Internal Temperature Variation on Spontaneous Combustion of Coal Gangue Dumps under the Action of a Heat Pipe: Case Study on Yinying Coal Mine in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
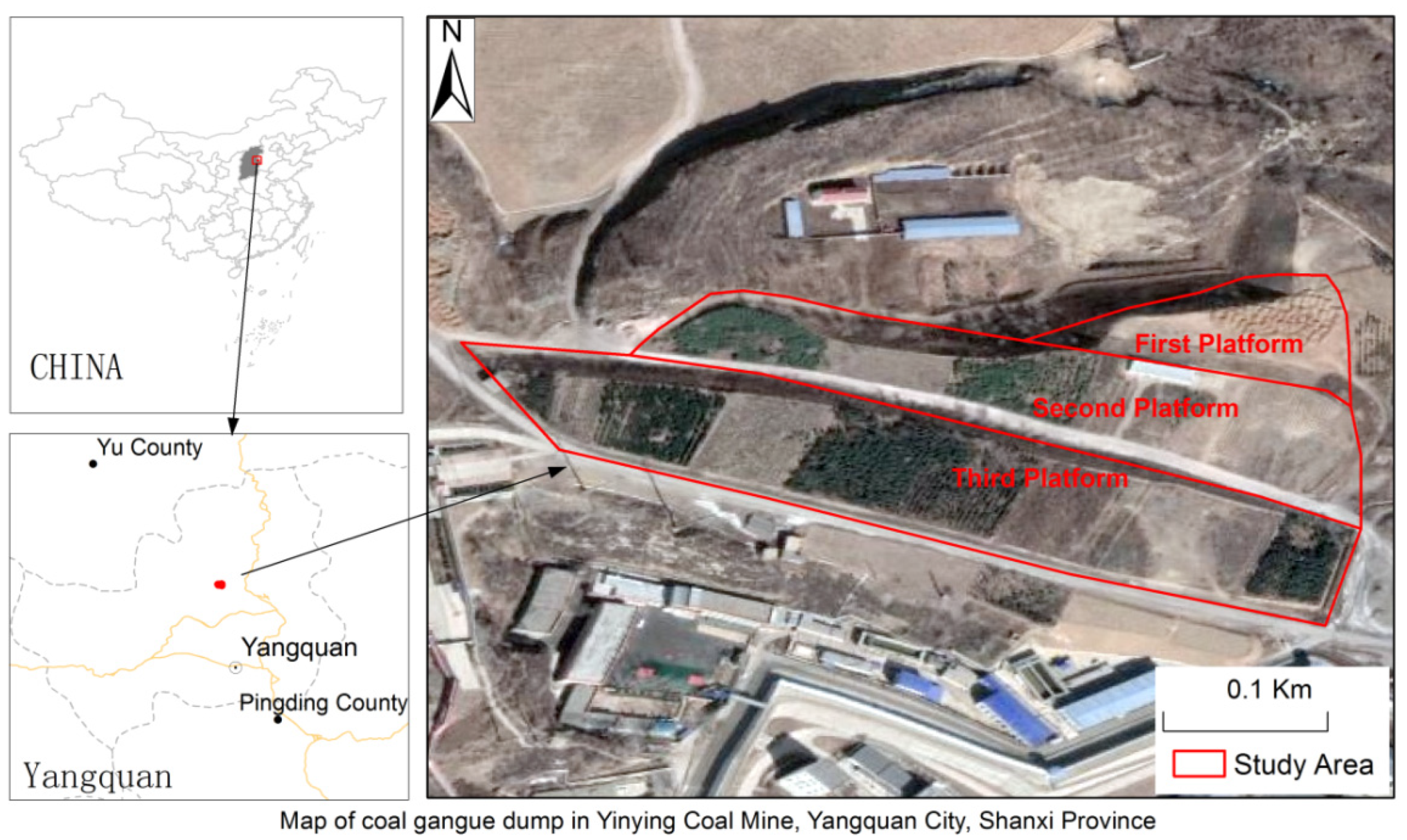
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
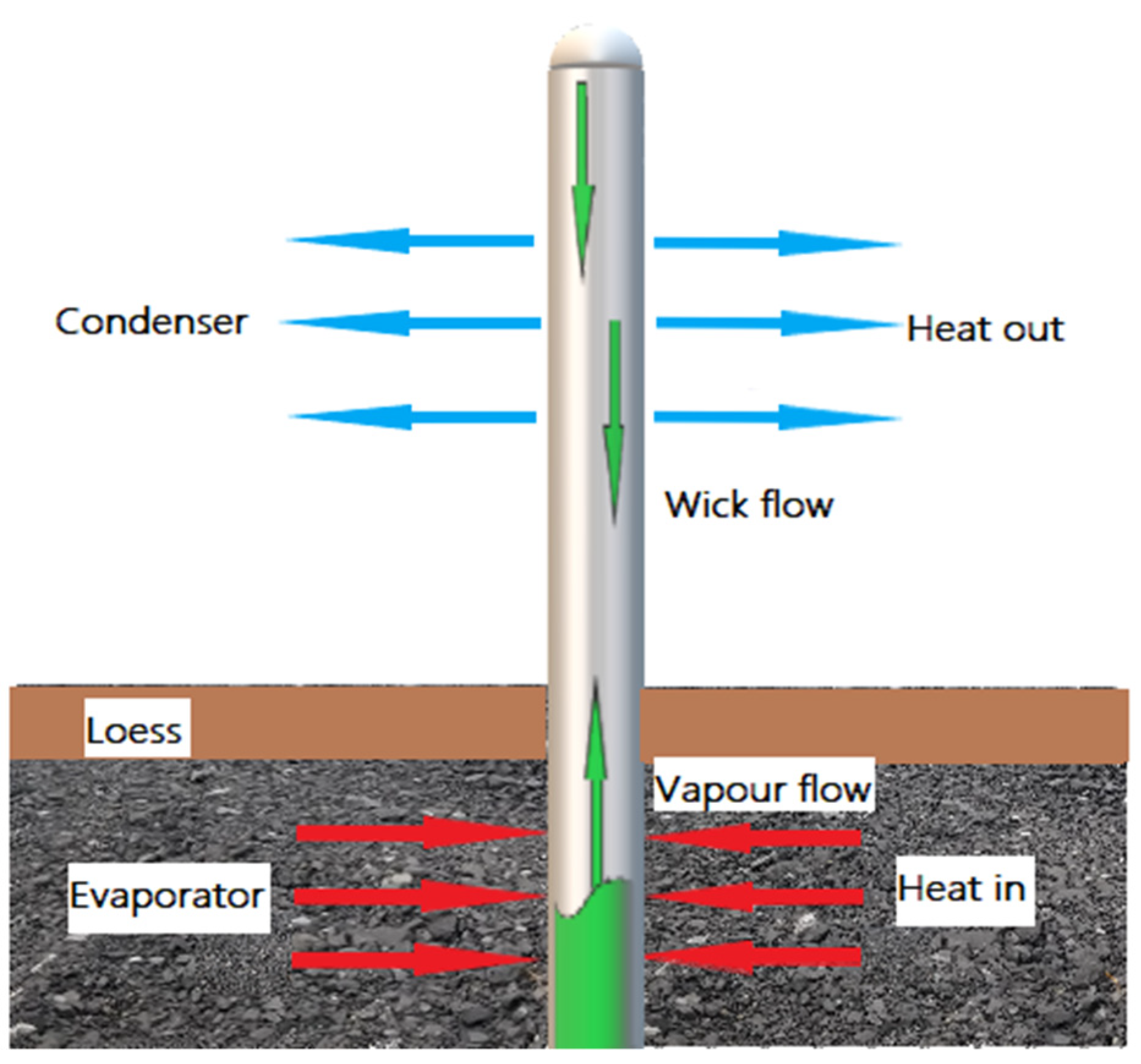
2.2. Working Principle of the HP
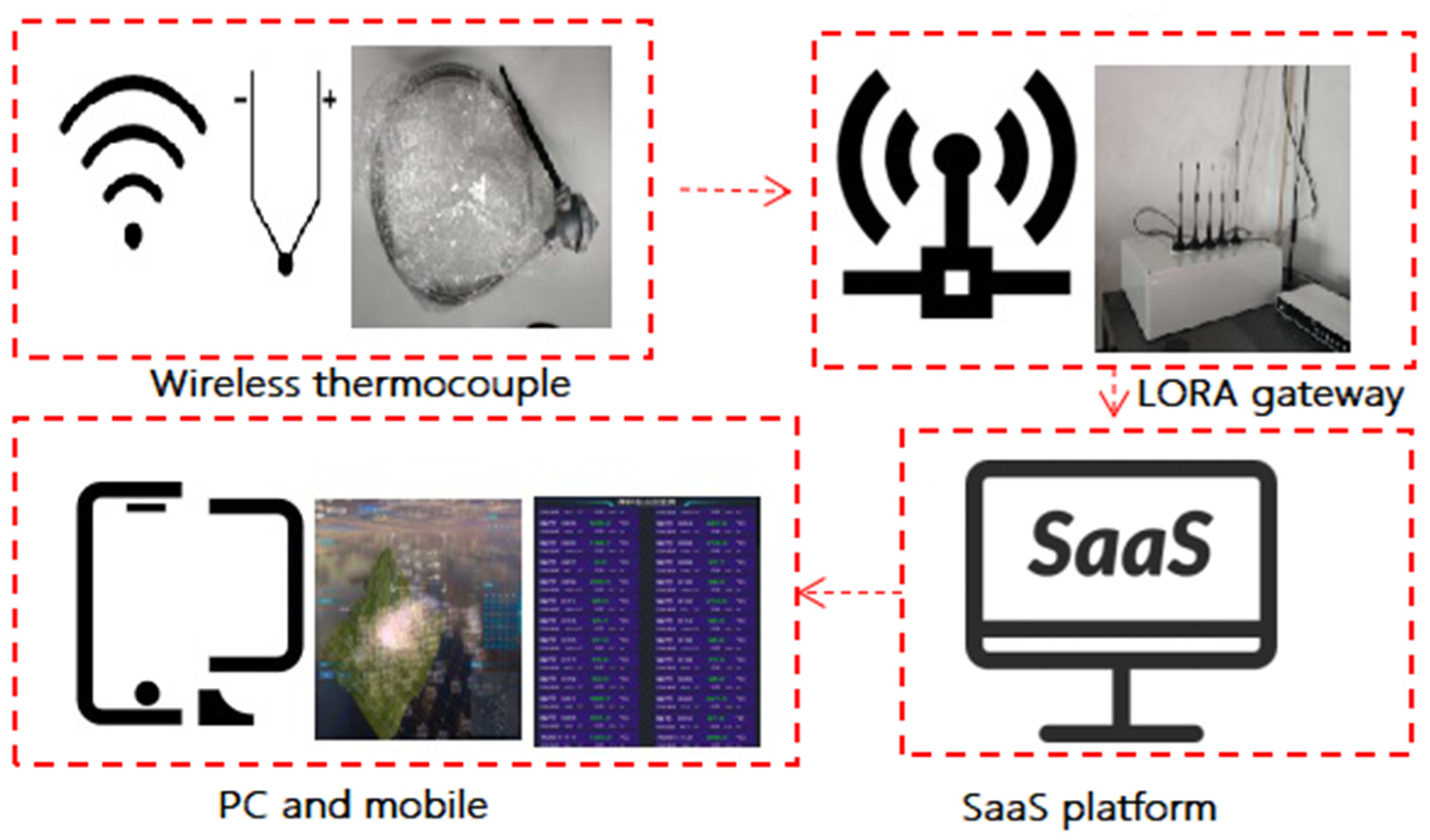
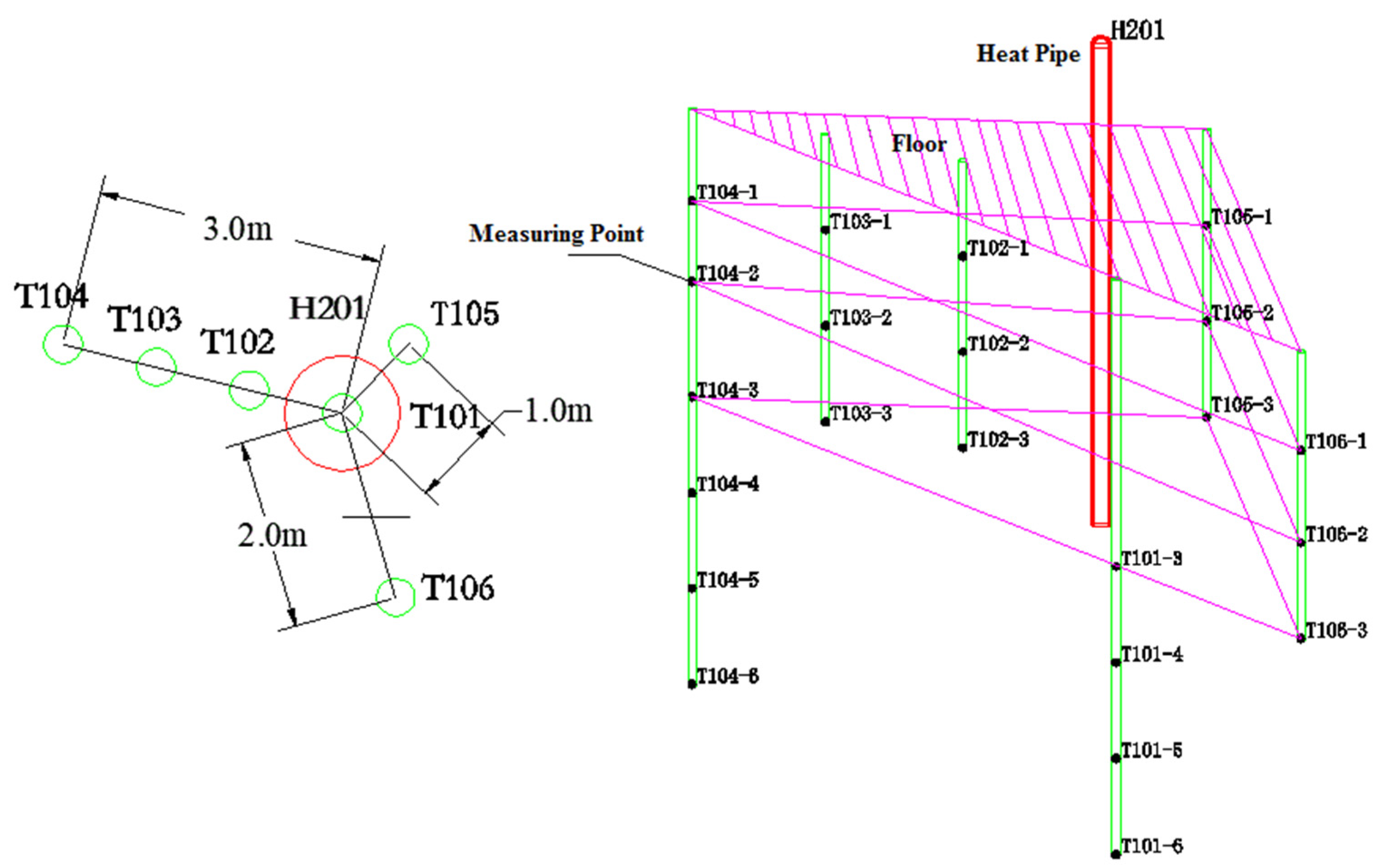
2.3. Experimental Scheme
2.4. Initial Temperature
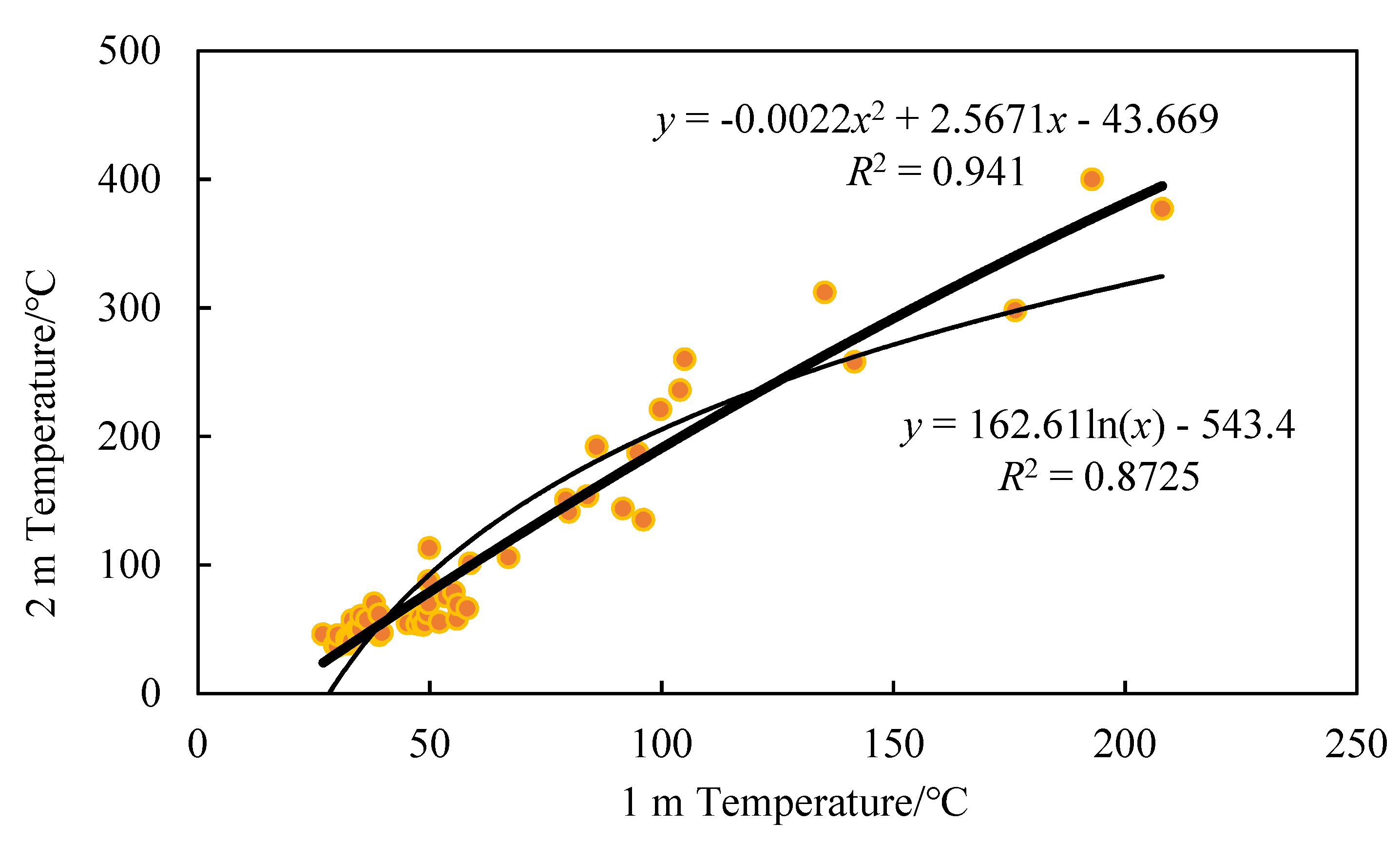
2.5. Fitting the Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Relationship between Shallow and Deep Temperatures
3.2. Model Significance Analysis
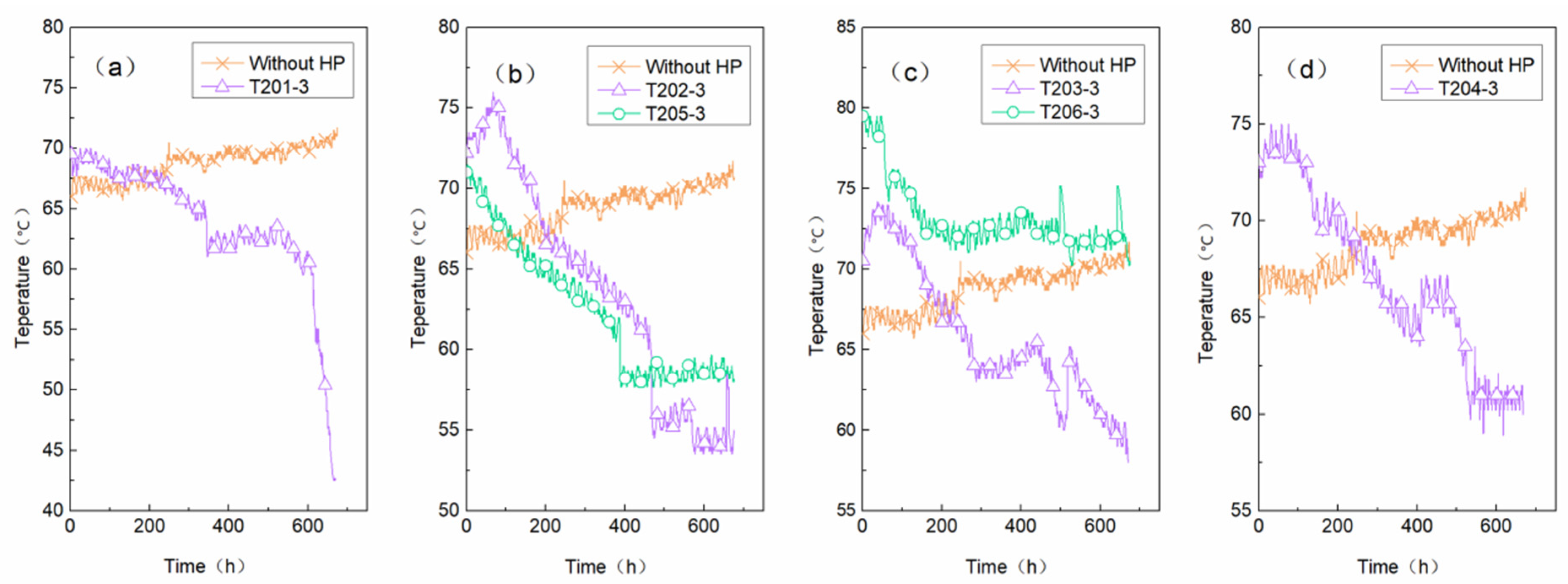
3.3. Effect of the HP on Gangue Dumps
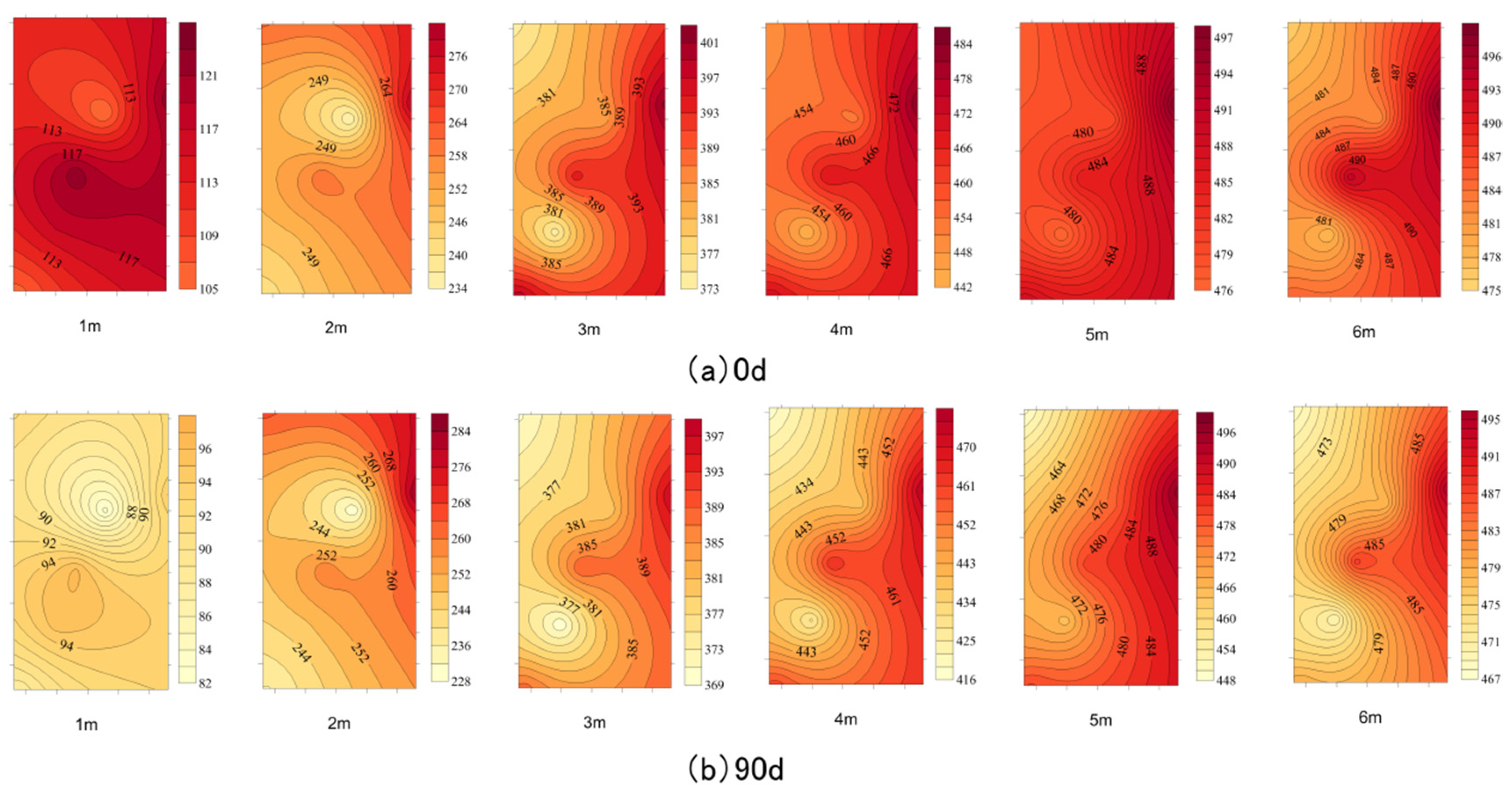
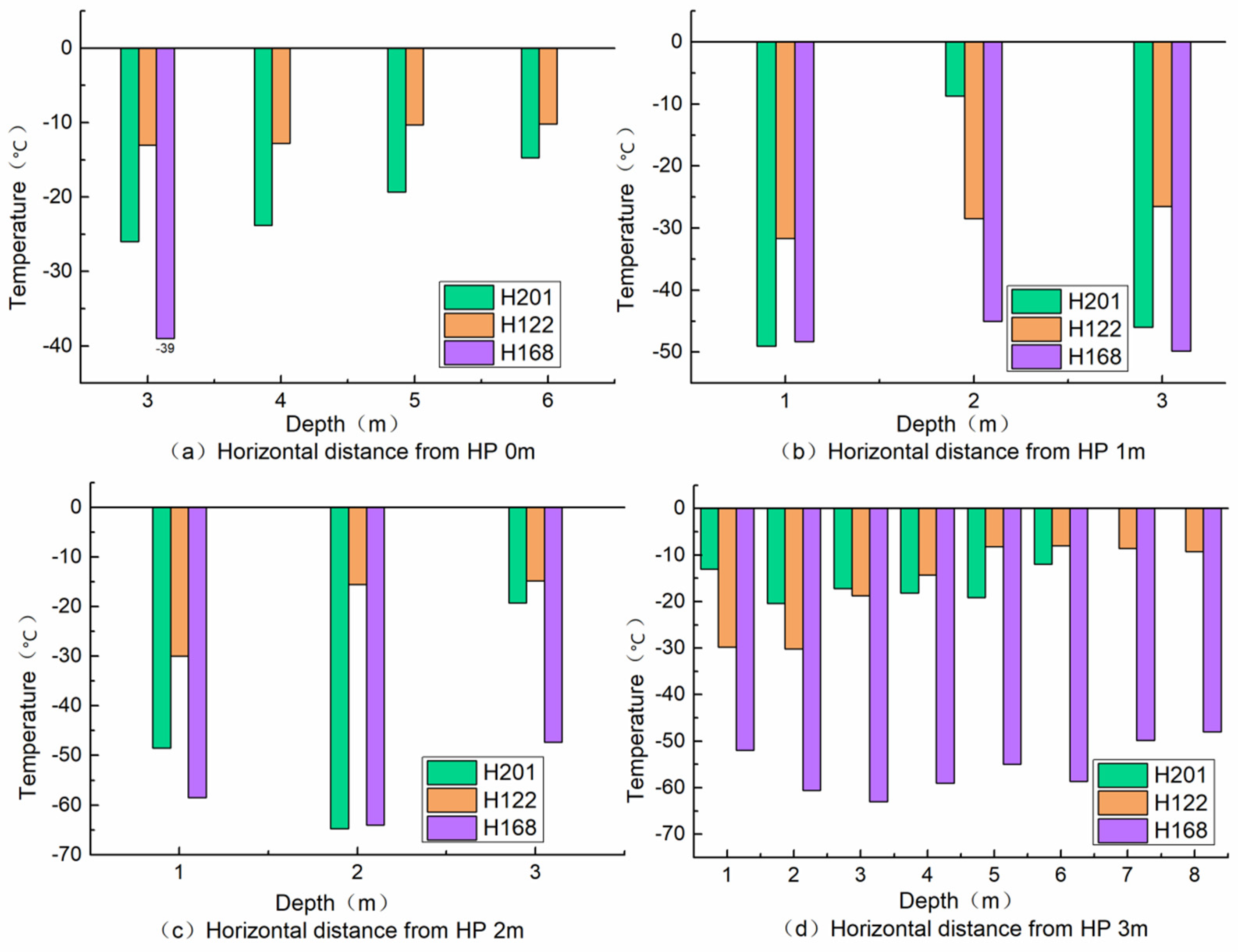
3.4. Horizontal Temperature Variation
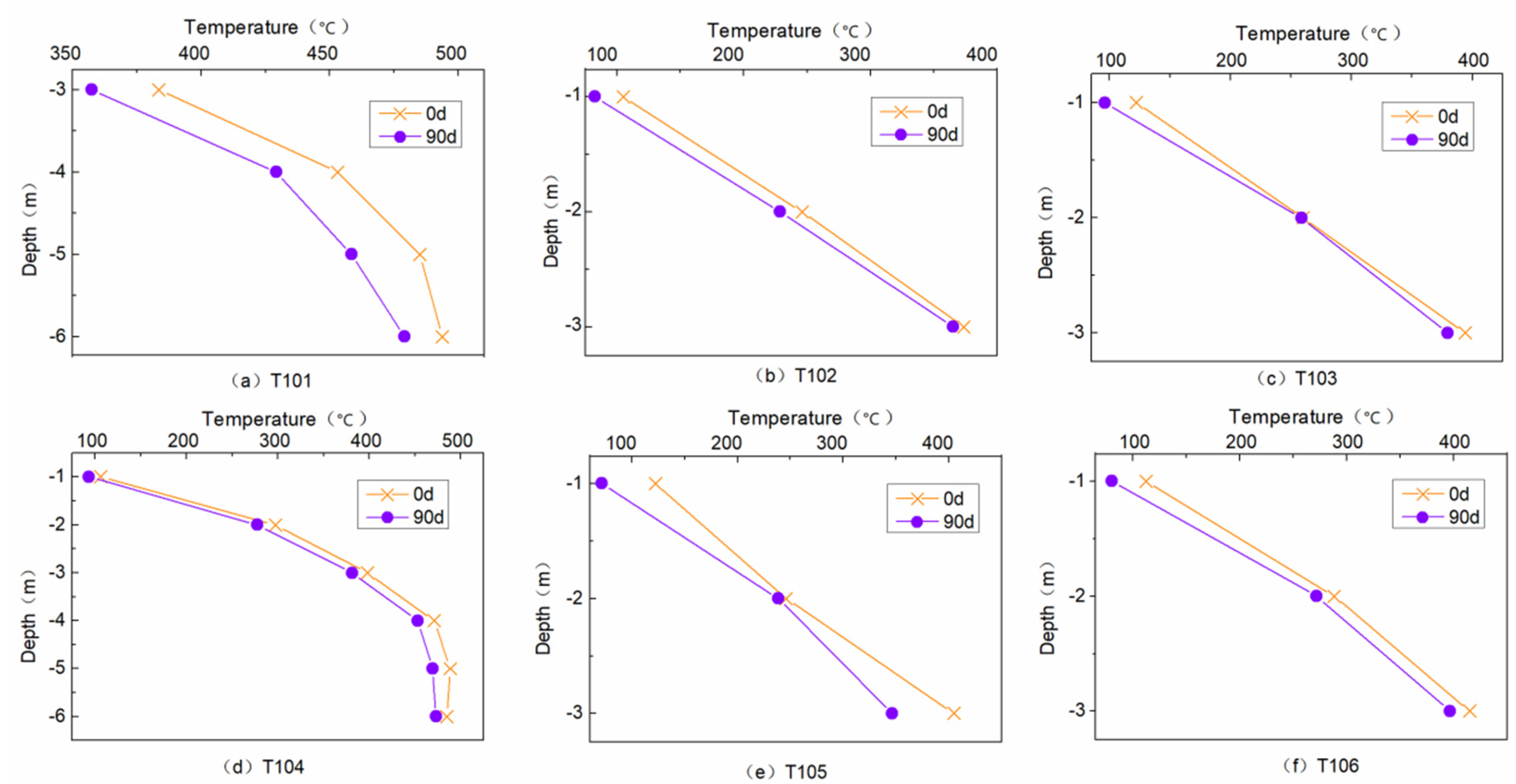
3.5. Vertical Temperature Variation
3.6. Maximum Cooling Range in Different Temperature Zones
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The quadratic regression model fits better than the logarithmic function model, and the regression is significant and can be used as an empirical regression formula for the temperature between shallow and deep layers.
- (2)
- The HP has high thermal conductivity and an obvious cooling effect on the coal gangue dump. In the low-temperature oxidation zone below 80~90 °C of the gangue dump, compared with the control group without an HP, the temperature of the HP decreased continuously after 700 h, and the HP needed a stable period of about 100 h in the early cooling period, with an average cooling range of 21.44%, while the control group without HP was in a continuous rising state, with a heating range of 8%. Under the action of the HP, the cooling range of the three single-pipe test groups is different, showing a regular change. The internal temperature drop of the coal gangue dump is inversely proportional to the horizontal distance and directly proportional to the working time, and the control radius for the three groups of tests is 3 m.
- (3)
- In the vertical direction, the temperature difference between the shallow layer and the deep layer is larger, and the internal temperature is proportional to the depth. The decrease is related to the spontaneous combustion, the depth of the HP, the location of the ignition point, and the temperature range. The HP mainly reduces the temperature of the gangue layer with a depth of 1~4 m. HP technology has an obvious control effect on different temperature zones of spontaneous combustion in the coal gangue dump, and can effectively improve the economy of spontaneous combustion treatment of the coal gangue dump.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, L.; Li, K.; Fu, W.; Liu, C.; Yang, S. Preparation, characteristics and mechanisms of the composite sintered bricks produced from shale, sewage sludge, coal gangue powder and iron ore tailings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 232, 117250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, C.; Hong, P.; Yao, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, L. Mineralogical characterization of the typical coarse iron ore particles and the potential to discharge waste gangue using a dry density-based gravity separation. Powder Technol. 2018, 342, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Zhang, J.; Tetzlaff, A.; van Dijk, P.; Voigt, S.; Mehl, H.; Wagner, W. Uncontrolled coal fires and their environmental impacts: Investigating two arid mining regions in north-central China. Appl. Geogr. 2007, 27, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffern, E.; Coates, D. Geologic history of natural coal-bed fires, Powder River basin, USA. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2004, 59, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.K.; Yu, M.G.; Xu, J.; Huang, Z. Harm of Gangue Dump and Cause Analysis of Spontaneous Combustion. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2006, 13, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.W.; Ma, L.; Zhu, G.; Huang, J.; Zheng, X. Study and practices on spontaneous combustion control technology of mine coal waste pile. Coal Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Wang, E.; Hu, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Fang, B.; Zhan, T. Critical slowing down on acoustic emission characteristics of coal containing methane. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 24, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stracher, G.B.; Taylor, T.P. Coal fires burning out of control around the world: Thermodynamic recipe for environmental catastrophe. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2004, 59, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Kuenzer, C. Coal fires in China over the last decade: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 133, 72–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W. Forming Mechanism and Influence Factors of Gangue Hill Spray Explosion. J. Liaoning Technol. Univ. 2002, 21, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, K.; Zhou, L. Anatomy of explosives spontaneous combustion accidents in the Chinese underground coal mine: Causes and prevention. Process Saf. Prog. 2016, 35, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Q.; Lu, J.; Wen, H. Experimental studies of spontaneous combustion and anaerobic cooling of coal. Fuel 2015, 157, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fang, X.; Du, F.; Tan, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, C. Three-dimensional distribution and oxidation degree analysis of coal gangue dump fire area: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.D.; Lian, F.Y.; Deng, H.Y.; Yu, S.S.; Zhang, X.J. Application principle and prospect of thermal-probe technique in cold region engineering. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2003, 22, 2673–2676. [Google Scholar]
- Xiu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Jiang, W. Temperature characteristic and inhibition effect on insect pest in grain storehouse based on heat pipe technology. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 14, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.L.; Li, J.W. Experiments of lowering the temperature of sandy soil speedily at night by heat-pipe technology. J.-Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2007, 35, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Cheng, Q.L.; Han, H.S.; Wei, L.X.; Liu, Y.J. Study of Heat Transfer Characteristic in Gravity Heat Pipe of Well bore. Energy Conserv. Technol. 2013, 31, 46–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.W. Role of Liquid Filling Ratio on Heat Transfer Characteristics in Miniaturized Gravitational Heat Pipe. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2018, 39, 2749–2754. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.D. Laboratory Experiment and Field Test of Gravity Heat Pipe. J. Southwest Petrol. Univ. 2008, 1, 140–142. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.; Suhendra, S.; Rüter, H. Heat pipes-Suitable for extinguishing underground coal fires? Fed. Minist. Educ. Res. 2010, 2, 433–437. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, Q.U. Experimental Research of Gravity Heat Pipe Used to Extract Spontaneous Heat Storage in the Coal. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Wang, J.G.; Ji, C.F.; Ma, L.; So, E. Cooling effect analysis of heat pipe suppressing coal spontaneous combustion. Coal Eng. 2017, 49, 100–102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.W. Study on Influence Factors of Heat Transfer Capacity of Heat Pipe Used for Coal Storage Pile. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.H.; Sun, M.H.; Su, G.Y. Influence of Gravity Heat Hipe on Temperature Field in Coal Pile. Saf. Coal Mines. 2018, 49, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Li, B.; Ma, L. Influence of heat pipes on temperature distribution in coal storage pile. China Saf. Sci. 2015, J25, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.M.; Chang, Z.C.; Li, B. Numerical simulation on thermal migration behavior of spontaneous combustion coal pile based on heat pipe cooling technology. J. Xian Univ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 581–588. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Deng, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhai, X.; Shu, C.-M.; Gao, W. Heat transfer capacity of heat pipes: An application in coalfield wildfire in China. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 54, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, B.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, C.P.; Lai-Wang, B.; Shu, C.M. Combustion properties of coal gangue using thermogravimetry-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 116, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, R.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Sivaraman, B. Comparative study on heat pipe performance using aqueous solutions of alcohols. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 48, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Z. Experimental investigation on the heat transfer performance of a flat parallel flow heat pipe. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 168, 120856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Liao, G.; Sun, J.; Li, P. Experimental research on index gas of the coal spontaneous at low-temperature stage. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2004, 17, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.A.; Glasser, D. Spontaneous combustion of carbonaceous stockpiles. Part I: The relative importance of various intrinsic coal properties and properties of the reaction system. Fuel 2005, 84, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.G.; Wu, J.M. Experimental study on significant gases of coal spontaneous combustion by temperature programmed (TP)-Science Direct. Proc. Eng. 2011, 26, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, K.; Zhong, X.; Wang, D.; Shi, G.; Wang, Y.; Shao, Z. Prevention and control of coalfield fire technology: A case study in the Antaibao Open Pit Mine goaf burning area, China. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. of HP | No. of Measuring Point | Depth/m | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| HP201 | T101 | 383.5 °C | 453 °C | 485 °C | 493.7 °C | ||||
| T102 | 104.7 °C | 244 °C | 373.7 °C | ||||||
| T103 | 122.2 °C | 260 °C | 394 °C | ||||||
| T104 | 106.2 °C | 297.4 °C | 398.2 °C | 471.2 °C | 488.5 °C | 485.2 °C | |||
| T105 | 122.2 °C | 246.7 °C | 404.7 °C | ||||||
| T106 | 112.2 °C | 287.3 °C | 415 °C | ||||||
| HP122 | T201 | 64 °C | 79.5 °C | 88 °C | 98 °C | ||||
| T202 | 47.7 °C | 65 °C | 74.5 °C | ||||||
| T203 | 49.7 °C | 77.2 °C | 74.2 °C | ||||||
| T204 | 48 °C | 74 °C | 71.2 °C | 76 °C | 87.2 °C | 93.2 °C | 99.7 °C | 165 °C | |
| T205 | 46.7 °C | 63.5 °C | 71.5 °C | ||||||
| T206 | 60.7 °C | 79 °C | 81 °C | ||||||
| HP168 | T301 | 260.7 °C | |||||||
| T302 | 84.5 °C | 141.7 °C | 254.5 °C | ||||||
| T303 | 94.2 °C | 157.5 °C | 251 °C | ||||||
| T304 | 101.7 °C | 156.5 °C | 262 °C | 442.7 °C | 528.7 °C | 550.2 °C | 573 °C | 545 °C | |
| T305 | 92 °C | 145.7 °C | 238 °C | ||||||
| T306 | 101.2 °C | 175.5 °C | 298.2 °C | ||||||
| Fitted Models | Quadratic Fitting Equations | Logarithmic Fitting Equations |
|---|---|---|
| 1 m and 2 m | y = −0.0022x2 + 2.5671x − 43.669 (R2 = 0.941) | y = 162.61ln(x) − 543.4 (R2 = 0.8725) |
| 1 m and 3 m | y = −0.0089x2 + 4.7838x − 78.533 (R2 = 0.9141) | y = 238.25ln(x) − 778.17 (R2 = 0.8909) |
| 1 m and 4 m | y = −0.0201x2 + 7.9185x − 164.62 (R2 = 0.9646) | y = 292.7ln(x) − 945.83 (R2 = 0.9437) |
| 1 m and 5 m | y = −0.0212x2 + 8.1371x − 143.95 (R2 = 0.9699) | y = 293.32ln(x) − 920.61 (R2 = 0.953) |
| 1 m and 6 m | y = −0.0268x2 + 9.5022x − 150.73 (R2 = 0.9511) | y = 308.68ln(x) − 939.78 (R2 = 0.9364) |
| Fitted Models | Freedoms | F-Value | F Critical Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 m and 2 m | 34 | 7.825 | 5.29 |
| 1 m and 3 m | 29 | 6.438 | 5.42 |
| 1 m and 4 m | 8 | 11.312 | 8.65 |
| 1 m and 5 m | 5 | 15.496 | 13.3 |
| 1 m and 6 m | 6 | 12.852 | 10.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Niu, J.; Shi, H.; Yang, N.; Gao, T.; Guo, L. Internal Temperature Variation on Spontaneous Combustion of Coal Gangue Dumps under the Action of a Heat Pipe: Case Study on Yinying Coal Mine in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9807. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14169807
Zhao N, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Niu J, Shi H, Yang N, Gao T, Guo L. Internal Temperature Variation on Spontaneous Combustion of Coal Gangue Dumps under the Action of a Heat Pipe: Case Study on Yinying Coal Mine in China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(16):9807. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14169807
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Na, Yongbo Zhang, Xuehua Zhao, Jinrong Niu, Hong Shi, Na Yang, Tong Gao, and Lina Guo. 2022. "Internal Temperature Variation on Spontaneous Combustion of Coal Gangue Dumps under the Action of a Heat Pipe: Case Study on Yinying Coal Mine in China" Sustainability 14, no. 16: 9807. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14169807
APA StyleZhao, N., Zhang, Y., Zhao, X., Niu, J., Shi, H., Yang, N., Gao, T., & Guo, L. (2022). Internal Temperature Variation on Spontaneous Combustion of Coal Gangue Dumps under the Action of a Heat Pipe: Case Study on Yinying Coal Mine in China. Sustainability, 14(16), 9807. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14169807





