Fertiliser Effect of Ammonia Recovered from Anaerobically Digested Orange Peel Using Gas-Permeable Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Procedure for N Extraction
2.2. Experimental Procedure for Fertiliser Assessment
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. FT-Raman Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
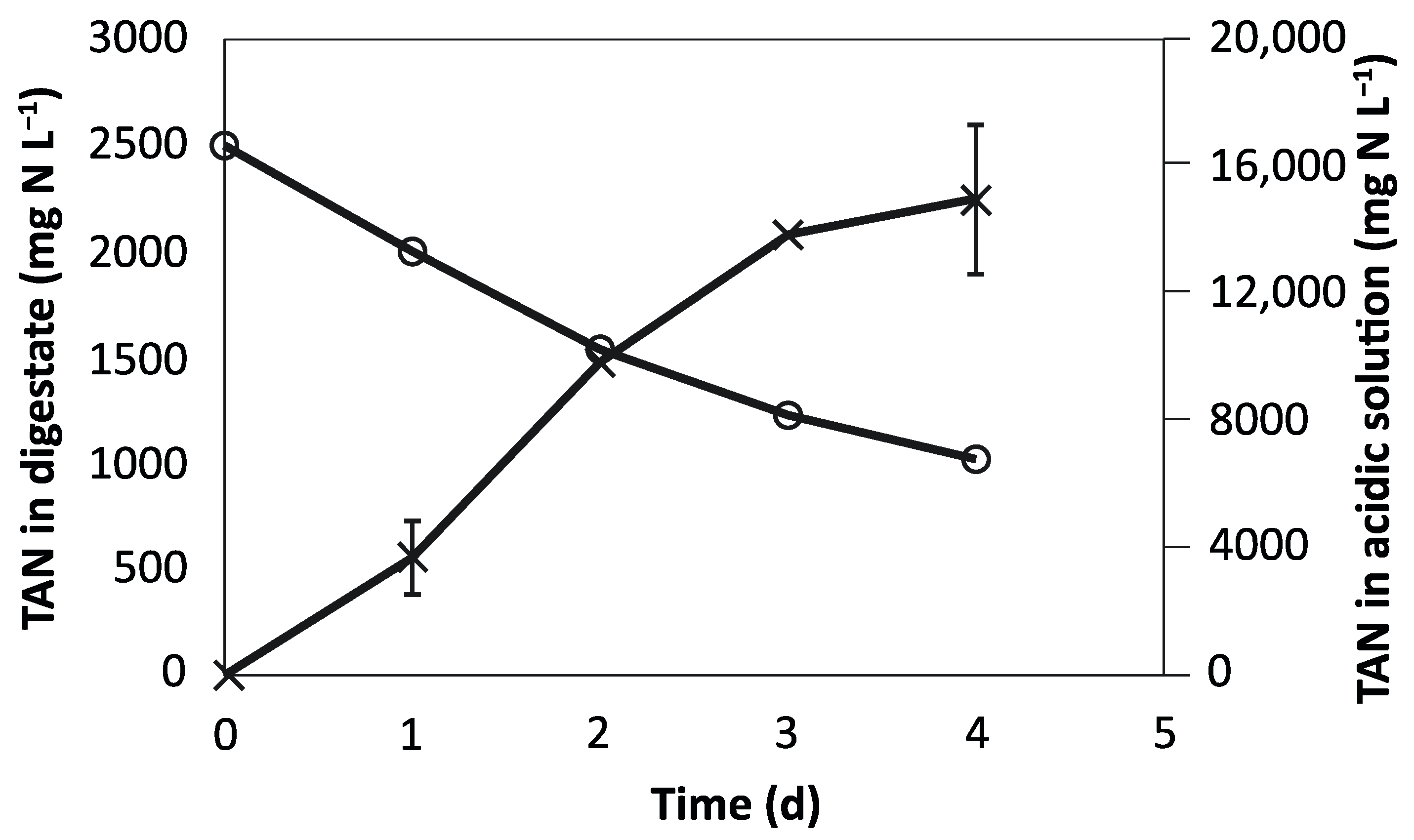
3.1. N Recovery from the Digestate
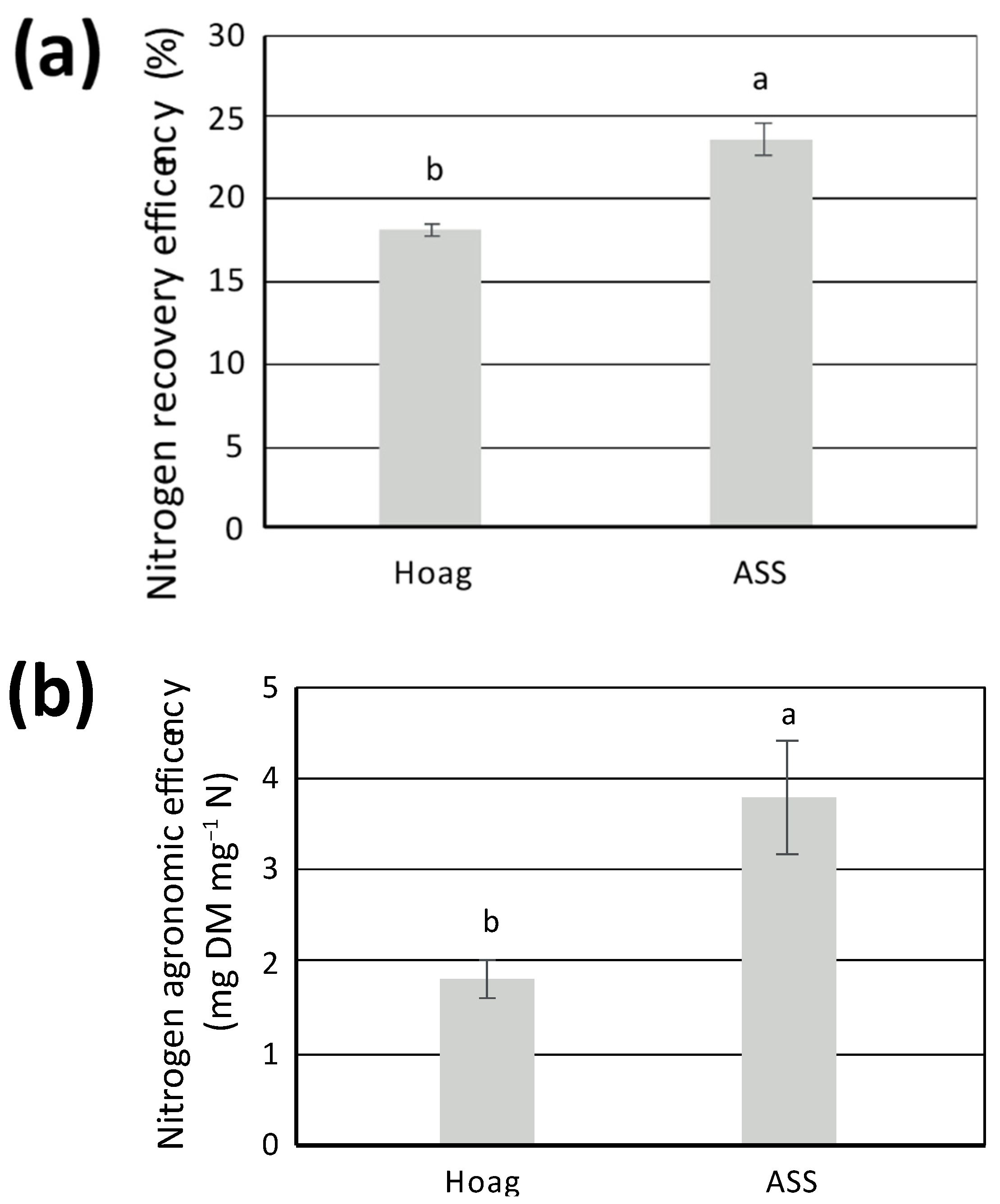
3.2. Agronomic Assessment of the N Recovery Solution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, B. Nitrogenase reveals its inner secrets. Science 2002, 297, 1654–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munasinghe-Arachchige, S.P.; Nirmalakhandan, N. Nitrogen-Fertilizer Recovery from the Centrate of Anaerobically Digested Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño, B.; Molinuevo-Salces, B.; Vanotti, M.B.; García-González, M.C. Ammonia recovery from digestate using gas-permeable membranes: A pilot-scale study. Environments 2021, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, M.K.; Englehardt, J.D.; Dvorak, A.C. Technologies for recovering nutrients from wastewater: A critical review. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 36, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Cowling, E.B. Reactive nitrogen and the World: 200 years of change. Ambio 2002, 31, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurnjak, I.; Michels, E.; Crappé, S.; Buysens, S.; Tack, F.M.G.; Meers, E. Utilization of derivatives from nutrient recovery processes as alternatives for fossil-based mineral fertilizers in commercial greenhouse production of Lactuca sativa L. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 198, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurnjak, I.; Brienza, C.; Snauwaert, E.; De Dobbelaere, A.; De Mey, J.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Michels, E.; Schoumans, O.; Adani, F.; Meers, E. Production and performance of bio-based mineral fertilizers from agricultural waste using ammonia (stripping-) scrubbing technology. Waste Manag. 2019, 89, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaneeckhaute, C.; Ghekiere, G.; Michels, E.; Vanrolleghem, P.A.; Tack, F.M.G.; Meers, E. Chapter four—Assessing nutrient use efficiency and environmental pressure of macronutrients in biobased mineral fertilizers: A review of recent advances and best practices at field scale. In Advances in Agronomy; Donald, L.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 137–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majd, A.M.S. Application of Gas-Permeable Membranes for Mitigation of Ammonia Gas from Animal Manure. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2015. Available online: https://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/bitstream/handle/1969.1/156351/SAMANIMAJD-DISSERTATION-2015.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- García-Sánchez, M.; Siles, J.A.; Cajthaml, T.; García-Romera, I.; Tlustoš, P.; Száková, J. Effect of digestate and fly ash applications on soil functional properties and microbial communities. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2015, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Settineri, G.; Papalia, T.; Attinà, E.; Basile, C.; Panuccio, M.R.S. Anaerobic co-digestion of recalcitrant agricultural wastes: Characterizing of biochemical parameters of digestate and its impacts on soil ecosystem. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 586, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panuccio, M.R.; Romeo, F.; Mallamaci, C.; Muscolo, A. Digestate Application on Two Different Soils: Agricultural Benefit and Risk. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 4341–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horta, C.; Carneio, J.P. Use of digestate as organic amendment and source of nitrogen to vegetable crops. App. Sci. 2022, 12, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayibi, S.; Monlau, F.; Marias, F.; Thevenin, N.; Jimenez, R.; Oukarroum, A.; Alboulkas, A.; Zeroual, Y.; Barakat, A. Industrial symbiosis of anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis: Performances and agricultural interest of coupling biochar and liquid digestate. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, J.; de la Fuente, C.; Campoy, M.; Carrasco, L.; Nájera, I.; Baixauli, C.; Caravaca, F.; Roldan, A.; Cegarra, J.; Bernal, M.P. Agricultural use of digestate for horticultural crop production and improvement of soil properties. Eur. J. Agron. 2012, 43, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Müller, T. Effects of anaerobic digestion on digestate nutrient availability and crop growth: A review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, C.; Orzi, V.; Carozzi, M.; Acutis, M.; Boccasile, G.; Lonati, S.; Tambone, F.; D’Imporzano, G.; Adani, F. Short-term experments in using digestate products as substitutes for mineral (N) fertilizer: Agronomic performance, odours, and ammonia emission impacts. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 547, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogn, T.A.; Dragicevic, I.; Linjordet, R.; Krogstad, T.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Eich-Greatorex, S. Recycling of biogas digestates in plant production: NPK fertilizer value and risk of leaching. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2018, 7, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tayibi, S.; Monlau, F.; Marias, F.; Cazaudehore, G.; Fayoud, N.-E.; Oukarroum, A.; Zeroual, Y.; Barakat, A. Coupling anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis processes for maximizing energy recovery and soil preservation according to the circular economy concept. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño, B.; Molinuevo-Salces, B.; Vanotti, M.B.; García-González, M.C. Application of Gas-Permeable Membranes For-Semi-Continuous Ammonia Recovery from Swine Manure. Environments 2019, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-González, M.C.; Vanotti, M.B.; Szogi, A.A. Recovery of ammonia from swine manure using gas-permeable membranes: Effect of aeration. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 152, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garau, M.C.; Simal, S.; Rosselló, C.; Femenia, A. Effect of air-drying temperature on physico-chemical properties of dietary fibre and antioxidant capacity of orange (Citrus aurantium v. Canoneta) by products. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, S.M.; Schnitzer, H.; Aly, M.H.; Smuda, S.S. Physical and chemical properties of wastes generated during processing of mango and orange juices. J. Food Ind. 2012, 2, 177–289. [Google Scholar]
- Nicoli, M.C.; Anese, M.; Parpinel, M. Influence of processing on the antioxidant properties of fruit and vegetables. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viuda-Marcos, M.; Fernandez-Lopez, J.; Sayas-Barbera, E.; Sendra, E.; Perez-Alvarez, J.A. Physicochemical characterization of the orange juice waste water of a citrus by-product. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2011, 35, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. World Soil Resources Reports No. 103; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, Wastewater APHA. In American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- García-González, M.C.; Vanotti, M.B.; Szogi, A.A. Recovery of ammonia from anaerobically digested manure using gas-permeable membranes. Sci. Agric. 2016, 73, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanotti, M.B.; Dube, P.J.; Szogi, A.A.; García-González, M.C. Recovery of ammonia and phosphate minerals from swine wastewater using gas-permeable membranes. Water Res. 2017, 112, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dube, P.J.; Vanotti, M.B.; Szogi, A.A.; Garcia-González, M.C. Enhancing recovery of ammonia from swine manure anaerobic digester effluent using gas-permeable membrane technology. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-González, M.C.; Vanotti, M.B. Recovery of ammonia from swine manure using gas-permeable membranes: Effect of waste strength and pH. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.L.; Simplicio, W.S.; Wu, G.; Hu, Z.; Hu, H.; Zhan, X. Nutrient recovery from digestate of anaerobic digestion of livestock manure: A review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2018, 4, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttobene, R.; Avola, G.; Gresta, F.; Abbate, V. Industrial Orange waste as organic fertilizer in durum wheat. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 29, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizil, R.; Irudayaraj, J.; Seetharaman, K. Characterization of irradiated starches by using FT-Raman and FTIR spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3912–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickless, E.M.; Holroyd, S.E.; Stephens, J.M.; Gordon, K.C.; Wargent, J.J. Analytical FT-Raman spectroscopy to chemotype Leptospermum scoparium and generate predictive models for screening for dihydroxyacetone levels in floral nectar. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2014, 45, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjos, O.; Santos, A.J.A.; Paixão, V.; Estevinho, L.M. Physicochemical characterization of Lavandula spp. honey with FT-Raman spectroscopy. Talanta 2018, 178, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.H.; Singh, G.P.; Park, S.H.; Chua, N.-H.; Ram, R.J.; Park, B.S. Early diagnosis and management of nitrogen deficiency in plants utilizing Raman spectroscopy. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathlouthi, M.; Luu, C.; Meffroy-Biget, A.M.; Luu, D.V. Laser-raman study of solute-solvent interactions in aqueous solutions of D-fructose, D-glucose, and sucrose. Carbohydr. Res. 1980, 81, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, M.; Yildirim, E.; Ekinci, M.; Argin, S. Effect of biostimulants on yield and quality of cherry tomatoes growth in fertile and stressed soils. HortScience 2021, 56, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, A.A.; Takacs-Hajos, M. The effect of plant biostimulants on the macronutrient content and ion ratio of several lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) cultivars grown in a plastic house. South Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 147, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, I.; La Bella, E.; Rovetto, E.I.; Lo Piero, A.R.; Baglieri, A. Biostimulant effect and biochemical response in lettuce seedlings treated with a Scenedesmus quadricauda Extract. Plants 2020, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machado, V.P.O.; Pacheco, A.C.; Carvalho, M.E.A. Effect of biostimulant application on production and flavonoid content of marigold (Calendula officinallis L.). Rev. Ceres 2014, 61, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EU 2019/1009. Official Journal of the European Union. Regulation (EU) 2019/1009 of the European Parliament and of the Council. 5 June 2019. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32019R1009&from=EN (accessed on 30 March 2022).






| Initial | Final | |
|---|---|---|
| Alkalinity (mg CaCO3 L−1) | 13,880 | 7431 |
| TS (g L−1) | 35.4 ± 0.7 | 25.5 ± 3.5 |
| VS (g L−1) | 22.3 ± 0.7 | 15.9 ± 2.3 |
| TCOD (mg L−1) | 35,124 ± 847 | 22,866 ± 357 |
| SCOD (mg L−1) | 3196 ± 171 | 4323 ± 342 |
| TKN (mg N L−1) | 3474 ± 197 | 1823 ± 139 |
| TAN (mg N L−1) | 2462 ± 47 | 1019 ± 24 |
| Pt (mg L−1) | 1022 ± 1 | 541 ± 153 |
| Treatments | Type of N Fertilisation | Applied N | 1 Other Nutrients |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2O (W) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Control (C) | Hoagland without N | 0 | yes |
| Hoagland (Hoag) | Hoagland with N | 2 100 mg per pot | yes |
| ASS | ASS + Hoag. without N | 2 100 mg per pot | yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horta, C.; Riaño, B.; Anjos, O.; García-González, M.C. Fertiliser Effect of Ammonia Recovered from Anaerobically Digested Orange Peel Using Gas-Permeable Membranes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7832. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137832
Horta C, Riaño B, Anjos O, García-González MC. Fertiliser Effect of Ammonia Recovered from Anaerobically Digested Orange Peel Using Gas-Permeable Membranes. Sustainability. 2022; 14(13):7832. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137832
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorta, Carmo, Berta Riaño, Ofélia Anjos, and María Cruz García-González. 2022. "Fertiliser Effect of Ammonia Recovered from Anaerobically Digested Orange Peel Using Gas-Permeable Membranes" Sustainability 14, no. 13: 7832. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137832
APA StyleHorta, C., Riaño, B., Anjos, O., & García-González, M. C. (2022). Fertiliser Effect of Ammonia Recovered from Anaerobically Digested Orange Peel Using Gas-Permeable Membranes. Sustainability, 14(13), 7832. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137832








