An Empirical Study of Situational Teaching: Agricultural Location in High School Geography
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- What is the current status of situational learning in geography education?
- (2)
- Are the effects of teaching with OSTE better than those of traditional teaching methods?
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. The Result of Survey of Geography Teacher
4.2. Experimental Results
Comparative Analysis of Test Scores before and after the Test
4.3. Achivement of Other Teaching Objectives
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- MOE&PRC. The Ministry of Education Held a Kick-Off Meeting for the Revision of Curriculum Standards for Ordinary Senior High Schools. Available online: http://www.moe.gov.cn/jyb_xwfb/gzdt_gzdt/moe_1485/201412/t20141208_180670.html (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- MOE&PRC. High School Geography Curriculum Standard; People’s Education Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- He, J. Opinions of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on Accelerating the Construction of Ecological Civilization. People’s Daily, 6 May 2015; 1. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J. Geography should be the forerunner of education in ecological civilization. Teach. Mater. Educ. Prim. Second. Sch. 2015, 10, 52–53. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Xu, X. Practice and thinking of geography situational teaching in junior middle school-taking the “World Settlements” as an example. Geogr. Teach. 2019, 1, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Arendt, M. Situational teaching—Versuch Einer Abgrenzung (Situational Teaching—An Attempt at Delimitation). Englisch 1979, 14, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.S.; Collins, A.; Duguid, P. Situated cognition and culture of learning. Educ. Res. 1989, 18, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Ten key points of core competencies evaluation. People’s Educ. 2017, 1, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.; Yang, X.; Pan, Y. Learning progression of problem finding in real-world complex geographic tasks. Glob. Educ. 2020, 49, 44–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J. Exploring the path of situational teaching under the background of core competencies. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Politics 2021, 29, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, W. The use of “One situation to the end” in senior high school geography teaching-taking “the influence of ocean currents on geographical environment” as an example. Geogr. Teach. 2020, 4, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.; Duan, Y.; He, S.; Gong, Q.; Yao, Z. Analysis of sustainable development questions of college entrance examination geography papers in China: 2010–2020. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clivaz, S. Lesson study as a fundamental situation for the knowledge of teaching. Int. J. Lesson Leaning Stud. 2018, 7, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allport, G.W. The teaching-learning situation. Public Health Rep. 1953, 68, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, J. Situational Teaching of Chinese in Primary Schools; Jiangsu Education Press: Nanjing, China, 1996; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lave, J.; Wenger, E. Situated Learning: Legitimate Peripheral Participation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, R. Contemporary Educational Psychology; Beijing Normal University Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, D.J. Assessing constructions and constructing assessment: A dialogue. Educ. Technol. 1991, 31, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.H. Situational instruction: A strategy for facilitating the learning process. Lifelong Learn. 1989, 12, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Merrill, M.D. Constructivism and instructional design. Educ. Technol. 1991, 31, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Hornby, A.S. The situational approach in language teaching (I). ELT J. 1950, 4, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornby, A.S. The situational approach in language teaching (III). ELT J. 1950, 4, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.R. The structured dialogue: An attempt to integrate structural and situational. Approaches Lang. Teach. 1969, 7, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.; Loewen, S. Situational language teaching. TESOL Encycl. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2018, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognition and Technology Group. Anchored instruction and situated cognition revisited. Educ. Technol. 1993, 33, 52–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, A.; Hogg, G.; Ker, J. Innovative teaching in situational awareness. Clin. Teach. 2015, 12, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Z. The research of situational teaching mode of programming in high school with Scratch. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference, Chongqing, China, 20–22 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Nazir, S. Role of 5G and artificial intelligence for research and transformation of english situational teaching in higher studies. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021, 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. The setting-up of studying scene in class in the multimedia network. E-Educ. Res. 2001, 5, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. 40 years of situational education innovation. China Teach. Dly. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Luo, L. Psychological explanation on affective teaching—Remarks on the educational thoughts of Li Jilin. Educ. Res. 2007, 2, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hauptman, P.C. A structural approach vs. a situational approach to foreign-language teaching. Lang. Learn. 1971, 21, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, M. Learning and Memory: The Brain in Action; China Light Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005; p. 15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rotgans, J.I.; Schmidt, H.G. Situational interest and academic achievement in the active-learning classroom. Learn. Instr. 2011, 21, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, D.H.; Dixon, J.; Archer, J. Identifying underlying causes of situational interest in a science course for preservice elementary teachers. Sci. Educ. 2016, 100, 103–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y. Strategy of Situational Teaching in Junior Middle School Geography Classroom. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F. Use and thinking of situational teaching in junior middle school geography-taking “Change and distribution of precipitation” as an example. Geogr. Teach. 2015, 18, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, F.; Tang, J. Practice of situational teaching in junior middle school geography teaching-take “India ancient oriental civilization” as an example. Geogr. Teach. 2020, 12, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- McEnerney, K. Active learning and situational teaching: How to ACE a course. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1999, 12, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, A.F. Some reflections on motivating situations and situational teaching. Scand. J. Educ. Res. 1994, 38, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. The unique advantage of situational education and its construction. Educ. Res. 2009, 30, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Dohn, N.B.; Madsen, P.T.; Malte, H. The situational interest of undergraduate students in zoophysiology. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2009, 33, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulistyowati, F.; Budiyono; Slamet, I. The didactic situation in geometry learning based on analysis of learning obstacles and learning trajectory. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference, Malang, Indonesia, 2–3 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, D. The innovation based on transformative practice—Re-understanding of Li Jilin’s situational education thought. Curric. Teach. Mater. Method 2009, 29, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, L. Optimizing situations, realizing discipline education. Teach. Thought Political Study 2018, 6, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y. Application of situational teaching in college ideological and political course. China High. Educ. 2015, 2, 74–75. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y. On the value orientation in situational teaching. Geogr. Teach. 2019, 16, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z. Comparison between “one case to the end” and individualized teaching. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Politics 2020, 39, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.; Chen, Z. The application of “one case to the end” teaching method in politics teaching. Jiangxi Educ. 2005, 8, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M. One case to the end: An effective way to cultivate the core competencies of the discipline. Teach. Thought Political Study 2018, 3, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, D.; Yue, D. A case to the end for geographical situation design. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2021, 21, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W. A Study on the Teaching Design of “One Situation to the End” in Senior Middle School thought and Political Courses. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Practical research on life-oriented situational teaching—Take “the integrity and difference of the natural geographical environment” as an example. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2021, 8, 49–50. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. The instructional design strategy of situational thematic review of “One situation to the end”—Take Longyangxia as an example. Geogr. Teach. 2021, 10, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Perlstein, A.; Mortimer, M.; Robertson, D. Making sustainable development real through role-play: “The Mekong game” example. J. Sustain. Educ. 2017, 2, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Buchs, A.; Blanchard, O. Exploring the concept of sustainable development through role-playing. J. Econ. Educ. 2011, 42, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z. Relying on the local situation to implement the core competencies of geography—Taking “the change of agricultural location factors” as an example. Geogr. Teach. 2022, 4, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, P.; Zhang, S. Cultivate comprehensive competencies skillfully used local resources—Taking “the agriculture location factors” as an example. Geogr. Teach. 2022, 5, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Shao, J. Teaching discussion on agriculture location factors from the perspective of rural revitalization—Taking Xuwen pineapple as an Example. Geogr. Teach. 2021, 14, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, N. Teaching design based on real geographical situation—Taking agricultural location factors as an example. Geogr. Teach. 2020, 24, 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X. Develops local geographical resources and cultivates students’ practical ability in geography—Taking “Agriculture location” as an example. Geogr. Teach. 2019, 24, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Infiltration of geographical core competencies in classroom teaching—Take “the agriculture location factors and their changes” as an example. Ref. Middle Sch. Teach. 2020, 13, 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Huang, J. Exploration of geography teaching in senior high schools based on the cultivation of geographical practical ability—Taking “the change of agricultural location factors” as an example. Geogr. Teach. 2021, 24, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.; Yao, W. Instructional design of “Agriculture location” in senior high school geography under the new background—Taking “the excellent apple production area in China” as a situational case. Geogr. Teach. 2021, 14, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Wen, Z. Asking tea in Badong, tea fragrance floating in the Three Gorges—Instructional design” the choice of agriculture location” based on local geography. Geogr. Teach. 2017, 15, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Susan, S.M. How to Assess Higher-Order Thinking Skills in your Classroom; ASCD: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2010; pp. 5–68. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, J. Problems and Countermeasures of “One Case to the End” Teaching Method in High School Thinking and Political Teaching. Master’s Thesis, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. The Study of “One case to the end” is Used in the Teaching of “Economic Life.”. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Normal University, Hohhot, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W. Core Competencies-Oriented Classroom Teaching; Shanghai Educational Publishing House: Shanghai, China, 2017; pp. 196–255. [Google Scholar]
- Voogt, J.; Roblin, N.P. A comparative analysis of international frameworks for 21st century competences: Implications for national curriculum policies. J. Curric. Stud. 2012, 44, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CGE; IGU. International Charter on Geographical Education; International Geographical Union; Commission on Geographical Education: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
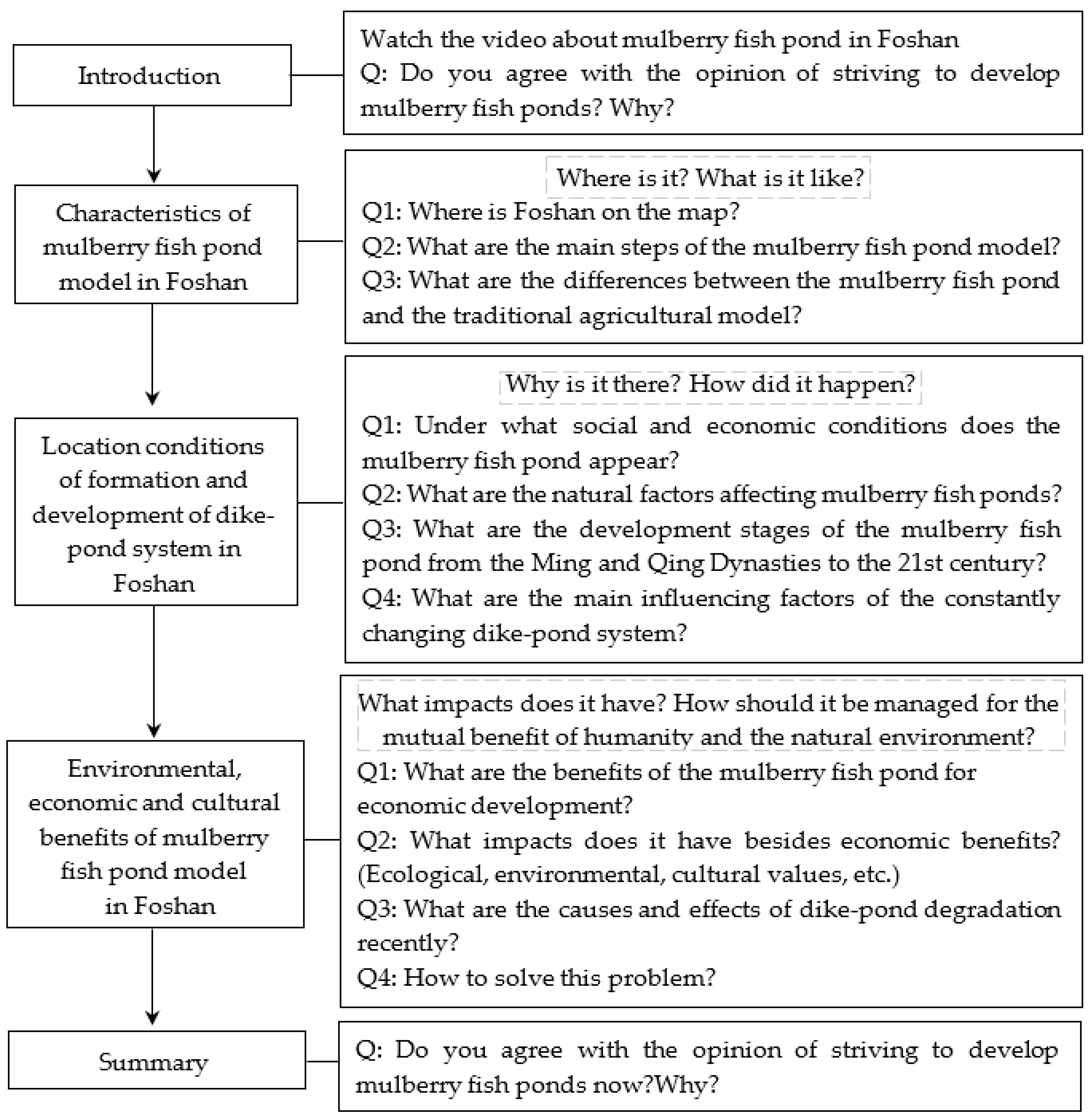




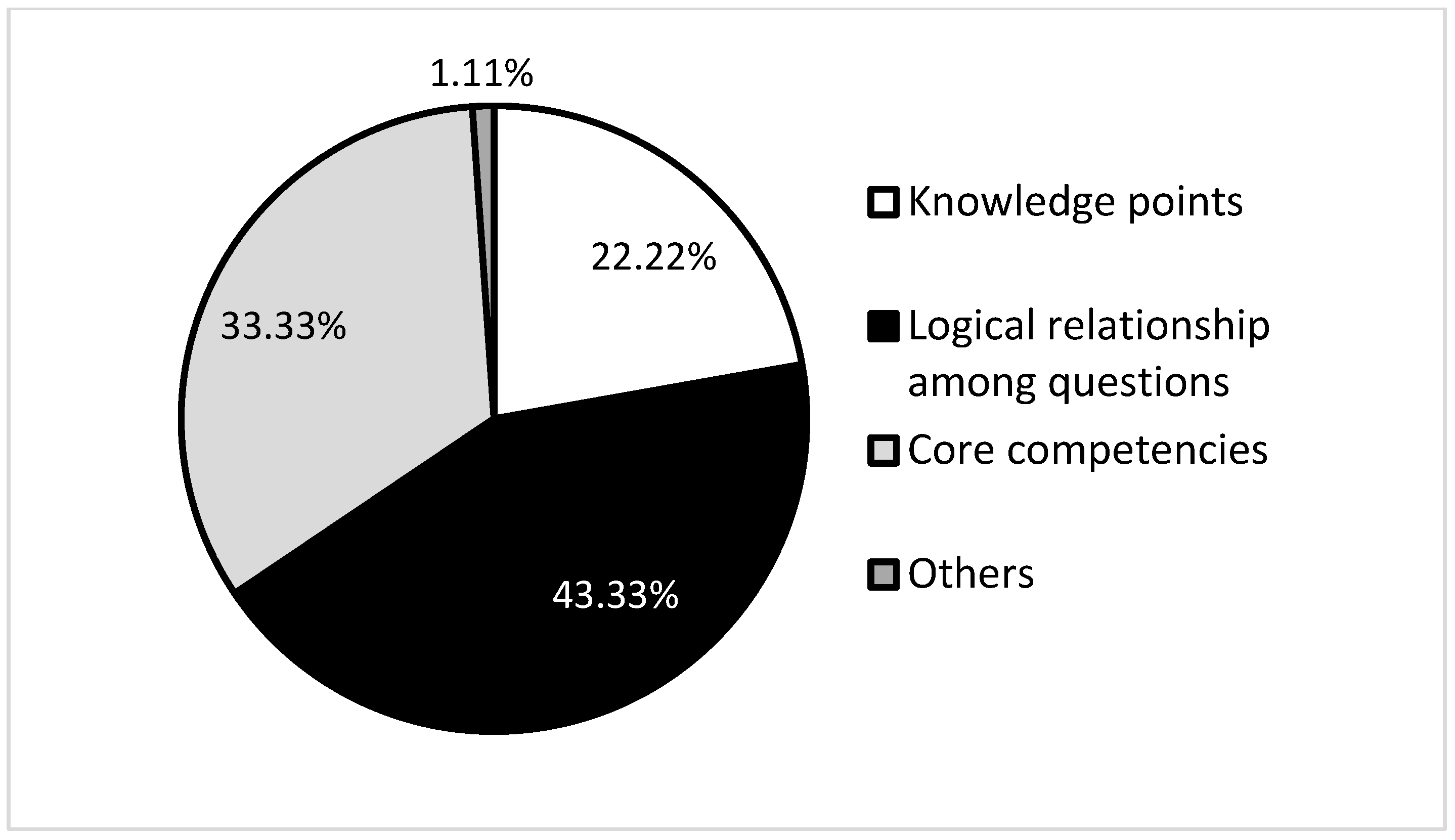


| Dimension | Cronbach’s Alpha Based on Standardized Items (First Survey) | Cronbach’s Alpha Based on Standardized Items (Second Survey) |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge-based | 0.897 | 0.925 |
| Affection | 0.751 | 0.801 |
| Test | Mean (S.D.) | Independent-Samples t Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental Class (n = 33) | Control Class (n = 33) | t | Sig. (2-Tailed) | |
| Pretest | 10.48 (3.768) | 10.61 (4.562) | −0.118 | 0.907 |
| Posttest | 22.09 (3.440) | 13.15 (5.063) | 8.389 | 0.001 |
| Sub-Dimension | Questions | Mean (S.D.) | Independent Sample t Test | Cohen’s d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental Class | Control Class | t | Sig. (2-Tailed) | |||
| Comprehension of knowledge | Q1 | 4.48 (0.508) | 3.66 (0.602) | 6.009 | 0.001 | 1.47 |
| Q2 | 4.55 (0.506) | 3.34 (0.653) | 8.311 | 0.001 | 2.07 | |
| Q3 | 4.52 (0.508) | 3.38 (0.707) | 7.449 | 0.001 | 1.85 | |
| Sum | 13.55 (1.481) | 10.38 (1.497) | 8.582 | 0.001 | 2.23 | |
| Higher-order thinking | Q4 | 4.52 (0.508) | 3.28 (0.813) | 7.317 | 0.001 | 1.83 |
| Q5 | 4.52 (0.508) | 3.25 (0.718) | 8.221 | 0.001 | 2.04 | |
| Q6 | 4.48 (0.508) | 3.31 (0.693) | 7.801 | 0.001 | 1.93 | |
| Sum | 13.52 (1.439) | 9.84 (1.609) | 9.705 | 0.001 | 2.41 | |
| Willingness | Q7 | 4.45 (0.506) | 3.06 (0.914) | 8.062 | 0.001 | 1.88 |
| Q8 | 4.52 (0.508) | 2.94 (0.914) | 8.570 | 0.001 | 2.14 | |
| Sum | 9.06 (0.966) | 6.00 (1.646) | 9.176 | 0.001 | 2.27 | |
| Affection | Q9 | 4.45 (0.506) | 3.19 (0.644) | 8.834 | 0.001 | 2.18 |
| Q10 | 4.52 (0.508) | 3.47 (0.671) | 7.103 | 0.001 | 1.76 | |
| Sum | 8.97 (0.951) | 6.66 (1.066) | 9.238 | 0.001 | 2.29 | |
| Overall | 45.09 (4.619) | 32.88 (4.549) | 10.740 | 0.001 | 2.66 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, F.; Duan, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Q.; Miao, S. An Empirical Study of Situational Teaching: Agricultural Location in High School Geography. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8676. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148676
Guo F, Duan Y, He S, Zhang Q, Xu Q, Miao S. An Empirical Study of Situational Teaching: Agricultural Location in High School Geography. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8676. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148676
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Fengtao, Yushan Duan, Shanbo He, Qi Zhang, Qiangqiang Xu, and Sheng Miao. 2022. "An Empirical Study of Situational Teaching: Agricultural Location in High School Geography" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8676. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148676
APA StyleGuo, F., Duan, Y., He, S., Zhang, Q., Xu, Q., & Miao, S. (2022). An Empirical Study of Situational Teaching: Agricultural Location in High School Geography. Sustainability, 14(14), 8676. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148676






