Spatiotemporal Evolution of Tourism Eco-Efficiency in Major Tourist Cities in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.1.1. Super-SBM Model Based on Undesirable Outputs
2.1.2. “Bottom-up” Calculation of Carbon Emissions
2.1.3. Correlation Analysis
- (1)
- Global spatial autocorrelation is measured using the global Moran index I, which can reflect the correlation of each regional unit in the study area with its neighboring regional units [26]. The equation is as follows:where and are the observed values in regions and , respectively is the mean; is the spatial vector matrix; and is the total sample size. The value range for is [−1, 1], and indicate negative and positive correlations, respectively, and the closer I is to 0, the weaker the correlation is.
- (2)
- The Moran index measures the correlation between spatial units but cannot fully reflect the specific characteristics of such correlations. Local spatial autocorrelation can be used to characterize the spatial distribution of the clustered similarity of regional units [26]. The equation is as follows:where positive and negative values of indicate that the similarity of local spatial units tends to be spatially clustered and dispersed, respectively.
2.1.4. Malmquist Model
2.1.5. Cluster Analysis
2.2. Composition of the Indicator System
2.3. Data Sources
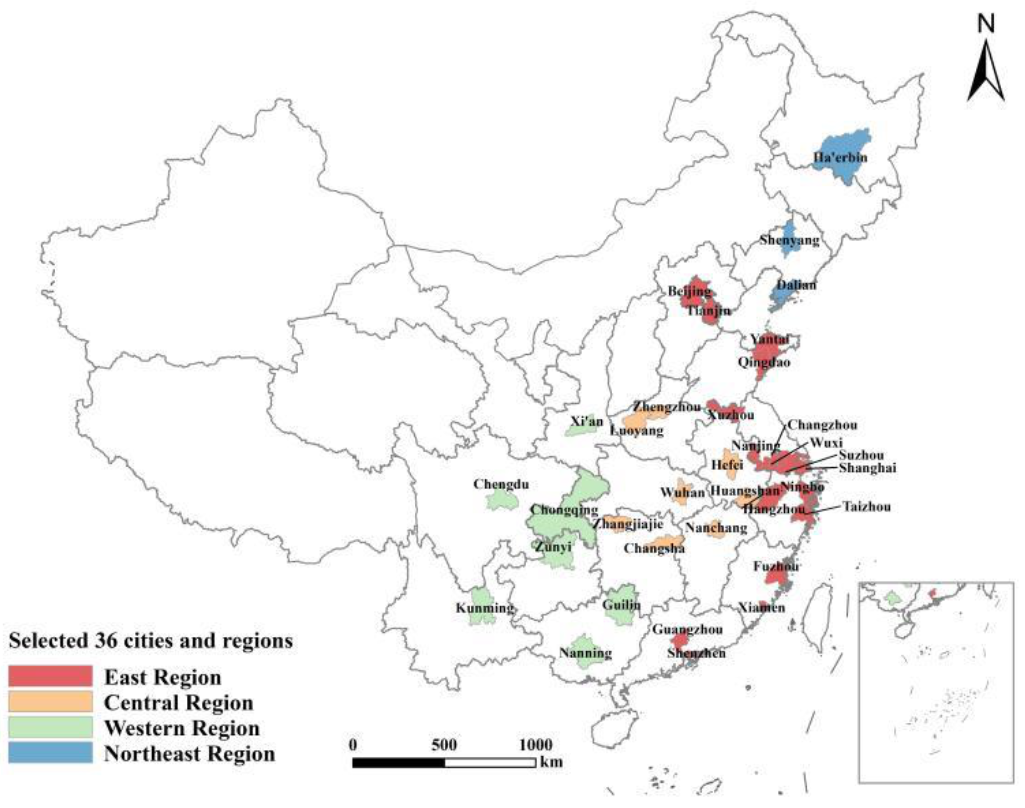
2.4. Overview of the Study Area
2.5. Factors That Influence TEE
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Eco-Efficiencies of Tourist Cities
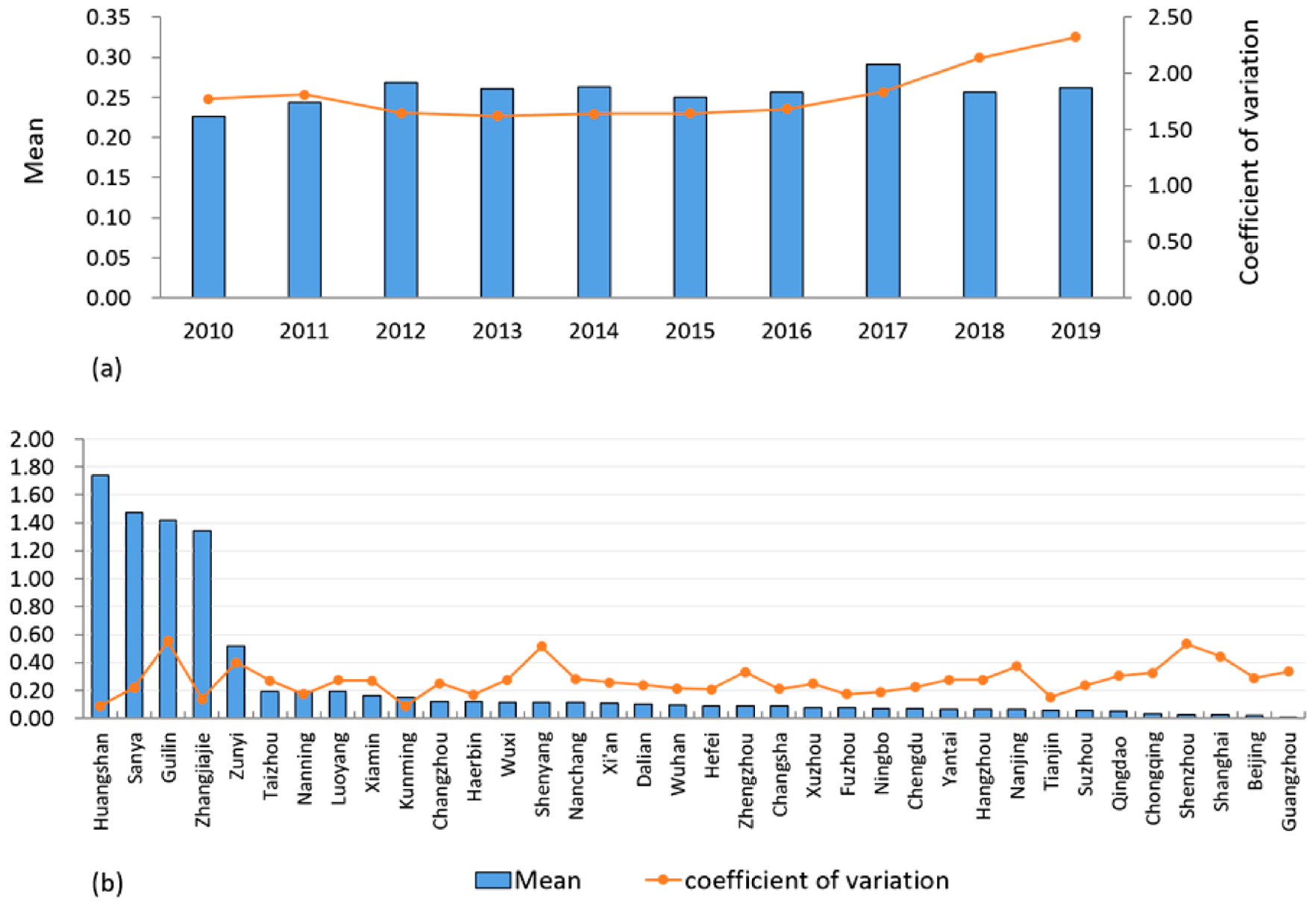
3.1.1. Analysis of TEE
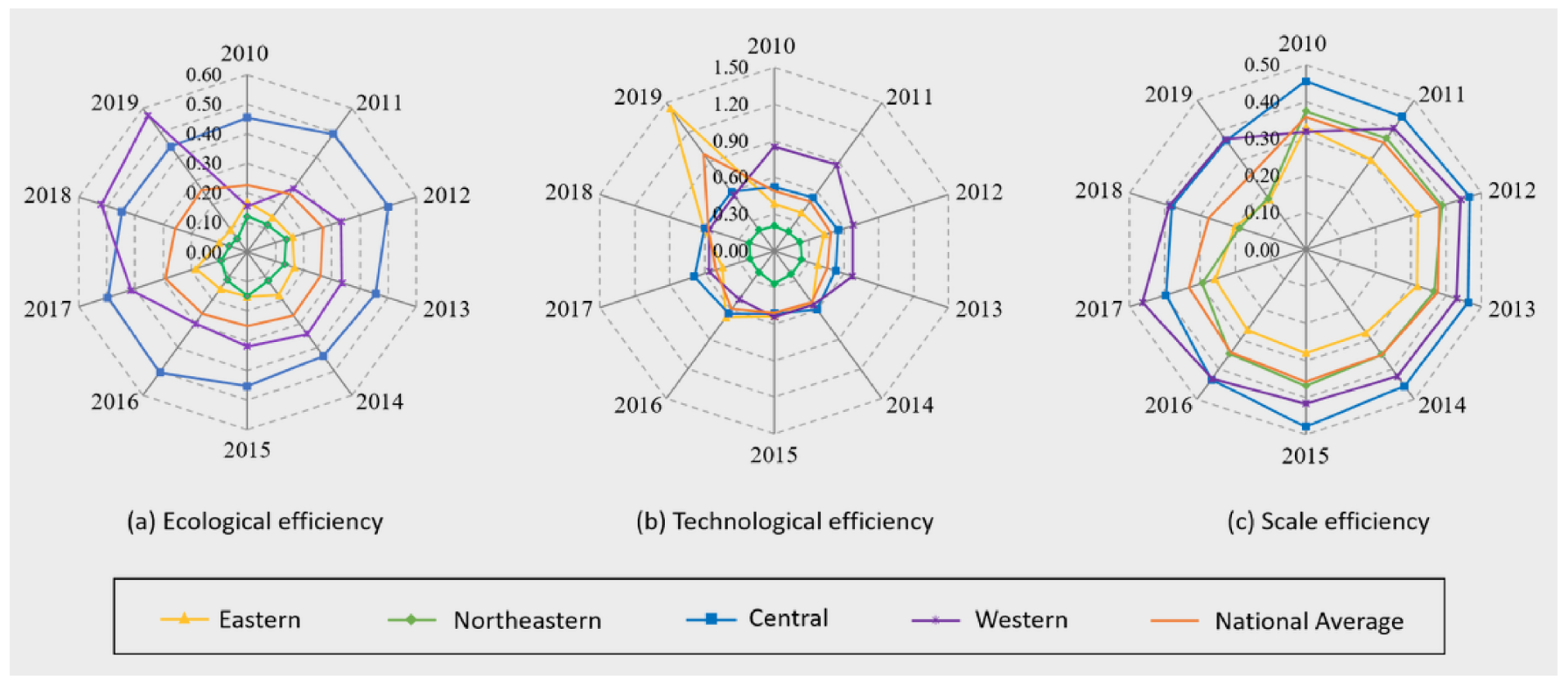
3.1.2. Analysis of TEE by Region
3.2. Malmquist Model Results
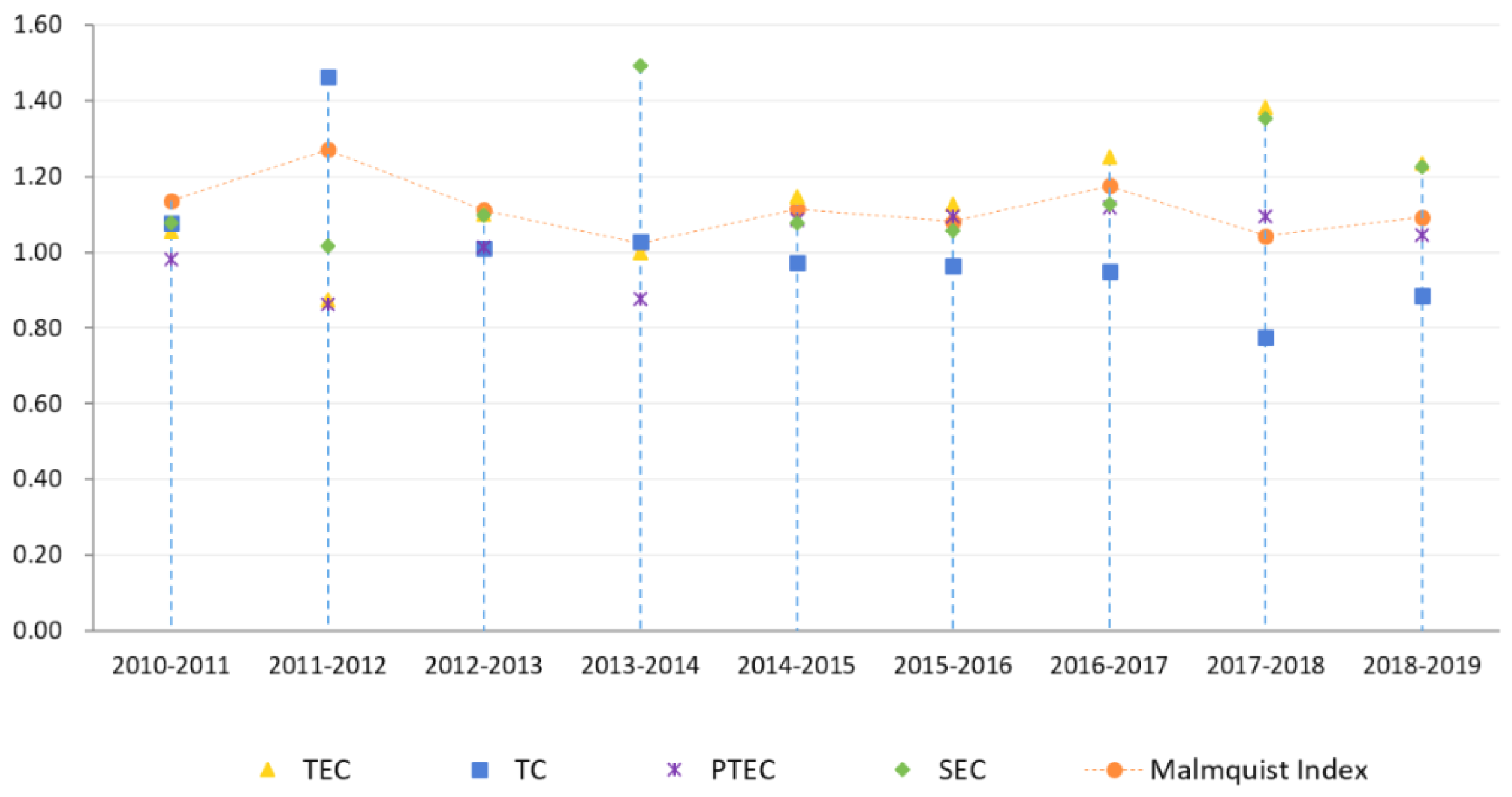
3.2.1. Temporal Changes in the Average Eco-Efficiency of Tourism
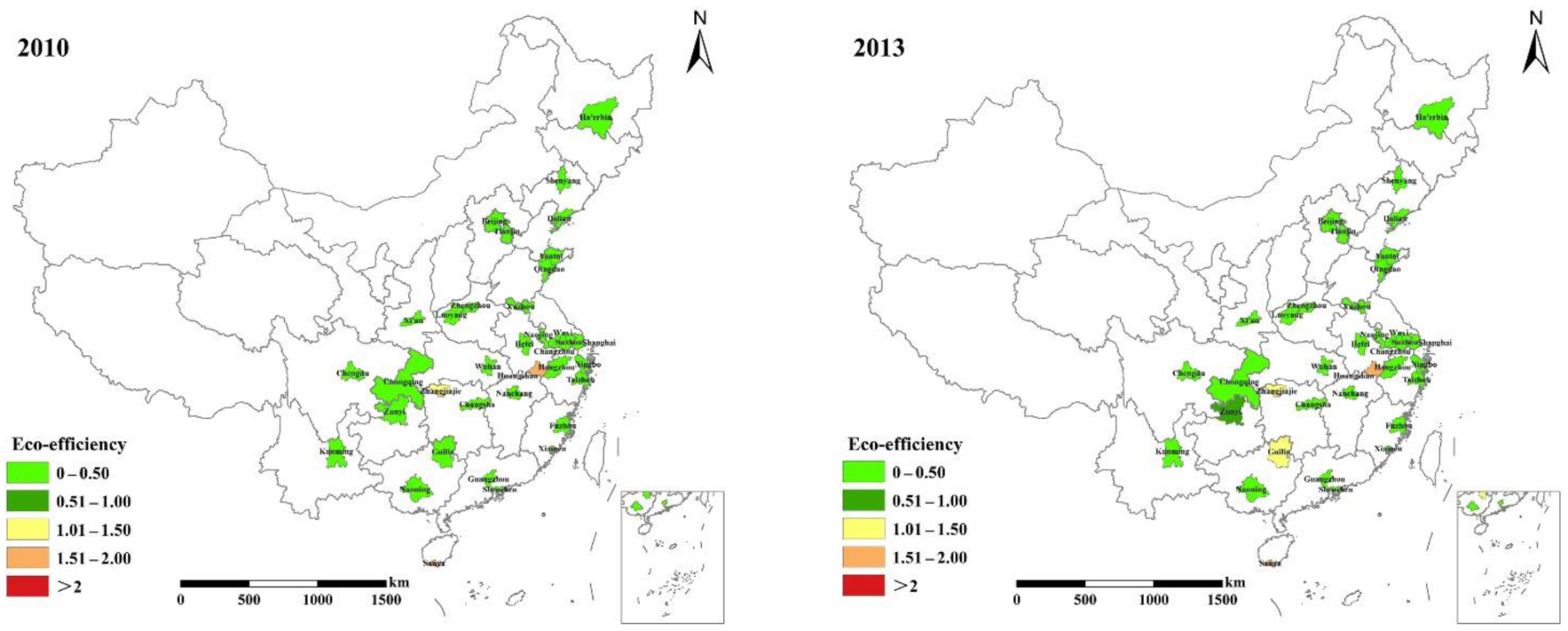
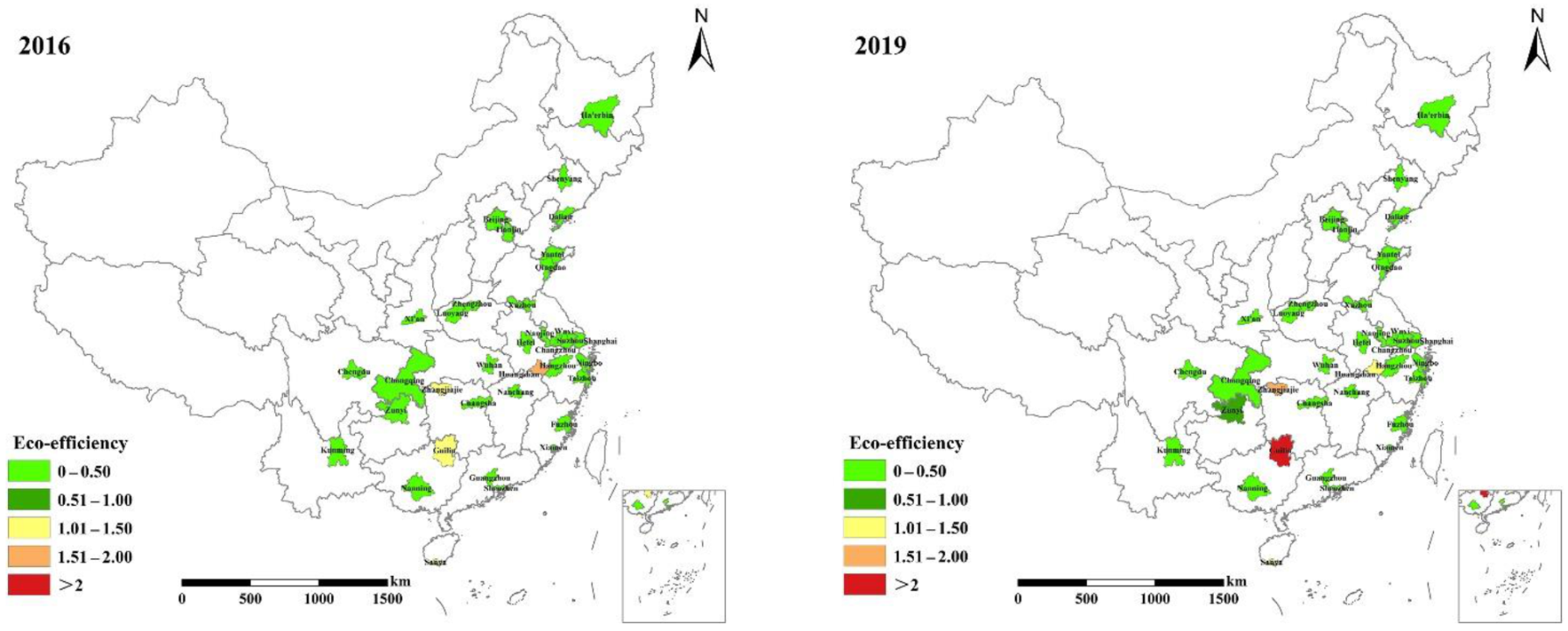
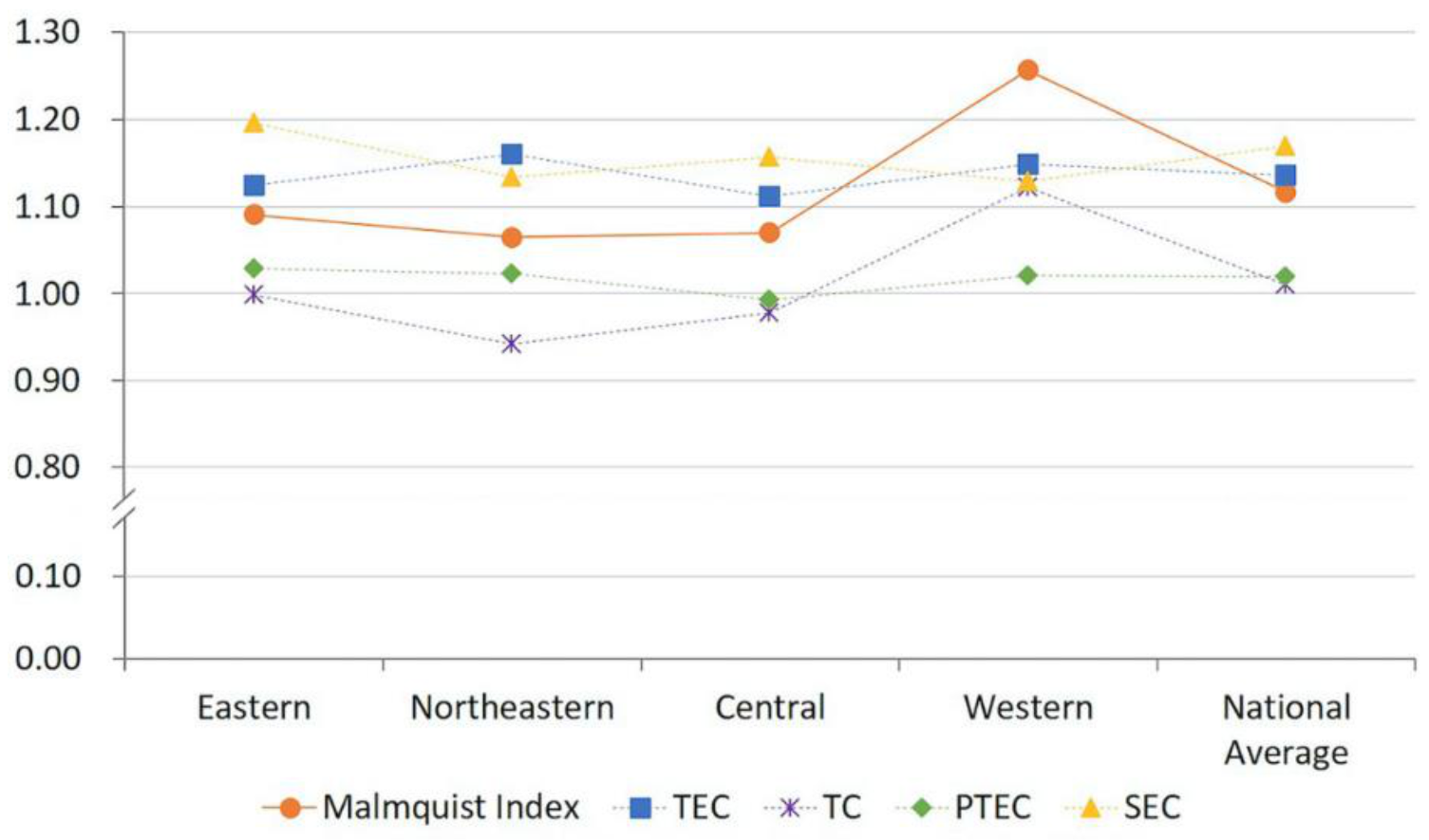
3.2.2. Spatial Evolution of TEE
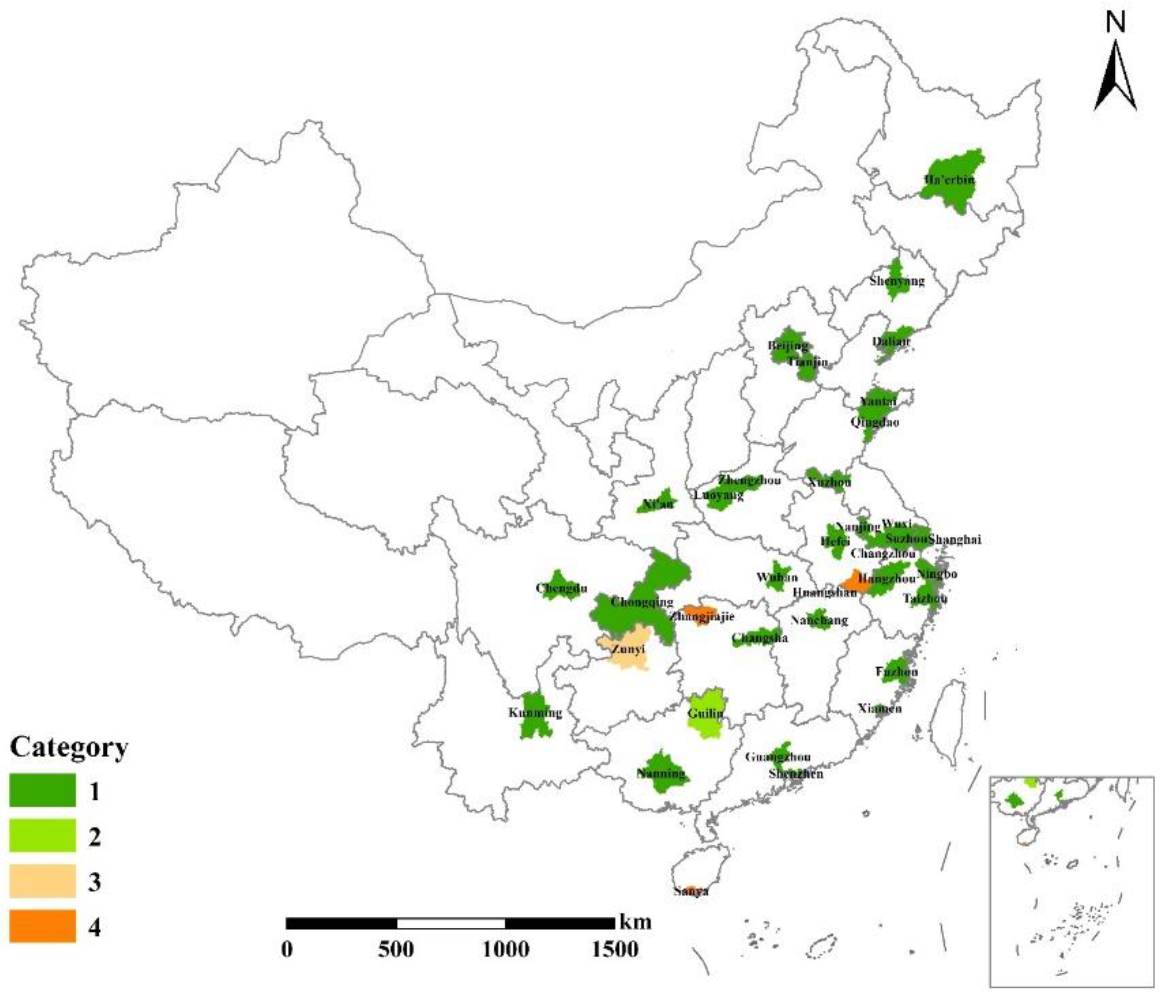
3.3. Cluster Analysis
3.4. Empirical Results and Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lenzen, M.; Sun, Y.Y.; Faturay, F.; Ting, Y.P.; Geschke, A.; Malik, A. The carbon footprint of global tourism. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Shang, J.; Shi, C.; Liu, Z.; Bi, K. Decoupling indicators of CO2 emissions from the tourism industry in China: 1990–2012. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 46, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Carbon tax, tourism CO2 emissions and economic welfare. Ann. Tour. Res. 2018, 69, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.C.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, J. The nexus of water-energy-food in China’s tourism industry. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenghu, Z.; Arif, M.; Shehzad, K.; Ahmad, M.; Oláh, J. Modeling the Dynamic Linkage between Tourism Development, Technological Innovation, Urbanization and Environmental Quality: Provincial Data Analysis of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2021, 18, 8456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mao, Y.; Morrison, A.M. Impacts of Environmental Regulations on Tourism Carbon Emissions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikayilov, J.I.; Mukhtarov, S.; Mammadov, J.; Azizov, M. Re-evaluating the environmental impacts of tourism: Does EKC exist? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 19389–19402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderwood, L.U.; Soshkin, M. The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2019. World Economic Forum, Geneva. 2019, p. 31. Available online: https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TTCR_2019.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Song, M.; Li, H. Estimating the efficiency of a sustainable Chinese tourism industry using bootstrap technology rectification. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2019, 143, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yu, M. Assessing the Environmental Impact and Cost of the Tourism-Induced CO2, NOx, SOx Emission in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhu, B.; Hu, S. Eco-efficiency trends in china, 1978–2010: Decoupling environmental pressure from economic growth. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 24, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S.; Peeters, P.; Ceron, J.; Dubois, G.; Patterson, T.; Richardson, R.B. The eco-effificiency of tourism. Ecol. Econ. 2005, 54, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Y. The perspective of tourism sustainable development: A review of eco-effificiency of tourism. Tour. Trib. 2017, 32, 47–56. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Becken, S.; Frampton, C.; Simmons, D.G. Energy consumption patterns in the accommodation sector: The New Zealand case. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 39, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becken, S.; Patterson, M. Measuring national carbon dioxide emissions from tourism as a key step towards achieving sustainable tourism. J. Sustain. Tour. 2006, 14, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, A.G.; Josiassen, A. Frontier analysis: A state-of-the-art review and meta- analysis. J. Travel Res. 2016, 55, 612–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Fang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhu, F. Tourism eco-efficiency measurement, characteristics, and its influence factors in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrouznejad, A.; Yang, G.L. A survey and analysis of the first 40 years of scholarly literature in DEA: 1978–2016. Soc. Econ. Plann. Sci. 2018, 61, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altin, M.; Koseoglu, M.A.; Yu, X.; Riasi, A. Performance measurement and management research in the hospitality and tourism industry. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 30, 1172–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perch-Nielsen, S.; Sesartic, A.; Stucki, M. The greenhouse gas intensity of the tourism sector: The case of Switzerland. Environ. Sci. Policy 2010, 13, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, M.J. The measurement of productive efficiency. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1957, 120, 253–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision-making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R. An Introduction to Data Envelopment Analysis: A Tool for Performance Measurement; Sage: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sexton, T.R.; Silkman, R.H.; Hogan, A.J. Data envelopment analysis: Critique and extensions. New Dir. Program Eval. 1986, 1986, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantri, J.K. Research Methodology on Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA); Universal-Publishers: Irvine, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C. Evaluation and drive mechanism of tourism ecological security based on the DPSIR-DEA model. Tour. Manag. 2019, 75, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, A.; Calonder, G.P.; Hagedorn, F. Regional CO2 budget, countermeasures and reduction aims for the Alpine tourist region of Davos, Switzerland. Energy Policy 2008, 36, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, T. Climate Change Mitigation: Methods, Greenhouse Gas Reductions and Policies; NHTV: Breda, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Susanne, B. Developing indicators for managing tourism in the face of peak oil. Tour. Manag. 2008, 29, 695–705. [Google Scholar]
- Gossling, S. Carbon Management in Tourism: Mitigating the Impacts on Climate Change; Routledge: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Janet, E.; Dickinson, D.R.; Les, L. Holiday travel discourses and climate change. J. Transp. Geogr. 2010, 18, 482–489. [Google Scholar]
- Aigner, D.; Lovell, C.A.K.; Schmidt, P. Formulation, and estimation of stochastic frontier production function models. J. Econom. 1977, 6, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeusen, W.; Van, D.; Broeck, J. Efficiency estimation from Cobb-douglas production functions with composed error. Int. Econ. Rev. 1977, 18, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reifschneider, D.; Stevenson, R. Systematic departures from the frontier: A framework for the analysis of firm inefficiency. Int. Econ. Rev. 1991, 32, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbhakar, S.C.; Ghosh, S.; McGuckin, J.T. A generalized production frontier approach for estimating determinants of inefficiency in U.S. dairy farms. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 1991, 9, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Battese, G.E.; Coelli, T.J. Frontier production functions, technical efficiency, and panel data: With application to paddy farmers in India. J. Prod. Anal. 1992, 3, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battese, G.E.; Coelli, T.J. A model for technical inefficiency effects in a stochastic frontier production function for panel data. Empir. Econ. 1995, 20, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.J.; Zeng, L.G.; Li, P.L.; Lu, H.Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Li, C.M.; Zheng, M.Y.; Li, H.T.; Yu, Z.Y.; Yuan, D.; et al. China’s transportation sector carbon dioxide emissions efficiency and its influencing factors based on the EBM DEA model with undesirable outputs and spatial Durbin model. Nat. Energy 2022, 238, 121934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedolin, D.; Six, J.; Nemecek, T. Assessing between and within Product Group Variance of Environmental Efficiency of Swiss Agriculture Using Life Cycle Assessment and Data Envelopment Analysis. Agron. J. 2021, 11, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çağlar, O.D. The Turkish Cypriot Municipalities’ Productivity and Performance: An Application of Data Envelopment Analysis and the Tobit Model. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2021, 14, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.Z.; Yu, W.H.; Farouk, A. Regional Variation in the Carbon Dioxide Emission Efficiency of Construction Industry in China: Based on the Three-Stage DEA Model. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2021, 2021, 4021947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, P.; Petersen, N.C. A Procedure for Ranking Efficient Units in Data Envelopment Analysis. Manag. Sci. 1993, 39, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Weng, G.; Li, C. Coupling Coordination and Influencing Factors among Tourism Carbon Emission, Tourism Economic and Tourism Innovation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xia, D.S.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Ba, D.; Zhang, W.B. Research on the Spatial Differentiation and Driving Forces of Eco-Efficiency of Regional Tourism in China. Sustainability 2020, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hou, G.; Huang, Z.; Zhong, Y. Spatial-Temporal Differences and Influencing Factors of Tourism Eco-Efficiency in China’s Three Major Urban Agglomerations Based on the Super-EBM Model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ma, X.; Chen, K. Eco-efficiency measurement and spatial–temporal evolution of forest tourism. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilho, D.; Fuinhas, J.A.; Marques, A.C. The impacts of the tourism sector on the Eco-efficiency of the Latin American and Caribbean countries. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2021, 78, 101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Chen, T.; Yu, S.; Wang, H. Study on spatial-temporal distribution and dynamic evolution of Eco-efficiency in China’s coastal provinces. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 106, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Ecological effificiency management of tourism scenic spots based on carbon footprint analysis. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2020, 15, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Tang, G.; Yan, B.; Xiao, X.; Han, Y. Eco-effificiency and its determinants at a tourism destination: A case study of Huangshan National Park, Tour. Manag. 2017, 60, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.J.; Ding, Z.S.; Li, Z.J.; Zhou, N.X.; Li, X.; Zhang, C. Ecological Welfare and driving factors of tourism in the perspective of ecological efficiency—A case study of Changzhou City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 1944–1955. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; He, H.; Wang, G. Progress, and prospects for tourism footprint research. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Lindgren, B. Productivity changes in Swedish pharamacies 1980-1989: A non-para-metric Malmquist approach. J. Prod. Anal. 1992, 3, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmatov, R.; Fernandez, L.X.L.; Coto, M.P.P. Tourism, hospitality, and DEA: Where do we come from and where do we go? Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 95, 102883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sten, M. Index numbers and indifference surfaces. Trab. Estad. 1953, 4, 202–242. [Google Scholar]
- Capacci, S.; Scorcu, A.E.; Vici, L. Seaside tourism and eco-labels: The economic impact of Blue Flags. Tour. Manag. 2015, 47, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.J.; Li, C.; Peng, H.S.; Zhong, S.E.; Zhang, J.H.; Yu, H. Evaluation and spatial pattern of China’s provincial tourism ecological efficiency under the constraints of energy conservation and emission reduction. Prog. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 40, 1284–1297. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavasileiou, E.F.; Tzouvanas, P. Tourism Carbon Kuznets-Curve Hypothesis: A Systematic Literature Review and a Paradigm Shift to a Corporation-Performance Perspective. J. Travel Res. 2021, 60, 896–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayamba, E.C.; Haibo, C.; Ke, D.; Fangfang, W. The spatial effect of tourism economic development on regional ecological efficiency. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 27, 38241–38258. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, K.; Shahbaz, M.; Loganathan, N.; Raza, S.A. Tourism development, energy consumption and Environmental Kuznets Curve: Trivariate analysis in the panel of developed and developing countries. Tour. Manag. 2016, 54, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Yue, L.; Ahmad, F.; Draz, M.U.; Chandio, A.A. Urban eco-efficiency and its influencing factors in Western China: Fresh evidence from Chinese cities based on the US-SBM. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Dong, S.; Li, Z.; Zhao, M.; Sun, D.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y. Eco-Efficiency and Its Drivers in Tourism Sectors with Respect to Carbon Emissions from the Supply Chain: An Integrated EEIO and DEA Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Hou, G. Analysis on the Spatial-Temporal Evolution Characteristics and Spatial Network Structure of Tourism Eco-Efficiency in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 5, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Yuan, W.; Dai, J.; Tan, T.; He, L. Eco-efficiency, eco-productivity and tourism growth in china: A non-convex metafrontier DEA-based decomposition model. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 28, 663–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Yan, J.X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y. Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Spatial Spillover Effect of Tourism Ecological Efficiency in the Yellow River Valley-Analysis Based on 73 City Data. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 20, 1–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiia, S.S.; Guo, S.F. Ecological Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin: Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors-Based on the Panel Data of 51 Prefecture-level Cities. J. Stat. 2021, 2, 43–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

| Indicator Type | Indicator |
|---|---|
| Input indicator | Number of A-grade and above tourist attractions (counts) |
| Number of star-rated hotels (counts) | |
| Number of travel agencies (counts) | |
| Number of tourism employees (people) | |
| Desirable output indicator | Ratio of total tourism revenue to regional GDP in current-year prices |
| Undesirable output indicator | Tourism carbon emissions (100 tons) |
| Tourism wastewater discharge (10,000 m3) |
| Year | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s index | −0.02 | −0.02 | −0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.01 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Z | 0.11 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.60 | 0.61 | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 1.02 |
| P | 0.46 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.16 |
| Year | High-High Agglomeration | Low-High Agglomeration | Low-Low Agglomeration | High-Low Agglomeration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | Xiamen and Zunyi | Changsha, Chengdu, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Guilin, Hangzhou, Hefei, Kunming, Nanchang, Nanjing, Nanning, Ningbo, Shenzhen, Taizhou, Wuhan, Xi’an, Zhengzhou, and Chongqing | Beijing, Changzhou, Dalian, Harbin, Luoyang, Qingdao, Shanghai, Shenyang, Suzhou, Tianjin, Wuxi, Xuzhou, and Yantai | Huangshan, Sanya, and Zhangjiajie |
| 2015 | Guilin, Sanya, Zhangjiajie, and Zunyi | Changsha, Chengdu, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Hangzhou, Hefei, Kunming, Nanchang, Nanjing, Nanning, Ningbo, Shenzhen, Taizhou, Wuhan, Xi’an, Xiamen, and Chongqing | Beijing, Changzhou, Dalian, Harbin, Luoyang, Nanjing, Ningbo, Qingdao, Shanghai, Shenyang, Suzhou, Tianjin, Wuxi, Xuzhou, Yantai, and Zhengzhou | Huangshan |
| 2019 | Guilin, Sanya, Zhangjiajie, and Zunyi | Changsha, Chengdu, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Kunming, Nanchang, Nanning, Shenzhen, Wuhan, Xi’an, Xiamen, and Chongqing | Beijing, Changzhou, Dalian, Harbin, Hefei, Kunming, Luoyang, Nanjing, Ningbo, Qingdao, Shanghai, Shenyang, Suzhou, Taizhou, Tianjin, Wuxi, Xuzhou, Yantai, and Zhengzhou | Huangshan |
| Variable | Test Type (C, T, K) | LLC | IPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eco-efficiency (TEE) | (C, T, AS) | −13.1805 *** | −1.4568 * |
| Δ Eco-efficiency (ΔTEE) | (C, T, AS) | −11.0157 *** | −8.1261 *** |
| Urbanization (URB) | (C, T, AS) | −10.7293 *** | −3.2082 *** |
| Government intervention (GOV) | (C, T, AS) | −15.4721 *** | −2.0311 ** |
| Contribution of tourism to employment (EMP) | (C, T, AS) | −13.8652 *** | −2.6796 *** |
| Degree of economic openness (OPEN) | (C, T, AS) | −4.2916 *** | −2.8584 *** |
| Level of economic development (PGDP) | (C, T, AS) | −3.6593 *** | −2.7062 *** |
| Method | Statistic | Statistical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Kao | ADF statistic | −4.9398 *** |
| Pedroni | Panel PP statistic | −8.7546 *** |
| Panel DF statistic | −11.9113 *** |
| Eco-Efficiency | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMP | 0.195 *** | 0.185 *** | 0.144 *** | 0.148 *** | 0.090 *** |
| (0.042) | (0.039) | (0.038) | (0.037) | (0.033) | |
| URB | −0.597 *** | −0.832 *** | −0.715 *** | 0.271 | |
| (0.131) | (0.138) | (0.124) | (0.171) | ||
| GOV | −0.175 *** | −0.225 *** | −0.405 *** | ||
| (0.058) | (0.056) | (0.055) | |||
| OPEN | 0.160 *** | 0.064 ** | |||
| (0.027) | (0.028) | ||||
| PGDP | 0.473 *** | ||||
| (0.060) | |||||
| Constant | −0.631 *** | 4.489 *** | 7.253 *** | 6.465 *** | 1.579 |
| (0.176) | (1.137) | (1.328) | (1.209) | (1.269) | |
| Observations | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 |
| R squared | 0.069 | 0.372 | 0.376 | 0.389 | 0.423 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, C.; Muhtar, P.; Xiao, Z. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Tourism Eco-Efficiency in Major Tourist Cities in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13158. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013158
An C, Muhtar P, Xiao Z. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Tourism Eco-Efficiency in Major Tourist Cities in China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(20):13158. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013158
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Chaogao, Polat Muhtar, and Zhenquan Xiao. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Evolution of Tourism Eco-Efficiency in Major Tourist Cities in China" Sustainability 14, no. 20: 13158. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013158
APA StyleAn, C., Muhtar, P., & Xiao, Z. (2022). Spatiotemporal Evolution of Tourism Eco-Efficiency in Major Tourist Cities in China. Sustainability, 14(20), 13158. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013158






