Abstract
Spatial and temporal variations in the potential yields of highland barley is important for making policies on adaptation of agriculture to climate change in the Three Rivers Region (TRR), one of the main highland barley growing areas on the Tibetan Plateau. This research tries to explore a suitable strategy for simulating potential yields of highland barley by the WOFOST (WOrld FOod STudies) crop growth model, and further to identify variations in climate conditions and potential yields in TRR from 1961 to 2020 for making policies on adaptation of agricultural production to the climate change impacts on the Tibetan Plateau. Validation results indicated that WOFOST could accurately simulate the potential yields of highland barley with the global radiation estimated by the calibrated Angstrom model. The global radiation during the growth periods decreased at a rate of 0.047 MJ/m2a, while the temperature during the growth periods increased at rates ranging from 0.019 to 0.087 °C/a, which was greater than the average warming rate of the globe. The simulated potential yields ranged from 10,300 to 14,185 kg/ha in TRR, with an average decreasing rate of 28 kg/ha/a. The decrease in the potential yields was mainly attributed to the shortened critical period caused by warming effects, so cultivation of new varieties of highland barley with longer growth periods is suggested as an achievable strategy for the adaptation of highland barley to climate change in TRR.
1. Introduction
Food security plays an essential role in regional development [1]. To make optimal policies on food security, potential yield is often used as an important indicator to identify the yield gaps and the limiting environmental factors, which is beneficial to improve the productivity of a crop [2,3]. Currently, global warming has been well acknowledged in modern society [4], with its non-negligible impacts on food security [5]. Thus, identification of the spatial and temporal variations in the potential yields becomes an important task to provide important information on policy-making for achieving the sustainable agricultural development in a region.
Potential yield is defined as the yield under no water- and nutrition-limited conditions [6]. Initially, potential yields were estimated mainly by statistical regression methods [7]. However, without consideration of any crop growth process, the results based on statistical methods are believed to be inaccurate [8]. In recent decades, crop growth models have become popular in quantifying potential yields for various crops in different regions, as these models perform more reliably than statistical methods due to the involvement of the crop growth mechanism processes [9]. To date, many crop growth models have been developed for studies and assessments in agriculture [10], among which the WOFOST crop model is one of the most popular models widely used in the world [6]. Having taken account of the mechanism processes such as phenology, photosynthesis and dry matter allocation, the WOFOST model has been identified to be capable of simulating evapotranspiration, soil water content, grain yield, and total above-ground biomass in the arid and semi-arid regions [11]. To date, the WOFOST model has been used to reveal the potential yields for various crops including winter wheat, spring barley, maize, winter rapeseed, potato, sugar, beet, pulses and sunflower [12], showing its high accuracy of prediction in regional application under different climate conditions around the world [8,13,14,15,16]. The WOFOST model has also been used as an effective tool to investigate in changes in the potential yields of many crops in the context of the climate change [12,17,18].
As potential yield is defined as the crop yield under no water- and nutrition-limited conditions, global radiation and temperature become the meteorological determinants of the potential yields [6,12]. Though temperature is a routinely observed item in the weather station, global radiation is not recorded in most of weather stations due to scarcity of instruments and high cost of maintenance [19,20]. Under this circumstance, empirical radiation models are often used to estimate global radiation to meet the model input requirements [8,21,22]. However, based on investigation in the effect of radiation estimation on the yields simulated by WOFOST, Pohlert [22] found that global radiation estimated by empirical formula was suitable to drive WOFOST at temperate locations but resulted in large errors in the simulated yields at tropical locations, implying the hypothesis that approaches to driving WOFOST with global radiation estimated by empirical formula might be regionally restricted.
Located in the southwest of China (25°–4° N, 74°–104° E), the Tibetan Plateau has unique climate regime due to its high altitude ranging from 3000 to 5000 m a.s.l. [23]. Highland barley has played an essential role in facilitating permanent human occupation of the Tibetan Plateau for about 3600 years [24], and has become the irreplaceable staple food for the Tibetans in their daily lives [25]. Analysis of temperature from 1901 to 2016 indicated that the warming rate was 0.037 °C/a on the Tibetan Plateau, which is much higher than the average national value of 0.023 °C/a in China [26]. The increase in temperature has significantly influenced the spatial and temporal distribution of highland barley over the Tibetan Plateau [27], which justifies the necessity to further explore changes in potential yields of highland barley by the crop growth models. However, to date, while there exist a few investigations in the potential yields of highland barley on the Tibetan Plateau based on the DSSAT (Decision Support System for Agrotechnology Transfer) crop growth model [28], WOFOST has never been tested and applied to reveal the detailed information on the potential yields of the highland barley in its main growing area over the Tibetan Plateau.
In this study, to test the above hypothesis that approaches to driving WOFOST with global radiation estimated by empirical formula might be regionally restricted, the WOFOST model was used to simulate the potential yields of highland barley in the Three Rivers Region (TRR), the main growing area of the highland barley in the southern part of the Tibetan Plateau. The objectives of this study were: (1) to explore the suitable strategy on estimation of global radiation for applying WOFOST in simulating potential yields of highland barley in TRR, (2) to detect the dimming and warming changes in TRR, and (3) to reveal the spatial and temporal variations in the potential yields of highland barley in TRR in the recent 60 years, which will provide important information for the local government to make effective policies for the adaptation of agricultural production to climate change challenges over the Tibetan Plateau.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area was the Three River Region (TRR), which covers the drainage areas of Yarlung Zangbo River and its two tributaries in the southern part of the Tibetan Plateau, with altitudes ranging from 3500 to 4000 m above sea level (Figure 1). TRR is the main growing area of highland barley due to the favorable irrigation conditions. The highland barley was usually sown in April and matured in August. The growth period of highland barley in TRR is featured by the remarkable high global radiation and low temperature due to the unique climate regime on the Tibetan Plateau. There are in total ten weather stations distributed in TRR, but the global radiation was only routinely measured in Lhasa. In addition, phenophases were only observed in Lhasa and Rikaze according to the instruction by China Meteorological Administration (CMA). Detailed information on the weather stations is shown in Table 1.
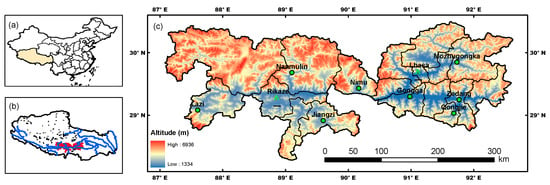
Figure 1.
Location of the Tibetan Autonomous Region (yellow color area) in China (a), and location of the Three River Region (pink color area) on the Tibetan Autonomous Region (b). Distribution of weather stations in the Tree Rivers Region (c). The five-pointed stars denote stations for calibration of the WOFOST model.

Table 1.
Detailed information of the weather stations in this study.
2.2. Phenophase Observation and Meteorological Data Collection
Two cultivars of the highland barley, Chunqing and Zangqing, were the same genotypes, which were planted in Lhasa and Rikaze, respectively. The phenophases of highland barley were observed and recorded from 1980 to 2020 with occasional interruption by some missing values. The phenophase items included sowing date, anthesis date and maturity date, which were necessary for calibration of the development stages in the WOFOST model. In addition, statistical yields of highland barley were also recorded from 1980 to 2020 in Lhasa and Rikaze stations.
Both phenotypic parameters and meteorological variables were needed as input items to drive the WOFOST model [6]. The key phenotypic parameters include the base temperature, the effective temperature sum from emergence to anthesis (TSUM1), and the effective temperature sum from anthesis to maturity (TSUM2). The input meteorological variables of the WOFOST model include global radiation, maximum and minimum temperature, vapor pressure, wind speed, and precipitation [6]. With the exception of global radiation, the other items were measured in all stations in TRR. Global radiation was measured only in Lhasa. For other stations, the global radiation was estimated by the Angstrom model as follows [29,30].
where Ra is the global radiation, Re the extra-terrestrial global radiation, S the recorded sunshine hours, and S0 the potential sunshine hours, respectively. Re and S were calculated according to the FAO method [31]. Two strategies were used to determine the coefficients of a and b in the Angstrom model. The first one was to directly use the coefficients suggested by Allen et al. [31], while the second was to calibrate the Angstrom model with the observed global radiation and sunshine hours in Lhasa.
2.3. Description of the WOFOST Model
The WOFOST model is a dynamic model simulating crop growth on a daily time step. The WOFOST model has fully taken account of crop characteristics, meteorological conditions and crop management [32], based on which the processes of phenological development, assimilation and respiration, evapotranspiration and allocation of dry matter are reasonably involved to simulate crop growth in the field environments [33]. The WOFOST model has been successfully implemented in the Crop Growth Monitoring System (CGMS) to calculate yield gaps of various crops in European countries, showing its excellent performance in estimating potential yield under different growing conditions [34,35]. A more detailed description of the WOFOST model can be found in the latest version of model introduction provided by de Wit et al. [32].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The Nash-Sutchiffe Efficiency (NSE), and the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) were used as criteria to evaluate the model performance in this study [36,37].
where Mi is the measured value, Si the simulated value, the average measured value, and n the total number of the sample, respectively. A higher value of NSE and lower value of RMSE mean better model performance.
Trends in time series of the variables were analyzed by the non-parametric Theil-Sen’s estimator [38].
where Xi and Xj are the variables for year i and j, respectively. The trend significance was tested by Mann-Kendall (MK) method. The Mann–Kendall trend test statistic Z can be calculated as in the following equations [39].
where m shows the number of series, and t is the extent of any given tie. A positive value for Z indicates an increasing trend in the time series of the variables, whereas a negative value indicates a decreasing trend. For significance levels (1 − α) of 90%, 95%, and 99%, the absolute critical values of Z are 1.65, 1.96, and 2.58, respectively. More detailed information on MK test can be referred to the relevant descriptions [39,40,41].
3. Results
3.1. Model Performances
As suggested by Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the coefficients of a and b in the Angstrom model were 0.25 and 0.50, respectively [31]. Fitted with the measured global radiation and sunshine hours in Lhasa, the coefficients of a and b were calibrated as 0.28 and 0.52, respectively, which is different from the suggested values [31].
When the suggested coefficients were used directly in Angstrom model for radiation estimation, the NSE and RMSE were 0.79 and 2.5 MJ/m2d, respectively. In contrast, validation of the Angstrom model with the fitted coefficients resulted in a better model performance with greater NSE of 0.84 and smaller RMSE of 2.2 MJ/m2d (Figure 2). So, the calibrated Angstrom model was used to estimate global radiation for the other nine stations in this study.
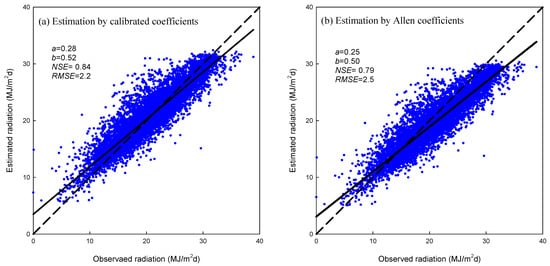
Figure 2.
Estimation of global radiation in Lhasa by calibrated coefficients and Allen Coefficients.
When calibrated with longer dataset and validated against the shorter dataset, the crop model always showed very high accuracy in prediction of the crop yield [8]. However, when the calibrated parameters are used in simulating long-term series of the crop yields, the simulated results might be inaccurate. As one of the main objectives of this study was to reveal the trends in the long time series of the highland barley yields, the WOFOST model was first calibrated with the shorter dataset, and then validated against the longer dataset to show its reliability in prediction of the long time series of the highland barley yields in TRR. Using the “trial and error” method [28], the WOFOST model was first calibrated with the phenological data observed in Lhasa and Rikaze from 1981 to 1990. Calibration results indicated that the base temperature should be set as 0 °C in this study, just the same as the spring barley parameter used in European regions [6]. The other two key phenotypic parameters, TSUM1 and TSUM2, were calibrated as 1067.4 and 578.6 °C day, respectively. Then, the calibrated model was validated against the data from 1991–2020. Validation results indicated that WOFOST model could accurately simulate the flowering dates and maturity dates of the highland barley, and the prediction was accurate with NSE of 0.73 and 0.7, respectively (Figure 3a,b). WOFOST also performed well in simulating the grain yields in Lhasa and Rikaze, with the NSE value of 0.901. The RMSE in estimated grain yields was 189.3 kg/ha, a small error in percentage of about 3.9% in contrast to the average yield of 8012 kg/ha (Figure 3c).
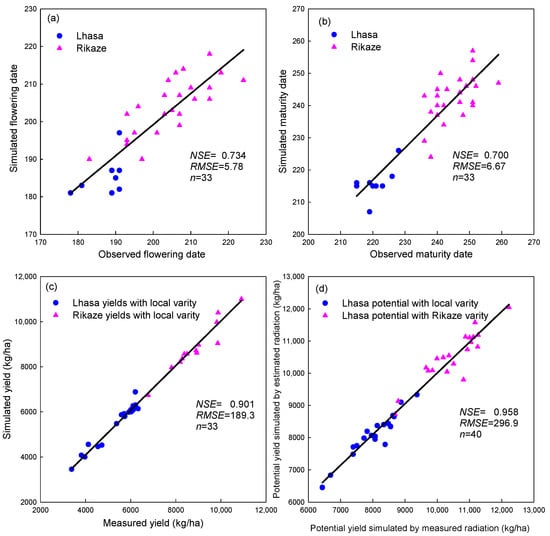
Figure 3.
Validation of the WOFOST model against the flowering date (a), maturity date (b), grain yield (c), and potential yield (d) in Lhasa and Rikaze stations.
The main varieties planted in Lhasa and Rikaze were Chunqing and Zangqing, respectively. However, Zangqing was also planted as the main variety in Lhasa in recent years. Thus, Zangqing was used for calculating potential yields for all stations in this study. In fact, the varieties changed every several years in each station, but calculation of potential yields with different varieties would make it hard to identify the effects of climate change on potential yields due to the involvement of genotype differences.
In order to identify the possible error in the potential yields caused by radiation estimation, the potential yields in Lhasa were simulated by the WOFOST model driven with measured and estimated global radiation, respectively. The results indicated that the potential yields could be accurately simulated with the estimated global radiation for both varieties, with the NSE value of 0.958. The RMSE in potential yields simulated by the estimated radiation was 296.9 kg/ha, which resulted in an error in percentage of about 4.3% in contrast to the average potential yield of 10,231 kg/ha (Figure 3d).
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Climate Conditions during the Highland Barley Growth Periods
The yield of highland barley is determined by several parameters such as number in grain by spike, thousand grain weight, and the stresses during seed development. As for the meteorological factors, potential yield is mainly determined by the global radiation and temperature during the growth period according to its definition [6], so the spatial and temporal variations in the global radiation and temperature were analyzed, in order to provide the fundamental climatic information for further analysis of the variations in the potential yields of highland barley in TRR. The highland barley is sown in April and matured in late August in TRR.
Spatial and temporal variations in global radiation during the growth period of highland barley in TRR is shown in Figure 4. The daily global radiation ranged from 23.32 MJ/m2d in Qiongjie to 24.38 MJ/m2d in Gongga, with an average value of 23.89 MJ/m2d in TRR (Figure 4a). It was obvious that global radiation has decreased in all the stations from 1961 to 2020 (Figure 4b). Radiation in Qongjie decreased at the greatest rate of 0.095 MJ/m2d/a, while the smallest decreasing rate of 0.002 MJ/m2d/a occurred in Nimu. The average decreasing trend was 0.047 MJ/m2d/a in TRR.
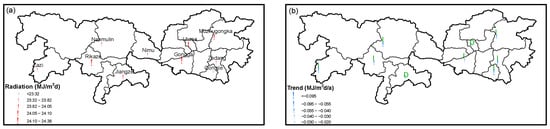
Figure 4.
Spatial (a) and temporal (b) variation in global radiation during highland barley growth period from 1961 to 2020. Plus, | and D signs denote confidence levels of 90%, 95% and 99%, respectively. The symbols denote the same meaning in the following figure legends.
On the whole, the temperature during the growth period in the western part of TRR was higher than that in the east (Figure 5a), mainly due to the difference in the altitude (Figure 1 and Table 1). During the growth period, Zedang had the highest temperature of 13.82 °C, while the lowest temperature of 10.48 °C occurred in Lazi. The average temperature during growth periods of the highland barley in TRR was 12.44 °C. As for the temporal trends, temperature in Qongjie and Nanmulin decreased slightly at the very small rates of 0.002 °C/a and 0.004 °C/a, respectively (Figure 5b), and neither of these decreasing trends was significant with an absolute Z value smaller than 1.65. Temperature in Namulin decreased at a small rate of 0.004 °C/a, with the significance level of 90%. In contrast, the temperature in all the other stations exhibited remarkable increasing trends from 0.019 to 0.087 °C/a, with the significance level of 99% (Figure 5b). The average increasing trend in temperature was 0.026 °C/a for all stations in TRR.
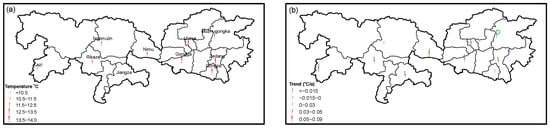
Figure 5.
Spatial (a) and temporal (b) variation in daily mean temperature during highland barley growth periods from 1961 to 2020.
3.3. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Growth Durations and Potential Yields of Highland Barley in TRR
In this study, the whole growth period was defined as the growth period from the sowing day to the maturity day, while the critical period was referred to as the period from the anthesis day to the maturity day. As for the whole growth period, the growth duration ranged from 120 to 144 days with an average value of 127 days in TRR (Figure 6a). From 1961 to 2020, only Nanmulin and Mozhugo presented slightly increasing trends at the rate of 0.022 and 0.083 d/a, respectively (Figure 6b). These increasing trends were not significant, with both Z values being smaller than 1.65. In contrast, the growth durations exhibited significant decreasing trends in all the other stations at an average decreasing rate of 0.191 d/a, with the significance level of 99% (Figure 6b). As for the critical period, the growth duration ranged from 36 to 50 days with an average value of 41 days in TRR (Figure 6c). All stations in TRR exhibited decreasing trends at the rates ranging from 0.065 to 0.161 d/a, with an average decreasing rate of 0.075 d/a (Figure 6d). The decrease in the growth durations of both the whole growth periods and the critical periods has become more evident in recent years (Figure 7).
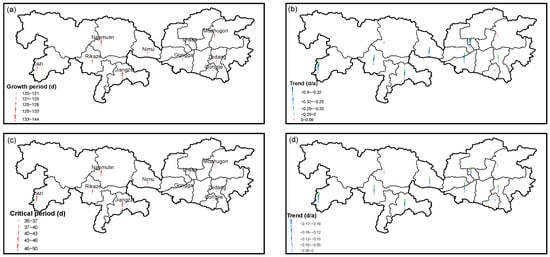
Figure 6.
Spatial and temporal variations in the growth periods and the critical periods of the highland barley. (a,b) indicate spatial variation in the growth periods and the critical periods, respectively. (c,d) indicate temporal trends in the growth periods and the critical periods, respectively.
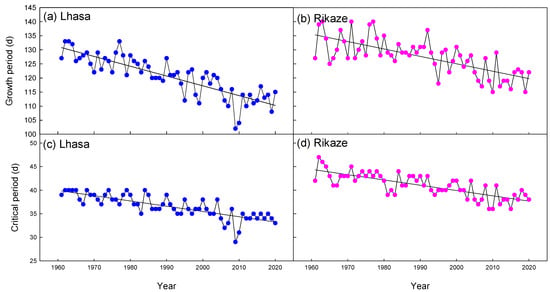
Figure 7.
Decreasing trends in the growth periods in Lhasa (a) and Rikaze (b), and the decreasing trends in the critical periods in Lhasa (c) and Rikaze (d), respectively.
In TRR, the greatest potential yield of the highland barley was 14,185 kg/ha in Jiaze, while the smallest was 10,300 kg/ha in Nimu. The average potential yield was 11,823 kg/ha in TRR (Figure 8a). Only two out of these ten stations showed increasing trends in potential yields from 1961 to 2020, but these increasing trends were not statistically significant with Z value lower than 1.65 (Figure 8b). In contrast, all the other stations exhibited the significant decreasing trends in the potential yields at the rates from 7.3 to 60.3 kg/ha/a. The average decreasing trend was 27.8 kg/ha/a for all the stations in TRR (Figure 8b), and the decreasing trends seemed to become more evident in the recent years (Figure 9). It should be noted that the potential yield was very low in 2018 (Figure 9a). Analysis of the meteorological conditions indicated that the temperature was abnormally low with the monthly mean value of 9.8 °C in April, which made the growth rate very low in the initial stage and resulted in a very small leaf area index. The low growth rate, together with the small leaf area index, finally led to a small accumulated photosynthesis and very low potential yield of the highland barley in 2018.
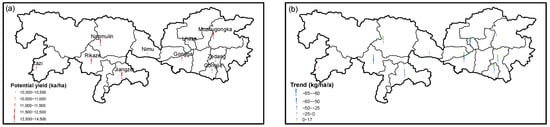
Figure 8.
Spatial (a) and temporal (b) variations in potential yields of highland barley in the last 60 years.
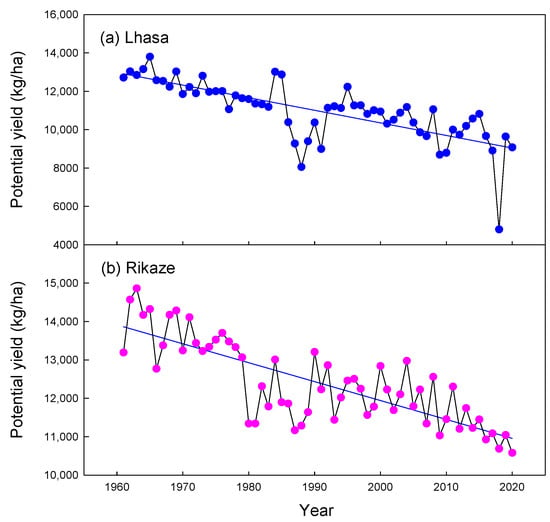
Figure 9.
Decreasing trend in the potential yields of highland barley in Lhasa (a) and Rikaze (b) from 1961 to 2020.
4. Discussion
4.1. Applicability of the WOFOST Model in Simulating the Potential Yields of Highland Barley in TRR
The leaf photosynthesis rate is influenced by many factors, including CO2 concentration, global radiation, and temperature, etc. [42]. Yu et al. [42] developed a leaf photosynthesis model based on the observed photosynthesis rate of winter wheat over the Tibetan Plateau, indicating that photosynthesis rate was approximately a linear function of the global radiation at low light levels [42]. As the global radiation during the growth period was very high on the Tibetan Plateau (Figure 4), the photosynthesis rate became accordingly very large, which contributed to the high daily photosynthesis simulated by the WOFOST model [6]. In the WOFOST model, the total photosynthesis of the highland barley was accumulated at a daily step, and further resulted in the high potential yields. In short, the high global radiation on the Tibetan Plateau contributes to the high yield of highland barley in TRR, though the extremely high radiation could result in photoinhibition at very few cases on the Tibetan Plateau [42].
The WOFOST model simulates crop growth based on the mechanism processes [6], which makes it suitable for application in different climate conditions when the key parameters were reasonably calibrated [43]. The WOFOST model has been identified to be efficient at simulating potential yields of winter wheat and summer maize in the North China Plain [8,44], and rice in the Yangtze River Delta of China [45]. Song et al. [26] successfully used WOFOST to simulate the potential yields of winter wheat over the Tibetan Plateau. In TRR, the highest simulated potential yield of highland barley was 14185 ka/ha in Jiaze under no water and nutrition conditions (Figure 8a), while the highest actual yield was recorded as 11,453 ka/ha. These high yields can be attributed to the high radiation and cool temperature during the growth period over Tibetan Plateau. With the similar growth period, the yields of spring wheat greater than 13,000 ka/ha were reported for several locations over the Tibetan Plateau, with the highest yield being 15,200 ka/ha [46]. Sinclair et al. [46] believed the high yields of spring wheat on the Tibetan Plateau could be attributed to the high solar radiation and cool temperature due to the high altitude of the Tibetan Plateau. Sinclair et al. [46] further explored the suitability of the crop model for simulating high-level yields of spring wheat over Tibetan Plateau, and concluded that the dynamic crop model could be successfully used as a framework in which the key relevant parameters could be adjusted to match the observed crop growth. In this study, the WOFOST model has accurately simulated the growth durations and the grain yields of highland barley with NSE of 0.700 and 0.901 (Figure 3a–c), respectively, indicating its high accuracy in the regional applicability on the Tibetan Plateau.
For most weather stations, the global radiation can be estimated by the sunshine-based Angstrom model [47], which performs much better than the temperature-based models on the Tibetan Plateau [19]. However, the coefficients in Angstrom model are site-dependent [48], which makes calibration of the coefficients necessary. In this study, the calibrated Angstrom model accurately estimated the global radiation in Lhasa with high NSE of 0.82 and small RMSE of 2.2 MJ/m2d (Figure 2), which resulted in a high NSE of 0.958 in the simulation of the potential yields by the WOFOST model (Figure 3d). This result is in agreement with that by Hunt et al. [49], who also emphasized the importance of model calibration to estimate global radiation for use in crop models.
4.2. Decreasing Trends in the Potential Yields Caused by Dimming and Warming Effects over the Tibetan Plateau
Global radiation has decreased at a rate of 0.021 MJ/m2d/a from 1984 to 2012 over the Tibetan Plateau [50]. This dimming could not be explained by the changes in cloud cover or the increase in aerosols, but might be caused by the increase in water vapor amount and deep cloud cover, which in turn are related to the rapid warming over the Tibetan Plateau [50]. A later analysis showed that the temperature has increased at the rates ranging from 0.016 to 0.067 °C/a on the Tibetan Plateau since 1950 [51]. In this study, the average decreasing rate during the growth period of highland barley was 0.047 MJ/m2d/a (Figure 4b), more than two times larger than the annual decreasing rate of 0.021 MJ/m2d/a [50]. In addition, the temperature during growth periods increased significantly at the rates ranging from 0.019 to 0.087 °C/a in most stations in TRR (Figure 5b). The increasing rates were larger than the warming rates on the Tibetan Plateau mentioned above [51], which is believed to be greater than the average warming rate of the globe [52]. In short, dimming and warming were significant during the growth periods of highland barley in TRR in recent decades.
As the potential yield is determined by global radiation and temperature conditions [6], the distinguish dimming and warming during the growth period might negatively influence the potential yields of highland barley in TRR. Due to high altitude, the global radiation on the Tibetan Plateau is much higher than that in the other regions [19]. Based on the investigation in the response of leaf photosynthesis to light intensity, Yu et al. [42] found that the global radiation was always higher than the light saturation point due to high altitude on the Tibetan Plateau. In very few cases, the few extremely high radiation could even have a negative effect on photosynthesis through photoinhibition, which suggests that dimming on the Tibetan Plateau would not be the leading factor for decreasing yields in recent decades (Figure 8 and Figure 9). In contrast, the crop growth period can be significantly shortened due to warming effects [53], which would further lead to the decrease in the simulated grain yields. Statistical analysis revealed that the potential yield of highland barley was positively correlated with the growth duration of the critical period (Figure 10). With the growth duration of the critical period decreasing under warming conditions (Figure 6 and Figure 7), the potential yields decreased accordingly with the shortened growth duration of the critical period (Figure 8 and Figure 9).
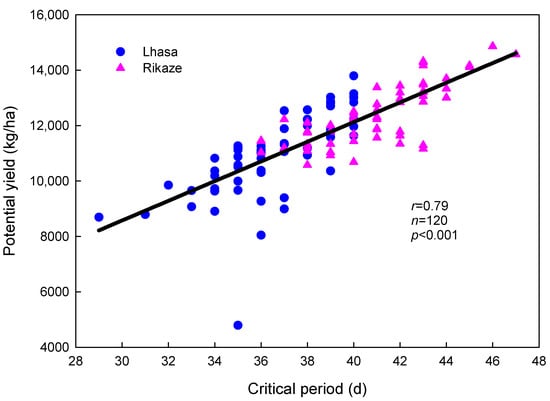
Figure 10.
Relationship between critical periods and potential yields of highland barley simulated by the WOFOST model.
4.3. Uncertainties in the Simulated Potential Yields and Possible Measures to Adapt Highland Barley Production to the Climate Change
4.3.1. Uncertainties in the Simulated Potential Yields
Though the WOFOST model performed well in simulating the phenophases and grain yields, uncertainties still existed in the simulated potential yield of highland barley in TRR. Potential yield is defined as a theoretical yield under optimal water and nutrition conditions. However, many factors such as the occasional chilling or pests can seriously influence the grain yields even if the crop is planted under no water- and nutrition conditions, which makes it impossible to directly measure the potential yield in the field. Without a measured standard, it is hard to ascertain the most reliable value for the potential yield of a crop planted in a certain region. In other words, the potential yields of a crop might be different when simulated by different crop models, and it is hard to declare which one is more reliable. Using the DSSAT crop growth model, Gong et al. [28] calculated the potential yield of highland barley in Rikaze as 10,425 ka/ha. In this study, the calculated potential yield in Rikaze was 12,409 ka/ha (Figure 8). The recorded statistical yields of highland barley in Rikaze was 11,454 ka/ha in 2012, which is much higher than the corresponding value reported by Gong et al. [28]. So, we cautiously envisage that the potential yields simulated in this study might be more reliable, as the potential yields should not be smaller than the statistical yields measured in the fields [6]. The muti-model ensemble is recommended to be used as an effective method to improve reliability in the simulated potential yields of highland barley in TRR in the future research.
4.3.2. Possible Adaptation of Highland Barley Production to Climate Change
The impacts of climate change on agricultural production have been well documented in recent decades [54,55,56,57]. Climate change plays different roles in positively prolonging or negatively shortened the growth duration, and further leads to the gains and losses in the grain yields for different crops under different climate conditions [58]. So, the strategies on agricultural adaptation to climate change should be made in line with local realities [58]. In this study, it was identified that the decreasing trends in the potential yields of highland barley in TRR were mainly caused by the shortened critical periods due to the significant warming effects (Figure 6 and Figure 7). Thus, extension of the crop growth duration can be viewed as an efficient way to mitigate the negative warming impacts in TRR. Based on this recognition, Song et al. [26] argued that winter wheat should be planted as the main crop for adaptation of agriculture to climate change over the Tibetan Plateau. However, the highland barley is referred to as the indispensable staple food for all Tibetans living in the Tibetan Plateau, which makes this countermeasure unfeasible in reality. In fact, the highland barley has successfully evolved to adapt to the high stressful environment over the Tibetan Plateau with its unique genes for more than 3000 years [25], so cultivation of new varieties with longer growth duration through genetic breeding might be an achievable strategy for adaptation of highland barley to the climate change challenges in TRR. In addition, the higher temperature may contribute to changing barley sowing dates and possible production of highland barley in the higher altitudes under global warming scenarios, which might provide optimal strategies for adaptation of highland barley production to climatic change in TRR in the future.
5. Conclusions
The WOFOST model was used to simulate the potential yields of highland barley in TRR. Validation results indicated that the WOFOST model could accurately simulate the growth durations and grain yields with the NSE of 0.700 and 0.901, respectively.
Climate change during the growth periods of highland barley was significant in TRR from 1961 to 2020. The global radiation in the growth period decreased with an average rate of 0.047 MJ/m2d/a in TRR. The temperature increased in most stations in TRR during the growth period, with the increasing rates ranging from 0.019 to 0.087 °C/a, which was greater than the average warming rate of the globe.
The high potential yields of highland barley in TRR can be attributed to the high global radiation and cool temperature during the growth periods on the Tibetan Plateau. In the past 60 years, the significant decreasing trends in the potential yields occurred in most locations of TRR, which can be attributed to the shortened critical periods due to warming effects. In response to this situation, cultivation of new varieties with longer growth duration through genetic breeding is suggested as an achievable strategy for adaptation of highland barley to climate change in TRR. In addition, planting the highland barley at higher altitude would become possible under warming conditions, together with the changes in the sowing dates of the highland barley. It has been identified that WOFOST model performed well in simulating the potential yields of highland barley in TRR with the global radiation estimated by the calibrated Angstrom model, so the calibrated WOFOST can be used as a useful tool to explore the optimal sowing dates and suitable altitudes for the highland barley production, in order to achieve sustainable agricultural development on the Tibetan Plateau.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L., H.W.L., D.-L.L., J.D. and G.Z.; methodology, J.L., Y.S. (Yanling Song) and Y.S. (Yanbo Shen); software, J.L.; validation, J.L., D.-L.L. and G.Z.; formal analysis, J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, D.-L.L., Q.Y. and H.W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Opening Project of Institute of Tibet Plateau and Polar Research, Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, under the grant No. ITPP2021K03, and the Second Tibetan Plateau Comprehensive Research Project under the grant No. 2019QZKK0106.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to the agro-meteorological observers in the Lhasa and Rikaze stations for their careful observation work under high altitude hypoxia environments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kotykova, O.; Babych, M.; Semenchuk, I. Monitoring of food security at regional level. Manag. Theory Stud. Rural. Bus. Infrastruct. Dev. 2019, 41, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatia, V.S.; Singh, P.; Wani, S.P.; Chauhan, G.S.; Rao, A.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Srinivas, K. Analysis of potential yields and yield gaps of rainfed soybean in India using CROPGRO-Soybean model. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1252–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naab, J.B.; Singh, P.; Boote, K.J.; Jones, J.W.; Marfo, K.O. Using the CROPGRO-peanut model to quantify yield gaps of peanut in the Guinean Savanna Zone of Ghana. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harvey, L.D.D. Global Warming: The Hard Science; Pearson Education Limited: Harlow, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, T.; von Braun, J. Climate change impacts on global food security. Science 2013, 341, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Diepen, C.V.; Wolf, J.V.; Van Keulen, H.; Rappoldt, C. WOFOST: A simulation model of crop production. Soil Use Manag. 1989, 5, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.D.; Fu, B.P.; Lin, Z.S.; Lu, Q.Y. The numerical simulation of the winter wheat photosynthetic potential in the Huang Huai Hai area. Geogr. Res. 1998, 17, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Yu, Q.; Lu, C.; Hengsdijk, H. Quantifying production potentials of winter wheat in the North China Plain. Eur. J. Agron. 2006, 24, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ittersum, M.K.; Leffelaar, P.A.; van Keulen, H.; Kropff, M.J.; Bastiaans, L.; Goudriaan, J. On approaches and applications of the Wageningen crop models. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 18, 201–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, A.; Valentini, R.; Santini, M. An overview of available crop growth and yield models for studies and assessments in agriculture. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewenam, L.E.F.; Er-Raki, S.; Ezzahar, J.; Chehbouni, A. Performance evaluation of the WOFOST model for estimating evapotranspiration, soil water content, grain yield and total above-ground biomass of winter wheat in Tensift Al Haouz (Morocco): Application to yield gap estimation. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supit, I.; Van Diepen, C.A.; De Wit, A.J.W.; Kabat, P.; Baruth, B.; Ludwig, F. Recent changes in the climatic yield potential of various crops in Europe. Agric. Syst. 2010, 103, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidsma, P.; Ewert, F.; Boogaard, H.; van Diepen, K. Regional crop modelling in Europe: The impact of climatic conditions and farm characteristics on maize yields. Agric. Syst. 2009, 100, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengsdijk, H.; Meijerink, G.W.; Mosugu, M.E. Modeling the effect of three soil and water conservation practices in Tigray, Ethiopia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rötter, R.; Van Keulen, H.; Jansen, M.J.W. Variations in yield response to fertilizer application in the tropics: I. Quantifying risks and opportunities for smallholders based on crop growth simulation. Agric. Syst. 1997, 53, 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglar, A.; van der Wijngaart, R.; de Wit, A.; Lecerf, R.; Boogaard, H.; Seguini, L.; Berg, M.V.D.; Toreti, A.; Zampieri, M.; Fumagalli, D.; et al. Improving WOFOST model to simulate winter wheat phenology in Europe: Evaluation and effects on yield. Agric. Syst. 2019, 168, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilardelli, C.; Confalonieri, R.; Cappelli, G.A.; Bellocchi, G. Sensitivity of WOFOST-based modelling solutions to crop parameters under climate change. Ecol. Model. 2018, 368, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; van Diepen, C.A. Effects of climate change on grain maize yield potential in the European Community. Clim. Chang. 1995, 29, 299–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Linderholm, H.W.; Chen, D.; Yu, Q.; Wu, D.; Haginoya, S. Observation and calculation of the solar radiation on the Tibetan Plateau. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 57, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, J.; Xu, F.; Zhang, T.; Chen, S.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, W.; Wang, R.; He, L.; Feng, H.; et al. Improving solar radiation estimation in China based on regional optimal combination of meteorological factors with machine learning methods. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 220, 113111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, F.; Varas, E. Estimation of mean monthly solar global radiation as a function of temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 100, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlert, T. Use of empirical global radiation models for maize growth simulation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 126, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domros, M.; Peng, G.B. The Climate of China; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.H.; Dong, G.H.; Zhang, D.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Jia, X.; An, C.B.; Ma, M.M.; Xie, Y.W.; Barton, L.; Ren, X.Y.; et al. Agriculture facilitated permanent human occupation of the Tibetan Plateau after 3600 BP. Science 2015, 347, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Q.; Mascher, M.; Guo, G.; Li, S.; Mao, L.; Liu, Q.; Xia, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. Origin and evolution of qingke barley in Tibet. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wang, C.; Linderholm, H.W.; Tian, J.; Shi, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y. Agricultural adaptation to global warming in the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, J.; Leng, G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, W. Future potential distribution and expansion trends of highland barley under climate change in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau (QTP). Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; He, L.; Wu, D.; Lv, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Yu, Q. Spatial-temporal variations of photo-temperature potential productivity and yield gap of highland barley and its response to climate change in the cold regions of the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2020, 53, 720–733. [Google Scholar]
- Angstrom, A. Solar and terrestrial radiation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1924, 50, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, J.A. Evaporation from a water surface in relation to solar radiation. Trans. R. Soc. South Aust. 1940, 46, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements-FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300, p. D05109. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, A.; Boogaard, H.L.; Supit, I.; van den Berg, M. System Description of the WOFOST 7.2, Cropping Systems Model; Wageningen Environmental Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, A.; Boogaard, H.; Fumagalli, D.; Janssen, S.; Knapen, R.; van Kraalingen, D.; van Diepen, K. 25 years of the WOFOST cropping systems model. Agric. Syst. 2019, 168, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogaard, H.; Wolf, J.; Supit, I.; Niemeyer, S.; van Ittersum, M. A regional implementation of WOFOST for calculating yield gaps of autumn-sown wheat across the European Union. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 143, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, A.; Duveiller, G.; Defourny, P. Estimating regional winter wheat yield with WOFOST through the assimilation of green area index retrieved from MODIS observations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 164, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Linderholm, H.; Chen, D.; Zhou, X.; Flerchinger, G.N.; Yu, Q.; Du, J.; Wu, D.; Shen, Y.; Yang, Z. Changes in the relationship between solar radiation and sunshine duration in large cities of China. Energy 2015, 82, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, V.S.; Francos, W.Z. Statistical Analysis in Climate Research; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, R.; Leblanc, S.G. Parametric (modified least squares) and non-parametric (Theil–Sen) linear regressions for predicting biophysical parameters in the presence of measurement errors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirnia, A.; Golshan, M.; Darabi, H.; Adamowski, J.; Rozbeh, S. Using the Mann–Kendall test and double mass curve method to explore stream flow changes in response to climate and human activities. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2019, 10, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, T. Simulation of leaf photosynthesis of winter wheat on Tibetan Plateau and in North China Plain. Ecol. Model. 2002, 155, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Shen, S.; Xiong, S.; Ma, X.; Fan, Z.; Han, H. Water stress is a key factor influencing the parameter sensitivity of the WOFOST model in different agro-meteorological conditions. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2021, 15, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yu, Q.; Wang, E.; Hengsdijk, H. Impact of spatial-temporal variations of climatic variables on summer maize yield in North China Plain. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2008, 2, 71–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Liu, X.; Liu, M. Assimilating remote sensing phenological information into the WOFOST model for rice growth simulation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinclair, T.R.; Bai, Q. Analysis of high wheat yields in northwest China. Agric. Syst. 1997, 53, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Ersi, K.; Yang, J.; Lu, S.; Zhao, W. Validation of five global radiation models with measured daily data in China. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mei, X.; Li, Y.; Porter, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Choice of the Ångström–Prescott coefficients: Are time-dependent ones better than fixed ones in modeling global solar irradiance? Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 2565–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, L.A.; Kuchar, L.; Swanton, C.J. Estimation of solar radiation for use in crop modelling. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1998, 91, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ding, B.; Qin, J.; Tang, W.; Lu, N.; Lin, C. Can aerosol loading explain the solar dimming over the Tibetan Plateau? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L20170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuang, X.; Jiao, J.J. Review on climate change on the Tibetan Plateau during the last half century. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 3979–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Huang, J.; Guan, X.; Chen, B.; Zhang, L. Long-term trends of precipitable water and precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau derived from satellite and surface measurements. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2013, 122, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Asseng, S.; Wong, M.T.F.; Yu, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, E. Quantifying the interactive impacts of global dimming and warming on wheat yield and water use in China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 182, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Gourdji, S.M. The influence of climate change on global crop productivity. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Fang, J. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howden, S.M.; Soussana, J.F.; Tubiello, F.N.; Chhetri, N.; Dunlop, M.; Meinke, H. Adapting agriculture to climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19691–19696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Møller, H.B.; Sørensen, P.; Olesen, J.E.; Petersen, S.O.; Nyord, T.; Sommer, S.G. Agricultural biogas production—Climate and environmental impacts. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Li, M.; Dou, X. Climate change affects crop production potential in semi-arid regions: A case study in Dingxi, Northwest China, in recent 30 years. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).