Spatiotemporal Change of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Oasis City and Its Correlation with Urbanization Based on RSEI: A Case Study of Urumqi, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data sources
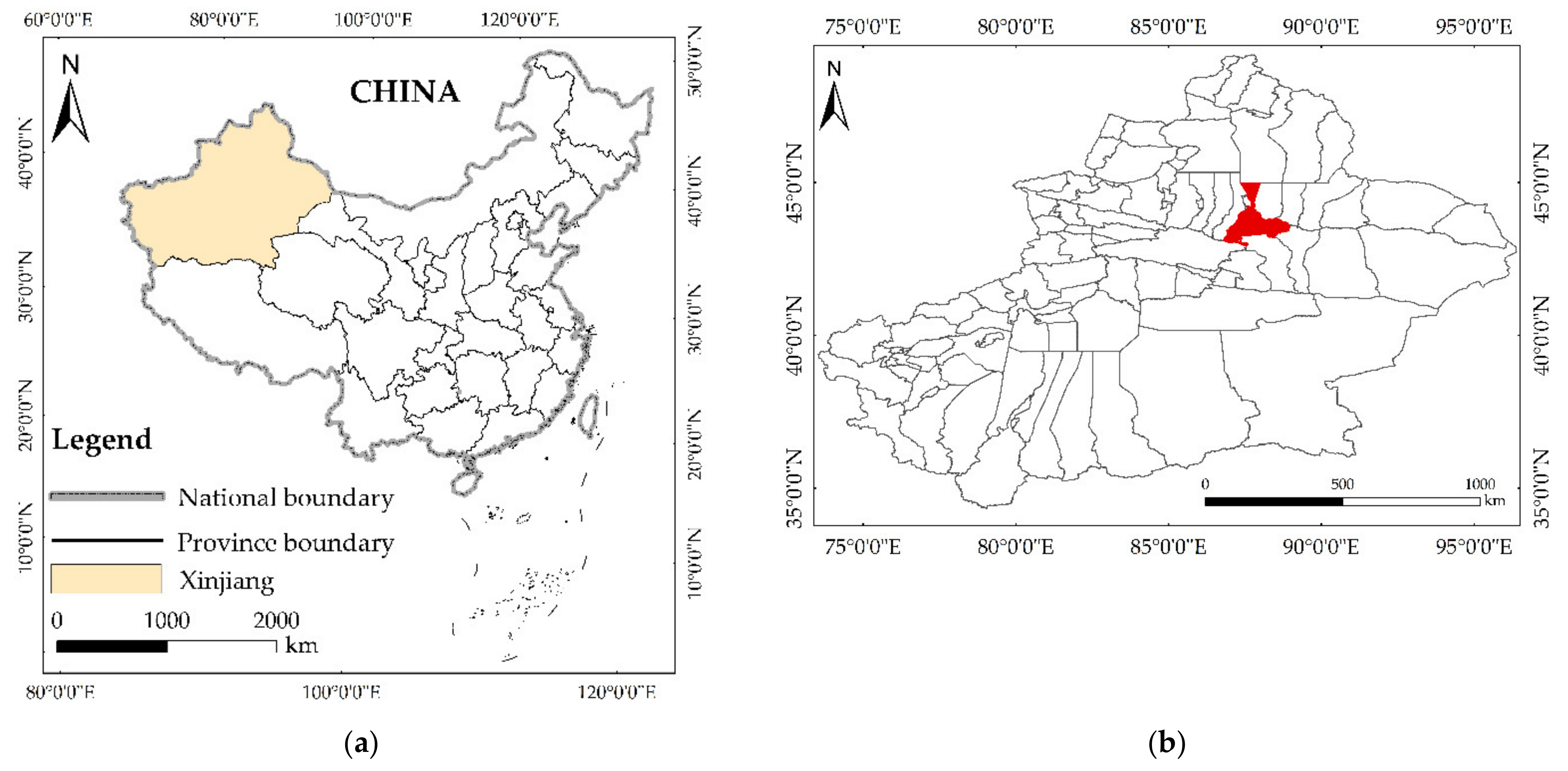
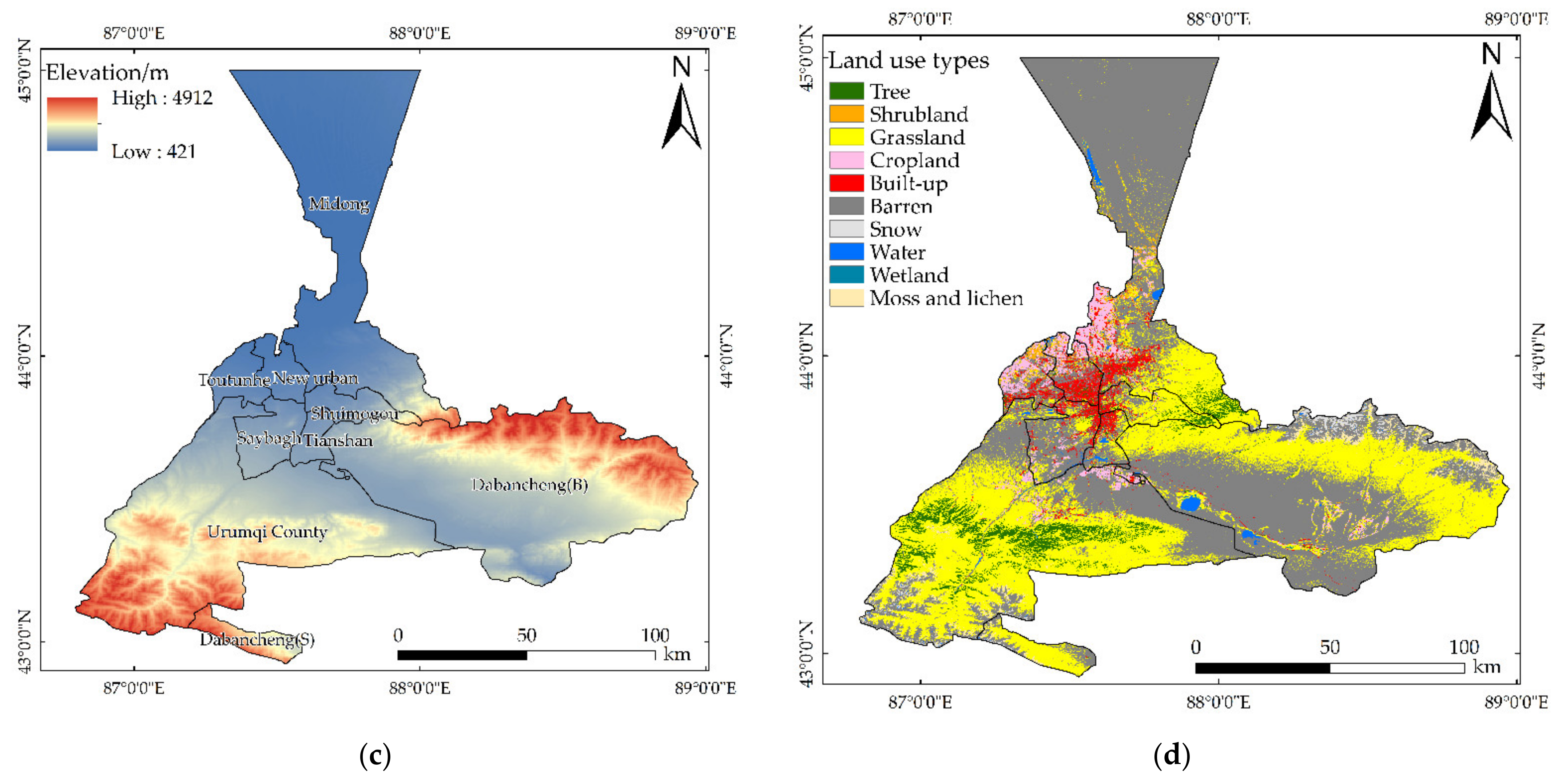
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Pre-Processing
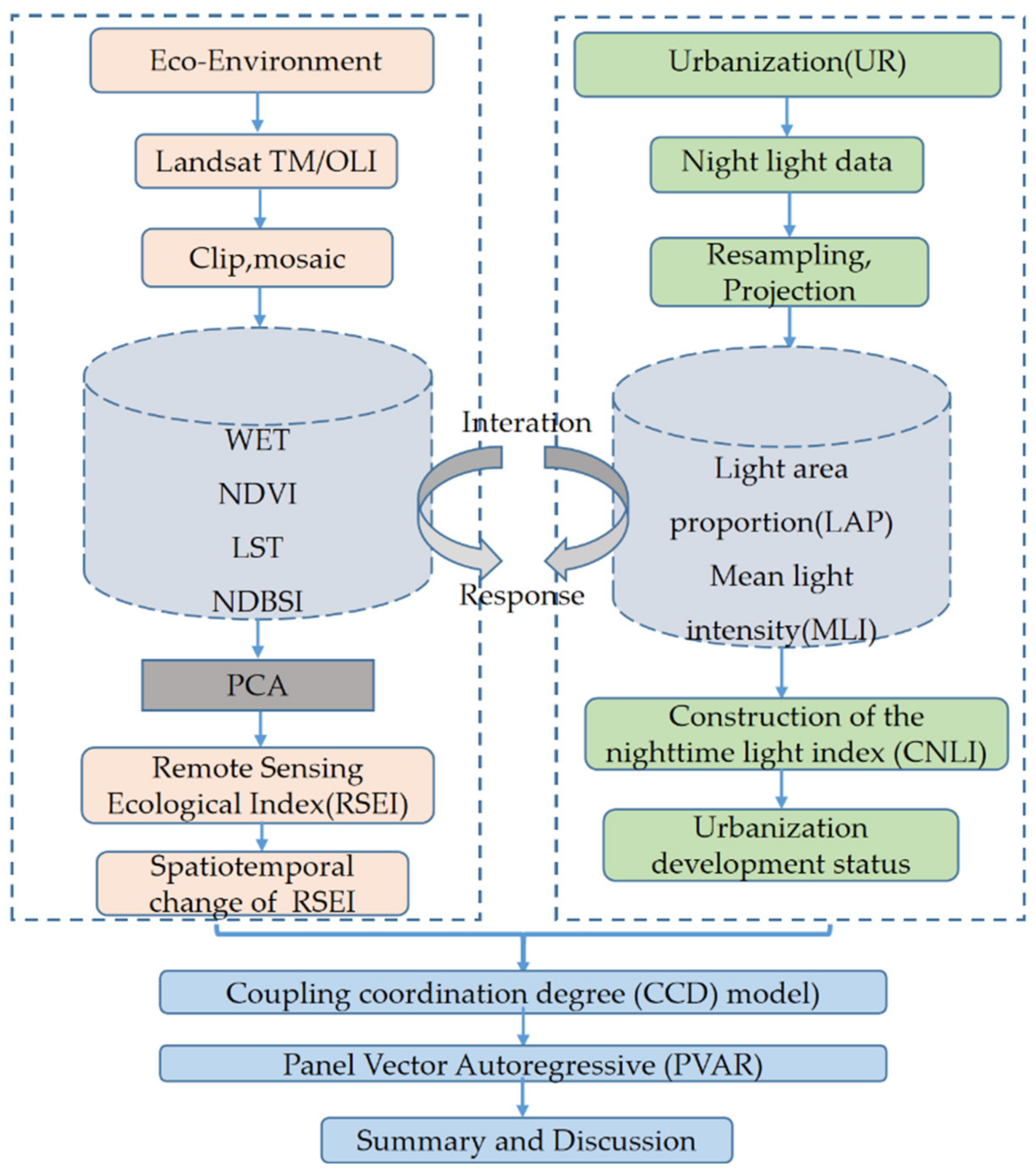
3. Methods
3.1. Construction of Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI)
- (1)
- Wetness: The wetness in RSEI is calculated by the wetness component wet in the tassel cap transformation [38], and the formula is as follows:where ρBlue, ρGreen, ρRed, ρNIR, ρSWIR1, and ρSWIR2 represent the reflectance of ground objects corresponding to the TM image and OLI image in the Blue wave band, Green wave band, Red wave band, Near Infrared band, Short Wave Infrared 1 band, and Short Wave Infrared 2 band, respectively.
- (2)
- Greenness: The greenness of RSEI can be solved by the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) [25].
- (3)
- Heat: The heat index of land surface temperature (LST) is obtained by a single window algorithm.where T: the luminance temperature of heat radiation intensity transformation; λ: central wavelength of the thermal infrared band; θ: constant, ε: surface emissivity. Please refer to the reference for the calculation method [39].
- (4)
3.2. Construction of the Nighttime Light Index
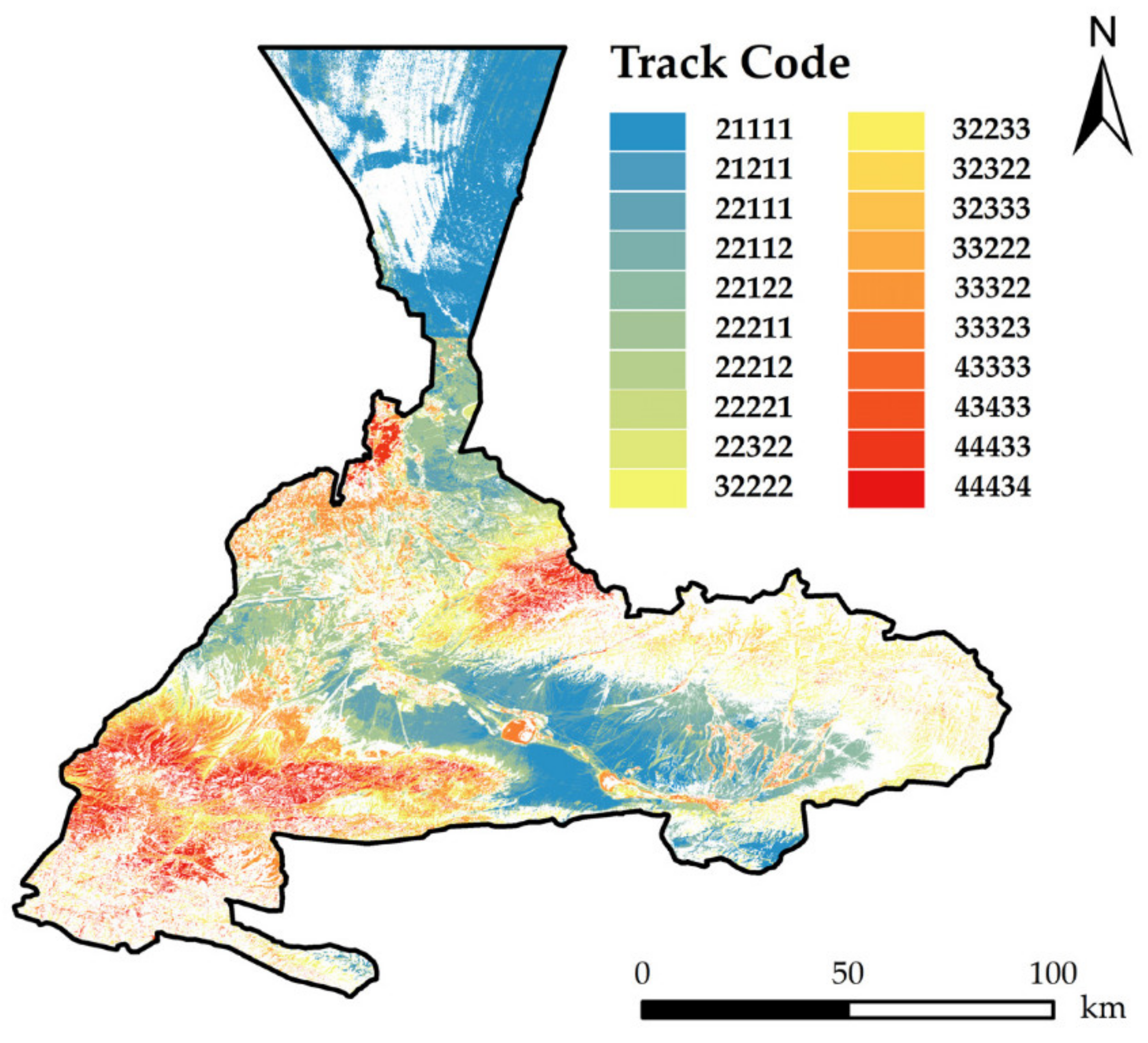
3.3. Change Trajectory Analysis Method
3.4. Coupling Coordination Degree (CCD) Model
- (1)
- Calculate system coupling:where U represents CNLI, E represents RSEI, and C is the coupling degree value of the coupled system of CNLI and RSEI, characterizing the strength of the interaction between systems, 0 ≤ C ≤ 1. The larger the value is, it shows that the ecological environment and urbanization development are more coordinated, and vice versa.
- (2)
- Calculate the composite coordination index:where α and β are the weights to be determined, and α + β = 1. Considering that in the interactive coupling process of the two systems of urbanization and ecological environment, urbanization is a very key factor affecting the change of the ecological environment, and the ecological environment is only one of the many factors affecting urbanization. Therefore, greater weight should be given to the urbanization system (α = 0.65; β = 0.35) [47].
- (3)
- Calculate the coupling coordination degree:where D is the degree of coupling coordination, 0 ≤ D ≤ 1; the larger the D value, the higher the level of system coupling coordination development; the smaller the D value, the more serious the system disorder. The classification criteria of C and D are shown in Table 2 [48].
3.5. Panel Vector Autoregressive (PVAR)
4. Results
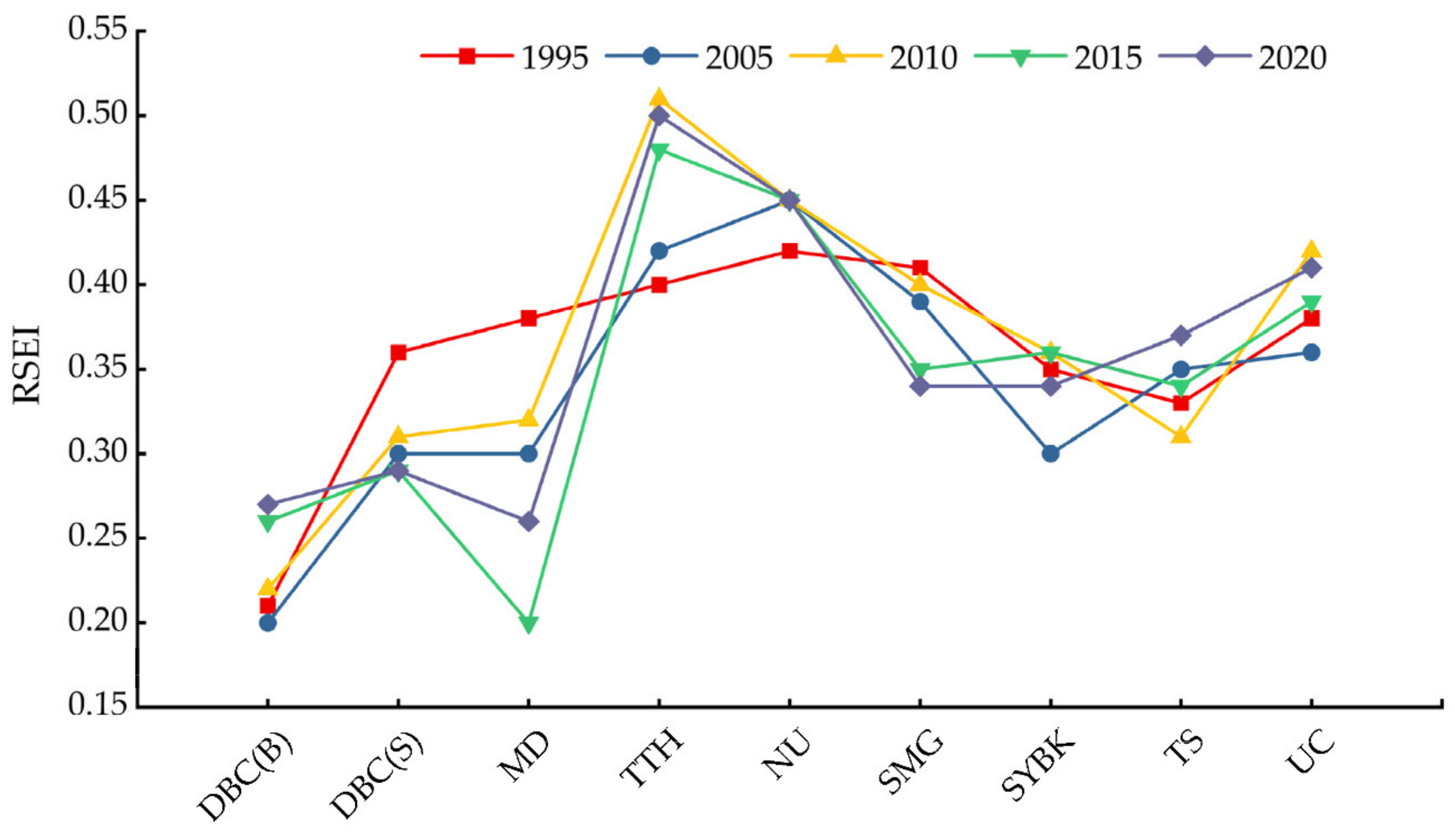
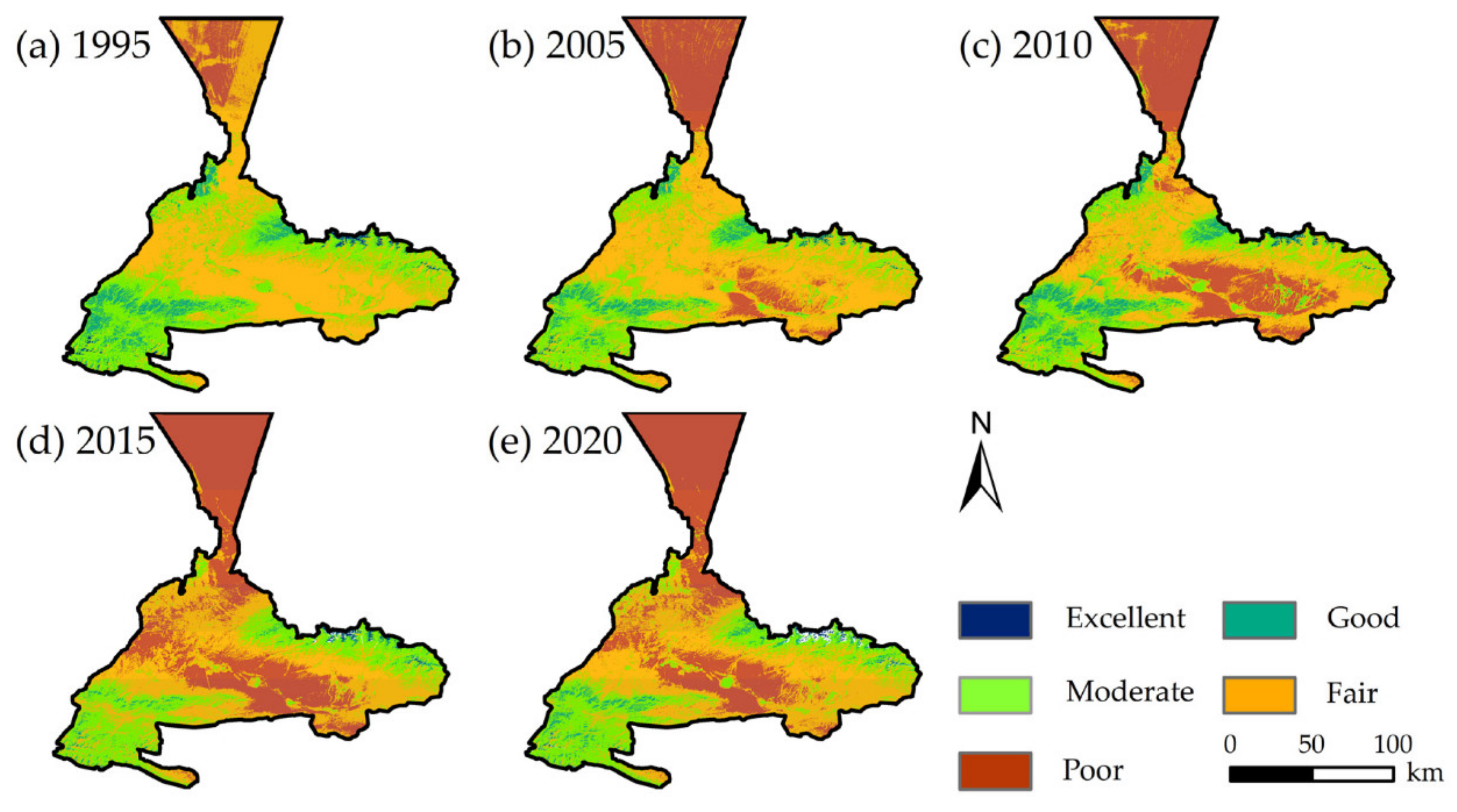
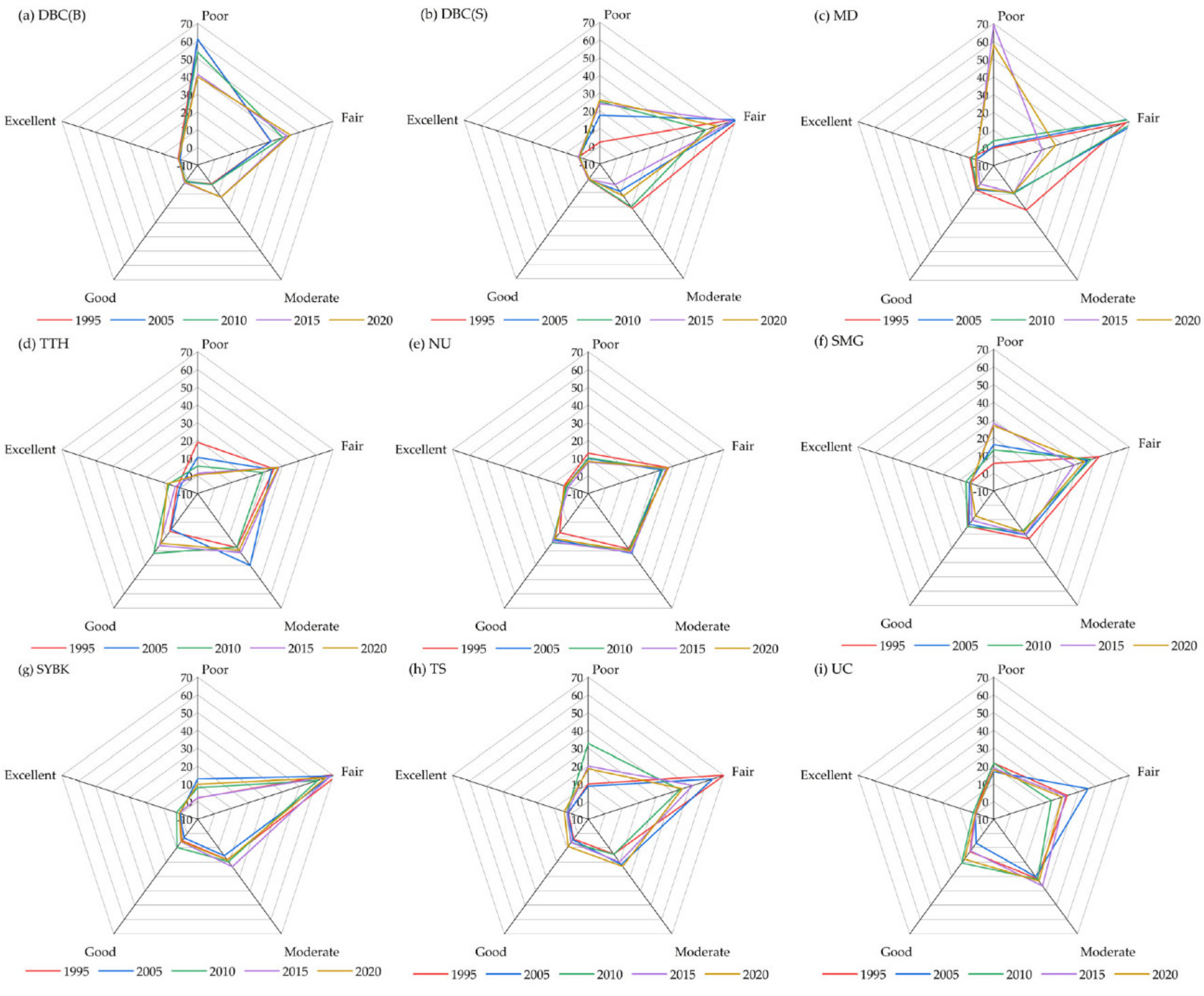
4.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of RSEI
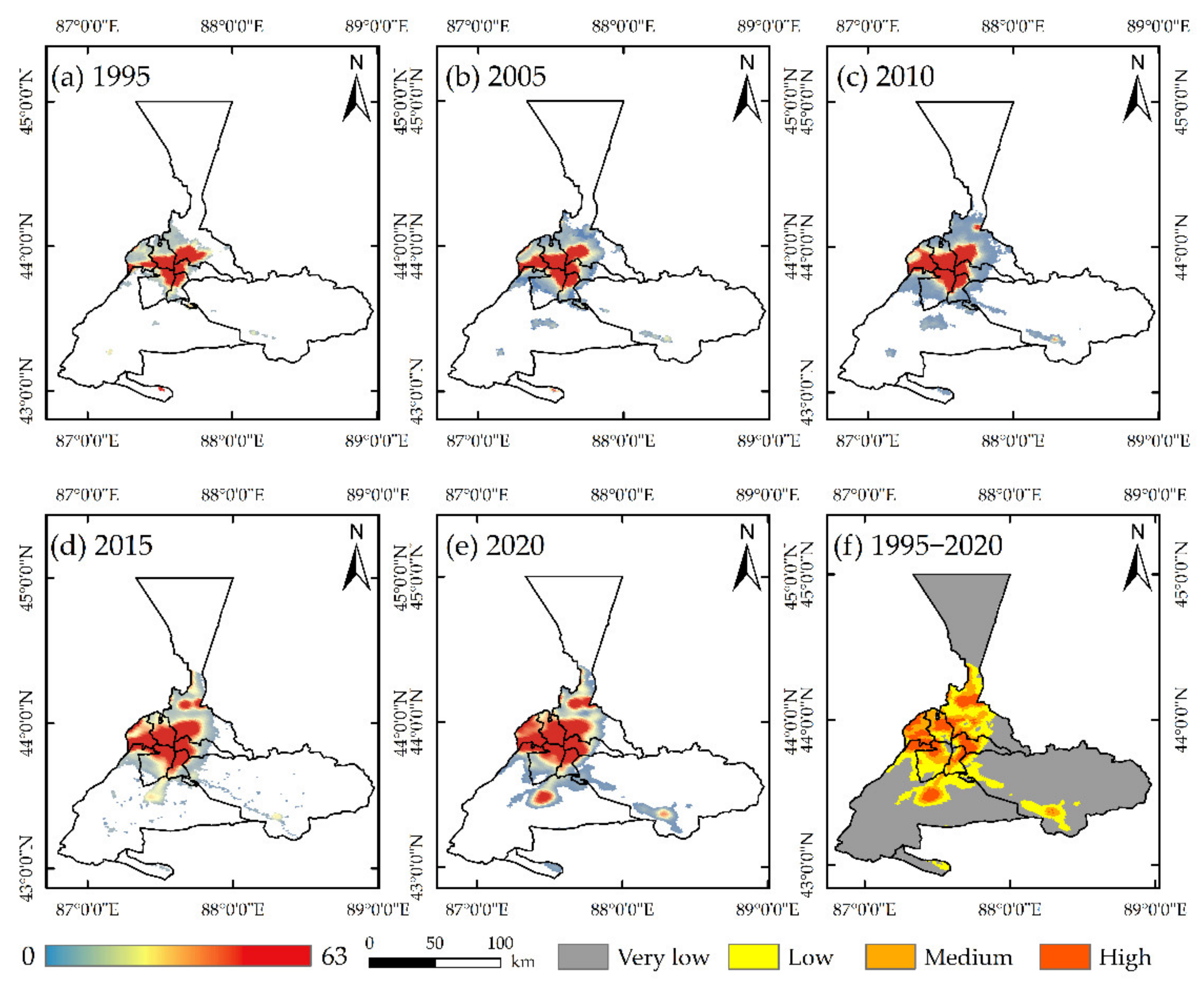
4.2. Urbanization of Urumqi
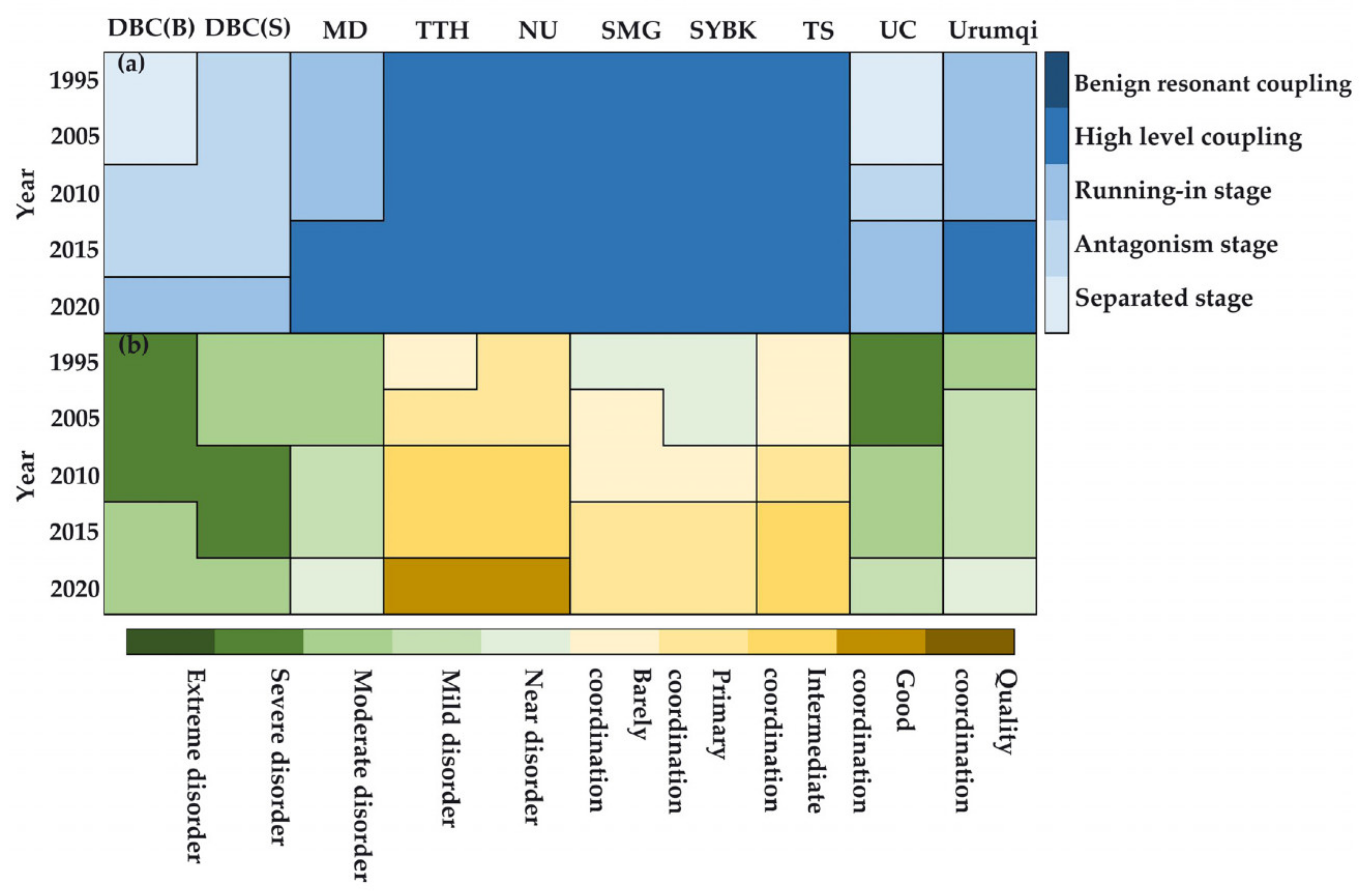
4.3. Coupling Analysis of Urbanization and Ecological-Quality in Urumqi and Its Subsystems
4.4. Analysis of the Interactive Relationship between Urbanization and Eco-Environment
4.4.1. Analysis of Test Results
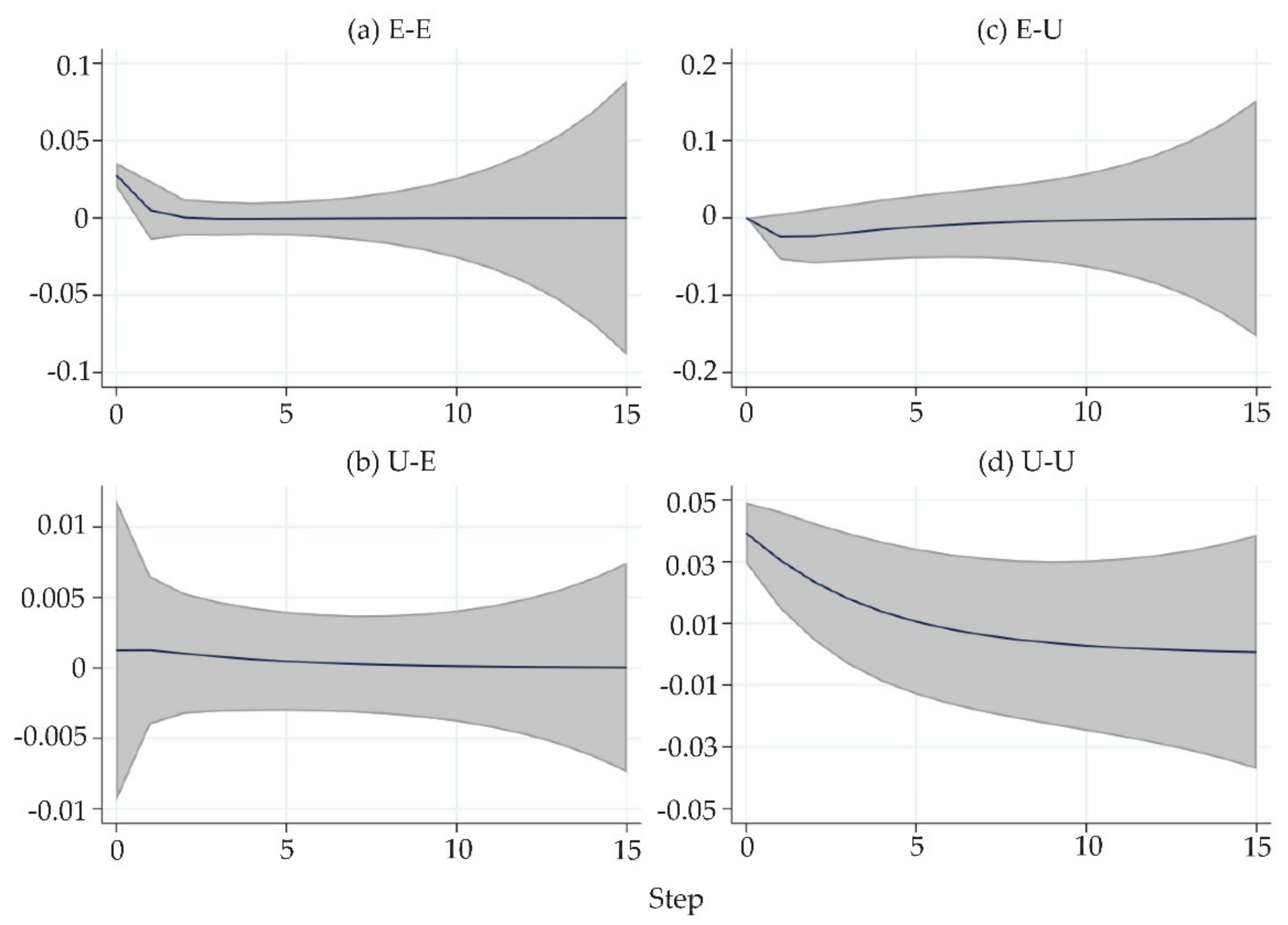
4.4.2. Analysis of Impulse Response and Variance Decomposition Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Assessment of RSEI and CNLI
5.2. The Interactive Relationship between Urbanization and the Ecological Environment
5.3. Policy Implications
- (1)
- The government should increase its efforts to support the rapid urbanization development of Urumqi. Although the CNLI has increased year by year, the urbanization level of Urumqi is lower than that of other cities. For example, it can establish friendly cooperative relations with developed cities, introduce a large amount of capital for investment, and rapidly develop the economy.
- (2)
- Continue to take the road of resource-saving urbanization. Renewable resources should not be grabbed faster than their natural refresh rate. For non-renewable resources such as oil, development and occupation should be minimized, and efforts should be attempted to seek alternative friendly resources. The reasonable use of local advantages, in areas with high urbanization, such as SYBK and TS, encourage the upgrading of industrial structure and give play to the role of the market in resource allocation. In areas with low urbanization, such as DBC and UC, vigorously develop urban agriculture and create comprehensive leisure agriculture projects with integrated functions.
- (3)
- Continue to take the road of environment-friendly urbanization. At present, environmental problems are becoming more and more prominent, so it is necessary to increase investment in environmental prevention and control and improve the construction of environmental infrastructure. The government should comprehensively promote ecological optimization and a circular economy.
5.4. Limitations and Prospects
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The mean value of RSEI in Urumqi gradually decreased, the overall ecological environment deteriorated, and there were spatial differences.
- (2)
- The urbanization level of Urumqi is on the rise, but it is sluggish.
- (3)
- At present, the coupling of the ecological environment and urbanization in Urumqi is in a disordered state. In the interactive relationship between urbanization and the ecological environment, the development of Urumqi’s ecological environment is mainly affected by its own development inertia, and the development of urbanization is limited by the ecological environment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hermanns, T.; Li, Q.R. Sustainability Impact Assessment of Land Use Changes in the Anthropocene; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 167–181. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights. Available online: https://www.un.org/ (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. The Coupling Curve between Urbanization and the Eco-Environment: China’s Urban Agglomeration as a Case Study. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonorahardjo, S.; Sutjahja, I.M.; Mardiyati, Y.; Andoni, H.; Achsani, R.A.; Steven, S.; Thomas, D.; Tunçbilek, E.; Arıcı, M.; Rahmah, N.; et al. Effect of Different Building Façade Systems on Thermal Comfort and Urban Heat Island Phenomenon: An Experimental Analysis. Build. Environ. 2022, 217, 109063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, F.; Sadiq, M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Hussain, M.S.; Tran, T.D.; Le Thanh, T. A Step toward Reducing Air Pollution in Top Asian Economies: The Role of Green Energy, Eco-Innovation, and Environmental Taxes. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Kumar, R.; Sam, L. Analysing Geospatial Techniques for Land Degradation Studies in Hindu Kush-Himalaya; Saikia, A., Thapa, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 117–135. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, A.; Dorn, R.I. Soil Erosion from Urbanization Processes in the Sonoran Desert, Arizona, USA. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 20, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, P. The Effects of Urbanisation on Ecological Interactions. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2022, 52, 100922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.O.; Zin, W.W.; Kyi, C. Analysis of Streamflow Response to Changing Climate Conditions Using SWAT Model. Civ. Eng. J. 2020, 6, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Hou, F.; Le, H.P. The Impact of Natural Resources, Energy Consumption, and Population Growth on Environmental Quality: Fresh Evidence from the United States of America. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, O. Collaborative Environmental Governance: Achieving Collective Action in Social-Ecological Systems. Science 2017, 357, aan1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maler, K.G. Economic Growth and the Environment. Encycl. Biodivers. 2001, 2, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapio, P. Towards a Theory of Decoupling: Degrees of Decoupling in the EU and the Case of Road Traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transp. Policy 2005, 12, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, C.; Cuddihy, J.; Engel-Yan, J. The Changing Metabolism of Cities. J. Ind. Ecol. 2007, 11, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, V.; Liu, J. Telecoupling: A New Frontier for Global Sustainability. Ecol. Soc. 2018, 23, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; He, S.; Li, G. Interaction between Urbanization and the Eco-Environment in the Pan-Third Pole Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 148011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhuo, H.; Song, H.; Wang, J.; Ren, L. Examination of a Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urbanization and the Eco-Environment: A Case Study in Qingdao, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 23981–23993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.N.; Wang, G.; Jiang, G.H.; Zhao, Y.X.; Zi, F.J.; Ye, L.; Liu, H.Y. Spatial-temporal differentiation and influencing factors of coupling coordination between urbanization and eco-environmental quality in Liaoning Province from 2005 to 2019. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Nieves, J.J.; Bondarenko, M.; Kerr, D.; Ves, N.; Yetman, G.; Sinha, P.; Clarke, D.J.; Sorichetta, A.; Stevens, F.R.; Gaughan, A.E. Measuring the Contribution of Built-Settlement Data to Global Population Mapping. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Open 2021, 3, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, J.; Olivia, S. Night Lights in Economics: Sources and Uses. J. Econ. Surv. 2020, 34, 955–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sindín, X.S.; Chen, T.-H.K.; Prishchepov, A.V. Are Night-Time Lights a Good Proxy of Economic Activity in Rural Areas in Middle and Low-Income Countries? Examining the Empirical Evidence from Colombia. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 24, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.H.; Wu, Z.F.; Chen, Y.B.; Yang, Z.W.; Marinello, F. Analyzing the ecological environment and urbanization characteristics of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration based on Google Earth Engine. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anees, S.A.; Zhang, X.; Shakeel, M.; Al-Kahtani, M.A.; Khan, K.A.; Akram, M.; Ghramh, H.A. Estimation of Fractional Vegetation Cover Dynamics Based on Satellite Remote Sensing in Pakistan: A Comprehensive Study on the FVC and Its Drivers. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine-Rodríguez, R.; Inostroza, L.; Zepp, H. Does Urban Climate Follow Urban Form? Analysing Intraurban LST Trajectories versus Urban Form Trends in 3 Cities with Different Background Climates. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, D. Correlations between Urbanization and Vegetation Degradation across the World’s Metropolises Using DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2067–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.Q. A remote sensing urban ecological index and its application. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 7853–7862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boori, M.S.; Choudhary, K.; Paringer, R.; Kupriyanov, A. Spatiotemporal Ecological Vulnerability Analysis with Statistical Correlation Based on Satellite Remote Sensing in Samara, Russia. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, I.A.; Aziz, N.A. Monitoring of Surface Ecological Change Using Remote Sensing Technique over Al-Hawizeh Marsh, Southern Iraq. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 27, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.K.; Amoushahi, S.; Gholipour, M. Spatiotemporal Ecological Quality Assessment of Metropolitan Cities: A Case Study of Central Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Xie, P.; He, W.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Khanal, R. Spatiotemporal Change of Ecologic Environment Quality and Human Interaction Factors in Three Gorges Ecologic Economic Corridor, Based on RSEI. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Recent Changes in Glaciers in the Northern Tien Shan, Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Liu, X. A Simple Method to Improve Estimates of County-Level Economics in China Using Nighttime Light Data and GDP Growth Rate. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.; Ye, X.; Zheng, Z.; Li, D.; Sun, L.; Li, R.; Benya, S. Modeling Polycentric Urbanization Using Multisource Big Geospatial Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Lian, T.; Huang, Y.; Yao, S.; Ye, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, C.; Wu, J. Integration of Nighttime Light Remote Sensing Images and Taxi GPS Tracking Data for Population Surface Enhancement. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2019, 33, 687–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Shi, K.F.; Chen, Z.Q.; Liu, S.R.; Chang, Z.J. An Improved Time-Series DMSP-OLS-Like Data (1992–2020) in China by Integrating DMSP-OLS and SNPP-VIIRS. 2022. Harvard Dataverse, V3. Available online: https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN/GIYGJU (accessed on 14 April 2022). [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Wu, C. Intercalibration between DMSP/OLS and VIIRS Night-Time Light Images to Evaluate City Light Dynamics of Syria’s Major Human Settlement during Syrian Civil War. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5934–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.H.; Yang, Z.W.; Chen, Y.B.; Wu, Z.F.; Marinello, F. The Interannual Calibration and Global Nighttime Light Fluctuation Assessment Based on Pixel-Level Linear Regression Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baig, M.H.A.; Zhang, L.; Shuai, T.; Tong, Q. Derivation of a Tasselled Cap Transformation Based on Landsat 8 At-Satellite Reflectance. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Paolini, L. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval from LANDSAT TM 5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.S.; Xu, H.Q. A New Remote Sensing Index for Assessing the Spatial Heterogeneity in Urban Ecological Quality: A Case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. Integr. Monit. Assess. Manag. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.S.; Rikimaru, A.; Miyatake, S. Tropical Forest Cover Density Mapping. Trop. Ecol. 2002, 43, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.L.; Wang, C.X.; Gong, W.K.; Chen, Z.Q.; Shi, K.F.; Wu, B.; Hong, Y.C.; Li, Q.X.; Wu, J.P. Nighttime light remote sensing and urban studies: Data, methods, applications, and prospects. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 342–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews-Meyer, K.A. Agricultural Landscape Change and Stability in Northeast Thailand: Historical Patch-Level Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 101, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworek-Jakubska, J.; Filipiak, M.; Napierała-Filipiak, A. Understanding of Forest Cover Dynamics in Traditional Landscapes: Mapping Trajectories of Changes in Mountain Territories (1824–2016), on the Example of Jeleniogórska Basin, Poland. Forests 2020, 11, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomal, M. Evaluation of Coupling Coordination Degree and Convergence Behaviour of Local Development: A Spatiotemporal Analysis of All Polish Municipalities over the Period 2003–2019. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 71, 102992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X. The Spatial Differentiation of the Coupling Relationship between Urbanization and the Eco-Environment in Countries Globally: A Comprehensive Assessment. Ecol. Model. 2017, 360, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.H.; Dai, W.Y.; Huang, H.F.; Hu, Q.F. Coupling Coordination Analysis of Urbanization and Eco-environment System in Jinjiang Using Landsat Series Data and DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. J. Fujian Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2018, 34, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, F.; Jin, L.; Yang, Y.; Bilgaev, A. Quantitative Analysis of the Coupling Coordination Degree Between Urbanization and Eco-Environment in Mongolia. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Dan, S.R.; Yu, Y. Dynamics between Global Value Chain Participation, CO2 Emissions, and Economic Growth: Evidence from a Panel Vector Autoregression Model. Energy Econ. 2022, 109, 105965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütkepohl, H. New Introduction to Multiple Time Series Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 21–774. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, R.; Tzavalis, E. Inference for Unit Roots in Dynamic Panels Where the Time Dimension Is Fixed. J. Econom. 1999, 91, 201–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Das, S.; Pattanayak, J.M.; Bera, B.; Shit, P.K. Assessment of Ecological Environment Quality in Kolkata Urban Agglomeration, India. Urban Ecosyst. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariken, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, K.; Fang, C.; Kung, H.-T. Coupling Coordination Analysis of Urbanization and Eco-Environment in Yanqi Basin Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naustdalslid, J. Circular Economy in China—The Environmental Dimension of the Harmonious Society. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2014, 21, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.H.; Wu, Z.F.; Chen, Y.B.; Yang, Z.W.; Marinello, F. Exploration of Eco-Environment and Urbanization Changes in Coastal Zones: A Case Study in China over the Past 20 Years. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liu, C.; Xia, Y.; Da, B. Examining the Coordination between Urbanization and Eco-Environment Using Coupling and Spatial Analyses: A Case Study in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yang, F.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Huang, J.; Wei, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Quantization of the Coupling Mechanism between Eco-Environmental Quality and Urbanization from Multisource Remote Sensing Data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.H.; Wang, C. Unprecedented Urbanisation in Asia and Its Impacts on the Environment. Aust. Econ. Rev. 2014, 47, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.; Antonelli, P.; Pozzi, C. Emerging Green-Tech Specializations and Clusters—A Network Analysis on Technological Innovation at the Metropolitan Level. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Data | Spatial Resolution | Time Resolution | Source | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 5, 8 | 30 m | 16-Day | Google Earth Engine | Calculate the NDVI, NDBSI, WET, LST |
| DMSP-OLS | 1000 m | Annual | Dataset ([35]) | Calculate the LAP, MLI, CNLI |
| The administrative division data | 1:1 million | 2015 | RESDC 1 | Use basic base map data and perform zonal statistics |
| Coupling Degree | Coupling Coordination Degree | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0.0, 0.3] | Separated stage | [0, 0.1] | Extreme disorder | (0.5, 0.6] | Barely coordination |
| (0.3, 0.5] | Antagonism stage | (0.1, 0.2] | Severe disorder | (0.6, 0.7] | Primary coordination |
| (0.5, 0.8] | Running-in stage | (0.2, 0.3] | Moderate disorder | (0.7, 0.8] | Intermediate coordination |
| (0.8, 1.0) | High-level coupling | (0.3, 0.4] | Mild disorder | (0.8, 0.9] | Good coordination |
| 1.0 | Benign resonant coupling | (0.4, 0.5] | Near disorder | (0.9, 1.0] | Quality coordination |
| Region | Urumqi | SYBK | TS | SMG | TTH | NU | UC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalue | PC1 1 | 0.022 | 0.016 | 0.031 | 0.045 | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.023 |
| PC2 2 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.007 | |
| PC3 3 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| PC4 4 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| The eigenvalue contribution rate of PC1/% | 74.72 | 86.67 | 74.93 | 86.32 | 92.59 | 91.21 | 75.25 | |
| Track Code | Proportion | Track Code | Proportion | Track Code | Proportion | Track Code | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21111 | 11.43% | 22211 | 5.86% | 32233 | 1.48% | 33323 | 2.31% |
| 21211 | 0.59% | 22212 | 2.93% | 32322 | 1.03% | 43333 | 0.98% |
| 22111 | 5.26% | 22221 | 1.20% | 32333 | 0.72% | 43433 | 0.70% |
| 22112 | 1.79% | 22322 | 0.61% | 33222 | 0.96% | 44433 | 2.38% |
| 22122 | 1.97% | 32222 | 6.26% | 33322 | 3.95% | 44434 | 1.05% |
| Variable | U | E |
|---|---|---|
| Harris–Tzavalis test | −0.786 1 (0.0000) | −0.585 1 (0.0016) |
| Stationarity | Stationary | Stationary |
| Order | Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) | Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) | Hannan-Quinn Information Criterion (HQIC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −3.596 a | −5.412 a | −1.605 a |
| 2 | −1.809 | −2.415 | −1.146 |
| Variable | Stage | DU 1 | DE 2 | Variable | Stage | DU | DE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DU | 1 | 1 | 0 | DU | 11 | 0.642 | 0.358 |
| DE | 1 | 0.002 | 0.998 | DE | 11 | 0.007 | 0.993 |
| DU | 2 | 0.804 | 0.196 | DU | 12 | 0.641 | 0.359 |
| DE | 2 | 0.004 | 0.996 | DE | 12 | 0.007 | 0.993 |
| DU | 3 | 0.719 | 0.281 | DU | 13 | 0.641 | 0.359 |
| DE | 3 | 0.005 | 0.995 | DE | 13 | 0.007 | 0.993 |
| DU | 4 | 0.681 | 0.319 | DU | 14 | 0.641 | 0.359 |
| DE | 4 | 0.006 | 0.994 | DE | 14 | 0.007 | 0.993 |
| DU | 5 | 0.663 | 0.337 | DU | 15 | 0.641 | 0.359 |
| DE | 5 | 0.006 | 0.994 | DE | 15 | 0.007 | 0.993 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, M.; Liu, H. Spatiotemporal Change of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Oasis City and Its Correlation with Urbanization Based on RSEI: A Case Study of Urumqi, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9227. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159227
Zhang J, Zhou Q, Cao M, Liu H. Spatiotemporal Change of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Oasis City and Its Correlation with Urbanization Based on RSEI: A Case Study of Urumqi, China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(15):9227. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159227
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingjing, Qian Zhou, Min Cao, and Hong Liu. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Change of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Oasis City and Its Correlation with Urbanization Based on RSEI: A Case Study of Urumqi, China" Sustainability 14, no. 15: 9227. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159227
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhou, Q., Cao, M., & Liu, H. (2022). Spatiotemporal Change of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Oasis City and Its Correlation with Urbanization Based on RSEI: A Case Study of Urumqi, China. Sustainability, 14(15), 9227. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159227





