Application of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Based Tools for Modelling and Enhancing Sustainable Optimization of the Classical/Photo-Fenton Processes for the Landfill Leachate Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Modelling and prediction of the sustainable treatment of landfill leachate performed by c-Fenton and p-Fenton processes via SVR, FFNN, and RBFNN.
- Comparison of the ML-based produced results with the RSM’s outcomes by the different paths; the use of some statistical error metrics, the discussion of some features of simple linear regression analysis, and the creating and interpreting of some visual graphs.
- Investigation of the effects of the oxidation pH, Fe2+ and H2O2 dose, and contact time on both Fenton processes,
- Computational optimizing of the parameters of the treatment of landfill leachate realized by c-Fenton and p-Fenton processes via Genetic Algorithm (GA),
- Evaluation and discussion of the findings as a whole.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Leachate
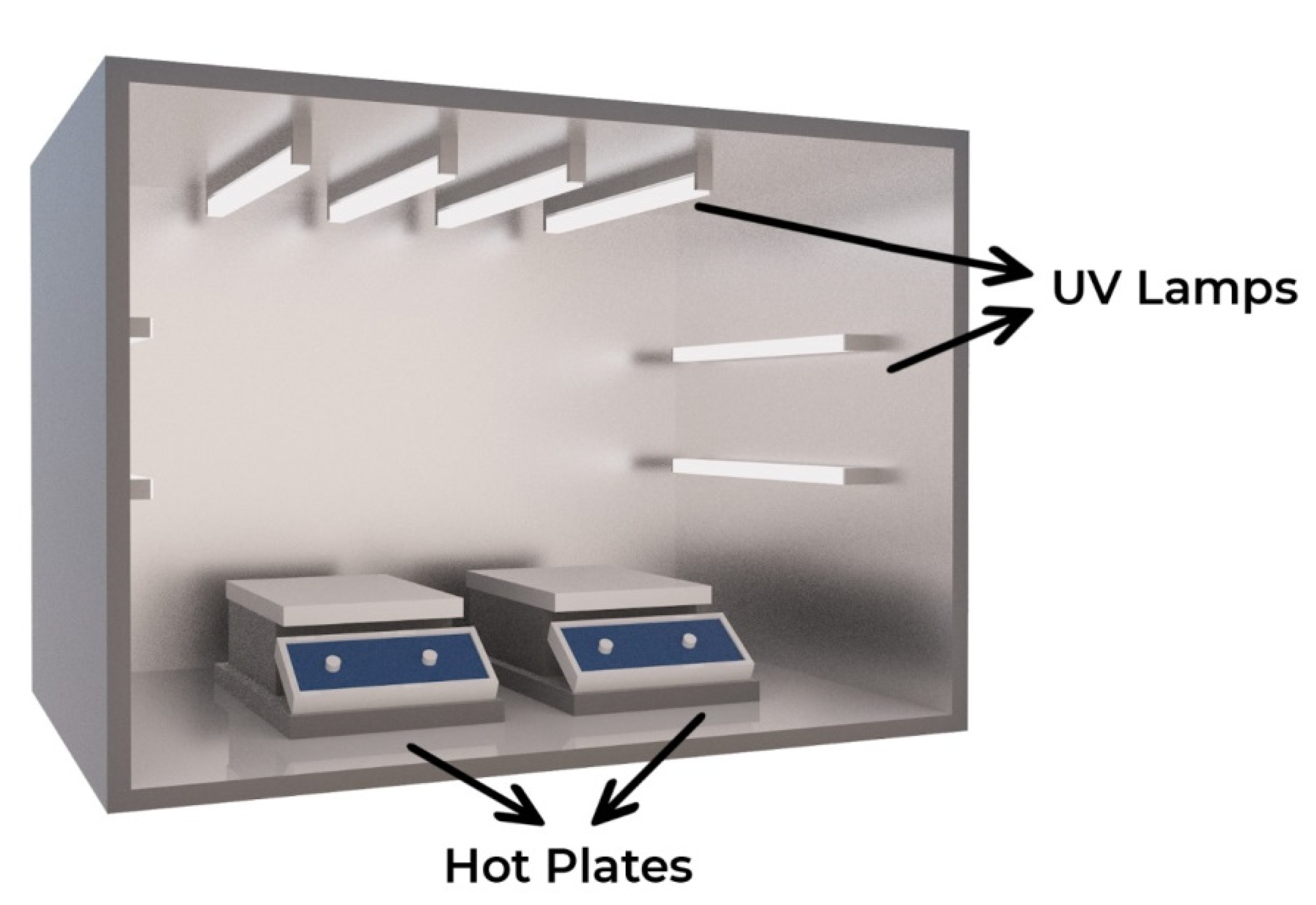
2.2. The Experiment Procedures of the Fenton Processes
2.3. Machine Learning-Based Modelling Methods
2.3.1. Support Vector Regression
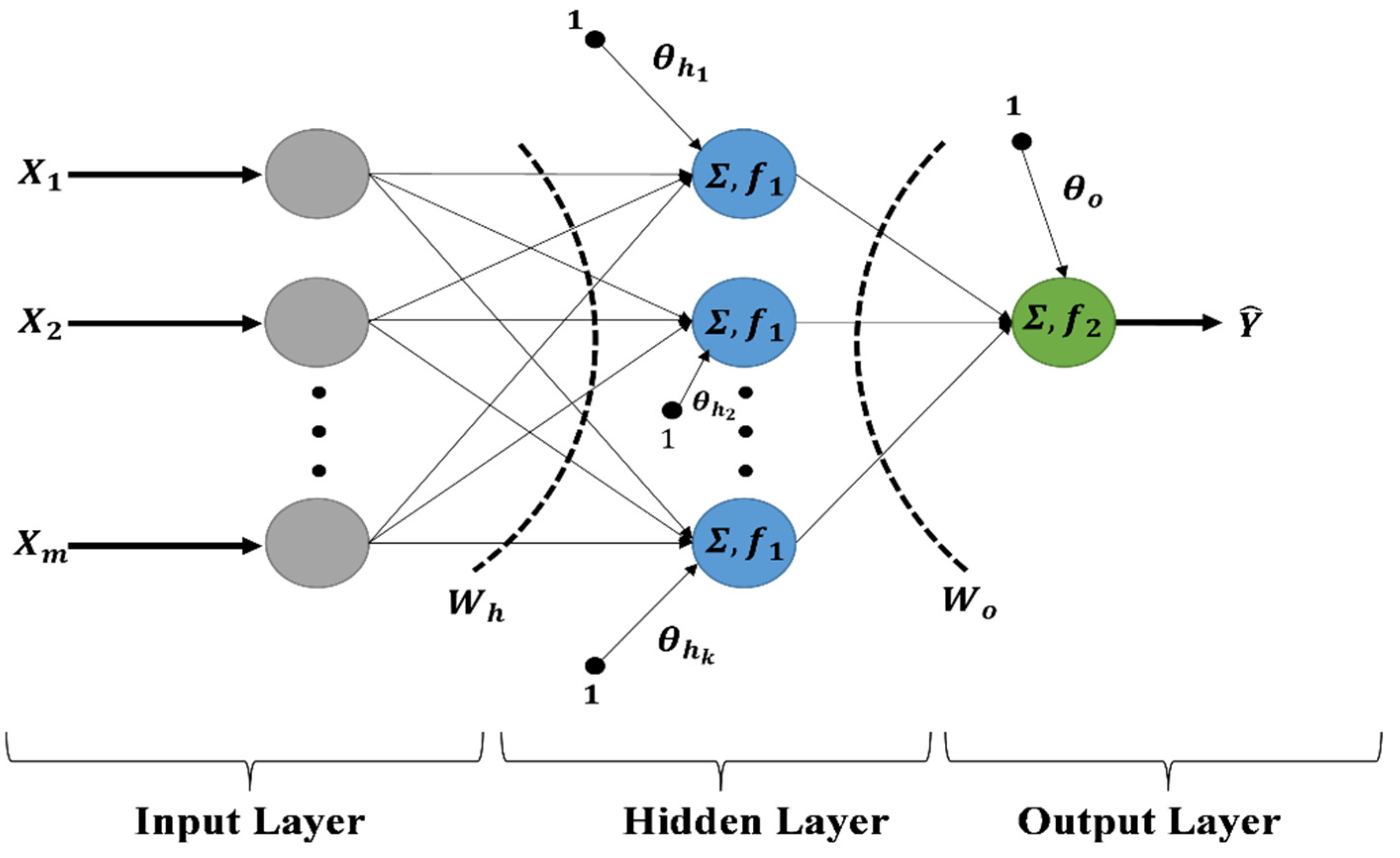
2.3.2. Feed Forward Neural Networks
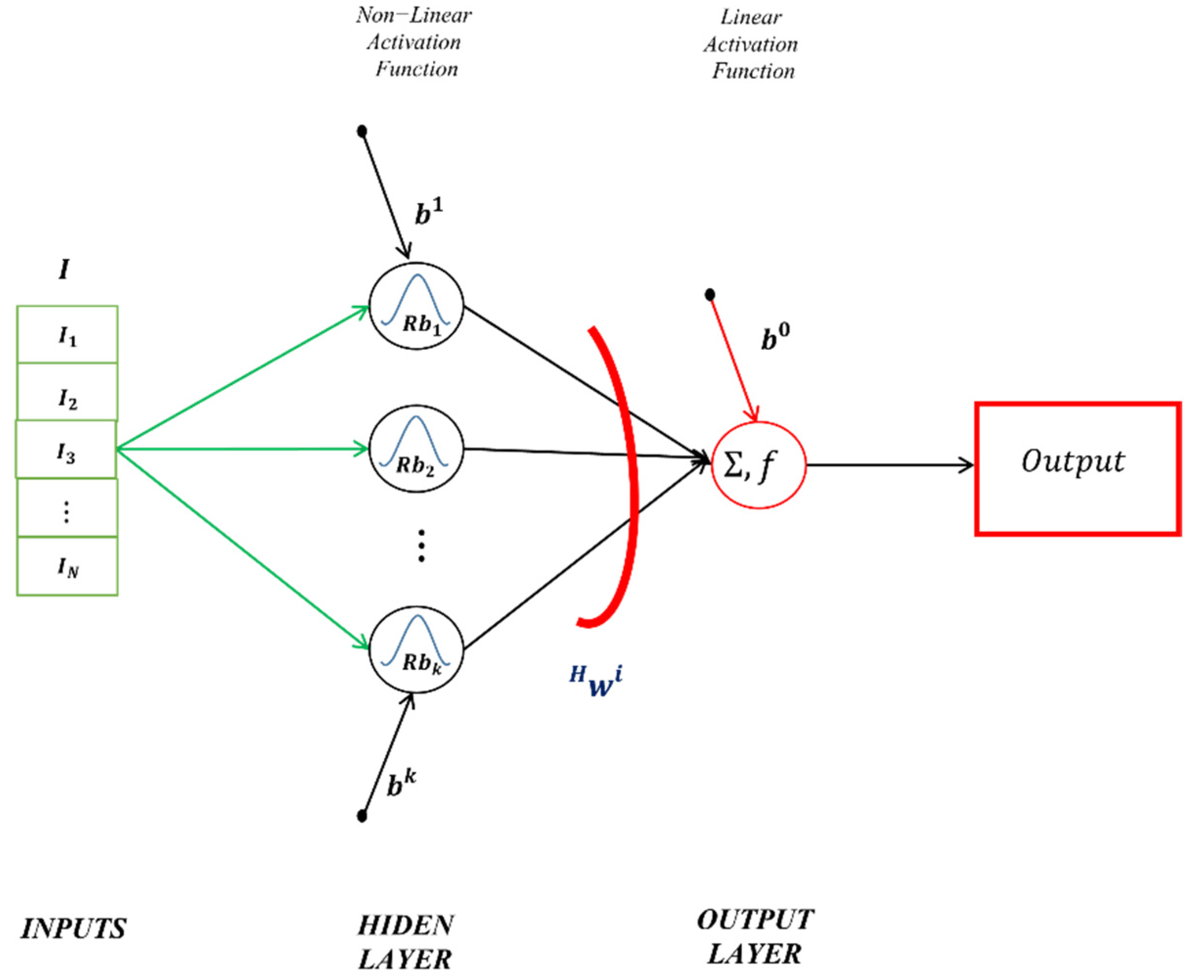
2.3.3. Radial Basis Function Networks
2.4. Modelling the Treatment Process
Evaluation Perspectives
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of the Results in Comparison with the Error Criteria
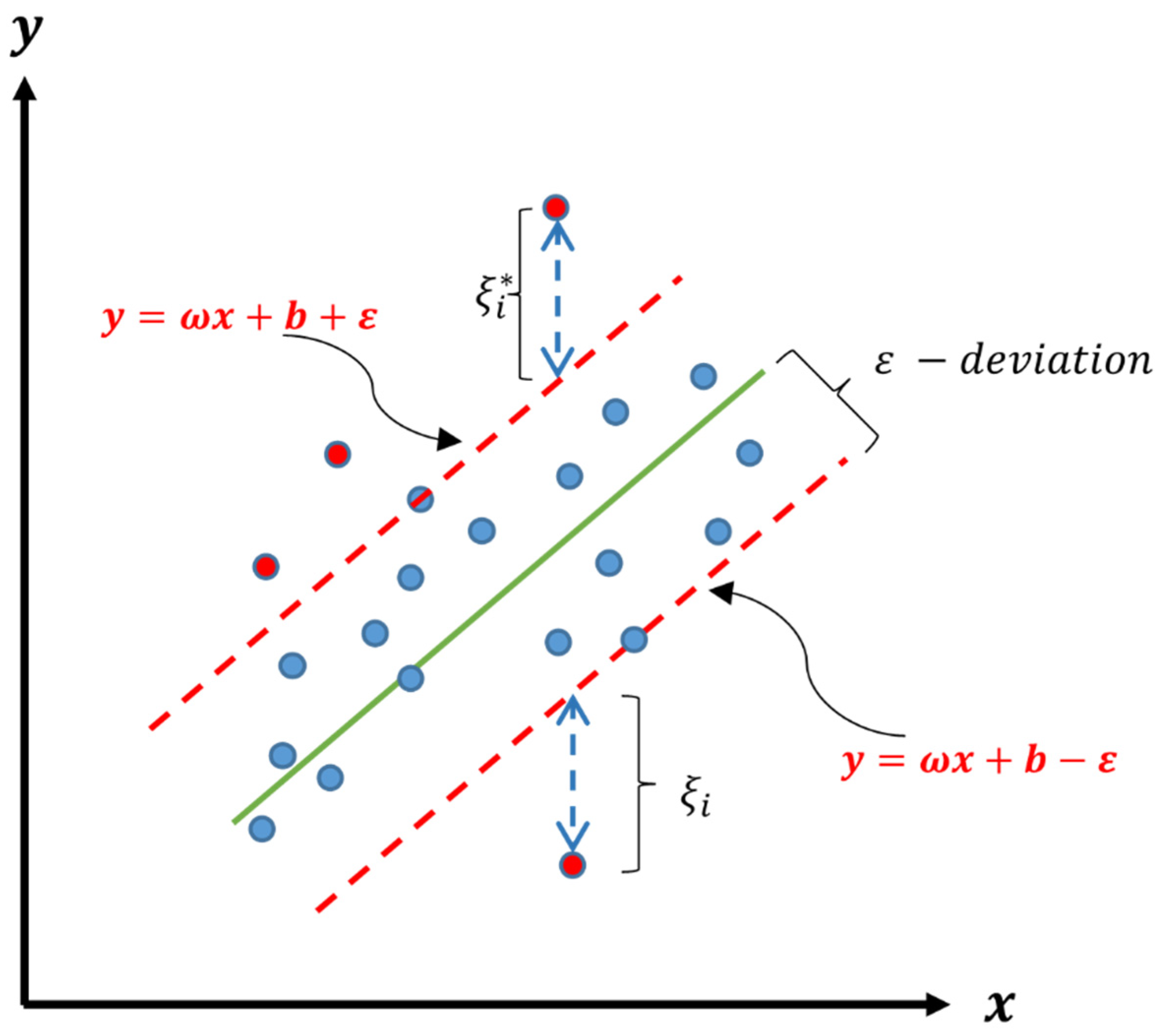
3.2. Examining Model Fit: Regression Analysis and Using Some of Its Features
3.3. Interpreting Some Visuals: Scatter Plots and Some Typical Graphs
3.4. Optimization of the Parameters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaban, A.; Zaki, F.-E.; Afefy, I.H.; Di Gravio, G.; Falegnami, A.; Patriarca, R. An Optimization Model for the Design of a Sustainable Municipal Solid Waste Management System. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejera, J.; Gascó, A.; Hermosilla, D.; Alonso-Gomez, V.; Negro, C.; Blanco, Á. Uva-led technology’s treatment efficiency and cost in a competitive trial applied to the photo-fenton treatment of landfill leachate. Processes 2021, 9, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, Y.; He, D.; Pan, X. Recent advances in municipal landfill leachate: A review focusing on its characteristics, treatment, and toxicity assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshadi, M.A.M.; Bazargan, A.; McKay, G. A review of the application of adsorbents for landfill leachate treatment: Focus on magnetic adsorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 138863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejera, J.; Miranda, R.; Hermosilla, D.; Urra, I.; Negro, C.; Blanco, Á. Treatment of a mature landfill leachate: Comparison between homogeneous and heterogeneous photo-Fenton with different pretreatments. Water 2019, 11, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, E.R.; Silva, E.J.; Lopes, W.S.; do Nascimento, M.R.; Leite, V.D.; de Sousa, J.T. Fenton treatment of sanitary landfill leachate: Optimization of operational parameters, characterization of sludge and toxicology. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 2637–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, F.A.; Yolcu, Ö.C.; Kuleyin, A. A multilayer perceptron-based prediction of ammonium adsorption on zeolite from landfill leachate: Batch and column studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtab, M.S.; Islam, D.T.; Farooqi, I.H. Optimization of the process variables for landfill leachate treatment using Fenton based advanced oxidation technique. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, C.; De Torres-Socías, E.; Peres, J.A.; Maldonado, M.I.; Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Lucas, M.S. Mature landfill leachate treatment by coagulation/flocculation combined with Fenton and solar photo-Fenton processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poblete, R.; Pérez, N. Use of sawdust as pretreatment of photo-Fenton process in the depuration of landfill leachate. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, N.; Dehvari, M.; Alekhamis, G.; Goudarzi, G.; Neisi, A.; Babaei, A.A. Application of electro-Fenton process for treatment of composting plant leachate: Kinetics, operational parameters and modeling. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renou, S.; Givaudan, J.; Poulain, S.; Dirassouyan, F.; Moulin, P. Landfill leachate treatment: Review and opportunity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 468–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zazouli, M.A.; Yousefi, Z.; Eslami, A.; Ardebilian, M.B. Municipal solid waste landfill leachate treatment by fenton, photo-fenton and fenton-like processes: Effect of some variables. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2012, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welter, J.B.; Soares, E.V.; Rotta, E.H.; Seibert, D. Bioassays and Zahn-Wellens test assessment on landfill leachate treated by photo-Fenton process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, O.I.; Jantan, A.; Omolara, A.E.; Dada, K.V.; Mohamed, N.A.; Arshad, H. State-of-the-art in artificial neural network applications: A survey. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyikçi, F.; Kılıç, E.; Çoruh, S.; Elevli, S. Modelling of lead adsorption from industrial sludge leachate on red mud by using RSM and ANN. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Değermenci, N.; Akyol, K. Decolorization of the Reactive Blue 19 from aqueous solutions with the Fenton oxidation process and modeling with deep neural networks. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, M.; Tahroudi, M.N.; Ye, F.; Dutta, J. Prediction of heterogeneous Fenton process in treatment of melanoidin-containing wastewater using data-based models. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, A.; Najafpoor, A.A.; Navaei, A.A.; Zhou, J.L.; Altaee, A.; Ramezanian, N.; Dehghan, A.; Bao, T.; Yazdani, M. Improving Formaldehyde Removal from Water and Wastewater by Fenton, Photo-Fenton and Ozonation/Fenton Processes through Optimization and Modeling. Water 2021, 13, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cüce, H.; Temel, F.A.; Yolcu, O.C. Modelling and optimization of Fenton processes through neural network and genetic algorithm. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 38, 2265–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanafin, Y.N.; Makhatova, A.; Zarikas, V.; Arkhangelsky, E.; Poulopoulos, S.G. Photo-Fenton-like treatment of municipal wastewater. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.K.; Santana, R.M.; de Moraes, N.F.; Júnior, S.G.S.; de Lucena, A.L.; Zaidan, L.E.; Elihimas, D.R.; Napoleao, D.C. Treatment of direct black 22 azo dye in led reactor using ferrous sulfate and iron waste for Fenton process: Reaction kinetics, toxicity and degradation prediction by artificial neural networks. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varank, G.; Yazici Guvenc, S.; Dincer, K.; Demir, A. Concentrated leachate treatment by electro-fenton and electro-persulfate processes using central composite design. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2020, 14, 439–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Mirza, S.A.; Keating, C.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Ali, S.; Campos, L.C. Machine Learning Approach to Predict Quality Parameters for Bacterial Consortium-Treated Hospital Wastewater and Phytotoxicity Assessment on Radish, Cauliflower, Hot Pepper, Rice and Wheat Crops. Water 2022, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglarijoo, N.; Mirbagheri, S.A.; Bagheri, M.; Ehteshami, M. Assessment of effective parameters in landfill leachate treatment and optimization of the process using neural network, genetic algorithm and response surface methodology. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 106, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thind, P.S.; John, S. Optimizing the Fenton based pre-treatment of landfill leachate using response surface methodology. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2020, 42, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jia, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, R. Multivariate optimization of the electrochemical degradation for COD and TN removal from wastewater: An inverse computation machine learning approach. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Franco, G.; Santurro, M. Machine learning, artificial neural networks and social research. Qual. Quant. 2021, 55, 1007–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolcu, O.C.; Temel, F.A.; Kuleyin, A. New hybrid predictive modeling principles for ammonium adsorption: The combination of Response Surface Methodology with feed-forward and Elman-Recurrent Neural Networks. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, H.; Burges, C.J.; Kaufman, L.; Smola, A.; Vapnik, V. Support vector regression machines. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1996, 9, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Babbar, N.; Kumar, A.; Verma, V.K. Crop management: Wheat yield prediction and disease detection using an intelligent predictive algorithms and metrological parameters. In Deep Learning for Sustainable Agriculture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 273–295. [Google Scholar]
- Helman, D.; Lensky, I.M.; Bonfil, D.J. Early prediction of wheat grain yield production from root-zone soil water content at heading using Crop RS-Met. Field Crops Res. 2019, 232, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werbos, P.J. The Roots of Backpropagation: From Ordered Derivatives to Neural Networks and Political Forecasting; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation; California University San Diego La Jolla Institute for Cognitive Science: San Diego, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifahmadian, A. Numerical Models for Submerged Breakwaters: Coastal Hydrodynamics and Morphodynamics; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; Mirjalili, S. Evolving radial basis function networks using moth–flame optimizer. In Handbook of Neural Computation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 537–550. [Google Scholar]
- Hamedi, S.; Kordrostami, Z.; Yadollahi, A. Artificial neural network approaches for modeling absorption spectrum of nanowire solar cells. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 8985–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, A.; Zhang, L. Application of radial basis function networks for solar-array modelling and maximum power-point prediction. IEE Proc.-Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2000, 147, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.-C.; Jeng, J.-T.; Lin, P.-T. Annealing robust radial basis function networks for function approximation with outliers. Neurocomputing 2004, 56, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslahati Roudi, A.; Chelliapan, S.; Wan Mohtar, W.H.M.; Kamyab, H. Prediction and optimization of the fenton process for the treatment of landfill leachate using an artificial neural network. Water 2018, 10, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Sabour, M.R. Multi-response optimization of Fenton process for applicability assessment in landfill leachate treatment. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2528–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| COD (mg L−1) | 4671 |
| pH | 6.9 |
| Electrical conductivity (µS cm−1) | 6200 |
| Ortho-phosphate (mg L−1 PO4−2) | 9.6 |
| Sulfate (mg L−1 SO4−2) | 478 |
| Expr. No | Treatment Process | Independent Variables | Fixed Variables | The # of Data Set |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | c-Fenton | A. pH (2–7) | 1. Temperature/23 ± 2°C 2. Fast/slow mixing speed/400–90 rpm 3. Fe(II)/H2O2 = (300/2000) mg/L dose 4. Process duration/60 min | Training—2 Validation—2 Testing—2 |
| 2 | p-Fenton | A. pH (2–7) | 1. Temperature/23 ± 2°C 2. Fast/slow mixing speed/400–90 rpm 3. Fe(II)/H2O2 = (300/2000) mg/L dose 4. Process duration /60 min 5. Light intensity/8 lamps/64 Watt | Training—2 Validation—2 Testing—2 |
| 3 | c-Fenton | A. Fe (II) dose (50–400 mg/L) B. H2O2 dose (1000, 2000 mg/L) | 1. pH/3 ± 0.2 2. Temperature/23 ± 2°C 3. Fast/slow mixing speed/400–90 rpm | Training—8 Validation—4 Testing—4 |
| 4 | p-Fenton | A. Fe (II) dose (50–400 mg/L) B. H2O2 (1000, 2000 mg/L) | 1. pH/3 ± 0.2 2. Temperature/23 ± 2°C 3. Fast/slow mixing speed/400–90 rpm 4. Light intensity/8 lamps/64 Watt | Training—8 Validation—4 Testing—4 |
| 5 | c-Fenton | A. H2O2 dose (100–3000 mg/L) B. Fe (II) dose (150, 300, 400 mg/L) | 1. pH/3 ± 0.2 2. Temperature/23 ± 2°C 3. Fast/slow mixing speed/400–90 rpm | Training—31 Validation—10 Testing—10 |
| 6 | p-Fenton | A. H2O2 dose (100–3000 mg/L) B. Fe (II) dose (100, 125, 300 mg/L) | 1. pH/3 ± 0.2 2. Temperature/23 ± 2°C 3. Fast/slow mixing speed/400–90 rpm 4. Light intensity/8 lamps/64 Watt | Training—31 Validation—10 Testing—10 |
| 7 | c-Fenton | A. Contact time (0–60 min) B. H2O2 (500, 1000 mg/L) | 1. Temperature/23 ± 2°C 2. Fast/slow mixing speed/400–90 rpm 3. Fe(II) dose/300 mg/L 4. Light intensity/8 lamps/64 Watt | Training—8 Validation—4 Testing—4 |
| 8 | p-Fenton | A. Contact time (0–60 min) B. Fe(II) dose (125, 300 mg/L) C. H2O2 dose (400, 1000 mg/L) | 1. Temperature/23 ± 2°C 2. Fast/slow mixing speed/400–90 rpm 3. Light intensity/8 lamps/64 Watt | Training—8 Validation—4 Testing—4 |
| 9 | p-Fenton | A. Light intensity (16–64 Watt) B. Number of UV lamps (2–8) | 1. pH/3 ± 0.2 2. Temperature/23 ± 2°C 3. Fast/slow mixing speed/400–90 rpm 4. Fe/H2O2 rate/(300/1000) | Training—2 Validation—2 Testing—2 |
| 10 | p-Fenton | A. Light intensity (16–64 Watt) B. Number of UV lamps (2–8) | 1. pH/3 ± 0.2 2. Temperature/23 ± 2°C 3. Fast/slow mixing speed/400–90 rpm 4. Fe/H2O2 rate/(125/400) | Training—2 Validation—2 Testing—2 |
| Exp. No | 95% Confidence Interval of β | R2 % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||
| 1 | 0.978643 | 1.016869 | 99.9722 | |
| 2 | 0.976662 | 1.010421 | 99.9782 | |
| 3 | 0.990734 | 1.012538 | 99.9609 | |
| 4 | 0.981088 | 1.023909 | 99.8496 | |
| 5 | 0.992655 | 1.006016 | 99.9446 | |
| 6 | 0.986571 | 1.011369 | 98.8094 | |
| 7 | 0.989394 | 1.005151 | 99.9793 | |
| 8 | 0.995374 | 1.009528 | 99.9835 | |
| 9 | 0.979712 | 1.011710 | 99.9804 | |
| 10 | 0.982863 | 1.039267 | 99.9412 | |
| Exp. No | Process | Constraints | Optimal Values | Desired Values (Max Obs. of Expr.) | Objective Function Values | Desirability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z1 | c-Fenton | 3.0000 | 56.7926 | 56.7929 | 100.00% | |
| 2 | p-Fenton | 3.0002 | 58.4413 | 58.4420 | 100.00% | |
| 3 | c-Fenton | 222.6556 1002.5186 | 58.1045 | 58.1055 | 100.00% | |
| 4 | p-Fenton | 110.58628 1000.0000 | 81.7062 | 81.7072 | 100.00% | |
| 5 | c-Fenton | 1117.6526 150.0000 | 62.6541 | 62.6539 | 99.99% | |
| 6 | p-Fenton | 2844.3457 192.3732 | 82.2726 | 82.2721 | 99.99% | |
| 7 | c-Fenton | 36.4969 500.6874 | 63.7555 | 63.7565 | 100.00% | |
| 8 | p-Fenton | 50.9427 624.8495 290.3516 | 85.0166 | 85.0176 | 100.00% | |
| 9 | p-Fenton | 63.8444 8 | 89.0204 | 89.0215 | 100.00% | |
| 10 | p-Fenton | 52.8736 7 | 62.9911 | 62.9921 | 100.00% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cüce, H.; Özçelik, D. Application of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Based Tools for Modelling and Enhancing Sustainable Optimization of the Classical/Photo-Fenton Processes for the Landfill Leachate Treatment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11261. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811261
Cüce H, Özçelik D. Application of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Based Tools for Modelling and Enhancing Sustainable Optimization of the Classical/Photo-Fenton Processes for the Landfill Leachate Treatment. Sustainability. 2022; 14(18):11261. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811261
Chicago/Turabian StyleCüce, Hüseyin, and Duygu Özçelik. 2022. "Application of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Based Tools for Modelling and Enhancing Sustainable Optimization of the Classical/Photo-Fenton Processes for the Landfill Leachate Treatment" Sustainability 14, no. 18: 11261. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811261
APA StyleCüce, H., & Özçelik, D. (2022). Application of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Based Tools for Modelling and Enhancing Sustainable Optimization of the Classical/Photo-Fenton Processes for the Landfill Leachate Treatment. Sustainability, 14(18), 11261. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811261







