Decomposition of Rapeseed Green Manure and Its Effect on Soil under Two Residue Return Levels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
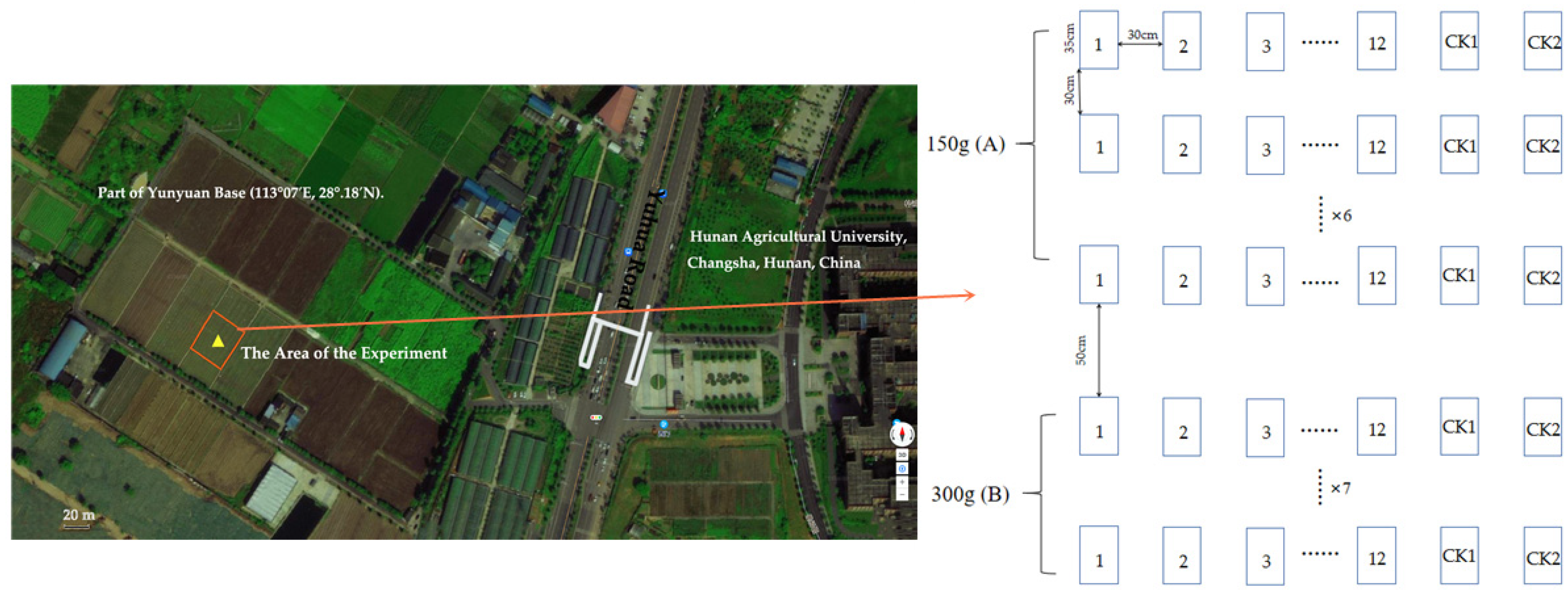
2.1. Overview of the Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Test Methods and Data Analysis
3. Results
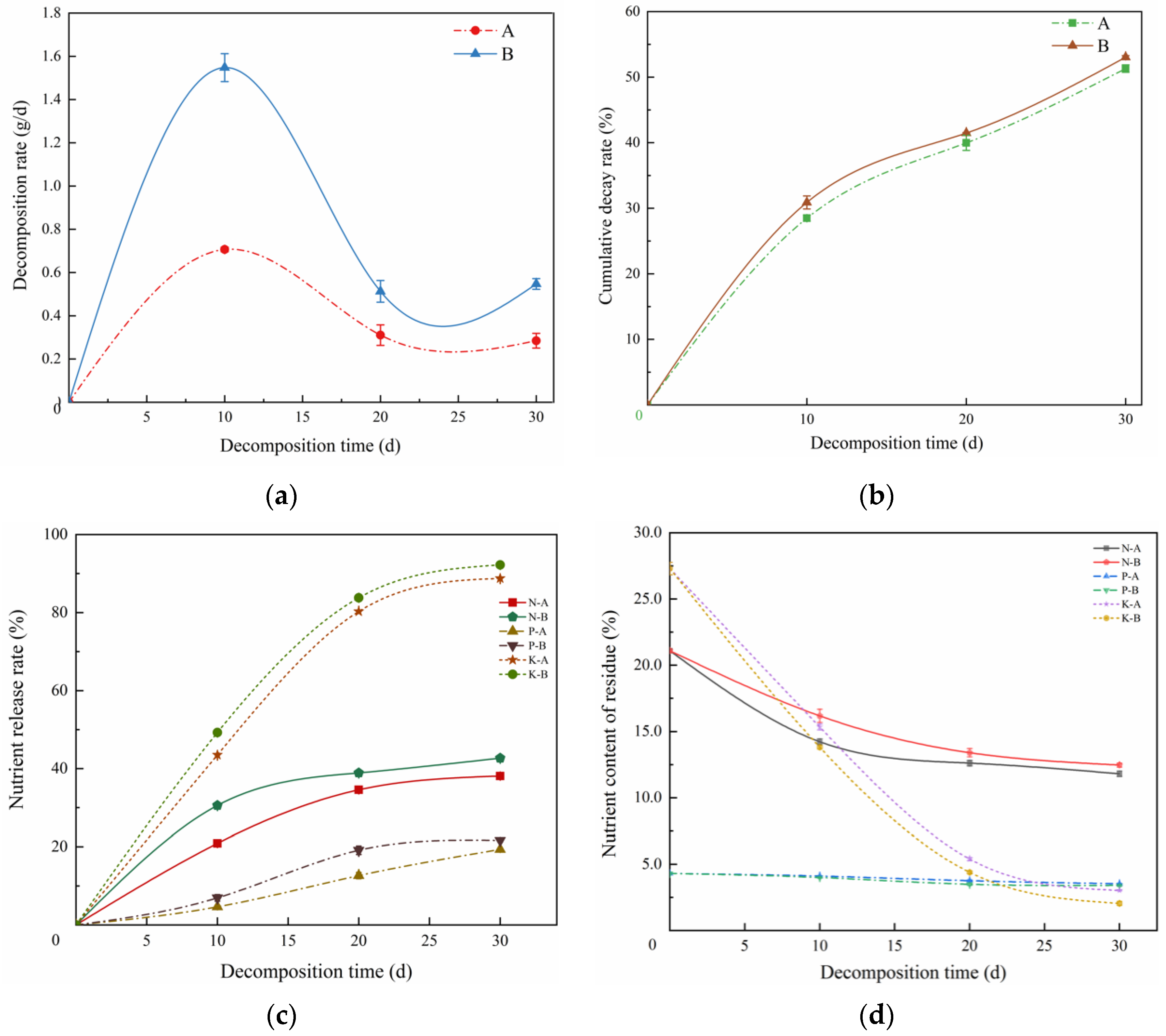
3.1. Plant Decomposition and Its Effect on Soil Nutrients under Two Residue Return Levels
3.1.1. Plant Decomposition under Two Residue Return Levels
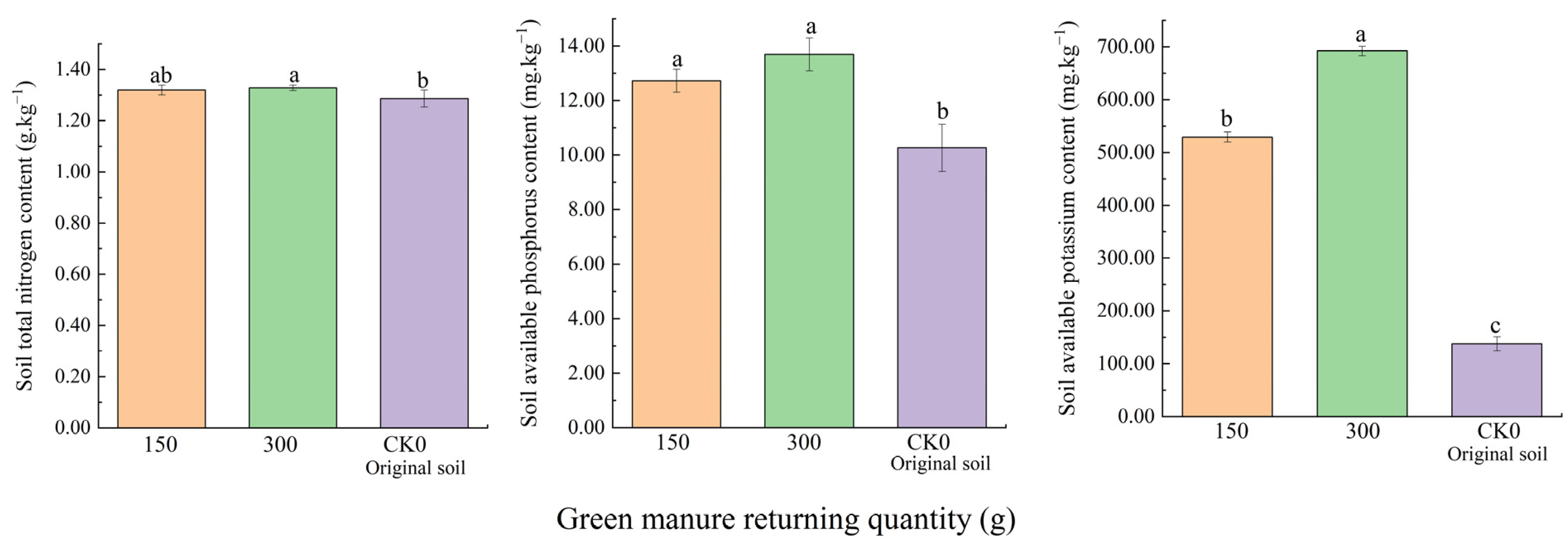
3.1.2. The Effect on Soil Nutrients under Two Residue Return Levels
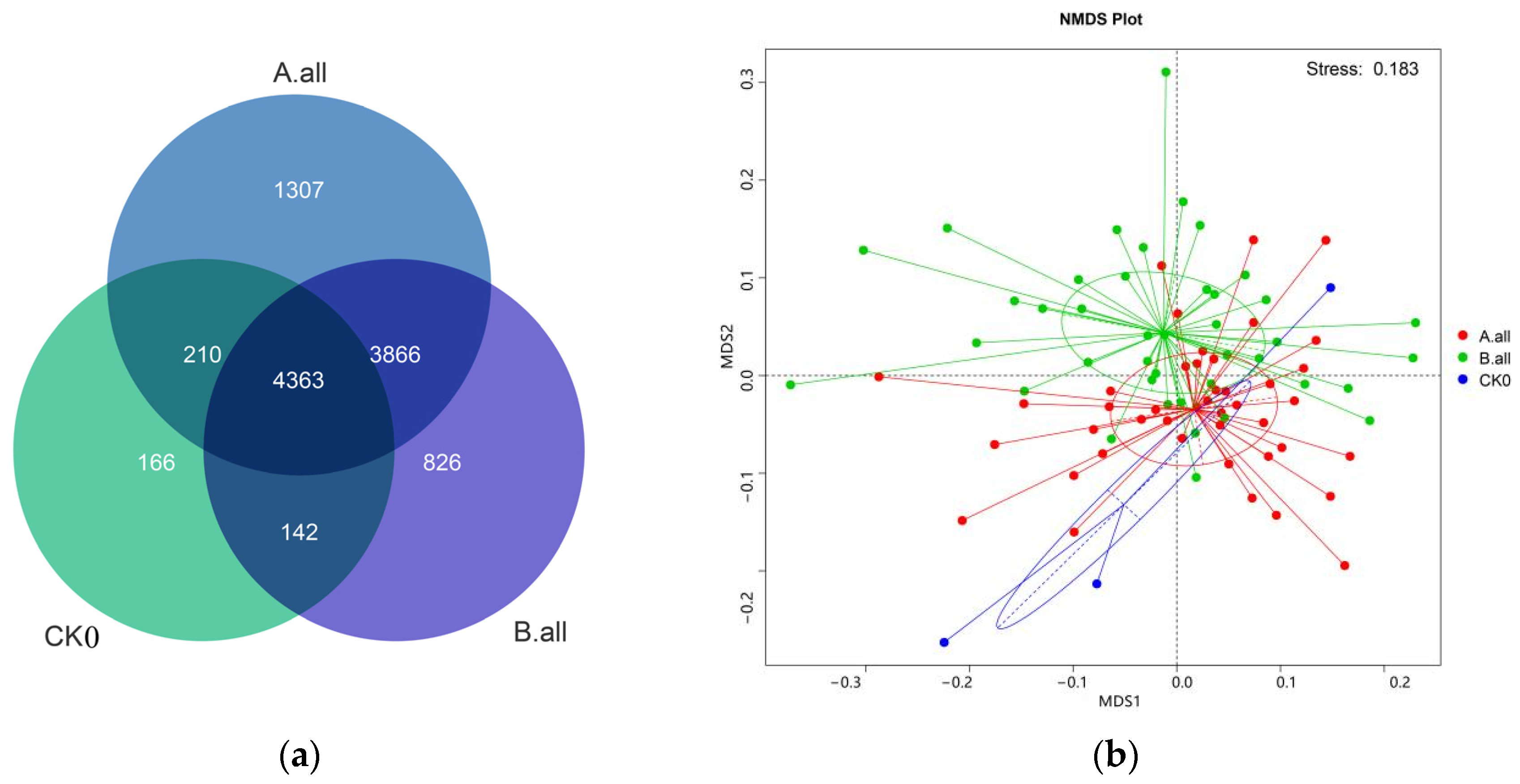
3.2. The Effect on Soil Microorganisms under Two Residue Return Levels
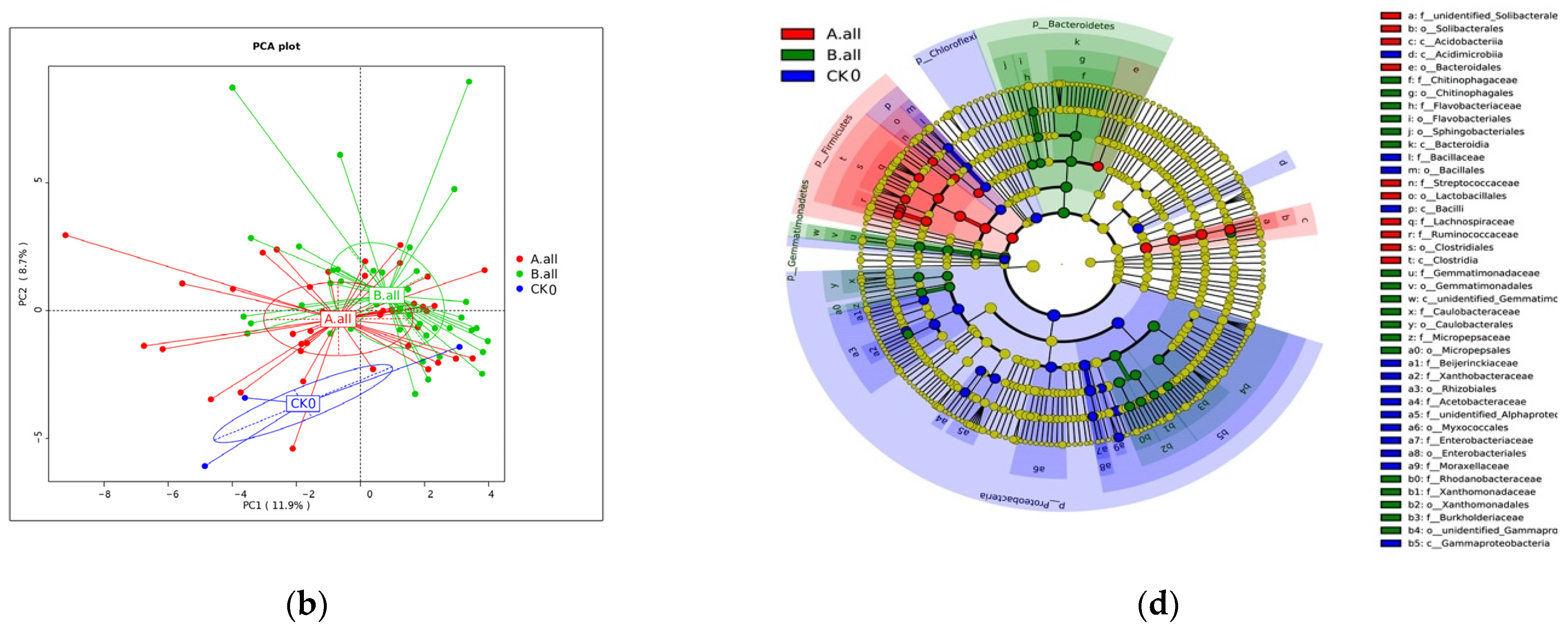
3.2.1. The Effect on Soil Bacterial Community Diversity
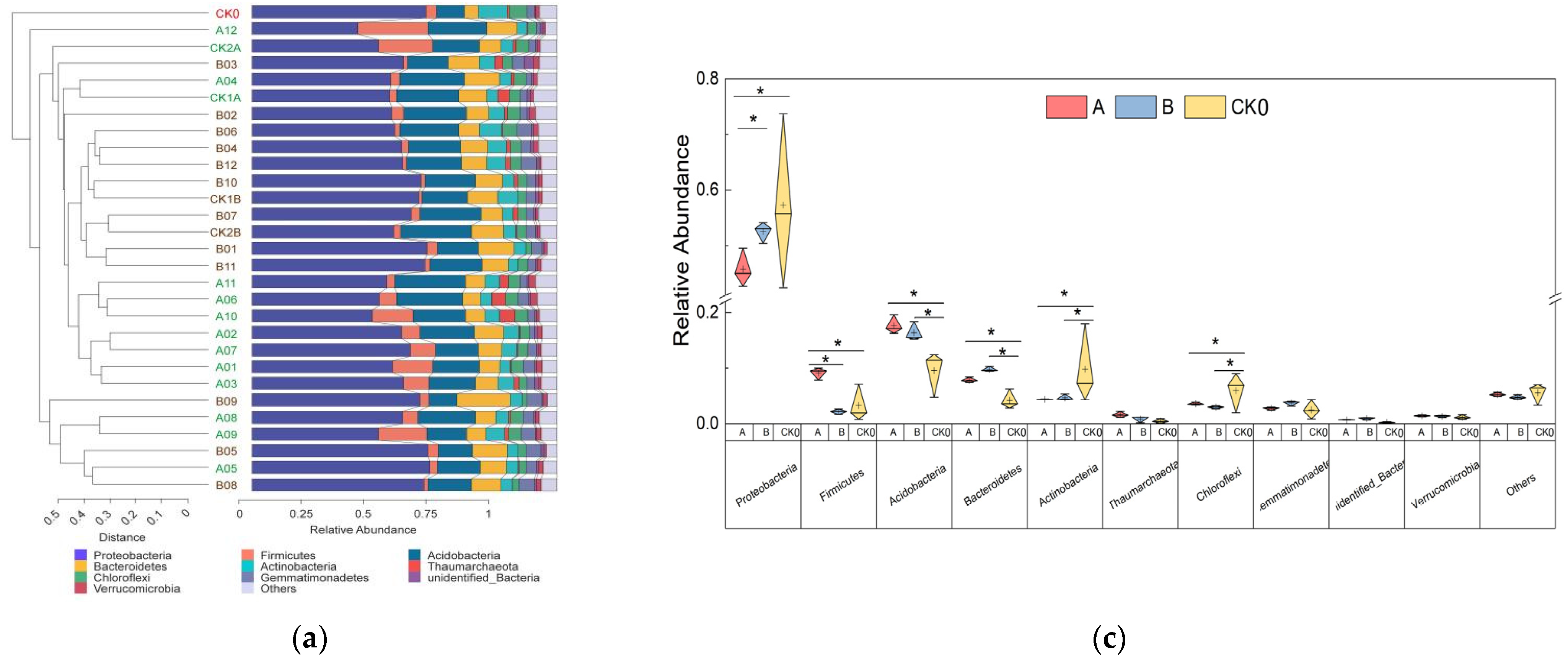
3.2.2. The Effect of Soil Bacterial Content at the Phylum Level
3.2.3. The Effect of Soil Bacterial Content and Function at the Genus Level
3.3. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook 2021; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Delang, C.O. The consenquences of soil degradation in China: A review. Geoscape 2018, 12, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntakirutimana, L.; Li, F.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Yin, C. Green manure planting incentive measures of local authorities and farmers’ perceptions of the utilization of rotation fallow for sustainable agriculture in Guangxi, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahalvi, H.N.; Rafiya, L.; Rashid, S.; Nisar, B.; Kamili, A.N. Chemical fertilizers and their impact on soil health. In Microbiota and Biofertilizers; Dar, G.H., Bhat, R.A., Mehmood, M.A., Hakeem, K.R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 2, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Zheng, X.C.; Wei, X.C.; Zhang, K.; Xu, Y. Excessive application of chemical fertilizer and organophosphorus pesticides induced total phosphorus loss from planting causing surface water eutrophication. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walling, E.; Vaneeckhaute, C. Greenhouse gas emissions from inorganic and organic fertilizer production and use: A review of emission factors and their variability. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 276, 111211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Shao, C.; He, R.; Shi, R. Evolution and efficiency assessment of pesticide and fertiliser inputs to cultivated land in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.B.; Ali, A.; Prasad, M.; Yadav, A.; Shrivastav, P.; Goyal, D.; Dantu, P.K. Role of organic fertilizers in improving soil fertility. In Contaminants in Agriculture; Naeem, M., Ansari, A., Gill, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.J.; Zhang, D.Q.; Song, Z.X.; Ren, L.R.; Jin, X.; Fang, W.S.; Yan, D.D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.X.; Cao, A.C. Organic fertilizer activates soil beneficial microorganisms to promote strawberry growth and soil health after fumigation. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 295, 118653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, S. The principal role of organic fertilizer on soil properties and agricultural productivity—A review. Agric. Res. Tech. Open Access J. 2019, 22, 556192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, X.L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.L.; Jiang, R.F.; Feng, G.; Liu, X.J.; Zuo, Y.M.; Yuan, H.M.; et al. Field management practices drive ecosystem multifunctionality in a smallholder-dominated agricultural system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 313, 107389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Pak, H.; Yan, T.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Wu, D.; Jiang, L. Genome-wide association study reveals a patatin-like lipase relating to the reduction of seed oil content in Brassica napus. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.R.; Chen, W.J.; Yu, X.Z.; Wang, H.; Ren, J.R.; Zhang, Y.W. Effectiveness of health benifit of double-low rapeseed oil and its high oil content breeding. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2016, 38, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, X.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, F.; Liu, N.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Tan, B.; Chen, J.; et al. Rapeseed meal and its application in pig diet: A review. Agriculture 2022, 12, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Wang, J.P.; Zeng, Q.F.; Ding, X.M.; Bai, S.P.; Peng, H.W.; Xuan, Y.; Zhang, K.Y. Effects of rapeseed meal on laying performance and egg quality in laying ducks. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.H.; Jiang, L.Y.; Mason, A.S.; Xiao, M.L.; Zhu, L.R.; Li, L.Z.; Zhou, Q.H.; Shen, C.J.; Huang, C.H. Research progress and strategies for multifunctional rapeseed: A case study of China. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Lin, T.; Wang, G.; Peng, J.; Su, S. The in vitro and in vivo wound-healing effects of royal jelly derived from Apis mellifera L. during blossom seasons of Castanea mollissima Bl. and Brassica napus L. in South China exhibited distinct patterns. BMC Complementary Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.W.; Golden, A.M.; Auld, D.L.; Sumner, D.R. Effects of rapeseed and vetch as green manure crops and fallow on nematodes and soil-borne pathogens. J. Nematol. 1992, 24, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeromela, A.M.; Mikić, A.M.; Vujić, S.; Ćupina, B.; Krstić, Đ.; Dimitrijević, A.; Vasiljević, S.; Mihailović, V.; Cvejić, S.; Miladinović, D. Potential of legume–brassica intercrops for forage production and green manure: Encouragements from a temperate southeast european environment. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haramoto, E.; Gallandt, E. Brassica cover cropping for weed management: A review. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2004, 19, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J.; Eugui, D.; Velasco, P. Natural control of plant pathogens through glucosinolates: An effective strategy against fungi and oomycetes. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Clements, D.R.; Yang, S.; Wen, L.; Zhang, F.; Dong, L. Effects of various nitrogen regimes on the ability of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) to suppress littleseed canarygrass (Phalaris minor Retz.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.; Li, J.; Lu, J.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Fahad, S.; Li, X. Effects of fertilization on crop production and nutrient-supplying capacity under rice-oilseed rape rotation system. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, Y.; Liao, J.; Luo, L.; Ji, S.; Li, J.; Dai, K.; Zhu, S.; Yang, M. Tobacco rotated with rapeseed for soil-borne phytophthora pathogen biocontrol: Mediated by rapeseed root exudates. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Zhou, X.; Deng, L.C.; Fan, L.Y.; Qu, L.; Li, M. Decomposition characteristics of rapeseed green manure and effect of nutrient release on soil fertility. Hunan Agric. Sci. 2020, 416, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.J.; Li, F.P.; Gu, H.H.; Chi, X.J.; Yuan, X.T.; Han, D.Y. Combined effects of green manure returning and addition of sewage sludge compost on plant growth and microorganism communities in gold tailings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 31686–31698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Du, X.; Mu, Y. Astragalus sinicus incorporated as green manure for weed control in corn. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 29, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.T.; Lu, J.W.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, Y.T.; Cong, R.H.; Li, X.K.; Ren, T. Rapeseed as a previous crop reduces rice N fertilizer input by improving soil fertility. Field Crop. Res. 2022, 281, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.; Sansinenea, E. The role of beneficial microorganisms in soil quality and plant health. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Ma, H.; Guan, C.Y.; Guan, M. Germplasm screening of green manure rapeseed through the effects of short-term decomposition on soil nutrients and microorganisms. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.Y.; Liu, Q.M.; Zhong, Y.S.; Liao, F.P.; Lin, J.R. Mechanism of CP7 antibacterial protein against aeromonas hydrophila. Microbiol. China 2012, 39, 949–957. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y. Evaluation of Different Varieties of Mung Bean Used as Green Manure. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett, J.K. The semi-micro Kjeldahl method for the determination of nitrogen. J. Med. Lab. Technol. 1954, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R.; Cole, C.V.; Watanabe, F.S.; Dean, L.A. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agrochemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; Chinese Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 44–107. [Google Scholar]
- Valadares, R.V.; Ávila-Silva, L.D.; Teixeira, R.D.S.; Sousa, R.D.; Vergütz, L. Green manures and crop residues as source of nutrients in tropical environment. In Organic Fertilizers; Larramendy, M.L., Soloneski, S., Eds.; From basic concets to applied outcomes; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 51–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, G.G. Litter decomposition and nutrient release from monospecific and mixed litters: Comparisons of litter quality, fauna and decomposition site effects. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, B.L.; Fagodiya, R.K.; Prajapat, K.; Dotaniya, M.L.; Kaledhonkar, M.J.; Sharma, P.C.; Meena, R.S.; Mitran, T.; Kumar, S. Legume green manuring: An option for soil sustainability. In Legumes for Soil Health and Sustainable Management; Meena, R., Das, A., Yadav, G., Lal, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Chang, D.; Gao, S.; Liang, T.; Liu, R.; Cao, W.D. Co-incorporating leguminous green manure and rice straw drives the synergistic release of carbon and nitrogen, increases hydrolase activities, and changes the composition of main microbial groups. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 2021, 57, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.B.; Li, W.X.; Zhang, Y.W.; Cheng, J.K.; Jia, X.Y.; Li, S.; Yang, H.R.; Chen, B.M.; Xin, G.R. Effects of Italian ryegrass residues as green manure on soil properties and bacterial communities under an Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum L.)-rice (Oryza sativa L.) rotation. Soil. Till. Res. 2020, 196, 104487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Wang, T.J.; Kan, C. Diffusion performance of fertilizer nutrient through polymer latex film. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10868–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.M.; Zhong, S.J.; Yan, J.H.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.B. Effect Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) as a green manure on grape productivity and quality, nutrient contents, and microbiologic properties of vineyard soils. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 33, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Chiba, A.; Uchida, Y.; Kublik, S.; Vestergaard, G.; Buegger, F.; Schloter, M.; Schulz, S. Soil bacterial diversity is positively correlated with decomposition rates during early phases of maize litter decomposition. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedysh, S.N.; Ivanova, A.A. Planctomycetes in boreal and subarctic wetlands: Diversity patterns and potential ecological functions. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiy227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.C.; Yang, S.R.; Wu, Y.X.; Ru, Y.N.; Yu, X.N.; Wang, L.S.; Guo, W.H. Shifts in soil microbial community composition, function, and co-occurrence network of phragmites australis in the yellow river delta. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 858125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Sun, X.; Sun, F.W.; Zhao, Y.N.; Sun, W.; Guo, J.X.; Zhang, T. Sensitivity of soil fungal and bacterial community compositions to nitrogen and phosphorus additions in a temperate meadow. Plant Soil. 2022, 471, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Cui, Y.; Ma, D.; Li, X.; Liu, L. Spatial variation of microbial community structure and its driving environmental factors in two forest types in permafrost region of greater Xing′an mountains. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, S.; Basu, A.; Ahmad, I.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Suriani, N.L. Recent understanding of soil acidobacteria and their ecological signifificance: A critical review. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 580024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.S.; Song, J.M.; Fan, J.S.; Yan, C.; Dong, S.K.; Ma, C.M.; Gong, Z.P. Changes in soil organic carbon fractions and microbial community under rice straw return in northeast China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becraft, E.D.; Woyke, T.; Jarett, J.; Ivanova, N.; Godoy-Vitorino, F.; Poulton, N.; Brown, J.M.; Brown, J.; Lau, M.C.Y.; Onstott, T.; et al. Rokubacteria: Genomic giants among the uncultured bacterial phyla. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolińska, A.; Kuźniar, A.; Zielenkiewicz, U.; Izak, D.; Szafranek-Nakonieczna, A.; Banach, A.; Błaszczyk, M. Bacteroidetes as a sensitive biological indicator of agricultural soil usage revealed by a culture-independent approach. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2017, 119, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, Z.; Hou, H.; Lan, X.; Ji, J.; Liu, X. Long-term effects of combination of organic and inorganic fertilizer on soil properties and microorganisms in a Quaternary Red Clay. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Tao, R.; Ling, N.; Chu, G. Chemical, organic and bio-fertilizer management practices effect on soil physicochemical property and antagonistic bacteria abundance of a cotton field: Implications for soil biological quality. Soil. Till. Res. 2017, 167, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, L.; Wang, W. Response of soil bacterial community structure to different reclamation years of abandoned salinized farmland in arid China. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Zu, M.; Liu, L.; Song, X.M.; Yuan, Y.D. Composition and diversity of bacterial communities in the rhizosphere of the chinese medicinal herb dendrobium. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Factor Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Weather | Climate type | Humid subtropical monsoon climate |
| Cumulative rainfall | 157.8 mm | |
| Daily average temperature | 16.5 °C | |
| Soil | Soil type | Yellow-brown loam soil comprised of 31.5% sand, 38.8% silt, and 29.7% clay |
| pH | 5.70 | |
| Organic matter | 21.60 g·kg−1 | |
| Total nitrogen | 1.29 g·kg−1 | |
| Available phosphorus | 10.23 mg·kg−1 | |
| Available potassium | 137.76 mg·kg−1 | |
| Community Richness | Community Diversity | Sequencing Depth Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao1 | Ace | Shannon | Simpson | Good’s Coverage | |
| A | 6528.89 ± 104.37 a | 4289.27 ± 46.46 a | 9.46 ± 0.02 a | 0.9942 ± 0.0009 a | 96.28% |
| B | 4770.01 ± 38.06 c | 3470.84 ± 26.66 c | 9.28 ± 0.02 a | 0.9939 ± 0.0005 a | 97.14% |
| CK0 | 5669.44 ± 217.12 b | 3922.29 ± 105.13 b | 8.99 ± 0.38 a | 0.9815 ± 0.0152 a | 96.68% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Guan, C.; Guan, M. Decomposition of Rapeseed Green Manure and Its Effect on Soil under Two Residue Return Levels. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711102
Wang X, Ma H, Guan C, Guan M. Decomposition of Rapeseed Green Manure and Its Effect on Soil under Two Residue Return Levels. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):11102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711102
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaodan, Hua Ma, Chunyun Guan, and Mei Guan. 2022. "Decomposition of Rapeseed Green Manure and Its Effect on Soil under Two Residue Return Levels" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 11102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711102
APA StyleWang, X., Ma, H., Guan, C., & Guan, M. (2022). Decomposition of Rapeseed Green Manure and Its Effect on Soil under Two Residue Return Levels. Sustainability, 14(17), 11102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711102




