Green Intellectual Capital and Green Supply Chain Performance: Does Big Data Analytics Capabilities Matter?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
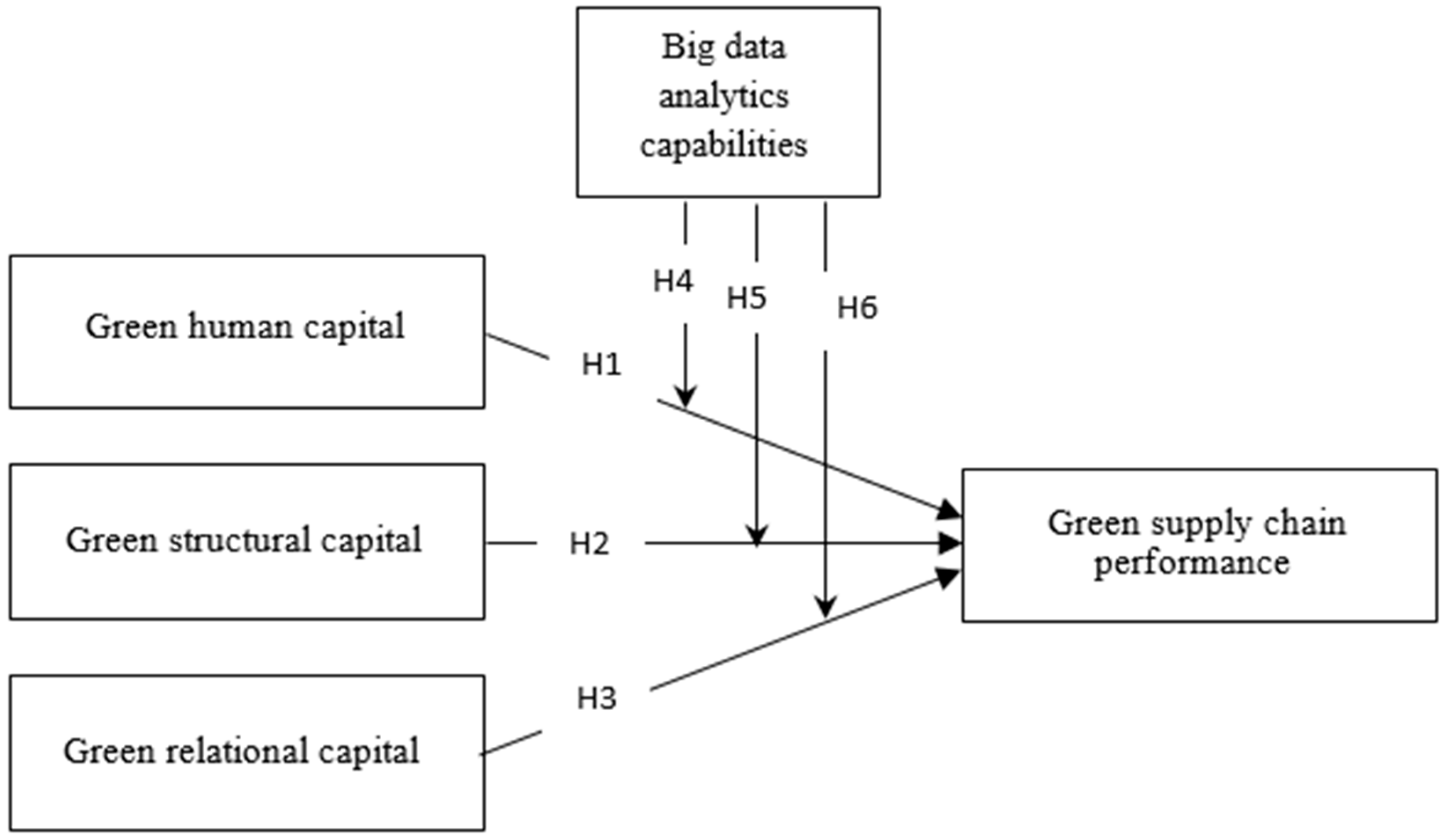
2. Theoretical Framework and Hypotheses Development
2.1. Intellectual Capital and Green Supply Chain Performance
2.1.1. Green Human Capital and Green Supply Chain Performance
2.1.2. Green Structural Capital and Green Supply Chain Performance
2.1.3. Green Relational Capital and Green Supply Chain Performance
2.2. The Moderating Role of Big Data Analytics Capabilities
3. Methodology
3.1. Measures and Instruments
3.2. The Study Population and Sample
4. Data Analysis and Results
4.1. The Measurement Model
4.2. Structural Model
5. Discussion and Conclusions
6. Implications
6.1. Theoretical Implications
6.2. Managerial Implications
6.3. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, S.H.; Hu, T.C. Knowledge transfer and competitive advantage on environmental uncertainty: An empirical study of the Taiwan semiconductor industry. Technovation 2007, 27, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, H. The growth of knowledge through the resource-based view. Manag. Decis. 2020, 58, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permatasari, A.; Dhewanto, W.; Dellyana, D. The role of traditional knowledge-based dynamic capabilities to improve the sustainable performance of weaving craft in Indonesia. J. Enterp. Communities People Places Glob. Econ. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Sharma, M. Impact of sustainable supply chain management on performance of SMEs amidst COVID-19 pandemic: An Indian perspective. Int. J. Logist. Econ. Glob. 2022, 9, 248–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiral, O.; Brotherton, M.C.; Rivaud, L.; Guillaumie, L. Organizations’ management of the COVID-19 pandemic: A scoping review of business articles. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregurec, I.; Tomičić Furjan, M.; Tomičić-Pupek, K. The impact of COVID-19 on sustainable business models in SMEs. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Gustafsson, A. Effects of COVID-19 on business and research. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 117, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairlie, R.W. The Impact of COVID-19 on Small Business Owners: Continued Losses and the Partial Rebound in May 2020; University of California: Santa Cruz, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, A.O.; Koh, S.G. COVID-19 and extended reality (XR). Curr. Issues Tour. 2020, 24, 1935–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altig, D.; Baker, S.; Barrero, J.M.; Bloom, N.; Bunn, P.; Chen, S.; Davis, S.J.; Leather, J.; Meyer, B.; Mihaylov, E.; et al. Economic uncertainty before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Public Econ. 2020, 191, 104274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.B.; Vanapalli, K.R.; Cheela, V.S.; Ranjan, V.P.; Jaglan, A.K.; Dubey, B.; Goel, S.; Bhattacharya, J. Challenges, opportunities, and innovations for effective solid waste management during and post COVID-19 pandemic. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 162, 105052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenstein, N.O. Supply chain risk management in the COVID-19 pandemic: Strategies and empirical lessons for improving global logistics service providers’ performance. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grida, M.; Mohamed, R.; Zaied, A.N.H. Evaluate the impact of COVID-19 prevention policies on supply chain aspects under uncertainty. Transp. Res. Interdiscip. Perspect. 2020, 8, 100240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, R.K.; Saunoris, J.W.; Goel, S.S. Supply chain performance and economic growth: The impact of COVID-19 disruptions. J. Policy Model. 2021, 43, 298–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, D. Growth and trade in the United States and the world economy: Overview. J. Policy Model. 2020, 42, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, N.; Upadhyay, A.; Kumar, A.; Gilani, H. Achieving operational excellence through the lens of lean and Six Sigma during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirkolaee, E.B.; Goli, A.; Ghasemi, P.; Goodarzian, F. Designing a sustainable closed-loop supply chain network of face masks during the COVID-19 pandemic: Pareto-based algorithms. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 333, 130056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusi-Sarpong, S.; Mubarik, M.S.; Khan, S.A.; Brown, S.; Mubarak, M.F. Intellectual capital, blockchain-driven supply chain and sustainable production: Role of supply chain mapping. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 175, 121331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Boura, M.; Lekakos, G.; Krogstie, J. Big data analytics and firm performance: Findings from a mixed-method approach. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 98, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frare, A.B.; Beuren, I.M. The role of green process innovation translating green entrepreneurial orientation and proactive sustainability strategy into environmental performance. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.L. A natural-resource-based view of the firm. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1995, 20, 986–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.L.; Dowell, G. Invited editorial: A natural-resource-based view of the firm: Fifteen years after. J. Manag. 2011, 37, 1464–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés-González, J.F.; Avilés-Sacoto, S.V.; Cárdenas-Barrón, L.E. An overview of tourism supply chains management and optimization models (TSCM–OM). In Handbook of Research on Holistic Optimization Techniques in the Hospitality, Tourism, and Travel Industry; Business Science Reference: Hershey, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 227–250. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A.; Sokolov, B.; Ivanova, M. Literature review on disruption recovery in the supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 6158–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sony, M. Lean Supply Chain Management and Sustainability: A Proposed Implementation Model. In Ethical and Sustainable Supply Chain Management in a Global Context; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 57–76. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, Q. Involving second-tier suppliers in Green supply chain management: Drivers and heterogenous understandings by firms along supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.R.; Kim, S.T.; Lee, H.H. Green Supply Chain Management Efforts of First-Tier Suppliers on Economic and Business Performances in the Electronics Industry. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuah, J.S.Y.; Fernando, Y. Green supply chain integration in automotive industry. In Encyclopedia of Information Science and Technology, 3rd ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 5056–5064. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna, Y. Development of Supply Chain Framework for the Circular Economy. In Handbook of Research on Entrepreneurship Development and Opportunities in Circular Economy; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 231–250. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, D.; Kwon, C. Structure of Green Supply Chain Management for Sustainability of Small and Medium Enterprises. Sustainability 2022, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.C.; Ding, J.H.; Chen, P.S. The effects of GSCM drivers and institutional pressures on GSCM practices in Taiwan’s textile and apparel industry. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 135, 618–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Sarkis, J.; Lai, K.H. Confirmation of a measurement model for green supply chain management practices implementation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 111, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Khatib, A.W. Intellectual capital and innovation performance: The moderating role of big data analytics: Evidence from the banking sector in Jordan. EuroMed J. Bus. 2022; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dost, M.; Badir, Y.F.; Ali, Z.; Tariq, A. The impact of intellectual capital on innovation generation and adoption. J. Intellect. Cap 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.U.; Anwar, M.; Li, S.; Khattak, M.S. Intellectual capital, financial resources, and green supply chain management as predictors of financial and environmental performance. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19755–19767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubarik, M.S.; Bontis, N.; Mubarik, M.; Mahmood, T. Intellectual capital and supply chain resilience. J. Intellect. Cap. 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Hu, W.; Xu, Y. Exploring the role of intellectual capital in supply chain intelligence integration. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2018, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Prester, J.; Li, Y. The impact of intellectual capital on supply chain collaboration and business performance. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2018, 67, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.Y.; Cao, Y.; Mughal, Y.H.; Kundi, G.M.; Mughal, M.H.; Ramayah, T. Pathways towards sustainability in organizations: Empirical evidence on the role of green human resource management practices and green intellectual capital. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusliza, M.Y.; Yong, J.Y.; Tanveer, M.I.; Ramayah, T.; Faezah, J.N.; Muhammad, Z. A structural model of the impact of green intellectual capital on sustainable performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.Y.; Yusliza, M.Y.; Ramayah, T.; Fawehinmi, O. Nexus between green intellectual capital and green human resource management. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Wang, Z.; Mohsin, M.; Jiang, W.; Abbas, H. Multidimensional perspective of green financial innovation between green intellectual capital on sustainable business: The case of Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 5552–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Building competitive advantage for hospitality companies: The roles of green innovation strategic orientation and green intellectual capital. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2022, 102, 103161. [Google Scholar]
- Wankmüller, C.; Reiner, G. Coordination, cooperation and collaboration in relief supply chain management. J. Bus. Econ. 2020, 90, 239–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemai, J.; Do Chung, B.; Sarkar, B. Environmental effect for a complex green supply-chain management to control waste: A sustainable approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 122919. [Google Scholar]
- Micheli, G.J.; Cagno, E.; Mustillo, G.; Trianni, A. Green supply chain management drivers, practices and performance: A comprehensive study on the moderators. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 121024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmarco, G.; Ramalho, F.R.; Barros, A.C.; Soares, A.L. Providing industry 4.0 technologies: The case of a production technology cluster. J. High Technol. Manag. Res. 2019, 30, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Cai, Y.; DeFranco, A.; Lee, J. Exploring influential factors affecting guest satisfaction: Big data and business analytics in consumer-generated reviews. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2020, 11, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Agyeman, F.O.; Ud Din Khan, H.S. Research on the influence of industry-university-research cooperation innovation network characteristics on subject innovation performance. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 4771113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsakanda, A.L. Introduction to the Supplement: Advancing the practice of operations management and innovation to drive Africa forward in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). Afr. J. Manag. 2021, 7 (Suppl. 1), 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsadi, A.K.; Alaskar, T.H.; Mezghani, K. Adoption of big data analytics in supply chain management: Combining organizational factors with supply chain connectivity. Int. J. Inf. Syst. Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 14, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Mangalaraj, G. Big Data Analytics in Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review and Research Directions. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2022, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, S.; Gautam, P.; Jaggi, C.K. Role of big data analytics in supply chain management: Current trends and future perspectives. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 1875–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Wee, H.M.; Daryanto, Y. Big data analytics in supply chain management between 2010 and 2016: Insights to industries. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 115, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wong, C.Y.; Chavez, R.; Jacobs, M.A. Integrating big data analytics into supply chain finance: The roles of information processing and data-driven culture. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 236, 108135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.Y.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, H.K.; Mahmood, M.; Dawi, N.M. The Use of Big Data Analytics to Improve the Supply Chain Performance in Logistics Industry. In Software Engineering in IoT, Big Data, Cloud and Mobile Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kache, F.; Seuring, S. Challenges and opportunities of digital information at the intersection of Big Data Analytics and supply chain management. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2017, 37, 10–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kassar, A.N.; Singh, S.K. Green innovation and organizational performance: The influence of big data and the moderating role of management commitment and HR practices. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 144, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, A.; Gruenwald, L.; Leal, E.; Panjei, E. A GPU Algorithm for Detecting Contextual Outliers in Multiple Concurrent Data Streams. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–18 December 2021; pp. 2737–2742. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.S.; Lai, S.B.; Wen, C.T. The influence of green innovation performance on corporate advantage in Taiwan. J. Bus. Ethics 2006, 67, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzidia, S.; Makaoui, N.; Bentahar, O. The impact of big data analytics and artificial intelligence on green supply chain process integration and hospital environmental performance. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 165, 120557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Wood, L.C.; Xu, L.; Dhamija, P.; Kayikci, Y. Big data analytics as an operational excellence approach to enhance sustainable supply chain performance. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 153, 104559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Tan, K.H.; Ji, G.; Chung, L.; Chiu, A.S. Green and lean sustainable development path in China: Guanxi, practices and performance. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 128, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, A.B.; Nabass, I.H. Supply chain antecedents of agile manufacturing in a developing country context: An empirical investigation. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2018, 29, 1042–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khatib, A.W.; Al-ghanem, E.M. Radical innovation, incremental innovation, and competitive advantage, the moderating role of technological intensity: Evidence from the manufacturing sector in Jordan. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2021, 34, 344–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barghouth, D.; Al-Abdallah, G.M.; Abdallah, A.B. Pharmacy service factors and pharmacy performance: The role of patient satisfaction in community pharmacies. Int. J. Pharm. Healthc. Mark. 2021, 15, 410–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, C.J.C.; de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L. Green human resource management and green supply chain management: Linking two emerging agendas. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1824–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J. A boundaries and flows perspective of green supply chain management. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2012, 17, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.L.; How, B.S.; Hong, B.H. Green supply chain toward sustainable industry development. In Assessing and Measuring Environmental Impact and Sustainability; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 409–449. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.R.; Khan, M.I. The Petroleum Engineering Handbook: Sustainable Operations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bag, S.; Rahman, M.S. The role of capabilities in shaping sustainable supply chain flexibility and enhancing circular economy-target performance: An empirical study. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Biswas, I.; Avittathur, B. Green retailing: A new paradigm in supply chain management. In Green Business: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 1489–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Taş, M.A.; Akcan, S. Investigation of Green Criteria with Clustering Analysis in Green Supplier Selection. In Disruptive Technologies and Eco-Innovation for Sustainable Development; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 207–228. [Google Scholar]
- Jum’a, L.; Ikram, M.; Alkalha, Z.; Alaraj, M. Factors affecting managers’ intention to adopt green supply chain management practices: Evidence from manufacturing firms in Jordan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 5605–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Nguyen, D.; Le, Q.; Trinh, D. Green supply chain management practices and destination image: Evidence from Vietnam tourism industry. Uncertain Supply Chain Manag. 2020, 8, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Gunasekaran, A.; Papadopoulos, T.; Hazen, B. Green supply chain performance measures: A review and bibliometric analysis. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2017, 10, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B. Research on performance evaluation of green supply chain of automobile enterprises under the background of carbon peak and carbon neutralization. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Pham, H. Improving green performance of construction projects through supply chain integration: The role of environmental knowledge. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VenkatesaNarayanan, P.T.; Thirunavukkarasu, R. Indispensable link between green supply chain practices, performance and learning: An ISM approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Shen, N.; Liao, H.; Wang, Q. Multiple network embedding, green knowledge integration and green supply chain performance—Investigation based on agglomeration scenario. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daddi, T.; Heras-Saizarbitoria, I.; Marrucci, L.; Rizzi, F.; Testa, F. The effects of green supply chain management capability on the internalisation of environmental management systems and organisation performance. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2021, 28, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Luo, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Z. Joint Green Marketing Decision-Making of Green Supply Chain Considering Power Structure and Corporate Social Responsibility. Entropy 2021, 23, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Soomro, B.A. Internal green integration and environmental performance: The predictive power of proactive environmental strategy, greening the supplier, and environmental collaboration with the supplier. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganbold, O.; Matsui, Y.; Rotaru, K. Effect of information technology-enabled supply chain integration on firm’s operational performance. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaidy, P.J.; Lavastre, O.; Ageron, B.; Chaze-Magnan, L. Consumer integration in supply chain management: A taxonomy. Supply Chain Forum: Int. J. 2021, 22, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y. Critical success factors of green innovation: Technology, organization and environment readiness. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.Y.; Wong, C.W.; Boon-itt, S. Effects of green supply chain integration and green innovation on environmental and cost performance. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 4589–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Ming, X.; Liu, H.C. Identifying critical risk factors of sustainable supply chain management: A rough strength-relation analysis method. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S. The positive effect of green intellectual capital on competitive advantages of firms. J. Bus. Ethics 2008, 77, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, M.A.M.; Ahmad, R.; Abad, A. Antecedents and consequences of green supply chain management practices: A study of Indian food processing industry. Benchmarking Int. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirakraisiri, J.; Badir, Y.F.; Frank, B. Translating green strategic intent into green process innovation performance: The role of green intellectual capital. J. Intellect. Cap. 2021, 22, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.; Kroon, B. Family capital in family businesses: Complementarities of human and social capital. In Handbook of Research on the Strategic Management of Family Businesses; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Shoaib, M.; Zámečník, R.; Abbas, Z.; Javed, M.; Rehman, A.U. Green human resource management and green human capital: A systematic literature review. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference: Contemporary Issues in Business, Management and Economics Engineering, Vilnius, Lithuania, 13–14 May 2021; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mosey, S.; Wright, M. From human capital to social capital: A longitudinal study of technology–based academic entrepreneurs. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2007, 31, 909–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curado, C. Perceptions of knowledge management and intellectual capital in the banking industry. J. Knowl. Manag. 2008, 12, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryscynski, D.; Coff, R.; Campbell, B. Charting a path between firm-specific incentives and human capital-based competitive advantage. Strateg. Manag. J. 2021, 42, 386–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Gupta, S. Examining the effect of green human capital availability in adoption of reverse logistics and remanufacturing operations performance. Int. J. Manpow. 2019, 41, 1097–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, C.J.C.; Sarkis, J.; de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L.; Renwick, D.W.S.; Singh, S.K.; Grebinevych, O.; Kruglianskas, I.; Godinho Filho, M. Who is in charge? A review and a research agenda on the ‘human side’ of the circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyabeng-Mensah, Y.; Tang, L. The relationship among green human capital, green logistics practices, green competitiveness, social performance and financial performance. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2021, 32, 1377–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.Y.; Yusliza, M.Y.; Ramayah, T.; Chiappetta Jabbour, C.J.; Sehnem, S.; Mani, V. Pathways towards sustainability in manufacturing organizations: Empirical evidence on the role of green human resource management. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020, 29, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, Y.M.; Omar, M.K.; Zaman, M.D.K.; Samad, S. Do all elements of green intellectual capital contribute toward business sustainability? Evidence from the Malaysian context using the Partial Least Squares method. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.M. Green intellectual capital and social innovation: The nexus. J. Intellect. Cap. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M. Environmental regulation and economic growth: A new perspective based on technical level and healthy human capital. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquah, I.S.K.; Agyabeng-Mensah, Y.; Afum, E. Examining the link among green human resource management practices, green supply chain management practices and performance. Benchmarking Int. J. 2020, 28, 267–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyabeng-Mensah, Y.; Ahenkorah, E.N.K.; Korsah, G.N.A. The Mediating Roles of Supply Chain Quality Integration and Green Logistics Management Between Information Technology and Organisational Performance. J. Supply Chain Manag. Syst. 2019, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Barão, A.; da Silva, A.R. How to value and monitor the relational capital of knowledge-intensive organizations. In Handbook of Research on Enterprise 2.0: Technological, Social, and Organizational Dimensions; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 220–243. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, P.Y.; Lin, Y.L.; Hsiung, H.H.; Liu, T.Y. Intellectual capital: An empirical study of ITRI. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2006, 73, 886–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbery, D.C.; Torres, C.L. The Importance of Leadership, Corporate Climate, Use of Resources, and Strategic Planning in Family Business. In Handbook of Research on Entrepreneurial Leadership and Competitive Strategy in Family Business; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 212–230. [Google Scholar]
- Asiaei, K.; Jusoh, R.; Bontis, N. Intellectual capital and performance measurement systems in Iran. J. Intellect. Cap. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, A.W.; Valeri, M. Can intellectual capital promote the competitive advantage? Service innovation and big data analytics capabilities in a moderated mediation model. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2022; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benevene, P.; Buonomo, I.; Kong, E.; Pansini, M.; Farnese, M.L. Management of Green Intellectual Capital: Evidence-Based Literature Review and Future Directions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S. The driver of green innovation and green image–green core competence. J. Bus. Ethics 2008, 81, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amores-Salvadó, J.; Cruz-González, J.; Delgado-Verde, M.; González-Masip, J. Green technological distance and environmental strategies: The moderating role of green structural capital. J. Intellect. Cap. 2021, 22, 938–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, T.; Ceylan, C. Factors impacting the innovative capacity in large-scale companies. Technovation 2007, 27, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secundo, G.; Ndou, V.; Del Vecchio, P.; De Pascale, G. Sustainable development, intellectual capital and technology policies: A structured literature review and future research agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 153, 119917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londoño MA, V.; Espinosa EO, C. Valuing intellectual capital at the postgraduate level in higher education institutions. In Enhancing Academic Research and Higher Education with Knowledge Management Principles; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Khanlarov, E.; Lyeonov, S.; Starchenko, L. Green intellectual capital and company performance. In Economic and Social Development: Book of Proceedings, Proceedings of the 55th International Scientific Conference on Economic and Social Development Development, Baku, Azerbaijan, 18–19 June 2020; pp. 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Arie, A.A.P.G.B.; Kumalasari, P.D.; Manuari, I.A.R. The role of green intellectual capital on competitive advantage: Evidence from Balinese financial institution. Sriwij. Int. J. Dyn. Econ. Bus. 2019, 3, 227–242. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Huo, B. The impact of relational capital on green supply chain management and financial performance. Prod. Plan. Control 2021, 32, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.V.; Wang, Y.H. The Value Creation Process in Networked Organizations. In Encyclopedia of Networked and Virtual Organizations; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2008; pp. 1743–1749. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Shang, Y.; Yu, W.; Liu, F. Intellectual capital, technological innovation and firm performance: Evidence from China’s manufacturing sector. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, H.; Cepeda-Carrion, I.; Ortega-Gutierrez, J.; Edvardsson, B. The role of intellectual capital in fostering SD-Orientation and firm performance. J. Intellect. Cap. 2020, 22, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiku, S.O. Institutionalizing Social Responsibility through Workplace Green Behavior. In Contemporary Multicultural Orientations and Practices for Global Leadership; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 183–199. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.S.; Chang, C.H. Utilize structural equation modeling (SEM) to explore the influence of corporate environmental ethics: The mediation effect of green human capital. Qual. Quant. 2013, 47, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Kraus, S.; Shah, S.A.; Khanin, D.; Mahto, R.V. Analyzing the relationship between green innovation and environmental performance in large manufacturing firms. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 163, 120481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Huo, B.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Quality and green management for operational and environmental performance: Relational capital in supply chain management. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2020, 25, 471–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X. The impact of relationship quality and supplier development on green supply chain integration: A mediation and moderation analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huo, B. The impact of environmental orientation on supplier green management and financial performance: The moderating role of relational capital. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claro, D.P.; de Oliveira Claro, P.B.; Hagelaar, G. Coordinating collaborative joint efforts with suppliers: The effects of trust, transaction specific investment and information network in the Dutch flower industry. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2006, 11, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalmi, F.; Adala, L. Big Data for Healthcare: Opportunities and Challenges. In The Fourth Industrial Revolution: Implementation of Artificial Intelligence for Growing Business Success; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 217–229. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, R.; Alraja, M.N.; Khashab, B. Sustainable performance and green innovation: Green human resources management and big data as antecedents. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Honggang, X.; Ahmad, N.; Khan, S.A.R.; Iqbal, M. Big data analytics as a roadmap towards green innovation, competitive advantage and environmental performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 323, 128998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaoteng, Z.; Xin, L. Research on green innovation countermeasures of supporting the circular economy to green finance under big data. J. Enterprise Inf. Manag. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, G.; Fiano, F.; Bertoldi, B.; Ciampi, F. Big data for business management in the retail industry. Manag. Decis. 2019, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Gawankar, S.A. Achieving sustainable performance in a data-driven agriculture supply chain: A review for research and applications. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 219, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.; Shuqqo, H.; Qtaishat, L.; Asmar, H.; Salah, B. Sustainable competitive advantage driven by big data analytics and innovation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamba, S.F.; Gunasekaran, A.; Dubey, R.; Ngai, E.W. Big data analytics in operations and supply chain management. Ann. Oper. Res. 2018, 270, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Delgado, C.; Hazen, B.T.; Patel, P. Mitigating supply chain risk via sustainability using big data analytics: Evidence from the manufacturing supply chain. Sustainability 2017, 9, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Li, Z.H.O.U.; Spiegler, V.; Ieromonachou, P.; Lin, Y. Big data analytics in supply chain management: A state-of-the-art literature review. Comput. Oper. Res. 2018, 98, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedan, M.; Mafakheri, F. Predictive big data analytics for supply chain demand forecasting: Methods, applications, and research opportunities. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Childe, S.J. Big data analytics capability in supply chain agility: The moderating effect of organizational flexibility. Manag. Decis. 2018, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S. An examination of the importance of big data analytics in supply chain agility development: A dynamic capability perspective. Manag. Res. Rev. 2018, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, L. Big data in product lifecycle management. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 81, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeb, A.; Keogh, J.G.; Rejeb, K. Big data in the food supply chain: A literature review. J. Data Inf. Manag. 2022, 4, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbuke, N.J.; Yusuf, Y.Y.; Dharma, K.; Mercangoz, B.A. Big data supply chain analytics: Ethical, privacy and security challenges posed to business, industries and society. Prod. Plan. Control 2022, 33, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, R.; Khan, M.S. Social media big data analytics for demand forecasting: Development and case implementation of an innovative framework. In Research Anthology on Big Data Analytics, Architectures, and Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 902–920. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, N.R. Big Data Driven Supply Chain Management: A Framework for Implementing Analytics and Turning Information into Intelligence; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, M.; van der Voort, H.; Wahyudi, A. Factors influencing big data decision-making quality. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 70, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gunasekaran, A.; Ngai, E.W.; Papadopoulos, T. Big data analytics in logistics and supply chain management: Certain investigations for research and applications. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 176, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Shishodia, A.; Gunasekaran, A.; Min, H.; Munim, Z.H. The role of artificial intelligence in supply chain management: Mapping the territory. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Childe, S.J.; Bryde, D.J.; Giannakis, M.; Foropon, C.; Roubaud, D.; Hazen, B.T. Big data analytics and artificial intelligence pathway to operational performance under the effects of entrepreneurial orientation and environmental dynamism: A study of manufacturing organisations. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 226, 107599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadi, A.; Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Zkik, K.; Touriki, F.E. A Big Data Analytics-driven Lean Six Sigma framework for enhanced green performance: A case study of chemical company. Prod. Plan. Control 2021, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kumari, S.; Malekpoor, H.; Mishra, N. Big data cloud computing framework for low carbon supplier selection in the beef supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, S.; Liu, Y.; Sakao, T.; Huisingh, D. A framework for Big Data driven product lifecycle management. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchiato, R. Environmental uncertainty, foresight and strategic decision making: An integrated study. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2012, 79, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, T.; Gunasekaran, A.; Dubey, R.; Altay, N.; Childe, S.J.; Fosso-Wamba, S. The role of Big Data in explaining disaster resilience in supply chains for sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Singh, R.K.; Gunasekaran, A. Supply chain risks in Industry 4.0 environment: Review and analysis framework. Prod. Plan. Control 2021, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadi, A.; Kamble, S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Mani, V. Analyzing the mediating role of organizational ambidexterity and digital business transformation on industry 4.0 capabilities and sustainable supply chain performance. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J. Essentials of business research: A guide to doing your research project. Essent. Bus. Res. 2014, 5018032. [Google Scholar]
- Sekaran, U.; Bougie, R. Research Methods for Business: A Skill Building Approach; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.L.; Kung, F.H. Environmental consciousness and intellectual capital management: Evidence from Taiwan’s manufacturing industry. Manag. Decis. 2011, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim, S.; Zeng, J.; Khan, Z.; Zia, N.U. Big data analytics capability and decision making performance in emerging market firms: The role of contractual and relational governance mechanisms. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 161, 120315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N. Developing business risk resilience through risk management infrastructure: The moderating role of big data analytics. Inf. Syst. Manag. 2020, 39, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; Singh, S. Building supply chain risk resilience: Role of big data analytics in supply chain disruption mitigation. Benchmarking Int. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, F.; Gigliotti, M.; Annunziata, E. Exploring the nexus between GSCM and organisational culture: Insights on the role of supply chain integration. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkind & Rainwater, N.J.; Rainwater, T. Exploring Research; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Podsakoff, N.P. Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2012, 63, 539–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, J.M.; Lance, C.E. What reviewers should expect from authors regarding common method bias in organizational research. J. Bus. Psychol. 2010, 25, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubona, G.; Belkhamza, Z. Testing a moderated mediation in PLS-SEM: A full latent growth approach. Data Anal. Perspect. J. 2021, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. J. Market. Res. 1981, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.W. The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. Mod. Methods Bus. Res. 1998, 295, 295–336. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Sarstedt, M.; Hopkins, L.; Kuppelwieser, V.G. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM): An emerging tool in business research. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2014, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streukens, S.; Leroi-Werelds, S. Bootstrapping and PLS-SEM: A step-by-step guide to get more out of your bootstrap results. Eur. Manag. J. 2016, 34, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Brint, A.; Shi, E.; Upadhyay, A.; Ruan, X. Integrating sustainable supply chain practices with operational performance: An exploratory study of Chinese SMEs. Prod. Plan. Control 2019, 30, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, C.; Kim, M.G.; Chung, Y.; Rho, J.J. Suppliers’ communication capability and external green integration for green and financial performance in Korean construction industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibenrissoul, A.; Kammoun, S.; Tazi, A. The Integration of CSR Practices in the Investment Decision: Evidence from Moroccan Companies in the Mining Industry. In Adapting and Mitigating Environmental, Social, and Governance Risk in Business; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 256–270. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, H. The role of big data analytics in enabling green supply chain management: A literature review. J. Data Inf. Manag. 2020, 2, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kung, L.; Byrd, T.A. Big data analytics: Understanding its capabilities and potential benefits for healthcare organizations. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 126, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Construct | Item Code | Item | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green Human Capital | GHC1 | The firm’s employees have sufficient functional and scientific skills related to environmental protection. | [90,91,112,161] |
| GHC2 | The firm is constantly training employees to provide them with new environmental skills and knowledge. | ||
| GHC3 | The firm’s employees have good environmental service performance. | ||
| GHC4 | The firm’s employees work as a team when carrying out environmental work and activities within the firm. | ||
| GHC5 | The firm’s employees are considered environmentally better compared to competitors from other firms. | ||
| Green Structural Capital | GSC1 | The firm has an advanced management system to protect the environment. | [90,91,112,161] |
| GSC2 | The firm is constantly spending on environmentally friendly facilities. | ||
| GSC3 | The firm has efficient processes that achieve resource savings, leading to environmental protection. | ||
| GSC4 | The firm applies knowledge management systems to share environmental knowledge among employees. | ||
| GSC5 | The firm documents the environmental knowledge and experience of employees through databases. | ||
| GSC6 | The firm documents intellectual property rights related to the environment (such as patents and software) as a way to store knowledge. | ||
| Green Relational Capital | GRC1 | The firm takes into consideration the environmental aspects of its customers when designing or manufacturing its products. | [90,91,112,161] |
| GRC2 | Customers feel satisfied when the firm offers products of an environmentally friendly nature. | ||
| GRC3 | The firm has long-term, environmentally focused, collaborative relationships with suppliers. | ||
| GRC4 | The firm has long-term, environmentally focused, collaborative relationships with customers. | ||
| GRC5 | The firm actively cooperates with external parties to develop new environmental innovations or improve environmentally friendly ways of working. | ||
| Big Data Analytics Capabilities | BDAC1 | The firm continuously invests in big data analysis software. | [33,58,162,163,164] |
| BDAC2 | The firm invests in technical infrastructure that includes information integration using advanced technology. | ||
| BDAC3 | The firm invests in processes that ensure the availability of high-quality and timely data. | ||
| BDAC4 | The firm’s management attracts human resources with knowledge and experience in big data analytics. | ||
| BDAC5 | The firm encourages employees to make use of their skills in big data analysis to solve various problems in creative ways. | ||
| BDAC6 | The firm has administrative and organizational resources to take relevant actions on insights derived from big data analytics. | ||
| Green Supply Chain Performance | GSCP1 | The firm’s manufacturing system is energy-saving. | [80,90,165] |
| GSCP2 | The firm’s management encourages suppliers to improve environmentally oriented transportation processes continuously. | ||
| GSCP3 | The firm’s management provides continuous support and training to suppliers concerning environmental aspects and considerations. | ||
| GSCP4 | The firm’s management is interested in enhancing the communication level with its main customers and providing them with the firm’s latest environmental developments. | ||
| GSCP5 | The stock level has decreased over the past period. | ||
| GSCP6 | The cost of purchasing materials has decreased over the past period. |
| Characteristics | Category | No. | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Males | 253 | 57.8% |
| Females | 185 | 42.2% | |
| Academic Qualification | Diploma or Less | 109 | 24.9% |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 282 | 64.4% | |
| Postgraduate Degree | 47 | 10.7% | |
| Job in Company | Manager/Head of Department | 39 | 8.90% |
| Administrative Employee | 137 | 31.3% | |
| Nonadministrative Employee | 262 | 59.8% | |
| Total | 438 | 100 | |
| Construct | Item | Factor Loading | AVE | Composite Reliability | Cronbach’s Alpha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Human Capital | GHC1 | 0.883 | 0.804 | 0.925 | 0.878 |
| GHC2 * | - | ||||
| GHC3 | 0.910 | ||||
| GHC4 | 0.897 | ||||
| GHC5 * | - | ||||
| Green Structural Capital | GSC1 * | - | 0.802 | 0.924 | 0.877 |
| GSC2 * | - | ||||
| GSC3 | 0.892 | ||||
| GSC4 * | - | ||||
| GSC5 | 0.885 | ||||
| GSC6 | 0.910 | ||||
| Green Relational Capital | GRC1 | 0.808 | 0.664 | 0.888 | 0.832 |
| GRC2 | 0.811 | ||||
| GRC3 | 0.849 | ||||
| GRC4 | 0.790 | ||||
| GRC5 * | - | ||||
| Big Data Analytics Capabilities | BDAC1 | 0.820 | 0.670 | 0.910 | 0.876 |
| BDAC2 | 0.782 | ||||
| BDAC3 | 0.855 | ||||
| BDAC4 | 0.781 | ||||
| BDAC5 | 0.850 | ||||
| BDAC6 * | - | ||||
| Green Supply Chain Performance | GSCP1 | 0.686 | 0.712 | 0.936 | 0.917 |
| GSCP2 | 0.859 | ||||
| GSCP3 | 0.862 | ||||
| GSCP4 | 0.890 | ||||
| GSCP5 | 0.885 | ||||
| GSCP6 | 0.864 |
| No | Construct | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Big Data Analytics Capabilities | 0.818 | ||||
| 2 | Green Human Capital | 0.684 | 0.897 | |||
| 3 | Green Structural Capital | 0.737 | 0.697 | 0.896 | ||
| 4 | Green Relational Capital | 0.733 | 0.758 | 0.699 | 0.815 | |
| 5 | Green Supply Chain Performance | 0.737 | 0.744 | 0.732 | 0.775 | 0.844 |
| Path | Path Coefficient (β) | Std Error | T Statistic | p Value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GHC ⇒ GSCP | 0.207 | 0.057 | 3.620 | 0.000 | Supported |
| GSC ⇒ GSCP | 0.193 | 0.049 | 3.931 | 0.000 | Supported |
| GRC ⇒ GSCP | 0.339 | 0.053 | 6.385 | 0.000 | Supported |
| BDAC ⇒ GSCP | 0.230 | 0.056 | 4.102 | 0.000 | Supported |
| GHC × BDAC ⇒ GSCP | −0.05 | 0.052 | 0.962 | 0.336 | Not Supported |
| GSC × BDAC ⇒ GSCP | 0.014 | 0.050 | 0.273 | 0.785 | Not Supported |
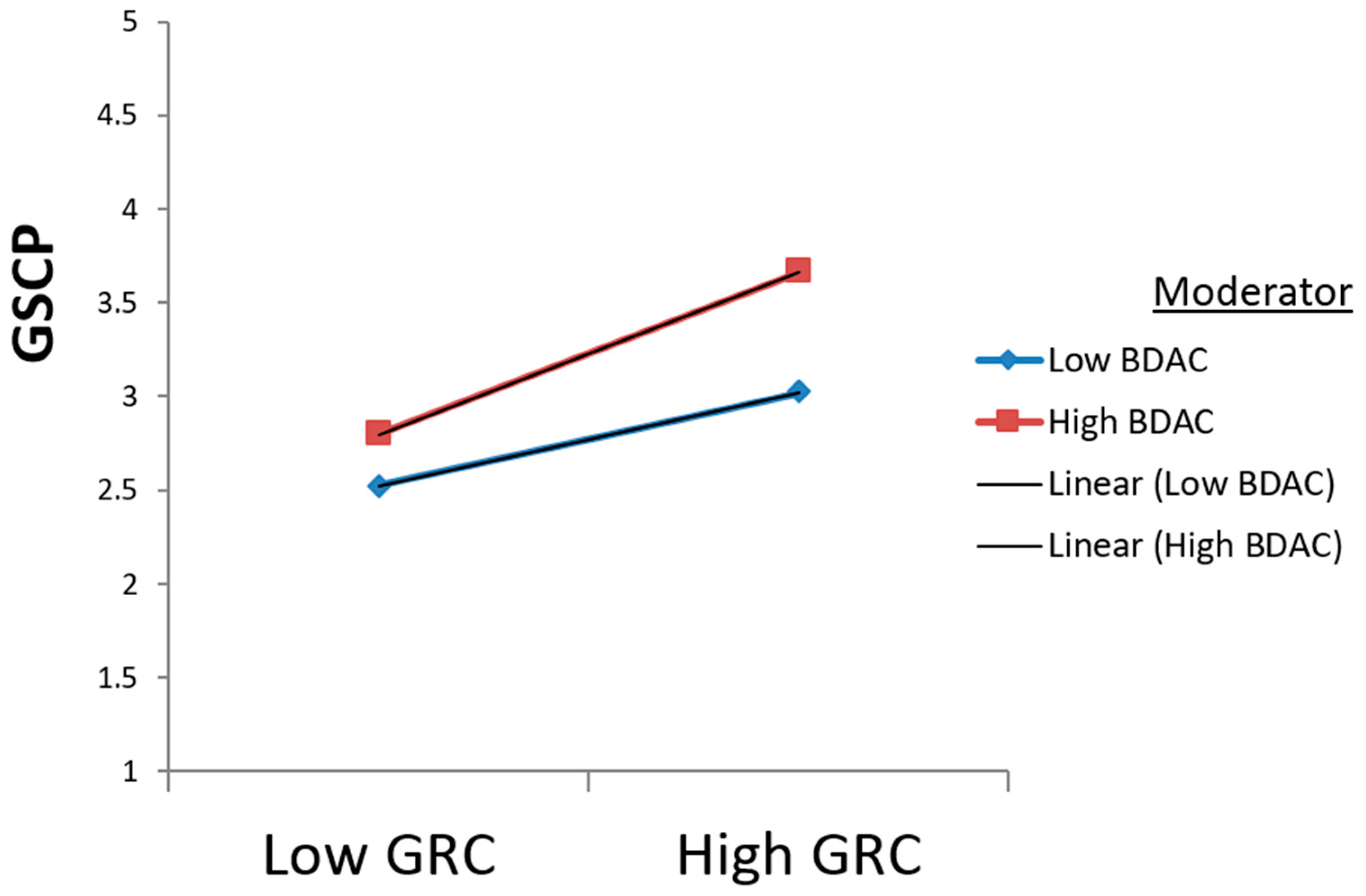
| GRC × BDAC ⇒ GSCP | 0.092 | 0.042 | 2.207 | 0.027 | Supported |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AL-Khatib, A.w.; Shuhaiber, A. Green Intellectual Capital and Green Supply Chain Performance: Does Big Data Analytics Capabilities Matter? Sustainability 2022, 14, 10054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610054
AL-Khatib Aw, Shuhaiber A. Green Intellectual Capital and Green Supply Chain Performance: Does Big Data Analytics Capabilities Matter? Sustainability. 2022; 14(16):10054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610054
Chicago/Turabian StyleAL-Khatib, Ayman wael, and Ahmed Shuhaiber. 2022. "Green Intellectual Capital and Green Supply Chain Performance: Does Big Data Analytics Capabilities Matter?" Sustainability 14, no. 16: 10054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610054
APA StyleAL-Khatib, A. w., & Shuhaiber, A. (2022). Green Intellectual Capital and Green Supply Chain Performance: Does Big Data Analytics Capabilities Matter? Sustainability, 14(16), 10054. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141610054






