Abstract
Pesticide packaging waste recycling is crucial in promoting the development of agricultural modernization and ensuring the safety of agricultural products, but, currently, studies on pesticide packaging waste recycling behavior at the farmer level are still scarce, especially from the perspective of social psychology and regulation paths. In the current study, we surveyed 198 farmers in Shaanxi Province, China. Structural equation modeling (SEM) was used to explore the associated factors of farmers’ pesticide waste packaging recycling behavior based on the theory of planned behavior (TPB). The results indicate that a degree of convenience and time spent affected recycling behavior. Attitude toward the behavior (AB) and subject norm (SN) showed significant associations with fruit farmers’ behavior intention (IN) in pesticide packaging waste recycling, while perceived behavior control (PBC) presented insignificant association. However, the direct association between PBC and fruit famers’ behavior in regards to pesticide packaging waste recycling was statistically significant. Our study’s results suggest that measures such as improving the policy system of pesticide packaging recycling and treatment, strengthening science popularization, publicity and guidance, standardizing pesticide packaging tips, carrying out pilot recycling programs, and improving infrastructures could be effective in promoting fruit farmers’ behavior in regards to the recycling of pesticide packaging waste.
1. Introduction
Pesticide packaging waste is difficult for the environment to decompose, and may trigger serious agricultural nonpoint source pollution. In recent years, pesticide packaging waste has attracted worldwide attention, and responsive control measures have been taken [1]. For instance, the National Institute of Empty Containers had been established in Brazil to promote the recycling and treatment of waste pesticide packages [2]. China had promulgated and implemented the Administrative Measures for the Recycling and Treatment of Pesticide Packaging Waste in 2020, which stipulates the responsibilities of the government, pesticide producers, operators, and users in the recycling or harmless treatment of pesticide packaging waste [3]. However, the recycling situation of pesticide packaging waste in reality is not optimistic, as few farmers adopt more reasonable treatment methods such as centralized recycling [4,5], which causes a huge challenge to the protection of rural environment.
A lot of research has been done regarding the process, mechanism, and incentive measures of pesticide packaging waste recycling, involving different stakeholders like the government, pesticide manufacturers, distributors, and farmers [6,7,8]. A series of policy suggestions, such as intensifying propaganda and training and strengthening department cooperation, has also been put forward aiming to establish a better recycling system [9,10,11]. More and more scholars have realized that farmers’ behavior is at the core of pesticide packaging waste recycling and treatment, especially in areas dominated by smallholder farmers [12].
Farmers are agricultural producers and pesticide users, as well as direct implementers of pesticide packaging waste recycling and treatment. The underlying driving factors of farmers’ pesticide packaging waste recycling behaviors have been studied. For instance, farmers with a higher education level showed stronger willingness to recycle pesticide packaging waste [13], and farmers’ expectations of economic benefits were more likely to promote their participation in environmentally friendly activities [14]. In addition, sex, training, awareness, subsidies, and social norms also showed prominent influence [15,16].
Many published studies have suggested that social psychological factors, such as behavior perception, social norms, behavioral attitudes, etc., may have a significant impact on various environmental behaviors of farmers [17,18,19]. However, while most published studies have focused on the relationship between individual social and economic characteristics and treatment behavior, the social psychological regulation path of packaging waste treatment behavior remains severely under discussed, which restricts deeper understanding of the problem and the pertinence and effectiveness of relevant management measures.
Some social psychological models were used to study the farmers’ behavior, such as a logit model, the technology acceptance model, and the theory of planned behavior (TPB) [20,21,22]. Among all these models, the TPB is widely used to study the internal mechanism and influence path of farmers’ behaviors, such as pesticide use [19], express packaging recycling [23], household waste classification and treatment [24], and green production willingness [25]. TPB explores influencing factors of behavior intention from behavior attitude, subjective norms, and perceptual behavior control, and establishes the relationship between behavior intention and actual behavior, with strong predictive and explanatory abilities [26,27]. Therefore, it is reasonable to suspect that TPB can also be applied to explain farmers’ pesticide packaging waste recycling behaviors. Nevertheless, after careful literature review, we did not find published studies which investigated this topic thoroughly.
Aiming to address this deficiency, in the current study, we adopted the TPB model to investigate pesticide packaging waste recycling behaviors of Chinese farmers. The basic assumption is that pesticide packaging waste recycling behavior (B) is comprehensively influenced by intention (IN), subjective norms (SN), perceptual behavior control (PBC), and attitude toward the behavior (AB). From the framework of TPB, we put forward the following specific hypotheses as illustrated in Figure 1:
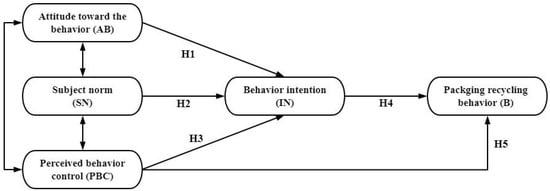
Figure 1.
Study assumptions based on the theory of planned behavior (TPB).
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
AB has a significant impact on IN;
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
SN has a significant impact on IN;
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
PBC has a significant impact on IN;
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
IN has a significant impact on B;
Hypothesis 5 (H5).
PBC has a significant influence on B.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Sampling Design
Fruit tree planting reports the largest demand for pesticides in many agricultural production types, among which apple is one of the most produced fruits in the world [28]. Thus, in this study, we selected 6 counties and districts that are main apple production counties in Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province, China as our study sites. In consideration of representativeness of the sample and the feasibility of sampling process, a multi-stage sampling method had been used: in stage one, 3 townships of apple production within each county or district were randomly chosen; in stage two, 3–5 villages were randomly selected from each chosen township; in stage three, 5–10 apple growers were randomly selected in each chosen village as the respondents.
For the required sample size, we chose a conservative prevalence of 40% for any pesticide waste packaging recycling behavior in farmers. Statistical significance and acceptable error were set as 5% and 25%, respectively, which yielded a preliminarily calculated sample size of 96. Considering that the sampling error of multi-stage design is inevitably larger than simple random sampling, we used a design effect (Deff) of 2 to further adjust the final sample size into 192. A total of 210 eligible respondents were included and surveyed, and 198 of them (94.29%) provided valid and complete information. The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Yan’an University (Approval code: YAU-20210113).
2.2. Questionnaire and Variables
We used a self-development questionnaire to collect relevant information from the apple farmers. This questionnaire is a comprehensive instrument that contains multiple modules, mainly addressing demographics, socioeconomic status, agricultural production capacity, and pesticide packaging waste recycling. Questions regarding the five aspects (AB, SN, PBC, IN, B) of pesticide packaging waste recycling were designed following the concept of TPB. Each aspect was measured by using four specific questions, and the answers to every question used a seven-point Likert scale, from “completely disagree” to “completely agree”, with assigned scores from 1 to 7 (Table 1). In addition, the opinions of farmers and management departments on pesticide packaging waste recycling were collected through semi-structured interviews. Prior to the formal survey, we performed a pre-survey among 30 apple farmers to test the validity, reliability, and readability of the questionnaire, and further revised it accordingly. Face-to-face interviews were used to collect relevant information from the respondents by pre-trained interviewers.

Table 1.
All the questions regarding pesticide packaging waste recycling.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to present the general characteristics of the respondents. Exploratory factor analysis and principal component analysis were used to estimate the internal and structural validity of the questionnaire. Because the five aspects of pesticide packaging recycling (AB, SN, PBC, IN, B) were all latent variables, which cannot be measured directly, in order to illustrate their complicated intercorrelations, we adopted Structural Equation Modeling (SEM), a powerful statistical model and ideal choice for latent variables analysis [29]. The AMOS software was used to perform SEM. Significance level was set as a two-tailed p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Apple Farmers
The respondents were mainly young and middle-aged apple farmers under the age of 50, with men accounting for 58.59%. As for education, 20.71% of the farmers had received “University and above” education, and 2.53% did not receive school education. The family size in the surveyed area was mostly 4–5 people, accounting for 61.61%. The household labor force size was generally 1–2 people. Less than half (43.94%) of the farmers reported planting less than 10 years, and 33.84% reported 11–20 years. Most (80.31%) farmers planted an orchard area of 0.2–0.67 hectares, indicating that the orchard area in the survey site was managed mainly by small-scale farmers (Table 2).

Table 2.
Basic characteristics of the farmers surveyed.
The average annual total income of peasant households in the survey area was 51.74 ± 46.62 thousand yuan, among which the agricultural income was 29.03 ± 33.80 thousand yuan, accounting for 56.12% of the total income and indicating that this area is an agricultural crop area (Table 3). The income of fruit trees was the main agricultural income, with an average of 15.16 ± 21.74 thousand yuan, accounting for 29.30% of the total income and 48.27% of the agricultural income. Agricultural income from facilities and other agricultural income only accounted for 14.75% of the total income. The average total expenditure of peasant households was 40.04 ± 31.41 thousand yuan, among which the average agricultural expenditure was 12.44 ± 15.68 thousand yuan, accounting for 31.06% of the total expenditure. Seed and seedling expenditure was the most important agricultural expenditure item, accounting for 7.81% of the total expenditure and 32.18% of the agricultural expenditure. Pesticide expenditure accounted for 5.23% of the total expenditure and 13.81% of the agricultural expenditure.

Table 3.
Household income and expenditures of agricultural production (Unit: Thousand Yuan).
3.2. Validity of the Questionnaire
The Cronbach’s α coefficient is generally used to test sample reliability, with a coefficient greater than 0.9 indicating very good internal reliability [30,31]. The overall Cronbach’s α coefficient for all variables in the survey questionnaire of this study was 0.935, and between 0.893 and 0.935 for different dimensions, indicating an ideal internal reliability (Table 4). Factor analysis was used to test the structural validity of the data, the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin test result was 0.902, and Bartlett’s spherical test was statistically significant, indicating suitability for factor analysis (Table 4). Principal component analysis further revealed that the cumulative load on the main components reached 78.02%. Altogether four components can be extracted, and factor loading for all indicators was above 0.65, all indicating that the structural validity of the questionnaire is good.

Table 4.
Exploratory factor analysis and questionnaire reliability test results.
3.3. SEM Fitting Results
Model fitting indexes of the proposed SEM are shown in Table 5: the Chi-square degrees of freedom ratio (comparative fit index) was 2.222, and the RMSEA was 0.079. Except for the Goodness of Fit Index (GFI), all the other fitting indexes met the threshold conditions, suggested an ideal fitting of the SEM. The AMOS fitting results for the TPB structural model are shown in Figure 2: AB, SN, and PBC were all correlated, indicating a reciprocal relationship between behavioral attitudes, social norms, and perceptual behavioral control. The most important determinant of IN is SN, with a standardized path coefficient of 0.449 (p < 0.05), followed by AB, with a standardized path coefficient of 0.43 (p < 0.05), indicating that the more positive the farmers’ attitude and the more perfect the social norms, the easier it will be for taking pesticide packaging waste recycling measures. The insignificant correlation between PBC and IN (p > 0.05) suggested that perceptual behavioral control had no effect on the behavioral intention of pesticide packaging waste recycling. The above findings were supportive to hypothesis H1 and H2, but not to H3. The standardized path coefficient of PBC to B was 0.305 (p < 0.05), supportive of H5, indicating that the perceptual behavior control had a direct and significant regulatory effect on the pesticide packaging waste recycling behaviors of fruit growers. IN had a significant positive regulatory effect on B, with a standardized path coefficient of 0.726 (p < 0.05), supporting H4 (Figure 2). The standardized path coefficients between the observed variables and the latent variables are displayed in Table 6.

Table 5.
Goodness-of-fit indexes of SEM model.
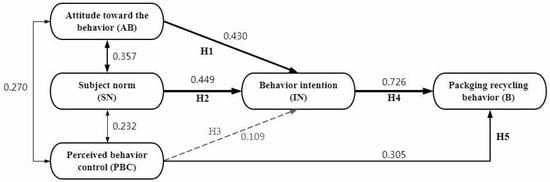
Figure 2.
SEM fitting results for the proposed model. Note: Solid arrow indicates significant (p < 0.05), dotted arrow indicates insignificant (p > 0.05).

Table 6.
Standardized path coefficients and significance between observable and latent variables.
4. Discussion
The misbehavior of farmers in dealing with pesticide packaging waste threatens the agricultural ecological environment and the quality and safety of agricultural products. However, there are few in-depth studies investigating pesticide packaging waste recycling behaviors of the famers through the perspective of a social psychological regulation path. In this study, we used the TPB model to analyze associated factors of pesticide packaging waste recycling behaviors of Chinese fruit farmers. Model fitting results were generally consistent with the basic theory of Ajzen [32], which confirmed the applicability of TPB theory in explaining pesticide packaging waste treatment in fruit farmers. The model results showed that stronger intention (IN) was positively associated with pesticide packaging waste recycling behavior (B). This is consistent with previous studies, which suggested that behavior intention is the most direct factor affecting the actual action, and individual behavior intention can promote the implementation of behavior [30,31,33]. Therefore, measures to enhance farmers’ intention of recycling pesticide packaging waste are crucial.
Analytical results indicated that farmers’ behavior attitude (AB) and social norms (SN) were statistically associated with farmers intention to recycle pesticide packaging waste, indicating that farmers’ recycling intention could be driven by both social norms and personal behavioral attitude. Similar findings were reported for other behaviors of rural residents [16]. Usually, farmers’ behavioral decisions are based on the predictive consequences of behavioral choices [34,35]. In this study, SN is the most important explanation factor of farmers’ behavioral intentions, and pesticide packaging safety tips are the main variable of social behavior, showing that pesticide packaging safety tips are an important way to convey packaging processing knowledge, which may play an important role in farmers’ behavior. Lin et al. reported that pesticide packaging specifications affected pesticide packaging recycling and the recycling process [36], thus, improving the packaging design of pesticides probably can increase the possibility of being recycled. Government policy publicity and training are also crucial for farmers’ behavioral intention, which has also been confirmed in other behaviors of farmers [37]. Through policy training and publicity, positive direction and guidance can enhance farmers’ awareness of recycling [38]. Furthermore, farmers’ behavioral intention could be influenced by behaviors and attitudes of other surrounding farmers, which suggests that farmers can establish typical “good behavior” in pesticide packaging waste recycling and guide other farmers to follow.
Attitude toward behavior (AB) was the second most important factor affecting farmers’ intention to recycle pesticide packaging waste, with a statistically positive standardized path coefficient, indicating that the more positive the farmers’ attitude is, the higher the degree of behavioral intention to take part in the recycling treatment of pesticide packaging waste will be, which is consistent with previous research results [39]. Farmers’ behavioral attitude is reflected in the recognition of serious consequences of discarded pesticide packaging and the environmental benefits that follow recycling. A previous study reported that farmers’ attitude towards pesticide packaging waste recycling was affected by multiple personal factors, among which the cognitive level of pesticide harm was particularly obvious [40]. These study results state that deeper understanding of the ecological and environmental harm caused by discarded pesticide packaging is associated with an elevated level of a supportive attitude and stronger behavioral intention in farmers. Therefore, extensive publicity, training, and social science popularization should be promoted, to help farmers realize the harm of pesticide packaging waste and cultivate positive motivation for pesticide packaging waste recycling behaviors.
Another interesting finding is that although perceived behavior control (PBC) was insignificantly related to behavioral intention of fruit farmers, it was directly associated with farmers’ recycling behavior. This finding is comparable to previous studies on farmers’ garbage classification behavior and seed treatment behavior [15,41]. It may suggest that the easier pesticide packaging waste recycling is, the higher farmers’ participation in pesticide packaging waste recycling will be. The easiness of pesticide packaging waste recycling is jointly influenced by many factors, such as the accessibility of centralized recycling or treatment facilities, time spent for household processing, availability of pesticide packaging waste recycling knowledge, and the perceived difficulty of recycling. Hence, measures such as establishing an accessible pesticide packaging waste recycling system (such as setting up more recycling points), reducing time required for farmers’ implementation behavior, and providing more recycling science and knowledge (such as policy publicity, packaging tips, retailer introduction, etc.) could be effective in promoting the implementation of farmers’ recycling behavior.
The major findings of our study suggest that improving farmers’ attitude and willingness, enhancing social norms, and optimizing behavioral perception could be effective in promoting the implementation of farmers’ recycling behavior in terms of pesticide packaging waste. Specific measures that can be taken include: (1) establishing a sound pesticide packaging recycling and treatment policy system; (2) strengthening publicity of popular science, such as the environmental harm of pesticide packaging waste and the necessity of recycling and treatment, to enhance farmers’ awareness of environmental protection; (3) standardizing the relevant contents of pesticide packaging, to guide farmers in carrying out packaging waste recycling; (4) carrying out pilot programs on comprehensive recovery and treatment of pesticide packaging waste in key areas; and (5) improving infrastructure to help pesticide packaging waste recycling, such as increasing the number of centralized recycling points, timely processing of the packaging after recycling, and reducing time and economic cost of recycling and treatment by farmers. Moreover, incentives can be considered when implementing these measures, when appropriate.
5. Conclusions
This study revealed that the TPB can explain well the mechanisms behind the behavior of Chinese fruit farmers in regards to pesticide packaging waste recycling and treatment. Specifically, farmers’ pesticide packaging waste recycling behavior is influenced by their behavioral intention and perceived behavioral control, and behavioral intention can be affected by attitudes toward the behavior and subject norm. This study highlights the important role of socio-psychological structural models in understanding fruit farmers’ pesticide packaging waste recycling behavior, and provides valuable information for constructing effective intervention policies and measures.
Author Contributions
L.Y.: Data curation, statistical analysis, writing of the original draft. X.Z.: Data curation, statistical analysis. D.Z.: Data curation, editing. J.D.: Data curation, conceptualization, critically edited and reviewed the original draft. Y.Z.: Participated in writing, critically edited and reviewed the original draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number. 32160296). Scientific research project of Yan’an University (grant number. YDY2020-33).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Yan’an University.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the survey participants.
Data Availability Statement
The database of the current study will be available from the corresponding authors under reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, Z.S.; Huan, A.H.; Hu, J.H.; Ding, C.G. Current status and countermeasures of pesticide packaging waste management in rice field in China. World Pestic. 2009, 31, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.B.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Kuang, Y.J.; Li, C.; Sun, M.X.; Zhang, L.X.; Chang, D.H. Waste Pesticide Bottles Disposal in Rural China: Policy Constraints and Smallholder Farmers’ Behavior. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, PRC, Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Administrative Measures for the Recycling and Treatment of Pesticide Packaging Waste; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, PRC: Beijing, China, 27 August 2020.
- Li, Z.S.; Yang, H.C. Investigation and approach analysis of pesticide packaging waste. Chin. Agric. Inf. 2013, 13, 273–274. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, W.W.; Wang, M.Y.; Cao, M.K.; Bao, W.X. Investigation of Pesticide Packaging waste Recycling and Disposal Recommendations. Pestic. Sci. Adm. 2014, 35, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.J. Treatment of Rural Pesticide Packaging Waste under Ecological Civilization. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2022, 5, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.F.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y. Research on Farmers Pesticide Packaging Waste Management Behavior. Liaoning Agric. Sci. 2022, 2, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Zhou, H. Can Social Trust and Policy of Rewards and Punishments Promote Farmers’ Participation in the Recycling of Pesticide Packaging Waste? J. Arid. Land Res. Environ. 2021, 35, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.H.; Gu, B.G. CurrentSituation and future Prospects for International pesticide management. Pestic. Sci. Adm. 2020, 41, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Jin, S. Institutional arrangements and pattern for pesticide packaging wastes collection: A comparative analysis of international experiences. World Agric. 2013, 12, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Marnasidis, S.; Stamatelatou, K.; Verikouki, E.; Kazantzis, K. Assessment of the generation of empty pesticide containers in agricultural areas. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.Q. Pesticide packaging recycling is an important breakthrough of agricultural non-point source pollution control. Pestic. Manag. Sci. 2016, 37, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Stadlinger, N.; Mmochi, A.J.; Dobo, S.; Gyllbäck, E.; Kumblad, L. Pesticide use among smallholder rice farmers in Tanzania. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2011, 13, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofenk, D.; Pennings, J.M.E.; Trujillo-Barrera, A. Understanding Producers’ Motives for Adopting Sustainable Practices: The Role of Expected Rewards, Risk Perception, and Risk Tolerance. Appl. Econ. Assoc. 2014, 7, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.L.; Yang, B.C.; Wan, X.W. Analysis of the influencing factors of pesticide waste treatment behavior—Based on the survey of rural households in Guangdong Province. Rural Econ. 2014, 9, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.W.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhu, Z.; Kong, F.B. How to encourage farmers to recycle pesticide packaging wastes: Subsidies vs social norms. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 133016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.P.; Sun, F.; Pan, C.; Yang, B.; Li, Y. The Deviation of the Behaviors of Rice Farmers from Their Stated Willingness to Apply Biopesticides—A Study Carried Out in Jilin Province of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondori, A.; Bagheri, A.; Allahyari, M.S.; Damalas, C.A. Pesticide Waste Disposal Among Farmers of Moghan Region of Iran: Current Trends and Determinants of Behavior. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y. Analysis of Influencing Factors of Pesticide Packaging Waste Recycling. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Boccia, F.; Sarnacchiaro, P. Chi-squared automatic interaction detector analysis on a choice experiment: An evaluation of responsible initiatives on consumers’ purchasing behavior. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Du, Z.X. Farmers’ Willingness to Participate in the Recycling of Pesticide Packaging Waste and its Influencing Factors-An Empirical Analysis Based on Logistic and Semi Logarithmic Model. World Agric. 2018, 1, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, P.K. Farmer behavior towards pesticide use for reduction production risk: A Theory of Planned Behavior. Clean. Circ. Bioecon. 2022, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.J. An Empirical Study on the Factors Influencing the Recycling Behavior of Express Packages of Rural Residents. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.H.; Wang, C.J. Research on the Behavior Mechanism of Farmers Participating in the Classification and Treatment of Rural Domestic Garbage. Ecol Econ. 2020, 36, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.Y.; Sun, H. Study on safety vegetable growing intention of farmers based on the theory of planned behavior. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2014, 41, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ajzen, I. The Theory of Planned Behaviors. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process; University of Massachusetts at Amherst: Amherst, MA, USA, 1991; Volume 50, pp. 179–211. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, W.T.; Jiang, G.R. Review of the planning and behavior theory. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 2008, 02, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Shaanxi Bureau of Statistics. 2021 Shaanxi Statistical Yearbook. Available online: http://tjj.shaanxi.gov.cn/upload/2021/zk/indexch.htm (accessed on 26 February 2022).
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 4th ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.N.; Li, S.P.; Zhang, J. From the Willingness to the Behaviors: The Impacts of Information Acquisition on Farmers’ Pro-Environmental Behaviors. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 34, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Li, D.L.; Miao, H.P.; Memti, M. Study on the Influence of Cotton Target Price System on Cotton Farmers in Southern Xinjiang-Empirical Analysis Based on TPB and SEM. Chin. J. Agric. Reg. Plann. 2018, 39, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Ajzen, I. From Intentions to Actions: A Theory of Planned Behaviour; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Natan, M.B.; Sharon, I.; Mahajna, M.; Mahajna, S. Factors affecting nursing students’ intention to report medication errors: An Application of the Theory of Planned Behavior. Nurs. Educ. Today 2017, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannell, D.J. Pests and pesticides, risk and risk aversion. Agric. Econ. 1991, 5, 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, L.; Gan, C.L.; Wu, M.; Cheng, Y.R. Study on the influence of farmland perceived value on their input behavior—Take the typical sample survey in Wuhan and Ezhou as an example. Chin. Land Sci. 2018, 32, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.S.; Duan, Z.C.; Zuo, L.J.; He, Z.F. Difficulties and reflections of the implementation of pesticide package recycling project: In the view of packaging management. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2018, 45, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yan, L. The influence of ecological cognition on farmers’ behavior of returning farmland to forest—Is based on planned behavior theory and multi-group structure equation model. Chin. Land Sci. 2019, 33, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, B.; Hou, J.; Wang, Z. Analyzing Farmers’ Low-Carbon Production Behavior: Based on the Theory of Planned Behavior. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2015, 24, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Senger, I.; Borges, J.A.R.; Machado, J.A.D. Using the theory of planned behavior to understand the intention of small farmers in diversifying their agricultural production. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 49, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J. Pesticide packaging waste recycling: Support attitude and mode selection. Rev. Econ. Manag. 2013, 12, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hurley, T.; Mitchell, P. Value of neonicotinoid seed treatments to US soybean farmers. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).