Response of Bread Wheat Cultivars Inoculated with Azotobacter Species under Different Nitrogen Application Rates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling and Analyses
2.3. Treatments and Experimental Design
2.4. Crop Sampling and Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
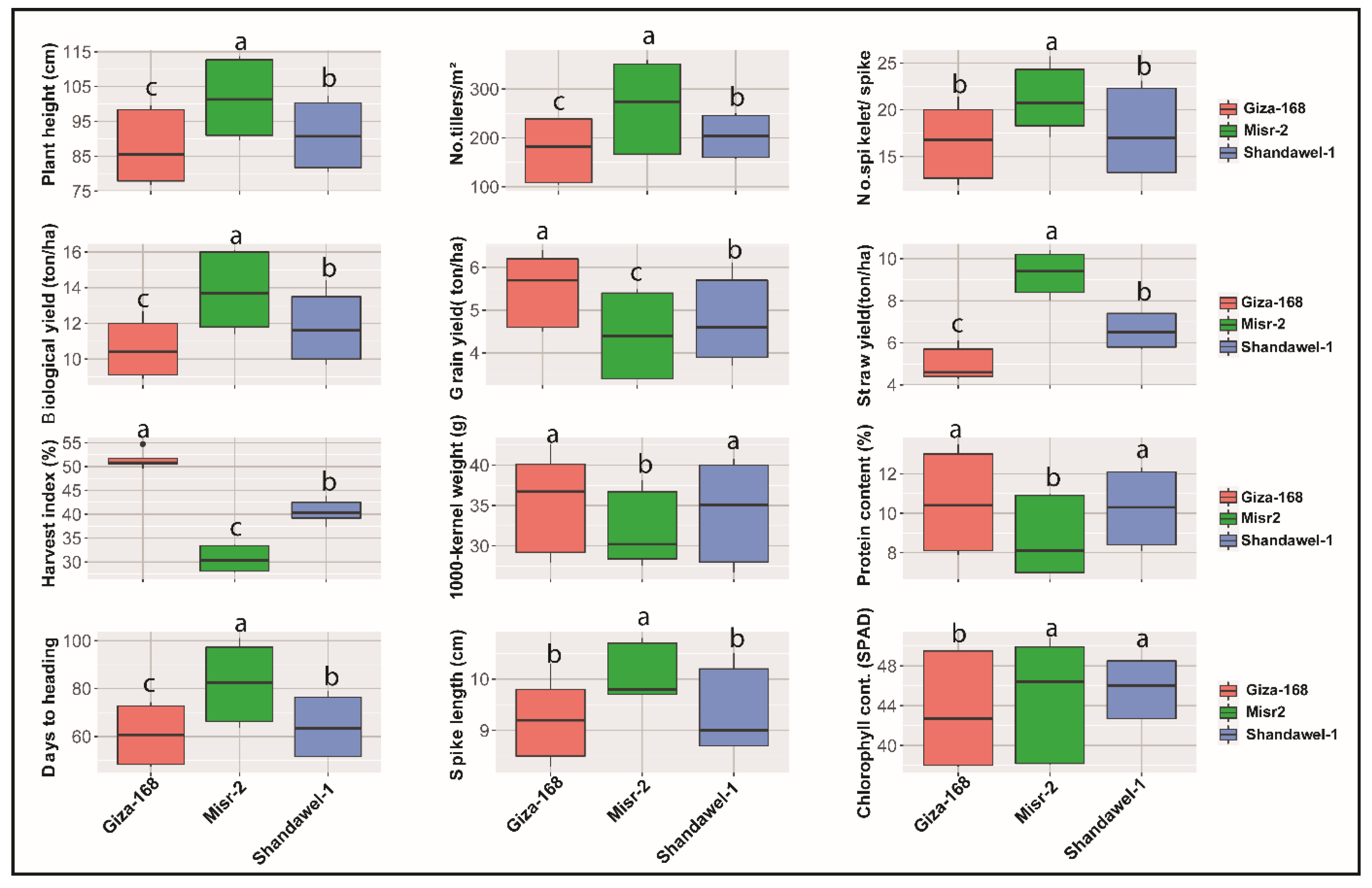
3.1. Plant Growth and Yield Parameters
3.1.1. Plant Height, Number of Tillers/m2, and Days to 50% Heading
3.1.2. Number of Spikelets/Spike and Spike Length
3.1.3. Yield and Yield-Related Traits
3.1.4. Chlorophyll and Protein Content
3.2. Correlation Coefficients
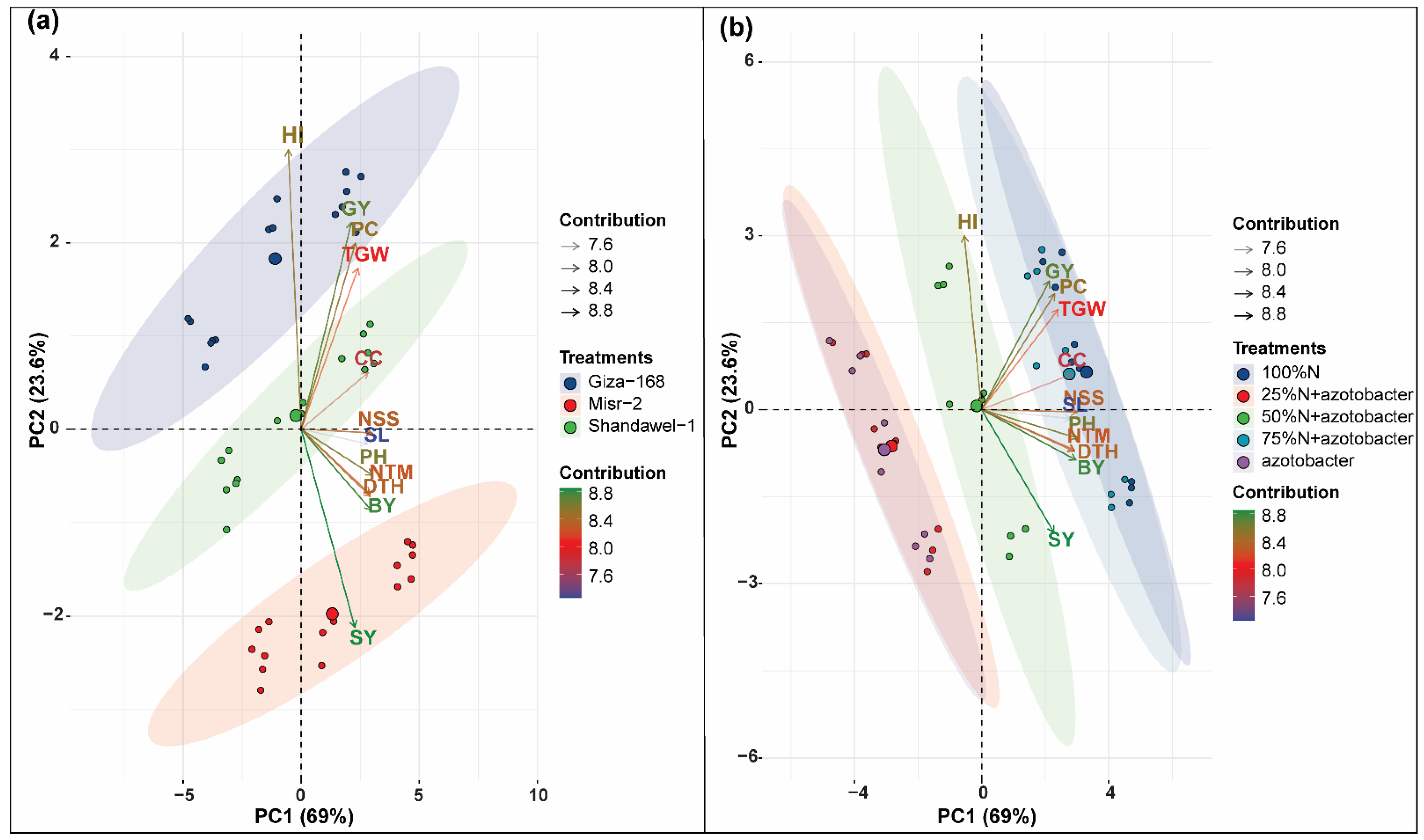
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marris, E. Agronomy: Five crop researchers who could change the world. Nature 2008, 456, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dixon, J.; Braun, H.-J.; Kosina, P.; Crouch, J.H. Wheat Facts and Futures 2009; Cimmyt: Veracruz, Mexico, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vessey, J.K. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant Soil 2003, 255, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.E.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Mackled, M.I.; Al-Jaddadi, M.A.M.; Ali, H.M.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Kandil, E.E. Soil Application of Nano Silica on Maize Yield and Its Insecticidal Activity Against Some Stored Insects After the Post-Harvest. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelsalam, N.R.; Kandil, E.E.; Al-Msari, M.A.; Al-Jaddadi, M.A.; Ali, H.M.; Salem, M.Z.; Elshikh, M.S. Effect of foliar application of NPK nanoparticle fertilization on yield and genotoxicity in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanullah; Iqbal, A.; Ali, A.; Fahad, S.; Parmar, B. Nitrogen Source and Rate Management Improve Maize Productivity of Smallholders under Semiarid Climates. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bindraban, P.S.; Dimkpa, C.; Nagarajan, L.; Roy, A.; Rabbinge, R. Revisiting fertilisers and fertilisation strategies for improved nutrient uptake by plants. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.; Ryan, J. Managing fertilizers to enhance soil health. Int. Fertil. Ind. Assoc. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, K.; Liu, W.; Gao, T.; Li, G.; Han, H.; Li, Z.; Ning, T. Responses of soil carbon, nitrogen, and wheat and maize productivity to 10 years of decreased nitrogen fertilizer under contrasting tillage systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dachler, M.; Köchl, A. Der einfluss von fruchtfolge, vorfrucht, stickstoffdüngung und einarbeitung der ernterückstände auf ertrag und rohproteingehalt von winterweizen und nachfolgender sommergerste. Die Bodenkult. 2003, 54, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Moitzi, G.; Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Kaul, H.-P.; Wagentristl, H. Energy efficiency of winter wheat in a long-term tillage experiment under Pannonian climate conditions. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 103, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moitzi, G.; Thünauer, G.; Robier, J.; Gronauer, A. Energieeinsatz und Energieeffizienz in der Körnermaisproduktion bei unterschiedlicher Stickstoffdüngung in der Südsteiermark. Die Bodenkult. 2015, 66, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fageria, N.K.; Baligar, V. Enhancing nitrogen use efficiency in crop plants. Adv. Agron. 2005, 88, 97–185. [Google Scholar]
- Barraclough, P.B.; Howarth, J.R.; Jones, J.; Lopez-Bellido, R.; Parmar, S.; Shepherd, C.E.; Hawkesford, M.J. Nitrogen efficiency of wheat: Genotypic and environmental variation and prospects for improvement. Eur. J. Agron. 2010, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yin, X.; Raza, S. Optimising nitrogen fertilisation: A key to improving nitrogen-use efficiency and minimising nitrate leaching losses in an intensive wheat/maize rotation (2008–2014). Field Crops Res. 2017, 206, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.-W.; Liu, X.-X.; Gu, S.-L.; Yu, J.-H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.-W.; Jiang, D.; Cao, W.-X.; Dai, T.-B. Postponed and reduced basal nitrogen application improves nitrogen use efficiency and plant growth of winter wheat. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2648–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, L.; Dai, X.; He, M. Delayed sowing improves nitrogen utilization efficiency in winter wheat without impacting yield. Field Crops Res. 2018, 221, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bargaz, A.; Lyamlouli, K.; Chtouki, M.; Zeroual, Y.; Dhiba, D. Soil microbial resources for improving fertilizers efficiency in an integrated plant nutrient management system. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, F.; Ahmad, I.; Khan, M. Screening of free-living rhizospheric bacteria for their multiple plant growth promoting activities. Microbiol. Res. 2008, 163, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasio, M.; Pepe, O.; Cirillo, T.; Palomba, S.; Blaiotta, G.; Villani, F. Selection and use of phytate-degrading LAB to improve cereal-based products by mineral solubilization during dough fermentation. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, M28–M35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oosten, M.J.; Pepe, O.; De Pascale, S.; Silletti, S.; Maggio, A. The role of biostimulants and bioeffectors as alleviators of abiotic stress in crop plants. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2017, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, B.; Patra, R.R.; Lawrence, R. Characterization of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria associated with chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Int. J. Plant. Prod. 2007, 1, 141–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J. Beneficial bacteria and fungi in hydroponic systems: Types and characteristics of hydroponic food production methods. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 195, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, D.; Valencia, G.; Soria, N.; Rueda, B.B.; Manjunatha, B.; Kundapur, R.R.; Selvanayagam, M. Effect of Azospirillum spp. and Azotobacter spp. on the growth and yield of strawberry (Fragaria vesca) in hydroponic system under different nitrogen levels. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 6, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanafy Ahmed, A.; Mishriky, J.; Khalil, M. Reducing nitrate accumulation in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) plants by using different biofertilizers. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2002, 47, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Arough, Y.K.; Sharifi, R.S.; Sedghi, M.; Barmaki, M. Effect of zinc and bio fertilizers on antioxidant enzymes activity, chlorophyll content, soluble sugars and proline in triticale under salinity condition. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2016, 44, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sudhakar, P.; Chattopadhyay, G.; Gangwar, S.; Ghosh, J. Effect of foliar application of Azotobacter, Azospirillum and Beijerinckia on leaf yield and quality of mulberry (Morus alba). J. Agric. Sci. 2000, 134, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aasfar, A.; Bargaz, A.; Yaakoubi, K.; Hilali, A.; Bennis, I.; Zeroual, Y.; Meftah Kadmiri, I. Nitrogen fixing Azotobacter species as potential soil biological enhancers for crop nutrition and yield stability. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjooei, Z.; Etemadi, M.; Eshghi, S.; Ramezanian, A.; Mirazimi Abarghuei, F.; Alizargar, J. Potential Role of Foliar Application of Azotobacter on Growth, Nutritional Value and Quality of Lettuce under Different Nitrogen Levels. Plants 2022, 11, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurav, R.G.; Jadhav, J.P. A novel source of biofertilizer from feather biomass for banana cultivation. Environ. Sci. Res. 2013, 20, 4532–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmageed, K.; Chang, X.-H.; Wang, D.-M.; Wang, Y.-J.; Yang, Y.-S.; Zhao, G.-C.; Tao, Z.-Q. Evolution of varieties and development of production technology in Egypt wheat: A review. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, M. Characterization of soil physical properties and organic matter under long-term primary tillage in a humid climate. Soil Tillage Res. 1996, 38, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- soil and allow regrowth of natural vegetation. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 139, 40–52. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-J.; Yin, B.-Z.; Hu, Z.-H.; Bao, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.-D.; Zhen, W.-C. Physiological response of flag leaf and yield formation of winter wheat under different spring restrictive irrigation regimes in the Haihe Plain, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 2343–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS. The SAS system for Windows. Release 9.4; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Koua, A.P.; Oyiga, B.C.; Baig, M.M.; Léon, J.; Ballvora, A. Breeding driven enrichment of genetic variation for key yield components and grain starch content under drought stress in winter wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 684205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia, M.A.; Shaban, K.A.; Sallam, A.M. Role of Humic, Ascorbic Acids with or without Compost to Improve Nutrients Content, Yield Components, and Seed Quality of Sesame. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2014, 5, 1049–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash-Shormillesy, S.M.; Yasin, M. Effectiveness of Organic and Bio-Fertilization on Reduce Rates of Mineral Nitrogen Fertilizers and Impact on Productivity of some Wheat Cultivars. J. Plant. Prod. 2021, 12, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, E.-S.M.; Ghanem, S.; Zeiton, O.; Omar, A. Effect of some bio-fertilizers on the yield and quality of three bread wheat cultivars under differed nitrogen levels. Zagazig J. Agric. Res. 2018, 45, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namvar, A.; Khandan, T. Response of wheat to mineral nitrogen fertilizer and biofertilizer (Azotobacter sp. and Azospirillum sp.) inoculation under different levels of weed interference. Ekologija 2013, 59, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khateeb, N.M.; Metwaly, M.M. Influence of some bio-fertilizers on wheat plants grown under graded levels of nitrogen fertilization. Int. J. Environ. 2019, 8, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Arif, M.S.; Riaz, M.; Shahzad, S.M.; Yasmeen, T.; Akhtar, M.J.; Riaz, M.A.; Jassey, V.E.; Bragazza, L.; Buttler, A. Associative interplay of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa QS40) with nitrogen fertilizers improves sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) productivity and fertility of aridisol. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 108, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafa, Z.N.; Sohrabi, Y.; Sayyed, R.; Luh Suriani, N.; Datta, R. Effects of the Combinations of Rhizobacteria, Mycorrhizae, and Seaweed, and Supplementary Irrigation on Growth and Yield in Wheat Cultivars. Plants 2021, 10, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, A.; Mohammadi, K. Effect of nitrogen and Aztobactor fertilizers on the grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of Moroccan single cross corn. Plant Ecophysiol. 2020, 12, 200–210. [Google Scholar]
- Du Jardin, P. Plant biostimulants: Definition, concept, main categories and regulation. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasari, E.; Patwardhan, A. Effects of (Azotobacter and Azosprillium) inoculants and chemical fertilizers on growth and productivity of canola (Brassica napus L.). Asian J. Plant. Sci. 2007, 6, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelghany, A.M.; El-Banna, A.A.A.; Salama, E.A.A.; Ali, M.M.; Al-Huqail, A.A.; Ali, H.M.; Paszt, L.S.; El-sorady, G.; Lamlom, S.F. The Individual and Combined Effect of Nanoparticles and Biofertilizers on Growth, Yield, and Biochemical Attributes of Peanuts (Arachis hypogea L.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghany, A.M.; Zhang, S.; Azam, M.; Shaibu, A.S.; Feng, Y.; Qi, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.-F.; Tian, Y.; Hong, H.-l.; et al. Exploring the Phenotypic Stability of Soybean Seed Compositions Using Multi-Trait Stability Index Approach. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.A.; Yousef, A.F.; Ali, M.M.; Ahmed, A.I.; Lamlom, S.F.; Strobel, W.R.; Kalaji, H.M. Exogenously applied nitrogenous fertilizers and effective microorganisms improve plant growth of stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni) and soil fertility. AMB Express 2021, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Siddiqui, Z. Effects of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms and Rhizobium sp. on the growth, nodulation, yield and root-rot disease complex of chickpea under field condition. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 3489–3496. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, C.; Liang-Gang, Z.; Jun, X.; Qian, Z.; Yan, Z. Effects of biofertilizer on organically cultured cucumber growth and soil biological characteristics. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2010, 21, 2587–2592. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, R.S.; Namvar, A.; Sharifi, R.S. Grain filling and fatty acid composition of safflower fertilized with integrated nitrogen fertilizer and biofertilizers. Pesqui. Agropecuária Bras. 2017, 52, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefan, M.; Munteanu, N.; Stoleru, V.; Mihasan, M. Effects of inoculation with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on photosynthesis, antioxidant status and yield of runner bean. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 18, 8132–8143. [Google Scholar]
- Emam, Y.; Eilkaie, M. Effect of plant density and chlormequat chloride (CCC) on morphological characteristics and grain yield of winter rape seed cv. Talayeh. Iran. J. Crop. Sci. 2002, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, P.; Chanemougasoundharam, A.; Khurana, S.P.; Kalloo, G. Genetic manipulation of carotenoid pathway in higher plants. Curr. Sci. 2003, 85, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, R.; Giri, B.; Mukerji, K.G. Improved growth and essential oil yield and quality in Foeniculum vulgare mill on mycorrhizal inoculation supplemented with P-fertilizer. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 93, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, Z.; Ajmal, S.U.; Munir, M. Estimation of correlation coefficient among some yield parameters of wheat under rainfed conditions. Pak. J. Bot 2008, 40, 1777–1781. [Google Scholar]
- Aycicek, M.; Yildirim, T.J.P.J.o.B. Path coefficient analysis of yield and yield components in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes. Pak. J. Bot. 2006, 38, 417. [Google Scholar]
- Kashif, M.; Khaliq, I. Heritability, correlation and path coefficient analysis for some metric traits in wheat. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2004, 6, 138–142. [Google Scholar]
- Mandic, V.; Krnjaja, V.; Tomic, Z.; Bijelic, Z.; Simic, A.; Ruzic Muslic, D.; Gogic, M. Nitrogen fertilizer influence on wheat yield and use efficiency under different environmental conditions. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 75, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahid, M.; Mohammad, F.; Tahir, M. Path coefficient analysis in wheat. Sarhad J. Agric. 2002, 18, 383–388. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, B.K.; Mudwari, A.; Thapa, D.B. Correlation and path coefficients among quantitative traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Nepal J. Sci. Technol. 2008, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janmohammadi, M.; Navid, A.; Segherloo, A.E.; Sabaghnia, N. Impact of nano-chelated micronutrients and biological fertilizers on growth performance and grain yield of maize under deficit irrigation condition. Biologija 2016, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rathnathilaka, T.; Premarathna, M.; Madawala, S.; Pathirana, A.; Karunaratne, K.; Seneviratne, G. Biofilm biofertilizer application rapidly increases soil quality and grain yield in large scale conventional rice cultivation: A case study. Plant. Nutr. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, S.K.; Rakshit, A.; Meena, V.S. Effect of seed bio-priming and N doses under varied soil type on nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under greenhouse conditions. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2016, 6, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Suhaibani, N.; Selim, M.; Alderfasi, A.; El-Hendawy, S. Comparative performance of integrated nutrient management between composted agricultural wastes, chemical fertilizers, and biofertilizers in improving soil quantitative and qualitative properties and crop yields under arid conditions. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Cortivo, C.; Ferrari, M.; Visioli, G.; Lauro, M.; Fornasier, F.; Barion, G.; Panozzo, A.; Vamerali, T. Effects of seed-applied biofertilizers on rhizosphere biodiversity and growth of common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the field. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, P.; Bainard, L.D.; Ma, B.; Liu, J. Bio-fertilizer and rotten straw amendments alter the rhizosphere bacterial community and increase oat productivity in a saline–alkaline environment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cultivars | Pedigree | Origin | Year of Release |
|---|---|---|---|
| Giza-168 | MRL/BUC//SERI-CM93046-8M-0Y-0M-2Y-0B-0SH | Egypt | 1999 |
| Misr-2 | SKAUZ/BAV92-CMSS96M03611S-1M-010SY-010M-010SY-8M-0Y-0S | Egypt | 2010 |
| Shandawel-1 | SITE/MO/4/NAC/TH.AC//3*PVN/3/MIRLO/BUC-CMSS93B00567S-72Y-010M-010Y-010M-3Y-0M-0HTY-0SH | Egypt | 2011 |
| Parameters | Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019/20 Season | 2020/21 Season | ||
| Particle size distribution | Clay % | 17.5 | 19.6 |
| Sand % | 70 | 68.5 | |
| Silt % | 12.5 | 11.9 | |
| Texture grade | Silt loam | Silt loam | |
| Available nutrients | N (mg kg−1) | 77.5 | 89.3 |
| P (mg kg−1) | 30.4 | 35.8 | |
| K (mg kg−1) | 379 | 436 | |
| Soluble cations and anions (cmol kg−1 soil) | Ca++ | 2.08 | 1.94 |
| Mg++ | 4.69 | 4.7 | |
| Na+ | 18.1 | 18.5 | |
| K+ | 0.72 | 0.77 | |
| HCO3− | 3.67 | 3.73 | |
| Cl− | 15.53 | 15.66 | |
| SO4− | 6.41 | 6.57 | |
| Chemical properties | pH (Susp. 1:2.5 soil-water) | 7.23 | 7.26 |
| EC (dSm−1) | 2.69 | 2.7 | |
| C.E.C (cmol kg−1) | 18.8 | 19.4 | |
| Organic matter (%) | 1.38 | 1.73 | |
| CaCO3 (%) | 43.2 | 42.3 | |
| SOV | PH | NTM | DTH | NSS | SL | BY | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | |
| Cultivars | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| Fertilizer | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| C × F | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | * | * | *** | *** |
| CV | 0.96 | 0.70 | 1.19 | 1.10 | 0.75 | 0.69 | 3.15 | 3.06 | 2.95 | 3.01 | 2.68 | 6.31 |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.97 |
| RMSE | 0.86 | 0.64 | 2.31 | 2.17 | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.60 | 0.610 | 0.288 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| SOV | GY | SY | HI | TGW | PC | CC | ||||||
| 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | |
| Cultivars | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | * | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| Fertilizer | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| C × F | *** | *** | *** | * | *** | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| CV | 2.30 | 6.31 | 4.61 | 4.96 | 8.47 | 3.76 | 0.70 | 0.99 | 0.37 | 0.51 | 2.11 | 2.20 |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.99 | 1.31 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| RMSE | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 9.53 | 1.78 | 0.25 | 0.41 | 0.041 | 0.056 | 0.94 | 0.98 |
| C | F | PH | NTM | DTH | NSS | SL | BY | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | ||
| Misr-2 | 100%N | 113.7 a | 116.7 a | 283 a | 280 a | 101.1 a | 102.1 a | 21.8 bcd | 22.1 abcd | 11.4 cd | 11.18 cde | 15.54 a | 16.1 a |
| 75%N + AZ | 112.7 a | 114.6 a | 279 a | 278 a | 97.3 a | 98.3 a | 20.0 cde | 21.4 bcde | 10.8 d | 10.9 de | 15.3 a | 15.9 a | |
| 50%N + AZ | 101.3 b | 101.3 b | 248 b | 243 b | 82.4 b | 83.8 b | 16.8 e | 17.2 fg | 8.2 ef | 8.2 fg | 13.5 b | 13.6 b | |
| 25%N + AZ | 91 cde | 91.1 cd | 187 ef | 183 ef | 63.7 e | 64.3 e | 12.7 f | 13.1 h | 7.1 f | 7.1 g | 11.6 ed | 11.8 de | |
| azotobacter | 89.5 def | 89.5 de | 183 ef | 182 ef | 66.3 de | 67.0 de | 11.9 f | 13.0 h | 7.1 f | 7.1 g | 11.1 e | 11.4 e | |
| Shandawel-1 | 100%N | 102.3 b | 104.4 b | 225 c | 219 c | 79.1 bc | 80.4 bc | 23.1 abc | 24.1 abc | 12.3 ab | 12.4 abc | 13.2 bc | 14.4 b |
| 75%N + AZ | 100.3 b | 102.1 b | 222 cd | 217 cd | 76.3 bc | 78.0 bc | 22.3 bcd | 23.2 abc | 12.1 bc | 12.1 bcd | 12. 8 bc | 13.5 bc | |
| 50%N + AZ | 90.7 cde | 90.7 cde | 201 de | 197 ed | 63.4 e | 64.8 e | 17.0 e | 19.5 def | 10.3 d | 10.4 e | 10.9 ef | 11.6 e | |
| 25%N + AZ | 81.7 efg | 82.2 def | 179 f | 178 ef | 63.4 e | 52.7 f | 13.3 f | 14.1 gh | 8.4 e | 8.8 f | 9.4 gh | 10.1 fg | |
| azotobacter | 80.5 gf | 82.1 ef | 179 f | 176 f | 51.3 f | 52.0 f | 13.2 f | 13.9 gh | 8.1 ef | 8.1 fg | 9. 3 gh | 9.7 gh | |
| Giza-168 | 100%N | 99.6 bc | 101.0 b | 220 cd | 218 c | 74.3 bcd | 75.7 bcd | 25.7 a | 25.0 a | 13.4 a | 13.5 a | 12.5 cd | 12.7 cd |
| 75%N + AZ | 98.4 bc | 98.4 bc | 219 cd | 216.33 cd | 72.7 cd | 74.1 cd | 24. 3 ab | 24.2 ab | 12.9 ab | 13.1 ab | 11.8 de | 12.1 de | |
| 50%N + AZ | 85.5 efg | 88.3 de | 190 ef | 185 ef | 60.7 e | 62.8 e | 20.66 cd | 20.8 cde | 10.4 d | 10.6 e | 10.1 fg | 10.4 f | |
| 25%N + AZ | 77.9 g | 78.1 f | 154 g | 150 g | 48.3 f | 48.5 f | 18.33 ed | 18.3 ef | 8.1 ef | 8.1 fg | 8.9 h | 9.1 gh | |
| azotobacter | 76.8 g | 78.1 f | 152 g | 198 g | 47.5 f | 48.5 f | 17.14 e | 16. 9 fd | 7.8 f | 7.9 fg | 8.5 h | 8.9 h | |
| a | B | GY | SY | HI | TGW | PC | CC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019/2020 | 2020/2201 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | 2019/2020 | 2020/2021 | ||
| Misr-2 | 100%N | 6.3 a | 6.4 a | 10.3 a | 10.6 a | 33.4 def | 34.1 cd | 38.1 bc | 36.3 ab | 10.8 a | 11.12 a | 50.8 a | 51.0 a |
| 75%N + AZ | 5.1 de | 5.4 c | 10.2 a | 10.6 a | 33.6 de | 33.9 cde | 36.7 bc | 35.5 b | 10.6 ab | 10.8 a | 49.9 a | 50.0 a | |
| 50%N + AZ | 4.1 fg | 4.4 d | 9.4 ab | 9.3 b | 30.3 ef | 31.9 de | 30.2 d | 28.2 c | 9.6 cd | 9.8 abc | 46.4 b | 46.6 b | |
| 25%N + AZ | 3.3 h | 3.4 fg | 8.4 bc | 8.4 bc | 27.8 f | 29.1 e | 28.4 d | 28. 1 c | 9.8 bcd | 9.8 abc | 38.2 d | 39.5 d | |
| Azotobacter | 3.1 h | 3.3 g | 7.9 cd | 8.0 c | 28.1 ef | 29.5 de | 27.6 d | 27.6 c | 9.6 cd | 9.8 abc | 38.12 d | 39.5 d | |
| Sandawel-1 | 100%N | 5.8 abc | 6.1 ab | 7.4 cde | 8.2 c | 48.8 b | 42.6 b | 40.6 ab | 39.4 ab | 10.2 abc | 10.7 a | 48.6 ab | 48.77 ab |
| 75%N + AZ | 5.4 cd | 5.7 ab | 7.3 de | 7.7 cd | 42.5 bc | 42.4 b | 39.9 ab | 38.5 ab | 10.5 abc | 10.7 a | 48.5 ab | 48.6 ab | |
| 50%N + AZ | 4.4 f | 4.6 d | 6.5 ef | 7.0 de | 40.3 bc | 39.7 b | 39.9 ab | 34.7 b | 9.0 de | 9.3 bcd | 46.1 b | 46.4 b | |
| 25%N + AZ | 3.7 gh | 3.9 ef | 5.7 f | 6.3 ef | 39.3 bc | 39.1 b | 27.9 d | 27.2 c | 8.7 e | 8.8 cd | 42.7 c | 42.6 c | |
| Azotobacter | 3.5 h | 3.7 fg | 5.8 f | 5.9 f | 37.3 cd | 38.4 bc | 26.7 d | 26.2 c | 8.7 e | 8.8 cd | 42.7 c | 43.1 c | |
| Giza-168 | 100%N | 6.1 ab | 6.2 ab | 6.1 f | 6.2 ef | 50.8 a | 50. a | 42.6 a | 40.4 a | 10.3 abc | 10.5 ab | 49.5 a | 50.1 a |
| 75%N + AZ | 5.2 d | 5.5 c | 5.7 f | 5.8 f | 51.7 a | 51.8 a | 40.1 ab | 39.1 ab | 9.8 bcd | 10.3 ab | 49.5 ab | 49.7 a | |
| 50%N + AZ | 5.5 bcd | 5.7 bc | 4.5 g | 7.7 g | 50.7 a | 50.6 a | 36.7 bc | 35.4 b | 9.2 de | 9.3 bcd | 42.7 c | 43.1 c | |
| 25%N + AZ | 4.5 ef | 4.6 d | 4.4 g | 4.5 g | 50.6 a | 50.5 a | 29.2 d | 28.1 c | 8.5 e | 8.7 cd | 37.9 d | 38.7 d | |
| Azotobacter | 4.2 gf | 4.5 d | 4.3 g | 4.4 g | 49.6 a | 50.2 a | 27.9 d | 27.7 c | 8.33 e | 8.50 d | 37.89 d | 38.26 d | |
| PH | NTM | NSS | BY | GY | SY | HI | TGW | PC | DTH | SL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTM | 0.97 *** | ||||||||||
| NSS | 0.98 *** | 0.92 *** | |||||||||
| BY | 0.99 *** | 0.96 *** | 0.97 *** | ||||||||
| GY | 0.54 * | 0.50 ns | 0.60 * | 0.47 ns | |||||||
| SY | 0.82 *** | 0.82 *** | 0.77 *** | 0.87 *** | −0.02 | ||||||
| HI | −0.32 ns | −0.33 ns | −0.25 ns | −0.4 ns | 0.61 * | −0.79 *** | |||||
| TGW | 0.68 ** | 0.60 * | 0.75 ** | 0.62 * | 0.94 *** | 0.17 ns | 0.41 ns | ||||
| PC | 0.59 * | 0.53 * | 0.64 ** | 0.52 * | 0.95 *** | 0.05 ns | 0.49 ns | 0.97 *** | |||
| DH | 0.99 *** | 0.98 *** | 0.96 *** | 0.98 *** | 0.49 ns | 0.85 *** | −0.36 ns | 0.61 * | 0.52 * | ||
| SL | 0.94 *** | 0.86 *** | 0.97 *** | 0.93 *** | 0.53 * | 0.77 ** | −0.31 ns | 0.69 ** | 0.59 * | 0.92 *** | |
| CC | 0.83 *** | 0.85 *** | 0.82 *** | 0.79 *** | 0.76 ** | 0.46 ns | 0.07 ns | 0.83 *** | 0.85 *** | 0.79 *** | 0.73 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Sorady, G.A.; El-Banna, A.A.A.; Abdelghany, A.M.; Salama, E.A.A.; Ali, H.M.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Hayatu, N.G.; Paszt, L.S.; Lamlom, S.F. Response of Bread Wheat Cultivars Inoculated with Azotobacter Species under Different Nitrogen Application Rates. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8394. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148394
El-Sorady GA, El-Banna AAA, Abdelghany AM, Salama EAA, Ali HM, Siddiqui MH, Hayatu NG, Paszt LS, Lamlom SF. Response of Bread Wheat Cultivars Inoculated with Azotobacter Species under Different Nitrogen Application Rates. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8394. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148394
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Sorady, Gawhara A., Aly A. A. El-Banna, Ahmed M. Abdelghany, Ehab A. A. Salama, Hayssam M. Ali, Manzer H. Siddiqui, Nafiu Garba Hayatu, Lidia Sas Paszt, and Sobhi F. Lamlom. 2022. "Response of Bread Wheat Cultivars Inoculated with Azotobacter Species under Different Nitrogen Application Rates" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8394. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148394
APA StyleEl-Sorady, G. A., El-Banna, A. A. A., Abdelghany, A. M., Salama, E. A. A., Ali, H. M., Siddiqui, M. H., Hayatu, N. G., Paszt, L. S., & Lamlom, S. F. (2022). Response of Bread Wheat Cultivars Inoculated with Azotobacter Species under Different Nitrogen Application Rates. Sustainability, 14(14), 8394. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148394












