Development and Evaluation of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) as a Preliminary Diagnostic Tool for Brown Root Rot Disease Caused by Phellinus noxius (Corner) G. H. Cunningham in Hong Kong Urban Tree Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Experimental Design and Setup
2.3.1. Fungal Isolation
2.3.2. LAMP Method Using Mycelium (mLAMP)
2.3.3. LAMP Method Using Wood Chips (wLAMP)
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Relationship between Sample Purity and LAMP Sensitivity
3.2. The Effectiveness of LAMPS in Diagnosing BRRD
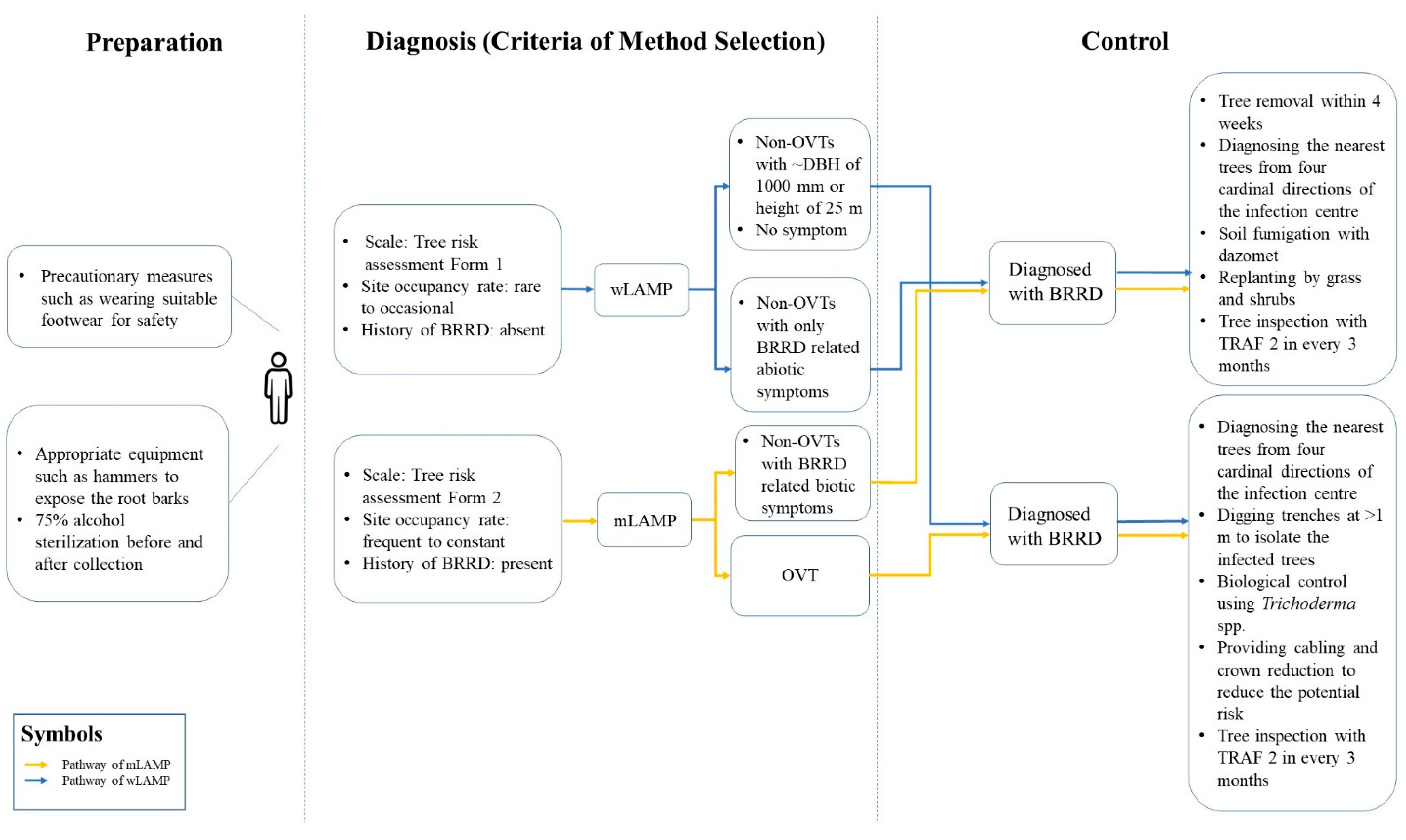
3.3. The Incorporation of LAMPs in the Current Tree Management Work
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, C.; Huang, S.; Huang, Y.; Tzean, S.; Ann, P.; Tsai, J.; Yang, C.; Lee, H.; Huang, T.; Huang, H.; et al. The genetic structure of Phellinus noxius and dissemination pattern of Brown Root Rot Disease in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ann, P.; Chang, T.; Ko, W. Phellinus noxius Brown Root Rot of fruit and ornamental Trees in Taiwan. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, F.E. Brown root rot disease in American Samoa’s tropical rain forests. Pac. Sci. 2002, 56, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xing, Y.; Brimblecombe, P. Trees and parks as “the lungs of cities”. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 48, 126552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughner, C.; Allen, D.; Zhang, D.; Pickering, K.; Dickerson, R.; Landry, L. Roles of urban tree canopy and buildings in urban heat island effects: Parameterization and preliminary results. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 1775–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Idilfitri, S.; Thani, S. Biodiversity by design: The attributes of ornamental plants in urban forest parks. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 105, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.Y.; Chen, W.Y. Perception and attitude of residents toward urban green spaces in Guangzhou (China). Environ. Manag. 2006, 38, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, H.; Gu, V.; Gu, J. Molecular diagnosis of the brown root rot disease agent Phellinus noxius on trees and in soil by rDNA ITS analysis. Appl. Environ. Biotechnol. 2016, 1, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasi, M.A.; Dehabadi, S.H.; Moradi, A.; Eftekhari, Z.; Ojaghkandi, M.A.; Aghaei, S. Development and application of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification assay for rapid detection of Fusarium Oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici. J. Plant Pathol. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Mori, Y.; Tomita, N.; Kanda, H. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): Principle, features, and future prospects. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.; Vu, N. Progress of loop-mediated isothermal amplification technique in molecular diagnosis of plant diseases. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2017, 60, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardinge, P.; Murray, J. Reduced false positives and improved reporting of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification using Quenched Fluorescent Primers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowledge about Brown Root Rot Disease (BRRD) You Should Know. Available online: https://www.cahk.org.hk/show_works.php?type=sid&u=161&lang=en (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Lau, Y.; Fong, M.; Mahmud, R.; Chang, P.; Palaeya, V.; Cheong, F.; Chin, L.; Anthony, C.; Al-Mekhlafi, A.; Chen, Y. Specific, sensitive and rapid detection of human Plasmodium knowlesi infection by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) in blood samples. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhama, K.; Karthik, K.; Chakrabort, S.; Tiwari, R.; Kapoor, S.; Kumar, A.; Thomas, P. Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification of DNA (LAMP): A new diagnostic tool lights the world of diagnosis of animal and human pathogens: A review. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 17, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monthly Meteorological Normals for Hong Kong. Available online: http://www.hko.gov.hk/cis/normal/1981_2010/normals_e.htm (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Tong, H.; Walton, A.; Sang, J.; Chan, J. Numerical simulation of the urban boundary layer over the complex terrain of Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3549–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, T.; Kuhn, J.; Müller, C. Proposal for field sampling of plants and processing in the lab for environmental metabolic fingerprinting. Plant Methods 2010, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.; Campbell, W.; Blaisdell, D. Differentiation of wood-decaying fungi by their reactions on gallic tannic acid medium. J. Agric. Res. 1938, 57, 683–695. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, R.S.; Cobb, F. Selective medium for the isolation of wood-rotting basidiomycetes. Can. J. Bot. 1971, 49, 2064–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechem, E.; Afanga, Y. Morphological and molecular identification of fungi associated with corm rot and blight symptoms on plantain (Musa paradisiaca) in macro- propagators. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2017, 11, 2793–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bartz, F. Pathogen Profile: Phellinus noxius (Corner) G. H. Cunningam. Available online: https://projects.ncsu.edu/cals/course/pp728/Phellinus/Phellinus_noxius.html (accessed on 17 July 2021).
- Larsen, R.; Hollingsworth, C.; Vandemark, G.; Gritsenko, M.; Gray, F. A rapid method using PCR-Based SCAR Markers for the detection and identification of Phoma sclerotioides: The cause of Brown Root Rot Disease of Alfalfa. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, K.R.; Heidelbach, S.; Zeuner, E.J.; Riisgaard-Jensen, M.; Nielsen, M.E.; Vestergaard, S.Z.; Bekker, N.S.; Skovmark, J.; Olesen, C.K.; Thomsen, K.H.; et al. The effects of different potato dextrose agar media on secondary metabolite production in Fusarium. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 347, 109171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Hung, T.; Wu, M.L.; Chang, T. Development of the detection method for tree brown Root Rot Disease based on the Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP). Plant Pathol. Bull. 2014, 23, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Inglis, P.; Pappas, M.; Resende, L.; Grattapaglia, D. Fast and inexpensive protocols for consistent extraction of high quality DNA and RNA from challenging plant and fungal samples for high-throughput SNP genotyping and sequencing applications. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboul-Maaty, N.; Oraby, H. Extraction of high-quality genomic DNA from different plant orders applying a modified CTAB-based method. Bull. Natil. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesenberg-Smith, K.; Pessarakli, M.; Wolk, D. Assessment of DNA yield and purity: An overlooked detail of PCR troubleshooting. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2012, 34, 1,3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Gomez, R. An empirical approach for quantifying Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) using Escherichia coli as a model system. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, T.; Srivastava, A.; Hanur, V.; Rao, M. An Effective Wood DNA Extraction Protocol for Three Economic Important Timber Species of India. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ebbinghaus, P.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Krücken, J. Direct loop-mediated isothermal amplification from Plasmodium chabaudi infected blood samples: Inability to discriminate genomic and cDNA sequences. Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 131, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, P.; Tangomo, M.; Hibbs, J.; Bonetti, E.; Boehme, C.; Notomi, T.; Perkins, M.; Schrenzel, J. Robustness of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction for diagnostic applications. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, A.; Almasi, M.; Jafary, H.; Mercado-Blanco, J. A novel and rapid loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the specific detection of Verticillium dahliae. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 116, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, A.; Nasiri, J.; Abdollahi, H.; Almasi, M. Development and evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detection of Erwinia amylovora based on chromosomal DNA. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbach, J.; Xander, N.; Frohme, M.; Glökler, J. Shining a light on LAMP assays— A comparison of LAMP visualization methods including the novel use of berberine. BioTechniques 2015, 58, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panno, S.; Matić, S.; Tiberini, A.; Caruso, A.; Bella, P.; Torta, L.; Stassi, R.; Davino, S. Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification: Principles and applications in plant virology. Plants 2020, 9, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Sun, B.; Guan, Y. Pullulan reduces the non-specific amplification of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 411, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, J. The Acute Effects of Isoflurane and Propofol on the Olfactory-Cognitive Ability of Brown Root Rot Disease Fungus Detection Dogs. Master’s Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, L.W. Study on Rapid Detection of Orange and Strawberry Storage Diseases and Trees Brown Root Rot by Electronic Nose. Master’s Thesis, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, K.; Cheung, M.; Lam, R.; Kwan, H. A preliminary examination of the bacterial, archaeal, and fungal rhizosphere microbiome in healthy and Phellinus noxius-infected trees. MicrobiologyOpen 2020, 9, e1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greening, Landscape and Tree Management Section, Development Bureau, HKSAR Government. Guidelines for Tree Risk Assessment and Management Arrangement; Development Bureau, HKSAR Government: Hong Kong, China, 2022. Available online: https://www.greening.gov.hk/filemanager/greening/common/pdf/tree_care/9th_Edition_of_TRAM_Guideline_rev_3-26-1-2022.pdf (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Jim, C.Y.; Zhang, H. Species diversity and spatial differentiation of old-valuable trees in urban Hong Kong. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Hu, B.; Chang, T.; Hsueh, K.; Hsu, W. Evaluation of dazomet as fumigant for the control of brown root rot disease. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Lee, T.; Akiba, M.; Lee, H.; Kuo, T.; Liu, D.; Ke, H.; Yokoi, T.; Roa, M.; Lu, M.; et al. Comparative and population genomic landscape of Phellinus noxius: A hypervariable fungus causing root rot in trees. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 6301–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omorusi, V. Effects of White Root Rot Disease on Hevea brasiliensis (Muell. Arg.)–Challenges and control approach. In Plant Science, 1st ed.; Dhal, N.K., Sahu, S.C., Eds.; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.; Ann, P.; Hsieh, W. Evaluation of fungicides for suppression of three major wood-decay fungi Phellinus noxius, Rosellinia necatrix and Ganoderma australe in Taiwan. Plant Pathol. Bull. 2005, 14, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, C.; Yen, P.; Yeh, T.; Cheng, S.; Chang, S. Antifungal agents from heartwood extract of Taiwania cryptomerioides against brown root rot fungus Phellinus noxius. Wood Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.; Chen, C.; You, B.; Lee, M.; Huang, J. Brown Root Rot Disease of Phyllanthus myrtifolius: The causal agent and two potential biological control agents. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 3043–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
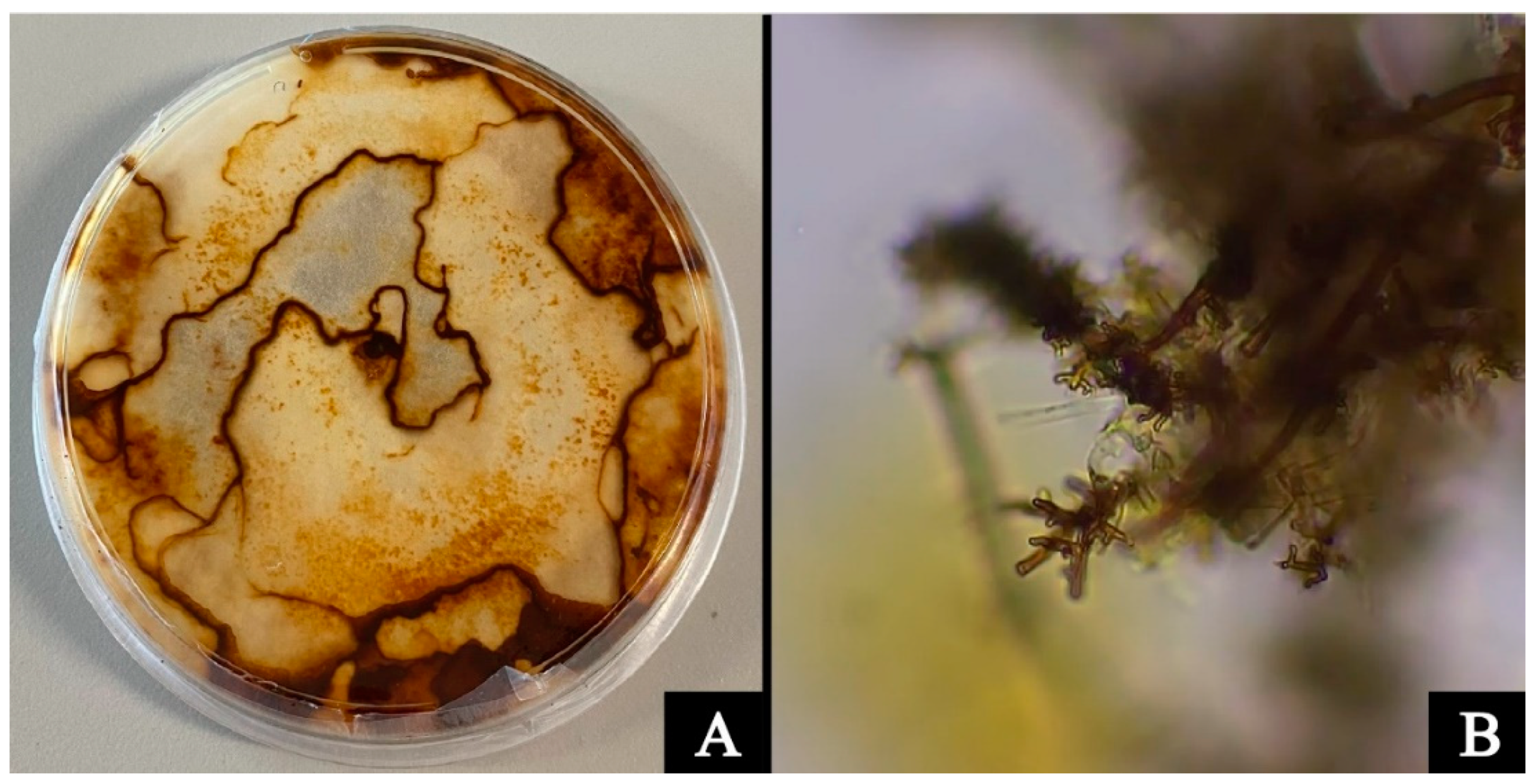


| Species 1 | Location (Slope No.) 2 | BRRD Symptoms | BRRD | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acacia confusa Merr. | 11SW-A/F31 | Absence | Yes | P01 |
| 11SW-D/CR1168 | Sparse foliage density; suspected root rotting | No | N01 | |
| Aleurites moluccanus (L.) Willd. | 11SW-A/CR185 | Absence | Yes | P02 |
| Cascabela thevetia (L.) Lippold | 11SW-A/CR80 | Absence | No | N02 |
| 11SW-C/FR43 | Sparse foliage density; medium density of die-back twigs | No | N03 | |
| Celtis sinensis Pers. | 3 SW- C/F 35 | Absence | No | N04 |
| Cinnamomum camphora (L.) J. Presl | 11SE-A/C324 | Suspected root rotting | Yes | P03 |
| Ficus microcarpa L. f. | 11SW-A/CR80 | Abnormal bark color | No | N05 |
| 11SW-A/R1148 | Absence | No | N06 | |
| 11SW-A/R427 | Abnormal bark color | No | N07 | |
| 3 SW- C/F 35 | Sparse foliage density; medium density of die-back twigs | No | N08 | |
| Ficus variegata Blume | 11SE-A/C211 | Absence | No | N09 |
| 11SE-A/C8 | Absence | No | N10 | |
| 11SW-A/CR185 | Absence | Yes | P04 | |
| 11SW-A/F31 | Absence | Yes | P05 | |
| 11SW-C/C341 | Absence | Yes | P06 | |
| Litsea glutinosa (Lour.) C. B. Rob. | 11SW-D/C385 | Sparse foliage density; medium density of die-back twigs; abnormal bark color | No | N11 |
| Livistona chinensis (Jacq.) R. Br. ex Mart. | 11SW-D/CR239 | Sparse foliage density; suspected root rotting; observable mycelial nets | Yes | P07 |
| 11SW-D/CR239 | Sparse foliage density; suspected root rotting; observable mycelial nets | Yes | P08 | |
| 11SW-D/CR239 | Sparse foliage density | Yes | P09 | |
| Lophostemon confertus (R. Br.) Peter G. Wilson & J. T. Waterh. | 11SE-A/CR565 | High density of die-back twigs; suspected root rotting | Yes | P10 |
| 11SE-A/CR565 | Absence | Yes | P11 | |
| Macaranga tanarius var. tomentosa (Blume) Müll. Arg. | 11SW-A/FR258 | Medium density of die-back twigs | Yes | P12 |
| 11SW-C/C387 | Sparse foliage density; abnormal leaf size; low density of die-back twigs; abnormal bark color | No | N12 | |
| 11SW-C/F396 | Absence | No | N13 | |
| 11SW-C/FR43 | Absence | No | N14 | |
| Machilus chekiangensis S. K. Lee | 11SW-D/CR239 | Abnormal bark color | No | N15 |
| 11SW-D/CR239 | Abnormal bark color | Yes | P13 | |
| Scolopia saeva Hance | 11SW-D/C385 | Medium density of die-back twigs; abnormal bark color | Yes | P14 |
| Senna siamea (Lam.) H. S. Irwin & Barneby | 11SW-C/FR43 | Absence | Yes | P15 |
| Primers | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| 1-F3 | TTTGAGGCCAAAGGTCAA |
| 1-B3 | GTGTCATGTTAATCTCAATACAACA |
| 1-LB | CAAGAGAAGCCGACTTACGC |
| 1-FIP | ACATTCACCGTTTACACTTGCTAATGTTAAGTGTTTGTCTCATTACAAGA |
| 1-BIP | TACACCAATTACTCGAGCAAAAGCTTAATATTGGACTTGGGGACTG |
| Code 1 | BRRD Symptoms 1 | Fungal Isolation 2 | mLAMP 2 | wLAMP 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRRD-positive trees | ||||
| P01 | Absence | + | + | − |
| P02 | Absence | + | + | + |
| P03 | Presence | + | + | + |
| P04 | Absence | + | + | + |
| P05 | Absence | + | + | + |
| P06 | Absence | + | + | + |
| P07 | Presence | + | + | + |
| P08 | Presence | + | + | + |
| P09 | Presence | + | + | − |
| P10 | Presence | + | + | + |
| P11 | Absence | + | + | − |
| P12 | Presence | + | + | + |
| P13 | Presence | + | + | + |
| P14 | Presence | + | + | + |
| P15 | Absence | + | + | − |
| BRRD-negative trees | ||||
| N01 | Presence | − | − | − |
| N02 | Absence | − | − | + |
| N03 | Presence | − | + | − |
| N04 | Absence | − | − | + |
| N05 | Presence | − | − | − |
| N06 | Absence | − | + | − |
| N07 | Presence | − | − | − |
| N08 | Presence | − | − | − |
| N09 | Absence | − | − | − |
| N10 | Absence | − | − | + |
| N11 | Presence | − | − | − |
| N12 | Presence | − | + | − |
| N13 | Absence | − | + | − |
| N14 | Absence | − | − | − |
| N15 | Presence | − | − | + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Ng, T.K.; Lee, K.C.; Leung, Z.W.; Yau, W.F.; Wong, W.S. Development and Evaluation of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) as a Preliminary Diagnostic Tool for Brown Root Rot Disease Caused by Phellinus noxius (Corner) G. H. Cunningham in Hong Kong Urban Tree Management. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9708. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159708
Zhang H, Ng TK, Lee KC, Leung ZW, Yau WF, Wong WS. Development and Evaluation of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) as a Preliminary Diagnostic Tool for Brown Root Rot Disease Caused by Phellinus noxius (Corner) G. H. Cunningham in Hong Kong Urban Tree Management. Sustainability. 2022; 14(15):9708. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159708
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hao, Tze Kwun Ng, Kai Chun Lee, Zoen Wing Leung, Wai Fu Yau, and Wai Shing Wong. 2022. "Development and Evaluation of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) as a Preliminary Diagnostic Tool for Brown Root Rot Disease Caused by Phellinus noxius (Corner) G. H. Cunningham in Hong Kong Urban Tree Management" Sustainability 14, no. 15: 9708. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159708
APA StyleZhang, H., Ng, T. K., Lee, K. C., Leung, Z. W., Yau, W. F., & Wong, W. S. (2022). Development and Evaluation of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) as a Preliminary Diagnostic Tool for Brown Root Rot Disease Caused by Phellinus noxius (Corner) G. H. Cunningham in Hong Kong Urban Tree Management. Sustainability, 14(15), 9708. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159708







