Impact of Information Asymmetry on the Operation of Green Closed-Loop Supply Chain under Government Regulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. CLSC Management under the Constraint of Carbon Emissions Reduction
2.2. Supply Chain Management with Information Asymmetry
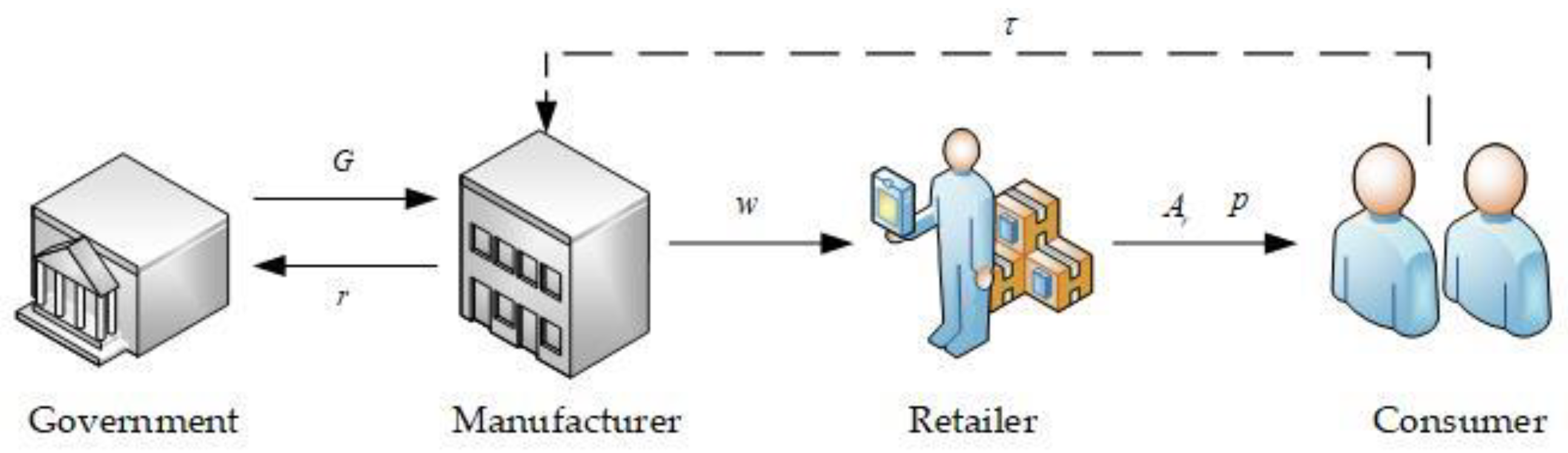
3. Problem Descriptions and Notations
3.1. Problem Description
3.2. Notations and Assumtions
4. Problem Formulation and Solutions
4.1. Information Symmetry Decision Model
4.2. Information Asymmetry Decision Model
4.3. Model Comparisons and Analysis
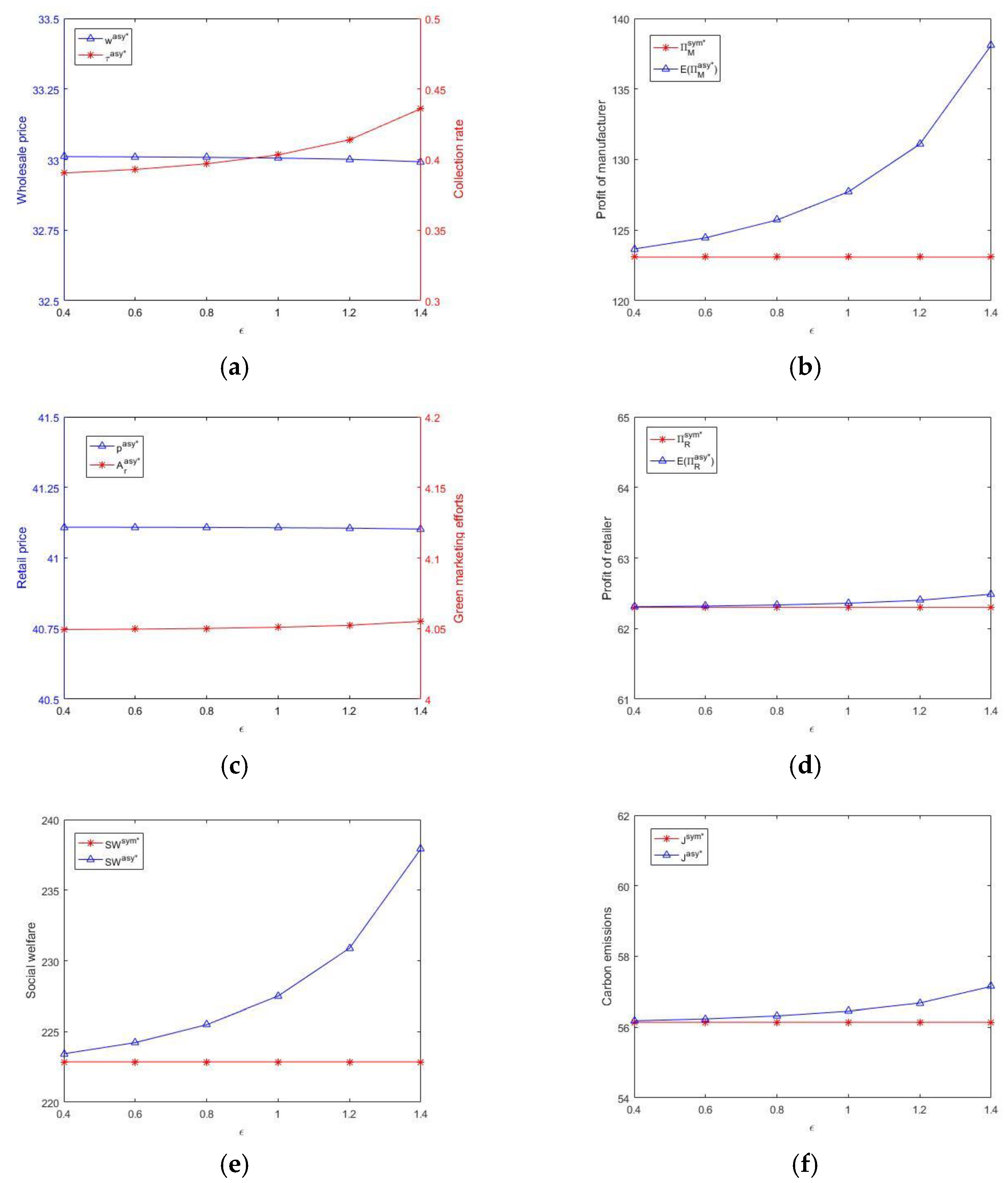
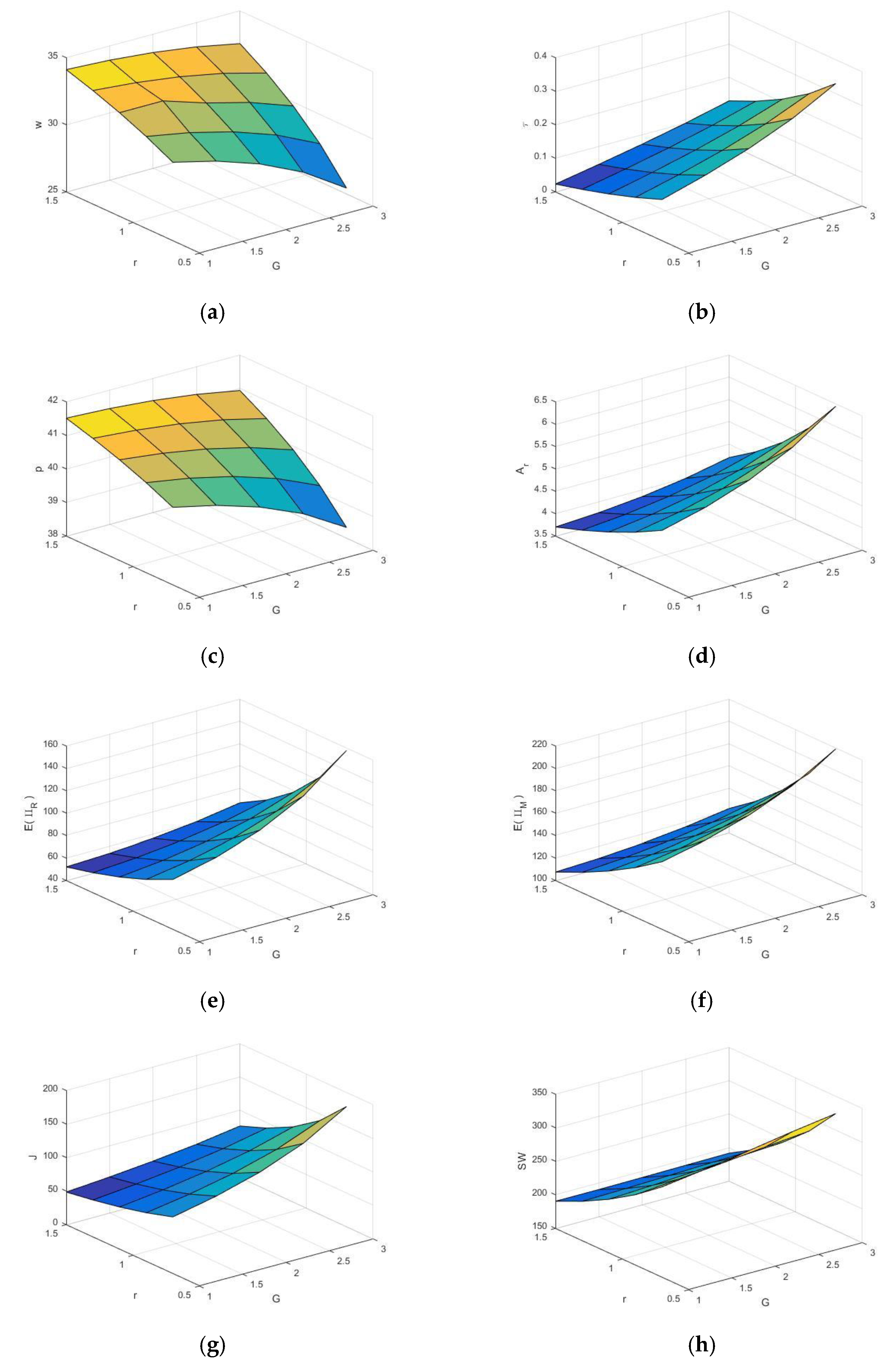
5. Numerical Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Guide, V.D.R.; Van Wassenhove, L.N. The evolution of closed-loop supply chain research. Oper. Res. 2009, 57, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Anderson, T.D.; Cruz, J.M. Consumer environmental awareness and competition in two-stage supply chain. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 218, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Jiang, G.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, G.; Mohamed, N. Newsvendor’s optimal decisions under stochastic demand and cap-and-trade regulation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 17764–17787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Yang, H.; Ji, Y. Low-carbon supply chain optimization considering warranty period and carbon emission reduction level under cap-and-trade regulation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 18040–18067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, G.; Cao, K. A joint analysis of environmental and economic performances of closed-loop supply chains under carbon tax regulation. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 146, 106624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantaras, I.; Skouri, K.; Benkherouf, L. Optimizing inventory decisions for a closed-loop supply chain model under a carbon tax regulatory mechanism. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 239, 108185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhari, W.A.; Pujawan, I.N.; Suef, M. A closed-loop supply chain inventory model with stochastic demand, hybrid production, carbon emissions, and take-back incentives. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Goodarzi, S.; Bozorgi, A.; Fahimnia, B. Carbon cap-and-trade schemes in closed-loop supply chains: Why firms do not comply? Transp. Res. E-Log. 2021, 156, 102486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, M.M.; Yang, F. Joint emission reduction strategy considering channel inconvenience under different recycling structures. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 169, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegoz, M.; Kaya, O.; Bayindir, Z.P. Closing the loop in supply chains: Economic and environmental effects. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 142, 106366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, N. The impact of CSR on the performance of a dual-channel closed-loop supply chain under two carbon regulatory policies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lai, K.K.; Li, Y.M. Remanufacturing and low-carbon investment strategies in a closed-loop supply chain under multiple carbon policies. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2022. online. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Xu, J.; Chauhan, S.S. Effects of sustainability investment and risk aversion on a two-stage supply chain coordination under a carbon tax policy. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 142, 106324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Xu, J.; Gong, Y.; Chauhan, S.S. Robust decisions for regulated sustainable manufacturing with partial demand information: Mandatory emission capacity versus emission tax. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2022, 298, 874–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, G.; Choi, T.M. Does implementing trade-in and green technology together benefit the environment? Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 295, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.P.; Qin, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, Y. Optimal decisions in a closed-loop supply chain under different policies of government intervention. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Li, L. Environmental sustainability EOQ model for closed-loop supply chain under market uncertainty: A case study of printer remanufacturing. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 151, 106525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golpira, H.; Javanmardan, A. Robust optimization of sustainable closed-loop supply chain considering carbon emission schemes. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 30, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, G.L.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liang, C.J.; Gen, M. Research on remanufacturing closed loop supply chain based on incentive-compatibility theory under uncertainty. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022; online. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Pokharel, S.; Elomri, A. An eco-friendly closed-loop supply chain facing demand and carbon price uncertainty. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022; online. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Peng, Z.Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Lai, K.K.; Yang, H. Government subsidy for remanufacturing or carbon tax rebate: Which is better for firms and a low-carbon economy. Sustainability 2017, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y. Emission reduction decision and coordination of a make-to-order supply chain with two products under cap-and-trade regulation. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 119, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wahab, M.I.M.; Zhang, G.; Ye, Y. Optimal strategy for a green supply chain considering shipping policy and default risk. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 131, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazan, E.; Jaber, M.Y.; EI Saadany, A.M.A. Carbon emissions and energy effects on manufacturing-remanufacturing inventory models. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 88, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, B. Manufacturing/remanufacturing decisions for a capital-constrained manufacturer considering carbon emission cap and trade. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, G.; Bai, Q. Quantity and collection decisions of the remanufacturing enterprise under both the take-back and carbon emission capacity regulations. Transp. Res. E-Log. 2020, 141, 102032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y. The distributionallly robust optimization model for a remanufacturing system under cap-and-trade policy: A newsvendor approach. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022, 309, 731–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, Z. Carbon emissions in a dual channel closed loop supply chain: The impact of consumer free riding behavior. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 134, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazan, E.; Jaber, M.Y.; Zanoni, S. Carbon emissions and energy effects on a two-level manufacturer-retailer closed-loop supply chain model with remanufacturing subject to different coordination mechanisms. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Huang, L. Collecting model selection in a remanufacturing supply chain under cap-and-trade regulation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 287, 480–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhari, W.A.; Adam, N.A.F.P.; Rosyidi, C.N.; Pujawan, I.N.; Shah, N.H. A closed-loop supply chain model with rework, waste disposal, and carbon emissions. Oper. Res. Perspect. 2020, 7, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekarian, E.; Marandi, A.; Majava, J. Dual-channel remanufacturing closed-loop supply chains under carbon footprint and collection competition. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 1050–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Q. Carbon emission reduction and product collection decisions in the closed-loop supply chain with cap-and-trade regulation. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 4359–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Netessine, S. Collaborative cost reduction and component procurement under information asymmetry. Manag. Sci. 2013, 59, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, P.; Shang, J.; Wang, H.Y. Enhancing corporate social responsibility: Contract design under information asymmetry. Omega-Int. J. Manag. S 2017, 67, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Mantrala, M.; Bian, Y.W. Strategic information management in a distribution channel. J. Retail. 2019, 95, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Guan, X.; Fan, T.J.; Zhou, L. The acquisition of quality information in a supply chain with voluntary vs. mandatory disclosure. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2020, 29, 595–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wang, Y.; Yi, Z.; Chen, Y.J. Inducing consumer online reviews via disclosure. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2020, 29, 1956–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xiong, Y.; Xiong, Z.K.; Yan, W. Designing contracts for a closed-loop supply chain under information asymmetry. Oper. Res. Lett. 2014, 42, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Govindan, K.; Li, Y.J.; Zhao, J. Pricing and collecting decisions in a closed-loop supply chain with symmetric and asymmetric information. Comput. Oper. Res. 2015, 54, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giovanni, P. Closed-loop supply chain coordination through incentives with asymmetric information. Ann. Oper. Res. 2017, 253, 133–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liang, Z.; Shang, J.; Xu, Z.S. Remanufacturing with patented technique royalty under asymmetric information and uncertain markets. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2020, 26, 599–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.B.; Zhou, S.Y.; Zhang, M.; Sun, H.; He, L. A closed-loop supply chain with competitive dual collection channel under asymmetric information and reward–penalty mechanism. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Huang, L.Z. Digital twins for information-sharing in remanufacturing supply chain: A review. Energy 2021, 220, 119712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, X.; Lin, R. Government incentive mechanism of closed-loop supply chain based on information asymmetry. Rairo-Oper. Res. 2021, 55, 3359–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, K.B.; Wang, S.B.; Cao, X.G. Optimal decisions in a closed-loop supply chain: Fairness concerns, corporate social responsibility and information value. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022, 309, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Liu, H.; Song, M. Production optimization considering environmental performance and preference in the cap-and-trade system. J. Clean Prod. 2016, 112, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qi, Q.; Bai, Q. Coordinating a dual-channel supply chain with price discount contracts under carbon emission capacity regulation. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 56, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| literature | Echelons of CLSC | Carbon Policy | Recycling Subsidy | Uncertainty | Information Asymmetry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dou and Cao [5] | Two | Carbon tax | × | × | × |
| Jauhari et al. [31] | Three | Cap-and-trade | × | × | × |
| Wang and Wu [33] | Three | Cap-and-trade | × | × | × |
| Xu et al. [20] | Two | Cap-and-trade | × | Demand and carbon price | × |
| Jauhari et al. [7] | Two | Carbon tax | × | Demand and return | × |
| Guo et al. [19] | One | Carbon tax | ✓ | Demand and recycled products quality | × |
| Gao et al. [42] | Two | × | × | Demand | ✓ |
| Wang et al. [43] | Three | × | × | Demand | ✓ |
| Wang et al. [46] | Two | × | × | Fairness concern | ✓ |
| Present work | Two | Carbon tax | ✓ | Marketing cost coefficient | ✓ |
| Parameters | |
|---|---|
| The total market demand (unit) | |
| Basic market scale of products (unit) | |
| Price-sensitive parameter of demand (unit/$) | |
| Elasticity coefficient of the demand to green marketing efforts (unit/unit effort) | |
| manufacturing cost per unit new product ($/unit) | |
| remanufacturing cost per unit used-product ($/unit) | |
| Coefficient of the retailer‘s green marketing effort cost ($) | |
| Coefficient of the manufacturer’s collection cost ($) | |
| Unit collection price of the manufacturer ($/unit) | |
| Unit government subsidy for used-products ($/unit) | |
| Unit carbon tax price ($/unit emission) | |
| Carbon emissions generated during manufacturing one product (kg/unit) | |
| Carbon emissions generated during remanufacturing one used-product (kg/unit) | |
| Decision variables | |
| Wholesale price charged by the manufacturer ($/unit) | |
| Collection rate of the manufacturer | |
| Selling price of retailer ($/unit) | |
| Green marketing efforts of the retailer (index of efforts level) | |
| Objective functions | |
| Profit of the retailer and manufacturer under information symmetry ($) | |
| Expected profit of the retailer and manufacturer under information asymmetry ($) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Wang, P.; Xu, Q. Impact of Information Asymmetry on the Operation of Green Closed-Loop Supply Chain under Government Regulation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7999. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137999
Xu J, Wang P, Xu Q. Impact of Information Asymmetry on the Operation of Green Closed-Loop Supply Chain under Government Regulation. Sustainability. 2022; 14(13):7999. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137999
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jianteng, Peng Wang, and Qi Xu. 2022. "Impact of Information Asymmetry on the Operation of Green Closed-Loop Supply Chain under Government Regulation" Sustainability 14, no. 13: 7999. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137999
APA StyleXu, J., Wang, P., & Xu, Q. (2022). Impact of Information Asymmetry on the Operation of Green Closed-Loop Supply Chain under Government Regulation. Sustainability, 14(13), 7999. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137999





