Importance of Top Management Commitment to Organizational Citizenship Behaviour towards the Environment, Green Training and Environmental Performance in Pakistani Industries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Underpinning Theories
2.2. Green Training and Organizational Citizenship Behaviour toward the Environment
2.3. Top Management Commitment and Environmental Performance
2.4. Top Management Commitment and Green Training
3. Research Variables and Measurement
4. Research Methodology
5. Data Analysis
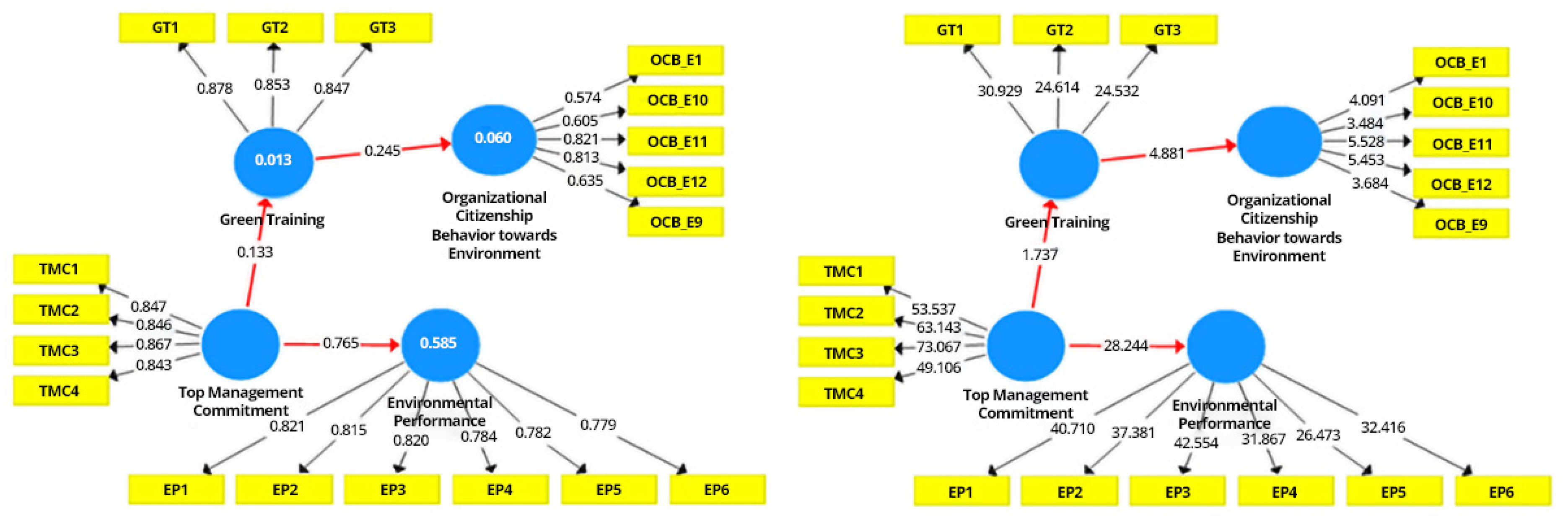
5.1. Outer Model (Factor Model) Analysis
5.2. Inner Model (Path Model) Analysis
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
7.1. Theoretical Contribution
7.2. Limitation and Directions for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, R.I., Jr.; Morrell, D.L.; Mullane, J.V. Reinvigorating the mission statement through top management commitment. Manag. Decis. 2014, 52, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusliza, M.Y.; Norazmi, N.A.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Fernando, Y.; Fawehinmi, O.; Seles, B.M.R.P. Top management commitment, corporate social responsibility and green human resource management: A Malaysian study. Benchmark. Int. J. 2019, 26, 2051–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muisyo, P.K.; Qin, S.; Ho, T.H.; Julius, M.M. The effect of green HRM practices on green competitive advantage of manufacturing firms. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2021, 33, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, T.; Zahid, M.; Martins, J.; Mata, M.; Rahman, H.; Mata, P. Perceived Green Human Resource Management Practices and Corporate Sustainability: Multigroup Analysis and Major Industries Perspectives. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.; Szuster, B. Beyond Unidimensionality: Segmenting Contemporary Pro-Environmental Worldviews Through Surveys and Repertory Grid Analysis. Environ. Commun. 2018, 12, 1062–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.E.; Renwick, D.W.S.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Muller-Camen, M. State-of-the-Art and Future Directions for Green Human Resource Management: Introduction to the Special Issue. Ger. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renwick, D.W.S.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Muller-Camen, M.; Redman, T.; Wilkinson, A. Contemporary developments in Green (environmental) HRM scholarship. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2015, 27, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, H.K.; Padfield, R.; Hansen, S.B.; Mohamad, S.E.; Yuzir, A.; Syayuti, K.; Tham, M.H.; Papargyropoulou, E. Global trends in environmental management system and ISO14001 research. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska, A.; Matuszak-Flejszman, A. Eco-design as a normative element of Environmental Management Systems—The context of the revised ISO 14001:2015. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2014, 19, 1794–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravi, L.; Santos, G.; Pagano, A.; Murmura, F. Environmental management system according to ISO 14001:2015 as a driver to sustainable development. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 2599–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, C.J.C.; Jugend, D.; de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L.; Gunasekaran, A.; Latan, H. Green product development and performance of Brazilian firms: Measuring the role of human and technical aspects. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.A.; Queirós, A.S. Economic growth, human capital and structural change: A dynamic panel data analysis. Res. Policy 2016, 45, 1636–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, H.A.; Jaaron, A.A. Assessing green human resources management practices in Palestinian manufacturing context: An empirical study. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 474–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiral, O.; Paillé, P. Organizational Citizenship Behaviour for the Environment: Measurement and Validation. J. Bus. Ethics 2012, 109, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, B.F.; Bishop, J.W.; Govindarajulu, N. A Conceptual Model for Organizational Citizenship Behavior Directed Toward the Environment. Bus. Soc. 2009, 48, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temminck, E.; Mearns, K.; Fruhen, L. Motivating Employees towards Sustainable Behaviour. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2013, 24, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiral, O. Greening the Corporation Through Organizational Citizenship Behaviors. J. Bus. Ethics 2008, 87, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasa, S.R.; Thatta, S. Green Work Life Balance & Green HRM: A New Replica for Organisational Triumph. 2018. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3163083 (accessed on 27 July 2022).
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z. The Indirect Effect of Top Management Commitment in Improving Green Performance. 2019. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3341074 (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- Spencer, S.Y.; Adams, C.; Yapa, P.W. The mediating effects of the adoption of an environmental information system on top management’s commitment and environmental performance. Sustain. Account. Manag. Policy J. 2013, 4, 75–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mendonca, T.R.; Zhou, Y. Environmental Performance, Customer Satisfaction, and Profitability: A Study among Large U.S. Companies. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif-Askari, H.; Abu-Hijleh, B. Review of museums’ indoor environment conditions studies and guidelines and their impact on the museums’ artifacts and energy consumption. Build. Environ. 2018, 143, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Australia. Energy Saving Tips for Your Office. Available online: https://www.energyaustralia.com.au/blog/work/energy-saving-tips-your-office (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Barney, J.B. Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibarras, L.D.; Coan, P. HRM practices used to promote pro-environmental behavior: A UK survey. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2015, 26, 2121–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombiak, E.; Marciniuk-Kluska, A. Green Human Resource Management as a Tool for the Sustainable Development of Enterprises: Polish Young Company Experience. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, M. Nonprobability Sampling. In Encyclopedia of Survey Research Methods; Lavrakas, P.J., Ed.; Sage Publications, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuriev, A.; Dahmen, M.; Paillé, P.; Boiral, O.; Guillaumie, L. Pro-environmental behaviors through the lens of the theory of planned behavior: A scoping review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 155, 104660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillé, P.; Boiral, O.; Chen, Y. Linking environmental management practices and organizational citizenship behaviour for the environment: A social exchange perspective. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2013, 24, 3552–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, M.; Pringle, C.D. The Missing Opportunity in Organizational Research: Some Implications for a Theory of Work Performance. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1982, 7, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raineri, N.; Paillé, P. Linking Corporate Policy and Supervisory Support with Environmental Citizenship Behaviors: The Role of Employee Environmental Beliefs and Commitment. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 137, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.L.; Barling, J. Toward a new measure of organizational environmental citizenship behavior. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 75, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, Z.; Khan, I.U.; Islam, T.; Sheikh, Z.; Naeem, R.M. Do green HRM practices influence employees’ environmental performance? Int. J. Manpow. 2020, 41, 1061–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, G.; Williams, K.; Probert, J. Greening the airline pilot: HRM and the green performance of airlines in the UK. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2013, 24, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoogah, D.B. The Dynamics of Green HRM Behaviors: A Cognitive Social Information Processing Approach. Ger. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. Z. Pers. 2011, 25, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, B.F.; Bishop, J.W.; Steiner, R. The Mediating Role Of EMS Teamwork As It Pertains To HR Factors And Perceived Environmental Performance. J. Appl. Bus. Res. 2011, 23, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Ramus, C. Encouraging innovative environmental actions: What companies and managers must do. J. World Bus. 2002, 37, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lober, D.J. Municipal Solid Waste Policy and Public Participation in Household Source Reduction. Waste Manag. Res. J. Sustain. Circ. Econ. 1996, 14, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nation Environment Programme (UNEP). ECOLEX—The Gateway to Environmental Law; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.H.; Ball, R. Achieving sustainable corporate competitiveness: Strategic link between top management’s (green) commitment and corporate environmental strategy. Greener Manag. Int. 2003, 44, 89–104. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/greemanainte.44.89 (accessed on 1 August 2022). [CrossRef]
- Welford, R. Corporate Environmental Management 1; Routledge: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrmeyer, W. Greening People: Human Resources and Environmental Management; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zaid, A.A.; Jaaron, A.A.M.; Bon, A.T. The impact of green human resource management and green supply chain management practices on sustainable performance: An empirical study. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 965–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.B.; Mabert, V.A. Supplier development: Improving supplier performance through knowledge transfer. J. Oper. Manag. 2006, 25, 42–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, S.R.; Joshi, A.W. Corporate Ecological Responsiveness: Antecedent Effects of Institutional Pressure and Top Management Commitment and Their Impact on Organizational Performance. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2011, 22, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon-Fowler, H.R.; Ellstrand, A.E.; Johnson, J.L. The Role of Board Environmental Committees in Corporate Environmental Performance. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 140, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Helo, P.; Papadopoulos, T.; Childe, S.J.; Sahay, B. Explaining the impact of reconfigurable manufacturing systems on environmental performance: The role of top management and organizational culture. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Saraf, N.; Hu, Q.; Xue, Y. Assimilation of Enterprise Systems: The Effect of Institutional Pressures and the Mediating Role of Top Management. MIS Q. 2007, 31, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S. Green Human Resource Management: Policies and practices. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2015, 2, 1030817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Chen, Y.; Du, J.; Oh, K.; Han, I.; Yan, J. The effect of environmental innovation behavior on economic and environmental performance of 182 Chinese firms. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, T.-Y.; Chan, H.K.; Lettice, F.; Chung, S.H. The influence of greening the suppliers and green innovation on environmental performance and competitive advantage in Taiwan. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2011, 47, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.Y.; Cao, Y.; Mughal, Y.H.; Kundi, G.M.; Mughal, M.H.; Ramayah, T. Pathways towards Sustainability in Organizations: Empirical Evidence on the Role of Green Human Resource Management Practices and Green Intellectual Capital. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, E.; Tosti-Kharas, J.; Williams, E.G. Read This Article, but Don’t Print It. Group Organ. Manag. 2013, 38, 163–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.J.; Gladwin, T.N. Sustainability metrics for the business enterprise. Environ. Qual. Manag. 1999, 8, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Gudergan, S.P. Advanced Issues in Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling; SAGE Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra, T.K.; Schermelleh-Engel, K. Consistent Partial Least Squares for Nonlinear Structural Equation Models. Psychometrika 2013, 79, 585–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, J.; Putnick, D.; Bornstein, M.H., II. More than just convenient: The scientific merits of homogeneous convenience samples. Monogr. Soc. Res. Child Dev. 2017, 82, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burki, A.A.; Munir, K.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, U.; Faheem, A.; Khalid, A.; Hussain, S.T. Industrial policy, its spatial aspects and cluster development in Pakistan. In Analysis Report to the Industrial Policy; Lahore University of Management Sciences: Lahore, Pakistan, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra, T.K.; Henseler, J. Consistent Partial Least Squares Path Modeling. MIS Q. 2015, 39, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, N.F.; Sinkovics, R.R.; Ringle, C.M.; Schlägel, C. A critical look at the use of SEM in international business research. Int. Mark. Rev. 2016, 33, 376–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulland, J. Use of partial least squares (PLS) in strategic management research: A review of four recent studies. Strategy Manag. J. 1999, 20, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viladrich, C.; Angulo-Brunet, A.; Doval, E. A journey around alpha and omega to estimate internal consistency reliability. An. Psicol. 2017, 33, 755–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, C.W. Issues and opinion on structural equation modelling. Manag. Inf. Syst. Q. 1998, 22, 1–8. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/249674 (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M.; Danks, N.P.; Ray, S. Evaluation of Reflective Measurement Models. In Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Using R; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.R.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Khan, S.S. The impact of green supply chain on enterprise performance: In the perspective of China. J. Adv. Manuf. Syst. 2017, 16, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandre, R.; Fabrigar, L.R.; Wegener, D.T. Exploratory Factor Analysis; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Knekta, E.; Runyon, C.; Eddy, S. One Size Doesn’t Fit All: Using Factor Analysis to Gather Validity Evidence When Using Surveys in Your Research. CBE—Life Sci. Educ. 2019, 18, rm1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moores, T.T.; Chang, J.C.J. Ethical Decision Making in Software Piracy: Initial Development and Test of a Four-Component Model. MIS Q. 2006, 30, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM); Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, R.; Price, J.; Fischlin, A.; de la Santos, S.N.; Midgley, G. Increasing impacts of climate change upon ecosystems with increasing global mean temperature rise. Clim. Chang. 2011, 106, 141–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, T.; Malik, S.Y.; Ren, D.; Yuan, W.; Mughal, Y.H.; Ullah, I.; Fiaz, M.; Riaz, S. The Moderating Role of Organizational Citizenship Behavior Toward Environment on Relationship Between Green Supply Chain Management Practices and Sustainable Performance. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 876516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Abbas, Z.; Yousaf, M.; Zámečník, R.; Ahmed, J.; Saqib, S. The role of GHRM practices towards organizational commitment: A mediation analysis of green human capital. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2021, 8, 1870798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable (s) | Sample (n = 222) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Male | 151 | 68.00% |
| Female | 71 | 32.00% |
| Age | ||
| 18–24 | 21 | 9.50% |
| 25–34 | 48 | 21.60% |
| 35–44 | 77 | 34.70% |
| 45–54 | 55 | 24.80% |
| 55–64 | 21 | 9.50% |
| Education | ||
| Intermediate | 21 | 9.50% |
| Technical Diploma | 51 | 23.00% |
| Graduate | 91 | 41.00% |
| Postgraduate | 59 | 26.60% |
| Position | ||
| Junior-level employee/manager | 29 | 13.10% |
| Mid-level employee/manager | 151 | 68.00% |
| Senior-level employee/manager | 42 | 18.90% |
| Employment Experience | ||
| 1–4 months | 17 | 7.70% |
| 5–8 months | 31 | 14.00% |
| 9–12 months | 37 | 16.70% |
| More than 1 year | 137 | 61.70% |
| Industry Type | ||
| Textile | 49 | 22.10% |
| Pharmaceutical | 29 | 13.10% |
| Rubber | 63 | 28.40% |
| Chemical & Fertilisers | 71 | 32.00% |
| Construct | Code | Item | Factor Loadings | Cronbach’s Alpha | AVE | CR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental performance (EP) | EP1 | My company is dedicated to reduce air emission | 0.756 | 0.889 | 0.632 | 0.872 |
| EP2 | My company is dedicated to reduce hazardous waste/scrap | 0.764 | ||||
| EP3 | My company is dedicated to reduce consumption of gasoline/fuel | 0.751 | ||||
| EP4 | My company is dedicated to improvise partnership with green companies and suppliers | 0.737 | ||||
| EP5 | My company is dedicated to environmental compliance | 0.731 | ||||
| EP6 | My company is keen to use environmental friendly material | 0.791 | ||||
| Top management commitment (TMC) | TMC1 | My company expresses how green supply chain partnering will provide significant business benefits to the firm | 0.719 | 0.873 | 0.681 | 0.802 |
| TMC2 | My company expresses how green supply chain partnering will create a significant competitive arena | 0.836 | ||||
| TMC3 | My company articulates vision for green supply chain collaboration | 0.858 | ||||
| TMC4 | My company establishes the metrics to monitor green supply chain success through partnering | 0.759 | ||||
| TMC5 | My company formulates strategy for effective information sharing | 0.719 | ||||
| Green training (GT) | GT1 | We develop training programs in environment management to increase environmental awareness, skills and expertise of employees | 0.982 | 0.826 | 0.571 | 0.888 |
| GT2 | We have integrated training to create the emotional involvement of employees in environment management | 0.822 | ||||
| Organisational Citizenship Behaviour towards Environment (OCB-E) | OCB-E1 | I am a person who recycles my bottles and other containers. | 0.556 | 0.767 | 0.603 | 0.805 |
| OCB-E9 | I am a person who uses a reusable water bottle instead of a paper cup at the water cooler. | 0.738 | ||||
| OCB-E10 | I am a person who uses a reusable coffee cup instead of a paper cup. | 0.752 | ||||
| OCB-E11 | I am a person who properly disposes of electronic waste. | 0.799 | ||||
| OCB-E12 | I am a person who makes sure all of the lights are turned off if I am the last to leave. | 0.795 |
| Outer Loadings | Outer Weights | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP | GT | OCB-E | TMC | EP | GT | OCB-E | TMC | |
| EP1 | 0.821 | 0.195 | ||||||
| EP2 | 0.815 | 0.207 | ||||||
| EP3 | 0.82 | 0.186 | ||||||
| EP4 | 0.784 | 0.193 | ||||||
| EP5 | 0.782 | 0.183 | ||||||
| EP6 | 0.779 | 0.287 | ||||||
| GT1 | 0.878 | 0.439 | ||||||
| GT2 | 0.853 | 0.43 | ||||||
| GT3 | 0.847 | 0.292 | ||||||
| OCB_E1 | 0.574 | 0.466 | ||||||
| OCB_E10 | 0.605 | 0.105 | ||||||
| OCB_E11 | 0.821 | 0.378 | ||||||
| OCB_E12 | 0.813 | 0.357 | ||||||
| OCB_E9 | 0.635 | 0.108 | ||||||
| TMC1 | 0.847 | 0.266 | ||||||
| TMC2 | 0.846 | 0.312 | ||||||
| TMC3 | 0.867 | 0.31 | ||||||
| TMC4 | 0.843 | 0.286 | ||||||
| R Square | R Square Adjusted | |
|---|---|---|
| EP | 0.585 | 0.584 |
| GT | 0.013 | 0.01 |
| OCB-E | 0.06 | 0.057 |
| Model Fit | ||
| SRMR | 0.128 | |
| Chi-Square | 1743.95 | |
| NFI | 0.629 | |
| Original Sample | Sample Mean | Std. Dev | T-Statistics | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT → OCB-E | 0.245 | 0.264 | 0.051 | 4.881 | 0.000 ** |
| TMC → EP | 0.765 | 0.769 | 0.027 | 28.244 | 0.000 ** |
| TMC → GT | 0.113 | 0.115 | 0.065 | 1.737 | 0.001 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Memon, S.B.; Rasli, A.; Dahri, A.S.; Hermilinda Abas, I. Importance of Top Management Commitment to Organizational Citizenship Behaviour towards the Environment, Green Training and Environmental Performance in Pakistani Industries. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711059
Memon SB, Rasli A, Dahri AS, Hermilinda Abas I. Importance of Top Management Commitment to Organizational Citizenship Behaviour towards the Environment, Green Training and Environmental Performance in Pakistani Industries. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):11059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711059
Chicago/Turabian StyleMemon, Salman Bashir, Amran Rasli, Abdul Samad Dahri, and Imelda Hermilinda Abas. 2022. "Importance of Top Management Commitment to Organizational Citizenship Behaviour towards the Environment, Green Training and Environmental Performance in Pakistani Industries" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 11059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711059
APA StyleMemon, S. B., Rasli, A., Dahri, A. S., & Hermilinda Abas, I. (2022). Importance of Top Management Commitment to Organizational Citizenship Behaviour towards the Environment, Green Training and Environmental Performance in Pakistani Industries. Sustainability, 14(17), 11059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141711059






