In Situ Carbonized Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Sponge by a Dehydration Reaction for Solar-Driven Interfacial Evaporation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. In Situ Carbonization of PVA Sponge
2.3. Characterization
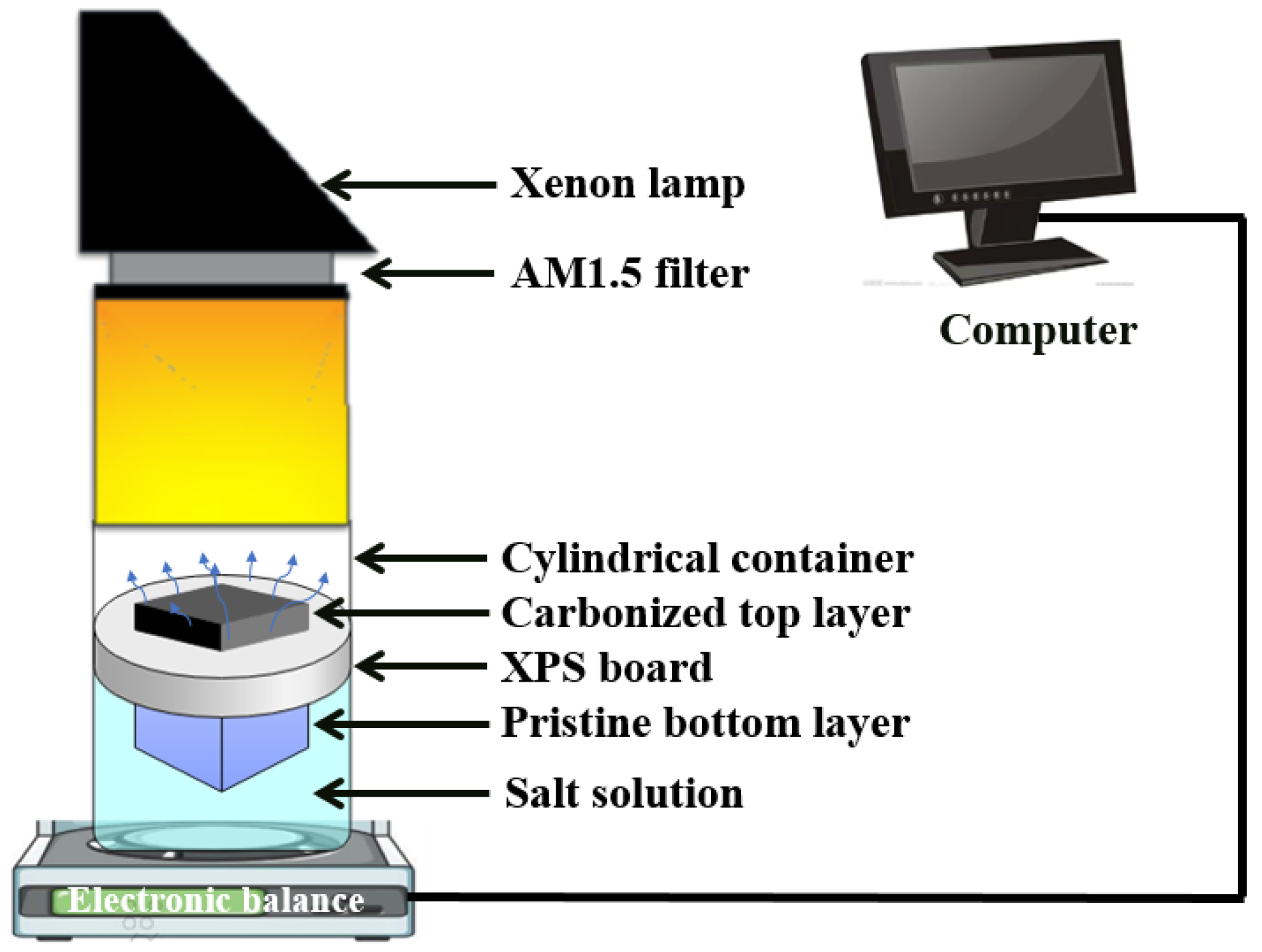
2.4. Evaporation Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
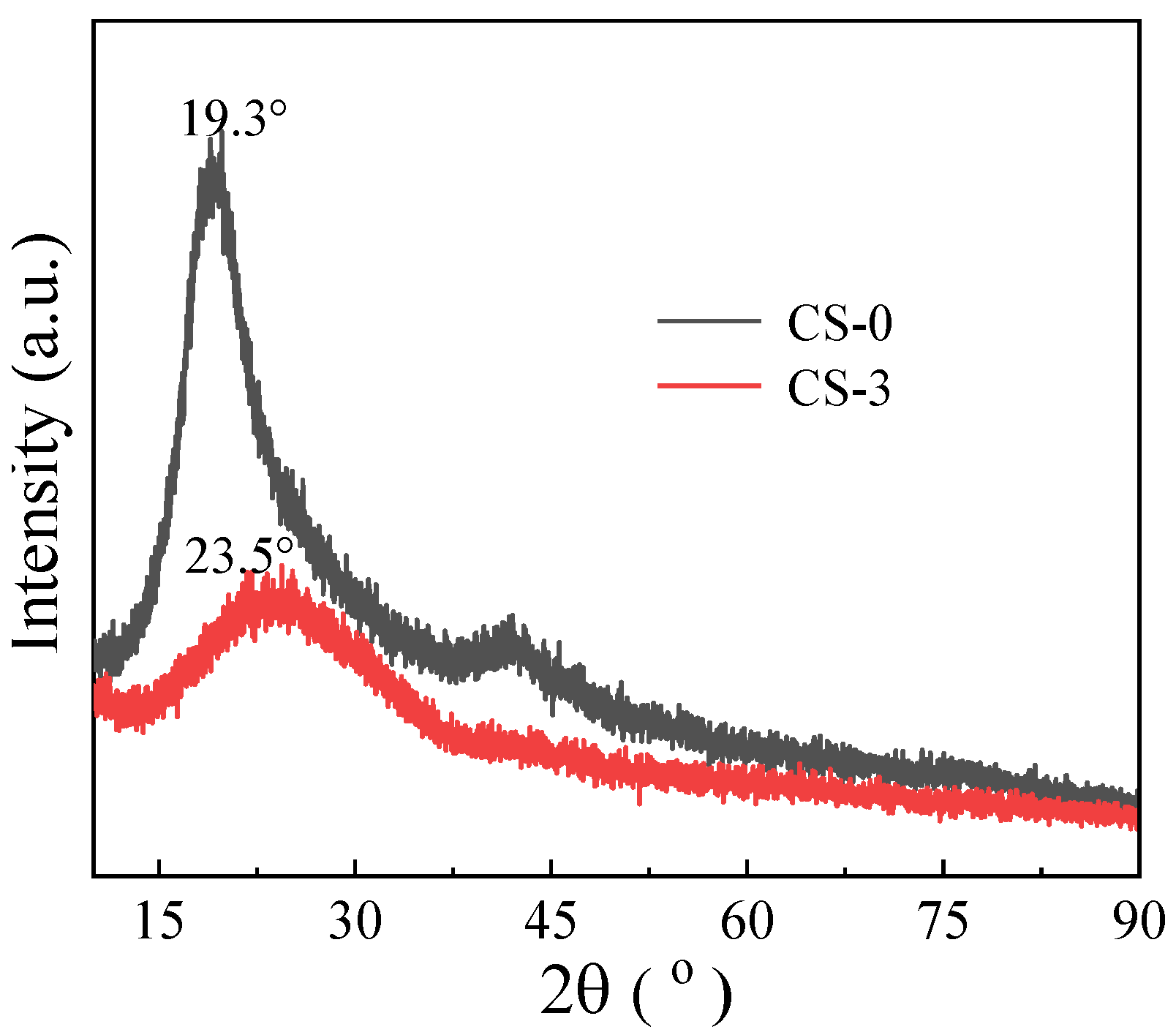
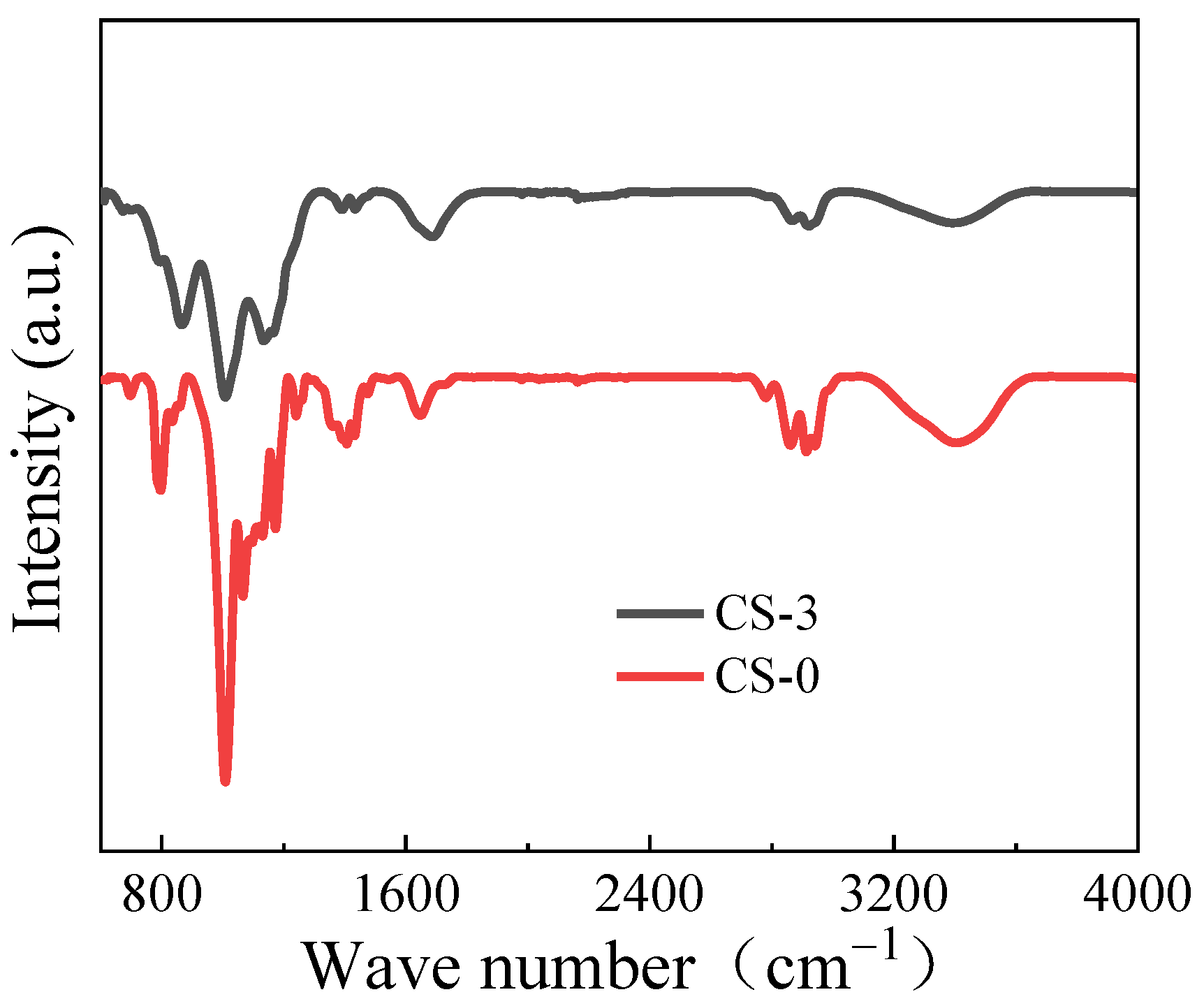
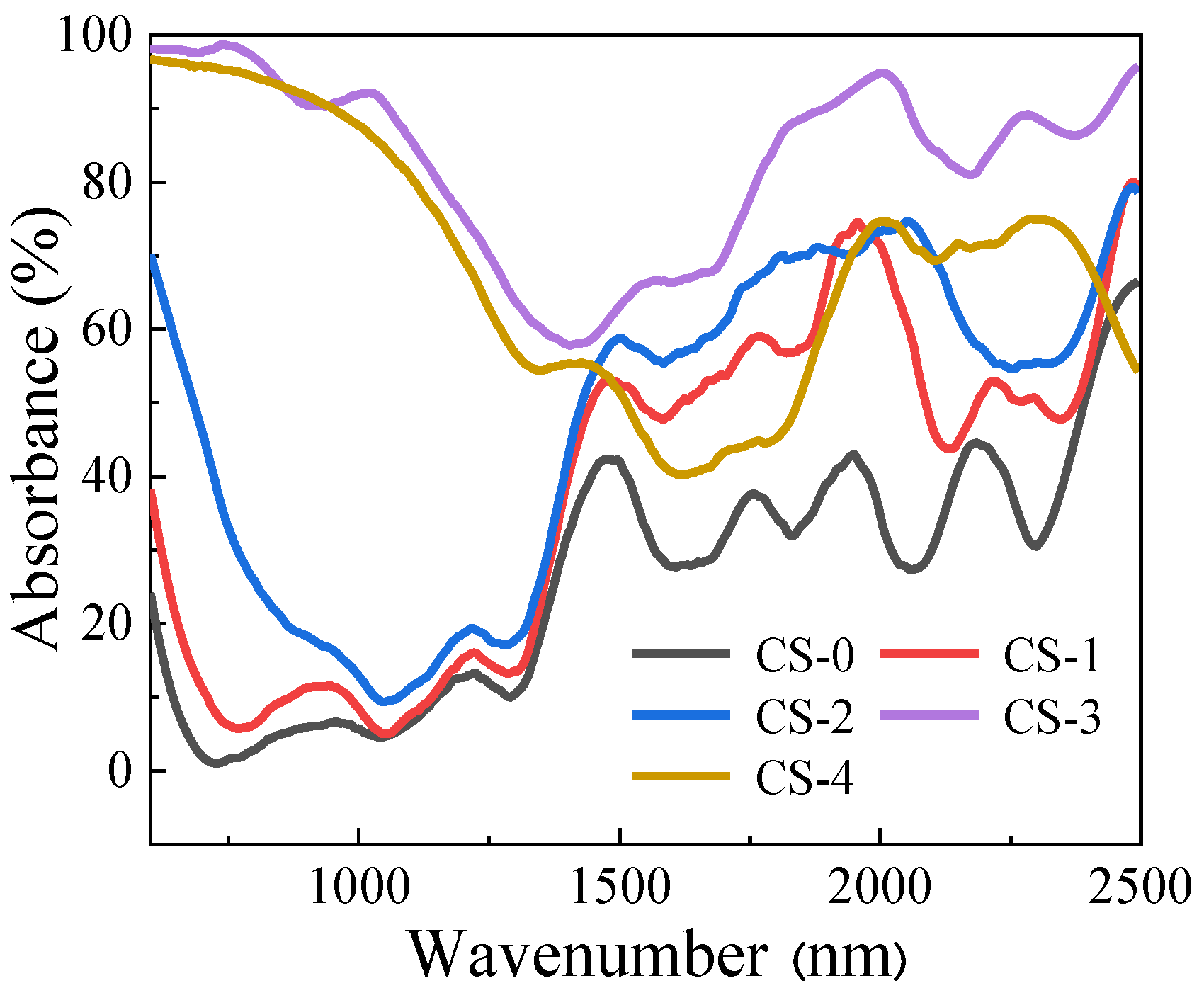
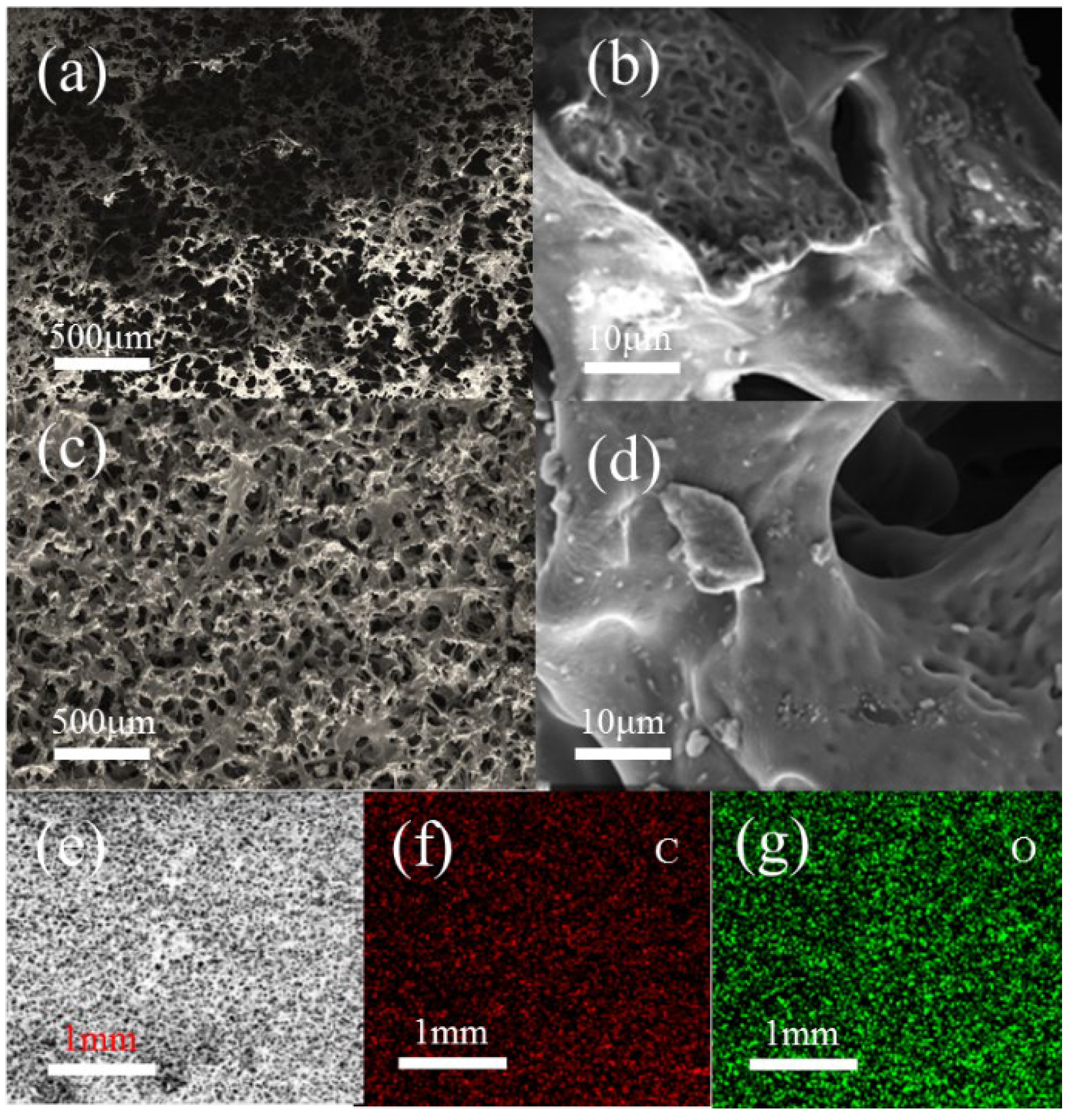
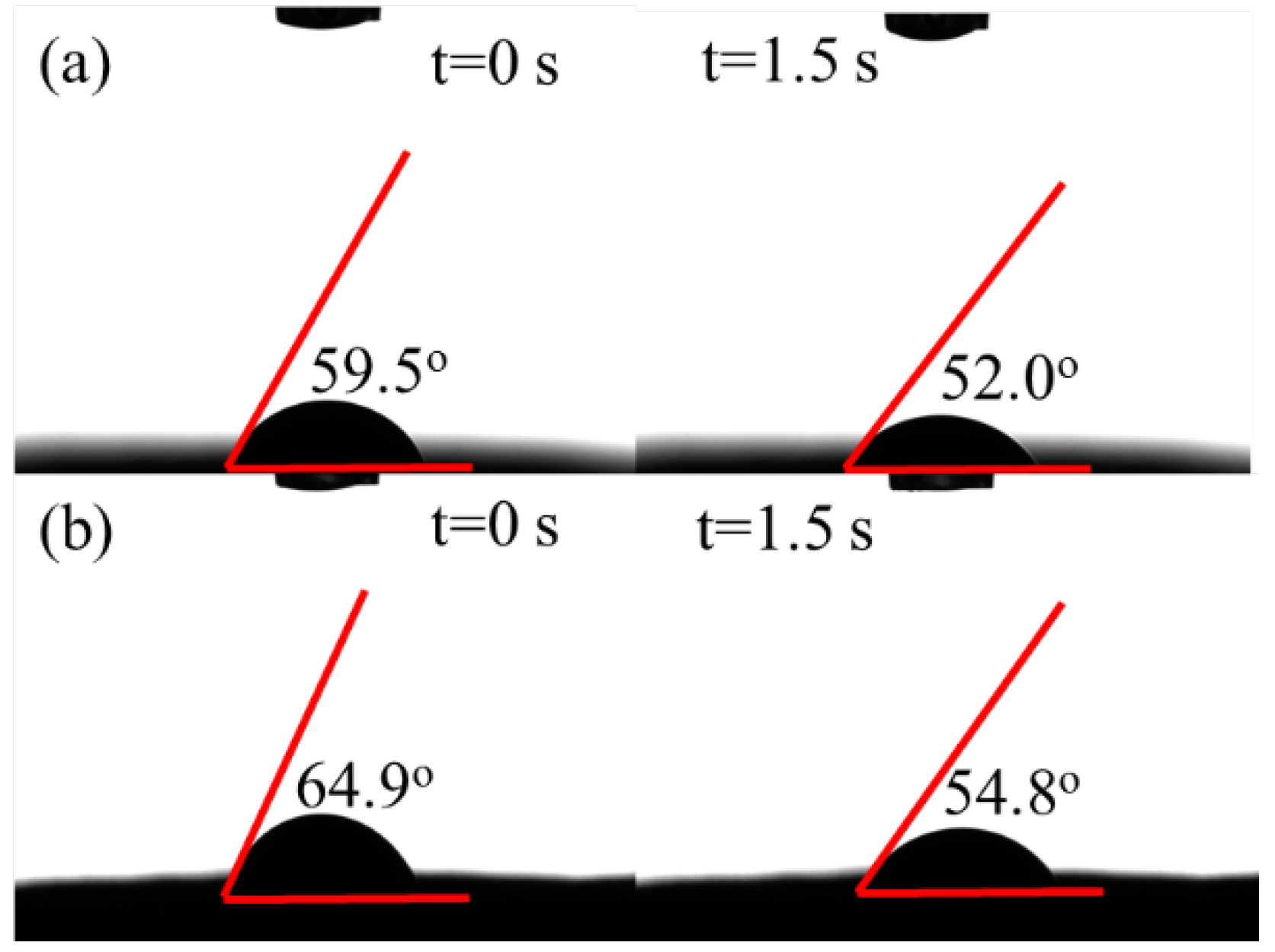
3.1. Characteristics
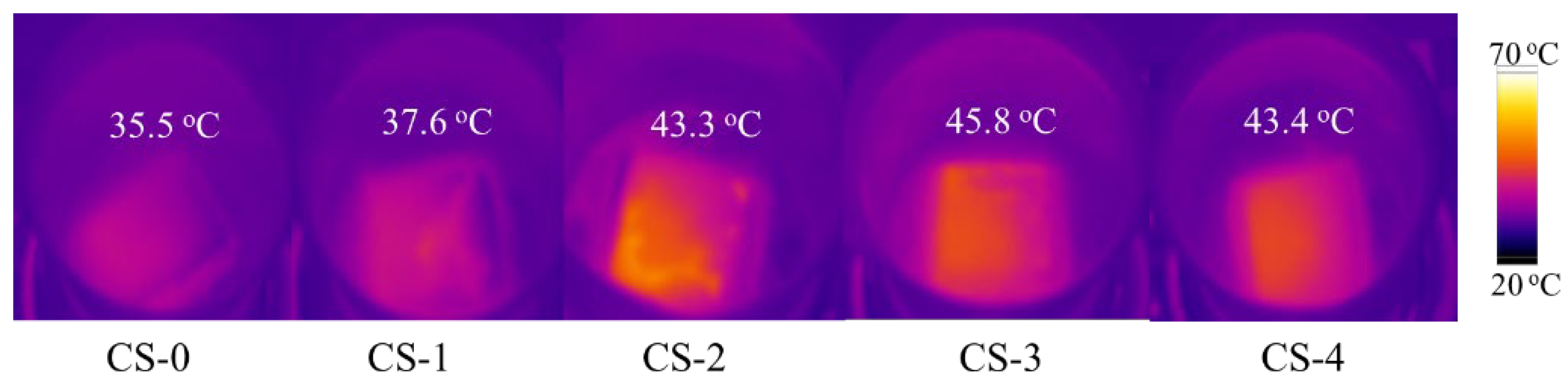
3.2. Solar Water Evaporation
3.3. Reusability
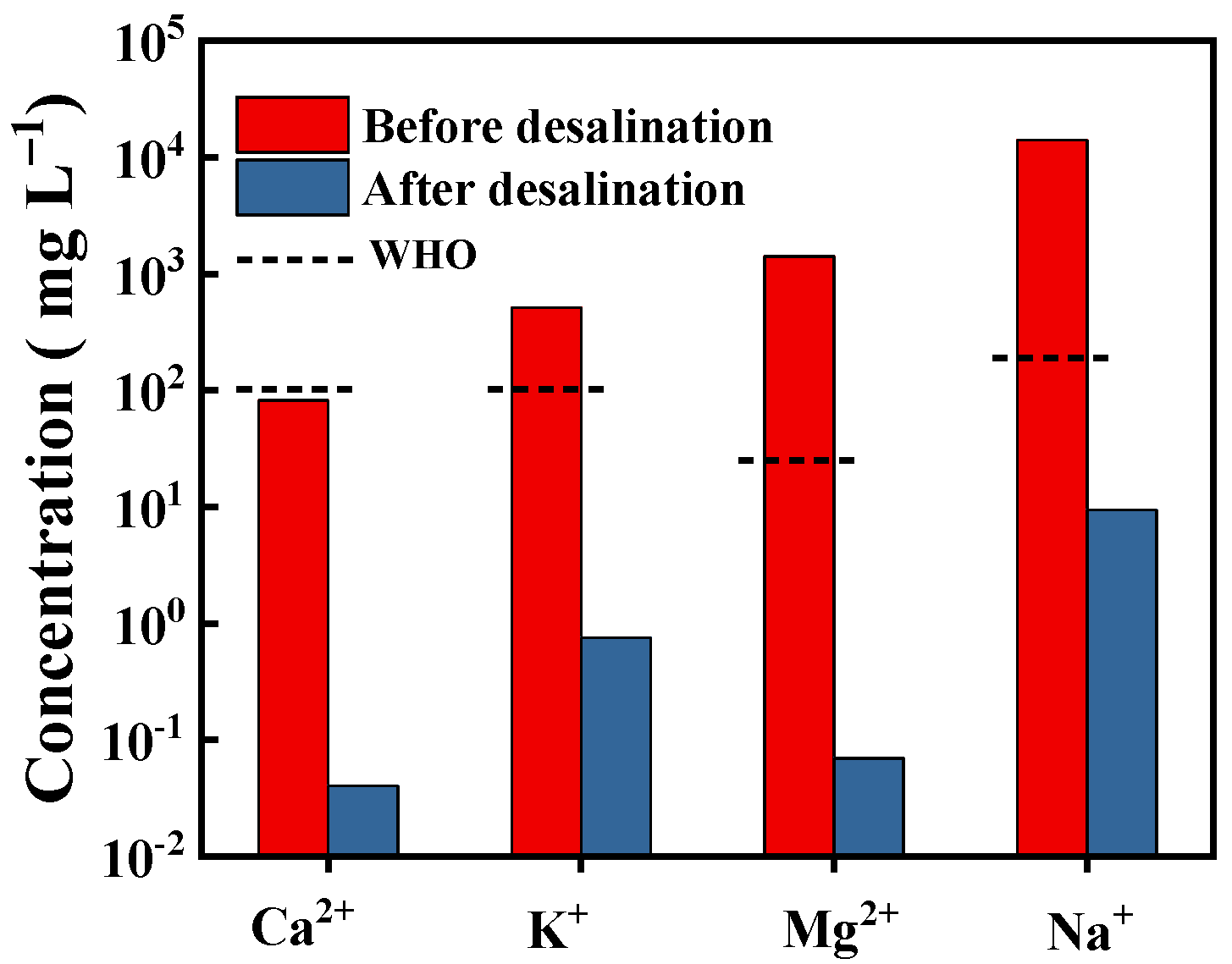
3.4. Seawater Desalination
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, F.; Ju, B.; Zhang, S.; Tango, B. Nano/microstructured materials for solar-driven interfacial evaporators towards water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 13746–13769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Zhao, C.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Z. Carbonized tofu as photothermal material for highly efficient solar steam generation. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 9213–9221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.X.; Zhao, J.X.; Liang, L.; Guo, C.L. Constructing a solar evaporator with salt-collecting paper by stacking hydrophilic sponges for freshwater production and salt collection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.M.; Li, J.H.; Zhong, L.S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, M.L.; Chen, H.; Hou, Y.P.; Zheng, Y.M. Excellent dual-photothermal freshwater collector with high performance in large-scale evaporation. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.J.; Yi, H.; Jia, F.F.; Song, S.X. Vertical porous MoS2/hectorite double-layered aerogel as superior salt resistant and highly efficient solar steam generators. Renew. Energy 2022, 194, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Miao, E.; Xie, Y. Constructing 3D optical absorption holes by stacking macroporous membrane for highly efficient solar steam generation. Renew. Energy 2020, 159, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Boldoo, T.; Ham, J.; Cho, H. Improvement of photo-thermal energy conversion performance of MWCNT/Fe3O4 hybrid nanofluid compared to Fe3O4 nanofluid. Energy 2020, 196, 117086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xing, J.; Kan, A.; Kan, A.; Xie, H.; Yu, W. Investigation of enhanced volumetric solar steam generation by a lower concentration of ZrC nanofluid. Nano 2020, 15, 2050030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Meng, Z.; Wu, D. Improvement of the efficiency of volumetric solar steam generation by enhanced solar harvesting and energy management. Renew. Energy 2022, 183, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.L.; Zhao, J.X.; Zhang, T.X. Development of a modified composite structure from polyurethane sponge for desalinating seawater polluted by oil. Desalination 2022, 524, 115471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.X.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, T.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Bian, Z.T. Preparing photo-thermal conversion membrane with CuS-Multi walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) composite for solar-driven interfacial evaporation. Mater. Lett. 2022, 317, 132145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.T.; Wu, Z.T.; Guan, F.Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, B.X.; Sheng, N.; Qu, X.Y.; Deng, L.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Hierarchically designed three-dimensional composite structure on a cellulose-based solar steam generator. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2022, 14, 12284–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.X.; Jiao, S.K.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J.G.; Wang, H.Y.; Guo, C.L. In situ synthesizing C-CuO composite for efficient photo-thermal conversion and its application in solar-driven interfacial evaporation. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 45, 7829–7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Han, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, P.; Han, X.; Nafady, A.; Ma, S.; Du, Y. Cotton cloth supported tungsten carbide/carbon nanocomposites as a Janus film for solar driven interfacial water evaporation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 23140–23148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Feng, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, P.; Wang, X.; Yin, W.; Wang, M.; Ge, X.; Yin, Y. Space-confined seeded growth of black silver nanostructures for solar steam generation. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Cui, T.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Tang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhu, G. Green-synthesizing Ag nanoparticles by watermelon peel extract and their application in solar-driven interfacial evaporation for seawater desalination. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; He, Y.; Zhu, J. Preparation of Au-Ag bimetallic nanoparticles for enhanced solar photothermal conversion. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 114, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.; Nan, J.; Shi, C.; Tang, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. A Flexible Polymer Nanofiber-Gold Nanoparticle Composite Film for Solar-Thermal Seawater Desalination. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 2000390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhou, C.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Tian, J.; Wu, W. Multifunctional cotton with PANI-Ag NPs heterojunction for solar-driven water evaporation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, E.D.; Ye, M.Q.; Guo, C.L.; Liang, L.; Liu, Q.; Rao, Z.H. Enhanced solar steam generation using carbon nanotube membrane distillation device with heat localization. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 149, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.J.; Sun, B.B.; Wang, Y.M.; Antwi-Afaric, M.F.; Mi, H.Y.; Guo, Z.H.; Liu, C.T.; Shen, C.Y. Carbon black and polydopamine modified non-woven fabric enabling efficient solar steam generation towards seawater desalination and wastewater purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 278, 119621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.S.; Li, D.Y.; Zuo, S.Y.; Guan, Z.Y.; Xu, H.M.; Ding, S.; Xia, D.S. Discarded-leaves derived biochar for highly efficient solar water evaporation and clean water production: The crucial roles of graphitized carbon. Colloid Surf. A 2022, 639, 128337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Hu, X.; Xu, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. Mushrooms as efficient solarsteam-generation devices. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, Y.S.; Cai, Q.L.; Dang, Y.Y.; Pang, H.Q.; Wu, X. High efficiency solar interfacial evaporator for seawater desalination based on high porosity loofah sponge biochar. Sol. Energy 2022, 238, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, G.; Kuang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Song, J.; Jia, C.; Xu, X.; Hitz, E.; Xie, H.; et al. High-performance solar steam device with layered channels: Artificial tree with a reversed design. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1701616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.L.; Miao, E.D.; Zhao, J.X.; Liang, L.; Liu, Q. Paper-based integrated evaporation device for efficient solar steam generation through localized heating. Sol. Energy 2019, 188, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.W.; Wu, H.Q.; Shi, Z.; Kong, Z.; Ma, S.Y.; Sun, Y.P.; Liu, X.G. Facile preparation of robust superhydrophobic/superoleophilic TiO2-decorated polyvinyl alcohol sponge for efficient oil/water separation. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 7084–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.C.; Pei, X.P.; Yang, Y.; Jia, E.; Zhou, H.; Xiang, S.; Lin, F.; Tan, Y. A robust PVA/C/sponge composite hydrogel with improved photothermal interfacial evaporation rate inspired by the chimney effect. Desalination 2022, 531, 115720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Hassan, A.Q.; Mohammed, S.J.; Karim, W.O.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Chan, N.N.M.Y.; Chan, N.M.Y. Structural and optical characteristics of PVA: C-dot composites: Tuning the absorption of ultra violet (UV) region. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.I.; Chen, J.W.; Cheng, W.Y.; Jang, L. The reinforcement of the physical strength of PVA sponge through the double acetalization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 198, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th Editon, Incorporating the 1st Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, H.; Wang, D.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, Y. In Situ Carbonized Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Sponge by a Dehydration Reaction for Solar-Driven Interfacial Evaporation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710945
Cao H, Wang D, Sun Z, Zhu Y. In Situ Carbonized Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Sponge by a Dehydration Reaction for Solar-Driven Interfacial Evaporation. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):10945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710945
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Hongxia, Dong Wang, Zeyu Sun, and Yanyan Zhu. 2022. "In Situ Carbonized Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Sponge by a Dehydration Reaction for Solar-Driven Interfacial Evaporation" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 10945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710945
APA StyleCao, H., Wang, D., Sun, Z., & Zhu, Y. (2022). In Situ Carbonized Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Sponge by a Dehydration Reaction for Solar-Driven Interfacial Evaporation. Sustainability, 14(17), 10945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710945





