Abstract
This study aims to explore whether capital structure (CS) has a contingent role in the relationship between corporate governance (CG) quality and firm performance. The empirical findings indicate that CG quality had a positive and significant effect on the performance of Jordanian non-financial firms listed on the Amman Stock Exchange (ASE) from 2014 to 2019. Additionally, the moderate effect of the CS reinforces this relationship. These results are robust to alternative econometric specifications and variable definitions. This study utilizes certain firm-specific characteristics to represent the CS to assess its role as a moderating variable in the relationship between CG quality and firm performance. This study makes a contribution to the literature by showing that CS can strengthen the relationship between CG quality and firm performance. The results have important managerial implications for the practice of CG in developing countries. Firms in developing countries can enhance performance by implementing and abiding by good governance practices. Moreover, firms in developing countries should adopt effective financial strategies regarding CS to enhance the relationship between CG quality and firm performance. Finally, potential investors should consider the debt level in the CS of non-financial firms in Jordan when making investment decisions.
1. Introduction
Due to the rapid growth of the capital market in Jordan and the unique institutional environment of Jordanian listed firms, there is growing interest in exploring the effect of CG on firm performance. According to [1], the capital market in Jordan now has the highest level of foreign investment in the world. Thus, recently, the openness of the capital market in Jordan to foreign investors has led to an urgent need for enhanced CG quality [2]. Good governance ensures that the business environment is fair and transparent and that companies can be held accountable for their actions [3]. Conversely, weak governance leads to waste, mismanagement, and corruption [4]. Thus, without good CG practices, a country may experience a financial crisis. However, the recent global financial crisis in 2008 was largely attributed to weakness in or lack of CG processes and practices [5,6]. Therefore, this study attempts to shed light on the effect of CG quality on firm performance in this unique setting (Mansour et al., 2022). In particular, this study investigates the relationship between CG as a composite measure and the performance of Jordanian firms from the perspective of CS.
On the other hand, agency theory expects a positive relationship between CG quality and firm performance and reduces the conflicts of interest between principal and agent [7,8]. Accordingly, numerous researchers have focused extensively on investigating the effect of CG quality on firm performance worldwide. Many studies show that there is a direct relationship between CG mechanisms and firm performance [9,10,11,12]. Others have found that the relationship is indirect [13,14]. Thus, up to now, findings regarding the effect of CG on firm performance are still inconclusive [15]. This may be attributed to differences in the sample size, sector, period covered, or the difference in the performance measure used [16].
According to Baron and Kenny [17], when a relationship between a dependent and independent variable is found to be extensively inconsistent in the literature, the indirect effects of a moderator variable may explain this inconsistency. Inconsistent empirical results may be attributable to multiple factors, such as firm-specific characteristics [15,18]. In particular, according to Cuomo [15,19,20], the suitability of a CG system is contingent on some key firm-related variables (e.g., CS). Prior research e.g., Refs. [15,18] indicates that such mechanisms are interrelated, and firms can choose an optimal combination. Conventionally, researchers have conducted in-depth studies into the evidence on the direct links between CG quality and firm performance [21]. In the Jordanian context specifically, there has been very little research examining the effect of CG on firm performance [22]. Yet, significantly, only a few studies have investigated the effect of moderating variables, which represents a gap into which many researchers in the field of CG have urged investigation because of the vital role that intervening factors may play [20,23,24]. In this regard, it would be instructive to understand whether CS affects the relationship between CG quality and firm performance. The past literature has tended to focus only on the correlation between each pair of these three factors, such as the effect of CG on firm performance [13], the effect of CG on CS [25], or the effect of CS on firm performance [26]. From the perspective of CS, however, it is unclear whether CG has a direct or indirect effect on firm performance, which is also a central topic in the recent CG debate. Thus, we combine these two strands of the literature and examine the moderating effect of CS on the relationship between CGI and firm performance. Therefore, this study aims to fill both a theoretical and practical gap by testing the moderating effect of CS on the relationship between CG quality and firm performance. It investigates this association from the perspective of CS, which is expected to have a synergistic effect that enhances the relationship between CG quality and firm performance.
This approach was adopted because firms, especially those in developing countries, may rely heavily on debt in financing their CS (high gearing) because of the presence of weak CG systems, and another financial crisis may arise [27]. The corporate financial decisions that are made in relation to CS are becoming increasingly important for survival and development [28,29,30], as well as the value maximization of firms. In addition, agency theory suggests that CS can reduce agency costs [8], and the trade-off theory of CS posits that firms that have optimal debt ratios in their CS have the ability to maximize tax shield benefits against the costs of bankruptcy that increase with the use of debt for financing [30]. Thus, many researchers contend that an optimal CS is critical to the success of the firm due to its link with risk and reward [27,29,30]. This control is manifested in the reduction of opportunistic management behavior and agency costs through the imposition of stringent debt covenants [30,31,32,33], thus improving profitability and performance [25]. Subsequently, the importance of the contingent role of CS in the relationship between CG quality and firm performance seems unambiguous.
Most of the CG studies were conducted with their individual characteristics. However, this study is considered different because it attempts to examine the effect of CG by developing a corporate governance index (CGI). However, as far as we know, no one has used a composite governance measure based on panel data to evaluate these mechanisms and explore its influence on corporate performance in the Jordanian setting. Regardless, this study is a pioneer because it investigates the moderating effect of CS, which is still a gap in the literature. Moreover, most of the previous studies in the CG scope were conducted in developed countries. However, this study focuses on Jordan as a developing country that has a unique institutional environment that differs from those in developed countries, such as the United States and the United Kingdom, where most studies on CG and firm performance have been conducted. Thus, the findings of prior studies cannot be generalized to markets in emerging or developing markets, such as the Jordanian market. Generally, the CG system is considered relatively new to the Jordanian environment, and the capital market is considered not as broad and deep as developed ones. Ref. [34] argued that emerging markets also differ widely among themselves due to cultural, economic, and political systems, hence the need for country-specific governance studies [35] to realize ultimately which CG mechanisms are significant for which kinds of firms and in which types of settings.
In Jordan, the bankruptcy of Petra Bank and the so-called “Shamaylaeh Gate” scandal forced supervisory bodies to undertake reforms by issuing a range of new legislation to boost accountability, transparency, and the rule of law in the economic life of Jordan [22]. These reforms included the enactment of the corporate governance code in 2009 [22]. This enactment of the corporate governance code aimed to reinforce the performance of the Jordanian economy and boost trust in its investment environment generally [36]. For example, Jordan’s regulatory and legislative authority has paid a great deal of attention to consolidating the pillars of corporate governance [36] to attract foreign and local investors. Over the past few decades, the Jordan economy, especially the non-financial firms’ sector (industrial and service firms), has faced several problems and challenges because of regional instability [4]. Since the Amman Stock Exchange (ASE) is reflective of the performance of the national economy and the surrounding circumstances, the statistics of the Jordan Securities Commission (JSC) have revealed that the total number of listed firms declined dramatically, reaching 194 firms at the end of 2017 compared with 277 firms at the end of 2010 (JSC Annual Report, 2018). The regulatory bodies in Jordan consider these firms to be either insolvent firms or firms that are suspended from trading (ASE, annual report, 2018). Furthermore, the Jordan Independent Economy Watch (JIEW) (2014) found that there has been sluggish growth in Jordan’s national economy since 2009, which is reflected in the country’s business environment in general, specifically in the performance of Jordanian firms. In light of the continued effects of the political and economic difficulties in the region, the performance of the ASE and the stock market continued to be affected by these circumstances and the turmoil faced by the region, and the trading value of the non-financial firms’ sector has decreased largely, reaching JOD 1.03 billion at the end of 2017 compared to JOD 2.515 billion at the end of 2010. Furthermore, as revealed by indicators of the ASE, the market capitalization of the non-financial firms’ sector has faced a sharp decline against GDP in the last ten years (ASE, annual reports). In this regard, Ref. [37] have established that Jordan has faced an episode of turmoil that has influenced the development of its institutions. Many studies have noted that most of the financial failures that affected Jordanian firms from 2000 to 2011 hardly hit the non-financial firms’ sector, which can be attributed to the lack of full adherence of firms in this sector to codes of corporate governance and other rules and regulations imposed by Jordan’s regulatory body [38]. In addition, the market performance of the non-financial firms’ sector in Jordan was below the average mean of the ASE, which was the result of significant losses incurred between 2008 and 2009.
Firms listed on the ASE were selected because the ASE is one of the oldest and largest stock markets in the Middle East and Asia region [1,4]. Non-financial firms (industrial and service firms) were chosen because they are considered to be an essential source of employment and economic growth in Jordan. The three most significant roles of non-financial firms in general are as producers of goods and services, as investors in non-financial assets, and as borrowers in financial markets. In addition, these firms have recently faced several problems and challenges because of regional instability [22], which has had a deleterious impact on their performance. Thus, this study anticipates that it will provide a unique insight into the effect of CG quality on firm performance that may depend on a firm’s specific strategy (financing decisions), which will also offer a novel perspective on the relevant theories. Furthermore, the results of this study are expected to have implications for the legislators, shareholders, and other stakeholders of Jordanian non-financial firms in relation to improving the outcome of CG quality and corporate financial decisions.
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
CG is one of companies’ best practices to enhance transparency, and many theories have discussed the importance of good governance, such as stakeholder theory and agency theory. Moreover, scientists have made many experimental contributions in this field. The debate of this study is associated with three main streams of prevailing research. As argued above, the primary research stream addresses the association between CG quality and firm performance. Although there is no consensus among researchers on the strength and direction of the relationship between these two variables, numerous studies have established that higher levels of CG practice are related to better firm performance [12,39]. This finding is supported by other studies such as [10,18,40]. For example, Ref. [41] found that well-governed Japanese firms significantly outperform poorly governed firms by up to 15% a year. According to agency theory [8], good governance practices greatly improve the performance of firms by reducing agency costs [42] and enhancing the alignment between the interests of managers and shareholders [43]. Generally, this situation arises because the relative efficiency of CG delivers advantageous information to the market (e.g., investors and creditors), which importantly stimulates firm performance [44]. Hence, adherence to good governance practices has become a central issue for corporations and stakeholders, not least because such practices are considered to act as a shield that can protect firms from exposure to future failures [27].
The literature has documented that good governance practices can help to ensure the proper management of firms, enhance competitive edge, attract investment, lower the cost of debt, and improve overall performance, as well as protect investors’ rights and improve confidence in financial markets, thereby contributing to sustainable economic development [13,45,46]. Furthermore, good governance is considered one of the basic demands of various stakeholders [33,47,48]. Recently, many researchers have focused on investigating the effect of CG mechanisms on firm performance in developed and developing countries [49]. However, the vast majority of previous studies are limited to advanced markets, for example, [35,50,51,52]. In general, developing countries face matters that are dissimilar to those experienced in developed economies. Traditionally, many studies have focused on a single or a few mechanisms of CG [40], such as board characteristics [1], board size [53], board composition [54], disclosure and transparency [55], audit committee [56], CEO duality [57], and ownership structure [58]. Such studies have yielded positive, negative, or mixed results, and some have found no relation at all between CG mechanisms and firm performance [15,44]. Interestingly, one potential explanation for this divergence in results is that the relationship between all the CG mechanisms is complementary, which means that the attributes of CG are working simultaneously and that the choice of a specific mechanism to test the relationship between CG and firm performance may not always be the correct one [43,50]. Moreover, the diverse results in the literature suggest that an evaluation of CG that is based on specific mechanisms might not demonstrate the same effect as one that is based on overall CG quality [50,59,60]. Thus, it is impossible to measure and capture the overall quality of CG through a single or a few mechanisms, and this is therefore an angle of investigation that requires further attention [40].
In line with the above observation, recently researchers have shifted away from using specific mechanisms of CG to explore the relationship between governance and performance to using a CGI [3,46,61]. This shift has occurred to compensate for the imperfections in individual mechanisms, such as protecting the interests of shareholders and stakeholders through disclosure, which are often insufficient [33,62]. According to stakeholder theory, protecting the broader group of stakeholders is one way to legitimize the activities of companies. Therefore, many companies seek to achieve transparency and accountability by applying the principles of good governance [31,63]. Moreover, the use of a CGI as an assessment tool for measuring the state of governance in firms offers a solution to the problem of an inadequate overall governance system, especially in firms in less-developed nations, and can encourage firms to establish optimal governance mechanisms to strengthen the relationship with stakeholders [64]. A CGI is useful because it integrates all the governance mechanisms into a single value, which can then be used to judge the governance quality in firms [39,65]. Hence, numerous researchers in the field of CG are now using a composite measure instead of focusing on individual mechanisms [14] and are developing their own indices to assess the quality of CG [42] because they perceive this approach to be more dependable. This more recent strand of the literature shows that the composite measurement of CG provides interesting evidence and can lead to desirable results, such as strengthening shareholder rights, reducing agency costs, boosting firm performance, increasing firm value, and raising stock prices [51,66]. Thus, the basic assumption that underlies the use of a CGI is that it can adequately capture the overall quality of CG [42]. Correspondingly, a number of studies, such as [10,18,67], have emphasized that a CGI has a positive impact on firm performance. Therefore, based on the above, the following hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 1 (H1):
The effect of CG quality on firm performance in the Jordanian non-financial sector is significant and positive.
Capital Structure as a Moderator
CS has been widely adopted as a core financing strategy by firms in a variety of sectors, including those in the non-financial sector [30,68,69]. CS can be seen as a mechanism that can contribute to reducing agency problems [8]. In addition, a proper CS may be considered as a major factor in determining firm performance [26,30,33,70]. Yet, the role of CS as an intervening factor is not addressed in the CG literature. The methodology of incorporating moderation variables into models is now commonly used in the social sciences to refine and gain a better understanding of the causal relationship between variables [8]. The literature has explored the moderating role of various mechanisms on the relationship between CG quality and firm performance. However, the moderating role of CS is missing from the debate. Surprisingly, prior studies have ignored interactions between CG quality and governance mechanisms such as CS despite this variable offering a potential avenue into gaining a deeper and more refined understanding of the causal relationship between CG mechanisms and firm performance, especially in the light of the inconclusive empirical results on this relationship [15,18,23]. Many studies e.g., Refs. [13,24,71] have mentioned that governance mechanisms are interrelated and that firms can choose an optimal combination thereof that best suits their particular circumstances. The rationale for this argument is based (rooted) on the agency theory perspective, which assumes that the CS can reduce agency costs [8,72]), while CG is intended to alleviate agency problems; thus, good governance and CS are related through their link with agency costs [30].
Some researchers have also suggested that CS has complemented governance mechanisms in mitigating agency conflicts [15,25]. Hence, many researchers have recommended exploring whether there is a complementary association between CS, CG, and firm performance [10,27,73]. This recommendation has arisen because CS as a third variable can be considered a discipline mechanism [30,31] and is thus expected to have a positive impact on the relationship between CG and firm performance [5,59,70,74,75]. Maranho and Leal [76] have suggested that a number of different moderators can help explain the relationship between CG and performance, and it has been postulated that CS is one of the most important e.g., Refs. [15,18] due to CS possibly confounding the relationship between CG and corporate performance since it can encourage (or discourage) some internal or external actors to join (or leave) the game. The moderating effect is established if, when the moderator variable (i.e., CS) has interacted with the explanatory variable (i.e., CGI), the strength of the association between the explanatory variable and the outcome variable (i.e., firm performance) is altered. Specifically, if CS accentuates (weakens) the effect of the CGI, the interaction term will have the same sign (opposite sign) as the CGI variable.
The CG quality and CS can be considered as having the potential to decrease the conflict of interest between management and shareholders by decreasing the agency costs associated with managers having access to free cash flows [25,72]. Previous works indicate that several mechanisms can moderate the governance–performance relationship [44,51]. It has also been postulated that CS as a moderating variable can alter the direction and strength of the causal relationship between CG quality and firm performance [15,18]. Furthermore, some researchers have strongly recommended studying the role of CS as a governance device to determine whether it can help to maintain governance competence and enhance firm performance [13,71]. This means that CS is like CG in terms of its ability to mitigate agency costs [25,69,70]. Thus, the CS can be viewed as a third variable, and its influence on the relationship between CG quality and firm performance should be explored (La Rocca, 2007). However, in spite of these recommendations, prior literature has tended to focus only on the correlation between each pair of these three factors, such as the effect of CG on firm performance [13], the effect of CG on CS [25,26], or the effect of CS on firm performance [71]. Nevertheless, it is expected that CS (corporate financial decisions) would enhance the relationship between CG and firm performance [71]. The CS is considered a governance mechanism because it plays a decisive role in decreasing the agency costs of free cash flows by prohibiting investments in negative net present value projects [13]. This means that optimal CS could restrict the freedom of managers to deal with free cash flows [33]. Thus, the CS becomes a complementary control mechanism, suggesting that CS as a governance mechanism improved the effectiveness of the other mechanisms [15,16,69]. Therefore, in light of the above, the following hypothesis and sub-hypotheses are proposed:
Hypothesis 2 (H2):
CS positively moderates the effect of CG quality on firm performance in the Jordanian non-financial sector.
3. Empirical Study
3.1. Variables and Data
In this study, the relevant data on Jordanian non-financial firms were used to examine the empirical model. For this purpose, a sample of Jordanian listed firms was constructed out of those that had the required information for the entire study period. The final sample consisted of a panel data set for 95 non-financial firms covering a period of 6 years from 2014 to 2019, which produced 570 observations, as illustrated in Table 1. These data were drawn from the official websites of the ASE, Securities Depository Center (SDC), and the websites of each firm. Specifically, the data related to the firms’ performance indicators, market-to-book ratio of equity (MBTV), and the CS were gathered from the official website of the SDC. The data relating to the composite measure of CG quality, i.e., the CGI, firm size, firm age, and sales growth, were manually collected from the annual reports of each firm for the pertinent years that were published on the websites of respective firms and/or the ASE. Thus, the balanced panel data set collected for the years under study was considered sufficient to serve the purpose of the study.

Table 1.
Sample selection procedures.
3.2. Independent Variable
A CGI was constructed to assess the quality of CG practices in a sample of non-financial firms listed on the ASE. The index was composed of three sub-indices (categories) to reflect the three main mechanisms of corporate governance, namely:
- Disclosure and transparency.
- Board effectiveness and composition.
- Shareholder rights.
The CGI was constructed based on the CGIs developed in recent studies such as [3,36,66,77]. Thus, the CGI in this study contained the most-cited individual mechanisms of CG quality from the most-cited studies. In addition, the CGI developed for this study was based on the best practices contained in the Jordanian Code of CG (hereinafter Code) issued in 2009, which is rooted in the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development guidelines of 2004 [78]. The CGI was altered to ensure compatibility with the Jordanian environment. In this context, this study builds a specific index by using specific CG attributes that reflect local firms, norms, and data availability and shows that this index predicts a firm’s performance in the country. Accordingly, the CGI was comprised of 32 attributes as follows:
- Fifteen criteria devoted to disclosure and transparency.
- Nine criteria devoted to board effectiveness and composition.
- Eight criteria devoted to shareholder rights.
The 32 attributes of the CGI are summarized in Table 2 below:

Table 2.
Corporate governance index (1),*.
Following the prior research, each attribute in the CGI was based on a binary scale (taking a value of one or zero [13,36,66]. The value of one indicated the existence of/compliance to the attribute discussed, and zero indicated absence/non-compliance. Earlier studies by [51,65,79], among others, used a dichotomous measure in constructing the CGI, which is considered an excellent approach in research that intends to present compliance scores [36,42]. As the regulatory body in Jordan does not require non-financial firms to prepare separate CG reports, this study depended on the governance information disclosed in the sample firms’ annual reports to construct the CGI. Hence, this approach is similar to that adopted by [36]. It is also in line with [80], who claim that there is a positive correlation between the likelihood of a firm disclosing information on a specific governance attribute and the attribute being adopted by the firm. Ref. [19] suggested that collecting data from secondary sources has some advantages, such as removing the risk of third-party bias in the research analysis.
In the current study, the overall CGI for each firm was calculated based on equally weighted scores for the 32 criteria. Consequently, the maximum score that was achievable was 32, which indicated full compliance (100%). The numeric score for each firm was converted (scaled) to a percentage for ease of comparison in the analysis. Thus, this study followed [9] by using an unweighted approach in constructing a CGI, which has the benefit of eliminating the risk of subjectivity [71]. Another advantage of the unweighted approach is that it is easily reproducible [65]. Moreover, such an index is considered reliable because it can be replicated by another researcher [42]. In addition, the unweighted approach is considered suitable for the examination of a comply-or-explain regime [59], such as that found in Jordan, where compliance with the Code is voluntary, whereas the weighted approach is usually used in commercial ratings in countries such as the United States [61]. Furthermore, empirical studies have established that there are no significant differences between the weighted and unweighted approaches when indices are constructed; thus, both types of the index are closely correlated e.g., [71].
Following the literature, the reliability and validity of the self-constructed CGI were constructed to possess a high degree of consistency and stability by undertaking four main steps. First, following Shahwan [71], the reliability of the CGI was initially assessed as follows:
- Each of the annual reports of the firms in the sample was read in its entirety twice.
- The ratings of the index for each firm were calculated twice, with the aim of obtaining a similar rate both times.
- If there were any differences in the score between the first and second round, the ratings for that firm should be subjected to a third and final evaluation.
Second, according to Nerantzidis [36,42], an index is considered reliable if another researcher can replicate the outcomes of scoring. Therefore, following Owusu and Weir [80], an independent researcher (second coder) was engaged to confirm the reliability of the CGI by checking the initial coding to ensure accuracy and consistency. Third, following [65], the content validity was scrutinized by evaluating all mechanisms (attributes) included in our CGI through reviewing these mechanisms in previous literature, as shown in Table 2, so as to assure that designed attributes or mechanisms make a difference in scores when added to the governance index [81]. Fourth and finally, the reliability of the CGI was evaluated by carrying out a Cronbach’s alpha test to measure the interrelationship between the mechanisms that composed the components of the index. A Cronbach’s alpha test is considered to be apt, particularly when dichotomous items are used, because it enables the evaluation of the internal consistency of each mechanism within the index [82]. According to Ararat [64,66], a high alpha value (high internal consistency) denotes that a CGI has high reliability. In this study, the Cronbach’s alpha value was 0.759, representing an acceptable internal consistency level and confirming that the developed CGI was valid for use.
3.3. Dependent Variable
The dependent variable in this study, namely firm performance, can be measured by ROA [1,11,31,33,83,84] and ROE [3,6,83]. Accordingly, the current study adopted ROA and ROE to measure the performance of Jordanian non-financial listed firms. These popular ratios are alternative measures of firm performance that are widely used in the accounting and financing literature [50] to measure the financial, accounting, and operating performance of the firms [49]. Indeed, many researchers have used accounting-based ROA/ROE as an integrative way to obtain a better picture of the performance of firms [35].
3.4. Moderator Variable
As stated earlier, the aim of this study was to investigate the potential moderating role of CS in the relationship between CG quality and the performance of non-financial firms. In addition, the relationship between governance and capital structure has been analyzed by a set of scholars e.g., [26,30,33]. In line with [26,48,85,86], this study measured CS as a ratio of total debt to total assets.
3.5. Control Variables
As in previous research, some firm-specific variables derived from the literature were considered as control variables, namely firm size [31,48], firm age [87], sales growth [13,31], MBTV [27], and year effect [88]. One of the underlying reasons for choosing these control variables was the availability of data. These variables can control a firm’s financial condition and cancel any specification errors in the estimation [71]. Thus, control variables are used to lessen the likely extent of omitted variable bias [89]. Some background on and justification for the use of each of these control variables are provided below:
3.5.1. Firm Size
As larger firms can devote enough resources to CG practices and corporate financial decisions [22,31,84], it is expected that they will perform better than smaller firms. Firm size has been widely used by many practical studies as an organization control e.g., [44]. These studies emphasize that firm performance can vary based on firm size [4,48]. This positive correlation suggests that larger firms may benefit from economies of scale and scope more than smaller ones [1]. Accordingly, total assets can be used as a proxy for firm size [90]. Thus, in the current study, firm size is measured as the natural logarithm of total assets in the same manner as in prior studies such as [66]. The motive behind transforming this variable into a logarithmic form was to lessen heteroscedasticity problems.
3.5.2. Sales Growth
Firms with higher sales growth are expected to show better performance because they have some more investment opportunities and thus more profit. Sales growth, also called the growth rate, was used in the current study because numerous previous studies have stated that firms with rising sales are expected to grow faster than other firms [13]. These growing firms call for greater external financing. Thus, they are more likely to adopt good CG practices in order to decrease the cost of capital [13]. In line with the above arguments, many prior studies have found a positive relationship between the performance of firms and their growth [51]. According to Yarram [91], sales growth captures the historical growth of firms. Accordingly, in the current study, sales growth was measured as current sales minus sales in the previous year, divided by sales in the previous year, in the same manner as prior studies such as [13,48,90].
3.5.3. Firm Age
A popular control variable that has frequently been used in recent CG literature is firm age [92]. Firm age is one of the important firm-specific characteristics in terms of its effect on firm performance [27,85]. According to Gaur [93], firm age is a measure of the longevity of a firm and impacts the sorts of decisions that firms make, including financial decisions. Previous studies have revealed that firms go through a financial growth cycle and their CS changes with age [94]. Thus, the age of a firm represents its stage of development and growth. Generally, mature firms are likely to have built up a level of market share through economies of scale and by providing different products [87]. Moreover, industry experience enables mature firms to be more resistant to crises [92]. According to the literature, firm age can be measured by a logarithm of the time period from the firm’s establishment date to the year(s) of analysis [43], and this method is therefore adopted by the current study.
3.5.4. Market Value to Book Value (MBTV) of Equity
A firm’s long-term value tends to be related to market perceptions [95] and is often represented by the MBTV. The MTBV can affect firm operating performance because this ratio is considered a proxy for the predicted growth of a firm’s operations [52]. Accordingly, this measure captures the future growth of firms [91]. Thus, a high MTBV ratio is an indicator that a firm has grown in operations and is expected to perform better than a firm with a low MTBV. Accordingly, following Abdallah and Ismail [27,67], MTBV is employed as a control variable in the current study because this ratio represents the firm’s investment opportunities that may be captured.
3.5.5. Year Effect
The year effect has frequently been used as a control variable in CG studies [9]. Therefore, the year effect was included in the current study as a dummy variable to catch any macro-shocks over time that are common to all firms, such as financial difficulty, changes in accounting standards, and changes in the regulatory framework [88]. Specifically, the current study used year-effect dummies (YRDMY) for the financial years from 2014 to 2019. The operational measurement of variables is presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Operational measurement of variables.
3.6. Descriptive Statistics
As mentioned above, the number of observations in this study was 570. There were no missing data, so all the data on the entire sample were available for use in the analysis. The descriptive statistics of the dependent, independent, and control variables as well as the correlation matrix of the sample are presented in Table 4 below.

Table 4.
Descriptive statistics and normality test for the entire sample.
First, the table presents the descriptive statistics for the performance indicators (ROA and ROE) as dependent variables for the full period under study (2014–2019) for the non-financial firms included in this study. As can be seen from Table 4, the ROA ranges from −10.6 to 15.325, with an average (standard deviation) of 2.69 (6.39). On the other hand, the ROE ranges from −25.15 to 21.78, with a mean of 3.41% and a standard deviation of 11.26%. The standard deviation values for ROA and ROE as accounting (operating)-based measures highlight the enormous volatility in the performance of the non-financial firms listed on the ASE, which is consistent with previous studies [1,22]. Overall, the outcomes of the descriptive analysis of the performance indicators demonstrate that, on aggregate, Jordanian non-financial firms have a low level of performance. This implies that the non-financial sector in Jordan experienced difficult conditions.
Second, the table provides the descriptive statistics for the CGI. It can be observed that the index score ranges between 0.5 and 0.968, with a standard deviation of 0.08. This result indicates that there is little difference (with a small variation) in governance quality across the non-financial firms listed on the ASE. This implies that the overall assessment of governance quality in Jordanian non-financial firms is close to 78%, which indicates that the firms in the sample only comply with 78% of the voluntary mechanisms addressed in the CGI. Thus, the firms in the non-financial sector offer different levels of protection to their investors because of their operational specificities and their motivation to voluntarily adopt good CG practices. It should be noted that the average percentage score of the CGI in the current study is close to some of the index scores of other countries in the Middle East, such as Oman and Saudi Arabia [65]. In addition, the CGI score in the current study is higher than that reported in some studies in developed and developing counties such as in Brazil at 67%, in Malaysia at 63.64%, in Bahrain at 62%, in Qatar at 67%, in Canada at 66.76%, in Turkey at 46.73%, and in South Africa at 61% [10,19,65,96].
In relation to the above, the principle-based approach seems to have helped non-financial firms in Jordan to implement the Code gradually, without incurring the heavy costs of immediate and fast implementation [78], but there remains much room for improvement. In addition, Ref. [37] have reported that Jordan is looking to progress more rapidly to achieve compliance with accounting standards and a CG code as compared to other countries in the Middle East and North Africa region. In any case, the existence of a large number of foreign investors in the Jordanian market is considered an efficient part of CG enhancement [1]. From the above discussion, the improvement in adherence to the components in the CGI may be reflected in the enhancement of firm performance.
Third, Table 4 presents the descriptive statistics on capital structure (CS). From the table, the range of CS is between 0.004% and 1.04%, with a standard deviation of 0.222. Thus, the mean CS ratio is 33%. These statistics are close to those reported by other studies conducted in the Jordanian context such as [97]. The statistics in the current study show that Jordanian non-financial firms still rely heavily on equity rather than debt, which is likely due to weakness in or lack of a debt market in Jordan [98]. Thus, most of the non-financial firms in Jordan adopt a low level of CS. Ref. [97] argued that the reason for the low level of debt in the CS in Jordanian firms is due to its lower returns in light of high debt interest.
Table 4 also contains the descriptive statistics for the control variables. These statistics indicate that there is a disparity in firm size and a large disparity in firm age among the firms in the study sample. In addition, the statistics indicate that the sales growth in non-financial firms in the Jordanian environment was low during the period of study, where the average MBTV was 1.26%.
Table 4 also presents the values for skewness and kurtosis. These values indicate that the sample is normally distributed because the values are within the acceptable range of normality for both skewness and kurtosis. According to Kline [99], the normality of data can be achieved if standard skewness is within a threshold of ±3 and standard kurtosis is within a threshold of ±10. However, it should also be noted that [100] state that large sample sizes (samples of 200 or more) have a tendency to lessen the harmful effects of non-normality. Thus, data collected for the years under study (570 observations) were considered sufficient to serve the purpose of the study.
Next, Table 5 provides the CGI results for the sample.

Table 5.
Pearson correlation matrix and multicollinearity test of study variables.
From Table 5, the CGI scores are a positively and significant relationship with both performance indicators (ROA and ROE) at the 5% significance level or better. On the other hand, the moderating variable, CS, and the dependent variables, ROA and ROE, are correlated negatively and significantly with each other at the 5% significance level or better. As for the control variables, firm size (FSZ), firm age (FAGE), sales growth (SAGR), and MBTV show a positive and significant correlation with the dependent variables (ROA and ROE) at the 5% significance level or better, except for firm age, which is insignificantly correlated with ROA. Table 5 also shows that none of the correlations among the explanatory variables have correlation coefficients above 0.415, which is between FSZ and CGI. Hence, there are no serious multicollinearity problems for the regression analysis because the degree of correlation between the explanatory variables is less than the benchmark of 0.7 suggested by [101]. In addition, the variance inflation factor test results are much lower than the threshold value of 10 [100], which confirms that there is no severe multicollinearity issue among the explanatory variables.
3.7. Estimation Methods and Models
Before running the main regression analysis, a preliminary data analysis was performed to check some assumptions of multivariate analysis for screening and preparing data [87]. To improve independence and linearity, this study performed a procedure to detect and eliminate outliers and influential observations. For this purpose, the study employed the Mahalanobis distance measure, the result of which revealed some outlying observations. To deal with this issue, variables with extreme values were winsorized at the 5th and 95th percentiles to restrict the power of outliers. Moreover, by using the Breusch–Pagan/Cook–Weisberg test along with the Wooldridge test, this study detected heteroscedasticity and autocorrelation problems in all the models fitted [31]. Therefore, this study decided to use the Driscoll–Kraay covariance matrix estimator to adjust standard errors and thereby address this problem to ensure correct estimates for the significance of the variables [102]. These results also justified employing panel data analysis techniques rather than ordinary least squares (OLS) estimators. For the final sample, this study obtained 570 firm-year observations.
To examine the impact of CG quality and the moderating role of CS on the CG quality–firm performance relationship, panel regression models were engaged to enrich the practical analysis [103]. This study considered two accounting-based performance indicators for non-financial firms: ROA and ROE [44,104,105], which are expected to be enhanced by higher governance and monitoring quality. Moreover, in order to capture CG quality, this study depended on the CGI constructed by Mansour [36] as the main explanatory variable of interest, while CS is the moderator variable that was expected to exert a positive interaction effect on the governance/performance association. Here, all the models contained the relevant control variables (FSZ, FAGE, SAGR, MTBA, and YRDMY) that could possibly confound the CG quality–firm performance relationship. The models for the analyses were devised as follows:
Performance (ROA, ROE)t = β0 + β1 CGIt−1 + β2 CSt−1 + β3 FSZt−1 + β4 FAGEt−1 + β5 SAGRt−1 + β6 MTBAt−1 + YEARt + Єi,t
Performance (ROA, ROE)t = β0 + β1 CGIt−1 + β2 CSt−1 + β3 CGI × CS + β4 FSZt−1 + β5 FAGEt−1 + β6 SAGRt−1 + β7 MTBAt−1 + YEARt + Єi,t
It is evident that firm performance in the current period is influenced by CG quality in the previous period. Accordingly, all right-hand side variables in all models were lagged by one period, which was carried out to address reverse-causality concerns to an acceptable extent by potentially controlling for unobservable heterogeneity, as suggested in the literature e.g., [4,13,27,31,39,44,90], where performance represents the firm’s performance in the current year, and CGIt−1, which is CGI, represents CGI in the previous year. The interaction term for CGI and CS was labelled interaction. Before creating the interaction variable, mean centering was used for both explanatory variables to alleviate multicollinearity problems [23,44]. According to Cohen [106], the centering of explanatory variables provides tremendous interpretation features in multiple regression equations.
In addition, a Breusch and Pagan’s (1980) Lagrange multiplier test was conducted to test of the pooled OLS model against the random-effects model based on the OLS residuals. The results of the test indicated that the null hypothesis should be rejected in favor of the random-effects model. Then, the Hausman test was carried out to differentiate between the random and fixed-effects models [107]. The significant results (prob > chi2 < 0.05) suggested that the assumptions for the random-effects estimation were violated. It was therefore decided that fixed effects would be more consistent and efficient when running all the regression models same as in other studies e.g., [48].
3.8. Multivariate Regression Analyses
As mentioned in the introduction, the aim of this study is to examine the contingent role of CS on the relationship between CG quality and firm performance in the Jordanian non-financial sector. However, before examining the moderating effect of CS, this study examined the individual effect of CG quality (as measured by the unweighted CGI) on performance. As shown in Table 6, the values of R2 (within) are reasonable for all the equations. In addition, the overall performance of all the models is satisfactory, as reflected in the F-statistic values. Hence, the results in Table 6 indicate that both models are statistically valid. The fixed-effects regression results for the impact of the CGI on financial performance, as measured by the ROA model and ROE model, which were analyzed separately, are also reported in Table 6.

Table 6.
Panel regression results for the relationship between CGI and performance indicators.
In the first part of the multivariate regression analysis to determine the impact of CGI on future performance, ROA was run on the CGI and the control variables in Model 1. Then, ROE was regressed on the CGI and the control variables in Model 2. These two models showed that CGI has a positive and significant impact on both future performance (ROA) at the 5% level and (ROE) at the 1% level, which supports H1 for ROA (p-value = 0.029) and H1 for ROE (p-value = 0.004), respectively. These results suggest that there is a strong positive relationship between the composite measure of CG and future performance when accounting (operating)-based measures are applied. Thus, these results demonstrate that CG matters for the ROA and ROE of non-financial firms listed on the ASE, specifically when implementing a holistic approach by applying a CGI appropriate for the Jordanian context. The current study’s findings support the argument adopted from the literature that a composite measure of CG is a more dependable instrument for assessing firm performance, which means that non-financial firms with a higher score on the constructed CGI have superior future performance according to ROA and ROE.
The study results are in line with the theoretical predictions of agency theory, as suggested by [8], which posits that good-quality CG greatly improves the performance of firms by reducing agency costs and enhancing the alignment between the interests of managers and shareholders [42]. The findings of the current study also support the argument by [35] that good-quality CG leads to a reduction in the defrauding of shareholders by management, better maintenance of corporate assets, and improved protection of shareholders, which in turn prompts investors to accept lower returns on their investments, reduces the cost of capital, and improves firm income and performance.
The results are also consistent with those reported by Bhatt and Bhatt [10], who found that a CGI self-developed for the purpose and context of that study is highly correlated with enhancing the ROA of listed firms in Malaysia. The results of the current study are also consistent with those of Wahyudin and Solikhah [105], who found that the CG rating influences the ROE of firms listed on the Indonesian Stock Exchange. The findings of the current study also support the outcome of research conducted by Sami [40], who found that a composite measure of CG is positively correlated to the ROE of Chinese firms. In the same vein, Mishra and Mohanty (2014) found that the composite CG measure is considered a good predictor of the ROA of firms listed on the Mumbai Stock Exchange in India. In addition, Brown and Caylor [50] found that better CG is highly correlated with better operating performance. Moreover, the current results seem to be in line with some other research studies that have used a composite measure of CG in the context of developing countries, such as [108] in Thailand, [89] in Turkey, and Abdallah and Ismail [67] in the Gulf Cooperative Council region. The findings of the current study also confirm the view of [16,105] that accounting (operating)-based performance measures provide a better reflection of managerial actions because these measures are under management’s control.
Furthermore, the empirical evidence obtained by the current study agrees with the findings of prior studies conducted in the Jordanian context, such as Zeitoun and Tian (2007) and [109]. These studies confirmed the explanatory power of accounting-based performance measures in CG literature, indicating the fact that measures are considered the most significant indicator used by investors in Jordan to evaluate a firm’s performance compared to other indicators. However, it should be noted here that some previous research studies conducted in different contexts have yielded contradictory results, such as [13] in the UK, [12] in Brazil, and [110] in the US, who found no statistical evidence that accounting/operating performance is related to CG indices. Due to the existence of contradictory results, the current study agrees with the view expressed in previous studies that caution should be exercised in using a one-size-fits-all approach for CG indices [111]. However, integrating the differences in institutional development should be taken into consideration, especially in developing countries [10]. As for the effect of the control variables, in the current study, FSZ, FAGE, and SAGR are positively associated with both performance indicators (ROA and ROE), but MTBA has an insignificant impact on performance indicators.
In regard to the moderating effect of CS, Models 3 and 4 in Table 6 show the fixed-effects regression results for the moderating effect of CS on the relationship between CGI and the three performance indicators. With reference to Model 3 for ROA, the results of the linear-multiplicative regression model show that the coefficient of the interaction terms between CGI and CS (CGI × CS) is 29.26 positive and significant at the 5% level (p-value = 0.015), which supports H2 for ROA. Regarding Model 4 for ROE, the results of the linear-multiplicative regression model show that the coefficient of the interaction term (CGI × CS) is 83.14 positive and significant at the 1% level (p-value = 0.003), which supports H2 for ROE. Thus, according to the results of the analysis on the moderating effect of CS, as the level of CS in non-financial firms increases to an optimal level, the positive effect of the CGI on both performance indicators seems to be enlarged. Thus, good quality of CG and CS can be considered more favorable for firms that use such mechanisms to decrease conflict through a reduction in the agency costs of free cash flow obtainable to managers [30]. This means that the non-financial firms listed in the ASE with better monitoring and control of managerial behavior coupled with greater alignment with all stakeholders’ interests translated into higher cash inflows, and accordingly, this is reflected in enhanced performance. The result reveals that the significance of interactions was as predicted by the study’s theoretical component. In addition, the complementary association between CS and CGI has been confirmed through the synergistic effects of the interaction. This proves that there is a positive and statistically significant relationship between interaction terms and ROA and as an indicator of the performance of non-financial firms listed in the ASE. This result indicates that a composite measure of CG and CS has the potential to decrease the conflict of interest between management and shareholders by decreasing the agency costs associated with managers [25,72], which means that greater control is exercised over management and consequently minimizes agency costs [72]. In a post hoc manner, it is also interesting to interpret the results from a different perspective, such as when a CS is inserted into the moderation equation with a CGI treated as the main independent variable and CS as a moderator; the CS makes a difference (positively interaction) in the relationship between CGI and ROA, which had been largely improved.
Crucially, it is clearly observable from the results that the level of CS significantly magnifies the effect of CG quality on the future performance of Jordanian non-financial listed firms, as predicted by the theoretical component of the current study. This result is consistent with agency theory, which assumes that CG quality and CS (which acts as a CG device) reduce agency costs [8,72]. That is, the result indicates that the composite measure of CG and the CS has critical synergistic roles in decreasing the conflict of interest between management and shareholders by decreasing the agency costs associated with managers [25,72].
This implies that the interaction term has a significant marginal effect on both of the performance indicators of Jordanian non-financial listed firms in each of the models used. Thus, the CS becomes a complementary control mechanism, suggesting that the adoption of the CS as a monitoring mechanism increased the effectiveness of the CGI [75]. Moreover, it means that CS affects the relationship between CGI and future performance, implying its interaction adds incremental information content for explaining the variability of future firm performance. As a consequence, some recent studies on CG have considered CS as an internal mechanism of CG e.g., [31,87] or as a proxy for CG e.g., [44]. As for the control variables, FSZ, FAGE, and SAGR are positively associated with all performance indicators (ROA and ROE).
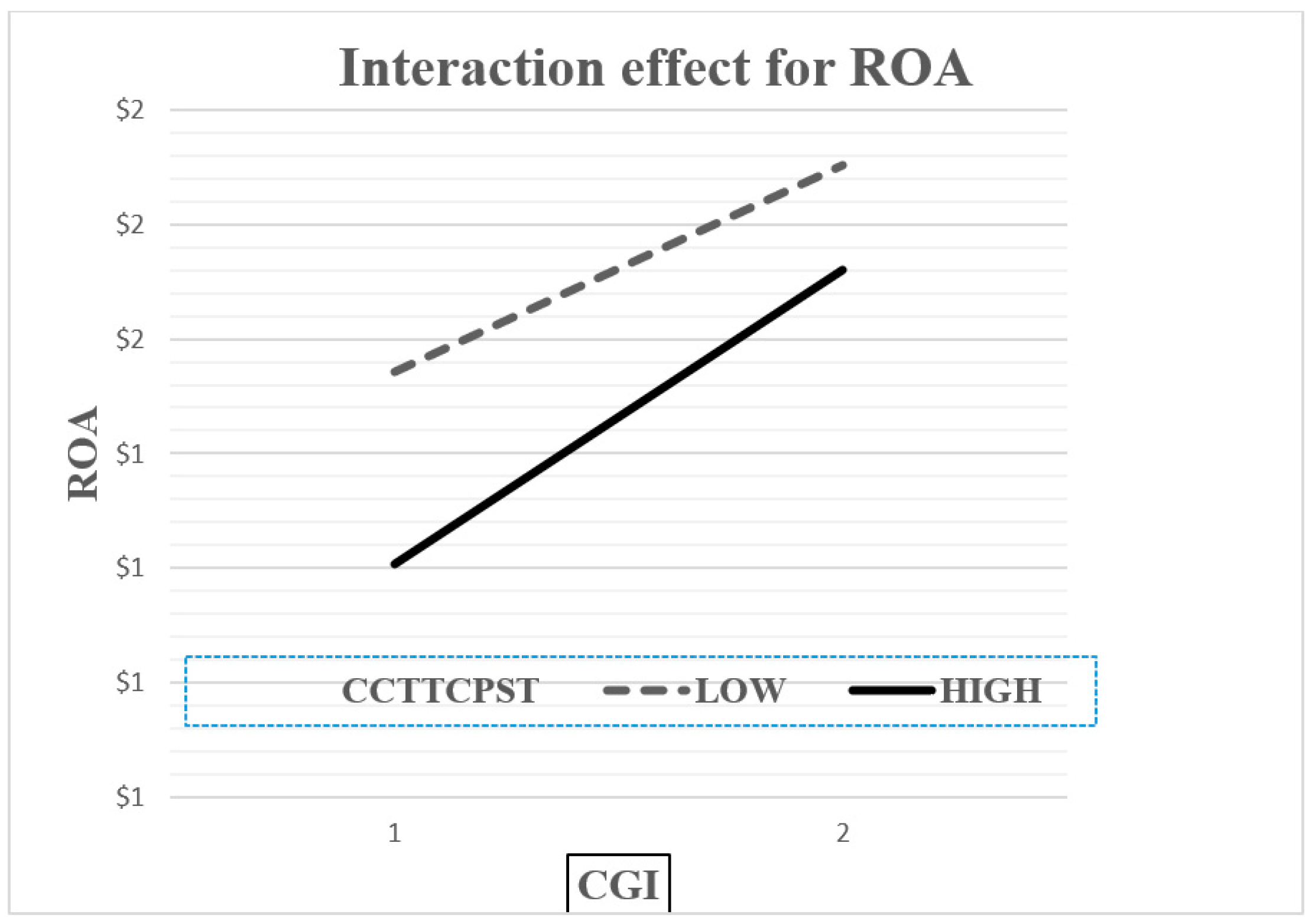
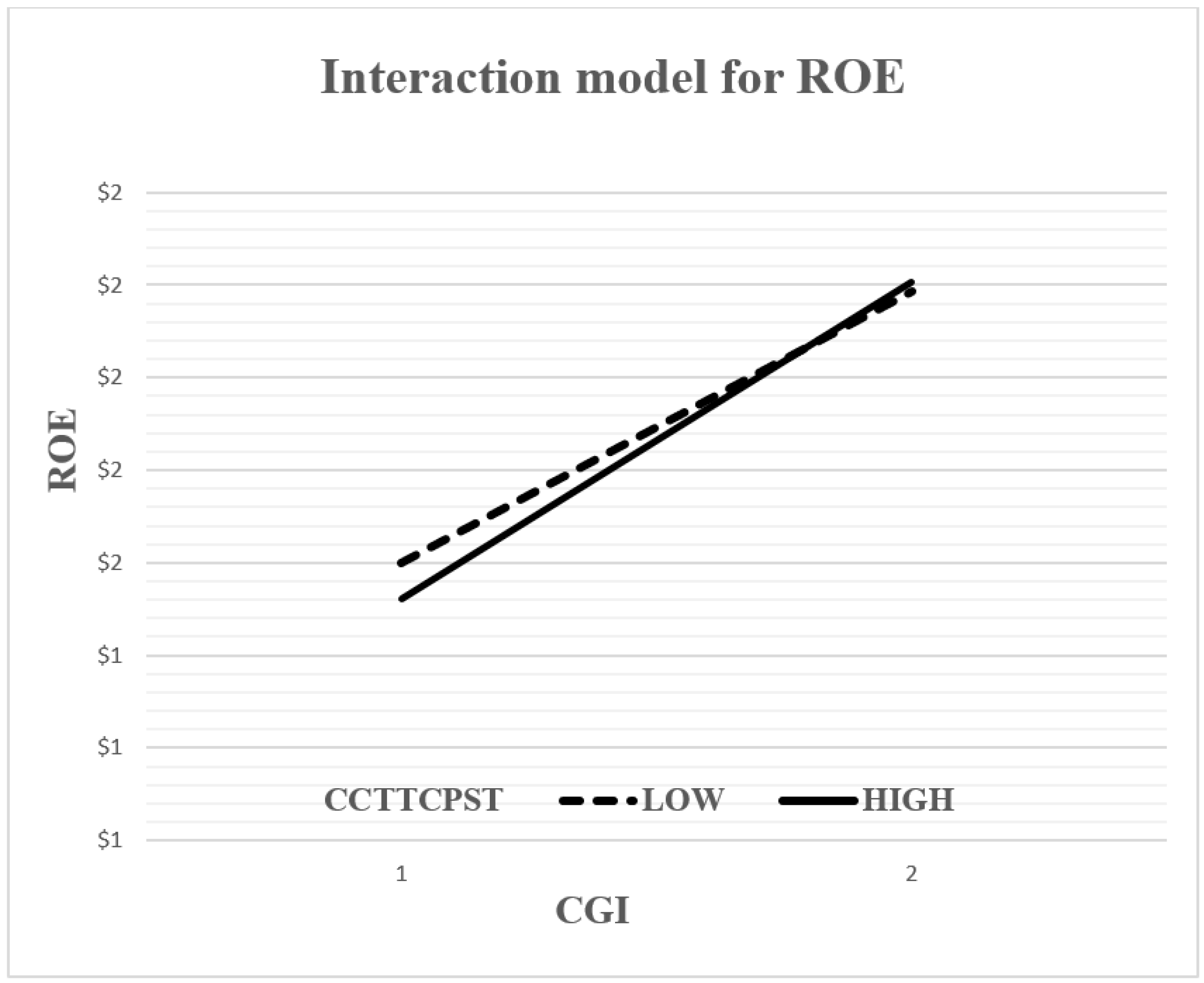
In order to gain further insights into the moderating effect, two-way interaction effects (simple regression slopes) [112] were plotted to confirm the presence of interaction as well as to facilitate the interpretation of conditional marginal effects [23,106]. Following the suggestion of [113], the sample was divided into two groups based on the mean value and standard deviation of the moderating variable (e.g., ±1 standard deviation from the mean of CS), and the respective interaction effects were examined by plotting the relationship between the CGI and performance indicators for both groups. Accordingly, both the figures (Figure 1 and Figure 2) offer further evidence that there is an interaction effect because the lines are not parallel [106], which is because the regression analysis of the performance indicators (ROA or ROE) and the CGI changes as a function of CS. Hence, these figures clarify the moderating effect of CS and show that, for low levels of CS, the positive relationship between the CGI and performance indicators (ROA or ROE) is more obvious compared to the slope attributed to high levels of CS which, although positive, is clearly less obvious. This means that when non-financial Jordanian firms have a lower level of CS, they perform better as compared to those with a higher level of CS. According to simple regression slopes, the optimal scenario occurs when the CS is at a low level and can capture higher performance when both accounting (operating)-based performance measures are applied to non-financial listed firms on the ASE rather than under a scenario involving a high CS. Thus, the main findings of this study are fully supported by graphical illustrations.
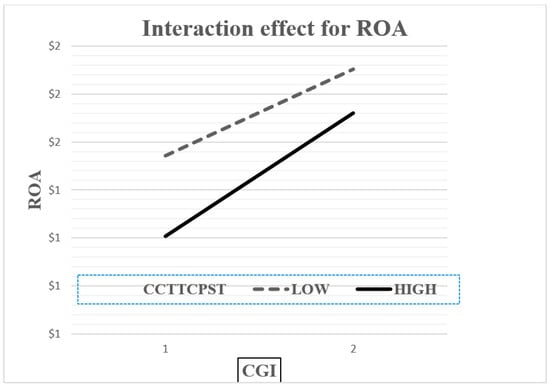
Figure 1.
Plotting the interactive effect of capital structure (CCTTCPST) on the relationship between CGI and ROA. Note: low and high values refer to one standard deviation below and above the mean values, respectively.
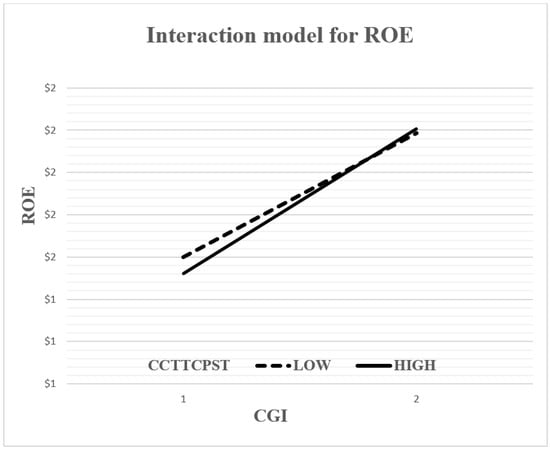
Figure 2.
Plotting the interactive effect of capital structure (CCTTCPST) on the relationship between CGI and ROE. Note: low and high values refer to one standard deviation below and above the mean values, respectively.
3.9. Robustness Tests
Following the literature (e.g., [22,27,33,44] and in order to assert the robustness of our results, the results were subjected to some robustness tests. First, the first multivariate regression model was tested by using an alternative market-based measure of firm performance, namely Tobin’s q. Table 7 provides the results of this robustness check.

Table 7.
Panel regression results for the relationship between CGI and alternative performance indicator.
From a comparison with Table 6, Tobin’s q results were found to be consistent with the main results. Thus, overall, the results are in line with the main study argument that firms with a good quality of CG perform better. Hence, the first hypothesis is further supported.
In addition, to infer correctly, we re-examined the main analysis (direct relationship between CGI and performance) using a well-developed dynamic generalized method of moments (GMM) estimator to overcome possible endogeneity concerns. Moreover, many scholars e.g., Refs. [30,49] argue that the governance–performance nexus may be biased, as it fails to control for potential endogeneity concerns. In this regard, an area of CG and corporate performance has been explored in-depth, yet very few papers have used GMM estimators to alleviate endogeneity concerns [13,30].
Second, thus, there may be a chance of reverse causality in the results, due to which changes in the internal features of firms can be accountable for the CG quality and corporate performance relationship. In order to address these endogeneity problems and to infer correctly, this present study used a two-step system GMM (second-order transformation) as an additional analysis to achieve robustness and generalizability of the main outcomes reported in Table 6. In order to acquire estimates of two-step system GMM, we ran xtabond2 in Stata 14 (Roodman, 2009). The two-step system GMM models are more vigorous to heteroscedasticity and autocorrelation and can take more care of the dynamic nature of endogeneity than those generated by a fixed-effect model [3,13,30].
In brief, the GMM estimator controlled for different kinds of endogeneity by including a past dependent variable (lagged value) as an explanatory variable in the model for ROA, and these lagged values are hired as instrument variables to tackle endogeneity problems [13,30].
As Table 8 shows, this study applies standard diagnostic tests (Hansen tests and Arellano–Bond test for first-order and second-order correlation) to determine whether the GMM estimator can be an appropriate econometric model to apply or not [30]. As reported in Table 8, the results of these tests imply that instruments involved in the GMM estimator are exogenous, and no autocorrelation (or no serial correlation) in the model indicates that the GMM estimator is valid to use. Table 8 shows that the GMM estimator produces the same outcomes that were shaped by fixed-effects regression, except FAGE and MTBA. Thus, we show that our outcomes are unlikely confounded by endogeneity problems. Therefore, they tend to be less vulnerable to endogeneity. As a result, the relationship between CGI and corporate performance is not spurious due to endogeneity in the Jordanian context.

Table 8.
Results of system GMM model estimation.
Third, following Zhang [44], a hierarchical regression analysis was conducted to confirm the results obtained from the multivariate regression analysis regarding the moderation effects. Previous literature, such as [17,114,115], proposed that hierarchical regression analysis is a frequently used technique in investigating moderating effects. According to Baron and Kenny [17], the statisticians and academic scholars primarily have stimulated the use of hierarchical regression analysis over the practice of comparing correlations between groups when the group variable is naturally categorical because different correlations between groups may reflect differential variances between groups rather than true moderator effects, which means that examination of the moderating effect of CS needs to inspect the unique influence of the interaction term (CGI × CS) by sequentially excluding the explanation for the variation in the firm performance (ROA and ROE) from the independent variable of CGI and the moderator of CS. Table 9 presents the results of this additional analysis:

Table 9.
Hierarchical regression results for return on equity.
These results further strengthened the main result of this study, i.e., that CS acts as a moderating variable that can positively moderate the relationship between the CGI and firm performance, thus confirming the second hypothesis.
4. Discussion
4.1. Theoretical Implications
As mentioned above, this study aimed to explore whether CS had a contingent role on the relationship between CG quality and the performance of Jordanian non-financial listed firms. Before examining the moderating effect of capital structure, this study examined the effect of CG quality (by using an unweighted CGI) on firm performance. The results indicated that there is a positive effect of the composite measure of CG on the future performance of non-financial firms listed on the ASE, which is consistent with the empirical findings of previous studies in developing countries [10,40,105]. Therefore, the results of this study imply that the underlying principles of CG apply in less-developed markets, in particular in Jordan. Moreover, the current study’s findings support the argument that a composite measure of CG greatly improves the performance of firms by reducing agency costs and enhancing the alignment between the interests of managers and shareholders. Accordingly, a holistic approach to the implementation of CG is considered suitable for the Jordanian context. Moreover, despite the divergence in institutional contexts between developed and developing countries, the evidence provided by the current study proves that the agency theory is applicable in the case of developing economies, particularly in the Jordanian context.
According to the results of the analysis of the moderating effect of CS, as the level of the CS in non-financial firms increases towards an optimal level, the positive effect of CGI on both performance indicators seems to be enlarged. That is, the result indicates that the composite measure of CG and the CS have critical synergistic roles in decreasing the conflict of interest between management and shareholders through decreasing the agency costs associated with managers [25,72]. In other words, the interaction term enables greater control to be exercised over management, which reduces managerial opportunistic behavior and hence minimizes agency costs, as compared to the control that can be exerted through the effect of each variable separately. This implies that the interaction term has a significant marginal effect on both performance indicators for the Jordanian non-financial listed firms in each of the models. Thus, CS becomes a complementary control mechanism, which suggests that the adoption of CS as a monitoring mechanism increases the effectiveness of CG quality [31,75]. Moreover, the result indicates that CS affects the relationship between CG quality and future performance and furthermore implies that the interactive effect adds incremental information content to explain the variability of future firm performance.
4.2. Managerial Implications
The results of the current study support the view that CG quality and CS play a pivotal role in enhancing firm performance. Thus, the principal implication of the current study is that all stakeholders should consider both CG quality and corporate financial decisions related to CS when they make decisions regarding investing in non-financial Jordanian firms. Thus, these results are significant for regulators aiming to develop novel policies in order to establish a superior regulatory infrastructure that boosts investor trust and appeals to more foreign investors. Indeed, legislators and policymakers in developing countries must continue to reform, develop, and update the recommendations of CG codes to enhance firm performance and prevent firms’ potential failure. The current study’s findings also support the call for the ASE to develop a CGI, which would be a good sign for prospective investors because it would create confidence in the firms listed on the ASE. In addition, the study findings offer some novel insights for policymakers interested in agency-based conflicts of interest within firms. They also provide evidence on the effectiveness of the use of different complementary mechanisms such as CS for reducing agency costs.
Regarding the implications of this study for non-financial firms and investors seeking to invest in the non-financial sector in Jordan, the study results indicate that the firms can enhance their performance by adhering to good-quality CG practices and maintaining a well-balanced capital structure. In addition, the findings indicate that increasing debt financing is not helpful for the performance of non-financial firms, which also implies that Jordanian listed firms in the non-financial sector should focus on optimizing their CS to distinguish themselves in the market. Finally, in terms of the implications for investors, the composite measure of CG practices used in this study provides investors with a quantitative tool that they can use to better assess the performance of non-financial Jordanian firms. Thus, investors should consider a firm’s governance score before making any investment decisions.
4.3. Limitations
As with all research, this study had some limitations. First, the study relied completely on archival data, which were mostly collected from annual reports. These data may or may not reflect what occurred in reality, where the regulatory and institutional framework may be considered to be weaker in developing markets than in advanced markets. Second, the study sample was limited to listed non-financial firms. This was due to the availability of the required CG information. Hence, the inclusion of unlisted firms in a future study would enhance understanding of CG mechanisms in the Jordanian context. Third, because this study only considered non-financial Jordanian firms, this limits the generalizability of the findings, and it is possible that the results would not be similar in other institutional settings. Nevertheless, in spite of these minor limitations, this study has a contribution to make by elucidating the association between a CGI and firm performance.
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the impacts of CG quality and CS on the performance of non-financial firms listed on the ASE during the period from 2014–2019. The study also investigated the moderating impact of CS on the relationship between CG quality and firm performance. In general, the results demonstrate that the CGI and CS matter for firms in the non-financial sector. Specifically, the findings supported the argument that a composite measure of CG offers a more accurate measurement of the quality of CG, which means that the non-financial Jordanian firms with a higher score on the constructed CGI showed superior performance. Furthermore, the results of the multivariate regression analysis indicated that the interaction terms between a composite measure of CG and CS have the potential to decrease the conflict of interest between management and shareholders by decreasing the agency costs associated with managers. This means that, in the case of the non-financial firms listed on the ASE, better monitoring and control of managerial behavior coupled with greater alignment with all stakeholders’ interests translated into higher cash inflows, and accordingly, this was reflected in enhanced performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M. and S.F.A.K.; methodology, H.A.A.; software, A.Y.A. and M.W.A.S.; validation, M.M., S.F.A.K. and A.Y.A.; formal analysis, S.F.A.K.; investigation, M.M. and M.W.A.S.; resources, M.W.A.S.; data curation, S.F.A.K.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M. and S.F.A.K.; writing—review and editing, H.A.A. and A.Y.A.; visualization, H.A.A. and M.W.A.S.; supervision, H.A.A. and A.Y.A.; project administration, M.M., M.W.A.S. and A.Y.A.; funding acquisition, H.A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Open Access funding provided by Qatar National Library.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Saidat, Z.; Silva, M.; Seaman, C. The relationship between corporate governance and financial performance: Evidence from Jordanian family and nonfamily firms. J. Fam. Bus. Manag. 2019, 9, 54–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Akra, M.; Ali, M.J.; Marashdeh, O. Development of accounting regulation in Jordan. Int. J. Account. 2009, 44, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahdal, W.M.; Alsamhi, M.H.; Tabash, M.I.; Farhan, N.H. The impact of corporate governance on financial performance of Indian and GCC listed firms: An empirical investigation. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2020, 51, 101083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdullah, T.T.Y. The relationship between ownership structure and firm financial performance: Evidence from Jordan. Benchmarking Int. J. 2018, 25, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najjar, B.; Clark, E. Corporate governance and cash holdings in MENA: Evidence from internal and external governance practices. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2017, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, H.; Ramzan, M.; Haq, M.Z.U.; Hwang, J.; Kim, K.B. Risk management in corporate governance framework. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fama, E.F.; Jensen, M.C. Separation of Ownership and Control. J. Law Econ. 1983, 26, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.C.; Meckling, W.H. Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. J. Financ. Econ. 1976, 3, 305–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, S.; Bolton, B. Corporate governance and firm performance: The sequel. J. Corp. Finance 2019, 58, 142–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.R.; Bhatt, R.R. Corporate governance and firm performance in Malaysia. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2017, 17, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Ponce, H.; Chamizo-González, J.; Arimany-Serrat, N. Disclosure of Environmental, Social, and Corporate Governance Information by Spanish Companies: A Compliance Analysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, R.W.; Contani, E.; Savoia, J.R.F.; Bergmann, D.R. Does better corporate governance increase operational performance? Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2017, 17, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Poletti-Hughes, J.; El-Faitouri, R.; Shah, S.Z.A. More on the relationship between corporate governance and firm performance in the UK: Evidence from the application of generalized method of moments estimation. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2016, 38, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.P.; Kennedy, D.B.; Weaver, S.C. Corporate Governance and Firm Value: Evidence from Canadian Capital Markets. Corp. Ownersh. Control. J. 2009, 6. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=1366045 (accessed on 27 May 2022). [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, F.; Mallin, C.; Zattoni, A. Corporate Governance Codes: A Review and Research Agenda. Corp. Gov. Int. Rev. 2016, 24, 222–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Halbouni, S.S. Corporate governance, economic turbulence and financial performance of UAE listed firms. Stud. Econ. Financ. 2013, 30, 118–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renders, A.; Gaeremynck, A.; Sercu, P. Corporate-Governance Ratings and Company Performance: A Cross-European Study. Corp. Gov. Int. Rev. 2010, 18, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, B.F.; Sanvicente, A.Z. Quality of Corporate Governance and Cost of Equity in Brazil. J. Appl. Corp. Financ. 2013, 25, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Na Yoon, Y.; Kang, K.H. The relationship between board diversity and firm performance in the lodging industry: The moderating role of internationalization. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 86, 102461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Tabassum, N.; Darwish, T.K.; Batsakis, G. Corporate Governance and Tobin’s Q as a Measure of Organizational Performance. Br. J. Manag. 2018, 29, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alodat, A.Y.; Salleh, Z.; Hashim, H.A.; Sulong, F. Corporate governance and firm performance: Empirical evidence from Jordan. J. Financ. Report. Account. 2021; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burks, J.J.; Randolph, D.W.; Seida, J.A. Modeling and interpreting regressions with interactions. J. Account. Lit. 2019, 42, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Terjesen, S.; Umans, T. Corporate governance in entrepreneurial firms: A systematic review and research agenda. Small Bus. Econ. 2018, 54, 43–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussainey, K.; Aljifri, K. Corporate governance mechanisms and capital structure in UAE. J. Appl. Account. Res. 2012, 13, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, N.A.; Wang, Z. Effects of corporate governance on capital structure: Empirical evidence from Pakistan. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2012, 12, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detthamrong, U.; Chancharat, N.; Vithessonthi, C. Corporate governance, capital structure and firm performance: Evidence from Thailand. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2017, 42, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najjar, B. Corporate governance and institutional ownership: Evidence from Jordan. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2010, 10, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardalan, K. Capital structure theory: Reconsidered. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2017, 39, 696–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, H.; Migliori, S.; Mohsni, S. Capital structure and firm performance: The role of corporate governance. Int. J. Bus. Gov. Ethic 2021, 15, 436–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acero, I.; Serrano, R.; Dimitropoulos, P. Ownership structure and financial performance in European football. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2017, 17, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, N.A.; Wang, Z.; Khan, S. The impact of internal attributes of corporate governance on firm performance: Evidence from Pakistan. Int. J. Commer. Manag. 2013, 23, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitropoulos, P.E.; Tsagkanos, A. Financial Performance and Corporate Governance in the European Football Industry. Int. J. Sport Financ. 2012, 7, 280–308. [Google Scholar]
- Outa, E.; Waweru, N.M. Corporate governance guidelines compliance and firm financial performance: Kenya listed companies. Manag. Audit. J. 2016, 31, 891–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, I. Corporate Governance and Performance around the World: What We Know and What We Don’t. World Bank Res. Obs. 2010, 26, 42–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.; Hashim, H.A.; Salleh, Z. Datasets for corporate governance index of Jordanian non-financial sector firms. Data Brief 2020, 30, 105603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boolaky, P.K.; Omoteso, K.; Ibrahim, M.U.; Adelopo, I. The development of accounting practices and the adoption of IFRS in selected MENA countries. J. Account. Emerg. Econ. 2018, 8, 327–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Amosh, H.; Khatib, S.F.A. Theories of corporate disclosure: A literature review. Corp. Gov. Sustain. Rev. 2022, 6, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, Y.-L.; Connelly, J.T.; Jiang, P.; Limpaphayom, P. Does Corporate Governance Predict Future Performance? Evidence from Hong Kong. Financ. Manag. 2011, 40, 159–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H. Corporate governance and operating performance of Chinese listed firms. J. Int. Account. Audit. Tax. 2011, 20, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, R.; Frijns, B.; Otten, R.; Tourani-Rad, A. The impact of corporate governance on corporate performance: Evidence from Japan. Pac. Basin Financ. J. 2008, 16, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerantzidis, M. The role of weighting in corporate governance ratings. J. Manag. Gov. 2018, 22, 589–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, K. Board size and corporate performance: The missing role of board leadership structure. J. Manag. Gov. 2011, 15, 415–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Feng, T. Mediation or Moderation? The Role of R&D Investment in the Relationship between Corporate Governance and Firm Performance: Empirical Evidence from the Chinese IT Industry. Corp. Gov. Int. Rev. 2014, 22, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazaea, S.A.; Al-Matari, E.M.; Zedan, K.; Khatib, S.F.A.; Zhu, J.; Al Amosh, H. Green Purchasing: Past, Present and Future. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, A.A.; Ntim, C.G.; Al-Najjar, B. Board diversity, corporate governance, corporate performance, and executive pay. Int. J. Finance Econ. 2019, 24, 761–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananzeh, H.; Al Amosh, H.; Albitar, K. The effect of corporate governance quality and its mechanisms on firm philanthropic donations: Evidence from the UK. Int. J. Account. Inf. Manag. 2022; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scafarto, V.; Dimitropoulos, P. Human capital and financial performance in professional football: The role of governance mechanisms. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2018, 18, 289–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Beekes, W.A.; Verhoeven, P. Corporate governance, accounting and finance: A review. Account. Financ. 2011, 51, 96–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.D.; Caylor, M.L. Corporate governance and firm operating performance. Rev. Quant. Financ. Account. 2009, 32, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gompers, P.; Ishii, J.; Metrick, A. Corporate Governance and Equity Prices. Q. J. Econ. 2003, 118, 107–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcker, D.F.; Richardson, S.A.; Tuna, I. Corporate Governance, Accounting Outcomes, and Organizational Performance. Account. Rev. 2007, 82, 963–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Amosh, H.; Khatib, S.F.A. Corporate governance and voluntary disclosure of sustainability performance: The case of Jordan. SN Bus. Econ. 2021, 1, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Hossain, M.; Adams, M.B. The Effects of Board Composition and Board Size on the Informativeness of Annual Accounting Earnings. Corp. Gov. Int. Rev. 2006, 14, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.K. A disclosure index to measure the extent of corporate governance reporting by UAE listed corporations. J. Financ. Rep. Account. 2012, 10, 4–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallamu, B.S.; Saat, N.A.M. Audit committee attributes and firm performance: Evidence from Malaysian finance companies. Asian Rev. Account. 2015, 23, 206–231x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J. CEO duality and firm performance: The moderating roles of other executives and blockholding outside directors. Eur. Manag. J. 2017, 35, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, N.A.M. Ownership structure, corporate governance and corporate performance in Malaysia. Int. J. Commer. Manag. 2010, 20, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, S.; Bolton, B. Corporate governance and firm performance. J. Corp. Financ. 2008, 14, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, S.; Bolton, B.; Romano, R. The promise and peril of corporate governance indices. Columbia Law Rev. 2008, 108, 1803–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozec, R.; Bozec, Y. The Use of Governance Indexes in the Governance-Performance Relationship Literature: International Evidence. Can. J. Adm. Sci. Rev. Can. des Sci. de l’Adm. 2012, 29, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaskati, N.; Bird, R.; Lu, Y.; Lu, S. Corporate governance, institutions, markets, and social factors. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2020, 51, 101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Amosh, H.A. The Role of Governance Attributes in Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Practices Evidence from Jordan. In Research Anthology on Developing Socially Responsible Businesses; Management Association, Information Resources, Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 1229–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-S.; Yu, S.-W.; Hung, C.-H. Firm risk and performance: The role of corporate governance. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2015, 9, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Malkawi, H.-A.N.; Pillai, R.; Bhatti, M. Corporate governance practices in emerging markets: The case of GCC countries. Econ. Model. 2014, 38, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ararat, M.; Black, B.S.; Yurtoglu, B.B. The effect of corporate governance on firm value and profitability: Time-series evidence from Turkey. Emerg. Mark. Rev. 2017, 30, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, A.A.-N.; Ismail, A.K. Corporate governance practices, ownership structure, and corporate performance in the GCC countries. J. Int. Financ. Mark. Inst. Money 2017, 46, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Amosh, H.; Khatib, S.F.; Alkurdi, A.; Bazhair, A.H. Capital structure decisions and environmental, social and governance performance: Insights from Jordan. J. Financ. Rep. Account. 2022; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, O. Effect of ownership concentration on capital structure: Evidence from the MENA region. Int. J. Islam. Middle East. Financ. Manag. 2015, 8, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosu, S.; Danso, A.; Ahmad, W.; Coffie, W. Information asymmetry, leverage and firm value: Do crisis and growth matter? Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2016, 46, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahwan, T.M. The effects of corporate governance on financial performance and financial distress: Evidence from Egypt. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2015, 15, 641–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.C. Agency costs of free cash flow, corporate finance, and takeovers. Am. Econ. Rev. 1986, 76, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitropoulos, P. Capital structure and corporate governance of soccer clubs: European evidence. Manag. Res. Rev. 2014, 37, 658–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokpin, G.A.; Isshaq, Z. Corporate governance, disclosure and foreign share ownership on the Ghana Stock Exchange. Manag. Audit. J. 2009, 24, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, O.; Asgarov, Z.; Guliyev, A.; Islam, T.; Kalinina, Y.; Pashayev, Z. Capital structure and value of reported earnings: Evidence from an emerging market. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2017, 24, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranho, F.S.; Leal, R. Corporate governance and firm performance in Latin America: A meta-analysis. Acad. Rev. Latinoam. De Adm. 2018, 31, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, B.S.; Kim, W.; Jang, H.; Park, K.-S. How corporate governance affect firm value? Evidence on a self-dealing channel from a natural experiment in Korea. J. Bank. Financ. 2015, 51, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, A.E.; Sbeiti, W.M.; Qasim, A. Accounting legislation, corporate governance codes and disclosure in Jordan: A review. Int. J. Law Manag. 2017, 59, 147–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, B.S.; de Carvalho, A.G.; Sampaio, J.O. The evolution of corporate governance in Brazil. Emerg. Mark. Rev. 2014, 20, 176–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, A.; Weir, C. The governance-performance relationship: Evidence from Ghana. J. Appl. Account. Res. 2016, 17, 285–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerantzidis, M. A multi-methodology on building a corporate governance index from the perspectives of academics and practitioners for firms in Greece. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2016, 16, 295–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, B.; De Carvalho, A.G.; Khanna, V.; Kim, W.; Yurtoglu, B. Corporate governance indices and construct validity. Corp. Gov. Int. Rev. 2017, 25, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas-Torres, F.; Bustamante-Ubilla, M.; Campos-Troncoso, R. Diversity of the Board of Directors and Financial Performance of the Firms. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmansouri, R.; Mehdiabadi, A.; Shahabi, V.; Spulbar, C.; Birau, R. An Investigation of the Link between Major Shareholders’ Behavior and Corporate Governance Performance before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Case Study of the Companies Listed on the Iranian Stock Market. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2022, 15, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Merino, D.; Rodríguez-Pérez, G. The Effects of Legal Origin and Corporate Governance on Financial Firms’ Sustainability Performance. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitun, R. Corporate Governance, Capital Structure and Corporate Performance: Evidence from GCC Countries. Rev. Middle East Econ. Financ. 2014, 10, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.; Al-Malkawi, H.-A. On the relationship between corporate governance and firm performance: Evidence from GCC countries. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2018, 44, 394–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, S.; Kimino, S.; Pye, A. Interlocking directorships and firm performance in highly regulated sectors: The moderating impact of board diversity. J. Manag. Gov. 2014, 18, 347–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ararat, M.; Black, B.S.; Yurtoglu, B.B. Corporate Governance, Business Groups, and Market Value: Time-Series Evidence from Turkey. Northwestern Law & Econ Research Paper No. 13–19; ECGI—Finance Working Paper. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2277768 (accessed on 27 May 2022).
- Ullah, S.; Akhtar, P.; Zaefarian, G. Dealing with endogeneity bias: The generalized method of moments (GMM) for panel data. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2018, 71, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarram, S. Corporate governance ratings and the dividend payout decisions of Australian corporate firms. Int. J. Manag. Finance 2015, 11, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftci, I.; Tatoglu, E.; Wood, G.; Demirbag, M.; Zaim, S. Corporate governance and firm performance in emerging markets: Evidence from Turkey. Int. Bus. Rev. 2019, 28, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, S.S.; Bathula, H.; A Singh, D. Ownership concentration, board characteristics and firm performance: A contingency framework. Manag. Decis. 2015, 53, 911–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujunwa, A. Board characteristics and the financial performance of Nigerian quoted firms. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2012, 12, 656–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.S. The association between corporate governance and firm performance—A meta-analysis. Int. J. Account. Inf. Manag. 2015, 23, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, S.; Morris, T.; Morrill, C. Corporate governance rating and financial performance: A Canadian study. Corp. Governance Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2010, 10, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitun, R.; Tian, G.G. Capital Structure and Corporate Performance: Evidence from Jordan. Australas. Account. Bus. Financ. J. Forthcom. 2014, 4, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Amman Stock Exchange (ASE). Available online: http://www.ase.com.jo (accessed on 27 May 2022).
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Hair, J.F., Jr., Black, W.C., Babin, B.J., Anderson, R.E., Eds.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S.; Ullman, J.B. Using Multivariate Statistics; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Hoechle, D. Robust Standard Errors for Panel Regressions with Cross-Sectional Dependence. Stata J. Promot. Commun. Stat. Stata 2007, 7, 281–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujarati, D.N. Basic Econometrics; Tata McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tshipa, J.; Brummer, L.; Wolmarans, H.; Du Toit, E. The impact of flexible corporate governance disclosures on value relevance. Empirical evidence from South Africa. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2018, 18, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyudin, A.; Solikhah, B. Corporate governance implementation rating in Indonesia and its effects on financial performance. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2017, 17, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Cohen, P.; West, S.G.; Aiken, L.S. Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, W.H. Econometric Analysis, 5th ed.; Pearson Education: Noida, India, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson, A.; Lhaopadchan, S.; Buakes, S. How informative is the Thai corporate governance index? A financial approach. Int. J. Account. Inf. Manag. 2011, 19, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedan, H.I.; Abu Nassar, M. The Effect of Corporate Governance on Operating Performance of Jordanian Manufacturing Companies: Evidence from Amman Stock Exchange. Dirasat Adm. Sci. 2014, 161, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epps, R.W.; Cereola, S.J. Do institutional shareholder services (ISS) corporate governance ratings reflect a company’s operating performance? Crit. Perspect. Account. 2008, 19, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, B.S.; de Carvalho, A.G.; Gorga, É. Does one size fit all in corporate governance? Evidence from Brazil (and other BRIK Countries). In ECGI Law Working Paper No. 30; Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Muhmad, S.N.; Hashim, H.A. The interaction effect of corporate governance and CAMEL framework on bank performance in Malaysia. Afro-Asian J. Financ. Account. 2017, 7, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, L.S.; West, S.G.; Reno, R.R. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions; Sage: Newcastle, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Amrah, M.R.; Hashim, H.A.; Ariff, A.M. The moderating effect of family control on the relationship between board of directors effectiveness and cost of debt: Evidence from Oman. Int. J. Econ. Manag. Account. 2015, 23, 217–239. [Google Scholar]
- Nas, T.I.; Kalaycioglu, O. The effects of the board composition, board size and CEO duality on export performance: Evidence from Turkey. Manag. Res. Rev. 2016, 39, 1374–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).