Linking Internal Mobility, Regional Development and Economic Structural Changes in Romania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A Brief Literature Overview
3. Methodology
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Economic Growth and Migration of the Workforce at National Level
4.2. Economic Growth and Sectorial Development at National Level
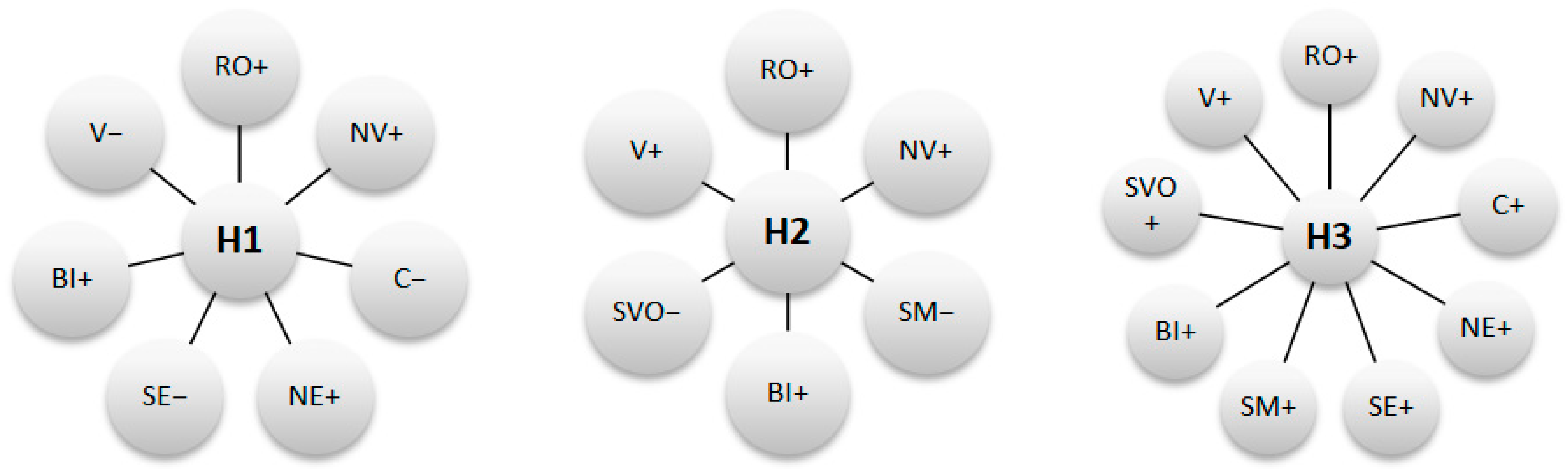
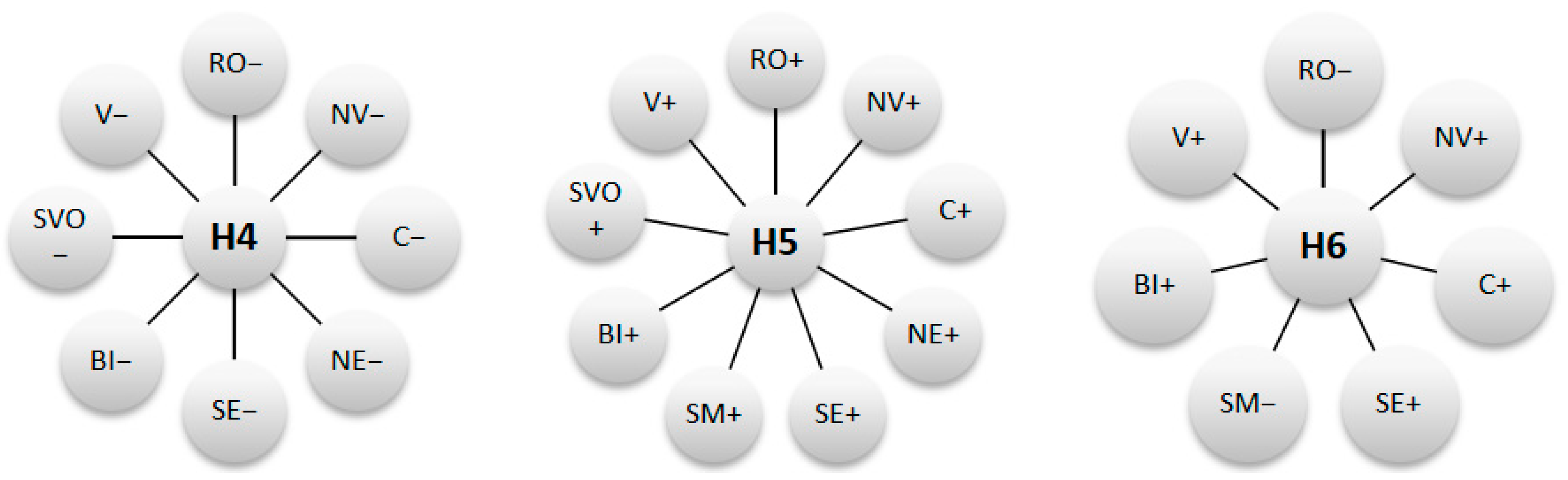
4.3. The Intra-Regional Relationship between Economic Growth and Migration of the Workforce
4.4. The Intra-Regional Relationship between Economic Growth and Sectorial Development
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sandu, D. Migrația Internă Dominată de Drumul Spre sat (The Internal Migration with Its Dominant Orientation towards Villages). In Ghețău, Vasile (coord.), Demografia României; Editura Academiei Române: Bucharest, Romania, 2018; pp. 222–244. ISBN 978-973-27-2935-9. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329673474_MIGRATIA_INTERNA_DOMINATA_DE_DRUMUL_SPRE_SAT_The_internal_migration_with_its_dominant_orientation_towards_villages_1990-2016 (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Dumitru, I. Reevaluarea Modelului de Creștere Economică în România—Lecții și Consecințe ale Crizei, Prezentare BNR. 2012. Available online: http://www.consiliulfiscal.ro/prezentare_BNR_29oct2012.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- OECD/European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies. Romania: Country Health Profile 2021, State of Health in the EU; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchberger, M. Measuring Internal Migration, Regional Science and Urban Economics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 91(C). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solow, R.M. A contribution to the theory of economic growth. Q. J. Econ. 1956, 70, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.E. On the mechanics of economic development. J. Monet. Econ. 1988, 22, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolado, J.; Goria, A.; Ichino, A. Immigration, human capital and growth in the host country. J. Popul. Econ. 1994, 7, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, P.M. The origins of endogenous growth. J. Econ. Perspect. 1994, 8, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipayalai, K. Impact of international labor migration on regional economic growth in Thailand. J. Econ. Struc. 2020, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.; Elin, C.E.; Ueffing, P.; Stillwell, J.; Kupiszewski, M.; Kupiszewska, D. Internal Migration and Development: Comparing Migration Intensities around the World. Popul. Dev. Rev. 2015, 41, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). Overcoming Barriers: Human Mobility and Development; Human Development Report; Palgrave Macmillan Houndmills: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, M.; Elin, C.E.; Kupiszewska, D.; Kupiszewski, M.; Stillwell, J.; Zhu, Y. Internal Migration Data around the World: Assessing Contemporary Practice. Popul. Space Place 2014, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Vignoli, J.; Rowe, F. How is internal migration reshaping metropolitan populations in Latin America? A new method and new evidence. Popul. Stud. 2018, 72, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, P.; Kupiszewski, M. Internal Migration and Regional Population Dynamics in Europe: A Synthesis; Council of Europe Publishing: Strasbourg, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, F. Establishing the extent and pace of the contemporary trend of migration decline in Europe. Reg. Mag. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, F. Is internal migration declining in Europe? In Proceedings of the Regional Studies Association Conference, a World of Flows, Labour Mobility, Capital and Knowledge in an Age of Global Reversal and Regional Revival, Lugano, Switzerland, 3–6 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, F.; Bell, M.; Bernard, A.; Charles-Edwards, E.; Ueffing, P. Impact of internal migration on population redistribution in Europe: Urbanisation, counter urbanisation or spatial equilibrium? Comp. Popul. Stud. 2019, 44, 201–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, F.; Patias, N. Mapping the spatial patterns of internal migration in Europe. Reg. Stud. Reg. Sci. 2020, 7, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, P.; Bell, M.; Kupiszewski, M.; Kupiszewska, D.; Ueffing, P.; Bernard, A.; Charles-Edwards, E.; Stillwell, J. The Impact of Internal Migration on Population Redistribution: An International Comparison. Popul. Space Place 2017, 23, e2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maza, A. Internal Migration in Spain: A Complementary Approach. Economies 2020, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, D.L.; Vasile, V.; Preda, D.; Nicolescu, L. Fenomenul Migraţionist din Perspectiva Aderării României la Uniunea Europeană; Institutul European din România: Bucharest, Romania, 2004.
- Pehoiu, G.; Costache, A. The Dynamics of Population Emigration from Romania—Contemporary and Future Trends. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 42, 594–599. [Google Scholar]
- Șerban, M. Dinamica Migrației Internaționale: Un Exercițiu Asupra Migrației Românești în Spania, Edit; Media Lumen: Iași, Romania, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Constantin, D.L.; Lilea, E.; Parlog, C. Resursele Umane în România. Mobilitatea Teritorială; Editura A.S.E.: Bucharest, Romania, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Suditu, B.A.; Prelipceanu, G.; Vîrdol, D.C.; Stângaciu, O.A. Perspectivele Politicii de Migraţie în Contextual Demografic Actual Din România, Studiu de Strategie şi Politici 2012, Nr.1.; Institutul European din România: Bucharest, Romania, 2013.
- Pîrvu, R.; Murtaza, F.A.; Toma, O. Socio-Demographic and Regional Analysis of Internal Mobility in Romania between 1990–2020. Rev. Stiinte Politice 2022, 73, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Török, I. Regional Inequalities in Romania before and After the EU Accession, IOP Conference Series. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 221, 012151. [Google Scholar]
- Benedek, J.; Varvari, S.; Litan, C.M. Urban growth pole policy and regional development: Old wine in new bottles? In Regional and Local Development in Times of Polarization; Lang, T., Gormar, F., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: Singapore, 2019; pp. 173–197. [Google Scholar]
- Albu, L.L.; Lupu, R.; Călin, A.C.; Popovici, O.C. Impactul aderării României la Uniunea Europeană Asupra Economiei Românești. Analiză Sectorială (Industrie, Agricultură, Servicii Etc.). 2018. Available online: http://ier.gov.ro/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/SPOS_2017_Studiul-1_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Restrepo Cadavid, P.; Cineas, G.; Quintero, L.L.E.; Zhukova., S. Cities in Europe and Central Asia: A Shifting Story of Urban Growth and Decline; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Török, I. From growth to shrinkage: The effects of economic change on the migration processes in rural Romania. Landbauforsch. Appl. Agric. For. Res. 2014, 64, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Fina, Ș.; Heider, B.; Raț, C. România inegală. Disparităţile Socio-Economice Regionale din România. Friedrich-Ebert-Stiftung România Juliane Schulte. 2021. Available online: http://library.fes.de/pdf-files/bueros/bukarest/18051-20210623.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Breusch, T.S.; Pagan, A. The Lagrange Multiplier Test and its Applications to Model Specification in Econometrics. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1980, 47, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, W.H. Econometric Analysis; Prentice Hall: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zaharia, R.M.; Ban, C.; Popescu, A.M. Relația Dintre Fenomenul Migrației Legale și Piața Muncii din România. Evoluții Relevante, Impact Potențial, Recomandări de Politici, București. 2017. Available online: http://ier.gov.ro/wp-content/uploads/publicatii/SPOS_2016_-Migratia_legala_si_piata_muncii.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- CONAF. Studiu Privind Ocuparea Forței de Muncă din Romania în Contextul UE, Septembrie. 2019. Available online: https://conaf.ro/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/studiu-privind-ocuparea-fortei-de-munca-din-romania-in-contextul-ue.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Ministerul Dezvoltării, Lucrărilor Publice și Administrației- Direcția Politici și Strategii. Zone Rurale în Declin Provocări, Acțiuni și Perspective Pentru GUVERNANȚA Teritorială. 2020. Available online: Https://www.mdlpa.ro/uploads/articole/attachments/5ffd97755e271209770379.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Guga, Ș.; Spatari, M. Sectorul Comerţ în România: Un Bilanţ După Trei Decenii de Transformări. 2019. Available online: http://library.fes.de/pdf-files/bueros/bukarest/15818.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Ministerul Dezvoltării, Lucrărilor Publice și Administrației- Direcția Politici și Strategii. Disparități Teritoriale în România Studiu de fundamentare. 2021. Available online: https://www.mdlpa.ro/uploads/articole/attachments/618cf3596cc0c316310799.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- ADR Sud Muntenia. Strategia Pentru Specializare Inteligentă în Regiunea Sud Muntenia, Instrument Inovativ Dedicat Dezvoltării Economice Regionale. 2015. Available online: https://www.adrmuntenia.ro/strategia-pentru-specializare-inteligenta-a-regiunii-sud-muntenia-pentru-perioad/static/892 (accessed on 28 April 2022).
| GDP | SSD_U | SSD_R | RA_T | PO_T | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 60,360.13 | −3699.211 | 3699.211 | 21,312.68 | 1055.981 |
| Median | 56,299.90 | −4102.000 | 3857.000 | 18,991.10 | 1054.150 |
| Maximum | 256,595.7 | 12,007.00 | 8298.000 | 105,613.7 | 1409.100 |
| Minimum | 7036.100 | −11,195.00 | −1159.000 | 2835.500 | 761.3000 |
| Std. Dev. | 43,125.18 | 3730.408 | 2067.671 | 16145.59 | 162.6694 |
| Skewness | 1.806648 | 1.361784 | −0.214557 | 2.312283 | −0.090895 |
| Kurtosis | 7.614577 | 6.003393 | 2.575190 | 10.29237 | 1.988374 |
| Jarque-Bera | 217.5515 | 104.1085 | 2.309151 | 472.2472 | 6.690750 |
| Probability | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.315191 | 0.000000 | 0.035247 |
| Observations | 152 | 152 | 152 | 152 | 152 |
| AGRI | IND | CONS | COM | SERV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 309.4908 | 239.9020 | 69.52697 | 136.4638 | 300.5974 |
| Median | 326.5500 | 237.6000 | 66.15000 | 133.9000 | 275.6500 |
| Maximum | 710.3000 | 348.2000 | 163.5000 | 260.2000 | 744.9000 |
| Minimum | 27.20000 | 151.4000 | 32.90000 | 67.50000 | 175.4000 |
| Std. Dev. | 150.3962 | 47.05989 | 29.50317 | 40.03814 | 117.9568 |
| Skewness | −0.058208 | 0.039036 | 1.637211 | 1.340697 | 2.218442 |
| Kurtosis | 2.786416 | 1.975799 | 5.520549 | 5.028011 | 7.524557 |
| Jarque-Bera | 0.374749 | 6.682190 | 108.1418 | 71.58379 | 254.3311 |
| Probability | 0.829133 | 0.035398 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| Observations | 152 | 152 | 152 | 152 | 152 |
| Dependent Variable: GDP | ||||
| Method: Panel Least Squares (Pooled OLS) | ||||
| Sample: 2000–2018 | ||||
| Cross-sections included: 8 | ||||
| Total panel (balanced) observations: 152 | ||||
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob. |
| SSD_U | 5.844952 | 0.582370 | 10.03649 | 0.0000 |
| SSD_R | 4.432444 | 1.084869 | 4.085694 | 0.0001 |
| RA_T | 1.509758 | 0.139847 | 10.79575 | 0.0000 |
| PO_T | 31.96012 | 5.441839 | 5.873037 | 0.0000 |
| Pooled OLS | Random Effects | Fixed Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breusch–Pagan LM test a | - | X2(1) = 134.07 *** | - |
| Hausman test b | - | - | X2(4) = 42.67 *** |
| Dependent Variable: GDP Sample: 2000–2018 | ||||
| Panel Least Squares (Fixed Effects) | Panel EGLS (Random Effects) | |||
| Variable | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value |
| C | −159,938.0 | 0.0000 | −97,216.73 | 0.0000 |
| SSD_U | 1.328143 | 0.0718 | 2.904543 | 0.0000 |
| SSD_R | 3.036681 | 0.0016 | 4.485426 | 0.0000 |
| RA_T | 2.256311 | 0.0000 | 2.129020 | 0.0000 |
| PO_T | 157.0955 | 0.0000 | 100.7155 | 0.0000 |
| Cross-sections included: 8 Total panel (balanced) observations: 152 | ||||
| Dependent Variable: GDP | ||||
| Method: Panel Least Squares | ||||
| Sample: 2000–2018 | ||||
| Cross-sections included: 8 | ||||
| Total panel (balanced) observations: 152 | ||||
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob. |
| AGRI | −51.31007 | 11.81204 | −4.343879 | 0.0000 |
| IND | −80.18535 | 39.57337 | −2.026245 | 0.0445 |
| CONS | 756.8052 | 195.3002 | 3.875086 | 0.0002 |
| COM | 558.7554 | 173.6035 | 3.218573 | 0.0016 |
| SERV | −109.4314 | 45.53271 | −2.403358 | 0.0175 |
| Pooled OLS | Random Effects | Fixed Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breusch–Pagan LM test a | - | X2(1) = 9.75 *** | - |
| Hausman test b | - | - | X2(5) = 288.37 *** |
| Dependent Variable: GDP Sample: 2000–2018 | ||||
| Panel Least Squares (Fixed Effects) | Panel EGLS (Random Effects) | |||
| Variable | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value |
| C | 7040.001 | 0.7494 | −29,523.81 | 0.0001 |
| AGRI | −176.6974 | 0.0000 | −36.13502 | 0.0000 |
| IND | −185.8649 | 0.0017 | −11.65458 | 0.6784 |
| CONS | 278.2935 | 0.0971 | 895.9835 | 0.0000 |
| COM | −192.2727 | 0.2384 | 557.7435 | 0.0000 |
| SERV | 530.5604 | 0.0000 | −114.9161 | 0.0000 |
| Cross-sections included: 8 Total panel (balanced) observations: 152 | ||||
| Dependent variable: GDP Time interval: 2000–2018 | ||||||||
| NV | C | NE | SE | SM | BI | SVO | V | |
| SSD_U | 3.88 (0.0064) | −6.02 (0.0017) | 0.99 (0.0133) | −1.58 (0.0025) | 1.51 (0.5181) | 1.43 (0.0129) | −2.37 (0.0261) | −0.70 (0.0638) |
| SSD_R | 4.46 (0.0003) | −7.70 (0.0024) | 2.11 (0.0004) | −0.70 (0.0682) | 1.13 (0.3196) | 1.23 (0.0905) | −1.42 (0.1518) | −0.21 (0.0732) |
| RA | 2.03 (0.0000) | 2.91 (0.0000) | 3.07 (0.0000) | 2.84 (0.0000) | 3.54 (0.0000) | 2.55 (0.0000) | 2.41 (0.0000) | 2.52 (0.0000) |
| PO | 8.35 (0.0100) | 6.64 (0.2405) | −1.93 (0.5086) | −5.33 (0.3555) | −2.44 (0.0008) | 3.49 (0.0022) | −3.28 (0.0972) | 4.12 (0.0885) |
| Dependent variable: GDP Period of time: 2000–2018 | ||||||||
| NV | C | NE | SE | SM | BI | SVO | V | |
| AGRI | −126.45 (0.0000) | −173.28 (0.0019) | −76.78 (0.0229) | −62.60 (0.0549) | −108.72 (0.0069) | −1765.63 (0.0165) | −87.04 (0.0036) | −238.68 (0.0019) |
| IND | −77.08 (0.4899) | −45.90 (0.5889) | −10.36 (0.9367) | −486.25 (0.0929) | 35.55 (0.8268) | −330.74 (0.0608) | −308.41 (0.1858) | −335.37 (0.0228) |
| CONS | 781.75 (0.0128) | 1247.56 (0.0011) | 1193.59 (0.0045) | 936.45 (0.0392) | 1477.10 (0.0067) | 961.09 (0.0470) | 831.39 (0.0080) | 434.01 (0.0912) |
| COM | −382.68 (0.0213) | −589.80 (0.0373) | 18.94 (0.9617) | −33.86 (0.9355) | 319.24 (0.5731) | 3.23 (0.0956) | −331.35 (0.0554) | 494.47 (0.0298) |
| SERV | 434.12 (0.0187) | 421.81 (0.0369) | 29.30 (0.8959) | 404.28 (0.0476) | −140.14 (0.0987) | 672.97 (0.0002) | 550.77 (0.1797) | 447.72 (0.0279) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pîrvu, R.; Bădîrcea, R.M.; Doran, N.M.; Jianu, E.; Țenea, L.; Murtaza, F. Linking Internal Mobility, Regional Development and Economic Structural Changes in Romania. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127258
Pîrvu R, Bădîrcea RM, Doran NM, Jianu E, Țenea L, Murtaza F. Linking Internal Mobility, Regional Development and Economic Structural Changes in Romania. Sustainability. 2022; 14(12):7258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127258
Chicago/Turabian StylePîrvu, Ramona, Roxana Maria Bădîrcea, Nicoleta Mihaela Doran, Elena Jianu, Lili Țenea, and Flavia Murtaza. 2022. "Linking Internal Mobility, Regional Development and Economic Structural Changes in Romania" Sustainability 14, no. 12: 7258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127258
APA StylePîrvu, R., Bădîrcea, R. M., Doran, N. M., Jianu, E., Țenea, L., & Murtaza, F. (2022). Linking Internal Mobility, Regional Development and Economic Structural Changes in Romania. Sustainability, 14(12), 7258. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127258






