The Practical Experience of “Zero Waste City” Construction in Foshan City Condenses the Chinese Solution to the Sustainable Development Goals
Abstract
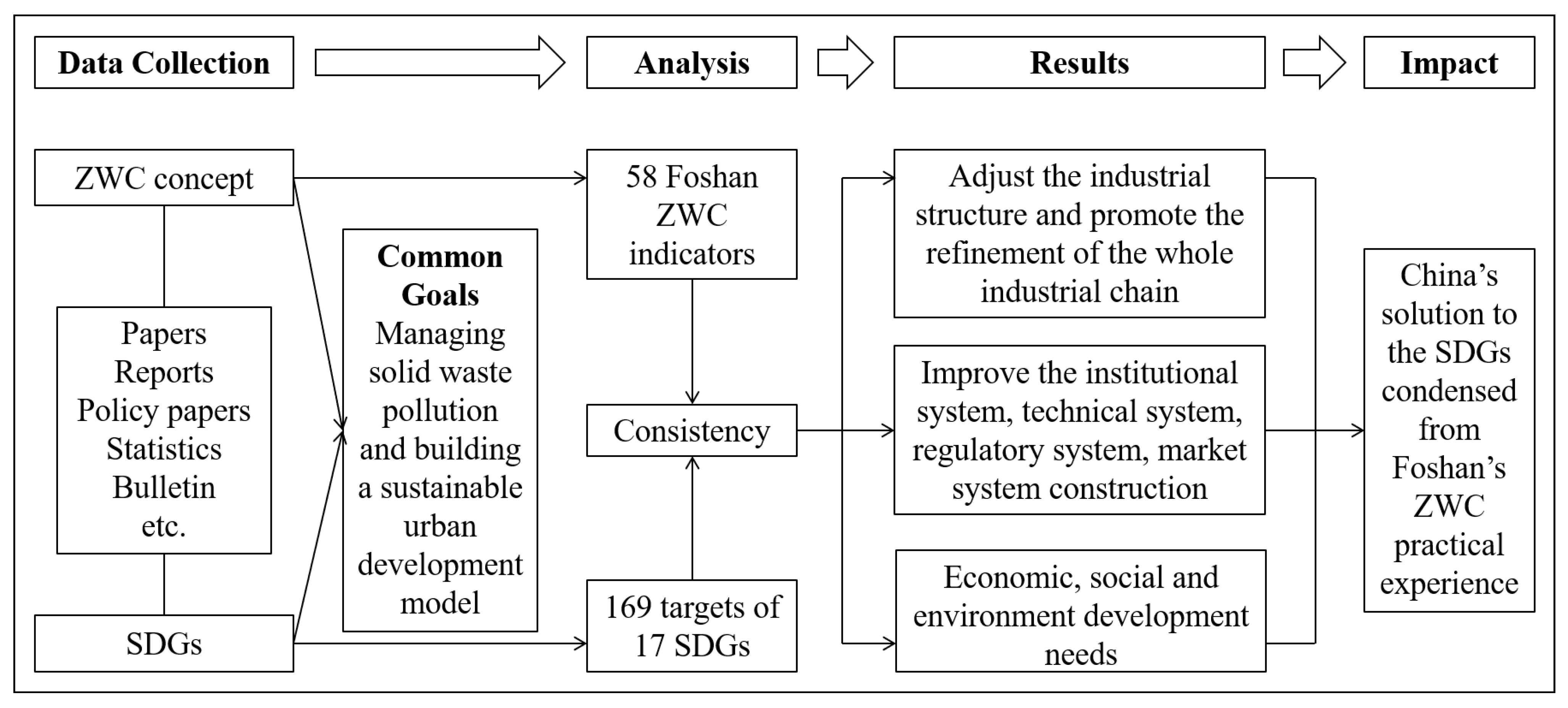
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Foshan ZWC Construction
3.2. Consistency of Foshan ZWC Index System with SDGs
3.3. Adjust the Industrial Structure and Promote the Refinement of the Whole Industrial Chain
3.3.1. Industrial Solid Waste Reduction at the Source and Resource Utilization for SDGs
3.3.2. Source Reduction and Resource Utilization of Domestic Waste for SDGs
3.3.3. Recyclability of Agricultural Solid Waste for SDGs
3.3.4. Hazardous Waste Whole Process Refinement Control to Ensure the Achievement of SDGs
3.4. Improve the Institutional, Technical, Markets, and Regulatory Systems in Various Fields
3.5. Benefits of Foshan City Practical Experience
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Wang, G. Data: Statistics and Trends in Advancing Research Related to the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 993–1000. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. A European Green Deal. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/strategy/priorities-2019-2024/european-green-deal_en#thebenefitsoftheeuropeangreendeal (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Sancino, A.; Stafford, M.; Braga, A.; Budd, L. What can city leaders do for climate change? Insights from the C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group network. Reg. Stud. 2022, 56, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, Y. Progress, problems and countermeasures of promoting construction of “Zero-waste City” in China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2022, 37, 995–1005. [Google Scholar]
- He, J. Global Low-Carbon Transition and China’s Response Strategies. Progress. Inquisitiones De Mutat. Clim. 2016, 12, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Xinhua News Agency. General Office of the State Council Issued the Work Plan of the “Zero-Waste City” Pilot Program in China. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2019-01/21/content_5359705.htm (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Theoretical Study Center Group of the Party Group of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Promote Comprehensive Green Transformation of Economic and Social Development. Available online: https://mee.gov.cn/ywdt/hjywnews/202104/t20210423_830032.shtml (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China. Letter on the Issuance of “Zero Waste City” Construction Pilot Implementation Program Preparation Guide and “Zero Waste City” Construction Index System (for Trial Implementation). Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk06/201905/t20190513_702598.html (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China. Notice on Recommending Candidate Cities for the Construction of “Zero Waste City” during the “14th Five-Year Plan” Period. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk06/202112/t20211231_965776.html (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China. Notice on the Release of the “14th Five-Year” Period “Zero Waste City” Construction List. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk06/202204/t20220425_975920.html (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China. Shenzhen “Zero Waste City” Construction Pilot Highlight Model (as of June 30, 2020). Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/home/ztbd/2020/wfcsjssdgz/sdjz/ldms/202008/t20200825_795084.shtml (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Wang, K. “Three systems” “three through” “three obvious”—Foshan City, hazardous waste third-party governance work to achieve effective. Environment 2021, 12, 58–59. [Google Scholar]
- General Office of the People’s Government of Guangdong Province. General Office of the Guangdong Provincial People’s Government on the Issuance of Guangdong Province to Promote “Zero Waste City” Construction Pilot Work Program Notice. Available online: http://www.gd.gov.cn/zwgk/gongbao/2021/7/content/post_3367126.html (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Office of Foshan Municipal People’s Government of Foshan City. Foshan Municipal People’s Government on the Issuance of the Fourteenth Five-Year Plan for the National Economic and Social Development of Foshan City and the Outline of the 2035 Vision. Available online: http://www.foshan.gov.cn/gkmlpt/content/4/4789/post_4789953.html (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Ni, P. China City Competitiveness Report No.18. Strong Grass to Meet the Blistering Wind: China’s Cities and Property Markets; China Social Sciences Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Huang, S.; Luo, W.; Fan, Z.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, N.; Xia, M.; Zhou, Z. A Review of Coating Organic Solid Waste Treatment & Disposal in Machinery Manufacturing Industry. Environ. Eng. 2020, 38, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Foshan Ecological Environment Bureau. Information on Prevention and Control of Solid Waste Pollution in Foshan City in 2020. Available online: http://sthj.foshan.gov.cn/zwgk/wryjgxx/wrfz/fzgb/content/post_4832826.html (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Office of Foshan Municipal People’s Government of Foshan City. Office of Foshan Municipal People’s Government on the Issuance of Foshan City, “Zero Waste City” Construction Pilot Implementation Program Notice. Available online: http://www.foshan.gov.cn/zwgk/zfgb/rmzfbgswj/content/post_5284702.html (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Whiteman, A.; Webster, M.; Wilson, D.C. The nine development bands: A conceptual framework and global theory for waste and development. Waste Manag. Res. 2021, 39, 1218–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Ren, Z.; Jiao, S.; Hu, H.; Chen, Y. Principles, methods and framework of solid waste classification system in China. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2022, 16, 738–745. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.B.; Miller, T.R.; Liu, G.; Tam, V.W.Y. Construction debris becomes growing concern of growing cities. Waste Manag. 2019, 83, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Wen, Z.G. Mapping the environmental impacts and policy effectiveness of takeaway food industry in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Wen, Z.; Luo, W.; Wang, S. Approaches and Policies to Promote Zero-Waste City Construction: China’s Practices and Lessons. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chen, Y.; Teng, J.; Hu, J.; Xue, N. Generation, Treatment and Supervision Countermeasures and Suggestions for General Industrial Solid Wastes in China. Environ. Eng. 2019, 37, 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Chen, L. Why is China struggling with waste classification? A stakeholder theory perspective. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 183, 106312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China. Annual Report on Environmental Prevention and Control of Solid Waste Pollution in Large and Medium-Sized Cities in 2020. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/gtfwyhxpgl/gtfw/202012/P020201228557295103367.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Ren, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Teng, J.; Qiao, P. Analysis of Influence of Domestic Waste Classification on Development of Waste Incineration Power Generation Industry in China. Environ. Eng. 2021, 39, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.C.S.; Kao, S.Y. Contesting Eco-Urbanism from Below: The Construction of ‘Zero-Waste Neighborhoods’ in Chinese Cities. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2020, 44, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Urban Management and Comprehensive Law Enforcement of Foshan City. Measures of Foshan City for Classified Management of Domestic Waste. Available online: http://fscg.foshan.gov.cn/gkmlpt/content/5/5129/post_5129826.html#1447 (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Bureau of Urban Management and Comprehensive Law Enforcement of Foshan City. The Work Program of Promoting Residential Areas of Domestic Waste Classification Incentive in Foshan City. Available online: http://www.foshan.gov.cn/zwgk/zwdt/bmdt/content/post_5304149.html (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Bureau of Urban Management and Comprehensive Law Enforcement of Foshan City. Foshan City Household Waste Classification Guidance Directory (for Trial Implementation). Available online: http://fscg.foshan.gov.cn/zxgz/ljfl/content/post_5116991.html (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Jiang, Y. Institutional Dilemma of source reduction of municipal solid waste and its solution. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. (Soc. Sci.) 2022, 16, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Ge, Q.; Huhetaoli; Chen, Y.; Cui, L.; Li, B.; Du, X. Constructing a “No-Waste Society”. Strateg. Study CAE 2019, 21, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Rizwan, M.; Saif, Y.; Almansoori, A.; Elkamel, A. Optimal processing route for the utilization and conversion of municipal solid waste into energy and valuable products. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tang, S.; Song, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Research on the Management Mode of Resource Utilization of Construction and Demolition (C&D) Waste—A Case Study of Shenzhen. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2019, 45, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.S.; Zhang, Z.S.; Liu, J.K. Exploring spatial heterogeneity and factors influencing construction and demolition waste in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 53269–53292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingjie, T.; Shiyue, Q.; Jiale, M.; Nana, Z.; Gang, L. Research on the method of zero-waste index: The case study of Zhejiang zero-waste index construction. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2022, 16, 723–731. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, N.; Teng, J.; Chen, Y. Current situation and analysis of agricultural waste management in China. World Environ. 2018, 4, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, J.B.; Zeng, Y.M. Knowledge domain and emerging trends of agricultural waste management in the field of social science: A scientometric review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Council of People’s Republic of China. State Council on the Issuance of the “Fourteenth Five-Year Plan” Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction Comprehensive Work Program of the Notice. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2022-01/24/content_5670202.htm (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China. Notice on Printing and Distributing the Action Plan for Tackling Tough Problems in Agricultural and Rural Pollution Control (2021–2025). Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk03/202201/t20220129_968575.html (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Xiaoqin, J.; Huimin, H.; Jia, J.; Yi, H.; Lizhen, Z.; Jiaming, M.; Hualong, H. Study on information traceability management of the whole process for hazardous waste. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 46, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y. Based on the Pilot Work of“Waste Free City”, Established the Hazardous Waste Management Evaluation System of Automobile Repair Industry. Leather Manuf. Environ. Technol. 2022, 3, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China. Notice on the Issuance of the “14th Five-Year” Period “Zero Waste City” Construction Work Program. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk03/202112/t20211215_964275.html (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Le, N.P.; Nguyen, T.T.P.; Zhu, D.J. Understanding the Stakeholders’ Involvement in Utilizing Municipal Solid Waste in Agriculture through Composting: A Case Study of Hanoi, Vietnam. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Barriga-Fernandez, A.D.; Santibanez-Aguilar, J.E.; Radwan, N.; Napoles-Rivera, F.; El-Halwagi, M.M.; Ponce-Ortega, J.M. Strategic Planning for Managing Municipal Solid Wastes with Consideration of Multiple Stakeholders. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 10744–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petoskey, J.; Stults, M.; Naples, E.; Hardy, G.; Quilici, A.; Byerly, C.; Clark, A.; Newton, D.; Santiago, E.; Teener, J. Envisioning a Circular Economy: The Journey of One Mid-Sized Midwestern City. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. Continuous improvement of environmental quality. China Environ. Superv. 2021, 1, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Huo, H.; Jiang, W.; Ding, H.; Jin, X.; Hu, H. Historical evolution of hazardous waste management in China—From “initial stage of exploration” to “all-round improvement stage”. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. World 2021, 15, 3801–3810. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.; Li, J. Development of Basel Convention and China’ s implementation practice. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 45, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kundariya, N.; Mohanty, S.S.; Varjani, S.; Ngo, H.H.; Wong, J.W.C.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Chang, J.S.; Ng, H.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Bui, X.T. A review on integrated approaches for municipal solid waste for environmental and economical relevance: Monitoring tools, technologies, and strategic innovations. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 125982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Park, S.; Yi, H.; Feiock, R. Evaluating the employment impact of recycling performance in Florida. Waste Manag. 2020, 101, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Feng, R.; Yue, C.; Shao, Y.; Han, J.; Xing, J.; Yang, W. Reinforced urban waste management for resource, energy and environmental benefits: China’s regional potentials. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 178, 106083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Zhao, W. Accelerating the SDGs to kick off the next decade of action and achievement—Accelerating the SDGs to kick off the next decade of action and achievement Achievements. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7788–7791. [Google Scholar]
| Type | General Industrial Solid Waste (Thousand Tons) | Industrial Hazardous Waste (Thousand Tons) | Medical Waste (Thousand Tons) | Electronic Waste (Thousand Units) | Domestic Waste (Thousand Tons) | Municipal Sewage Treatment Plant Sludge (Thousand Tons) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production | 4470.4 | 438.5 | 7.6 | 442.9 | 3885.7 | 271.1 |
| Main types | Fly ash, slag, sludge, and desulfurization gypsum | Incineration disposal residues, phenol-containing waste, refining and distillation residues, waste acids, and surface treatment wastes | - 1 | - | - | - |
| No | Level 1 Indicators | Level 2 Indicators | Level 3 Indicators | Units | Data (By 2020) | 2023 Goals | Related to the UN SDGs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Source reduction of solid waste | Industrial source reduction | Intensity of industrial solid waste generation | ton/CNY 10,000 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 9, 12, 17 | |
| 2 | Intensity of industrial hazardous waste generation | ton/CNY 10,000 | 0.0088 | 0.008 | 9, 12, 17 | |||
| 3 | Percentage of industrial enterprises assessed through cleaner production audit | % | 88 | 95 | 9, 12, 17 | |||
| 4 | Number of green factories | pcs | 31 | 35 | 9, 12, 17 | |||
| 5 | Percentage of industrial parks carrying out ecological industrial park construction, recycling, and green park construction | % | 100 | 100 | 9, 12, 17 | |||
| 6 | Green mine completion rate | % | 83.3 | 100 | 12, 15 | |||
| 7 | Reduction of carbon emission intensity | % | 3.87 | ≥0 | 9, 12, 13, 17 | |||
| 8 | Industrial source reduction | Number of green food and organic agricultural products | pcs | 12 | 16 | 2, 11, 12, 14, 15, 17 | ||
| 9 | Number of standardized demonstration farms for livestock and poultry breeding | pcs | 0 | 20 | 2, 11, 12, 14, 15, 17 | |||
| 10 | Number of “vegetable basket” bases | pcs | 68 | 100 (by2024) | 2, 11, 12, 14, 15, 17 | |||
| 11 | Number of exemplary beautiful fishery construction | / 1 | / | 8 (by 2025) | 2, 11, 12, 14, 15, 17 | |||
| 12 | Construction source reduction | Proportion of green buildings to new buildings | % | 59.21 | 90 | 7, 9, 11 | ||
| 13 | The proportion of assembled buildings to new buildings | % | 20.1 | 30 | 7, 9, 11 | |||
| 14 | Areas of life source reduction | Domestic waste removal volume | 10,000 ton/day | 1.2 | 1.35 | 12 | ||
| 15 | Coverage rate of domestic waste classification in urban residential areas | % | / | 100 | 11, 12 | |||
| 16 | Coverage rate of domestic waste sorting in rural areas | % | / | 100 | 10, 12 | |||
| 17 | Utilization rate of green packaging for express delivery | % | / | 60 | 12, 14 | |||
| 18 | Solid waste resource utilization | ISW resource utilization | General industrial solid waste utilization ratio | % | 86 | 90 | 9, 12, 17 | |
| 19 | Industrial hazardous waste utilization system construction | / | / | Establish a standard system of product for the resource utilization of hazardous waste; promote the construction of relevant comprehensive utilization facilities. | 9, 16, 17 | |||
| 20 | Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial hazardous waste | % | 51.66 | 60 | 6, 9, 12, 17 | |||
| 21 | Utilization of agricultural waste | Comprehensive utilization ratio of straw | % | 95.1 | 96 | 2, 6, 12, 14, 15, 17 | ||
| 22 | Comprehensive utilization ratio of livestock and poultry manure | % | 89.92 | 90 | 2, 6, 12, 14, 15, 17 | |||
| 23 | Coverage rate of pesticide packaging waste and agricultural film recycling system | % | 40 | 100 | 2, 6, 12, 14, 15, 17 | |||
| 24 | Film recovery rate | % | 95.57 | 97 | 2, 6, 12, 14, 15, 17 | |||
| 25 | Pesticide packaging waste recycling rate | % | 15.8 | 30 | 2, 6, 12, 14, 15, 17 | |||
| 26 | Chemical pesticide utilization rate | % | 40.8 | >40% | 2, 6, 12, 14, 15, 17 | |||
| 27 | Chemical fertilizer utilization rate | % | 40.17 | >40% | 2, 6, 12, 14, 15, 17 | |||
| 28 | Utilization of construction waste | Comprehensive utilization ratio of construction waste | % | / | 30 | 6, 12, 14, 15, 17 | ||
| 29 | Utilization of solid waste resources infield of life | Comprehensive utilization ratio of construction waste | % | / | 25 | 2, 6, 7, 12, 14, 15, 17 | ||
| 30 | Growth rate of renewable resource recycling | % | 12.9 | 10 | 6, 8, 12, 17 | |||
| 31 | Recovery rate of recoverable resources in medical and health institutions | % | / | 99 | 3, 12, 14, 15, 17 | |||
| 32 | Coverage of product-based waste recycling systems for automotive power batteries, end-of-life motor vehicles, etc. | % | / | 70 | 6, 8, 12, 17 | |||
| 33 | Final disposal of solid waste | Safe disposal of hazardous waste | Industrial hazardous waste landfill disposal volume decline | % | −198.9 | −22.73 | 8, 9, 11, 12 | |
| 34 | Medical waste collection and disposal system coverage ratio | % | 100 | 100 | 3, 9, 12, 17 | |||
| 35 | Safe disposal of industrial hazardous waste | 10,000 ton | 40.66 | 100 | 8, 9, 11, 12 | |||
| 36 | Social hazardous waste collection and disposal system coverage ratio | % | 100 | 100 | 6, 12, 17 | |||
| 37 | General ISW storage and disposal | General industrial solid waste storage and disposal volume decline | % | 18.6 | 19.8 | 9, 12, 17 | ||
| 38 | Solid waste disposal infield of life | Reduction in sanitary landfill volume of domestic waste | % | 28 | 75 | 9, 12, 17 | ||
| 39 | Incineration capacity of domestic waste treatment ratio | % | 62.5 | 90 | 7, 12, 17 | |||
| 40 | Harmless disposal rate of urban sewage sludge | % | 100 | 100 | 6, 11, 17 | |||
| 41 | Support capacity | Institutional system construction | Local regulations or policy documents for ZWC management | / | / | Develop and revise relevant local regulations and policies | 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 16, 17 | |
| 42 | Coordination mechanism for ZWC management | / | / | Forming a good collaboration mechanism | 6, 11, 16, 17 | |||
| 43 | ZWC construction included in local government performance appraisal | / | / | Put the ZWC construction work into the responsible units of ecological civilization construction assessment content | 6, 11, 16, 17 | |||
| 44 | Number of units carrying out ZWC cells (organs, enterprises and institutions, hotels, shopping centers, markets, communities, villages) | pcs | / | 500 | 4, 6, 11, 13, 16, 17 | |||
| 45 | Market system construction | Total investment in ZWC construction projects | 100 million CYN | / | 112 | 1, 2, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 17 | ||
| 46 | Hazardous waste management unit environmental pollution liability insurance coverage | % | / | 100 | 3, 8, 11, 12, 17 | |||
| 47 | Green industry guidance fund | 100 million CYN | / | 20 | 1, 2, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 17 | |||
| 48 | Technical system construction | Mainly involved in the development of technical standards and norms for the resourcefulness and harmlessness of solid waste | pcs | / | 5 | 9, 16, 17 | ||
| 49 | Solid waste recycling and disposal of key technology processes, equipment development, and transformation of results | / | / | Support the city’s research institutes and enterprises to carry out more than three solid waste recycling, utilization, disposal of key technology processes, equipment development, and transformation of results | 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 17 | |||
| 50 | Build an open network system of hazardous waste collection, storage, and transportation | / | / | More than 60% of the city’s waste production units are through the collection, storage, and transportation network system for collection | 6, 11, 12, 16, 17 | |||
| 51 | Regulatory system construction | Solid waste management information technology supervision | / | / | Completed Foshan ZWC service management platform (Phase II) | 6, 11, 12, 16 | ||
| 52 | Pass rate for standardized management of hazardous waste | Generating units | % | / | 98 | 6, 11, 12, 16 | ||
| Operating Units | % | 100 | 100 | 6, 11, 12, 16 | ||||
| 53 | Solid waste environmental pollution criminal case filing rate | % | 100 | 100 | 11, 12, 16 | |||
| 54 | Solid waste-related letters, complaints, reported cases completion rate | % | 100 | 100 | 11, 12, 16, 17 | |||
| 55 | Coverage of solid waste environmental pollution cases to carry out ecological and environmental damage compensation work | % | 100 | 100 | 11, 12, 16, 17 | |||
| 56 | Masses’ sense of acquisition | Masses’ sense of acquisition | ZWC construction publicity, education, and training popularization rate | % | / | 80 | 4, 5, 6, 11, 13, 16, 17 | |
| 57 | Degree of government, enterprise, institution, and public participation in ZWC construction | % | / | 80 | 16, 17 | |||
| 58 | Public satisfaction with the effectiveness of ZWC construction | / | / | Satisfaction | -2 | |||
| No | UN SDGs | Solid Waste Reduction at Source | Solid Waste Resource Utilization | Solid Waste Final Disposal | Protection Capacity | Public Satisfaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No poverty | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | Zero hunger | 4 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | Good health and well-being | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | Quality education | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | Gender equality | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 6 | Clean water and sanitation | 0 | 12 | 2 | 10 | 1 |
| 7 | Affordable and clean energy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 8 | Decent work and economic growth | 0 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 0 |
| 9 | Industry, innovation and lnfrastructure | 8 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| 10 | Reduced lnequalities | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| 11 | Sustainable cities and communities | 6 | 0 | 3 | 13 | 1 |
| 12 | Responsible consumption and production | 15 | 14 | 7 | 10 | 0 |
| 13 | Climate action | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 14 | Life below water | 5 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15 | Life on land | 5 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 16 | Peace, justice and strong institutions | 0 | 1 | 0 | 11 | 2 |
| 17 | Partnerships for the goals | 10 | 10 | 6 | 12 | 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, T.; She, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Xu, W.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, Z. The Practical Experience of “Zero Waste City” Construction in Foshan City Condenses the Chinese Solution to the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912118
Qin T, She L, Wang Z, Chen L, Xu W, Jiang G, Zhang Z. The Practical Experience of “Zero Waste City” Construction in Foshan City Condenses the Chinese Solution to the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability. 2022; 14(19):12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912118
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Tianyu, Lingling She, Zhaolong Wang, Luosong Chen, Wanyi Xu, Gaoming Jiang, and Zhe Zhang. 2022. "The Practical Experience of “Zero Waste City” Construction in Foshan City Condenses the Chinese Solution to the Sustainable Development Goals" Sustainability 14, no. 19: 12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912118
APA StyleQin, T., She, L., Wang, Z., Chen, L., Xu, W., Jiang, G., & Zhang, Z. (2022). The Practical Experience of “Zero Waste City” Construction in Foshan City Condenses the Chinese Solution to the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability, 14(19), 12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912118






