Drip Fertigation with Relatively Low Water and N Input Achieved Higher Grain Yield of Maize by Improving Pre- and Post-Silking Dry Matter Accumulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
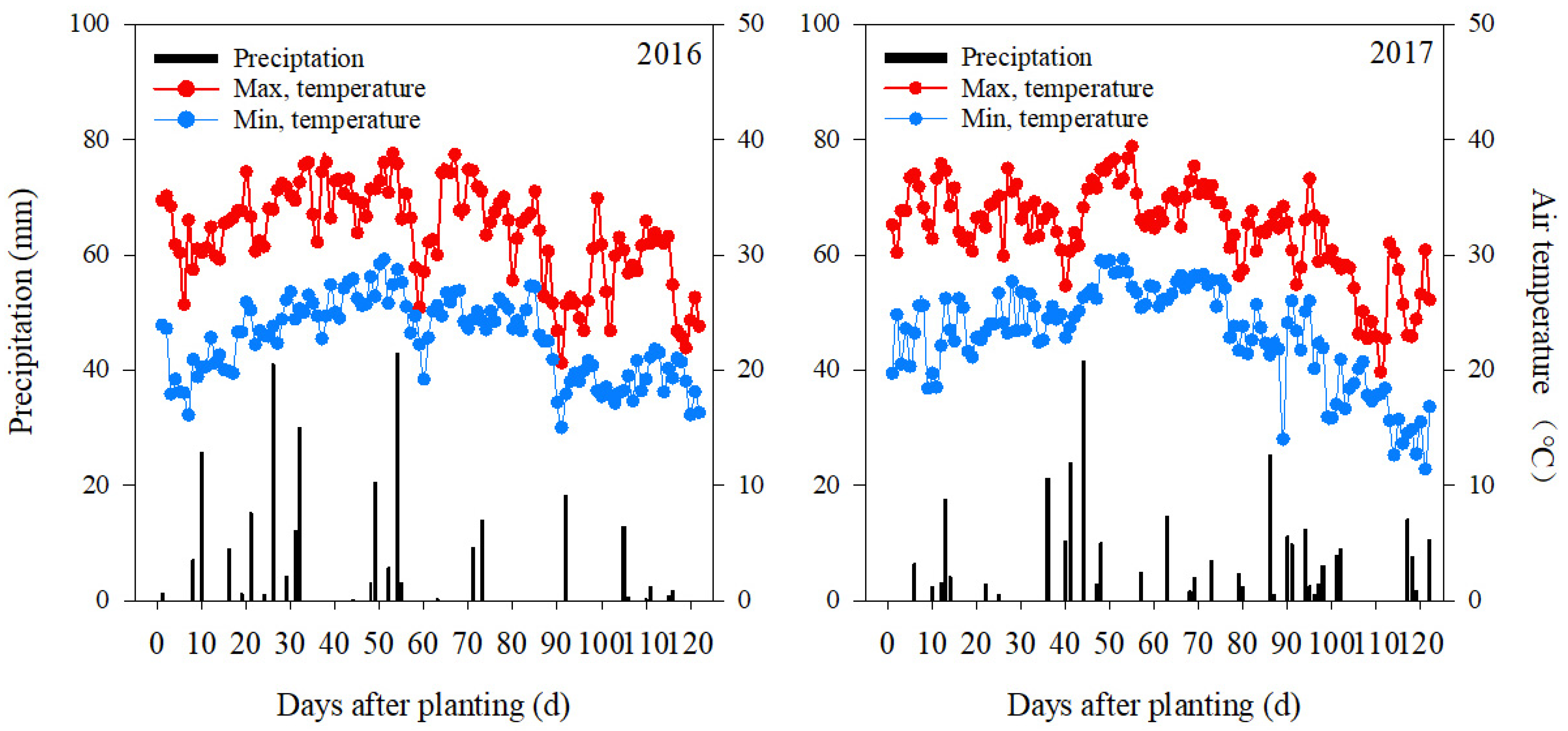
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling and Measurements
2.3.1. Soil Analysis
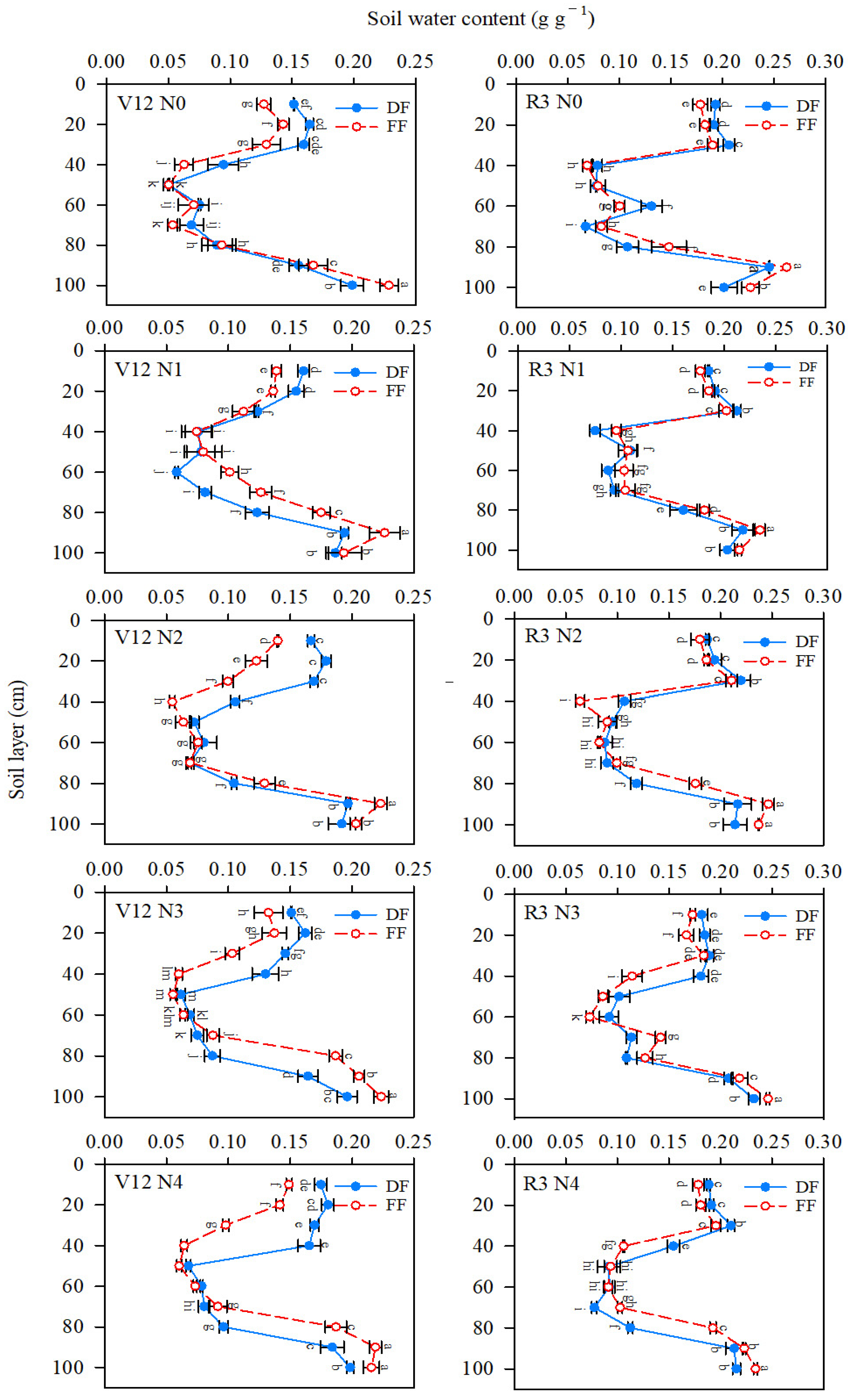
2.3.2. Soil Water Contents
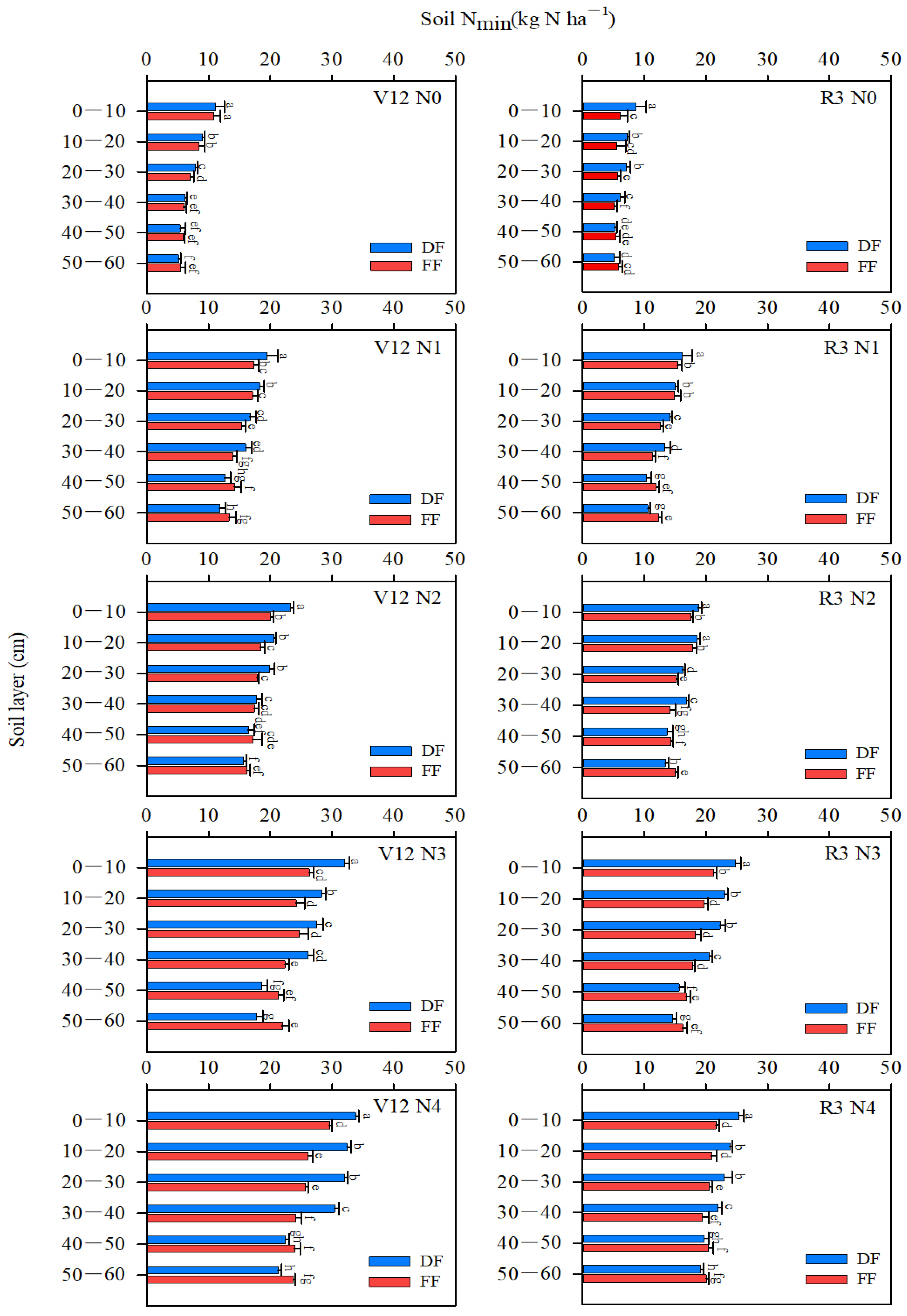
2.3.3. Soil Mineral N Content (Nmin)
2.3.4. Leaf Area Index
2.3.5. Dry Matter Accumulation
2.3.6. N Accumulation
2.3.7. Grain Yield
2.3.8. N Use Efficiency
2.3.9. Water Use Efficiency
2.3.10. Economic Benefits
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Soil Water Content
3.2. Mineral N Contents in Soils
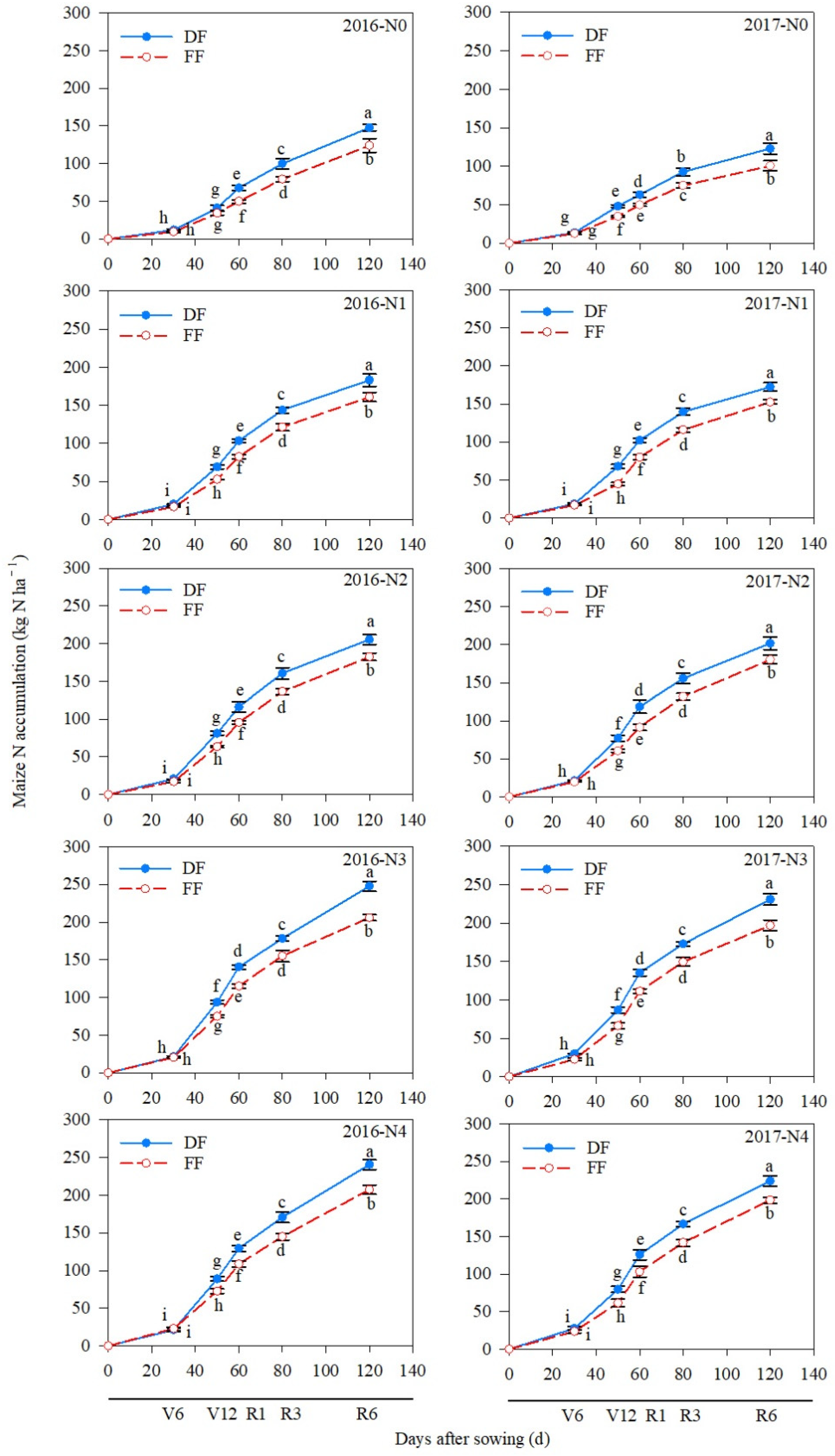
3.3. N Accumulation
3.4. Leaf Area Index
3.5. DM and DM Accumulation Rates
3.6. Grain Yield and Yield Components
3.7. Water and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
3.8. Economic Benefits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.K.; Zhao, J.R.; Dong, S.T.; Zhao, M.; Li, C.H.; Cui, Y.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Gao, J.L.; Xue, J.Q.; Wang, L.C.; et al. Advances and prospects of maize cultivation in China. Acta Agron. Sin. 2017, 50, 1941–1959. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of China Agricultural Yearbook. China Agricultural Yearbook; China Agricultural Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- White, C.M.; Finney, D.M.; Kemanian, A.R.; Kaye, J.P. Modeling the contributions of nitrogen mineralization to yield of corn. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.L.; Chen, D.L. Nitrogen fertilizer use in China–Contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management strategies. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 63, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, J.A.; Davis, S.J.; Lobell, D.B. Greenhouse gas mitigation by agricultural intensification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12052–12057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sylvester-Bradley, R.; Kindred, D.R. Analysing nitrogen responses of cereals to prioritize routes to the improvement of nitrogen use efficiency. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Z.L.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S. Current nitrogen management status and measures to improve the intensive wheat-maize system in China. Ambio 2010, 39, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, Q.F.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S.; Cao, M.H.; Cui, Z.L.; Bai, J.S.; Yue, S.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Müller, T. In-season root-zone nitrogen management strategies for improving nitrogen use efficiency in high-yielding maize production in China. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.F.; Sun, Q.P.; Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L.; Yue, S.C.; Zhang, F.S.; Romheld, V. Alternative cropping systems for sustainable water and nitrogen use in the North China Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Li, S.; Jin, L.Y.; Wang, H.T.; Li, C.J.; Wang, Y.L. Performance of an optimized nutrient management system for double-cropped wheat–maize rotations in North-central China. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, X.T.; Kou, C.L.; Zhang, F.S.; Christie, P. Nitrogen balance and groundwater nitrate contamination: Comparison among three intensive cropping systems on the North China Plain. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 143, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F. Significant acidification in major Chinese crop lands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Tao, F.L.; Du, J.A.; Shi, P.J.; Yu, D.Y.; Meng, Y.B.; Sun, Y. Surface water quality and its control in a river with intensive human impacts-a case study of the Xiangjiang River, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 2483–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Sui, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Herbert, S.J.; Ding, G. Soil degradation: A problem threatening the sustainable development of agriculture in Northeast China. Plant Soil Environ. 2010, 56, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steffen, W.; Richardson, K.; Rockstrom, J.; Cornell, S.E.; Fetzer, I.; Bennett, E.M.; Biggs, R. Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 2015, 347, 6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.X.; Liu, C.M.; Zhang, L. Water-saving agriculture in China: An overview. Adv. Agron. 2002, 75, 135–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, K.J.; Jiang, G.M.; Liu, M.Z.; Niu, S.L.; Gao, L.M. Post-anthesis changes in photosynthetic traits of maize hybrids released in different years. Field Crops Res. 2005, 93, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.S.; Sharma, R.; Brar, A.S. Optimising drip irrigation and fertigation schedules for higher crop and water productivity of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Irrig. Sci. 2021, 5, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, A.; Xu, G.; Levkovitch, I.; Soriano, S.; Bilu, A.; Wallach, R. High fertigation frequency: The effects on uptake of nutrients, water and plant growth. Plant Soil. 2003, 253, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farneselli, M.; Benincasa, P.; Tosti, G.; Simonne, E.; Guiducci, M.; Tei, F. High fertigation frequency improves nitrogen uptake and crop performance in processing tomato grown with high nitrogen and water supply. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 154, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.Y.; Sun, X.F.; Ding, Z.S.; Ma, W.; Zhao, M. Multisplit nitrogen application via drip irrigation improves maize grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 1687–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.Y.; Ma, D.; Sun, X.F.; Ding, Z.S.; Li, C.F.; Ma, W.; Zhao, M. Straw mulching under a drip irrigation system improves maize grain yield and water use efficiency. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 2806–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Yosef, B. Advances in fertigation. Adv. Agron. 1999, 65, 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.D.; Li, J.; Cheng, M.H.; Zhang, F.C.; Wang, X.K.; Fan, J.L.; Wu, L.F.; Fang, D.P. Optimal drip fertigation management improves yield, quality, water and nitrogen use efficiency of greenhouse cucumber. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 243, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.Y.; Zain, M.; Mehmood, F.; Wang, G.S.; Gao, Y.; Duan, A.W. Effects of nitrogen application rate and irrigation regime on growth, yield, and water-nitrogen use efficiency of drip-irrigated winter wheat in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 231, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, G.Y.; Mo, Y.; Cai, M.K.; Bian, X.Y. Evaluation of optimal nitrogen rate for corn production under mulched drip fertigation and economic benefits. Field Crop Res. 2018, 216, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Meng, F.Q.; Li, H.; Wang, L.G.; Wu, S.X.; Xiao, G.M.; Wu, W.L. Optimized fertigation maintains high yield and mitigates N2O and NO emissions in an intensified wheat–maize cropping system. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 211, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.F.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.F.; Lian, X.J.; Zhao, Y.M.; Li, Y.J.; Du, J.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Wang, J.G.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Drip fertigation significantly reduces nitrogen leaching in solar greenhouse vegetable production system. Environ Pollut. 2019, 245, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.R.; Hao, W.P.; Liu, Q.; Mao, L.L.; Nangia, V.; Guo, R.; Mei, X.R. Developing nitrogen management strategies under drip fertigation for wheat and maize production in the North China Plain based on a 3–year field experiment. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2019, 182, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.Q.; Li, Z.J.; Ning, T.Y.; Zheng, Y.H. Responses of photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence, and grain yield of maize to controlled-release urea and irrigation after anthesis. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 176, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeomans, J.C.; Bremner, J.M. A rapid and precise method for routine determination of organic carbon in soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1988, 19, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.D.; Li, F.S. Physical and Chemical Analysis of Soil; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M. Nitrogen-total. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3, Chemical Method; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; SSSA Book Series No. 5; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 1085–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Haby, V.A.; Russelle, M.P.; Skogley, E.O. Testing soils for potassium, calcium, and magnesium. In Soil Testing and Plant Analysis, 3rd ed.; Westerman, R.L., Ed.; SSSA Book Series No. 3; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1990; pp. 181–227. [Google Scholar]
- Fixen, P.E.; Grove, J.H. Testing soils for phosphorus. In Soil Testing and Plant Analysis, 3rd ed.; Westerman, R.L., Ed.; SSSA Book Series No. 3; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1990; pp. 141–180. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.Y.; Yu, Z.W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, Z.Q.; Luo, L.P.; Chu, P.F.; Guo, Z.J. Soil water use, grain yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in a long-term study of tillage practices and supplemental irrigation on the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 150, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckee, G.W. A coefficient for computing leaf area in hybrid maize. Agron. J. 1964, 56, 240–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.Y.; Sun, X.F.; Wang, D.; Ding, Z.S.; Li, C.F.; Ma, W.; Zhao, M. Integrated agronomic practice increases maize grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency under various soil fertility conditions. Crop J. 2019, 7, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.P.; Oweis, T. Water-yield relations and optimal irrigation scheduling of wheat in the Mediterranean region. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 38, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Qin, Y.B.; Yin, C.X.; Kong, L.L.; Wang, M.; Hou, Y.P.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Y.K.; Xu, C.; Liu, Z.Q. Effects of drip irrigation on yield, nutrient absorption and economic benefit of maize. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2022, 55, 1604–1616, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, C. Implementation of variance analysis of repeated measurement data in SPSS16.0 software. Stat. Decis. 2011, 11, 34–36, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janovicek, K.; Banger, K.; Sulik, J.; Nasielski, J.; Deen, B. Delta yield based optimal nitrogen rate estimates for corn are often economically sound. Agron. J. 2020, 2, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Zorita, M. Effect of deep-tillage and nitrogen fertilization interactions on dryland corn (Zea mays L.) productivity. Soil Till. Res. 2000, 54, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miriti, J.M.; Kironchi, G.; Esilaba, A.O.; Heng, L.K.; Gachene, C.K.K.; Mwangi, D.M. Yield and water use efficiencies of maize and cowpea as affected by tillage and cropping systems in semi-arid Eastern Kenya. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.H.; Al-Kaisi, M.M.; Zhang, Y.S.; Duan, L.S.; Tan, W.M.; Zhang, M.C.; Li, Z.H. Tillage practices affect biomass and grain yield through regulating root growth, root bleeding sap and nutrients uptake in summer maize. Field Crops Res. 2014, 157, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Han, H.F.; Ning, T.Y.; Li, Z.J.; Lal, R. Long-term effects of tillage and straw management on soil organic carbon, crop yield, and yield stability in a wheat-maize system. Field Crops Res. 2019, 233, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkalson, D.D.; Donk, S.V.; Petersen, J.L. Effect of nitrogen application timing on corn production using subsurface drip irrigation. Soil Sci. 2019, 174, 8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nafziger, E.D.; Rapp, D. Corn yield response to late-split nitrogen fertilizer. Agron. J. 2020, 20, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.L.; Huang, S.B.; Tian, B.J.; Ren, J.H.; Meng, Q.F.; Wang, P. Manipulating Planting Density and Nitrogen Fertilizer Application to Improve Yield and Reduce Environmental Impact in Chinese Maize Production. Front Plant Sci. 2017, 12, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, P.; Li, S.; Yu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.J. Post-silking accumulation and partitioning of dry matter, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in maize varieties differing in leaf longevity. Field Crops Res. 2013, 144, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.H.; Li, Y.N.; Xu, Y.B.; Zhou, C.M. Effects of mulches on water use in a winter wheat/summer maize rotation system in Loess Plateau, China. J. Arid Land. 2018, 2, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pommel, B.; Gallais, A.; Coque, M.; Quillere, I.; Hirel, B.; Prioul, J.L.; Andrieu, B.; Floriot, M. Carbon and nitrogen allocation and grain filling in three maize hybrids differing in leaf senescence. Eur. J. Agron. 2006, 24, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirel, B.; Le Gouis, J.; Ney, B.; Gallais, A. The challenge of improving nitrogen use efficiency in crop plants: Towards a more central role for genetic variability and quantitative genetics within integrated approaches. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2369–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echarte, L.S.; Rothstein, G.; Tollenaar, M. The response of leaf photosynthesis and dry matter accumulation to nitrogen supply in an older and a newer maize hybrid. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampitti, I.A.; Vyn, T.J. A comprehensive study of plant density consequences on nitrogen uptake dynamics of maize plants from vegetative to reproductive stages. Field Crops Res. 2011, 121, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, C.T.; Weiland, R.T. Nitrogen partitioning in maize during ear development. Crop Sci. 1992, 32, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajcan, I.; Tollenaar, M. Source: Sink ratio and leaf senescence in maize. II. Nitrogen metabolism during grain filling. Field Crops Res. 1999, 60, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.A.; Tollenaar, M. Physiological basis of successful breeding strategies for maize grain yield. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, S202–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Yue, S.C.; Qiu, M.L.; Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L.; Chen, F.J. Using maize hybrids and in-season nitrogen management to improve grain yield and grain nitrogen concentrations. Field Crops Res. 2014, 166, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, F. The spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and yield potential of medium-low yielded farmland in China. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2010, 26, 369–373, (In Chinese, with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.B.; Cui, H.Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.W.; Dong, S.T.; Liu, P. Effects of integrated agronomic management practices on yield and nitrogen efficiency of summer maize in North China. Field Crops Res. 2012, 134, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.G.; Yang, Y.; Yu, K.; Feng, H. Effects of straw mulching and plastic film mulching on improving soil organic carbon and nitrogen fractions, crop yield and water use efficiency in the Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, G.P.; Vitousek, P.M. Nitrogen in agriculture: Balancing the cost of an essential resource. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Hendawy, S.E.; El-Lattief, E.A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Schmidhalter, U. Irrigation rate and plant density effects on yield and water use efficiency of drip-irrigated corn. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, F.; Trooien, T. Subsurface Drip Irrigation for Corn Production: A Review of 10 Years of Research in Kansas. Irrig. Sci. 2003, 22, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadarunnisa, S.; Madhumathi, C.; Rao, G.S.; Sreenivasulu, B. Effect of fertigation on growth and yield of turmeric cv. Mydukur. J. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 5, 78–80. [Google Scholar]


| Irrigation System | 2016 | 2017 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planting (mm) | V6 (mm) | V12 (mm) | Total (mm) | Planting (mm) | V6 (mm) | V12 (mm) | Total (mm) | |
| DF | 20 | 15 | 10 | 45 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 55 |
| FF | 50 | 45 | 40 | 135 | 50 | 50 | 40 | 140 |
| Irrigation | Treatment | N | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Sowing kg ha−1 | V6 kg ha−1 | V12 kg ha−1 | R1 kg ha−1 | Total kg ha−1 | ||
| DF | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| N1 | 45 | 67.5 | 45 | 67.5 | 225 | |
| N2 | 60 | 90 | 60 | 90 | 300 | |
| N3 | 75 | 112.5 | 75 | 112.5 | 375 | |
| N4 | 90 | 135 | 90 | 135 | 450 | |
| FF | N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| N1 | 45 | 67.5 | 45 | 67.5 | 225 | |
| N2 | 60 | 90 | 60 | 90 | 300 | |
| N3 | 75 | 112.5 | 75 | 112.5 | 375 | |
| N4 | 90 | 135 | 90 | 135 | 450 | |
| Abbreviation | Full Name/Products Name |
|---|---|
| DF | Flood fertigation |
| FF | Drip fertigation |
| N | Nitrogen |
| V6 | 6-leaf stage |
| V12 | 12-leaf stage |
| R1 | Silking stage |
| R3 | Milk stage |
| R6 | Physiological maturity |
| ET | Evapotranspiration |
| WUE | Water use efficiency |
| AEN | Agronomic nitrogen efficiency |
| PFPN | Nitrogen partial factor productivity |
| SWC | Soil water content |
| Nmin | Ammonium nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen |
| LAI | Leaf area index |
| DM | Dry matter accumulation |
| DM+R | Dry matter accumulation rates |
| Chemical herbicides | Atrazine; Shandong Dacheng Pesticide Co., Ltd. |
| Insecticides | Phoxim; Sichuan Guoguang Agricultural Chemical Co., Ltd. |
| Fungicides | Kresoxim-methyl; Zhengda Nantong crop Protection Co., Ltd. |
| Year | Irrigation | Nitrogen | Grain Yield | Ear No. | Kernel No. | 1000-Kernel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Mg ha–1) | (104 ha–1) | per Ear | Weight (g) | |||
| 2016 | DF | N0 | 3.6 g | 6.7 | 157 g | 334.1 g |
| N1 | 8.8 d | 6.9 | 364 c | 358.3 e | ||
| N2 | 9.7 b | 6.9 | 371 b | 373.2 d | ||
| N3 | 10.4 a | 6.9 | 390 a | 389.8 a | ||
| N4 | 10.2 a | 6.9 | 387 a | 382.7 b | ||
| FF | N0 | 3.5 g | 6.7 | 150 h | 326.5 h | |
| N1 | 7.3 f | 6.8 | 312 f | 333.8 g | ||
| N2 | 8.3 e | 6.8 | 347 e | 348.9 f | ||
| N3 | 9.2 c | 6.8 | 359 d | 364.8 d | ||
| N4 | 9.7 b | 6.8 | 364 c | 370.1 c | ||
| 2017 | DF | N0 | 3.3 g | 6.7 | 154 g | 332.3 f |
| N1 | 8.3 e | 6.8 | 352 d | 348.2 e | ||
| N2 | 9.5 c | 6.8 | 370 b | 366.9 d | ||
| N3 | 10.2 a | 6.9 | 387 a | 388.6 a | ||
| N4 | 10.0 b | 6.9 | 385 a | 382.4 b | ||
| FF | N0 | 3.1 h | 6.7 | 145 h | 310.7 g | |
| N1 | 7.2 f | 6.8 | 304 f | 332.3 f | ||
| N2 | 8.2 e | 6.8 | 345 e | 345.6 e | ||
| N3 | 8.8 d | 6.8 | 354 d | 362.0 d | ||
| N4 | 9.5 c | 6.8 | 360 c | 368.1 c | ||
| Source of variation | ||||||
| Nitrogen(N) | ** | NS | ** | ** | ||
| Irrigation (I) | ** | NS | ** | ** | ||
| Year (Y) | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| Y × I | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| Y × N | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| I × N | ** | NS | ** | * | ||
| Y × I × N | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| Year | Irrigation | Nitrogen | ET (mm) | WUE (kg m−3) | AEN (kg kg−1) | PFPN (kg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | DF | N0 | 426.6 d | 0.83 f | ||
| N1 | 421.3 d | 2.09 c | 23.1 a | 39.1 a | ||
| N2 | 423.4 d | 2.10 c | 20.3 b | 32.3 b | ||
| N3 | 431.1 d | 2.53 a | 18.1 c | 27.7 c | ||
| N4 | 431.6 d | 2.37 b | 14.7 fg | 22.7 de | ||
| FF | N0 | 559.5 c | 0.63 g | |||
| N1 | 576.3 b | 1.25 e | 16.9 d | 32.4 b | ||
| N2 | 578.6 b | 1.47 d | 16.0 de | 27.7 c | ||
| N3 | 587.8 b | 1.48 d | 15.2 ef | 24.5 d | ||
| N4 | 614.7 a | 1.50 d | 13.8 g | 21.6 e | ||
| 2017 | DF | N0 | 356.4 f | 0.92 f | ||
| N1 | 349.1 g | 2.39 c | 22.2 a | 36.9 a | ||
| N2 | 352.3 fg | 2.49 b | 20.7 b | 31.7 b | ||
| N3 | 367.4 e | 2.71 a | 18.4 c | 27.2 c | ||
| N4 | 377.4 d | 2.54 b | 14.9 ef | 22.2 de | ||
| FF | N0 | 502.4 a | 0.59 g | |||
| N1 | 496.0 ab | 1.47 e | 18.2 c | 32.0 b | ||
| N2 | 476.3 c | 1.75 d | 17.0 d | 27.3 c | ||
| N3 | 491.9 d | 1.75 d | 15.2 e | 23.5 d | ||
| N4 | 498.4 ab | 1.81 d | 14.2 f | 21.1 e | ||
| Source of variation | ||||||
| Irrigation (I) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| Nitrogen(N) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| Year (Y) | ** | ** | NS | NS | ||
| Y × I | NS | ** | * | * | ||
| Y × N | ** | ** | NS | NS | ||
| I × N | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| Y × I × N | ** | ** | NS | NS | ||
| Year | Irrigation | Nitrogen | Total Input | Gross Income | Net Income | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilizer | Irrigation Equipment | Water, Electricity and Labor | Machinery, Seed and Pesticide | |||||
| 2016 | DF | N0 | 103 | 149 | 79 | 542 | 856 g | 0 |
| N1 | 163 | 149 | 79 | 542 | 2092 d | 1159 e | ||
| N2 | 183 | 149 | 79 | 542 | 2306 b | 1353 cd | ||
| N3 | 203 | 149 | 79 | 542 | 2496 a | 1523 a | ||
| N4 | 223 | 149 | 79 | 542 | 2435 a | 1442 b | ||
| FF | N0 | 103 | 0 | 130 | 542 | 808 h | 33 g | |
| N1 | 163 | 0 | 130 | 542 | 1736 f | 900 f | ||
| N2 | 183 | 0 | 130 | 542 | 1973 e | 1118 e | ||
| N3 | 203 | 0 | 130 | 542 | 2187 c | 1312 d | ||
| N4 | 223 | 0 | 130 | 542 | 2259 bc | 1363 c | ||
| 2017 | DF | N0 | 103 | 149 | 79 | 542 | 785 f | 0 |
| N1 | 163 | 149 | 79 | 542 | 1973 d | 1040 f | ||
| N2 | 183 | 149 | 79 | 542 | 2259 b | 1306 c | ||
| N3 | 203 | 149 | 79 | 542 | 2449 a | 1476 a | ||
| N4 | 223 | 149 | 79 | 542 | 2378 a | 1385 b | ||
| FF | N0 | 103 | 0 | 130 | 542 | 794 f | 19 h | |
| N1 | 163 | 0 | 130 | 542 | 1712 e | 877 g | ||
| N2 | 183 | 0 | 130 | 542 | 1950 d | 1094 e | ||
| N3 | 203 | 0 | 130 | 542 | 2092 c | 1217 d | ||
| N4 | 223 | 0 | 130 | 542 | 2235 b | 1339 bc | ||
| Source of variation | ||||||||
| Irrigation (I) | - | - | - | - | ** | ** | ||
| Nitrogen(N) | - | - | - | - | ** | ** | ||
| Year (Y) | - | - | - | - | ** | ** | ||
| Y × I | - | - | - | - | NS | NS | ||
| Y × N | - | - | - | - | NS | NS | ||
| I × N | - | - | - | - | ** | ** | ||
| Y × I × N | - | - | - | - | NS | NS | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, D.; Chen, C.; Zhou, B.; Ma, D.; Batchelor, W.D.; Han, X.; Ding, Z.; Du, M.; Zhao, M.; Li, M.; et al. Drip Fertigation with Relatively Low Water and N Input Achieved Higher Grain Yield of Maize by Improving Pre- and Post-Silking Dry Matter Accumulation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7850. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137850
Guo D, Chen C, Zhou B, Ma D, Batchelor WD, Han X, Ding Z, Du M, Zhao M, Li M, et al. Drip Fertigation with Relatively Low Water and N Input Achieved Higher Grain Yield of Maize by Improving Pre- and Post-Silking Dry Matter Accumulation. Sustainability. 2022; 14(13):7850. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137850
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Dong, Chuanyong Chen, Baoyuan Zhou, Di Ma, William D. Batchelor, Xiao Han, Zaisong Ding, Mei Du, Ming Zhao, Ming Li, and et al. 2022. "Drip Fertigation with Relatively Low Water and N Input Achieved Higher Grain Yield of Maize by Improving Pre- and Post-Silking Dry Matter Accumulation" Sustainability 14, no. 13: 7850. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137850
APA StyleGuo, D., Chen, C., Zhou, B., Ma, D., Batchelor, W. D., Han, X., Ding, Z., Du, M., Zhao, M., Li, M., & Ma, W. (2022). Drip Fertigation with Relatively Low Water and N Input Achieved Higher Grain Yield of Maize by Improving Pre- and Post-Silking Dry Matter Accumulation. Sustainability, 14(13), 7850. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137850








