Determination of the Risk on Human Health of Heavy Metals Contained by Ship Source Bilge and Wastewater Discharged to the Sea on the Mediterranean by Monte Carlo Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
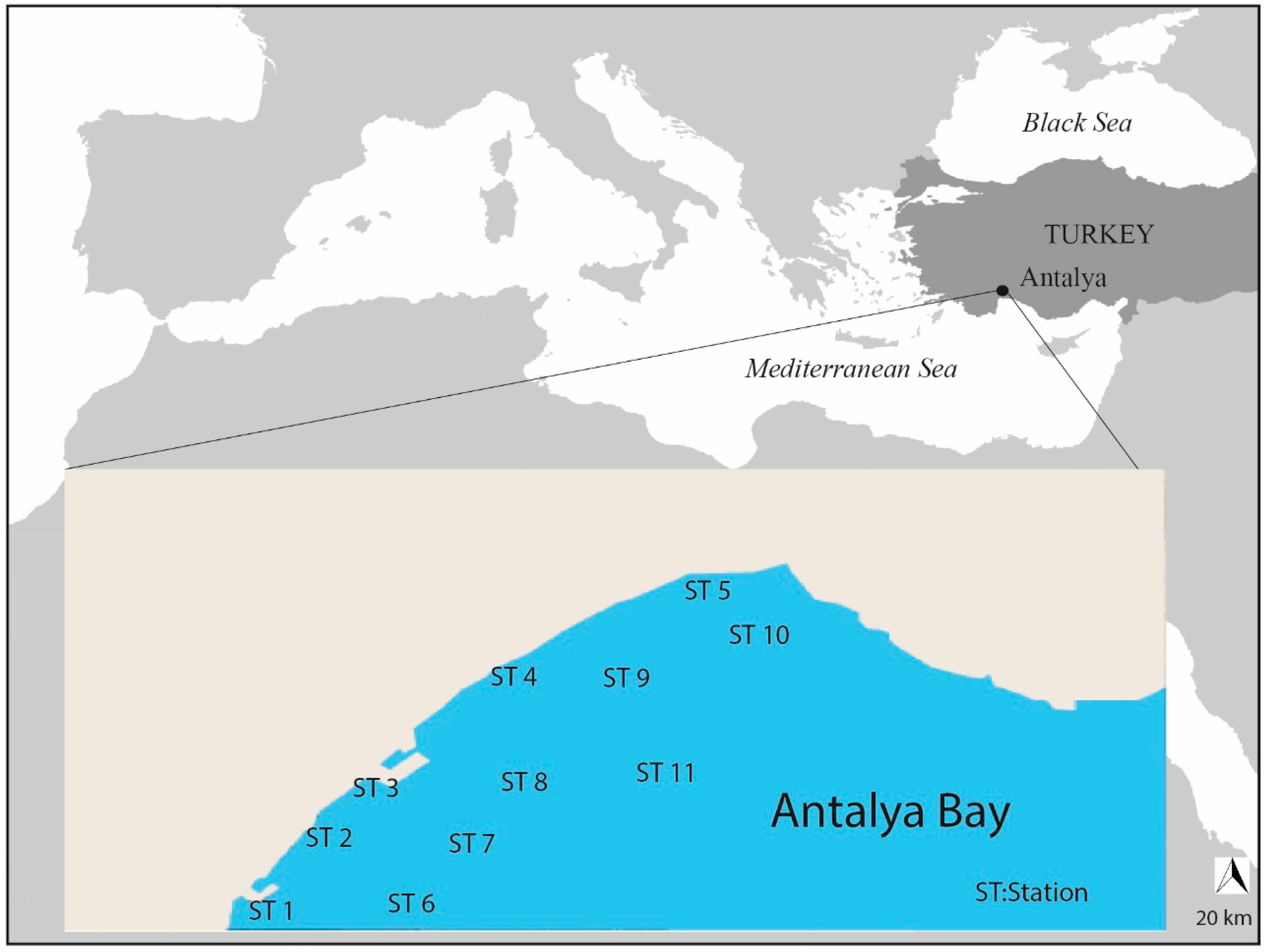
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Determination of Human Health Risk Caused by Bilge and Wastewater with MCS
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Measured Values
| Studies on Bilge Water | Tiselius and Magnusson [32] mg L−1 | Olorunfemi et al. [30] mg L−1 | EPA [61] mg L−1 | Present Study Passenger Boat mg L−1 | Present Study Merchant Ship mg L−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 0.0254 ± 0.0131 | 0.5 | 0.2775–0.426 | 2.85 | 3.87 |
| Fe | 3.204 ± 0.132 | n/d * | 0.432–0.531 | n/d | 81.8 |
| V | 0.0378 ± 0.0234 | n/d | n/d | n/d | 1.51 |
| Cr | 0.0192 ± 0.00853 | 1.4 | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Mn | 0.161 ± 0.0588 | 3.9 | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Co | 0.0897 ± 0.0604 | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Ni | 0.0754 ± 0.0192 | 0.3 | 0.09775–0.245 | n/d | n/d |
| Zn | 0.310 ± 0.066 | 11.6 | 0.514–1.33 | 4.18 | 13.6 |
| As | 0.00191 ± 0.00034 | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Cd | <0.0002 | 0.1 | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Hg | 0.00279 ± 0.00114 | n/d | 0.03205–0.0798 | n/d | n/d |
| Pb | <0.004 | n/d | N/A | n/d | n/d |
| Studies on Heavy Metal in Wastewater | Ytreberg et al. [33] mg L−1 | Onwuegbuchunam et al. [59] mg L−1 | Mearns et al. [60] mg L−1 | Present Study Passenger Boat mg L−1 | Present Study Merchant Ship mg L−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 0.267 | 0.0012 | 0.0829 | 2.47 | 1.68 |
| Fe | n/d * | 0.00202 | n/d | n/d | 8.7 |
| V | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Cr | 0.0073 | n/d | 0.00342 | n/d | n/d |
| Mn | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Co | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Ni | 0.025 | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Zn | 0.517 | 0.00004 | 0.13 | 4.63 | 4.64 |
| As | 0.006 | n/d | 0.0092 | n/d | n/d |
| Cd | 0.00016 | 0.00025 | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Hg | 0.00016 | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Pb | 0.0256 | n/d | 0.00296 | n/d | n/d |
3.2. Determination of Human Health Risk Caused by Bilge and Wastewater with MCS
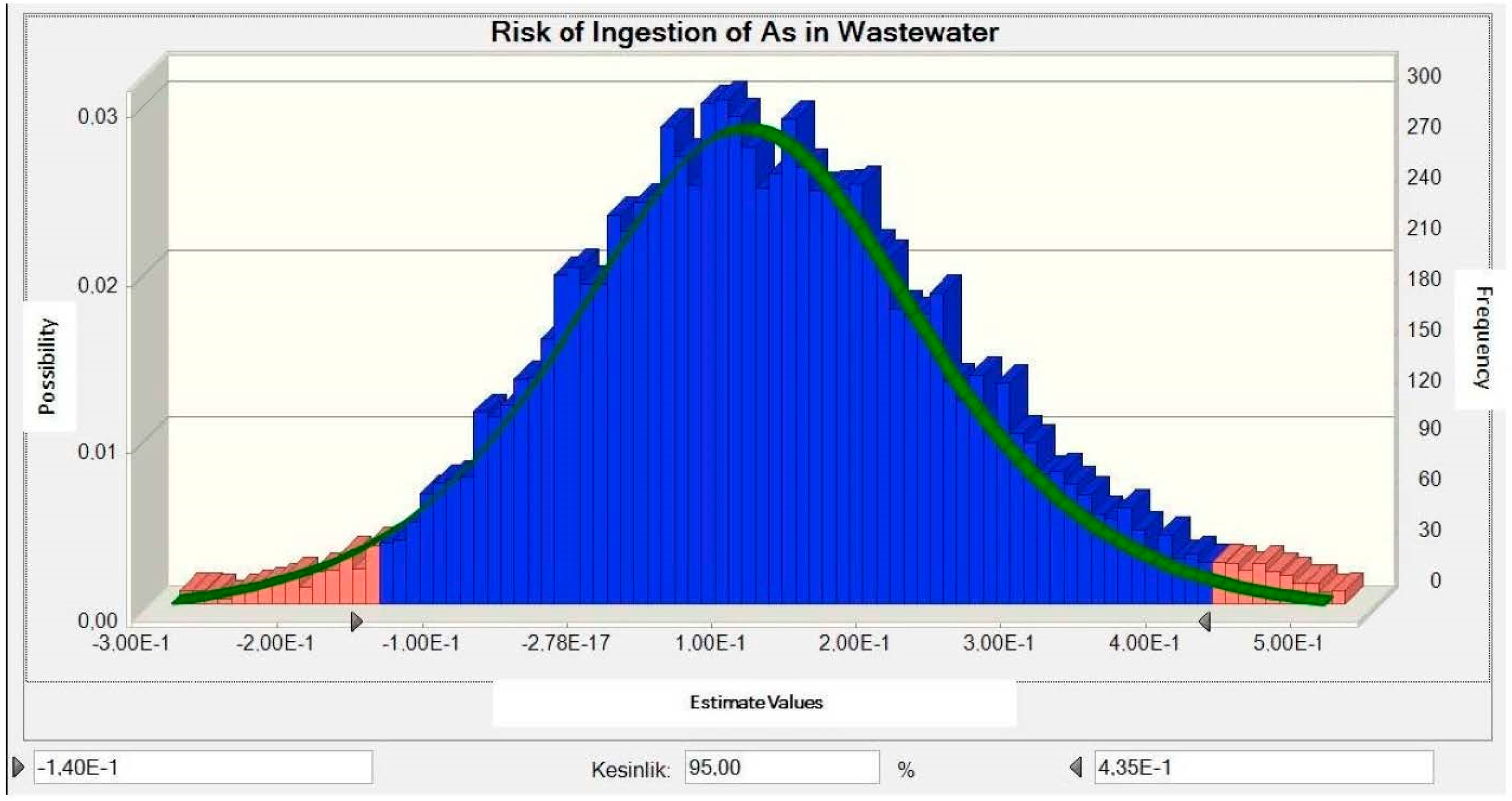
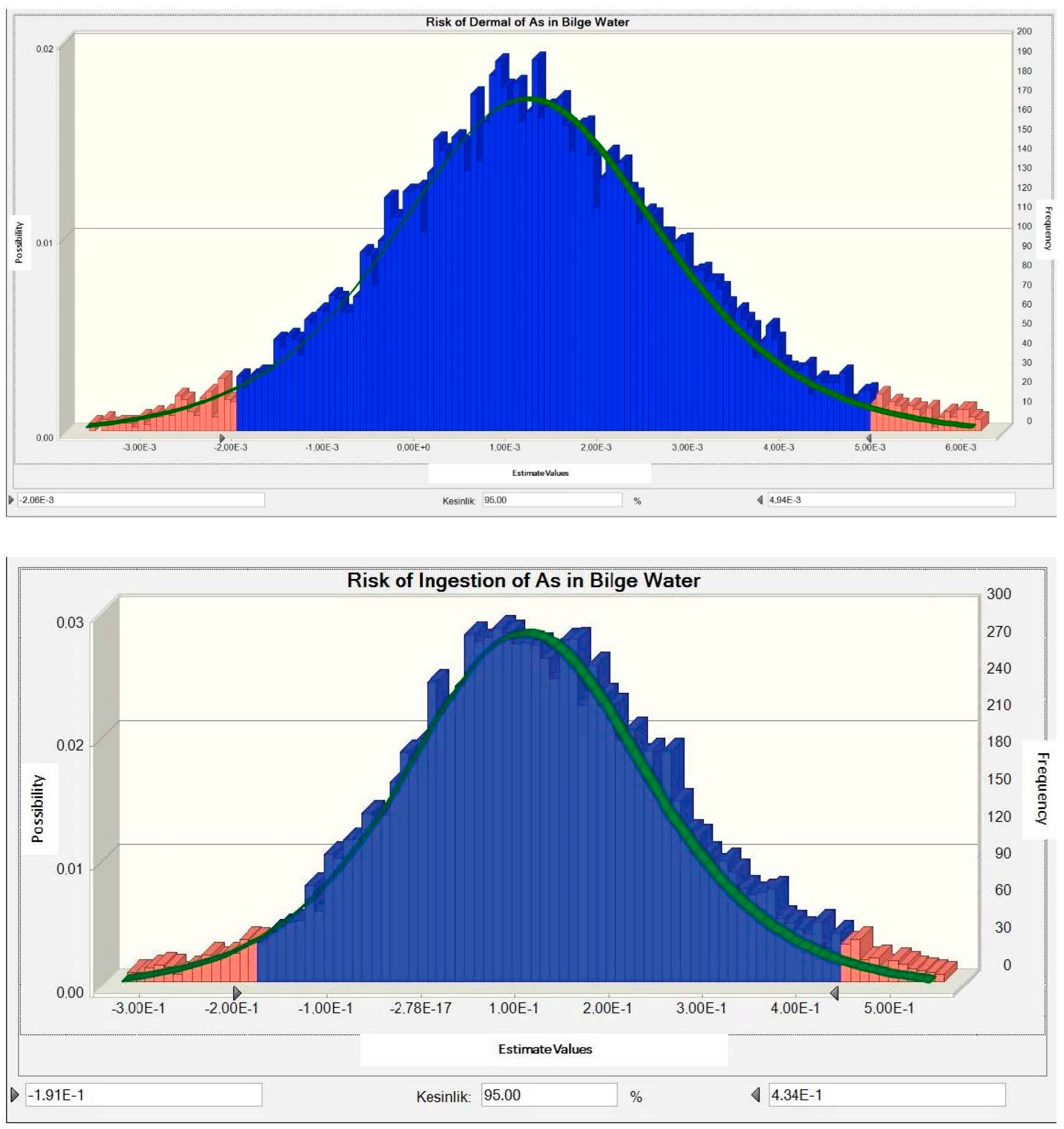
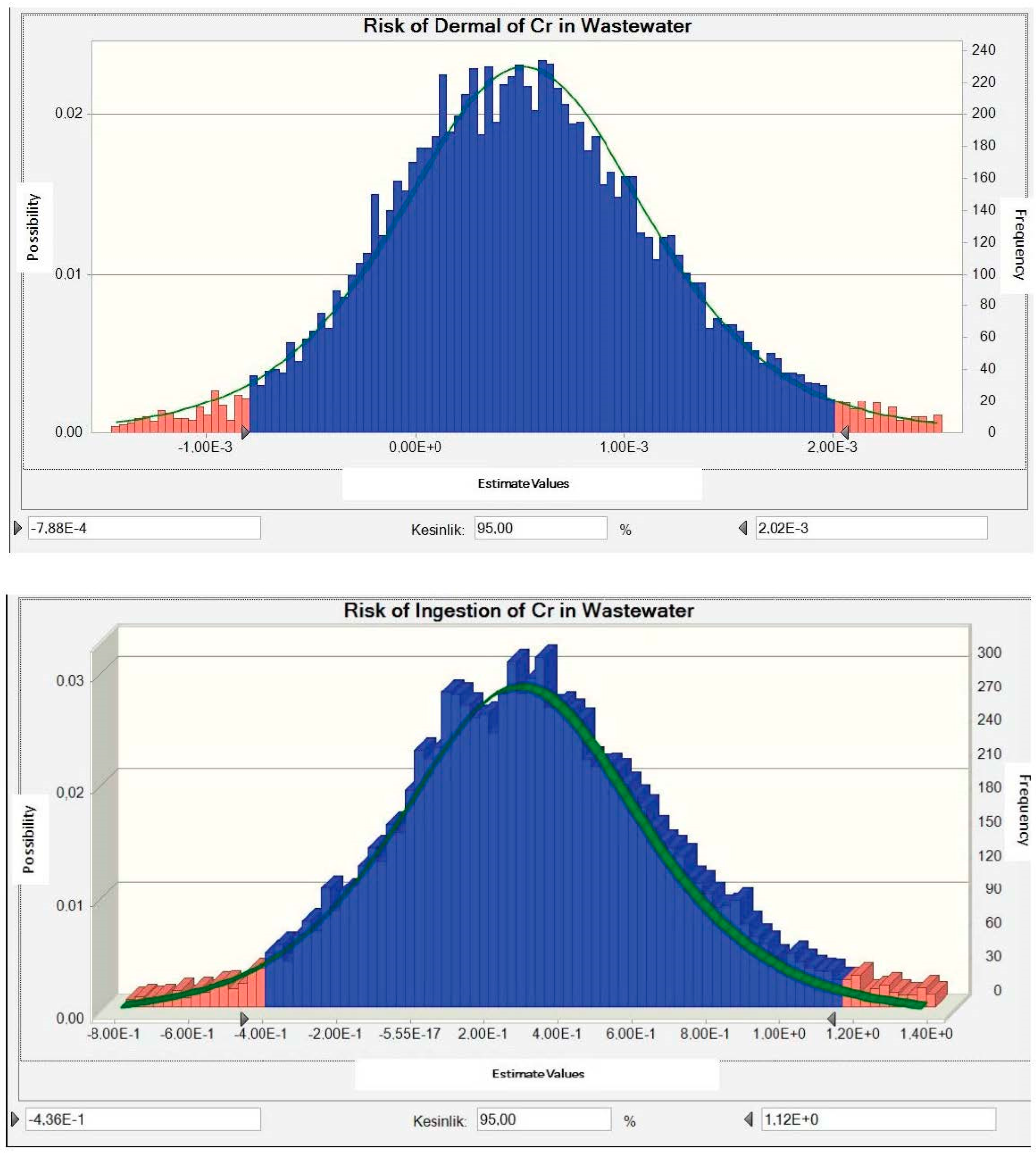
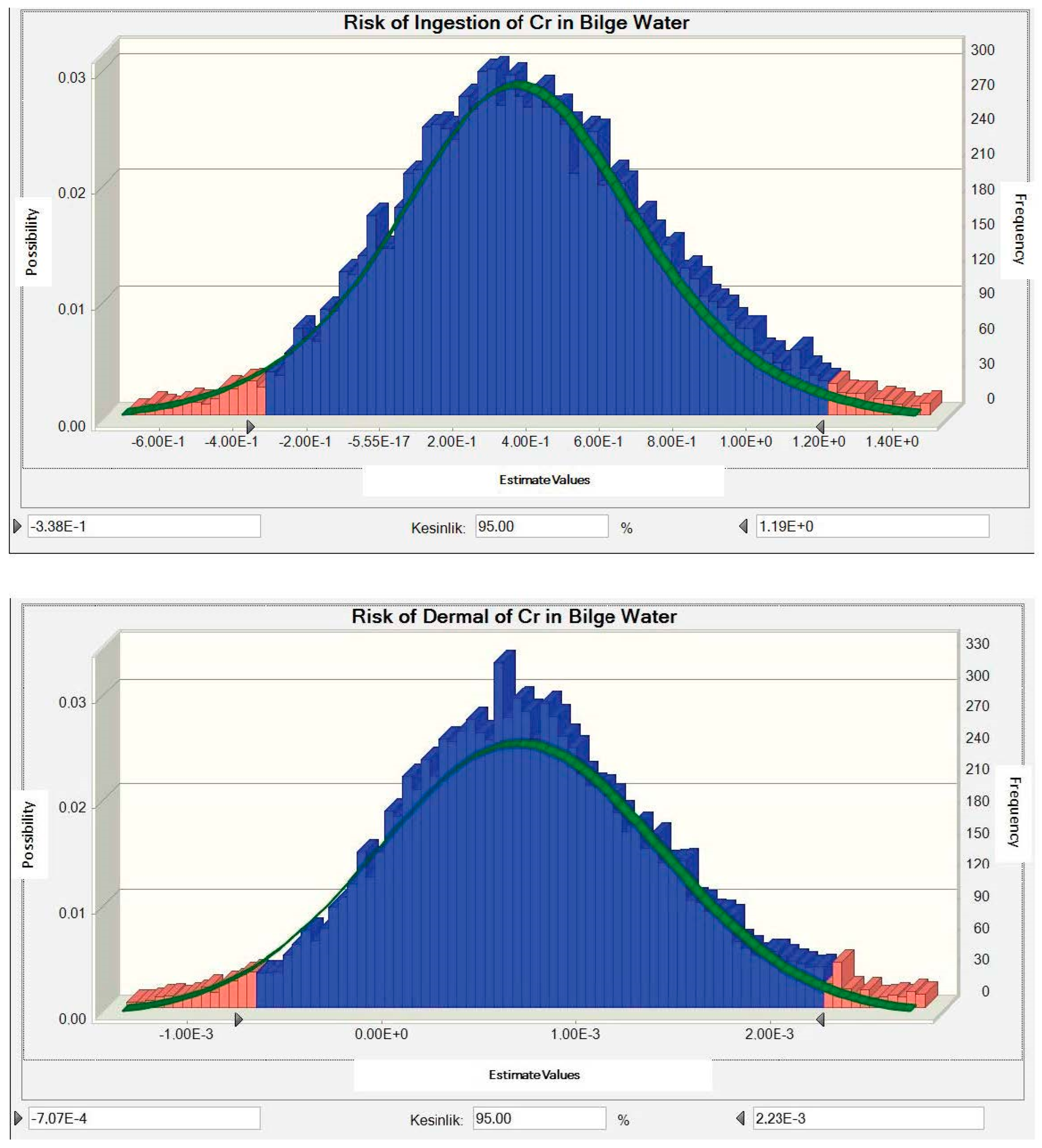
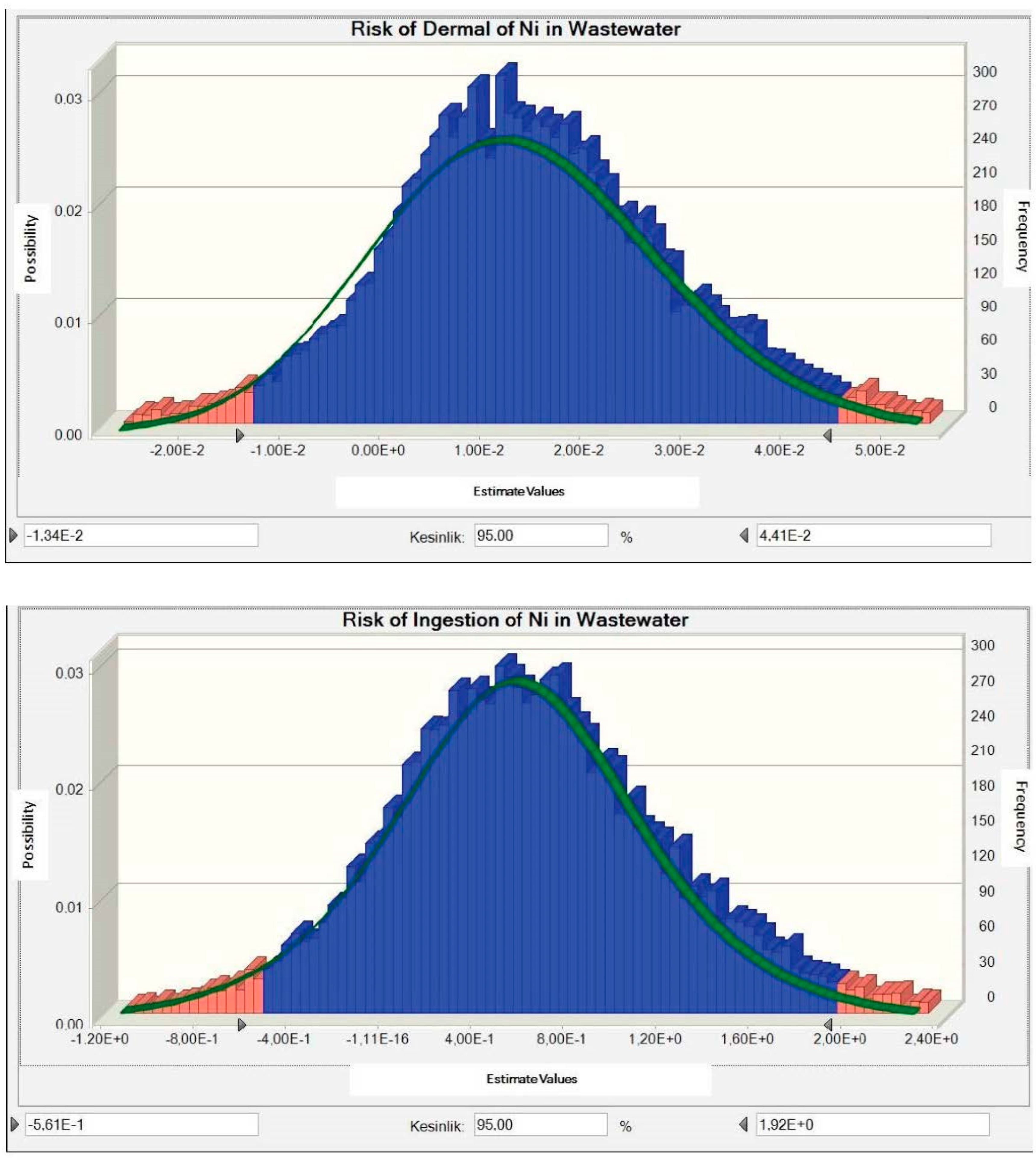
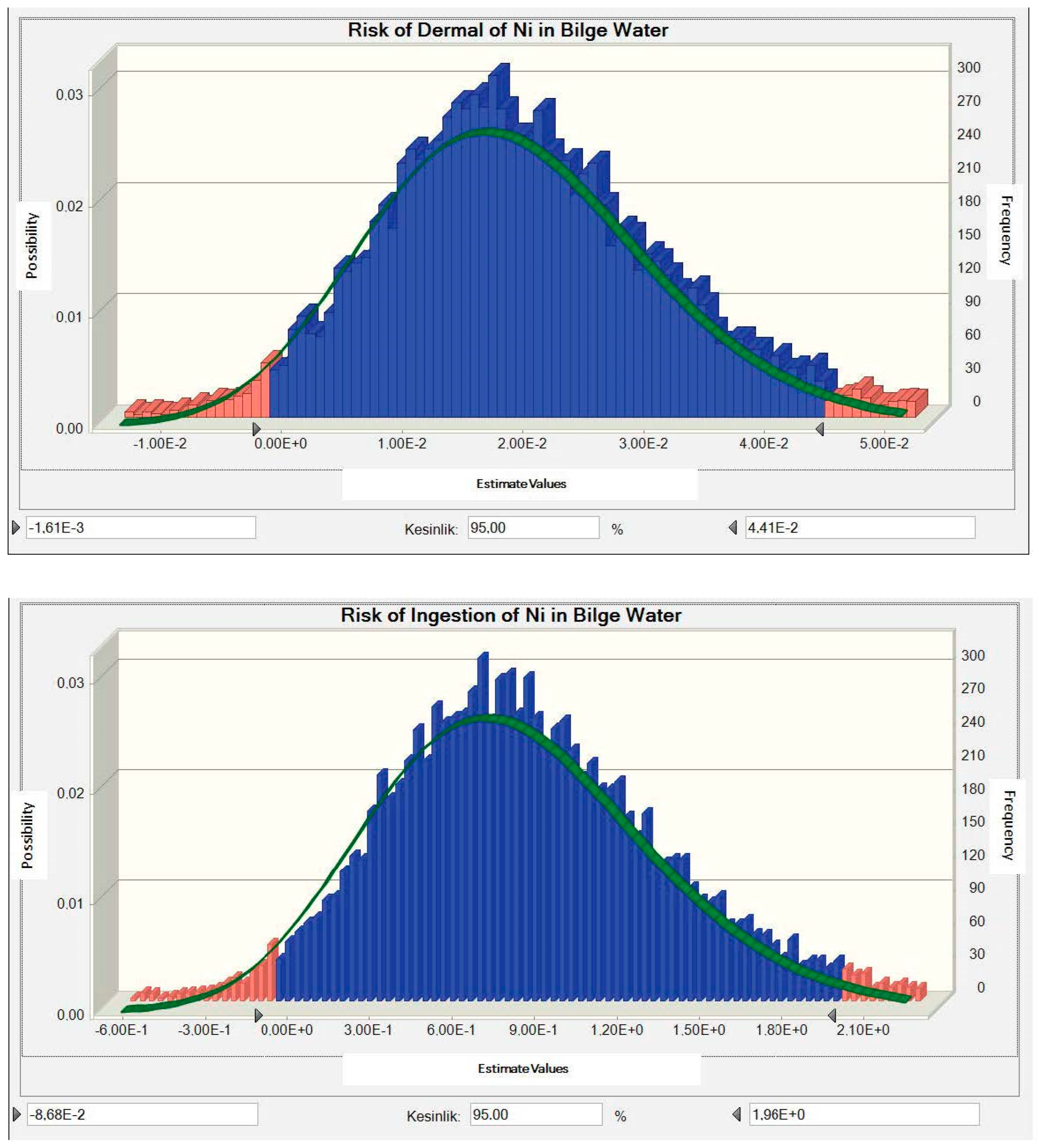
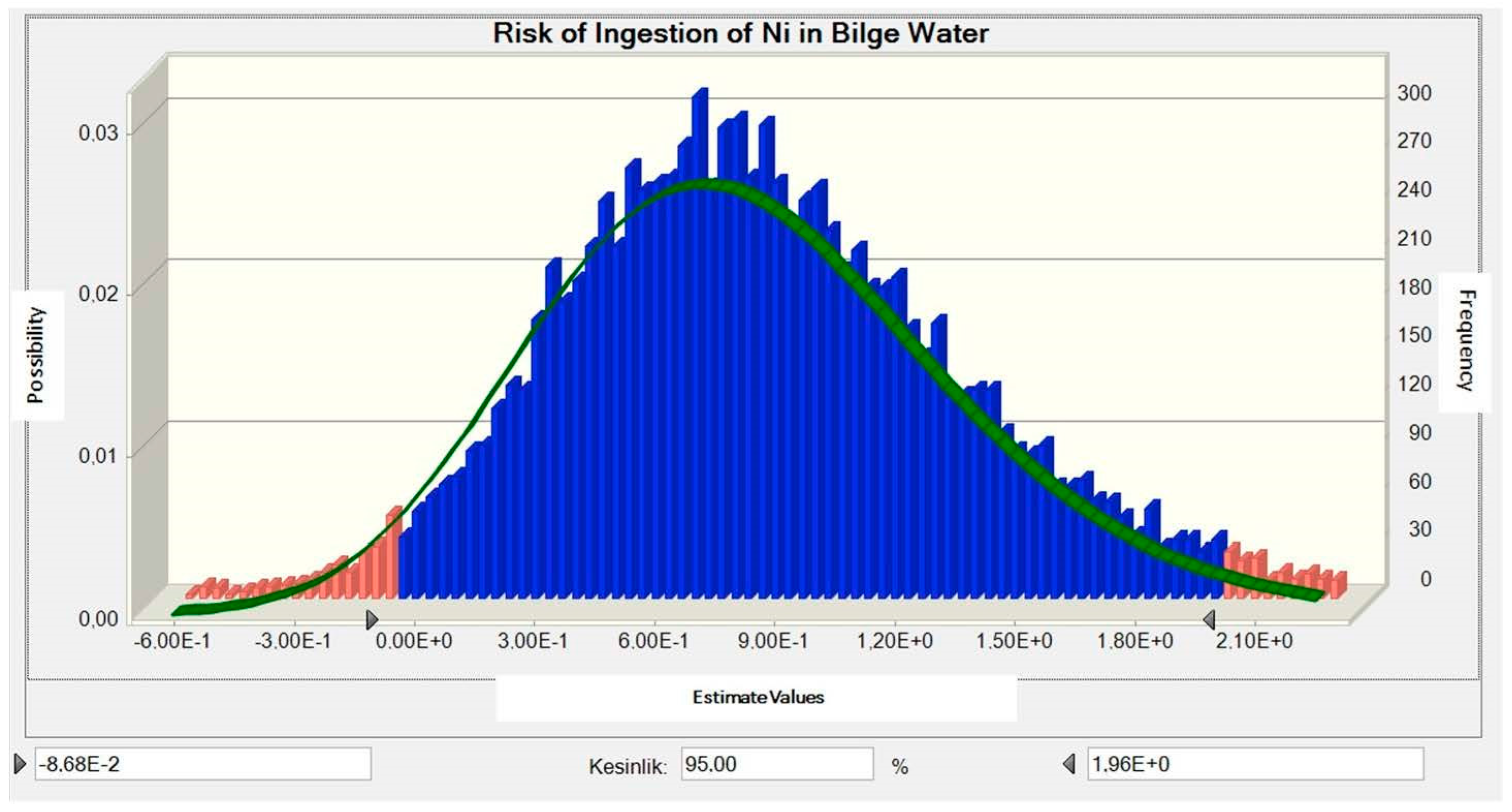
3.3. Determination of Carcinogenic Risk Distribution
3.4. Determination of Non-Carcinogenic Risk Distribution
3.5. Results Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Contaminant of Potential Concern | Oral CSF (Chen, 2019) | Dermal CSF (Chen, 2019) | Oral CSF (Soleimani vd. 2020) | Oral RfD (Chen, 2019) | Dermal RfD (Chen, 2019) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mgkg−1day−1)−1 | (mgkg−1day−1)−1 | (mgkg−1day−1)−1 | (mgkg−1day−1)−1 | (mgkg−1day−1)−1 | |
| Pb | n/d | n/d | 0.002 | 1.40 × 10−3 | 5.25 × 10−4 |
| Cr | 5.01 × 10−1 | 2.00 × 101 | n/d | 3.00 × 10−3 | 3.00 × 10−3 |
| Cd | n/d | n/d | 0.005 | 5.00 × 10−4 | 1.00 × 10−5 |
| Mn | n/d | n/d | n/d | 1.40 × 10−1 | 2.33 × 10−2 |
| Co | n/d | n/d | n/d | 3.00 × 10−4 | 6.00 × 10−5 |
| Ni | 1.70 | 4.25 × 101 | n/d | 2.00 × 10−2 | 5.40 × 10−3 |
| Zn | n/d | n/d | n/d | 3.00 × 10−1 | 6.00 × 10−2 |
| V | n/d | n/d | n/d | 9.00 × 10−3 | 9.00 × 10−3 |
| Fe | n/d | n/d | n/d | 7.00 × 10−1 | 1.40 × 10−1 |
| As | 1.50 | 3.66 | n/d | 3.00 × 10−4 | 1.23 × 10−4 |
| Hg | n/d | n/d | n/d | 3.00 × 10−4 | 2.10 × 10−5 |
| Cu | n/d | n/d | n/d | 4.00 × 10−2 | 1.20 × 10−2 |
| Parameters | Distribution (Saha vd. 2017) | Mean | SD | Unit | Uncertainty Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR (daily intake rate) (L/day) | Log-normal | 2.20 | 0.34 | L | −30% to 10% |
| BW (body weight) (kg) | Log-normal | 70 | 10.71 | kg | −30% to 20% |
| SA (surface area of the skin (m2) | Log-normal | 1.8 | 0.092 | m2 | −10% to 10% |
| EF (exposure frequency) (day/year) | Triangular | - | - | day | 350 (180–365) |
| ET (exposure time) | Triangular | - | - | h | 0.58 (0.4–0.7) |
| Kp (cm h−1) | Cd, Cr, As, Fe, Mn, Cu, V ve Hg 1 × 10−3 cm h−1; Pb 1 × 10−4 cm h−1; Zn 6 × 10−4 cm h−1; Ni 2 × 10−4 cm h−1; Co 4 × 10−4 cm h−1 | USEPA, 2011. Risk assessment guidance for superfund. In: Part A: Human Health Evaluation Manual; Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment; Part F, Supplemental Guidance for Inhalation Risk Assessment, vol. 1. | |||
| ED (Exposure Duration) (year) | considered 70 years for carcinogen and 30 years for others | Cr, Cd, As, Ni and Co are carcinogenic. | |||
| AT (Average Time) | AT = 365 × ED | ||||
| Metals | Cr | Fe | Cu | Zn | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stations | |||||
| 1 | n/d * | 6.5 | 2.69 | 4.19 | n/d |
| 2 | 0.901 | 6.01 | 2.43 | 3.99 | n/d |
| 3 | n/d | 5.57 | 3.04 | 4.05 | 15 |
| 4 | n/d | 5.61 | 2.975 | 3.63 | 17.9 |
| 5 | n/d | 5.59 | 2.23 | 3.66 | 13.95 |
| 6 | n/d | 5.9 | 2.78 | 4.02 | n/d |
| 7 | n/d | 6.17 | 2.89 | 4.18 | n/d |
| 8 | n/d | 5.47 | 2.76 | 3.73 | n/d |
| 9 | n/d | 6.46 | 2.9 | 4.67 | n/d |
| 10 | n/d | 5.17 | 2.06 | 4.06 | 13.6 |
| 11 | n/d | 5.81 | 2.61 | 3.77 | n/d |
| Statistics | Wastewater Ingestion | Wastewater Dermal | Bilge Water | Bilge Water | Sum of Row | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingestion | Dermal | |||||
| Cr | MEAN | 2.78 × 10−1 | 5.07 × 10−4 | 3.51 × 10−1 | 6.35 × 10−4 | 9.80 × 10−1 |
| SD | 3.89 × 10−1 | 6.97 × 10−4 | 3.98 × 10−1 | 7.36 × 10−4 | 7.89 × 10−1 | |
| 95% | 2.95 × 10−1 | 5.32 × 10−4 | 3.77 × 10−1 | 6.80 × 10−4 | 6.47 × 10−1 | |
| Ni | MEAN | 5.53 × 10−1 | 1.26 × 10−2 | 7.64 × 10−1 | 1.76 × 10−2 | 1.39 × 100 |
| SD | 6.27 × 10−1 | 1.39 × 10−2 | 5.16 × 10−1 | 1.17 × 10−2 | 1.17 × 100 | |
| 95% | 5.92 × 10−1 | 1.33 × 10−2 | 8.06 × 10−1 | 1.86 × 10−2 | 1.43 × 100 | |
| As | MEAN | 1.12 × 10−1 | 1.29 × 10−3 | 1.06 × 10−1 | 1.20 × 10−3 | 2.21 × 10−1 |
| SD | 1.45 × 10−1 | 1.61 × 10−3 | 1.53 × 10−1 | 1.73 × 10−3 | 3.02 × 10−1 | |
| 95% | 1.21 × 10−1 | 1.36 × 10−3 | 1.13 × 10−1 | 1.27 × 10−3 | 2.37 × 10−1 | |
| Sum of mean | 9.82 × 10−1 | 1.44 × 10−2 | 1.22 × 100 | 1.95 × 10−2 | 2.24 × 100 | |
| Sum of 95% | 1.01 × 100 | 1.51 × 10−2 | 1.27 × 100 | 2.06 × 10−2 | 2.31 × 100 | |
| Statistics | Wastewater Ingestion | Wastewater Dermal | Bilge Water | Bilge Water | Sum of Row | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingestion | Dermal | |||||
| Cu | MEAN | 0.0137676 | 0.0002062 | 0.0132393 | 0.000201 | 0.0274141 |
| SD | 0.023401 | 0.0003501 | 0.0213641 | 0.0003258 | 0.045441 | |
| 95% | 0.0147042 | 0.0002186 | 0.0139733 | 0.0002122 | 0.0291083 | |
| Fe | MEAN | 0.0048907 | 0.0001108 | 0.0035096 | 0.000083721 | 0.0085947 |
| SD | 0.0089712 | 0.0002109 | 0.0082978 | 0.0001897 | 0.0176696 | |
| 95% | 0.0052676 | 0.0001161 | 0.0036923 | 0.000087992 | 0.009164 | |
| V | MEAN | n/d | n/d | 0.8832509 | 0.0040042 | 0.8872551 |
| SD | n/d | n/d | 1.5450067 | 0.0070964 | 1.5521031 | |
| 95% | n/d | n/d | 0.9503096 | 0.0043296 | 0.9546392 | |
| Cr | MEAN | 1.5938608 | 0.0071553 | 2.5847651 | 0.0121605 | 4.1979417 |
| SD | 4.188305 | 0.0191794 | 4.7227134 | 0.0216054 | 8.9518031 | |
| 95% | 1.6869873 | 0.0074531 | 2.8437182 | 0.0130773 | 4.5512359 | |
| Mn | MEAN | n/d | n/d | 0.0595795 | 0.0016197 | 0.0611993 |
| SD | n/d | n/d | 0.1261246 | 0.0034331 | 0.1295577 | |
| 95% | n/d | n/d | 0.0627949 | 0.0017668 | 0.0645617 | |
| Co | MEAN | 2.3599987 | 0.0281829 | 1.5710246 | 0.0149318 | 3.974138 |
| SD | 3.4128698 | 0.0251617 | 2.8270833 | 0.0256707 | 6.2907855 | |
| 95% | 2.5563837 | 0.0299013 | 1.6919398 | 0.0156585 | 4.2938832 | |
| Ni | MEAN | 0.0594741 | 0.0001952 | 0.0335937 | 0.0001138 | 0.0933768 |
| SD | 0.1267451 | 0.00043 | 0.0948059 | 0.0003226 | 0.2223036 | |
| 95% | 0.0642419 | 0.0002052 | 0.0354411 | 0.0001242 | 0.1000124 | |
| Zn | MEAN | 0.0037113 | 0.000048516 | 0.0057477 | 0,000083186 | 0.0095908 |
| SD | 0.0066415 | 0.000090762 | 0.0071425 | 0,000096470 | 0.0139712 | |
| 95% | 0.0039896 | 0.00005116 | 0.0062195 | 0,000086554 | 0.0103468 | |
| As | MEAN | 2.7818464 | 0.0341568 | 2.9126479 | 0.0326103 | 5.7612614 |
| SD | 5.6162113 | 0.0622389 | 5.5312011 | 0.0622638 | 11.271915 | |
| 95% | 3.0538807 | 0.0357044 | 3.0963149 | 0.0344657 | 6.2203658 | |
| Cd | MEAN | 0.0241106 | 0.0056022 | 0.0357484 | 0.0082488 | 0.07371 |
| SD | 0.035465 | 0.0080373 | 0.0334968 | 0.0076138 | 0.0846128 | |
| 95% | 0.0254578 | 0.0058554 | 0.0381872 | 0.0088543 | 0.0783547 | |
| Hg | MEAN | n/d | n/d | 3.2346663 | 0.2038807 | 3.438547 |
| SD | n/d | n/d | 6.8524151 | 0.4456866 | 7.2981017 | |
| 95% | n/d | n/d | 3.3915152 | 0.2157773 | 3.6072926 | |
| Pb | MEAN | 0.3546892 | 0.0004249 | 0.4727835 | 0.001375 | 0.8292725 |
| SD | 0.7098101 | 0.0008595 | 0.8127913 | 0.0023161 | 1.525777 | |
| 95% | 0.3761364 | 0.0004584 | 0.5045601 | 0.0014653 | 0.8826202 | |
| Sum of mean | 7.1963494 | 0.07608275 | 11.81055 | 0.27931269 | 19.36230 | |
| Sum of 95% | 7.7870493 | 0.07996371 | 12.638666 | 0.29590572 | 20.801585 | |
References
- EPA. Cruise Ship Discharge Assessment Report; Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zodiatis, G.; Lardner, R.; Spanoudaki, K.; Sofianos, S.; Radhakrishnan, H.; Coppini, G.; Liubartseva, S.; Kampanis, N.; Krokos, G.; Hoteit, I.; et al. Operational oil spill modelling assessments. In Marine Hydrocarbon Spill Assessments; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 145–197. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP MAP. Barcelona Convention—Mediterranean 2017 Quality Status Report Land and Sea-Based Pollution: Common Indicator 19 etc. Conclusions (CI19). 2017. Available online: https://www.medqsr.org/conclusions-ci19 (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- UNEP MAP. Barcelona Convention—Mediterranean 2017 Quality Status Report. Results and Status, Including Trends (CI19). 2017. Available online: https://www.medqsr.org/results-and-status-including-trends-ci19 (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- UNESCO. The Integrated, Strategic Design Plan for the Coastal Ocean Observations Module of the Global Ocean Observing System. In IOC Information Documents Series 1183; GOOS Report N 125; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 2003; 190p. [Google Scholar]
- Cucco, A.; Daniel, P. Numerical modeling of oil pollution in the Western Mediterranean Sea. In Oil Pollution in the Mediterranean Sea: Part I—The International Context; Carpenter, A., Kostianoy, A.G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girin, M.; Daniel, P. Oil pollution in French waters. In Oil Pollution in the Mediterranean Sea: Part II—National Case Studies; Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Carpenter, A., Kostianoy, A.G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sajjadi, S.A.; Mohammadi, A.; Khosravi, R.; Zarei, A. Distribution, exposure, and human health risk analysis of heavy metals in drinking groundwater of Ghayen County, Iran. Geocarto Int. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, M.; Mahvi, A.H.; Hashemi, S.Y.; Arfaeinia, H.; Pasalari, H.; Zarei, A.; Changani, F. Spatial distribution, enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals in surface sediments near urban and industrial areas in the Persian Gulf. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 158, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, M.W.H.; Hasan, K.A.; Balthazar-Silva, D.; Mirani, Z.A.; Asghar, M. Evaluation of heavy metal pollutants in salt and seawater under the influence of the Lyari River and potential health risk assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bat, L.; Arici, E.; Öztekin, A. Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Black Sea: Evaluating Mussels. Curr. World Environ. 2018, 13, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Dong, K.F.; Xiao, G.; Ma, D. Heavy metal concentrations in aquatic organisms (fishes, shrimp and crabs) and health risk assessment in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 159, 111505. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0025326X20306238 (accessed on 28 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Mulsow, S.; Povince, P.; Wyse, E.; Benmansour, M.; Sammir, B.; Cahfik, A. Trace elements, heavy metals and Pb isotopic ratios in marine sediments of the south Mediterranean Sea (Morroco). Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Me’Diterranee 2001, 36, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Rouibah, M. Etat de pollution par les me’taux lourds dans le port de Djen-Djen et le port de Jijel (Alge’rie). Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Me’Diterranee 2001, 36, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, M.; Hamdi, H.; Abdulnasser, I.; Jedidi, N. Contamination of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in Bizerte lagoon bottom sediments, surface sediment and sediment repository. In Study on Environmental Pollution of Bizerte Lagoon; Ghrabi, A., Yoshida, M., Eds.; INRST-JICA Press: Tunis, Tunisia, 2004; pp. 31–54. [Google Scholar]
- Unep/Map. State of the Mediterranean marine and coastal environment. In United Nations Environment Programme/Mediterranean Action Plan (UNEP/MAP); Barcelona Convention: Athens, Greece, 2012; p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund; Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment); Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Botté, S.E.; Freije, R.H.; Marcovecchio, J.E. Distribution of several heavy metals in tidal flats sediments within Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 210, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessai, D.V.; Nayak, G.N. Distribution and speciation of selected metals in surface sediments, from the tropical Zuari estuary, central west coast of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 158, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tom, N.F.Y.; Wong, Y.S. Hong Kong Mangroves; City University of Hong Kong Press: Hong Kong, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, C.; Sun, K.; Wang, S.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. Monte carlo simulation-based health risk assessment of heavy metal soil pollution: A case study in the Qixia mining area, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2012, 18, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Ma, Z.; Yang, J.; Lie, Y.; Bi, J.; Huang, L. Human Exposure Path ways of Heavy Metal in a Lead-Zinc Mining Area. In Heavy Metal Contamination of Water and Soil: Analysis, Assessment, and Remediation Strategies; Srari, E.A., Ed.; Apple Academic Press: Oakville, ON, Canada, 2014; pp. 129–156. ISBN 9781771880046. [Google Scholar]
- Yalcin, F. Data Analysis of Beach Sands’ Chemical Analysis Using Multivariate Statistical Methods and Heavy Metal Distribution Maps: The Case of Moonlight Beach Sands, Kemer, Antalya, Turkey. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkmen, A. Investıgation of Heavy Metal Accumulation Occured in Seawater and Sediment from the Gulf of Iskenderun. Karadeniz Fen Bilimleri Derg. 2011, 2, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Göycincik, S.; Danahaliloğlu, H.; Karayiğit, H.B. Research of Trace Element Levels of Sea Water in İskenderun Bay. Karadeniz Fen Bilimleri Derg. 2018, 8, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçın, F.; Nyamsari, D.G.; Paksu, E.; Yalcin, M.G. Statistical assessment of heavy metal distribution and contamination of beach sands of Antalya-Turkey: An approach to the multivariate analysis techniques. Filomat 2016, 30, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiğit, F. Gemi Kaynaklı Kirleticiler ve Trabzon Limanına Gelen Bazı Gemilerin Atıksularının Incelenmesi. Ph.D. Dissertation, Karadeniz Teknik Üniversitesi/Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Trabzon, Turkey, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Şahin, V.; Vardar, N. Determination of Wastewater Behavior of Large Passenger Ships Based on Their Main Parameters in the Pre Design Stage. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselin, M.; Drogui, P.; Brar, S.K.; Benmoussa, H.; Blais, J.F. Organics removal in oily bilgewater by electrocoagulation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olorunfemi, D.I.; Duru, L.; Olorunfemi, O.P. Genotoxic effects of bilge water on mitotic activity in Allium cepa L. Caryologia 2015, 68, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, N.H.; Burton, J.D.; Tankere, S.P.C.; Martin, J.M. Distribution and behavior of some dissolved trace metals in the western Mediterranean Sea. Deep Sea Res. 1997, 2, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiselius, P.; Magnusson, K. Toxicity of treated bilge water: The need for revised regulatory control. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytreberg, E.; Eriksson, M.; Maljutenko, I.; Jalkanen, J.P.; Johansson, L.; Hassellöv, I.M.; Granhag, L. Environmental impacts of grey water discharge from ships in the Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 152, 110891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, P.; Gu, X.; Lin, C.; Xin, M.; Zhang, H.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, X.; He, M.; Wang, B. Distribution, sources, and ecological risks of potentially toxic elements in the Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea: Under the long-term impact of the Yellow River input. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Rao, Y.; Huang, H. Biological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments and Health Risk Assessment in Marine Organisms from Daya Bay, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, H.; Azhdarpoor, A.; Hashemi, H.; Radfard, M.; Nasri, O.; Ghoochani, M.; Azizi, H.; Ebrahimzadeh, G.; Mahvi, A.H. Probabilistic and deterministic approaches to estimation of non-carcinogenic human health risk due to heavy metals in groundwater resources of torbat heydariyeh, southeastern of Iran. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 100, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikibe, J.E.; Prasad, S. Determination and comparison of selected heavy metal concentrations in seawater and sediment samples in the coastal area of Suva, Fiji. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; p. 398. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, J. Risk analysis on heavy metal contamination in sediments of rivers flowing into Nansi Lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 24, 26910–26918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, G.; Luo, Z.; Sun, X.; Xu, J. Spatial distribution, source identification, and risk assessment of heavy metals in seawater and sediments from Meishan Bay, Zhejiang coast, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasnia, A.; Ghoochani, M.; Yousefi, N.; Nazmara, S.; Radfard, M.; Soleimani, H.; Yousefi, M.; Barmar, S.; Alimohammadi, M. Prediction of human exposure and health risk assessment to trihalomethanes in indoor swimming pools and risk reduction strategy. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 2098–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.H.; Baghani, A.N.; Fazlzadeh, M.; Ghaffari, H.R. Exposure and risk assessment of BTEX in indoor air of gyms in Tehran, Iran. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalyari, N.; Alinejad, A.; Hashemi, A.H.G.; RadFard, M.; Dehghani, M. Health risk assessment of nitrate in groundwater resources of Iranshahr using Monte Carlo simulation and geographic information system (GIS). MethodsX 2019, 6, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Republic of Turkey Ministry of Transport and Infrastructure. 2021. Available online: https://denizcilikistatistikleri.uab.gov.tr/gemi-istatistikler (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Antalya Provincial Directorate of Culture and Tourism. Antalya from Yesterday to Today; Part 2. Antalya: Geographical Situation; Antalya Provincial Directorate of Culture and Tourism: Antalya, Türkiye, 2019; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, B.; Gago, L.; Vilas, F.; Nombela, M.; Garcia-Gil, S.; Alejo, I.; Pazos, O. Interpretacion de tendencias historicas de contaminacion por metales pesados en tesigos de sedimentos de la Ria de Pontevedra. Thalassas 2000, 12, 137–152. [Google Scholar]
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). Guiding Principles for Monte Carlo Analysis (EPA/630/R-97/001); Risk Assessment Forum US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. RAGS Volume 3 Part A—Process for Conducting Probabilistic Risk Assessment Chapter 1. 31 December 2001. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/rags3adt_complete.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Zheng, X.-W.; Yuan, J.-G.; Mai, B.-X. Heavy metals in food, house dust, and water from an e-waster recycling area in South China and the potential risk to human health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 96, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.Z.; Duan, X.L.; Ma, Y.Q.; Zhao, X.G.; Qin, Y.W.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Zheng, B.H.; Wei, F.S. Health benefit from decreasing exposure to potentially harmful elements ct pollution control measures near a typical river basin area in China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S. Industrial metal pollution of water and probabilistic assessment of human health risk. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 185, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2013; pp. 1–108. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Liu, G. Health risk assessment of potentially harmful elements in subsidence water bodies using a Monte Carlo approach: An example from the Huainan coal mining area, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Part A: Human Health Evaluation Manual; Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment; Part F, Supplemental Guidance for Inhalation Risk Assessment. In Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund; Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Turekian, K.K.; Wedepohl, K.H. Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1961, 72, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.; Usmani, N. Accumulation of heavy metals and human health risk assessment via the consumption of freshwater fish Mastacembelus armatus inhabiting, thermal power plant effluent loaded canal. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Custodio, M.; Cuadrado, W.; Peñaloza, R.; Montalvo, R.; Ochoa, S.; Quispe, J. Human risk from exposure to heavy metals and arsenic in water from rivers with mining influence in the Central Andes of Peru. Water 2020, 12, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surface Water Quality Management Regulation (SWQMR). Number of Official Newspapers: 29327. 2015. Available online: https://www.resmigazete.gov.tr/eskiler/2015/04/20150415-18.htm (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Onwuegbuchunam, D.E.; Ebe, T.E.; Okoroji, L.I.; Essien, A.E. An analysis of ship-source marine pollution in Nigeria seaports. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mearns, A.; Krause, C.J.B.; Stekoll, M.; Hall, K.; Watson, M.; Atkinson, M. Biological and ecological effects of wastewater discharges from cruise ships in Alaska. In Oceans 2003. Celebrating the Past... Teaming toward the Future; IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37492; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 2, pp. 737–747. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Phase I Uniform National Discharge Standards for Vessels. 1999. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-08/documents/vessels.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Corrias, F.; Atzei, A.; Addis, P.; Secci, M.; Russo, M.; Angioni, A. Integrated environmental evaluation of heavy metals and metalloids bioaccumulation in invertebrates and seaweeds from different marine coastal areas of sardinia, mediterranean sea. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arı, H. Çevresel Risk Azaltma Yöntemleri İçin Toplam Maruziyet İndeksinin Kullanılması. Nevşehir Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü Derg. 2012, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Altomare, T.K. Estimating Children’s Health Risks from Recreatıonal Beach Play followıng an Oil Spill UT School of Public Health Dissertations (Open Access). 2020. Available online: https://digitalcommons.library.tmc.edu/uthsph_dissertsopen/153 (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Kentel, E.; Aral, M.M. 2D Monte Carlo versus 2D fuzzy Monte Carlo health risk assessment. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2005, 19, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Metal | Türkmen [24] mg L−1 | Göycincik et al. [25] mg L−1 | Morley et al. [31] mg L−1 | Present Study mg L−1 | Standard Values (Surface Water Quality Management Regulation (SWQMR)) Annual Average [58] mg L−1 | WHO ** [38] mg L−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 0.17 | 0.24 | n/d | 0.69 | 0.042 | 0.05 |
| Cu | 0.07 | 0.36 | n/d | 2.67 | 0.013 | NGL |
| Ni | 0.28 | 0.09 | 0.013 | n/d | 0.086 | 0.5 |
| Pb | 0.62 | n/d | 0.01 | n/d | 0.013 | 0.01 |
| Zn | 0.07 | n/d | n/d | 3.99 | 0.533 | NGL *** |
| Fe | 0.30 | 7.14 | 0.01 | 5.84 | 0.036 | NGL |
| As | * n/d | 0.05 | n/d | n/d | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| V | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d | 0.016 | NGL |
| Mn | 0.11 | n/d | n/d | n/d | 0.1–0.5 | NGL |
| Co | 0.26 | n/d | 0.01 | n/d | 0.003 | NGL |
| Cd | 0.06 | n/d | n/d | n/d | 0.002 | 0.03 |
| Hg | n/d | n/d | n/d | 15.11 | 0.007 | 0.06 |
| Statistics | Wastewater Ingestion | Bilge Water Ingestion | Wastewater Ingestion | Bilge Water Ingestion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carcinogenic Risk | Non-Carcinogenic Risk | |||
| Cr | 0.3 | 0.38 | 1.69 | 2.85 |
| Ni | 0.59 | 0.81 | n/c | n/c * |
| As | 0.12 | 0.11 | 3.06 | 0.03 |
| Co | n/c | n/c | 2.56 | 1.7 |
| Hg | n/c | n/c | n/d ** | 3.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Özkaynak, Ö.H.; İçemer, G.T.; Merdun, H. Determination of the Risk on Human Health of Heavy Metals Contained by Ship Source Bilge and Wastewater Discharged to the Sea on the Mediterranean by Monte Carlo Simulation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8408. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148408
Özkaynak ÖH, İçemer GT, Merdun H. Determination of the Risk on Human Health of Heavy Metals Contained by Ship Source Bilge and Wastewater Discharged to the Sea on the Mediterranean by Monte Carlo Simulation. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8408. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148408
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖzkaynak, Ömer Harun, Gönül Tuğrul İçemer, and Hasan Merdun. 2022. "Determination of the Risk on Human Health of Heavy Metals Contained by Ship Source Bilge and Wastewater Discharged to the Sea on the Mediterranean by Monte Carlo Simulation" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8408. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148408
APA StyleÖzkaynak, Ö. H., İçemer, G. T., & Merdun, H. (2022). Determination of the Risk on Human Health of Heavy Metals Contained by Ship Source Bilge and Wastewater Discharged to the Sea on the Mediterranean by Monte Carlo Simulation. Sustainability, 14(14), 8408. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148408






