Growth
5.3. How to Balance between Leverage and the Economic Growth
6. Robustness Check
7. Main Findings and Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, J.; Ma, G. Maroeconomic Stability and State-Owned Economic Investment: Mechanism and Evidence. Manag. World 2019, 9, 49–64, 199. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, S. Implicit Debt Risks of Local Government in a New Era. Financ. Mark. Res. 2020, 10, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Balance between Growth and Leverage. China Financ. 2019, 18, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Leverage, Economic Growth and Recession. Soc. Sci. China 2018, 6, 50–70, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Sun, W. Five key issues of mixed ownership reform of SOEs. Macroecon. Manag. 2018, 1, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, G.G. Too big to fail in banking: What does it mean? J. Financ. Stab. 2014, 13, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tölö, E.; Jokivuolle, E.; Viren, M. Have too-big-to-fail expectations diminished? Evidence from the European overnight interbank market. J. Financ. Serv. Res. 2021, 60, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hana, P. Contingent Government Liabilities: A Hidden Fiscal Risk. Financ. Dev. 1999, 3, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Handayani, D.; Damayanti, A.A. Contingent liabilities from government guarantee on SOE’s assignment: Issues and practice from the Fast Track Program Phase 1. In Public Sector Accountants and Quantum Leap: How Far We Can Survive in Industrial Revolution 4.0? Routledge: London, UK, 2020; pp. 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Soler, A.; Sy, M. How to Assess Fiscal Risks from State-Owned Enterprises: Benchmarking and Stress Testing. In How to Notes; IMF: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, L. The estimation of local governments’ hidden debt and its risks. In Macroeconomic Policy and Steady Growth in China; Routledge: London, UK, 2021; pp. 174–208. [Google Scholar]
- Razlog, L.; Irwin, T.; Marrison, C. A Framework for Managing Government Guarantees; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.E.; Hsieh, C.T.; Song, Z.M. The Long Shadow of a Fiscal Expansion; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, X. Research on local government contingent Debt Risk based on financing platform Companies. Sub Natl. Fisc. Res. 2016, 1, 85–89, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Bova, M.E. The Fiscal Costs of Contingent Liabilities; International Monetary Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L. Capital Allocation Efficiency, SOEs Reform and China’s Economic Growth. Preprints 2019, 2019010163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florio, M.; Fecher, F. The Future of Public Enterprise: Contributions to a New Discourse. Ann. Public Coop. Econ. 2011, 82, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thynne, I. Ownership as an Instrument of Policy and Understanding in the Public Sphere: Trends and Tesearch Agenda. Policy Stud. 2011, 32, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, M. Contemporary Public Enterprises: Innovation, Accountability, Governance. J. Econ. Policy Reform 2014, 17, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, M. The Return of Public Enterprise. Available at SSRN 2563560, 2014. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2563560 (accessed on 29 January 2014).
- Bernier, L. Public Enterprises as Policy Instruments: The Importance of Public Entrepreneurship. J. Econ. Policy Reform 2014, 17, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. The influence of Different Ownership on Economic Growth. China Soft Sci. 2011, 6, 178–185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, X.; Fang, F. The Reform of the State-owned Economy, and the Stabilizing Trend of China’s Economic Fluctuations. Manag. World 2012, 3, 11–22, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Qin, X.; Jebran, K. Does uncertainty influence the leverage-investment association in Chinese firms? Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2019, 50, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R. How State-Owned Enterprises Drag on Economic Growth; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Kyaw, N.N.A. Ownership structure and investment decisions of Chinese SOEs. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2018, 43, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.H. Effect of government share ownership on corporate risk taking: Case of the United Arab Emirates. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2016, 36, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Yoshino, N.; Kim, C.J.; Mortha, A. A Comprehensive Evaluation Framework on the Economic Performance of State-Owned Enterprises; ADBI Working Paper Series: Tokyo, Japan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.; Dai, Y.; Li, Y. The Policy Shock, the Market Environment and the Productivity of State-owned Enterprises: The Status Quo, the Trend, and the Development. Manag. World 2014, 8, 4–17, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Duan, Y.; Huang, Y. Policy Function of State-Owned Enterprises and Implicit Liabilities of Local Governments in China: Formation Mechanism, Measurement and Economic Impact. Manag. World 2020, 36, 36–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Kang, J. Some new efficient mean–variance portfolio selection models. Int. J. Financ. Econ. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Kang, J.; Wen, F. Predicting stock returns: A risk measurement perspective. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2021, 74, 101676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegkas, P. The effect of government debt and other determinants on economic growth: The Greek experience. Economies 2018, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Deng, P.; Guo, L. Impact of China’s Provincial Government Debt on Economic Growth and Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, V. Debt and growth: Decomposing the cause and effect relationship. Int. J. Financ. Econ. 2020, 25, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhong, P.; Wu, L. Has Local Government Debt Promoted Economic Growth in developing countries? New evidence from a survey in China”//E3S Web of Conferences. EDP Sci. 2021, 235, 01014. [Google Scholar]
- Bottero, M.; Lenzu, S.; Mezzanotti, F. Sovereign debt exposure and the bank lending channel: Impact on credit supply and the real economy. J. Int. Econ. 2020, 126, 103328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, F. Bank lending and the European sovereign debt crisis. J. Financ. Quant. Anal. 2019, 54, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cochrane, J.H. Understanding Policy in the Great Recession: Some Unpleasant Fiscal Arithmetic. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2011, 55, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, J.; Ogawa, K.; Sterken, E.; Tokutsu, I. Public debt, economic growth and the real interest rate: A panel VAR Approach to EU and OECD countries. Appl. Econ. 2020, 52, 1377–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanalp, S.; Liao, Y. Banking Sector Contingent Liabilities and Sovereign Risk. J. Empir. Financ. 2014, 29, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsafack, G.; Li, Y.; Beliaeva, N. Too-big-to-fail: The value of government guarantee. Pac.-Basin Financ. J. 2021, 68, 101313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, J.; Jara, M.; Kim, H.; Ter-Minassian, T.; Wagner, R. Fixing State-Owned Enterprises: New Policy Solutions to Old Problems; Inter-American Development Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, W. SOEs Reform’s Impact on Economic Growth. Econ. Res. J. 2015, 4, 122–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, M.; Yan, B.; Li, H. Leverage Structure, Level and Financial Stability: Theory and Empirics. J. Financ. Res. 2017, 2, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Kotz, D.M. The impact of state-owned enterprises on China’s economic growth. Rev. Radic. Political Econ. 2020, 52, 96–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Social Efficiency of SOEs. Available at SSRN 4032159. 2021. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4032159 (accessed on 6 July 2021).
- Florio, M. Rethinking on Public Enterprise: Editorial Introduction and Some Personal Remarks on the Research Agenda. Int. Rev. Appl. Econ. 2013, 27, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P. Business fixed investment of chinese manufacturing firms in the post-financial crisis era. China Econ. J. 2020, 13, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.; Chen, W.; Zheng, K. Puzzle of Deviation between Financing Advantage and Investment Efficiency for State-owned Enterprises: Based on a Comparative Analysis in the view of Property Right and Industry. Econ. Probl. 2019, 5, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Li, M. Over-investment and Productivity Loss of State-owned Enterprises. China Ind. Econ. 2016, 10, 109–125. [Google Scholar]
- Melecky, M. Hidden Debt: Solutions to Avert the Next Financial Crisis in South Asia; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Jiang, Z.; Shi, H. The business cycle implications of bank discrimination in China. Econ. Model. 2018, 73, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Hong, Z. Financial Development and Negative Efficiency Spillovers under Credit Discrimination. J. Financ. Res. 2016, 431, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, H. Zombie firms and soft budget constraints in the Chinese stock market. Asian Econ. J. 2020, 34, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. Understanding public sector debt: Financial vicious circle under the soft budget constraint. Public Organ. Rev. 2018, 18, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Zeng, J.; Liao, F.; Huang, J. Policy Burden of State-Owned Enterprises and Efficiency of Credit Resource Allocation: Evidence from China. SAGE Open 2021, 11, 21582440211005467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K. China’s Steroids Model of Growth. In Policies to Make Trade Work for All; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Ma, S.; Hsu, S.; Jiang, Y. Monetary Policy, Ownership Discrimination and Leverage Differentiation of Non-financial Enterprises. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3688713.2020 (accessed on 8 September 2020).
- Luo, S. Credit misallocation, endogenous TFP changes, and economic fluctuation in China. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2019, 55, 1909–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; He, D. Does State-owned Enterprises’ Over-investment Lead to Overcapacity of Private Enterprises. Mod. Financ. Econ. -J. Tianjin Univ. Financ. Econ. 2019, 6, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Janadi, Y.; Rahman, R.A.; Alazzani, A. Does government ownership affect corporate governance and corporate disclosure? Evidence from Saudi Arabia. Manag. Audit. J. 2016, 31, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Fan, B. China can effectively address the high leverage ratio of SOEs. People’s Wkly. 2017, 1, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Mascia, D.V.; Rossi, S.P.S. Is there a gender effect on the cost of bank financing? J. Financ. Stab. 2017, 31, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, L.; Wilson, L. Racial discrimination in TARP investments. Int. J. Financ. Eng. Risk Manag. 2019, 3, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellalage, N.; Locke, S. Access to credit by SMEs in South Asia: Do women entrepreneurs face discrimination. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2017, 41, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, W. Liquidity Shock, Credit Constraint and the Development of Private vs. State-Owned Enterprises. Front. Econom. China 2019, 14, 583–603. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.; Cao, T.; Li, W. Promotion Pressure, Officials’ Tenure and Lending Behavior of the City Commercial Banks. Econ. Res. J. 2011, 46, 72–85. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z. Modernization of China’s Financial System and Governance System in the New Era. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 53, 4–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Yue, H.; Rao, P. Local Governments’ Fiscal Pressure and Bank Credit Resource Allocation Efficiency: Evidence from Chinese City Commercial Bank. J. Financ. Res. 2020, 475, 88–109. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xiang, H.; Zhao, Q. Local Government Implicit Debt and Bank Liquidity Creation. J. Cent. Univ. Financ. Econ. 2021, 10, 30–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lupoli, M. Deleverage and Defaults in UK. School of Economics and Finance Discussion Paper No. 2102. 2021. Available online: https://www.st-andrews.ac.uk/~wwwecon/mysubmit/pdf-archive/4/2102.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Burriel Llombart, P.; Checherita-Westphal, C.; Jacquinot, P.; Schön, M.; Stähler, N. Economic Consequences of High Public Debt: Evidence from Three Large Scale DSGE Models. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3676264.2020 (accessed on 18 August 2020).
- Chen, M.J.; Finocchiaro, D.; Lindé, J.; Walentin, K. The Costs of Macroprudential Deleveraging in a Liquidity Trap; International Monetary Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shilling, A.G. The Age of Deleveraging: Investment Strategies for a Decade of Slow Growth and Deflation; IMF Economic Review: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Tian, T.; Ruan, Z.; Zhu, J. Financial Leverage, Economic Growth, and Financial Stability. J. Financ. Res. 2016, 6, 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R. Financial Repression, Ownership Discrimination, and Negative Spillovers: SOE Efficiency Losses Revisited. China Econ. Q. 2011, 2, 603–618. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Li, Z. A study on the impact of state-owned enterprises’ economic efficiency on SMEs’ financing constraints-Based on empirical evidence of Listed companies in China’s SME Board. Financ. Econ. 2019, 4, 36, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Checherita-Westphal, C.; Rother, P. The impact of high government debt on economic growth and its channels: An empirical investigation for the euro area. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2012, 56, 1392–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J. Study on the influence of regional green competitiveness on economic growth. Jiangxi Norm. Univ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Kong, D. Anti-corruption and Corporate Governance optimization in China: A Quasi-natural Experiment. J. Financ. Res. 2016, 8, 159–174. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Cao, J. A Review of the Literature on Local Government Debt in China. Public Financ. Res. J. 2019, 1, 75–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.; Ye, B. Mediating effect analysis: Methodology and model development. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 4, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Li, M.; Lu, Z. SOEs deleveraging while non-SOEs deleveraging. China Bus. News 2018, 5–29, A11. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Liu, K. Ownership Structure, Incentive and Restraint Mechanism and Enterprises Efficiency: An Empirical Test Based on A-Share State-owned Listed Companies. Econ. Probl. 2022, 3, 53–61, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X. Classified Reform of State-Owned Enterprises’ Mixed-Ownership and Capital Allocation Efficiency. Contemp. Financ. Econ. 2021, 7, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Yang, L. Mixed Ownership Reform of State-Owned Enterprises Since Reform and Opening-up: Course, Effect and Prospect. Manag. World 2021, 37, 4, 44–60. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Guo, J.; Zhu, W. Mixed ownership Reform of State-owned enterprises: Driving force, resistance and Realization path. Manag. World 2017, 10, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Xiao, H.; Wang, X. SOE Reform in the View of Competitive Neutrality. China Ind. Econ. 2019, 6, 22–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Property Rights, Credit Discrimination and Alternative Constraints on Enterprise Financing. J. Zhongnan Univ. Econ. Law 2016, 5, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Zhu, Y. Is Bank Credit Discrimination the Result of Government Intervention: Evidence from the Reform Process. Contemp. Financ. Econ. 2020, 50–63. [Google Scholar]
- Szarzec, K.; Nowara, W. The economic performance of state-owned enterprises in Central and Eastern Europe. Post-Communist Econ. 2017, 29, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Province | Numbers | Province | Numbers | Province | Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AnHui | 26 | BeiJing | 26 | FuJian | 23 |
| GanSu | 8 | GuangDong | 44 | GuangXi | 12 |
| GuiZhou | 5 | HaiNan | 4 | HeBei | 12 |
| HeNan | 14 | HeiLongJiang | 6 | HuBei | 16 |
| Hunan | 17 | JiLin | 7 | JiangSu | 28 |
| JiangXi | 12 | LiaoNing | 16 | Inner Mongolia | 2 |
| NingXia | 1 | QingHai | 3 | ShanDong | 35 |
| ShanXi | 16 | ShanXi | 13 | ShangHai | 56 |
| SiChuan | 17 | TianJin | 14 | Tibet | 3 |
| XinJiang | 10 | YunNan | 10 | ZheJiang | 25 |
| ChongQing | 6 |
| Variable Name | Variable Symbol | Variable Descriptions and Calculations | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variables | Standard deviation of economic growth | stdgdp | The degree of economic fluctuation in year t is expressed by the year-on-year standard deviation of GDP in a 5-year window period from year (t − 2) to year (t + 2) | Guo Jing and Ma Guangrong [1] |
| Economic growth rate | dgdp | Annual economic growth rate in each province | Rui-ming Liu [77] | |
| Total efficiency of money | ttm | efficiency of private enterprises | Guo Jiangshan and Li Zixuan [78] | |
| ttd | Replace the assets by debts, and the method is identical with ttm | |||
| Independent Variables | Changes in local governments’ implicit contingent liabilities | rcli | Rate of the implicit contingent liability index of local governments, which is calculated by Equations (1)–(5), | Arslanalp S and Liao Y [41] |
| The increase in cli | dcli | |||
| Instrument variables of rcli | rcli_iv | The index of one province’s implicit contingent liabilities adopts the average index of implicit contingent liabilities of the other 30 provinces as an instrument variable. | Checherita-Westphal and Rother [79] | |
| Proportion of enterprises’ assets | m_rstate | Asset of SOE/(asset of SOE + asset of POE) | Guo Jing and Ma Guangrong [1] | |
| m_rpri | Asset of non-SOEs/(asset of SOE + asset of POE) | |||
| Proportion of enterprises’ debts | d_rstate | Debt of SOE/(debt of SOE + debt of POE) | ||
| d_rpri | Debt of non-SOEs/(debt of SOE + debt of POE) | |||
| Enterprises’ efficiency of money | statettm | Prime operating revenue of SOE/asset of SOE | Guo Jiangshan and Li Zixuan [78] | |
| prittm | Prime operating revenue of non-SOEs/asset of non-SOEs | |||
| statettd | Prime operating revenue of SOE/debt of SOE | |||
| prittd | Prime operating revenue of non-SOEs/debt of non-SOEs | |||
| Increase rate of problem loans | dsbad | Increase rate of problem loans | Guo et al. [53] | |
| Region dummy variables | region | Central and western region = 1; eastern region = 0 | - | |
| Control Variables 1 | Governments’ role in the market | gov | Government spending in each province/GDP in each province | Guo Jing and Ma Guangrong [1] |
| Human capital | edu | College students’ enrollments in each province/population in each province | Rui-ming Liu [77] | |
| Foreign direct investment | dfdi | Increase rate of FDI | Guo Jing and Ma Guangrong [1] | |
| Investment rate | inv | Investments/GDP | Rui-ming Liu [77] | |
| Proportion of urban population | city | Populations in city/populations in each province | ||
| Control Variables 2 | Environment protection policy | lnpo | Investments in environmental pollution control | He Jue [80] |
| Anti-corruption policy | Corruption | Corruption governance indicators in WGI index (Worldwide Governance Indicators) published by the WB (World Bank) | Wang Maobin and Kong Dongmin [81] | |
| Management policy of local governments’ debts | policy | Take the No.43 policy as the representative, and build the dummy variables | Mao Jie and Cao Jing [82] | |
| Financial crisis | crisis | Financial crisis period is from 2008 to 2009, and we built the dummy variables | Arslanalp S and Liao Y [41] |
| Variables | Observations | Average | Median | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| stdgdp | 341 | 0.0149 | 0.0136 | 0.0084 | 0.0007 | 0.0487 |
| dgdp | 341 | 0.1313 | 0.1195 | 0.0716 | −0.2240 | 0.3227 |
| rcli | 341 | 0.0899 | 0.0570 | 0.3599 | −0.7806 | 6.1536 |
| cli | 341 | 3.705 | 1.3632 | 7.6134 | 0.0001 | 50.5189 |
| dcli | 341 | 0.2027 | 0.0623 | 0.6635 | −2.9019 | 6.8883 |
| rcli_iv | 341 | 0.0702 | 0.0729 | 0.0807 | −0.0587 | 0.3259 |
| gov | 341 | 0.3001 | 0.2794 | 0.0849 | 0.1895 | 0.6541 |
| dfdi | 341 | 0.1813 | 0.1173 | 0.4560 | −0.7134 | 6.9747 |
| edu | 341 | 0.0241 | 0.0222 | 0.0094 | 0.0090 | 0.0683 |
| inv | 341 | 0.7344 | 0.7336 | 0.2418 | 0.2366 | 1.5070 |
| city | 341 | 0.5349 | 0.5178 | 0.1434 | 0.2150 | 0.8960 |
| corruption | 341 | −0.4209 | −0.44 | 0.1193 | −0.5900 | −0.2500 |
| lnpo | 341 | 8.8452 | 9.0184 | 0.3484 | 8.1278 | 9.1670 |
| dsbad | 341 | 0.1114 | 0.0418 | 0.4316 | −0.8614 | 2.3913 |
| ttm | 341 | 0.9365 | 0.9376 | 0.3771 | 0.1194 | 1.9022 |
| ttd | 341 | 1.6303 | 1.6221 | 0.6879 | 0.2345 | 3.5278 |
| statettm | 341 | 0.6901 | 0.7108 | 0.2207 | 0.0959 | 1.1995 |
| prittm | 341 | 1.4961 | 1.5723 | 0.6314 | 0.2949 | 3.0722 |
| statettd | 341 | 1.1483 | 1.1629 | 0.3755 | 0.1963 | 2.1374 |
| prittd | 341 | 3.0165 | 2.8820 | 1.6525 | 0.6193 | 9.0214 |
| a_rstate | 341 | 0.7320 | 0.7751 | 0.1620 | 0.2541 | 0.9603 |
| a_rpri | 341 | 0.2680 | 0.2249 | 0.1620 | 0.0397 | 0.7459 |
| d_rstate | 341 | 0.7592 | 0.7922 | 0.1505 | 0.2316 | 0.9640 |
| d_rpri | 341 | 0.2408 | 0.2078 | 0.1505 | 0.0360 | 0.7684 |
| Cli | stdgdp | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| cli | −0.000866 * | −0.000372 ** | −0.000461 ** | ||
| (0.000436) | (0.000180) | (0.000171) | |||
| a_rstate | 9.810 ** | 11.13 ** | |||
| (4.346) | (5.125) | ||||
| gov | 1.458 | 0.521 | −0.0267 | −0.0522 * | |
| (2.560) | (1.974) | (0.0318) | (0.0299) | ||
| dfdi | 0.0265 | 0.127 | −0.000279 | 0.000435 | |
| (0.106) | (0.167) | (0.000478) | (0.000382) | ||
| edu | −52.88 * | −11.72 | 1.036 *** | 1.054 ** | |
| (27.84) | (43.26) | (0.377) | (0.398) | ||
| inv | 3.616 * | 3.505 * | −0.00451 | −0.00247 | |
| (1.861) | (1.793) | (0.00704) | (0.00821) | ||
| city | 10.06 *** | −1.469 | −0.0598 ** | −0.0743 * | |
| (3.483) | (7.477) | (0.0278) | (0.0414) | ||
| corruption | 0.797 | 0.0107 | |||
| (0.629) | (0.00920) | ||||
| lnpo | 1.172 | 0.00496 | |||
| (0.865) | (0.00323) | ||||
| policy | 0.125 | −0.00754 *** | |||
| (0.0933) | (0.00117) | ||||
| crisis | −0.00375 | −0.00211 ** | |||
| (0.0690) | (0.000936) | ||||
| Constant | −11.12 * | −16.64 | 0.0178 *** | 0.0346 ** | 0.0119 |
| (5.696) | (10.27) | (0.00142) | (0.0135) | (0.0169) | |
| Observations | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 |
| R-squared | 0.296 | 0.327 | 0.025 | 0.112 | 0.249 |
| Number of id | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 |
| Dgdp | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| rcli | −0.0321 *** | −0.0212 ** | −0.0190 *** | −0.0116 ** | −0.203 *** |
| (0.0109) | (0.00829) | (0.00710) | (0.00576) | (0.0393) | |
| gov | 0.568 *** | 0.469 *** | 0.340 *** | 0.451 *** | |
| (0.149) | (0.128) | (0.102) | (0.124) | ||
| dfdi | −0.00215 | −0.00635 | −0.00421 | −0.00646 | |
| (0.00672) | (0.00580) | (0.00459) | (0.00561) | ||
| edu | −0.506 | −4.470 *** | −1.659 | −4.445 *** | |
| (1.731) | (1.575) | (1.328) | (1.521) | ||
| inv | −0.0645 ** | −0.0350 | 0.0309 | −0.0448 * | |
| (0.0300) | (0.0255) | (0.0213) | (0.0247) | ||
| city | −0.666 *** | 0.505 ** | −0.158 | 0.544 *** | |
| (0.137) | (0.201) | (0.195) | (0.194) | ||
| corruption | −0.538 *** | 0.255 | −0.518 *** | ||
| (0.0684) | (0.330) | (0.0662) | |||
| lnpo | 0.00352 | 0.447 *** | −0.00187 | ||
| (0.0172) | (0.141) | (0.0166) | |||
| policy | 0.00965 | −0.642 *** | 0.00858 | ||
| (0.0112) | (0.135) | (0.0108) | |||
| crisis | −0.0195 ** | −0.255 *** | −0.0159 * | ||
| (0.00875) | (0.0398) | (0.00849) | |||
| Region*rcli | 0.189 *** | ||||
| (0.0398) | |||||
| time control variables | NO | NO | NO | YES | NO |
| Constant | 0.134 *** | 0.379 *** | −0.401 ** | −3.289 *** | −0.349 ** |
| (0.00399) | (0.0759) | (0.178) | (1.201) | (0.172) | |
| Observations | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 |
| R-squared | 0.027 | 0.458 | 0.621 | 0.770 | 0.648 |
| Number of id | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 |
| Mediating Effect Test | dgdp | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | ||
| dsbad | ttm | ttd | ||
| (1) | −0.0190 *** | −0.0190 *** | −0.0190 *** | |
| (0.00710) | (0.00710) | (0.00710) | ||
| (2) | 0.0912 * | −0.0302 * | −0.0658 * | |
| (0.0498) | (0.0161) | (0.0347) | ||
| (3) | −0.0139 ** | −0.0171 ** | −0.0171 ** | |
| (0.00658) | (0.00707) | (0.00708) | ||
| −0.0556 *** | 0.0647 ** | 0.0292 ** | ||
| (0.00758) | (0.0251) | (0.0117) | ||
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Mediating effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| (a) Ways to Balance Leverage and Economic Growth | |||||
| ttm | |||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| a_rpri*a_rpri | −1.265 ** | ||||
| (0.548) | |||||
| a_rstate | −0.895 *** | ||||
| (0.158) | |||||
| a_rpri | 0.895 *** | 1.750 *** | |||
| (0.158) | (0.402) | ||||
| statettm | 1.180 *** | ||||
| (0.0606) | |||||
| prittm | 0.318 *** | ||||
| (0.0185) | |||||
| gov | 0.641 ** | 0.641 ** | −0.286 | 0.460 ** | 0.685 ** |
| (0.278) | (0.278) | (0.199) | (0.207) | (0.276) | |
| dfdi | 0.00296 | 0.00296 | 0.00484 | 0.00140 | 0.00376 |
| (0.0127) | (0.0127) | (0.00882) | (0.00943) | (0.0126) | |
| edu | 3.591 | 3.591 | 4.410 * | 1.059 | 4.091 |
| (3.435) | (3.435) | (2.385) | (2.562) | (3.417) | |
| inv | 0.0408 | 0.0408 | 0.138 *** | −0.0672 | 0.0178 |
| (0.0558) | (0.0558) | (0.0389) | (0.0423) | (0.0563) | |
| city | −0.264 | −0.264 | −0.343 | 0.758 ** | −0.259 |
| (0.435) | (0.435) | (0.304) | (0.327) | (0.432) | |
| corruption | −0.493 *** | −0.493 *** | 0.171 | −0.415 *** | −0.475 *** |
| (0.149) | (0.149) | (0.110) | (0.111) | (0.148) | |
| lnpo | 0.144 *** | 0.144 *** | 0.0632 ** | 0.104 *** | 0.133 *** |
| (0.0379) | (0.0379) | (0.0267) | (0.0281) | (0.0379) | |
| policy | −0.0742 *** | −0.0742 *** | −0.0106 | −0.0303 | −0.0714 *** |
| (0.0244) | (0.0244) | (0.0174) | (0.0184) | (0.0242) | |
| crisis | −0.0234 | −0.0234 | 0.00257 | 0.00669 | −0.0276 |
| (0.0191) | (0.0191) | (0.0133) | (0.0142) | (0.0191) | |
| Constant | −0.0297 | −0.924 ** | −0.300 | −1.147 *** | −0.931 ** |
| (0.447) | (0.393) | (0.276) | (0.289) | (0.390) | |
| Observations | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 |
| R-squared | 0.363 | 0.363 | 0.689 | 0.645 | 0.374 |
| Number of id | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 |
| (b) Ways to Balance Leverage and Economic Growth with Lag Variables | |||||
| ttm | |||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | ||
| a_rstate | −0.663 *** | ||||
| (0.160) | |||||
| a_rpri | 0.663 *** | ||||
| (0.160) | |||||
| statettm | 0.829 *** | ||||
| (0.0591) | |||||
| prittm | 0.277 *** | ||||
| (0.0210) | |||||
| gov | 0.650 ** | 0.650 ** | 0.125 | 0.890 *** | |
| (0.284) | (0.284) | (0.229) | (0.233) | ||
| dfdi | 0.00694 | 0.00694 | 0.00959 | 0.00153 | |
| (0.0130) | (0.0130) | (0.0103) | (0.0106) | ||
| edu | 4.425 | 4.425 | 0.963 | −1.613 | |
| (3.509) | (3.509) | (2.811) | (2.910) | ||
| inv | 0.0705 | 0.0705 | 0.0387 | 0.0187 | |
| (0.0567) | (0.0567) | (0.0454) | (0.0466) | ||
| city | −0.351 | −0.351 | 0.983 *** | 0.922 ** | |
| (0.450) | (0.450) | (0.362) | (0.370) | ||
| corruption | −0.463 *** | −0.463 *** | −0.611 *** | −0.654 *** | |
| (0.153) | (0.153) | (0.122) | (0.125) | ||
| lnpo | 0.153 *** | 0.153 *** | 0.127 *** | 0.106 *** | |
| (0.0389) | (0.0389) | (0.0306) | (0.0316) | ||
| policy | −0.0833 *** | −0.0833 *** | −0.0102 | −0.0341 * | |
| (0.0250) | (0.0250) | (0.0205) | (0.0206) | ||
| crisis | −0.0190 | −0.0190 | −0.0196 | −0.0101 | |
| (0.0195) | (0.0195) | (0.0156) | (0.0159) | ||
| Constant | −0.256 | −0.919 ** | −1.633 *** | −1.413 *** | |
| (0.469) | (0.406) | (0.318) | (0.324) | ||
| Observations | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 | |
| R-squared | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.574 | 0.554 | |
| Number of id | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 | |
| Dgdp | rcli | dgdp | dgdp | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | ||
| Replace rcli by dcli | Replace rcli by rcli_iv | IV Regression (2SLS-1) | IV Regression (2SLS-2-FE) | IV Regression (2SLS-2-FD) | Dynamic Panel Regression (GMM) | ||
| - | - | - | - | - | - | L.dgdp | −0.195 *** |
| (0.0266) | |||||||
| - | - | - | - | - | - | L2.dgdp | −0.290 *** |
| (0.0194) | |||||||
| rcli | - | - | - | −0.231 *** | −0.242 ** | rcli | - |
| (0.0750) | (0.111) | ||||||
| dcli | −0.0249 *** | - | - | - | - | dcli | −0.0137 *** |
| (0.00459) | (0.00342) | ||||||
| rcli_iv | - | −0.222 *** | - | - | rcli_iv | - | |
| (0.0345) | |||||||
| gov | 0.406 *** | 0.409 *** | 0.797 *** | 0.834 | gov | 0.141 * | |
| (0.123) | (0.121) | (1.020) | (0.279) | (0.562) | (0.0856) | ||
| dfdi | −0.00747 | −0.00529 | −0.0522 | −0.0173 | −0.0640 ** | dfdi | −0.00480 |
| (0.00561) | (0.00549) | (0.0463) | (0.0122) | (0.0318) | (0.00325) | ||
| edu | −5.126 *** | −4.957 *** | −17.96 | −9.099 *** | −15.77 * | edu | −2.651 |
| (1.527) | (1.493) | (12.58) | (3.525) | (9.284) | (2.007) | ||
| inv | −0.0299 | −0.0107 | 0.00436 | −0.00969 | −0.0924 | inv | −0.0993 * |
| (0.0247) | (0.0245) | (0.207) | (0.0515) | (0.109) | (0.0535) | ||
| city | 0.636 *** | 0.613 *** | 2.996 * | 1.304 *** | 1.525 | city | 0.258 ** |
| (0.196) | (0.191) | (1.609) | (0.487) | (1.200) | (0.104) | ||
| corruption | −0.557*** | −0.518*** | 0.167 | −0.479*** | −0.265 | corruption | −0.363 *** |
| (0.0661) | (0.0650) | (0.548) | (0.138) | (0.275) | (0.0363) | ||
| lnpo | −0.00578 | −0.0327* | −0.135 | −0.0640 | −0.0294 | lnpo | −0.0723 *** |
| (0.0167) | (0.0174) | (0.147) | (0.0414) | (0.129) | (0.0130) | ||
| policy | 0.00944 | 0.0102 | −0.0391 | 0.00116 | −0.0161 | policy | −0.0358 *** |
| (0.0108) | (0.0106) | (0.0896) | (0.0225) | (0.0288) | (0.00325) | ||
| crisis | −0.0167** | −0.0106 | 0.0154 | −0.00700 | −0.0231 | crisis | −0.0938 *** |
| (0.00848) | (0.00844) | (0.0711) | (0.0180) | (0.0246) | (0.00593) | ||
| Constant | −0.363** | −0.106 | −0.367 | −0.190 | −0.00469 | Constant | 0.678 *** |
| (0.172) | (0.176) | (1.480) | (0.362) | (0.0266) | (0.126) | ||
| LM statistics | - | - | - | 10.995 (0.0009) | 5.503 (0.0190) | - | - |
| Observations | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 | 310 | Observations | 248 |
| R-squared | 0.647 | 0.659 | 0.084 | - | - | R-squared | - |
| Number of id | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 | Number of id | 31 |
| (a) Robustness Test 2 | |||||
| ttd | |||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| dpri*dpri | −2.452 * | ||||
| (1.442) | |||||
| d_rstate | −2.300 *** | ||||
| (0.357) | |||||
| d_rpri | 2.300 *** | 3.598 *** | |||
| (0.357) | (0.843) | ||||
| statettd | 1.289 *** | ||||
| (0.0640) | |||||
| prittd | 0.251 *** | ||||
| (0.0160) | |||||
| gov | 0.885 | 0.885 | −0.539 | 0.878 * | 0.960 |
| (0.588) | (0.588) | (0.415) | (0.466) | (0.588) | |
| dfdi | 0.0133 | 0.0133 | 0.0226 | −0.00759 | 0.0167 |
| (0.0268) | (0.0268) | (0.0186) | (0.0213) | (0.0268) | |
| edu | −0.590 | −0.590 | 5.701 | 6.320 | 0.135 |
| (7.328) | (7.328) | (5.030) | (5.728) | (7.318) | |
| inv | −0.114 | −0.114 | 0.262 *** | −0.180 * | −0.139 |
| (0.118) | (0.118) | (0.0830) | (0.0937) | (0.119) | |
| city | 2.527 *** | 2.527 *** | 0.662 | 1.029 | 2.476 *** |
| (0.921) | (0.921) | (0.643) | (0.731) | (0.919) | |
| corruption | −1.245 *** | −1.245 *** | 0.217 | −0.614 ** | −1.225 *** |
| (0.316) | (0.316) | (0.229) | (0.252) | (0.315) | |
| lnpo | 0.145 * | 0.145 * | 0.121 ** | 0.0847 | 0.147 * |
| (0.0797) | (0.0797) | (0.0549) | (0.0629) | (0.0794) | |
| policy | −0.100 * | −0.100 * | 0.00278 | −0.0441 | −0.0972 * |
| (0.0517) | (0.0517) | (0.0364) | (0.0412) | (0.0516) | |
| crisis | −0.00553 | −0.00553 | 0.0407 | −0.0259 | −0.00958 |
| (0.0403) | (0.0403) | (0.0282) | (0.0320) | (0.0403) | |
| Constant | 0.0816 | −2.218 *** | −1.366 ** | −0.945 | −2.335 *** |
| (0.909) | (0.822) | (0.574) | (0.657) | (0.822) | |
| Observations | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 |
| R-squared | 0.278 | 0.278 | 0.651 | 0.647 | 0.285 |
| Number of id | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 |
| (b) Robustness Test 2 with Lag Variables | |||||
| ttd | |||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | ||
| d_rstate | −2.295 *** | ||||
| (0.384) | |||||
| d_rpri | 2.295 *** | ||||
| (0.384) | |||||
| statettd | 0.904 *** | ||||
| (0.0680) | |||||
| prittd | 0.256 *** | ||||
| (0.0189) | |||||
| gov | 0.859 | 0.859 | 0.157 | 1.934 *** | |
| (0.594) | (0.594) | (0.501) | (0.501) | ||
| dfdi | 0.0125 | 0.0125 | 0.0437 * | 0.000775 | |
| (0.0270) | (0.0270) | (0.0227) | (0.0225) | ||
| edu | 2.491 | 2.491 | −5.599 | −7.956 | |
| (7.334) | (7.334) | (6.194) | (6.181) | ||
| inv | −0.0651 | −0.0651 | −0.0162 | −0.0820 | |
| (0.119) | (0.119) | (0.0995) | (0.0989) | ||
| city | 1.358 | 1.358 | 3.805 *** | 3.682 *** | |
| (0.935) | (0.935) | (0.788) | (0.782) | ||
| corruption | −1.035 *** | −1.035 *** | −1.330 *** | −1.354 *** | |
| (0.319) | (0.319) | (0.268) | (0.266) | ||
| lnpo | 0.149 * | 0.149 * | 0.195 *** | 0.00772 | |
| (0.0804) | (0.0804) | (0.0664) | (0.0681) | ||
| policy | −0.135 ** | −0.135 ** | 0.0206 | −0.0127 | |
| (0.0524) | (0.0524) | (0.0448) | (0.0440) | ||
| crisis | −0.0341 | −0.0341 | −0.0321 | −0.000372 | |
| (0.0409) | (0.0409) | (0.0342) | (0.0339) | ||
| Constant | 0.687 | −1.608 * | −3.660 *** | −2.053 *** | |
| (0.979) | (0.840) | (0.701) | (0.691) | ||
| Observations | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 | |
| R-squared | 0.265 | 0.265 | 0.483 | 0.489 | |
| Number of id | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, Y.; Guo, M.; Huang, Y. Leverage of Local State-Owned Enterprises, Implicit Contingent Liabilities of Government and Economic Growth. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14063481
Duan Y, Guo M, Huang Y. Leverage of Local State-Owned Enterprises, Implicit Contingent Liabilities of Government and Economic Growth. Sustainability. 2022; 14(6):3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14063481
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Yixuan, Min Guo, and Yixuan Huang. 2022. "Leverage of Local State-Owned Enterprises, Implicit Contingent Liabilities of Government and Economic Growth" Sustainability 14, no. 6: 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14063481
APA StyleDuan, Y., Guo, M., & Huang, Y. (2022). Leverage of Local State-Owned Enterprises, Implicit Contingent Liabilities of Government and Economic Growth. Sustainability, 14(6), 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14063481





