Feasibility Analysis of Biomass Hydrochar Blended Coal Injection for Blast Furnace
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
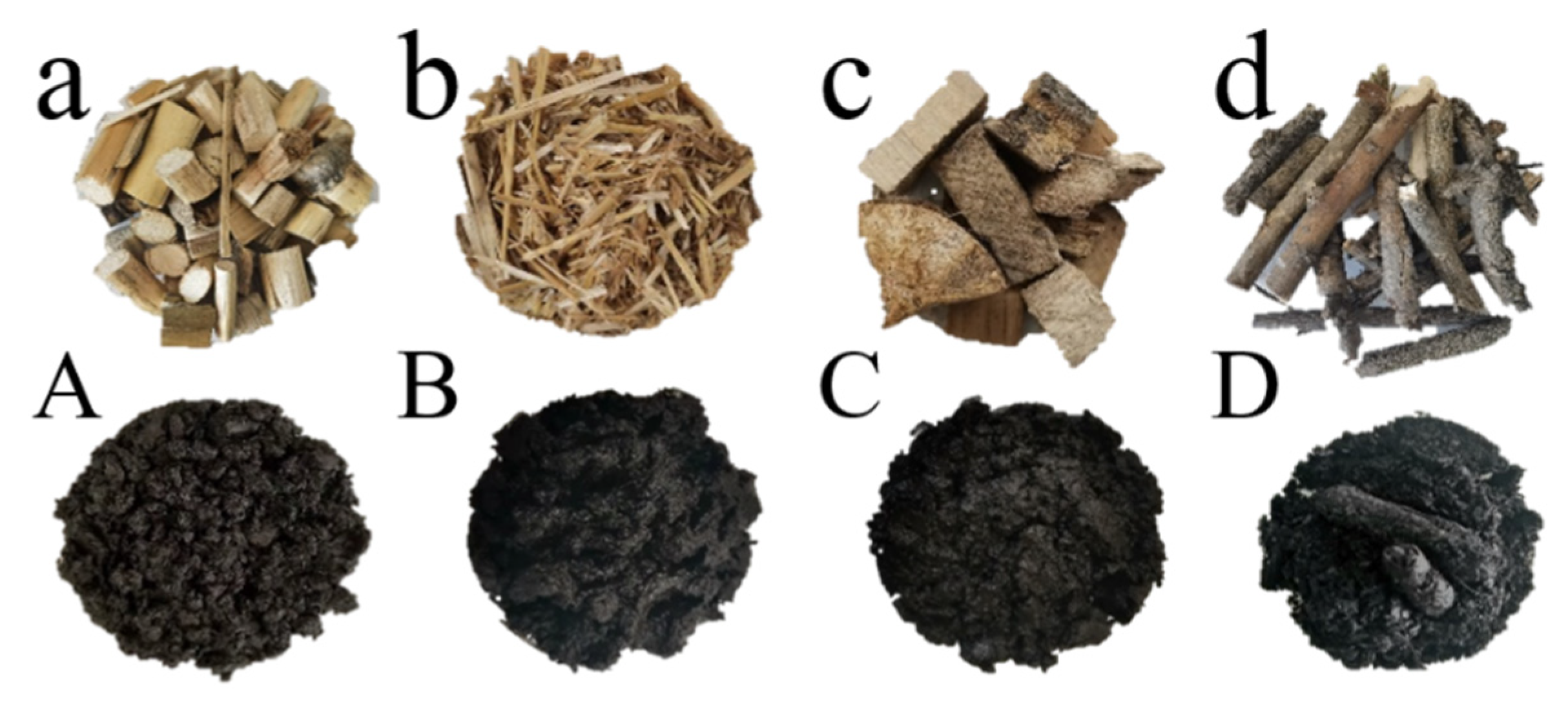
2.1. Raw Material Preparation
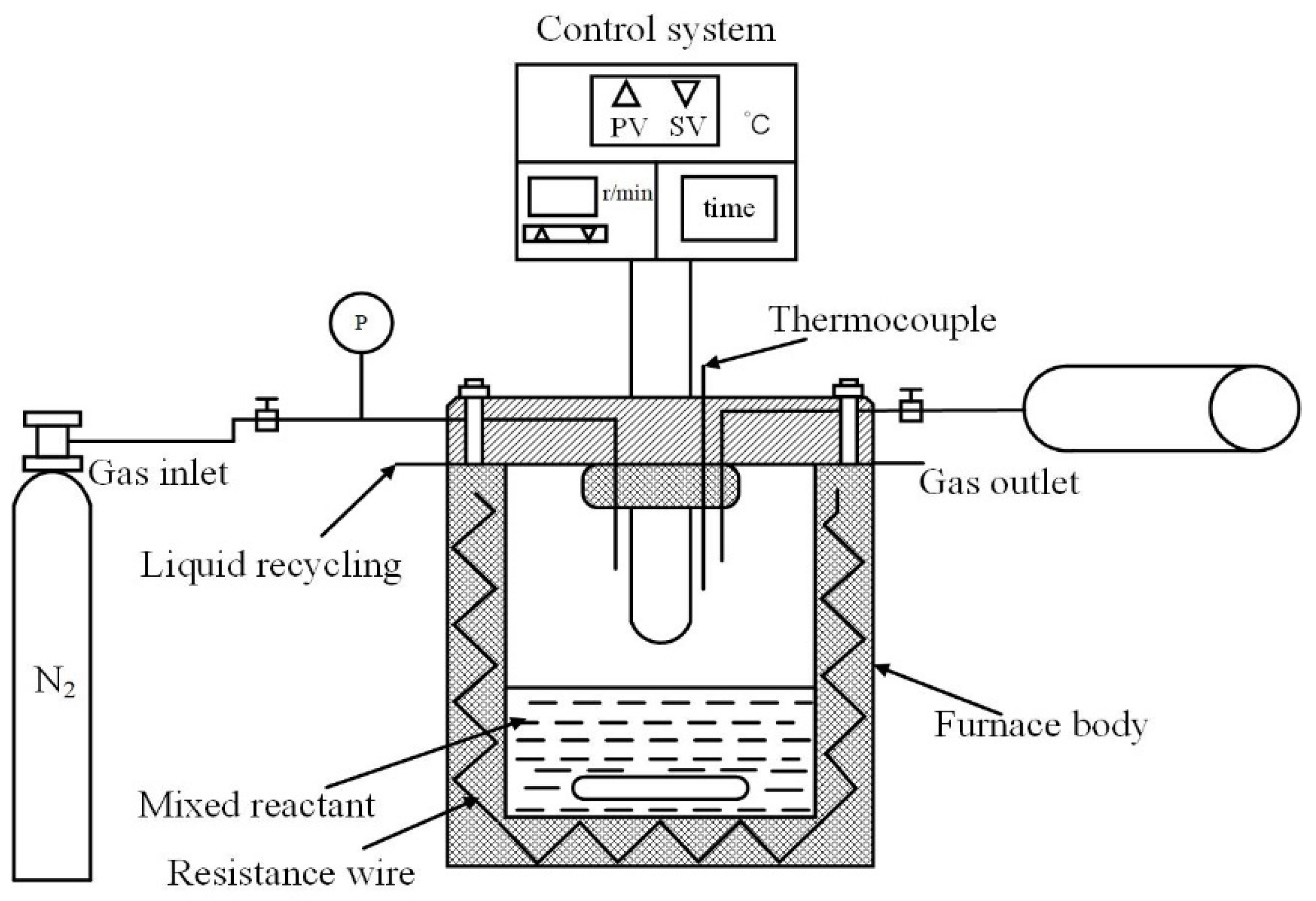
2.2. HTC Experiment
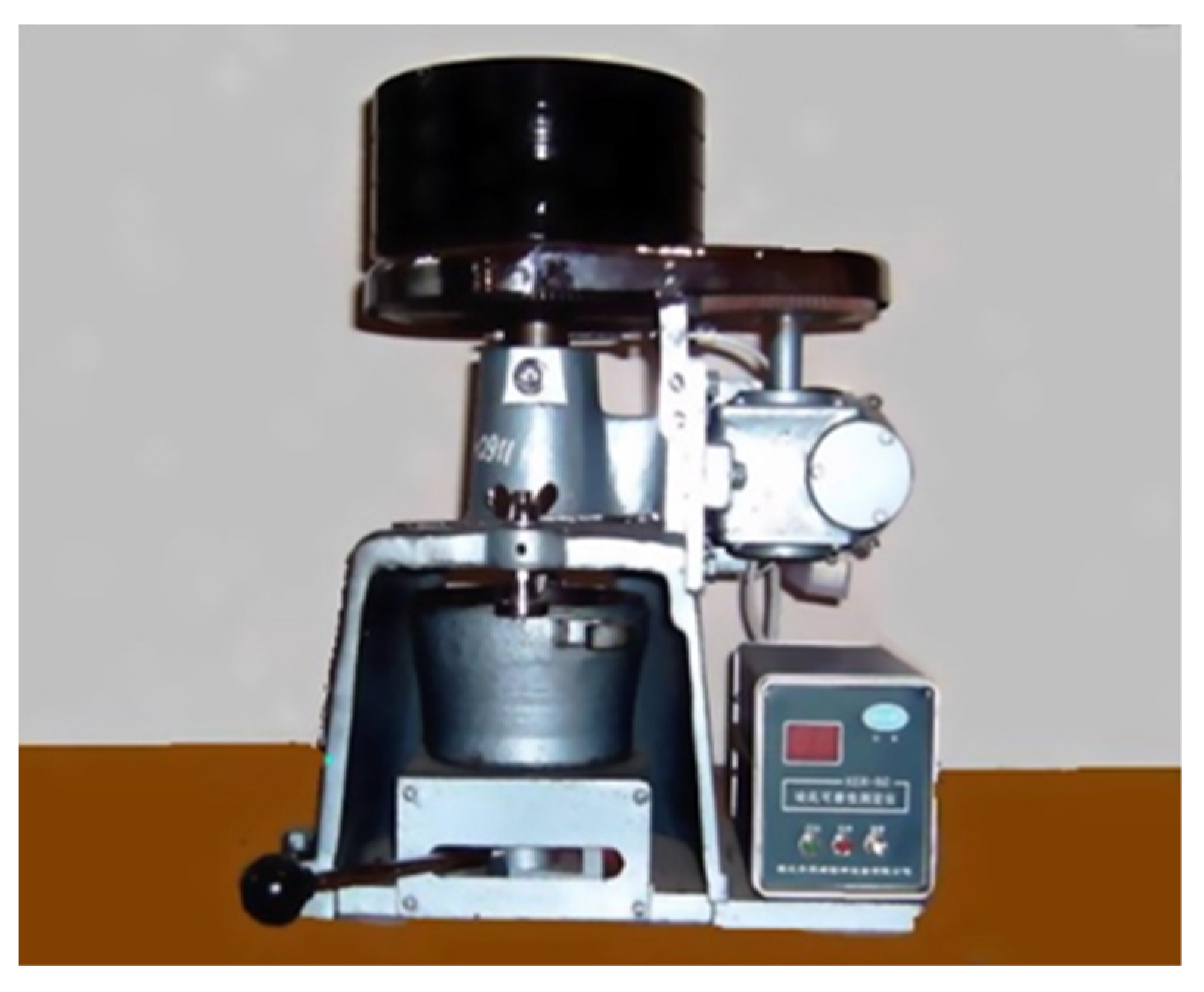
2.3. Basic Performance Analysis
2.4. Technological Property Analysis
2.5. Study on Optimization of Biomass Carbon/Pulverized Coal Blending
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance Test of Hydrochar Blast Furnace
3.1.1. Proximate and Ultimate Analyses
3.1.2. Alkali Metal Content
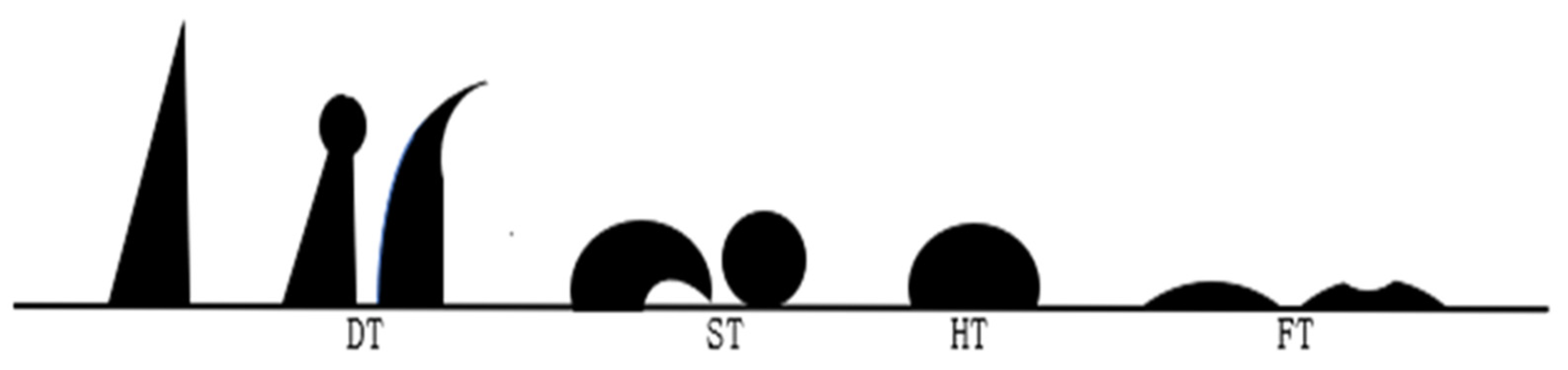
3.1.3. Ash Composition and Ash Fusion Characteristics
3.1.4. Grindability
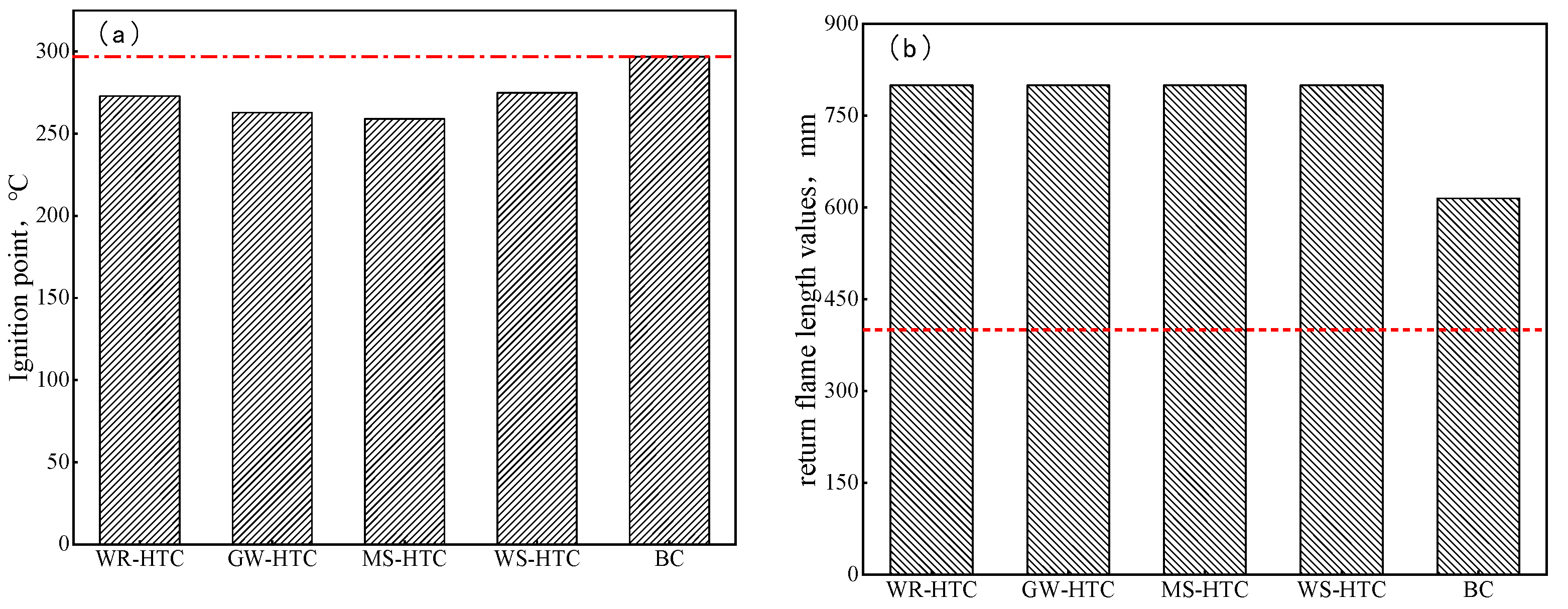
3.1.5. Safety Properties
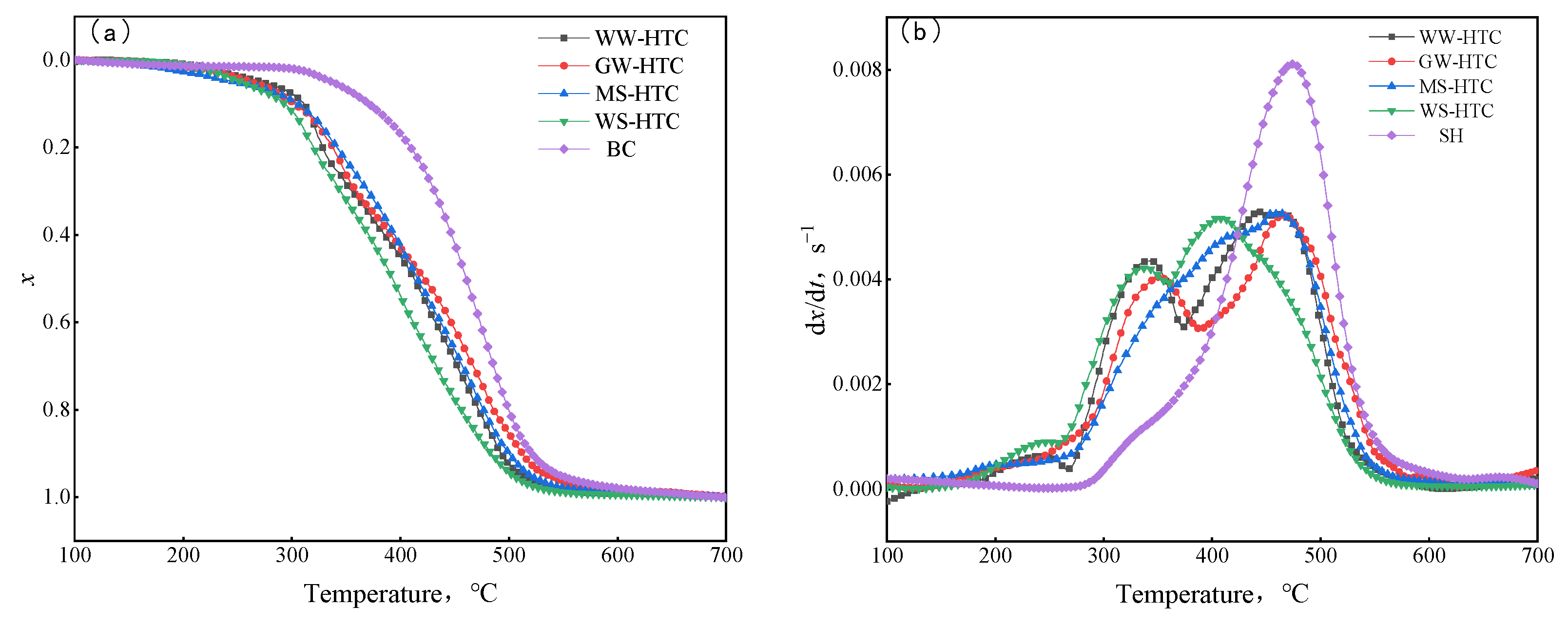
3.1.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.2. Performance Test of Blended Coal
3.2.1. Coal-Blending Scheme and Composition Analysis
3.2.2. Alkali Load Analysis
3.2.3. Ash Composition and Ash Fusion Characteristics
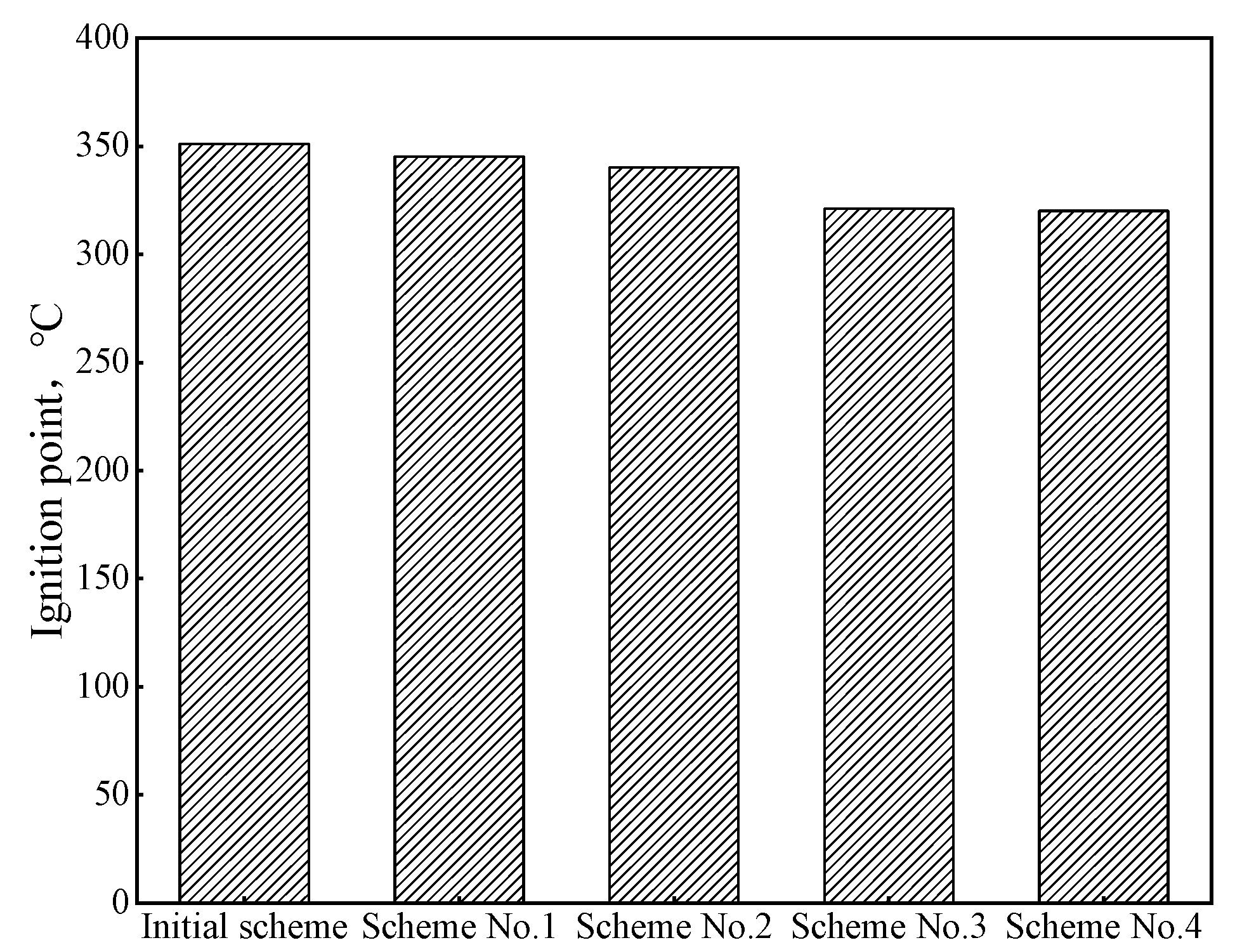
3.2.4. Safety Properties
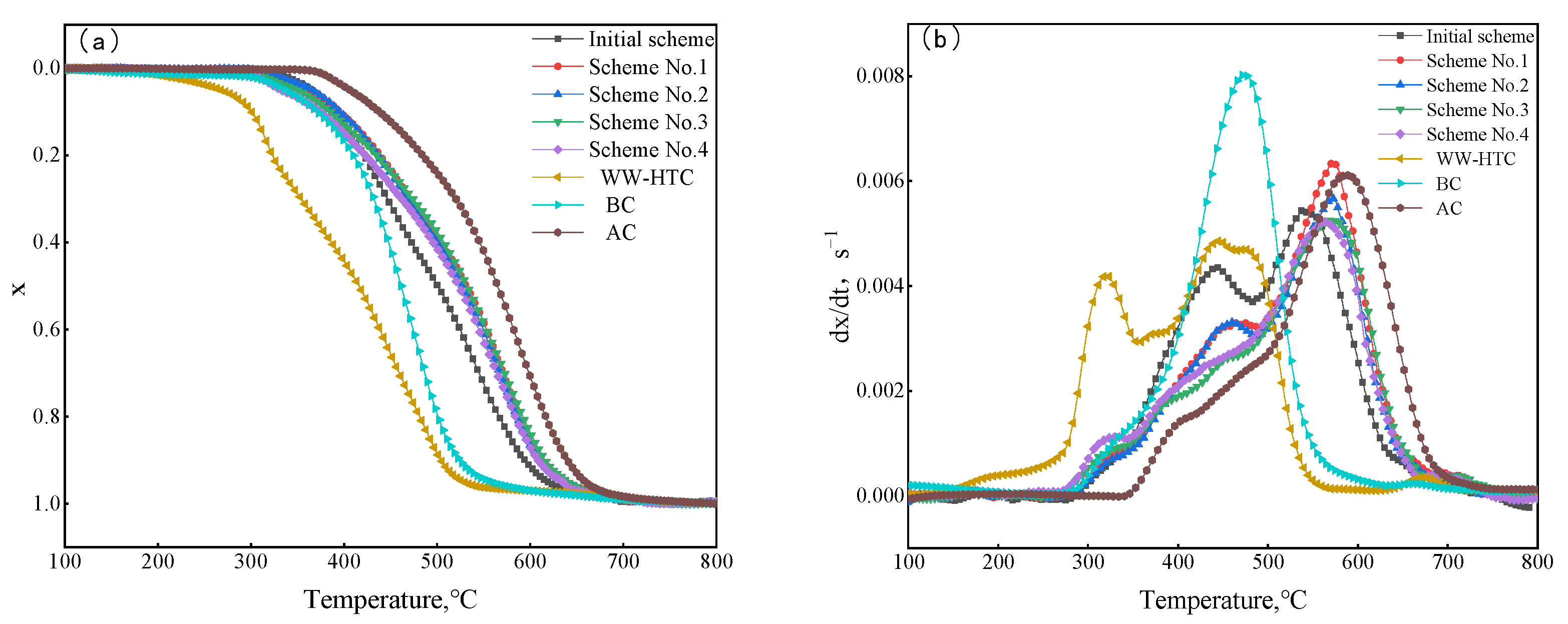
3.2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suopajärvi, H.; Pongrácz, E.; Fabritius, T. The potential of using biomass-based reducing agents in the blast furnace: A review of thermochemical conversion technologies and assessments related to sustainability. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Shan, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, X.Q.; Yang, Y.; Luque, R.; Duan, P.G. Hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge: Effect of inorganic salts on hydrochar’s physicochemical properties. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 7010–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhou, S.X. Comparison of energy consumption and environmental impact of replacement of coal with straw injection into blast furnace. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 36, 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.F.; Hu, X.Y.; Li, X.J. Biomass resource’s application in iron and steel enterprises of China. Res Iron. Steel 2015, 43, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Y.Q.; Deng, X.Q.; Luque, R.; Xu, Z.X.; Yan, L.; Duan, P.G. Hydrothermal carbonization of activated sewage sludge over ammonia-treated Fenton sludge to produce hydrochar for clean fuel use. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5077–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Song, H.; Li, P.J.; He, Z.X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K.; Duan, P.G. Hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge: Effect of aqueous phase recycling. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 123410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Cheng, W.Y.; Lu, K.M.; Huang, Y.P. An evaluation on improvement of pulverized biomass property for solid fuel through torrefaction. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3636–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mellin, P.; Lövgren, J.; Nilsson, L.; Yang, W.; Salman, H.; Hultgren, A.; Larsson, M. Biomass as blast furnace injectant–Considering availability, pretreatment and deployment in the Swedish steel industry. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 102, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suopajärvi, H.; Kemppainen, A.; Haapakangas, J.; Fabritius, T. Extensive review of the opportunities to use biomass-based fuels in iron and steelmaking processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 709–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Zhang, L.; Cang, D.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Xu, C.C. Current status and potential of biomass utilization in ferrous metallurgical industry. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumme, J.; Eckervogt, L.; Pielert, J.; Diakité, M.; Rupp, F.; Kern, J. Hydrothermal carbonization of anaerobically digested maize silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9255–9260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xue, G. Preparation and characterization of hydrochar from waste eucalyptus bark by hydrothermal carbonization. Energy 2016, 97, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergius, F. Production of hydrogen from water and coal from cellulose at high temperatures and pressures. J. Soc. Chem. Ind. 1913, 32, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, M.; Volpe, M.; Volpe, R.; Fiori, L.; Dahl, O. Spatially resolved spectral determination of polysaccharides in hydrothermally carbonized biomass. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yu, R.; Ji, X.; Guo, M. Hydrothermal carbonization of holocellulose into hydrochar: Structural, chemical characteristics, and combustion behavior. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Mao, X.; Ye, L.; Xu, W.; Ning, X.; Zhang, N.; Teng, H.; Wang, C. Hydrothermal carbonization of maize straw for hydrochar production and its injection for blast furnace. Appl. Energy 2020, 266, 114818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.R.; Schott, D.L.; Lodewijks, G. Physical properties of solid biomass. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 2093–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channiwala, S.A.; Parikh, P.P. A unified correlation for estimating HHV of solid, liquid and gaseous fuels. Fuel 2002, 81, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Yang, L.; Gao, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liao, C.; Lu, C.; Zhu, C. Characterization and pelletization of cotton stalk hydrochar from HTC and combustion kinetics of hydrochar pellets by TGA. Fuel 2019, 244, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Liu, P.; Xu, G.S.; Liu, Q.; He, Z.X.; Wang, Q. Bio-fuel oil characteristic from catalytic cracking of hydrogenated palm oil. Energy 2017, 133, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Shao, J.; Ren, S. Characterisation and model fitting kinetic analysis of coal/biomass co-combustion. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 591, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Wang, G.W.; Shao, J.G.; Chen, Y.X.; Yang, T.J. Pulverized coal combustion of nitrogen free blast furnace. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2013, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Hou, X.; Shao, J.; Geng, W. Study on CO2 gasification properties and kinetics of biomass chars and anthracite char. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladejo, J.; Adegbite, S.; Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Wu, T. Catalytic and non-catalytic synergistic effects and their individual contributions to improved combustion performance of coal/biomass blends. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; Zhan, Z.; Li, Z.; Yao, H. Effect of cellulose, lignin, alkali and alkaline earth metallic species on biomass pyrolysis and gasification. Fuel Processing Technol. 2010, 91, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, C.; Ning, X.; Zhang, J.; Mao, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, C. Comprehensive Study on the Feasibility of Pyrolysis Biomass Char Applied to Blast Furnace Injection and Tuyere Simulation Combustion. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 20166–20180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolcock, P.J.; Brown, R.C. A review of cleaning technologies for biomass-derived syngas. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 52, 54–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Mbeugang, C.F.M.; Liu, D.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Hu, X. Simulation of sorption enhanced staged gasification of biomass for hydrogen production in the presence of calcium oxide. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 26855–26864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, C.Q. Evaluation of pulverized coal utilization in a blast furnace by numerical simulation and grey relational analysis. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; He, Y.; Yu, X.; Banks, S.W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, R.; Bridgwater, A.V. Review of physicochemical properties and analytical characterization of lignocellulosic biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Sample | Proximate Analysis (wt, %) | Ultimate Analysis (wt, %) | Mass Yield/% | HHV/(MJ·kg−1) | Energy Yield/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ad | Vd | FCd * | Nd | Cd | Hd | Sd | Od * | ||||
| WC | 1.31 | 81.90 | 16.79 | 0.25 | 48.60 | 6.06 | 0.02 | 43.76 | / | 19.55 | / |
| GW | 2.83 | 80.65 | 16.52 | 0.33 | 48.67 | 6.55 | 0.02 | 41.60 | / | 20.34 | / |
| MS | 3.90 | 79.53 | 16.57 | 0.93 | 45.02 | 6.07 | 0.08 | 44.00 | / | 18.23 | / |
| WS | 7.14 | 80.75 | 12.11 | 0.59 | 44.79 | 6.29 | 0.09 | 41.11 | / | 18.64 | / |
| WC-HTC | 2.42 | 58.13 | 39.46 | 0.35 | 63.76 | 5.35 | 0.05 | 28.08 | 46.01 | 25.61 | 60.26 |
| GW-HTC | 1.67 | 65.78 | 32.55 | 0.97 | 63.62 | 5.81 | 0.04 | 27.89 | 59.51 | 26.13 | 76.44 |
| MS-HTC | 2.19 | 58.13 | 39.68 | 1.14 | 68.69 | 5.22 | 0.07 | 22.69 | 50.30 | 27.73 | 76.49 |
| WS-HTC | 6.92 | 50.42 | 42.66 | 0.96 | 61.68 | 5.02 | 0.07 | 25.36 | 45.40 | 24.67 | 60.07 |
| BC | 5.90 | 33.30 | 60.80 | 0.97 | 72.39 | 4.65 | 0.23 | 15.87 | / | 28.94 | / |
| Sample | w (K)/% | w (Na)/% | w (+Na)/% | Removal Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.11 | / |
| GW | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.20 | / |
| MS | 1.10 | 0.05 | 1.15 | / |
| WS | 0.81 | 0.09 | 0.90 | / |
| WC-HTC | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 74.90 |
| GW-HTC | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 91.07 |
| MS-HTC | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 94.75 |
| WS-HTC | 0.30 | 0.03 | 0.33 | 83.35 |
| BC | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.10 | / |
| Sample | CaO | K2O | MgO | SiO2 | SO3 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | Na2O | MnO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC | 77.60 | 10.40 | 4.83 | 1.93 | 1.41 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 0.29 | 0.08 |
| GW | 67.53 | 7.98 | 6.89 | 6.77 | 1.58 | 1.88 | 1.65 | 0.48 | 0.12 |
| MS | 11.03 | 34.31 | 11.28 | 12.16 | 2.50 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 1.75 | 0.04 |
| WS | 16.32 | 13.74 | 6.95 | 46.81 | 6.61 | 2.25 | 1.10 | 1.75 | 0.11 |
| WC-HTC | 73.57 | 2.76 | 3.21 | 5.70 | 2.53 | 1.59 | 3.78 | 0.56 | 0.08 |
| GW-HTC | 78.74 | 2.03 | 3.01 | 3.71 | 2.42 | 1.22 | 1.52 | 0.33 | 0.08 |
| MS-HTC | 11.26 | 6.31 | 2.63 | 60.45 | 1.46 | 2.74 | 2.28 | 0.47 | 0.12 |
| WS-HTC | 6.76 | 5.31 | 1.81 | 73.92 | 1.36 | 4.28 | 2.15 | 0.64 | 0.07 |
| BC | 24.25 | 0.44 | 3.13 | 36.39 | 10.43 | 14.93 | 6.42 | 1.76 | 0.19 |
| Sample | Deformation Temperature (DT) | Softening Temperature (ST) | Hemispheric Temperature (HT) | Flow Temperature (FT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC | 1148 | 1268 | 1287 | 1309 |
| GW | 1158 | 1242 | 1270 | 1281 |
| MS | 903 | 917 | 952 | 988 |
| WS | 981 | 1057 | 1120 | 1159 |
| WC-HTC | 1091 | 1312 | 1322 | 1332 |
| GW-HTC | 1259 | 1391 | 1340 | 1418 |
| MS-HTC | 910 | 1401 | 1478 | >1500 |
| WS-HTC | 1162 | 1279 | 1389 | 1470 |
| BC | 1092 | 1123 | 1140 | 1184 |
| Sample | Ti (°C) | Tf (°C) | Rmax (s−1) × 10−3 | Rmean (s−1) × 10−4 | S (s−2·°C−3) × 10−13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC-HTC | 302.12 | 512.23 | 7.70 | 1.65 | 2.71 |
| GW-HTC | 299.05 | 537.36 | 6.36 | 1.67 | 2.21 |
| MS-HTC | 290.15 | 519.86 | 6.71 | 1.71 | 2.63 |
| WS-HTC | 294.77 | 503.93 | 5.99 | 1.66 | 2.27 |
| BC | 336.94 | 547.59 | 9.21 | 1.64 | 2.43 |
| Coal-Blending Scheme | Hydrochar | Bituminous Coal | Anthracite Coal | Coke Powder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial scheme | 0 | 36 | 59 | 5 |
| Scheme No. 1 | 5 | 22 | 68 | 5 |
| Scheme No. 2 | 10 | 10 | 75 | 5 |
| Scheme No. 3 | 15 | 0 | 80 | 5 |
| Scheme No. 4 | 20 | 0 | 75 | 5 |
| Coal Blending Scheme | Ad, % | Vd, % | FCd, % | St, % | HHV (MJ·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC-HTC | 5.26 | 17.27 | 77.47 | 0.05 | 25.61 |
| BC | 5.90 | 33.30 | 60.80 | 0.23 | 28.94 |
| AC | 10.34 | 11.12 | 78.54 | 0.36 | 30.61 |
| Initial scheme | 9.13 | 17.90 | 72.97 | 0.34 | 30.17 |
| Scheme No. 1 | 9.08 | 17.87 | 73.05 | 0.34 | 30.16 |
| Scheme No. 2 | 9.21 | 17.56 | 73.23 | 0.34 | 30.11 |
| Scheme No. 3 | 9.26 | 17.70 | 73.04 | 0.34 | 30.02 |
| Scheme No. 4 | 8.86 | 20.05 | 71.09 | 0.32 | 29.77 |
| Scheme | Proportion | Alkali Load, kg/tHM |
|---|---|---|
| Initial scheme | 0-36-59-5 | / |
| Scheme No. 1 | 5-22-68-5 | +0.015 |
| Scheme No. 2 | 10-10-75-5 | +0.026 |
| Scheme No. 3 | 15-0-80-5 | +0.034 |
| Scheme No. 4 | 20-0-75-5 | +0.023 |
| Sample | Deformation Temperature (DT) | Softening Temperature (ST) | Hemispheric Temperature (HT) | Flow Temperature (FT) | CaO + MgO + K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial scheme | 1228 | 1397 | 1446 | 1490 | 10.76 |
| Scheme No. 1 | 1261 | 1420 | 1468 | >1500 | 10.95 |
| Scheme No. 2 | 1269 | 1399 | 1430 | 1498 | 11.17 |
| Scheme No. 3 | 1309 | 1366 | 1383 | 1433 | 11.73 |
| Scheme No. 4 | 1312 | 1339 | 1363 | 1424 | 12.43 |
| Sample | CaO | K2O | MgO | SiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | Al2O3 | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial scheme | 8.97 | 0.55 | 1.24 | 42.93 | 0.87 | 0.06 | 31.31 | 1.09 |
| Scheme No. 1 | 9.12 | 0.68 | 1.15 | 42.70 | 0.92 | 0.06 | 31.34 | 1.07 |
| Scheme No. 2 | 9.34 | 0.69 | 1.14 | 41.54 | 0.98 | 0.05 | 31.48 | 1.09 |
| Scheme No. 3 | 9.81 | 0.80 | 1.12 | 41.18 | 1.05 | 0.06 | 30.86 | 1.11 |
| Scheme No. 4 | 10.27 | 1.07 | 1.09 | 42.14 | 0.80 | 0.07 | 29.03 | 1.04 |
| Sample | Ti (°C) | Tf (°C) | Rmax (s−1) × 103 | Rmean (s−1) × 103 | S (s−2·°C−3) × 1014 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC-HTC | 302.13 | 528.78 | 5.74 | 1.38 | 16.41 |
| BC | 337.76 | 565.85 | 9.08 | 1.29 | 18.15 |
| AC | 406.49 | 661.73 | 7.00 | 1.35 | 8.64 |
| Initial scheme | 364.32 | 619.11 | 14.79 | 1.46 | 26.28 |
| Scheme No. 1 | 363.70 | 637.77 | 11.59 | 1.48 | 20.33 |
| Scheme No. 2 | 362.91 | 635.21 | 6.16 | 1.37 | 10.14 |
| Scheme No. 3 | 349.67 | 650.65 | 5.63 | 1.39 | 9.84 |
| Scheme No. 4 | 332.53 | 635.01 | 5.87 | 1.36 | 11.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Wu, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, J.; Ning, X.; Wang, G. Feasibility Analysis of Biomass Hydrochar Blended Coal Injection for Blast Furnace. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10885. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710885
Wang K, Zhang J, Wu S, Wu J, Xu K, Liu J, Ning X, Wang G. Feasibility Analysis of Biomass Hydrochar Blended Coal Injection for Blast Furnace. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):10885. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710885
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kai, Jianliang Zhang, Shengli Wu, Jianlong Wu, Kun Xu, Jiawen Liu, Xiaojun Ning, and Guangwei Wang. 2022. "Feasibility Analysis of Biomass Hydrochar Blended Coal Injection for Blast Furnace" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 10885. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710885
APA StyleWang, K., Zhang, J., Wu, S., Wu, J., Xu, K., Liu, J., Ning, X., & Wang, G. (2022). Feasibility Analysis of Biomass Hydrochar Blended Coal Injection for Blast Furnace. Sustainability, 14(17), 10885. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710885







