Potassium Source and Biofertilizer Influence K Release and Fruit Yield of Mango (Mangifera indica L.): A Three-Year Field Study in Sandy Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experiment
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Parameters
2.3. Kinetic Release of Soil Potassium (K)
2.4. Plant Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
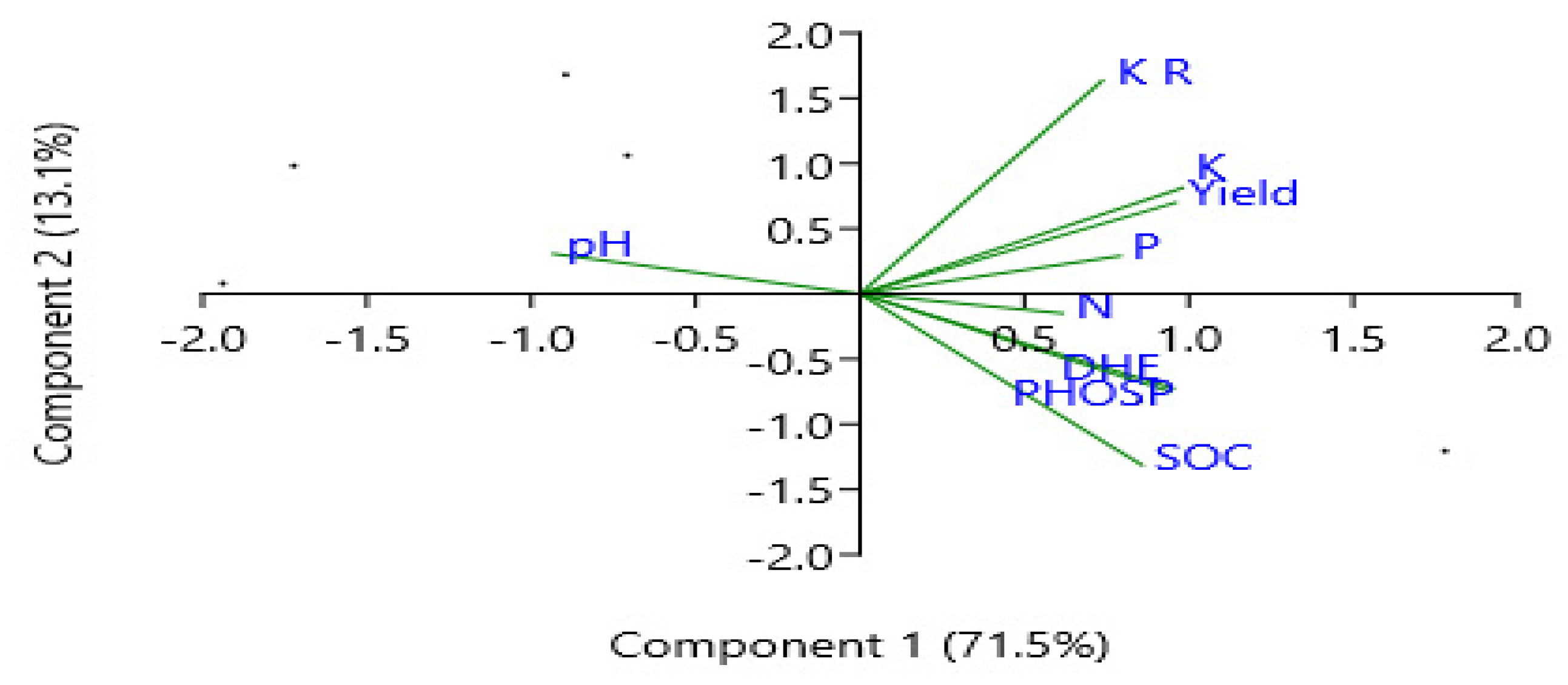
3. Results
3.1. Effect of KSB and K Source on K-Kinetics Release
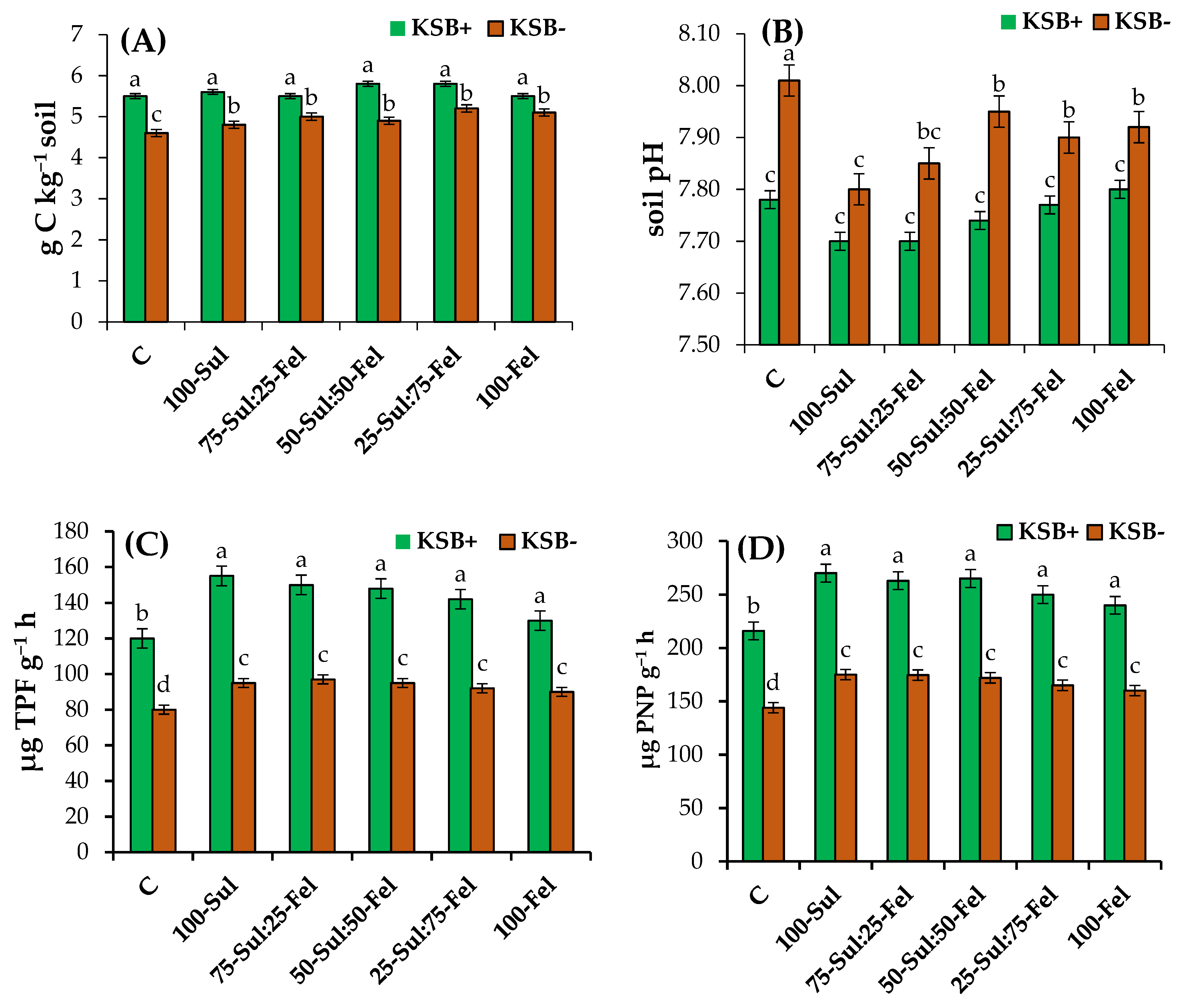
3.2. Effect of KSB and K Source on Soil Quality
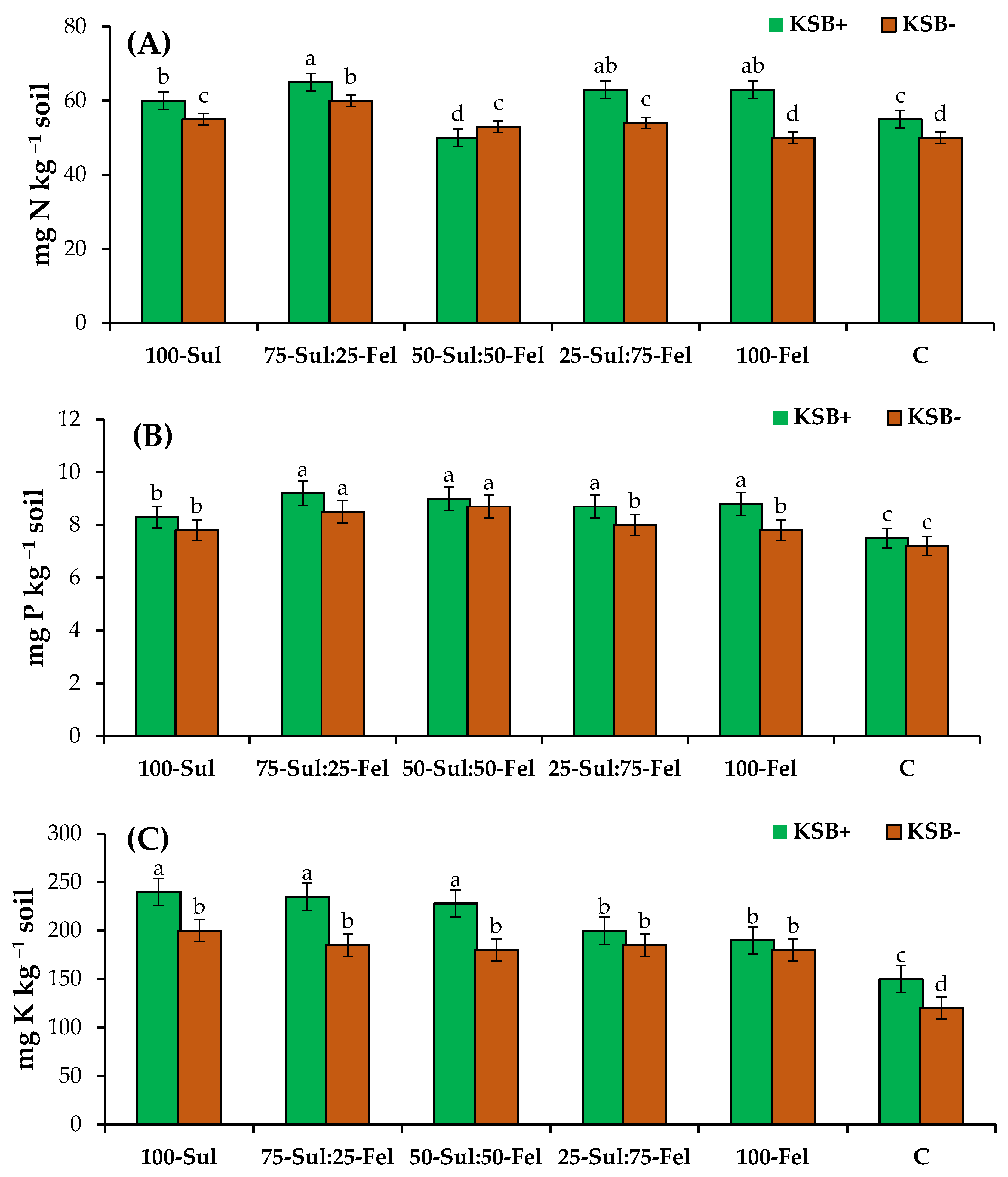
3.3. Effect of KSB and K Source on Nutrient Concentrations and Growth of Mango Plants
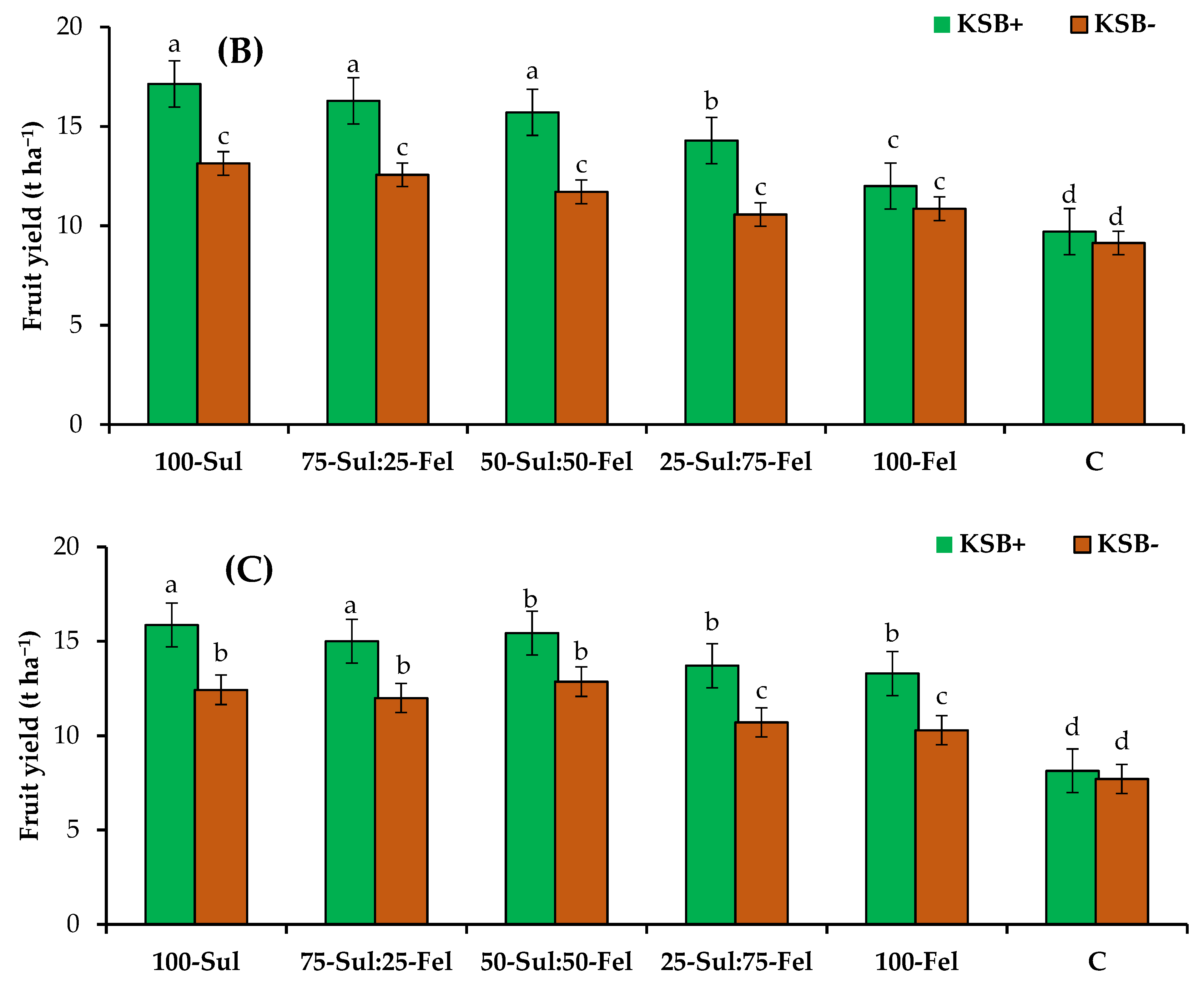
3.4. The Effect of KSB and K Source on Mango Plant Fruit Yield and Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Kinetics of K Release
4.2. Soil Quality
4.3. Fruit Yield and Quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.; Lounds-Singleton, A.J.; Talcott, S.T. Antioxidant phytochemical and quality changes associated with hot water immersion treatment of mangoes (Mangifera indica L.). Food Chem. 2009, 115, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. FAO Statistical Databases Agriculture. 2020. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Elsheshetawy, H.E.; Mossad, A.; Elhelew, W.K.; Farina, V. Comparative study on the quality characteristics of some Egyptian mango cultivars used for food processing. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2016, 61, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palafox-Carlos, H.; Yahia, E.; Islas-Osuna, M.A.; Gutierrez-Martinez, P.; Robles-Sánchez, M.; González-Aguilar, G.A. Effect of ripeness stage of mango fruit (Mangifera indica L., cv. Ataulfo) on physiological parameters and antioxidant activity. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 135, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolland, M.D.A.; Baker, M.J. Powdered granite is not an effective fertilizer for clover and wheat in sandy soils from Western Australia. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 2000, 56, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciceri, D.; Close, T.C.; Barker, A.V.; Allanore, A. Fertilizing properties of potassium feldspar altered hydrothermally. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 50, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, H. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Stino, R.G.; Abd El-Wahab, S.M.; Habashy, S.A.; Kelani, R.A. Productivity and fruit quality of three mango cultivars in relation to foliar sprays of calcium, zinc, boron or potassium. J. Hortic. Sci. Ornam. Plants 2011, 3, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, E.V.; Fernandes, D.; Caione, G.; Prado, R.M.; Boliani, A.C.; Corrêa, L.S. Liming in growing mango cultivar Keitt in production. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.J.; Ransom, M.D.; Thompson, M.L.; Hinsinger, P.; Florence, A.M.; Moody, P.W.; Guppy, C.N. Considering Soil Potassium Pools with Dissimilar Plant Availability. In Improving Potassium Recommendations for Agricultural Crops; Murrell, T.S., Mikkelsen, R.L., Sulewski, G., Norton, R., Thompson, M.L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.J.; Bell, M.J.; Djalovic, I.; Hinsinger, P.; Rengel, Z. Potassium Use Efficiency of Plants. In Improving Potassium Recommendations for Agricultural Crops; Murrell, T.S., Mikkelsen, R.L., Sulewski, G., Norton, R., Thompson, M.L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, D.A. Mineral Sources of Potassium for Plant Nutrition. In Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, R.A.; Hassan, H.A.; Shaaban, E.A. Effect of different potassium fertilizer forms on yield, fruit quality and leaf mineral content of Zebda mango trees. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2014, 21, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, B.B. Waste mica as alternative source of plant-available potassium: Evaluation of agronomic potential through chemical and biological methods. Nat. Resour. Res. 2019, 28, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, B.B.; Maity, A.; Ray, P.; Biswas, D.R.; Roy, S. Potassium supply in agriculture through biological potassium fertilizer: A promising and sustainable option for developing countries. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 68, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, V.S.; Maurya, B.R.; Verma, J.P.; Meena, R.S. Potassium Solubilizing Microorganisms for Sustainable Sgriculture; Springer: Uttar Pradesh, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, M.A.; Eissa, M.A. Comparison between organic and inorganic nutrition for tomato. J. Plant Nutr. 2017, 40, 1900–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toumi, M.; Nedjimi, B.; Halitim, A.; Garcia, M. Effects of K-Mg ratio on growth and cation nutrition of Vitis vinifera L. cv.“Dattier de Beiruth” grafted on SO4 rootstock. J. Plant Nutr. 2016, 39, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.A.; Ghoneim, M.F.; El-Gharably, G.A.; El-Razek, M.A. Phytoextraction of nickel, lead and cadmium from metals contaminated soils using different field crops and EDTA. World Appl. Sci. J. 2014, 32, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Narula, N.; Saharan, B.S.; Kumar, V.; Bhatia, R.; Bishnoi, L.K.; Lather, B.P.; Lakshminarayana, K. Impact of the use of biofertilizers on cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) crop under irrigated agro-ecosystem. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2005, 51, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.M.; Zhao, G.Y.; Gao, T.G.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.F.; Zhu, B.C. Solubilization of insoluble potassium and phosphate by Paenibacillus kribensis CX-7, A soil microorganism with biological control potential. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q. Isolation and identification of three potassium-solubilizing bacteria from rape rhizospheric soil and their effects on ryegrass. Geomicrobiol. J. 2017, 34, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Biswas, S.K.; Nagar, D.; Lal, K.; Singh, J. Impact of bio-fertilizer on growth parameters and yield of potato. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Guidelines for Soil Description, 4th ed.; Viale delle Terme di Caracalla: Rome, Italy, 2006.
- Burt, R. Soil Survey Laboratory Methods Manual; Soil survey investigations report no. 42, version 4.0; Natural Resources Conservation Service, US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Tabatabai, M.A. Soil enzymes. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, 2nd ed.; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; Agronomy 9; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1983; pp. 903–947. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Zhang, W.; Gulaqa, A.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Weng, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Jin, F. Effects of peanut shell biochar on soil nutrients, soil enzyme activity, and rice yield in heavily saline-sodic paddy field. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Wittling, C.; Houot, S.; Barriuso, E. Soil enzymatic response to addition of municipal solid-waste compost. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1995, 20, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houba, V.J.; Novozamsky, I.; Lexmond, T.M.; Van der Lee, J.J. Applicability of 0.01 M CaCl2 as a single extraction solution for the assessment of the nutrient status of soils and other diagnostic purposes. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1990, 21, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpur, A.R.; Motaghian, H.R. Application of kinetic models in describing soil potassium release characteristics and their correlations with potassium extracted by chemical methods. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 482.e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, A. Kinetics of soil potassium release under long-term imbalanced fertilization in calcareous soils. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlin, J.L.; Westfall, D.G. Potassium release kinetics and plant response in calcareous soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rahman, M. Relation of spraying silicon with fruiting of Keitt Mango trees growing under upper Egypt conditions. Stem Cell 2015, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, L.N.; Donato, S.L.; Santos, M.R.D.; Castro, L.G. Nutrient contents in ‘Tommy Atkins’mango leaves at flowering and fruiting stages. Eng. Agríc. 2016, 36, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Helaly, M.N.; El-Hoseiny, H.; El-Sheery, N.I.; Rastogi, A.; Kalaji, H.M. Regulation and physiological role of silicon in alleviating drought stress of mango. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 118, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, J.A.; Allen, S.E. A wet oxidation procedure suitable for the determination of nitrogen and mineral nutrients in biological material. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1975, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis, 21st ed.; Hurwitz, W., Ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Plata, L.G.; Ramos, C.G.; Oliveira, M.L.; Oliveira, L.F. Release kinetics of multi-nutrients from volcanic rock mining by-products: Evidences for their use as a soil remineralizer. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, S.; Platonova, N.P.; Karavaiko, G.I.; Stichel, E.; Glombitza, F. Chemical and microbiological solubilization of silicates. Acta Biotechnol. 1991, 11, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Gu, J.; Zhen, L.; Lv, R.; Chang, F.; Feng, A.J. Influences of potassium solubilizing bacteria and K-feldspar on enzyme activities and metabolic activities of the bacterial communities in kiwifruit planting soil. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 67, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sayed, H.M.; Hegab, S.A.; Youssef, M.A.; Khalafalla, M.Y.; Almaroai, Y.A.; Ding, Z.; Eissa, M.A. Evaluation of quality and growth of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) as affected by bio-fertilizers. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, J.; Kong, Q. Potassium-solubilizing activity of Bacillus aryabhattai SK1-7 and its growth-promoting effect on Populus alba L. Forests 2020, 11, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buragohain, S.; Nath, D.J.; Devi, Y.B.; Bhattacharyya, B.; Dutta, S. Molecular characterization of potassium solubilizing bacteria from crop rhizosphere of the North Eastern Region of India. Curr. Sci. 2018, 114, 2543–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.; Muhammad, Z.; Ahmad, H. Plant growth promoting bacteria: Role in soil improvement, abiotic and biotic stress management of crops. Plant Cell Rep. 2018, 37, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etesami, H. Can interaction between silicon and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria benefit in alleviating abiotic and biotic stresses in crop plants? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 253, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.P.; Ma, J.; Li, Y. Distribution of soil nutrient concentration in the rhizosphere system of desert halophytes under two soil conditions. J. Des. Res. 2008, 28, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Eissa, M.A.; Ahmed, E.M.; Reichman, S.M. Production of the forage halophyte Atriplex amnicola in metal-contaminated soils. Soil Use Manag. 2016, 32, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Y.; Song, C.C.; Shi, F.X.; Wang, M.Q.; Ren, J.S.; Wang, X.W.; Jiang, L. Linking plant community composition with the soil C pool, N availability and enzyme activity in boreal peatlands of Northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 140, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Das, S.; Molina, S.A.; Madgwick, D.; Katz, M.; Jena, S.; Bossmann, L.K.; Pal, D.; Takemoto, D.J. Investigation of the reciprocal relationship between the expression of two gap junction connexin proteins, connexin46 and connexin43. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 24519–24533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaduzzaman, M.; Asao, T. Improvement of Quality in Fruits and Vegetables through Hydroponic Nutrient Management; BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troufflard, S.; Mullen, W.; Larson, T.R.; Graham, I.A.; Crozier, A.; Amtmann, A.; Armengaud, P. Potassium deficiency induced the biosynthesis of oxylipins and glucosinolates in Arabiodopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Hakeem, S.S.; Fekry, W.A. Effect of K-feldspar, potassium sulphate and silicate dissolving bacteria on growth, yield and quality of sweet potato plants. Zagazig J. Agric. Res. 2014, 41, 467–477. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, G.H.; Seddik, W.M.; Osman, M.A. Efficiency of natural minerals in presence of different nitrogen forms and potassium dissolving bacteria on peanut and sesame yields. J. Am. Sci. 2010, 6, 647–660. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, V.S.; Maurya, B.R.; Bahadur, I. Potassium solubilization by bacterial strain in waste mica. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2014, 43, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, O.P.; Kumar, P.; Yadav, B.; Dua, M.; Johri, A.K. Sulfur nutrition and its role in plant growth and development. Plant Signal. Behav. 2022, 2030082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.A. Effect of sugarcane vinasse and EDTA on cadmium phytoextraction by two saltbush plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10247–10254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merwad, A. Efficiency of K-sulphate and K-feldspar combined with silicate dissolving bacteria on yield and nutrient uptake by maize plants. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 56, 249–259. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.M.E.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Selim, D.A.F.H.; Elbagory, M.; Othman, M.M.; Omara, A.E.-D.; Mohamed, M.H. Plant growth, yield and quality of potato crop in relation to potassium fertilization. Agronomy 2021, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

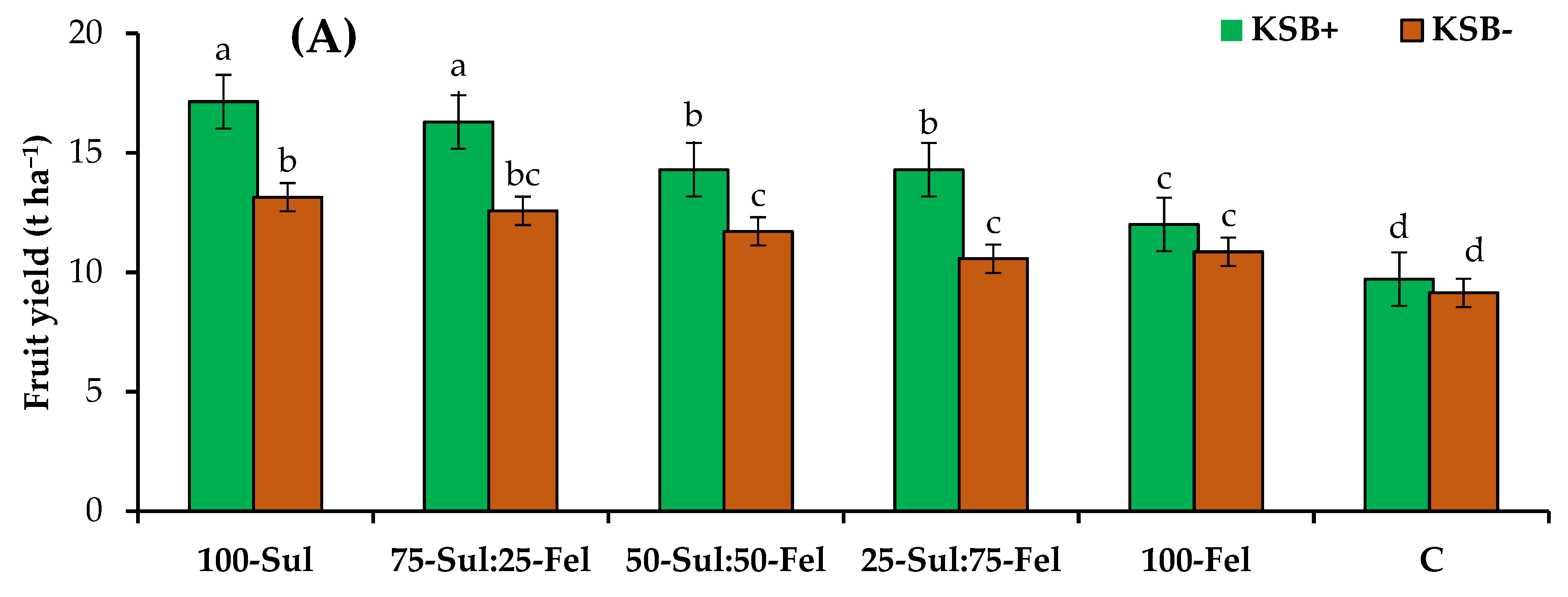
| Properties (Units) | Value |
|---|---|
| Sand (0.05 to 2.0 mm, g kg−1) | 900 ± 22 |
| Silt (0.002 to 0.05 mm, g kg−1) | 80 ± 7 |
| Clay (<0.002 mm, g kg−1) | 20 ± 2 |
| Texture | Sandy |
| CaCO3 (g kg−1) | 200 ± 6 |
| pH (1:2) | 8.00 ± 0.08 |
| ECe (dS m−1) | 1.5 ± 0.0 |
| Organic Carbon (g kg−1) | 4.5 ± 0.1 |
| Total N (mg kg−1) | 200 ± 7 |
| Available N (mg kg−1) | 30 ± 2 |
| Available P (Olsen) (mg kg−1) | 6.0 ± 0.0 |
| Available K (mg kg−1) | 130 ± 6 |
| Total K (mg kg−1) | 650 ± 12 |
| Inculation | Treaments | a (mg kg−1) | b (mg kg−1 day−1) | SEE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inoculated with KSB | 100-Sul | 25 ± 3 a | 0.64 ± 0.02 a | 2.42 | 0.89 |
| 75-Sul:25-Fel | 20 ± 2 b | 0.50 ± 0.01 b | 1.52 | 0.96 | |
| 50-Sul:50-Fel | 19 ± 1 b | 0.45 ± 0.02 bc | 1.18 | 0.94 | |
| 25-Sul:75-Fel | 20 ± 2 b | 0.35 ± 0.03 d | 2.55 | 0.93 | |
| 100-Fel | 19 ± 2 b | 0.37 ± 0.03 d | 2.62 | 0.95 | |
| C | 14 ± 2 c | 0.22 ± 0.01 e | 2.38 | 0.88 | |
| Without inoculation | 100-Sul | 24 ± 1 a | 0.53 ± 0.04 b | 1.02 | 0.89 |
| 75-Sul:25-Fel | 21 ± 2 b | 0.47 ± 0.02 b | 1.51 | 0.93 | |
| 50-Sul:50-Fel | 18 ± 2 c | 0.40 ± 0.01 cd | 1.60 | 0.94 | |
| 25-Sul:75-Fel | 21 ± 2 b | 0.33 ± 0.05 d | 2.57 | 0.90 | |
| 100-Fel | 20 ± 1 b | 0.30 ± 0.05 d | 2.12 | 0.95 | |
| C | 13 ± 1 c | 0.18 ± 0.01 e | 1.15 | 0.87 |
| Inculation | Treaments | N | P | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inoculated with KSB | 100-Sul | 22.2 ± 2.1 c | 4.6 ± 0.0 ab | 35.8 ± 2.1 c |
| 75-Sul:25-Fel | 22.0 ± 2.0 c | 5.0 ± 0.0 a | 42.6 ± 2.5 b | |
| 50-Sul:50-Fel | 31.5 ± 2.1 a | 5.2 ± 0.3 a | 55.2 ± 2.6 a | |
| 25-Sul:75-Fel | 25.1 ± 3.0 b | 5.0 ± 0.2 a | 47.2 ± 3.2 b | |
| 100-Fel | 18.2 ± 2.0 d | 4.7 ± 0.1 b | 28.0 ± 2.1 d | |
| C | 17.2 ± 1.2 d | 3.5 ± 0.0 bc | 28.0 ± 2.1 cd | |
| Without inoculation | 100-Sul | 21.0 ± 2.7 c | 4.5 ± 0.1 b | 33.8 ± 2.0 c |
| 75-Sul:25-Fel | 22.0 ± 2.3 c | 4.6 ± 0.2 b | 40.6 ± 3.5 b | |
| 50-Sul:50-Fel | 30.5 ± 2.5 a | 4.7 ± 0.2 b | 42.2 ± 3.6 b | |
| 25-Sul:75-Fel | 25.0 ± 3.4 b | 4.8 ± 0.3 b | 40.2 ± 3.5 b | |
| 100-Fel | 17.1 ± 1.8 d | 4.4 ± 0.3 b | 27.0 ± 2.3 d | |
| C | 15.2 ± 1.6 e | 3.2 ± 0.0 c | 25.0 ± 1.8 |
| Inculation | Treaments | Shoot Length mm | No. of Leaves /Shoot | Leaf Area mm2 | Chlorophyll-a mg g−1 | Chlorophyll-b mg g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inoculated with KSB | 100-Sul | 850 ± 33 a | 38 ± 2 a | 8600 ± 800 a | 2.44 ± 0.05 a | 1.42 ± 0.08 a |
| 75-Sul:25-Fel | 860 ± 25 a | 37 ± 2 a | 8500 ± 700 a | 2.34 ± 0.04 b | 1.39 ± 0.09 a | |
| 50-Sul:50-Fel | 830 ± 40 a | 36 ± 3 a | 8500 ± 800 a | 2.28 ± 0.07 c | 1.18 ± 0.07 c | |
| 25-Sul:75-Fel | 770 ± 42 b | 33 ± 2 b | 8000 ± 700 b | 2.17 ± 0.04 d | 1.20 ± 0.08 c | |
| 100-Fel | 650 ± 33 c | 33 ± 2 b | 8100 ± 600 b | 2.06 ± 0.08 d | 1.09 ± 0.09 d | |
| C | 540 ± 42 d | 31 ± 2 b | 7500 ± 700 c | 2.00 ± 0.07 e | 0.89 ± 0.09 e | |
| Without inoculation | 100-Sul | 720 ± 21 b | 35 ± 2 ab | 8400 ± 800 a | 2.36 ± 0.05 b | 1.38 ± 0.08 a |
| 75-Sul:25-Fel | 760 ± 20 b | 36 ± 2 a | 8300 ± 800 ab | 2.27 ± 0.04 c | 1.29 ± 0.09 b | |
| 50-Sul:50-Fel | 780 ± 64 b | 32 ± 3 b | 8300 ± 1000 ab | 2.12 ± 0.07 d | 1.30 ± 0.07 b | |
| 25-Sul:75-Fel | 720 ± 53 b | 33 ± 3 b | 8000 ± 700 b | 2.07 ± 0.04 d | 1.08 ± 0.08 d | |
| 100-Fel | 620 ± 36 c | 27 ± 2 c | 7900 ± 600 b | 1.87 ± 0.08 f | 0.95 ± 0.09 e | |
| C | 500 ± 42 d | 26 ± 2 c | 7100 ± 700 c | 1.85 ± 0.07 f | 0.75 ± 0.09 f |
| Inculation | Treaments | Total Soluble Solids (%) | Total Sugar (%) | Vitamin C mg kg−1 | Total Fibre (%) | Pulp (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inoculated with KSB | 100-Sul | 16 ± 2 a | 14 ± 2 a | 460 ± 15 ab | 0.75 ± 0.03 d | 78 ± 9 a |
| 75-Sul:25-Fel | 16 ± 2 a | 14 ± 2 a | 470 ± 10 a | 0.72 ± 0.01 d | 75 ± 8 b | |
| 50-Sul:50-Fel | 15 ± 2 ab | 13 ± 2 ab | 450 ± 13 b | 0.73 ± 0.02 d | 75 ± 6 b | |
| 25-Sul:75-Fel | 13 ± 1 bc | 10 ± 1 c | 440 ± 15 cd | 0.75 ± 0.04 d | 72 ± 9 c | |
| 100-Fel | 14 ± 1 b | 10 ± 1 c | 400 ± 16 e | 0.70 ± 0.04 d | 73 ± 8 c | |
| C | 12 ± 1 c | 10 ± 1 c | 350 ± 12 g | 1.00 ± 0.02 a | 65 ± 5 e | |
| Without inoculation | 100-Sul | 15 ± 1 ab | 13 ± 1 ab | 430 ± 12 cd | 0.76 ± 0.01 d | 73 ± 5 c |
| 75-Sul:25-Fel | 14 ± 1 b | 12 ± 1 b | 400 ± 10 e | 0.82 ± 0.03 c | 73 ± 7 c | |
| 50-Sul:50-Fel | 14 ± 1 b | 12 ± 1 b | 430 ± 13 cd | 0.83 ± 0.03 c | 70 ± 8 d | |
| 25-Sul:75-Fel | 12 ± 1 c | 10 ± 1 c | 400 ± 13 e | 0.86 ± 0.02 c | 71 ± 7 cd | |
| 100-Fel | 12 ± 1 c | 10 ± 1 c | 370 ± 12 f | 0.90 ± 0.01 b | 71 ± 9 cd | |
| C | 12 ± 1 c | 10 ± 1 c | 320 ± 14 h | 1.08 ± 0.02 a | 62 ± 5 f |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Ding, Z.; AL-Huqail, A.A.; Hui, Y.; He, Y.; Reichman, S.M.; Ghoneim, A.M.; Eissa, M.A.; Abou-Zaid, E.A.A. Potassium Source and Biofertilizer Influence K Release and Fruit Yield of Mango (Mangifera indica L.): A Three-Year Field Study in Sandy Soils. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9766. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159766
Wang J, Ding Z, AL-Huqail AA, Hui Y, He Y, Reichman SM, Ghoneim AM, Eissa MA, Abou-Zaid EAA. Potassium Source and Biofertilizer Influence K Release and Fruit Yield of Mango (Mangifera indica L.): A Three-Year Field Study in Sandy Soils. Sustainability. 2022; 14(15):9766. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159766
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiyue, Zheli Ding, Arwa Abdulkreem AL-Huqail, Yongyong Hui, Yingdui He, Suzie M. Reichman, Adel M. Ghoneim, Mamdouh A. Eissa, and Eman A. A. Abou-Zaid. 2022. "Potassium Source and Biofertilizer Influence K Release and Fruit Yield of Mango (Mangifera indica L.): A Three-Year Field Study in Sandy Soils" Sustainability 14, no. 15: 9766. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159766
APA StyleWang, J., Ding, Z., AL-Huqail, A. A., Hui, Y., He, Y., Reichman, S. M., Ghoneim, A. M., Eissa, M. A., & Abou-Zaid, E. A. A. (2022). Potassium Source and Biofertilizer Influence K Release and Fruit Yield of Mango (Mangifera indica L.): A Three-Year Field Study in Sandy Soils. Sustainability, 14(15), 9766. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159766










