Regional Differences and Spatial Convergence of Green Development in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
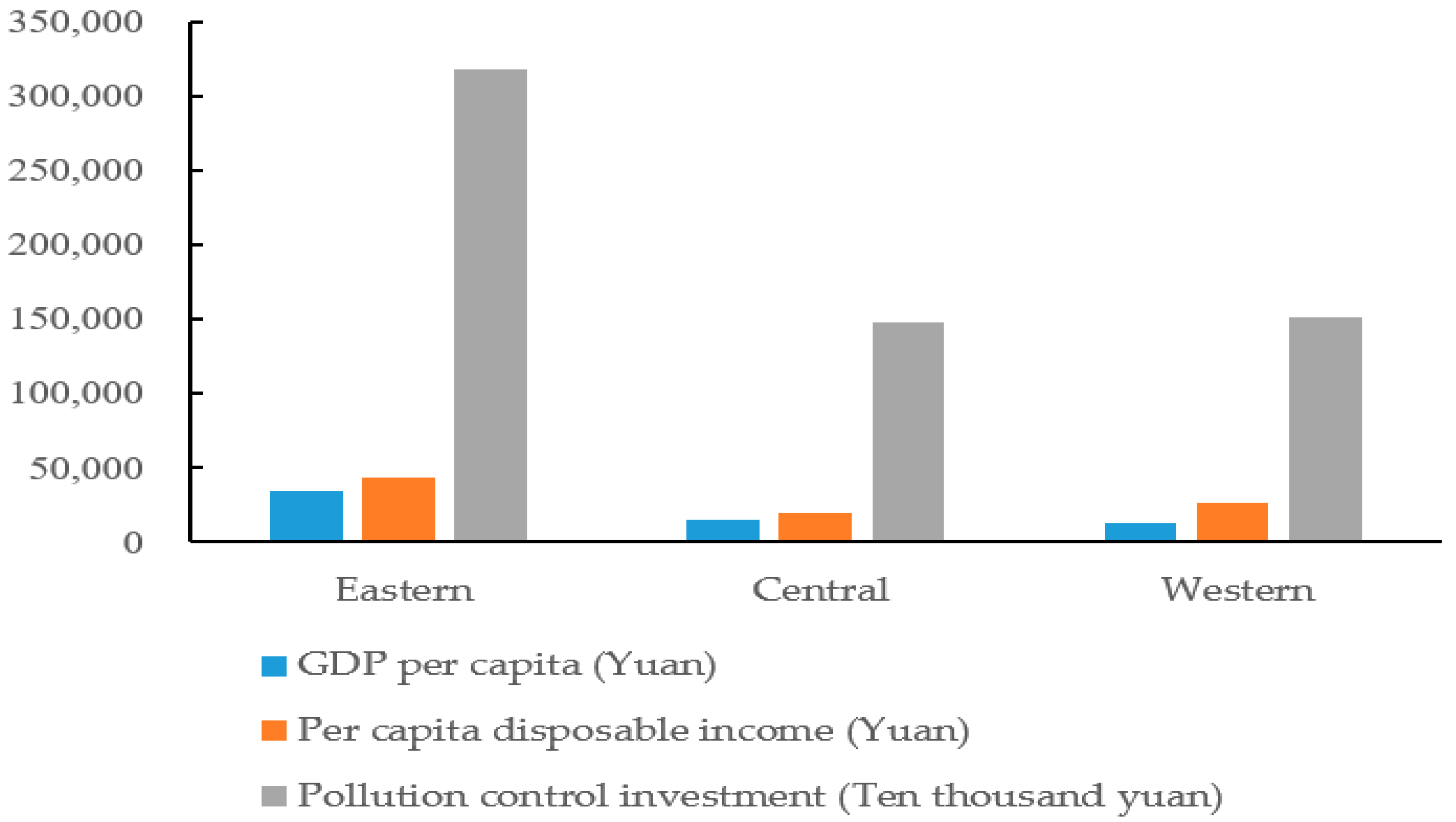
2.1. Research Scenario
2.2. Research Data
3. Methods
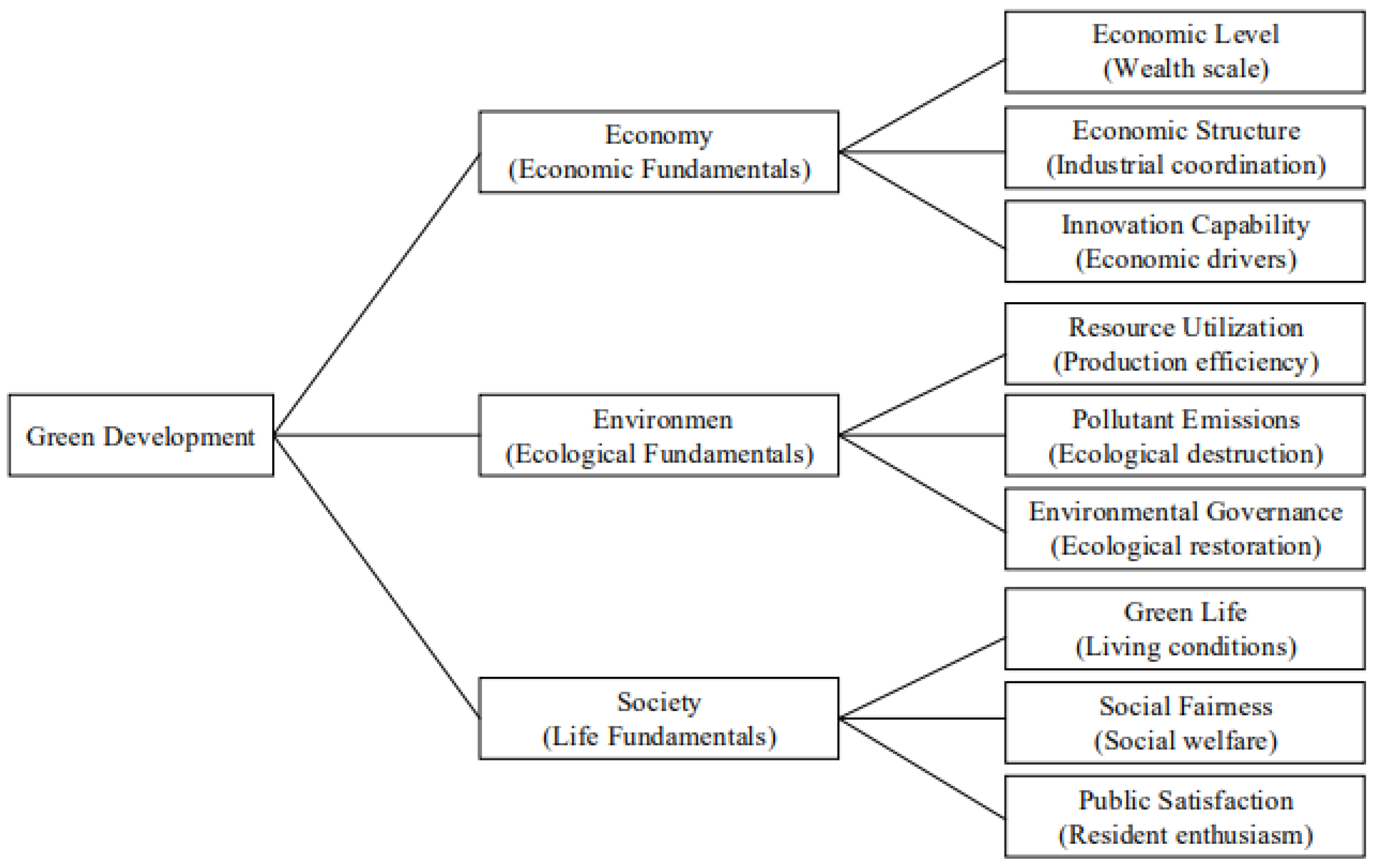
3.1. Indicator System and Calculation Method of GD
3.1.1. Indicator System
3.1.2. Evaluation Method
3.2. Calculation Method of Regional Difference
3.3. Spatial Convergence Model
4. Results and Discussion
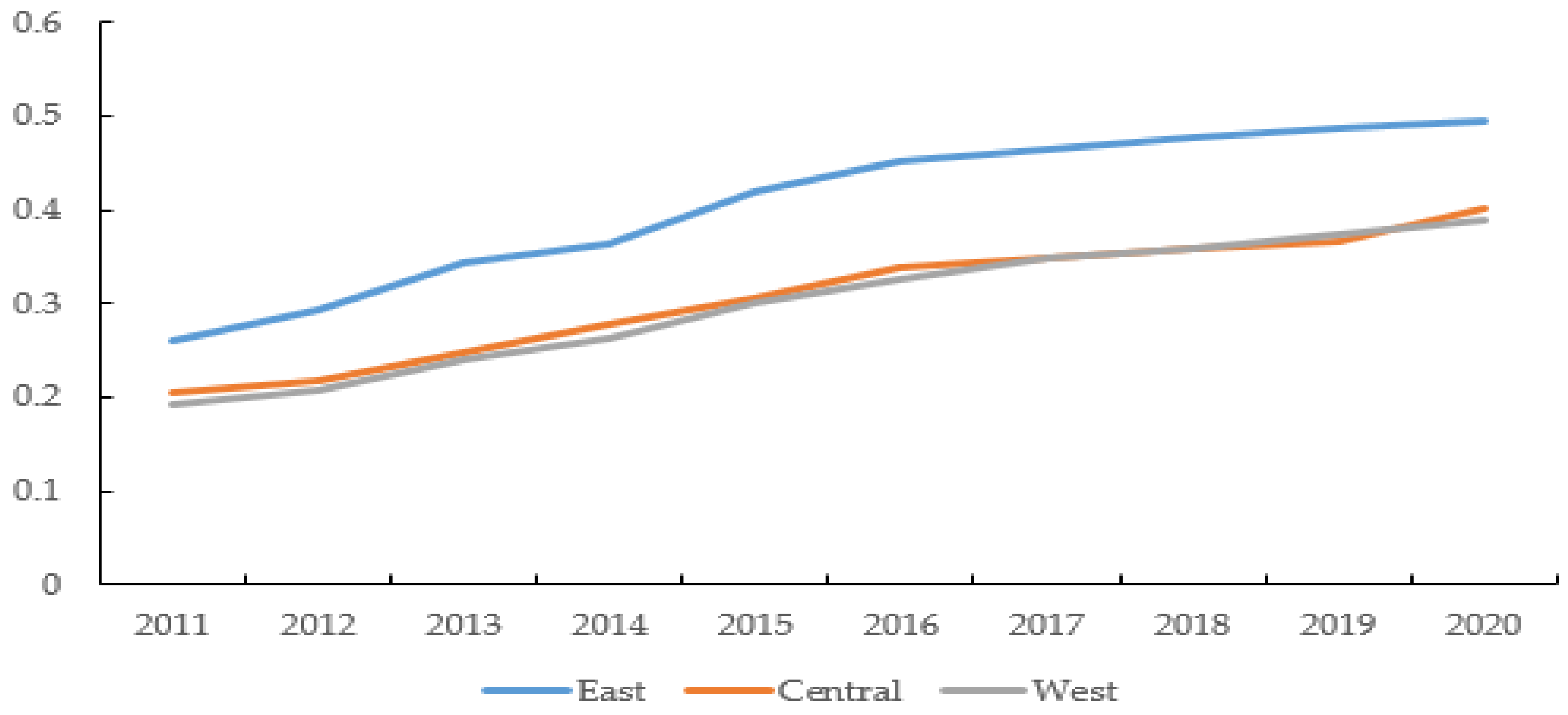
4.1. Measurement Results of GD
4.2. Analysis of Regional Differences
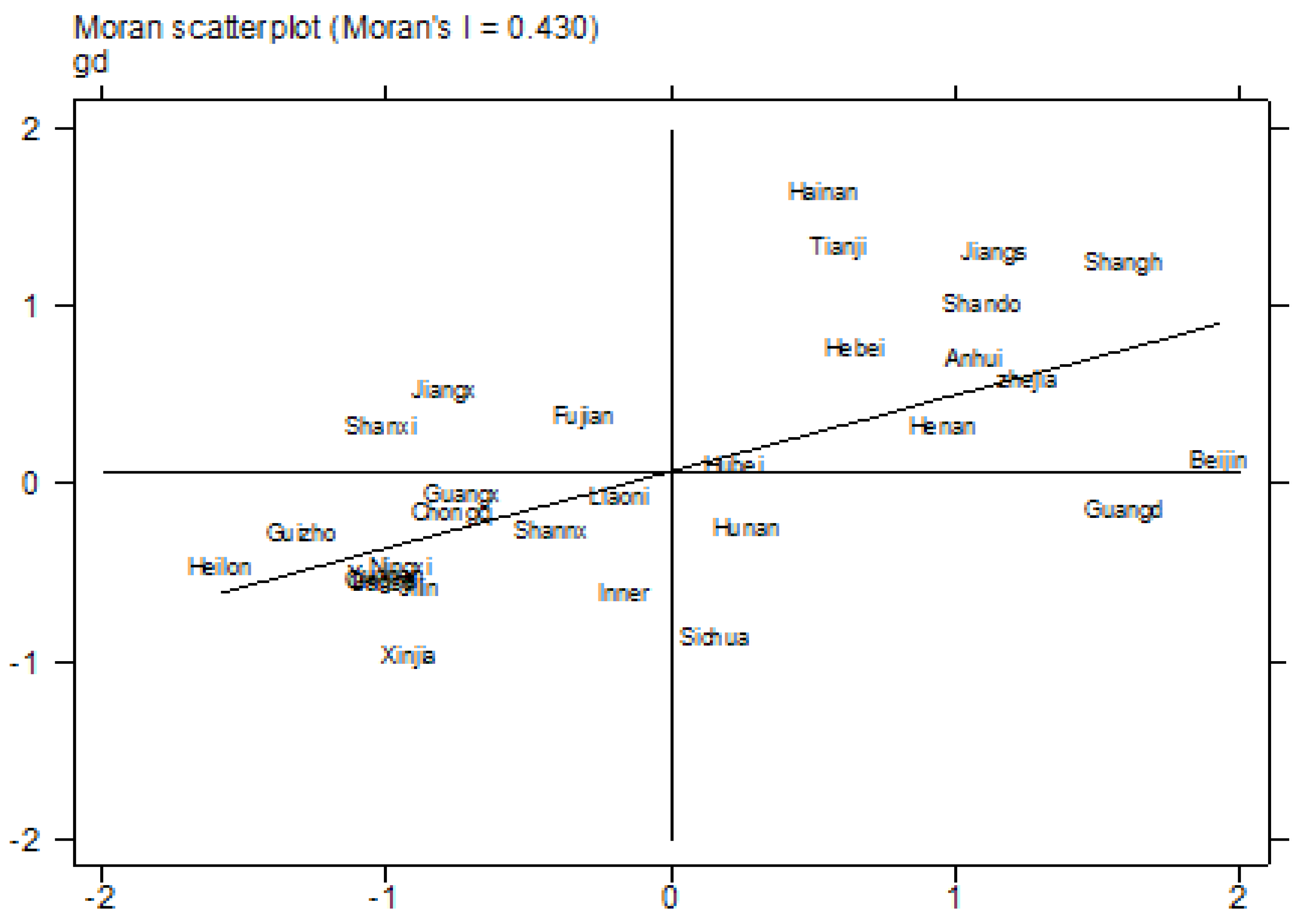
4.3. Spatial Dynamic Convergence Analysis
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, S.; Upadhyay, S.P.; Powar, S. Developing an integrated social, economic, environmental, and technical analysis model for sustainable development using hybrid multi-criteria decision making methods. Appl. Energy 2022, 308, 118235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzistamoulou, N.; Tyllianakis, E. Green growth & sustainability transition through information. Are the greener better informed? Evidence from European SMEs. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 306, 114457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbarma, J.; Choi, Y. A taxonomy of green governance: A qualitative and quantitative analysis towards sustainable development. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 79, 103693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Wang, Q.; Tian, L. Green development of Yangtze River Delta in China under Population-Resources-Environment-Development-Satisfaction perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brust, D.V.; Smith, A.M.; Sarkis, J. Managing the transition to critical green growth: The ‘Green Growth State’. Futures 2014, 64, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Long, R.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, S.; Liu, B. Has the Sustainable Development Planning Policy Promoted the Green Transformation in China’s Resource-based Cities? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 180, 106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, U.S.; Tariq, A.; Farrukh, M.; Raza, A.; Iqbal, M.K. Green bonds for sustainable development: Review of literature on development and impact of green bonds. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 175, 121378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, S. Impact of energy intensity, green economy and blue economy to achieve sustainable economic growth in GCC countries: Does Saudi Vision 2030 matters to GCC countries. Renew. Energy 2022, 191, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, D.; Korhonen, J. Integrating the green economy, circular economy and bioeconomy in a strategic sustainability framework. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 188, 107143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringel, M.; Schlomann, B.; Krail, M.; Rohde, C. Towards a green economy in Germany? The role of energy efficiency policies. Appl. Energy 2016, 179, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, S.; Rovenskaya, E. Optimal transition to greener production in a pro-environmental society. J. Math. Econ. 2022, 98, 102554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Pan, Y.; Agha, M.H.; Umar, M.; Chen, S. Industrial structure, energy intensity and environmental efficiency across developed and developing economies: The intermediary role of primary, secondary and tertiary industry. Energy 2022, 247, 123576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, R.; Paija, N.; Tyagi, B.; Harvie, C. Energy security, economic growth and environmental sustainability in India: Does FDI and trade openness play a role? J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Song, L. Market integration and regional green total factor productivity: Evidence from China’s province-Level Data. Sustainability 2021, 13, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Gao, Y.; Sun, X. How does artificial intelligence affect green economic growth?—Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attahiru, Y.B.; Aziz, M.; Kassim, K.A.; Shahid, S. A review on green economy and development of green roads and highways using carbon neutral materials. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 101, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi, M.; Zolfagharinia, H. Green product development and environmental performance: Investigating the role of government regulations. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 204, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeek, T.; Hincks, S. The ‘just’ management of urban air pollution? A geospatial analysis of low emission zones in Brussels and London. Appl. Geogr. 2022, 140, 102642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzoglou, I.; Ibrahim, B.M. Trading patterns in the European carbon market: The role of trading intensity and OTC transactions. Q. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2013, 53, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javeed, S.A.; Latief, R.; Jiang, T.; Ong, T.; Tang, Y. How environmental regulations and corporate social responsibility affect the firm innovation with the moderating role of Chief executive officer (CEO) power and ownership concentration? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Cao, X.; Anwar, A. Do green technology innovations, financial development, and renewable energy use help to curb carbon emissions? Renew. Energy 2022, 193, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Rai, P.; Garain, T.; Uday, S.; Hussain, C.M. Green Carbon Materials for the Analysis of Environmental Pollutants. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 33, e00156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, A.; Mazzanti, M.; Nicolli, F. Green technologies and environmental policies for sustainable development: Testing direct and indirect impacts. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 309, 127060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, S. Dynamic Nexus between Technological Innovation and Building Sector Carbon Emissions in the BRICS Countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Zakari, A.; Dagar, V.; Singh, S. World energy trilemma and transformative energy developments as determinants of economic growth amid environmental sustainability. Energy Econ. 2022, 108, 105884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yi, P. Assessment of city sustainability—Coupling coordinated development among economy, society and environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, C.; Pineda, J.; Villar, A.; Zambrano, E. Tracking progress towards accessible, green and efficient energy: The Inclusive Green Energy index. Appl. Energy 2020, 279, 115691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simarro, R.M. Inequality in China revisited. The effect of functional distribution of income on urban top incomes, the urban-rural gap and the Gini index, 1978–2015. China Econ. Rev. 2017, 42, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branis, M.; Linhartova, M. Association between unemployment, income, education level, population size and air pollution in Czech cities: Evidence for environmental inequality? A pilot national scale analysis. Health Place 2012, 18, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccherini, M.; Kopinska, J.; Palma, A. When particulate matter strikes cities: Social disparities and health costs of air pollution. J. Health Econ. 2021, 78, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Wang, J. Sustainable development evaluation of the society–economy–environment in a resource-based city of China: A complex network approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Gu, M.; Ke, X. Regional analysis of the green development level differences in Chinese mineral resource-based cities. Resour. Policy 2019, 61, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Yuan, Y. Spatiotemporal pattern assessment of China’s industrial green productivity and its spatial drivers: Evidence from city-level data over 2000–2017. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Development and Reform Commission of China (DRCC). The Development and Reform Commission of China Issued “the Green Development Index System” and “Ecological Civilization Construction Assessment Target System”. 2016. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016-12/22/content_5151575.htm (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Koengkan, M.; Fuinhas, J.A.; Kazemzadeh, E.; Osmani, F. Measuring the economic efficiency performance in Latin American and Caribbean countries: An empirical evidence from stochastic production frontier and data envelopment analysis. Int. Econ. 2022, 169, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.M.; Moutinho, V.F.; Moreira, A.C. Do social and economic factors affect the technical efficiency in entrepreneurship activities? Evidence from European countries using a two-stage DEA model. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2022, 82, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Qi, Z.; Shu, Y. Multiple relationships between fixed-asset investment and industrial structure evolution in China–Based on Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) analysis and VAR model. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2020, 55, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llop, M. Economic structure and pollution intensity within the environmental input–output framework. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 3410–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazi, M.; Mohammadi, E. Natural resource dependence and economic growth: A TOPSIS/DEA analysis of innovation efficiency. Resour. Policy 2018, 59, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamza, I.; Kubule, A.; Zihare, L.; Valters, K.; Blumberga, D. Bioresource utilization index–A way to quantify and compare resource efficiency in production. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminzadegan, S.; Shahriari, M.; Mehranfar, F.; Abramović, B. Factors affecting the emission of pollutants in different types of transportation: A literature review. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 2508–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyser, W.; Gevaert, V.; Verdonck, F.; Baets, B.; Benedetti, L. An emission time series generator for pollutant release modelling in urban areas. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, Y.P.; Buschke, F.T. Misaligned environmental governance indicators and the mismatch between government actions and positive environmental outcomes. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 112, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Bian, C.; Yang, J. How can public participation improve environmental governance in China? A policy simulation approach with multi-player evolutionary game. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 95, 106782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugoua, E.; Dumas, M. Green product innovation in industrial networks: A theoretical model. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2021, 107, 102420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, M.; Obrist, A. Are households living in green certified buildings consuming less energy? Evidence from Switzerland. Energy Policy 2022, 161, 112724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, M.; Luo, X. Environmental life cycle assessment of battery electric vehicles from the current and future energy mix perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 303, 114050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.A. Planting urban trees to improve quality of life? The life satisfaction impacts of urban afforestation. For. Policy Econ. 2021, 125, 102408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omri, A.; Omri, H.; Slimani, S.; Belaid, F. Environmental degradation and life satisfaction: Do governance and renewable energy matter? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 175, 121375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, C.; Volij, O. A simple proof of Foster’s (1983) characterization of the Theil measure of inequality. Econ. Model. 2013, 35, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barro, R.; Martin, X.S. Convergence. J. Polit. Econ. 1992, 100, 223–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, A.; Sosa, C.; Cabral, R.; Mollick, A.V. Energy reform and energy consumption convergence in Mexico: A spatial approach. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2022, 61, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losacker, S. ‘License to green’: Regional patent licensing networks and green technology diffusion in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 175, 121336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Xu, J. Green total factor productivity: A re-examination of quality of growth for provinces in China. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 62, 101454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Xue, R.; He, B.; Yang, D. Dynamic changes and convergence of China’s regional green productivity: A dynamic spatial econometric analysis. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2022, 13, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Mo, R.; Chen, X. New patterns in China’s regional green development: An interval Malmquist–Luenberger productivity analysis. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2021, 58, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| System | Description | Indicator | Correlation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic system | Economic level | Gross domestic product (yuan) | + | [35,36,37] |
| Per capita disposable income (yuan) | + | |||
| Total investment in fixed assets (yuan) | + | |||
| Foreign direct investment | + | |||
| Economic structure | Proportion of primary industry (%) | − | [12,38] | |
| Proportion of secondary industry (%) | + | |||
| Proportion of tertiary industry (%) | + | |||
| Innovation capability | R&D expenditure (yuan) | + | [39] | |
| R&D personnel | + | |||
| Number of patent applications | + | |||
| Environmental system | Resource utilization | Per capita resource consumption (standard coal) | − | [26,40] |
| Proportion of clean energy (%) | + | |||
| Ratio of GDP to total energy consumption (%) | − | |||
| Per capita arable land (kilometers) | + | |||
| Per capita forest area (kilometers) | + | |||
| Pollutant emissions | Industrial wastewater discharge (ton) | − | [41,42] | |
| Industrial exhaust emissions (ton) | − | |||
| Solid waste discharge (ton) | − | |||
| Environmental governance | Government’s investment in environmental governance (yuan) | + | [43,44] | |
| Urban sewage treatment rate (%) | + | |||
| Domestic waste disposal rate (%) | + | |||
| Social system | Green life | Population density (%) | − | [45,46,47] |
| Proportion of green products (%) | + | |||
| Proportion of green buildings (%) | + | |||
| Proportion of new energy vehicles (%) | + | |||
| Green area per capita (kilometers) | + | |||
| Social fairness | Urban–rural income gap (%) | − | [28,29,30] | |
| Average education level (year) | + | |||
| Number of beds per 10,000 people in medical institutions | + | |||
| Public satisfaction | Residents’ satisfaction with the quality of living environment (%) | + | [48,49] |
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.2935 | 0.3431 | 0.3803 | 0.4092 | 0.4691 | 0.5311 | 0.5869 | 0.6002 | 0.6758 | 0.6427 | 0.4932 |
| Tianjin | 0.2501 | 0.2762 | 0.3338 | 0.3586 | 0.3875 | 0.4454 | 0.4144 | 0.4153 | 0.4154 | 0.4743 | 0.3771 |
| Hebei | 0.2583 | 0.2886 | 0.3513 | 0.3617 | 0.4505 | 0.4464 | 0.4154 | 0.4079 | 0.4195 | 0.4144 | 0.3814 |
| Shanxi | 0.2036 | 0.1963 | 0.2149 | 0.2232 | 0.2304 | 0.2325 | 0.2418 | 0.2507 | 0.2790 | 0.2821 | 0.2355 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.2077 | 0.2232 | 0.2906 | 0.2961 | 0.3911 | 0.3789 | 0.3824 | 0.4056 | 0.4309 | 0.4956 | 0.3502 |
| Liaoning | 0.2521 | 0.2769 | 0.3358 | 0.3410 | 0.3720 | 0.3358 | 0.2873 | 0.2963 | 0.3048 | 0.2976 | 0.3100 |
| Jilin | 0.1674 | 0.1891 | 0.2284 | 0.2449 | 0.2067 | 0.2273 | 0.2563 | 0.2708 | 0.3048 | 0.3679 | 0.2464 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.1488 | 0.1374 | 0.1633 | 0.1746 | 0.2015 | 0.1974 | 0.2015 | 0.2143 | 0.2067 | 0.2253 | 0.1871 |
| Shanghai | 0.2749 | 0.2870 | 0.3845 | 0.3867 | 0.4447 | 0.4896 | 0.5258 | 0.5833 | 0.6397 | 0.6550 | 0.4671 |
| Jiangsu | 0.2286 | 0.2418 | 0.3397 | 0.3614 | 0.4606 | 0.5265 | 0.5322 | 0.5244 | 0.5156 | 0.5362 | 0.4267 |
| Zhejiang | 0.2566 | 0.2604 | 0.3618 | 0.3903 | 0.4763 | 0.5147 | 0.5163 | 0.5264 | 0.5355 | 0.5216 | 0.4360 |
| Anhui | 0.2871 | 0.2749 | 0.3194 | 0.3517 | 0.4186 | 0.4797 | 0.5270 | 0.5252 | 0.5224 | 0.5201 | 0.4226 |
| Fujian | 0.1850 | 0.2253 | 0.2480 | 0.2749 | 0.3162 | 0.3586 | 0.3379 | 0.3277 | 0.3369 | 0.3668 | 0.2977 |
| Jiangxi | 0.1467 | 0.2108 | 0.2056 | 0.2005 | 0.2408 | 0.2718 | 0.2769 | 0.2907 | 0.3038 | 0.4102 | 0.2558 |
| Shandong | 0.2362 | 0.2489 | 0.3242 | 0.3630 | 0.4695 | 0.5239 | 0.5419 | 0.5288 | 0.5146 | 0.4799 | 0.4231 |
| Henan | 0.2366 | 0.2645 | 0.3007 | 0.3751 | 0.4681 | 0.5115 | 0.4919 | 0.4896 | 0.5063 | 0.4526 | 0.4097 |
| Hubei | 0.2335 | 0.2480 | 0.2707 | 0.3007 | 0.3658 | 0.4009 | 0.4226 | 0.4153 | 0.4071 | 0.3906 | 0.3455 |
| Hunan | 0.2077 | 0.2346 | 0.2759 | 0.3441 | 0.3203 | 0.3792 | 0.3782 | 0.3836 | 0.4082 | 0.5549 | 0.3487 |
| Guangdong | 0.3033 | 0.3551 | 0.4109 | 0.4322 | 0.4783 | 0.5295 | 0.5318 | 0.5427 | 0.5525 | 0.5306 | 0.4667 |
| Guangxi | 0.1757 | 0.1808 | 0.2234 | 0.2476 | 0.2950 | 0.3479 | 0.3700 | 0.3761 | 0.3844 | 0.3851 | 0.2986 |
| Hainan | 0.3214 | 0.3834 | 0.2945 | 0.3317 | 0.2852 | 0.2811 | 0.4237 | 0.4412 | 0.4578 | 0.5167 | 0.3736 |
| Chongqing | 0.1602 | 0.1911 | 0.2245 | 0.2414 | 0.2930 | 0.3324 | 0.3648 | 0.3740 | 0.3855 | 0.3778 | 0.2945 |
| Sichuan | 0.2294 | 0.2531 | 0.3040 | 0.3344 | 0.3798 | 0.4296 | 0.4475 | 0.4759 | 0.5064 | 0.4399 | 0.3800 |
| Guizhou | 0.1932 | 0.1880 | 0.1955 | 0.2124 | 0.2372 | 0.2653 | 0.2935 | 0.3042 | 0.3173 | 0.2986 | 0.2505 |
| Yunnan | 0.1839 | 0.2025 | 0.2245 | 0.2434 | 0.2795 | 0.2983 | 0.3111 | 0.3164 | 0.3441 | 0.3546 | 0.2758 |
| Shannxi | 0.2718 | 0.2769 | 0.2854 | 0.2899 | 0.3281 | 0.3262 | 0.3483 | 0.3632 | 0.3803 | 0.3944 | 0.3264 |
| Gansu | 0.1819 | 0.1942 | 0.2048 | 0.2465 | 0.2775 | 0.3066 | 0.3328 | 0.3316 | 0.3328 | 0.3351 | 0.2744 |
| Qinghai | 0.1795 | 0.1890 | 0.2529 | 0.3062 | 0.2253 | 0.3035 | 0.3239 | 0.3032 | 0.3181 | 0.3376 | 0.2739 |
| Ningxia | 0.1633 | 0.1984 | 0.2286 | 0.2465 | 0.2888 | 0.2911 | 0.3348 | 0.3466 | 0.3607 | 0.3482 | 0.2777 |
| Xinjiang | 0.1746 | 0.1870 | 0.2121 | 0.2321 | 0.3033 | 0.2942 | 0.3255 | 0.3358 | 0.3483 | 0.4047 | 0.2808 |
| Mean | 0.2204 | 0.2409 | 0.2797 | 0.3041 | 0.3454 | 0.3752 | 0.3915 | 0.3989 | 0.4125 | 0.4270 | 0.3396 |
| Year | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-East | T-Central | T-West | ||||||
| 2011 | 0.0236 | 0.0143 | 0.0093 | 0.6057 | 0.3962 | 0.0098 | 0.0247 | 0.0123 |
| 2012 | 0.0255 | 0.0136 | 0.0118 | 0.5350 | 0.4632 | 0.0133 | 0.0196 | 0.0095 |
| 2013 | 0.0259 | 0.0118 | 0.0142 | 0.4545 | 0.5473 | 0.0080 | 0.0205 | 0.0106 |
| 2014 | 0.0251 | 0.0137 | 0.0114 | 0.5456 | 0.4532 | 0.0061 | 0.0336 | 0.0089 |
| 2015 | 0.0341 | 0.0212 | 0.0129 | 0.6220 | 0.3783 | 0.0129 | 0.0479 | 0.0130 |
| 2016 | 0.0370 | 0.0248 | 0.0122 | 0.6701 | 0.3303 | 0.0189 | 0.0567 | 0.0089 |
| 2017 | 0.0336 | 0.0236 | 0.0099 | 0.7034 | 0.2961 | 0.0201 | 0.0538 | 0.0064 |
| 2018 | 0.0329 | 0.0234 | 0.0096 | 0.7100 | 0.2907 | 0.0219 | 0.0461 | 0.0088 |
| 2019 | 0.0340 | 0.0245 | 0.0095 | 0.7200 | 0.2791 | 0.0259 | 0.0414 | 0.0104 |
| 2020 | 0.0284 | 0.0211 | 0.0072 | 0.7444 | 0.2544 | 0.0220 | 0.0352 | 0.0092 |
| Year | Moran’s I | Z Statistic |
|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 0.184 * | 1.793 |
| 2012 | 0.196 ** | 2.092 |
| 2013 | 0.225 ** | 2.357 |
| 2014 | 0.216 ** | 2.268 |
| 2015 | 0.307 *** | 3.083 |
| 2016 | 0.361 *** | 3.563 |
| 2017 | 0.378 *** | 3.732 |
| 2018 | 0.328 *** | 3.288 |
| 2019 | 0.273 *** | 2.813 |
| 2020 | 0.288 *** | 2.944 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | East | Central | West | |
| β | −0.356 ** | −0.446 ** | −0.302 *** | −0.362 ** |
| (−2.13) | (−2.09) | (−3.35) | (−2.01) | |
| λ | 0.214 ** | 0.236 *** | 0.198 ** | 0.259 ** |
| (2.12) | (3.11) | (2.16) | (2.29) | |
| s | 0.044 | 0.059 | 0.036 | 0.045 |
| T | 15.753 | 11.748 | 19.254 | 15.403 |
| N | 300 | 110 | 80 | 110 |
| R2 | 0.183 | 0.142 | 0.114 | 0.131 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | East | Central | West | |
| β | −0.462 ** | −0.513 ** | −0.457 ** | −0.483 ** |
| (−2.25) | (−2.12) | (−2.41) | (−2.20) | |
| gp | 0.328 *** | 0.274 ** | 0.359 ** | 0.327 ** |
| (2.91) | (2.20) | (2.41) | (2.26) | |
| λ | 0.217 ** | 0.241 *** | 0.199 ** | 0.260 ** |
| (2.13) | (2.99) | (2.15) | (2.27) | |
| s | 0.062 | 0.072 | 0.061 | 0.066 |
| T | 11.180 | 9.627 | 11.363 | 10.502 |
| N | 300 | 110 | 80 | 110 |
| R2 | 0.191 | 0.164 | 0.137 | 0.153 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Song, L. Regional Differences and Spatial Convergence of Green Development in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148511
Li C, Song L. Regional Differences and Spatial Convergence of Green Development in China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148511
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chuan, and Liangrong Song. 2022. "Regional Differences and Spatial Convergence of Green Development in China" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148511
APA StyleLi, C., & Song, L. (2022). Regional Differences and Spatial Convergence of Green Development in China. Sustainability, 14(14), 8511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148511





