Environmental Uncertainties and Competitive Advantage: A Sequential Mediation Model of Supply Chain Integration and Supply Chain Agility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theories and Hypotheses
2.1. Environmental Uncertainties
2.2. Supply Chain Integration
2.3. Supply Chain Agility
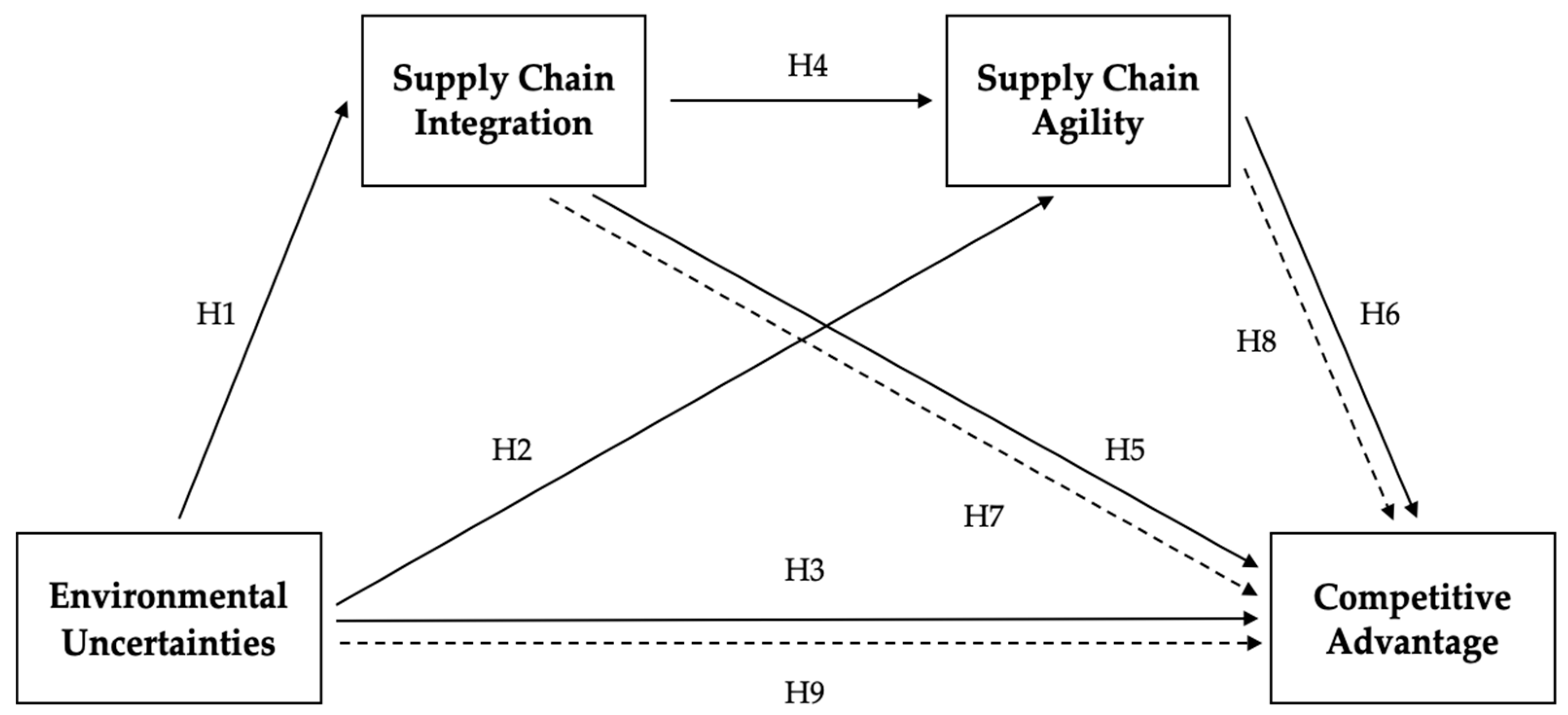
2.4. Sequential Mediation
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Design
3.1.1. Measurement Items
3.1.2. Data Collection
3.1.3. Common Method Bias and Non-Response Bias
3.2. Data Analysis
3.2.1. Demographic Data
3.2.2. Measurement Model Results
3.2.3. Structural Model Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Theoretical Implications
4.2. Managerial Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naughton, S.; Golgeci, I.; Arslan, A. Supply chain agility as an acclimatisation process to environmental uncertainty and organisational vulnerabilities: Insights from British SMEs. Prod. Plan. Control 2020, 31, 1164–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S. An empirical-relational investigation on supply chain responsiveness. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. 2015, 20, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merschmann, U.; Thonemann, U.W. Supply chain flexibility, uncertainty and firm performance: An empirical analysis of German manufacturing firms. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 130, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulis, A.; Wisker, Z. Modeling employee-based brand equity (EBBE) and perceived environmental uncertainty (PEU) on a firm’s performance. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 2016, 25, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukor, A.A.; Newaz, S.; Khalilur Rahman, M.; Taha, A.Z. Supply chain integration and its impact on supply chain agility and organizational flexibility in manufacturing firms. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2021, 16, 1721–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troise, C.; Corvello, V.; Ghobadian, A.; O’Regan, N. How can SMEs successfully navigate VUCA environment: The role of agility in the digital transformation era. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 174, 121227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krickx, G.A. The Relationship Between Uncertainty and Vertical Integration. Int. J. Organ. Anal. 2000, 8, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D.M.; Cooper, M.C.; Pagh, J.D. Supply Chain Management: Implementation Issues and Research Opportunities. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 1998, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Shang, K.C.; Lirn, T.C.; Lai, K.H.; Lun, Y.H.V. Supply chain resilience, firm performance, and management policies in the liner shipping industry. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2018, 110, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markley, M.J.; Davis, L. Exploring future competitive advantage through sustainable supply chains. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2007, 37, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredendall, L.D.; Hill, E. Basics of Supply Chain Management; The St. Lucie Press: Port St. Lucie, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Birasnav, M.; Bienstock, J. Supply chain integration, advanced manufacturing technology, and strategic leadership: An empirical study. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 130, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.B. Characteristics of Organizational Environments and Perceived Environmental Uncertainty. Quarterly 1972, 17, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, C.Y.; Boon-Itt, S.; Wong, C.W.Y. The contingency effects of environmental uncertainty on the relationship between supply chain integration and operational performance. J. Oper. Manag. 2011, 29, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, E.; Humphreys, P.; McIvor, R. Reducing supply chain environmental uncertainty through e-intermediation: An organisation theory perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 114, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Huo, B.; Sun, L. Relationships between intra-organizational resources, supply chain integration and business performance: An extended resource-based view. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2014, 114, 1186–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, J.H.; Singh, H. The relational view: Cooperative strategy and sources of interorganizational competitive advantage. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1998, 23, 660–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelilah, B.; el Korchi, A.; Amine Balambo, M. Agility as a combination of lean and supply chain integration: How to achieve a better performance. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2021, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, A.C.; Senna, P.P.; Marchiori, I.; Kalaitzi, D.; Balech, S. Scenario-Driven Supply Chain Charaterization Using a Multi-Dimensional Approach. In Next Generation Supply Chains; Fornasiero, R., Sardesai, S., Barros, A.C., Matopoulos, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, J.M. The effect of environmental uncertainty and strategic applications of IS on a firm’s performance. Inf. Manag. 2003, 40, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, R.A.; Green, K.W. Environmental uncertainty and supply chain performance: The effect of agility. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2022, 33, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Ellinger, A.E.; Kim, K.K.; Franke, G.R. Supply chain integration and firm financial performance: A meta-analysis of positional advantage mediation and moderating factors. Eur. Manag. J. 2016, 34, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W. The effect of supply chain integration on the alignment between corporate competitive capability and supply chain operational capability. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2006, 26, 1084–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Won Lee, C.; Kwon, I.G.; Severance, D. Relationship between supply chain performance and degree of linkage among supplier, internal integration, and customer. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2007, 12, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zailani, S.; Rajagopal, P. Supply chain integration and performance: US versus East Asian companies. Supply Chain Manag. 2005, 10, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammad, M.F.; Basu, S.; Munjal, S.; Clegg, J.; Shoham, O.B. Strategic agility, environmental uncertainties and international performance: The perspective of Indian firms. J. World Bus. 2021, 56, 101218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J. Developing a model for supply chain agility and innovativeness to enhance firms’ competitive advantage. Manag. Decis. 2019, 57, 1511–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qrunfleh, S.; Tarafdar, M. Lean and agile supply chain strategies and supply chain responsiveness: The role of strategic supplier partnership and postponement. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2013, 18, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, J.; Salancik, G. The External Control of Organizations: A Resource Dependence Perspective; Stanford University Press: Redwood City, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich, H. Organizations and Environments; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Milliken, F.J. Three Types of Perceived Uncertainty about the Environment: State, Effect, and Response Uncertainty. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1987, 12, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, O.E. The Economic Institutions of Capitalism Firms, Markets, Relational Contracting; Collier Macmillan Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, O.E. Transaction cost economics. In Handbook of Industrial Organizations, 1st ed.; Schmalensee, R., Willig, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 1, pp. 135–182. [Google Scholar]
- Rasi, R.E.; Abbasi, R.; Hatami, D. The Effect of Supply Chain Agility Based on Supplier Innovation and Environmental Uncertainty. Int. J. Supply Oper. Manag. 2019, 6, 94–109. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, B.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wei, J.; Hua, Z. Environmental uncertainty, specific assets, and opportunism in 3PL relationships: A transaction cost economics perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 203, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D. Organizations in Action; Mc-Graw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Fynes, B.; de Búrca, S.; Marshall, D. Environmental uncertainty, supply chain relationship quality and performance. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2004, 10, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.Y.; Boon-Itt, S. The influence of institutional norms and environmental uncertainty on supply chain integration in the Thai automotive industry. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 115, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhao, L.; Li, G.; Sun, L. The effect of environmental uncertainty on supply chain integration in Chinese manufacturing industry. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management, ICSSSM’ 10, Tokyo, Japan, 28–30 June 2010; pp. 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulraj, A.; Chen, I.J. Environmental Uncertainty and Strategic Supply Management: A Resource Dependence Perspective and Performance Implications. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2007, 43, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prater, E.; Biehl, M.; Smith, M.A. International supply chain agility: Tradeoffs between flexibility and uncertainty. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2001, 21, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christopher, M. The Agile Supply Chain Competing in Volatile Markets. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2000, 29, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sheu, C. The Impact of Competitive Strategy and Supply Chain Strategy on Business Performance: The Role of Environmental Uncertainty. Decis. Sci. 2011, 42, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sharifi, H. A methodology for achieving agility in manufacturing organisations. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2000, 20, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligor, D.M. The Role of Supply Chain Agility in Achieving Supply Chain Fit. Decis. Sci. 2016, 47, 524–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güner, H.M.; Çemberci, M.; Civelek, M.E. The effect of supply chain agility on firm performance. J. Int. Trade Logist. Law 2018, 4, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer, B.; Grønhaug, K. Uncertainty, flexibility, and sustained competitive advantage. J. Bus. Res. 2004, 57, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gamero, M.D.; Molina-Azorín, J.F.; Claver-Cortés, E. Environmental uncertainty and environmental management perception: A multiple case study. J. Bus. Res. 2011, 64, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagozoglu, N. Environmental uncertainty, strategic planning, and technological competitive advantage. Technovation 1993, 13, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Vonderembse, M.A.; Lim, J.S. Value chain flexibility: A dichotomy of competence and capability. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2002, 40, 561–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shannassy, T. Sustainable competitive advantage or temporary competitive advantage: Improving understanding of an important strategy construct. J. Strategy Manag. 2008, 1, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.H.; Hu, T.C. Knowledge transfer and competitive advantage on environmental uncertainty: An empirical study of the Taiwan semiconductor industry. Technovation 2007, 27, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Kim, S.H.; Seo, M.K. Franchise Core Competency and Its Relationship with Environmental Uncertainty, Competitive Advantage, and Financial Performance: An Empirical Assessment of Food-Service Franchise Firms. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2015, 20, 1151–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanpoucke, E.; Vereecke, A.; Muylle, S. Leveraging the impact of supply chain integration through information technology. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2017, 37, 510–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirunyawipada, T.; Beyerlein, M.; Blankson, C. Cross-functional integration as a knowledge transformation mechanism: Implications for new product development. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2010, 39, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.H.; Hsu, T.T. Cross-Functional collaboration, competitive intensity, knowledge integration mechanisms, and new product performance: A mediated moderation model. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2014, 43, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Narasimhan, R.; Talluri, S. Supplier integration—Finding an optimal configuration. J. Oper. Manag. 2006, 24, 563–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Pan, J.; Song, Y. Dependence on supplier, supplier trust and green supplier integration: The moderating role of contract management difficulty. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, E. Supplier integration in new product development: Computer mediated communication, knowledge exchange and buyer performance. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2013, 42, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cavusgil, E.; Cavusgil, S.T. An investigation of the black-box supplier integration in new product development. J. Bus. Res. 2014, 67, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, R.; Yu, W.; Gimenez, C.; Fynes, B.; Wiengarten, F. Customer integration and operational performance: The mediating role of information quality. Decis. Support Syst. 2015, 80, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrosen, S. Customer involvement in new product development: A relationship marketing perspective. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2005, 8, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmeier, P. Customer integration strategies for innovation projects: Anticipation and brokering. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2009, 48, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trkman, P.; Groznik, A. Measurement of supply chain integration benefits. Interdiscip. J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. 2006, 1, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Blackstone, J.H. APICS Dictionary, 14th ed.; APICS: Chicago, IL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, G.C.; Johnson, M. Integrating the Supply Chain … 25 years on. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2016, 46, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.L. The Triple—A Supply Chain. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2004, 82, 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Gligor, D.M. The role of demand management in achieving supply chain agility. Supply Chain Manag. 2014, 19, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, E.W.T.; Chau, D.C.K.; Chan, T.L.A. Information technology, operational, and management competencies for supply chain agility: Findings from case studies. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2011, 20, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Long, Y. The role of supply chain integration in the transformation of food manufacturers: A case study from China. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2021, 24, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayezi, S.; Zomorrodi, M. The role of relationship integration in supply chain agility and flexibility development: An Australian perspective. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2015, 26, 1126–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohlich, M.T.; Westbrook, R. Arcs of integration: An international study of supply chain strategies. J. Oper. Manag. 2001, 19, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, A.; Aslan, E. Supply Chain Integration, Competition Capability and Business Performance: A Study on Turkish SMEs. Asian J. Bus. Manag. 2011, 3, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Morash, E.A.; Clinton, S.R. Supply Chain Integration: Customer Value through Collaborative Closeness versus Operational Excellence. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 1998, 6, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W. An investigation on the direct and indirect effect of supply chain integration on firm performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2009, 119, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukati, I.; Bakar, A.; Holloway, R.; Hamid, A.; Baharun, R. Competitive Advantage through Supply Chain Responsiveness and Supply Chain Integration. Int. J. Bus. Commer. 2012, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L. Acquiring competitive advantage in industry through supply chain integration: A case study of Yue Yuen Industrial Holdings Ltd. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2007, 20, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Sheikhi, N. An Empirical Examination of Competitive Capability’s Contribution toward Firm Performance: Moderating Role of Perceived Environmental Uncertainty. Int. Bus. Res. 2012, 5, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinaga, O.; Riantani, S.; Hendayana, Y.; Mohd Saudi, M.H.; Zainudin, Z. Impact of Supply Chain Integration on Competitive Advantage. Int. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2019, 8, 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Feizabadi, J.; Gligor, D.M.; Alibakhshi, S. Examining the synergistic effect of supply chain agility, adaptability and alignment: A complementarity perspective. Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 26, 514–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme-Medina, M.; Stevenson, M.; Barrales-Molina, V.; Llorens-Montes, F.J. Coopetition in business Ecosystems: The key role of absorptive capacity and supply chain agility. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 146, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, E. A Bibliometric Analysis of Supply Chain Agility Literature. In Proceedings of the 20th International Business Congress, Giresun, Turkey, 10–13 June 2021; pp. 1092–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Power, D.J.; Sohal, A.S.; Rahman, S.U. Critical success factors in agile supply chain management an empirical study. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2001, 31, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhsin, M.; Taufik, H.; Ridwan, A.; Suryanto, T. The mediation role of supply chain agility on supply chain orientation-supply chain performance link. Uncertain Supply Chain Manag. 2022, 10, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimienė, K. Supply Chain Agility Concept Evolution (1990–2010). Econ. Manag. 2011, 16, 892–899. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Chai, S. The impact of supplier innovativeness, information sharing and strategic sourcing on improving supply chain agility: Global supply chain perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 187, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashi, P.; Centobelli, R.; Cerchione; Ertz, M. Agile supply chain management: Where did it come from and where will it go in the era of digital transformation? Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 90, 324–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahamid, S.; Awwad, A.; Mcadams, A.C. Effects of Organizational Agility and Knowledge Sharing on Competitive Advantage: An Empirical Study in Jordan. Int. J. Manag. 2010, 27, 387–404. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.J.; Tseng, M.L.; Chiu, A.S.F.; Lim, M.K. Achieving competitive advantage through supply chain agility under uncertainty: A novel multi-criteria decision-making structure. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 190, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfalla-Luque, R.; Machuca, J.A.D.; Marin-Garcia, J.A. Triple-A and competitive advantage in supply chains: Empirical research in developed countries. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 203, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Y.; Hsu, M.H.; Hwang, W.J. The impact of alignment between supply chain strategy and environmental uncertainty on SCM performance. Supply Chain Manag. 2009, 14, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. Towards a dynamic theory of strategy. Strateg. Manag. J. 1991, 12, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsakiene, R. Determining competitive advantage: The analytic hierarchy process. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2004, 5, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harsasi, M. Minrohayati, The impact of supply chain management practices on competitive advantage. Int. J. Econ. Policy Emerg. Econ. 2017, 10, 240–247. [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner, R.; Rogers, D.S.; Charvet, F.F. A Meta-Analysis of Supply Chain Integration and Firm Performance. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2013, 49, 34–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.B. Competing through manufacturing and the new manufacturing paradigm: Is manufacturing strategy passé? Prod. Oper. Manag. 1996, 5, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, B.B.; Schroeder, R.G.; Flynn, E.J. World class manufacturing: An investigation of Hayes and Wheel wright’s foundation. J. Oper. Manag. 1999, 17, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, G.A.; van der Vaart, T.; Pieter van Donk, D. The influence of business conditions on supply chain information-sharing mechanisms: A study among supply chain links of SMEs. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 113, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, B.B.; Huo, B.; Zhao, X. The impact of supply chain integration on performance: A contingency and configuration approach. J. Oper. Manag. 2010, 28, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.L.; Eisenhardt, K.M. Competing on the Edge: Strategy as Structured Chaos; Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Swafford, P.M.; Ghosh, S.; Murthy, N. The antecedents of supply chain agility of a firm: Scale development and model testing. J. Oper. Manag. 2006, 24, 170–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi, R.; Saranga, H. Uncertainty and supply chain risk: The moderating role of supply chain flexibility in risk mitigation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 193, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.J.; Roman, I.E.; Ramos, E.; Patrucco, A.S. The value of supply chain integration in the Latin American agri-food industry: Trust, commitment and performance outcomes. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2021, 32, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; Organ, D.W. Self-Reports in Organizational Research: Problems and Prospects. J. Manag. 1986, 12, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamoah, D.; Nuertey, D.; Agyei-Owusu, B.; Akyeh, J. The effect of supply chain responsiveness on customer development. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2021, 32, 1190–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.S.; Overton, T.S. Estimating Nonresponse Bias in Mail Surveys. J. Mark. Res. 1977, 14, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mani, V.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Mani, K.T.N. Supply chain social sustainability in small and medium manufacturing enterprises and firms’ performance: Empirical evidence from an emerging Asian economy. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 227, 107656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Textile, Ready-to-Wear Clothing and Leather Products Sectors Report; Türkiye Promotion Group (TTG): Ankara, Turkey, 2019.
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahi, S.; Ghani, M.A.; Alnaser, F.M.I. Predicting customer’s intentions to use internet banking: The role of technology acceptance model (TAM) in e-banking. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2017, 7, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, B.M. A Primer of LISREL; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.W.; Cudeck, R. Alternative Ways of Assessing Model Fit. Sociol. Methods Res. 1992, 21, 230–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The Moderator-Mediator Variable Distinction in Social Psychological Research: Conceptual, Strategic, and Statistical Considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Q.H. Influence of Supply Chain Uncertainty on the Agility Performance of Malaysian Companies: A Mediating Effect of Supply Chain Integration. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 754–762. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, A.K.W.; Tang, E.; Yam, R.C.M. Effects of Supplier and Customer Integration on Product Innovation and Performance: Empirical Evidence in Hong Kong Manufacturers. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2010, 27, 761–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, B.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shou, Y. The impact of human capital on supply chain integration and competitive performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 178, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.; Tran, O.; Park, K. Electronic commerce applications for supply chain integration and competitive capabilities: An empirical study. Benchmarking 2010, 17, 539–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Shah, R.; Babakus, E. When to Mass Customize: The Impact of Environmental Uncertainty. Decis. Sci. 2012, 43, 851–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghafoori, S.H.; Andalib, D.; Keshavarz, P. Developing Green Performance Through Supply Chain Agility in Manufacturing Industry: A Case Study Approach. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2017, 24, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, Y.Y.; Gunasekaran, A.; Musa, A.; Dauda, M.; El-Berishy, N.M.; Cang, S. A relational study of supply chain agility, competitiveness and business performance in the oil and gas industry. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 147, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.C. The influence of green supply chain integration and environmental uncertainty on green innovation in Taiwan’s IT industry. Supply Chain Manag. 2013, 18, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, W.; Nedelko, Z. Global Sourcing Strategies: A framework for lean, agile, and leagile. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zabidi, A.; Rehman, A.U.; Alkahtani, M. An approach to assess sustainable supply chain agility for a manufacturing organization. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, Z.J.H.; Siagian, H.; Jie, F. Impact of internal integration, supply chain partnership, supply chain agility, and supply chain resilience on sustainable advantage. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| N | % | N | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employee | Position | ||||
| 0–9 | 54 | 13 | Manufacturing Manager | 215 | 51.9 |
| 10–49 | 96 | 23.2 | Quality Control Manager | 26 | 6.3 |
| 50–249 | 126 | 30.4 | Chief Operating Officer | 4 | 1 |
| 250 and above | 138 | 33.3 | Product Development Manager | 19 | 4.6 |
| Sector | Purchasing Manager | 17 | 4.1 | ||
| Food products | 62 | 15 | Supply Chain Manager | 89 | 21.5 |
| Beverages | 5 | 1.2 | Production Planning Manager | 22 | 5.3 |
| Tobacco products | 2 | 0.5 | Assistant General Manager | 12 | 2.9 |
| Textiles | 116 | 28 | General Manager | 10 | 2.4 |
| Wearing apparel | 21 | 5.1 | Region | ||
| Leather and related products | 2 | 0.5 | Mediterranean | 23 | 5.6 |
| Paper and paper products | 9 | 2.2 | Aegean | 42 | 10.1 |
| Chemicals and chemical products | 22 | 5.3 | Marmara | 202 | 48.8 |
| Basic pharmaceutical products | 14 | 3.4 | Central Anatolia | 65 | 15.7 |
| Rubber and plastic products | 12 | 2.9 | Black Sea | 11 | 2.7 |
| Other non-metallic mineral products | 3 | 0.7 | East Anatolia | 40 | 9.7 |
| Manufacture of basic metals | 18 | 4.3 | Southeastern Anatolia | 31 | 7.5 |
| Fabricated metal products | 13 | 3.1 | Source of raw material | ||
| Comp., electronic and optical products | 2 | 0.5 | Domestic | 93 | 22.5 |
| Electrical equipment | 1 | 0.2 | Abroad | 27 | 6.5 |
| Machinery and equipment | 31 | 7.5 | Both of them | 294 | 71 |
| Motor veh., trailers and semi-trailers | 5 | 1.2 | Market | ||
| Other transport equipment | 2 | 0.5 | Domestic | 85 | 20.5 |
| Furniture | 7 | 1.7 | Abroad | 54 | 13 |
| Other manufacturing | 67 | 16.2 | Both of them | 275 | 66.4 |
| Construct | Loadings | t Value | AVE | CR | CA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Uncertainties | |||||
| Demand fluctuates drastically from week to week | 0.76 | 17.68 | 0.59 | 0.89 | 0.894 |
| Total manufacturing volume fluctuates drastically from week to week | 0.86 | 21.21 | |||
| Mix of products you produce changes drastically from week to week | 0.87 | 21.60 | |||
| Supply requirements (volume and mix) vary drastically from week to week | 0.86 | 21.42 | |||
| Products are characterized by a lot of technical modifications | 0.49 | 10.16 | |||
| Suppliers frequently need to carry out modifications to the parts/components they deliver to your plant | 0.70 | 15.86 | |||
| Supply Chain Integration | |||||
| The partners’ information is shared along the supply chain | 0.60 | 12.73 | 0.57 | 0.84 | 0.826 |
| The problems or difficulties of the partners are promptly addressed through the exchange of information | 0.76 | 17.36 | |||
| The supply chain partners rely on communication plans | 0.84 | 19.99 | |||
| The supply chain partners collaborate on the initiatives of new projects | 0.81 | 18.68 | |||
| Supply Chain Agility | |||||
| Speed in reducing manufacturing lead time | 0.71 | 16.95 | 0.51 | 0.86 | 0.856 |
| Speed in reducing product development cycle time | 0.78 | 18.03 | |||
| Speed in increasing frequency of new product introductions | 0.74 | 16.79 | |||
| Speed in increasing levels of product customization | 0.63 | 13.44 | |||
| Speed in adjusting delivery capability | 0.70 | 15.62 | |||
| Speed in improving responsiveness to changing market needs | 0.72 | 16.16 | |||
| Competitive Advantage | |||||
| Compared with our competitors, we offer unique benefits and novel features to our customers | 0.73 | 16.69 | 0.63 | 0.89 | 0.893 |
| Compared with our competitors, we offer high-quality products to our customers | 0.77 | 18.06 | |||
| Compared with our competitors, we provide dependable delivery | 0.80 | 19.19 | |||
| Compared with our competitors, we provide customized products | 0.87 | 21.73 | |||
| Compared with our competitors, we deliver products to the market quickly | 0.81 | 19.26 | |||
| CA | EU | SCA | SCI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Competitive Advantage | ||||
| Environmental Uncertainties | 0.316 | |||
| Supply Chain Agility | 0.734 | 0.373 | ||
| Supply Chain Integration | 0.532 | 0.477 | 0.583 |
| Hs | Hypothesized Path | Beta | t Value | p Value | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Environmental Uncertainties → Supply Chain Integration | 0.490 * | 9.756 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H2 | Environmental Uncertainties → Supply Chain Agility | 0.144 ** | 2.453 | 0.014 | Supported |
| H3 | Environmental Uncertainties → Competitive Advantage | 0.351 * | 7.865 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H4 | Supply Chain Integration → Supply Chain Agility | 0.516 * | 8.739 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H5 | Supply Chain Integration → Competitive Advantage | 0.151 ** | 2.242 | 0.025 | Supported |
| H6 | Supply Chain Agility → Competitive Advantage | 0.643 * | 11.363 | 0.000 | Supported |
| H7 | Environmental Uncertainties → Supply Chain Integration → Competitive Advantage | 0.074 ** | 2.119 | 0.034 | Supported |
| H8 | Environmental Uncertainties → Supply Chain Agility → Competitive Advantage | 0.092 ** | 2.305 | 0.021 | Supported |
| H9 | Environmental Uncertainties → Supply Chain Integration → Supply Chain Agility → Competitive Advantage | 0.162 * | 5.589 | 0.000 | Supported |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koç, E.; Delibaş, M.B.; Anadol, Y. Environmental Uncertainties and Competitive Advantage: A Sequential Mediation Model of Supply Chain Integration and Supply Chain Agility. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148928
Koç E, Delibaş MB, Anadol Y. Environmental Uncertainties and Competitive Advantage: A Sequential Mediation Model of Supply Chain Integration and Supply Chain Agility. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148928
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoç, Erdinç, Muhammet Burak Delibaş, and Yaprak Anadol. 2022. "Environmental Uncertainties and Competitive Advantage: A Sequential Mediation Model of Supply Chain Integration and Supply Chain Agility" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148928
APA StyleKoç, E., Delibaş, M. B., & Anadol, Y. (2022). Environmental Uncertainties and Competitive Advantage: A Sequential Mediation Model of Supply Chain Integration and Supply Chain Agility. Sustainability, 14(14), 8928. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148928






