Dynamic Simulation Research on the Effect of Governance Mechanism on Value Co-Creation of Blockchain Industry Ecosystem
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Value Co-Creation of the Blockchain Industry Ecosystem
2.2. Governance Mechanisms of the Blockchain Industry Ecosystem
2.3. Effect of Governance Mechanisms on Value Co-Creation
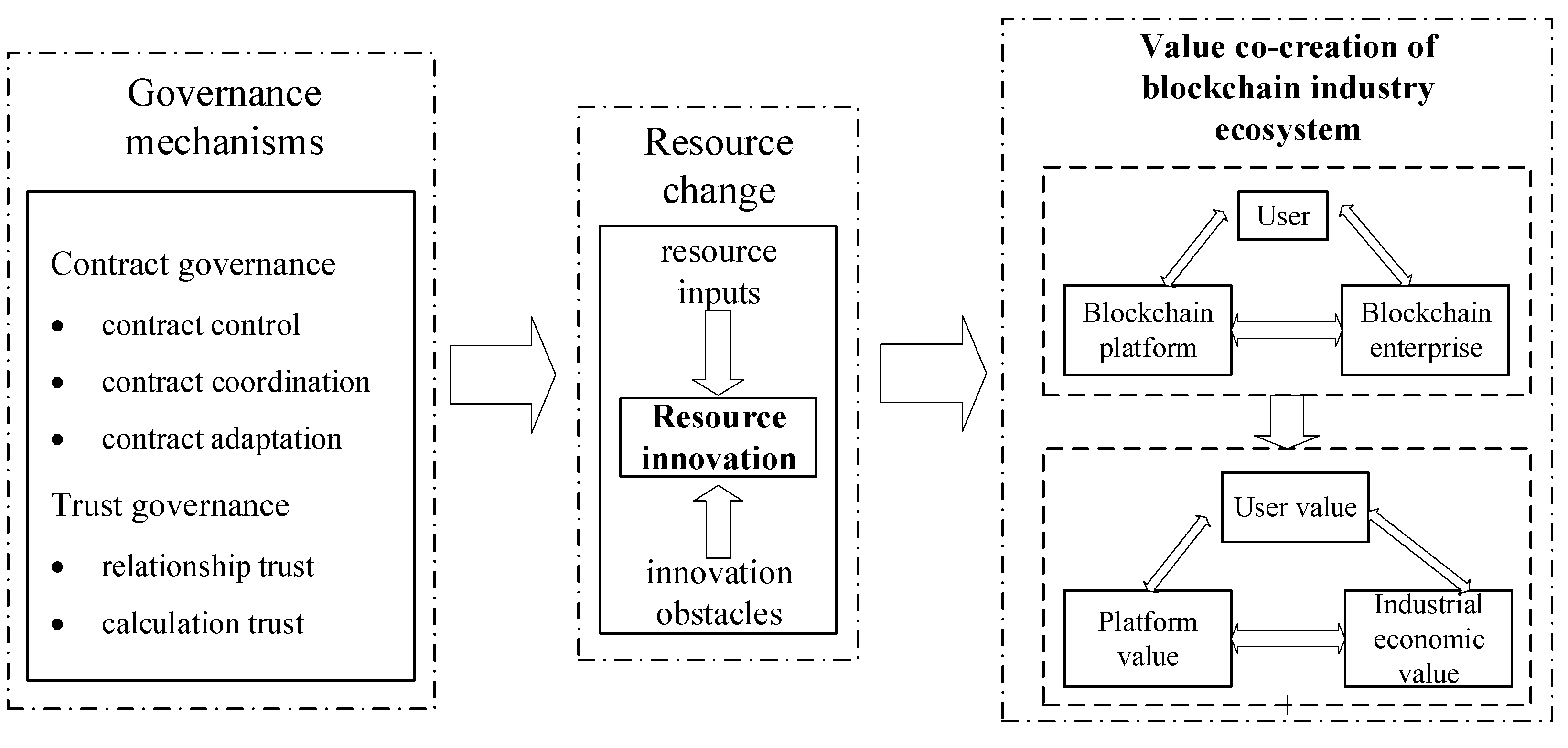
3. Construction of System Dynamics Model
3.1. System Description and Definition of Main Variables
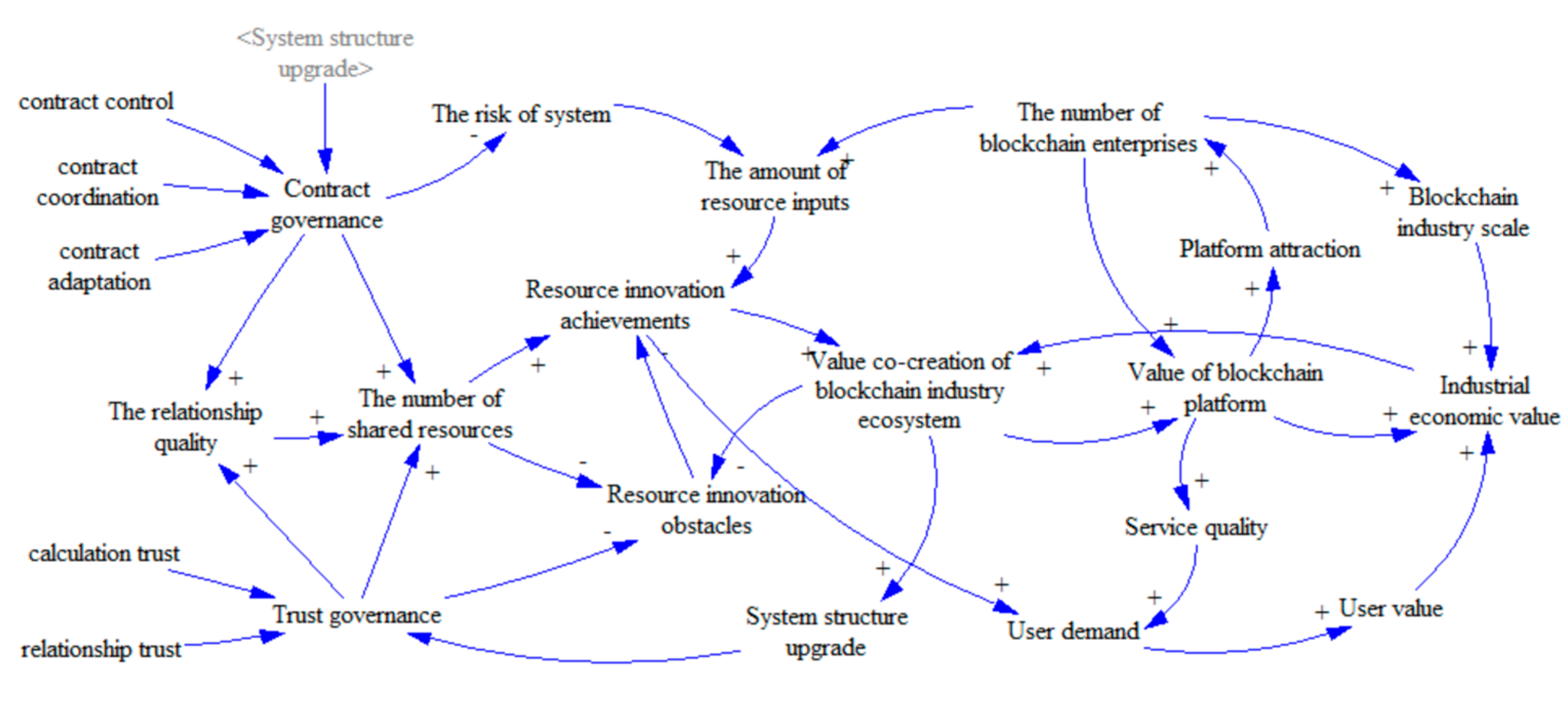
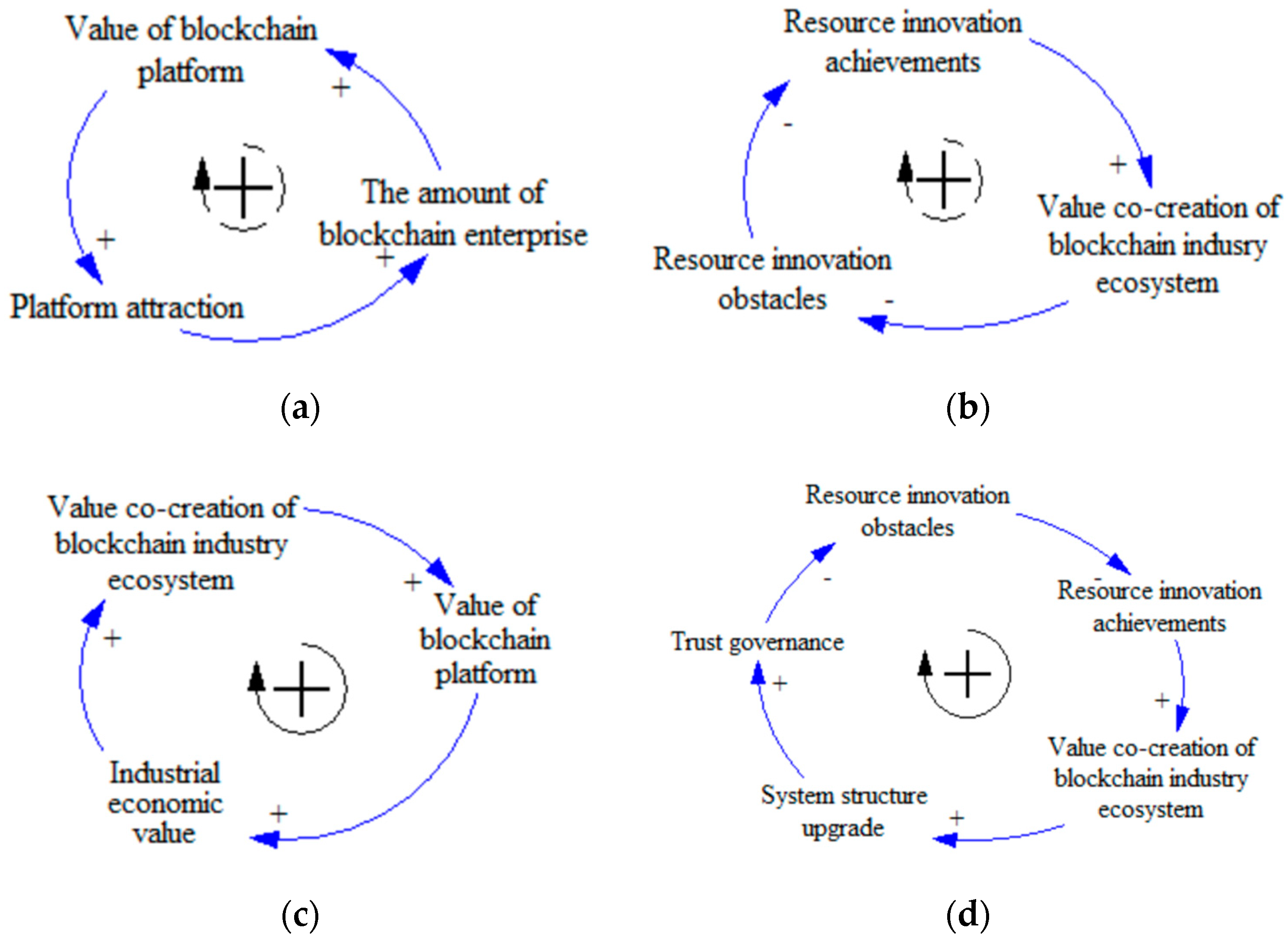
3.2. The Causality Model and Main Feedback Loops
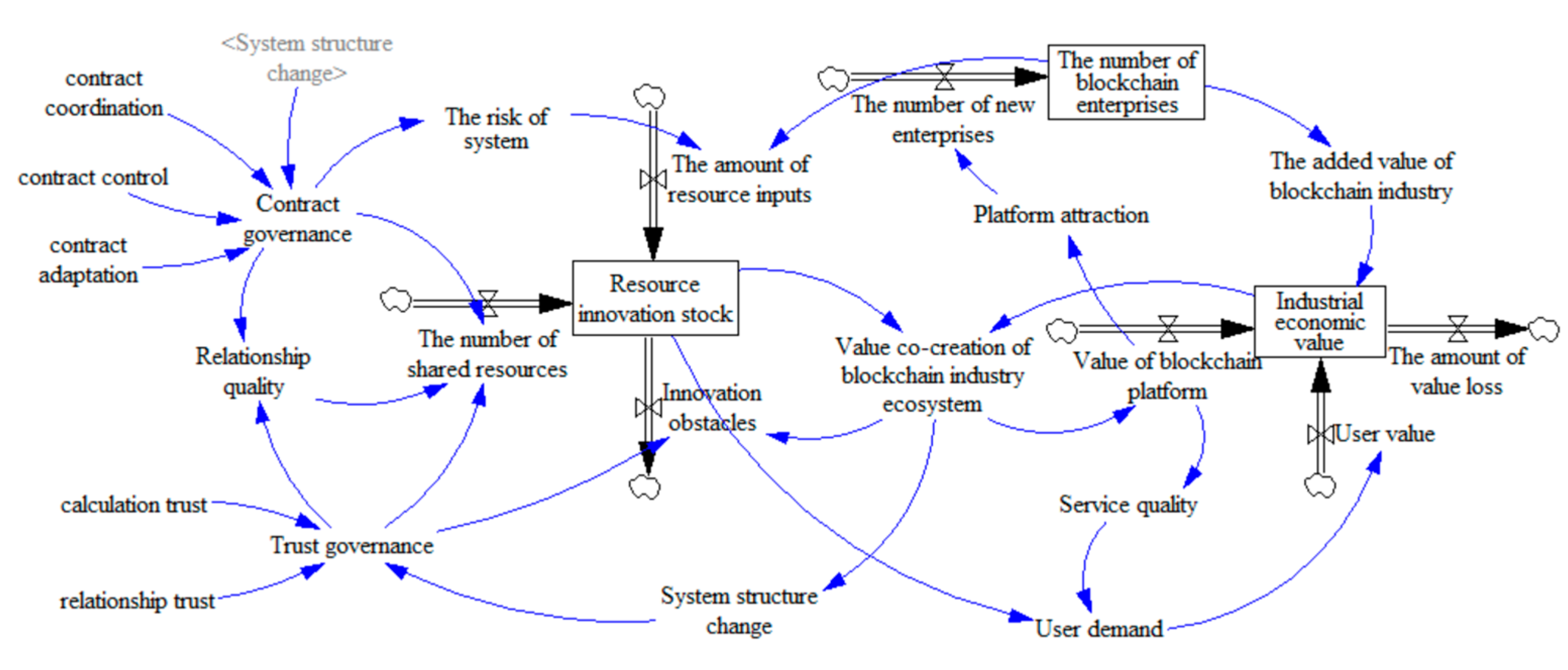
3.3. Model Assumptions and System Flow Chart
3.4. Model Equation Design
4. Simulation and Sensitivity Analysis
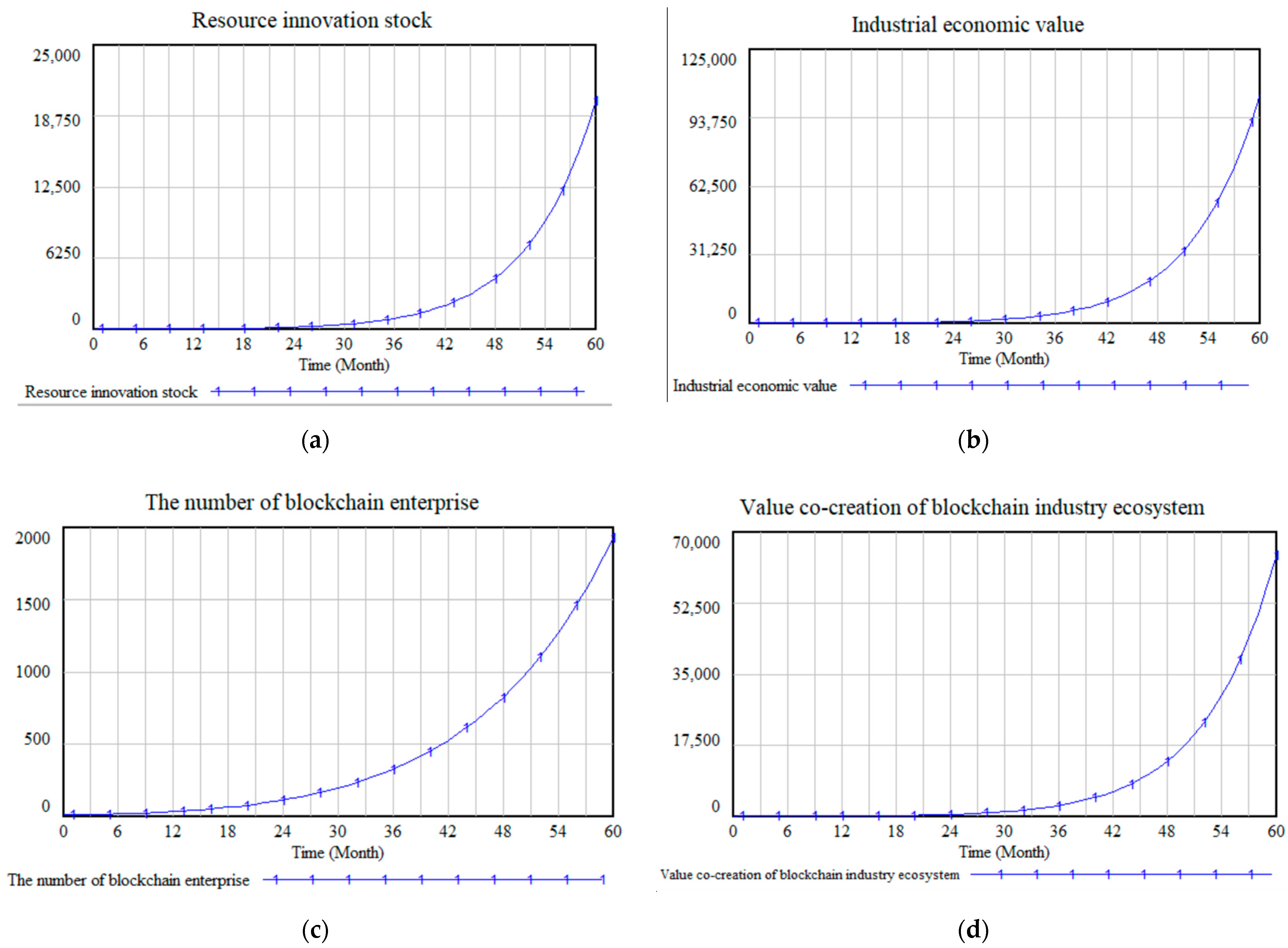
4.1. Simulation Analysis
4.2. Analysis of Simulation Results
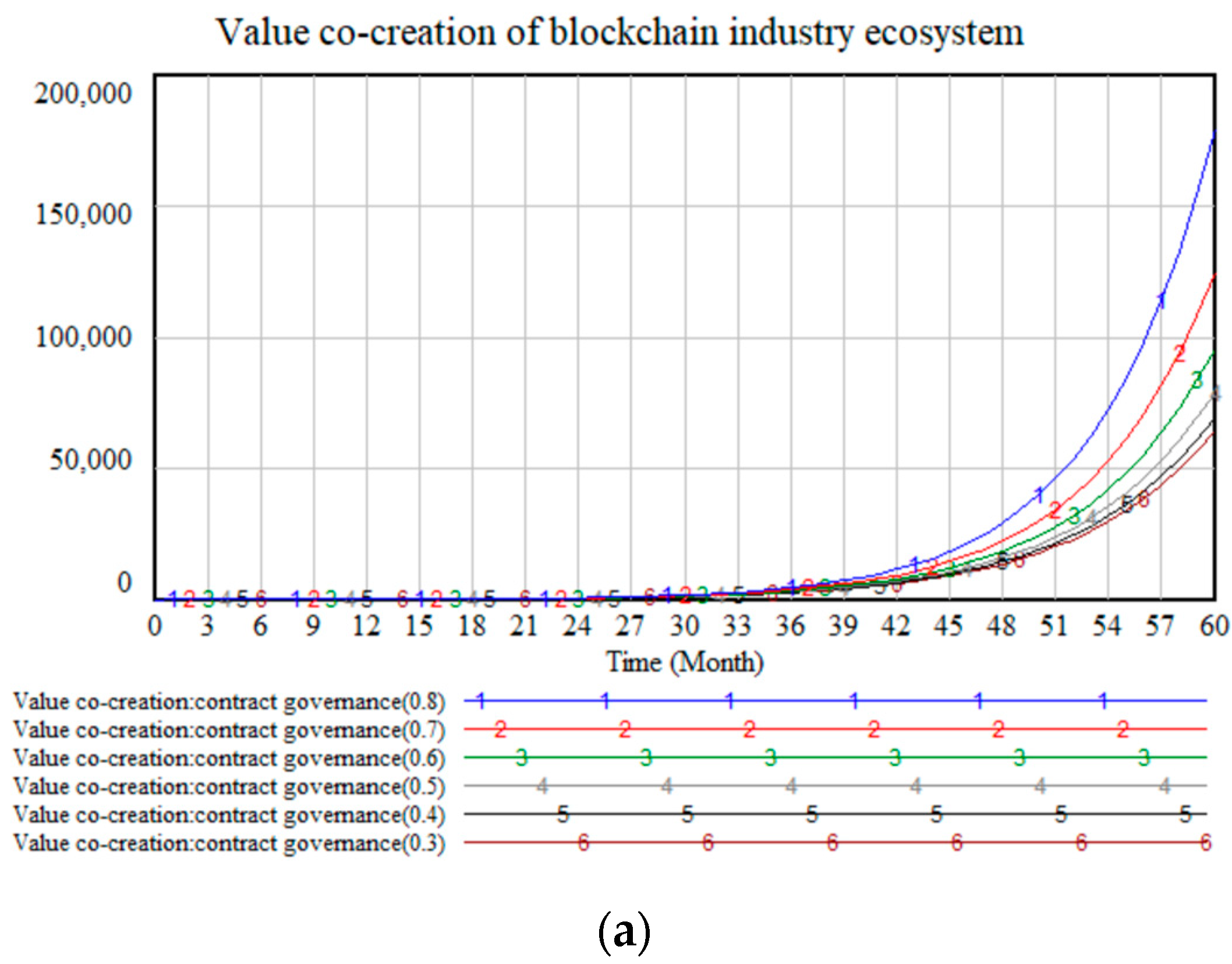
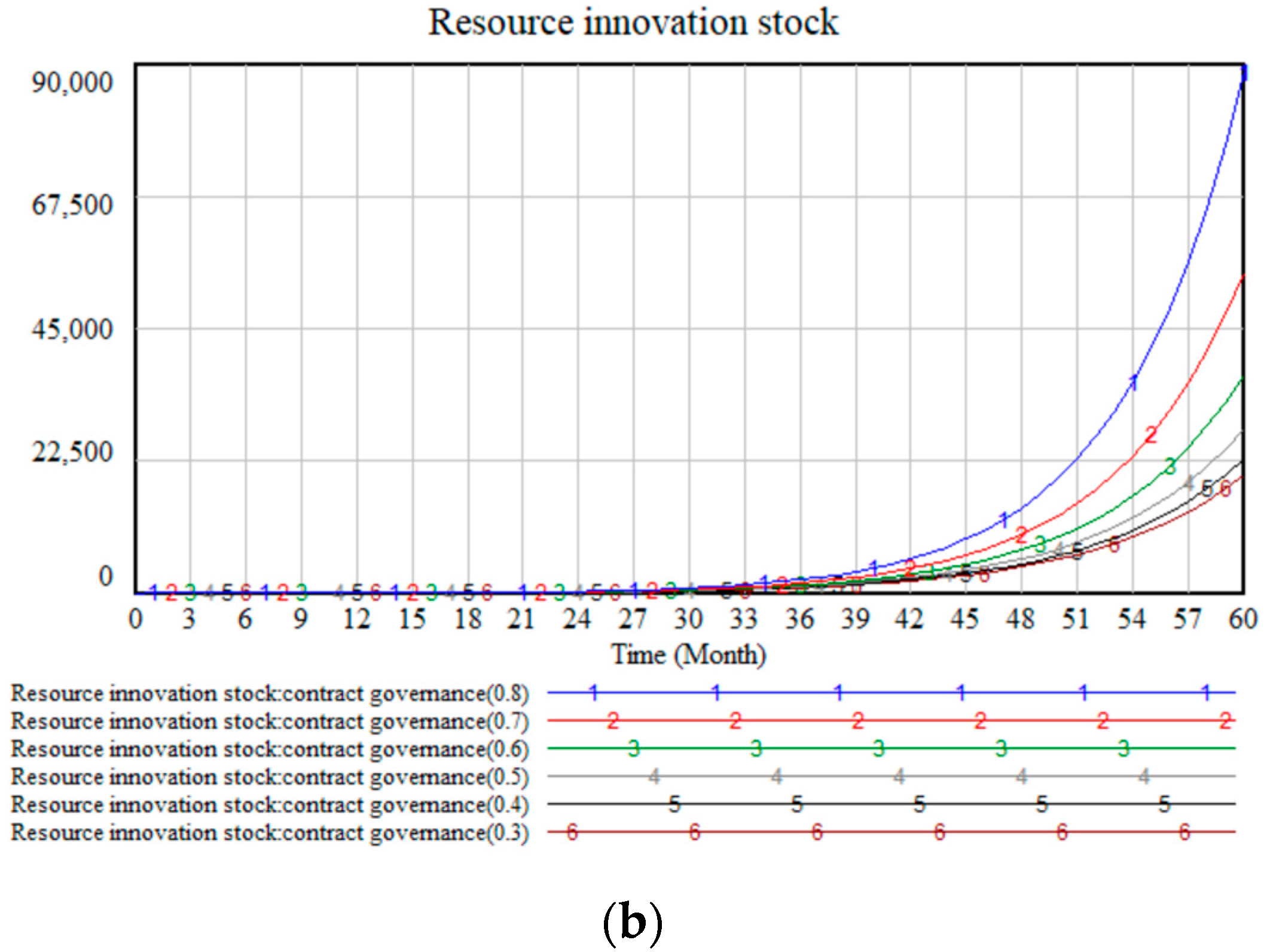
4.2.1. Sensitivity Analysis of Contract Governance
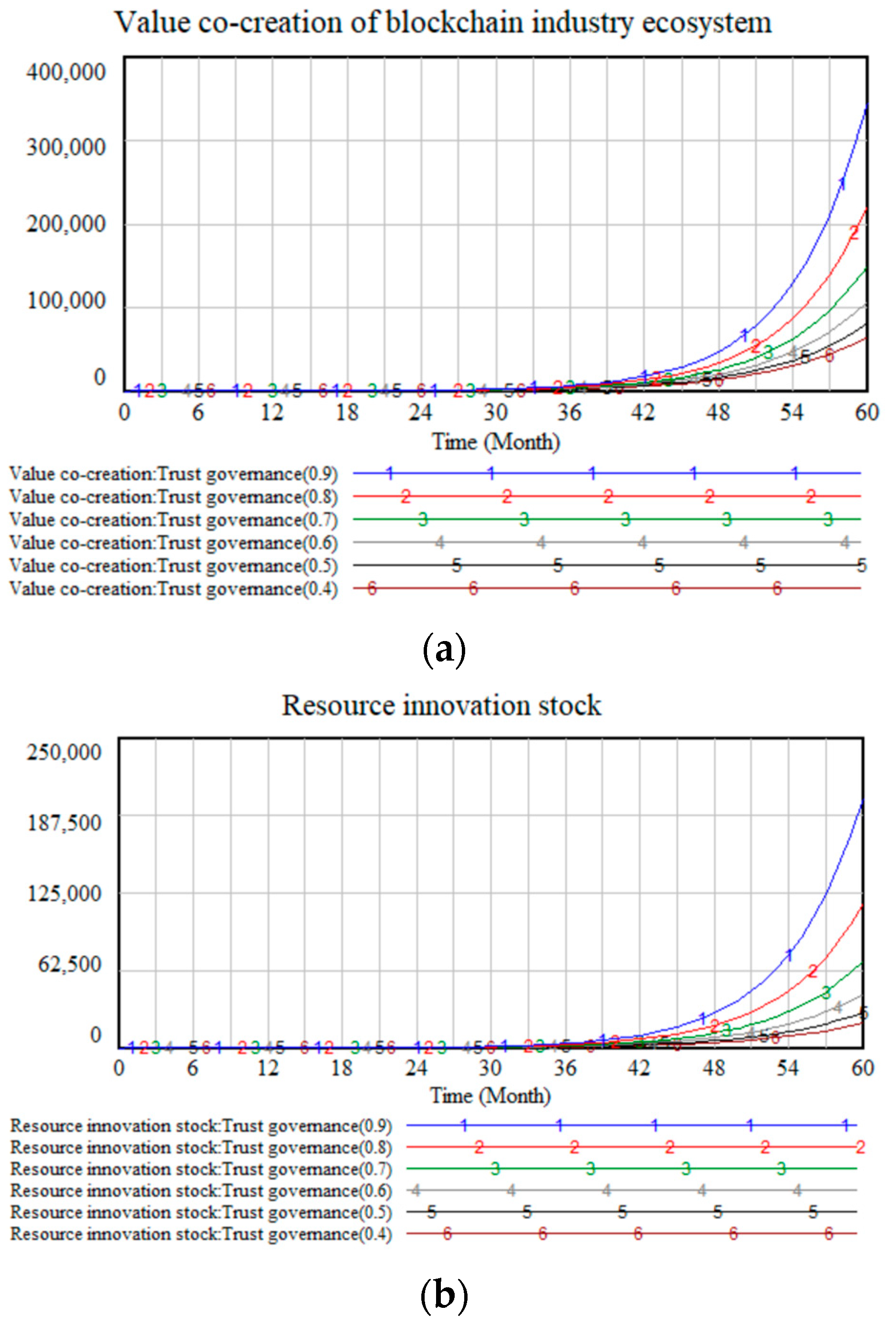
4.2.2. Sensitivity Analysis of Trust Governance
4.2.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Co-Existence Effect of Contract Governance and Trust Governance
5. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buhalis, D.; Harwood, T.; Bogicevic, V.; Viglia, G.; Beldona, S.; Hofacker, C. Technological disruptions in services: Lessons from tourism and hospitality. J. Serv. Manag. 2019, 30, 484–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, D.; Adams, K.; Attah-Boakye, R.; Ullah, S.; Frecknall-Hughes, J.; Kim, J. Blockchain, business and the fourth industrial revolution: Whence, whither, wherefore and how? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 161, 120254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y. Making smart manufacturing smarter—A survey on blockchain technology in Industry 4.0. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2021, 15, 1323–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausman, A. Innovativeness among small businesses: Theory and propositions for future research. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2005, 34, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghaish, F.; Hosseini, M.R.; Matarneh, S.; Talebi, S.; Wu, S.; Martek, I.; Poshdar, M.; Ghodrati, N. Blockchain and the ‘Internet of Things’ for the construction industry: Research trends and opportunities. Autom. Constr. 2021, 132, 103942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima, S.; Spiteri, J.; Romanova, I. A STEEP framework analysis of the key factors impacting the use of blockchain technology in the insurance industry. Geneva Pap. Risk Insur.-Issues Pract. 2020, 45, 398–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chong, H.-Y.; Chi, M. Modelling the blockchain adoption barriers in the AEC industry. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2021. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulos, A.; Piha, L.; Skourtis, G. Destination branding and co-creation: A service ecosystem perspective. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 2021, 30, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, E.H.M.; Dahl, A.J.; Peltier, J. Digital servitization value co-creation framework for AI services: A research agenda for digital transformation in financial service ecosystems. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 2021, 15, 200–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashideh, W. Blockchain technology framework: Current and future perspectives for the tourism industry. Tour. Manag. 2020, 80, 104125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Jang, K.; Han, J. Are the blockchain-based patents sustainable for increasing firm value? Sustainability 2020, 12, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, C.; Wang, Y.; Jin, C. The possibility of sports industry business model innovation based on blockchain technology: Evaluation of the innovation efficiency of listed sports companies. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, Y.; Kim, M.-S. Dynamic change of manufacturing and service industries network in mobile ecosystems: The case of Korea. Telemat. Inform. 2015, 32, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Lv, J.; Meng, Q. Sustainable development of the innovation ecosystem from the perspective of T-O-V. J. Math. 2021, 2021, 3419175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.J.; Won, D.; Park, K.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X. Growth of a platform business model as an entrepreneurial ecosystem and its effects on regional development. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2017, 25, 805–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, K.R.; Read, S. An ecosystem perspective synthesis of co-creation research. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2021, 99, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonamigo, A.; Frech, C.G. Industry 4.0 in services: Challenges and opportunities for value co-creation. J. Serv. Mark. 2021, 35, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, D.; Schiavone, F.; Appio, F.P.; Chiao, B. How does artificial intelligence enable and enhance value co-creation in industrial markets? An exploratory case study in the healthcare ecosystem. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 129, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, K.R.; Read, S. Value co-creation: Concept and measurement. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2016, 44, 290–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessmann, A.; Legner, C. Designing business models for cloud platforms. Inf. Syst. J. 2016, 26, 551–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, P.; Kar, A.K.; Janssen, M. Diffusion of blockchain technology insights from academic literature and social media analytics. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2019, 32, 735–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, H. Co-creation and innovation in public services. Serv. Ind. J. 2013, 33, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajvidi, M.; Wang, Y.; Hajili, N.; Love, P.E.D. Brand value co-creation in social commerce: The role of interactivity, social support, and relationship quality. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2021, 115, 105238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaaland, T.I.; Hakansson, H. Exploring interorganizational conflict in complex projects. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2003, 32, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orji, I.J.; Kusi-Sarpong, S.; Huang, S.; Vazquez-Brust, D. Evaluating the factors that influence blockchain adoption in the freight logistics industry. Transp. Res. Part E-Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 141, 102025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjodin, D. Knowledge processing and ecosystem co-creation for process innovation: Managing joint knowledge processing in process innovation projects. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2019, 15, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schreieck, M.; Wiesche, M.; Krcmar, H. Capabilities for value co-creation and value capture in emergent platform ecosystems: A longitudinal case study of SAP’s cloud platform. J. Inf. Technol. 2021, 36, 365–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareham, J.; Fox, B.P.; Cano, G.L.G. Technology ecosystem governance. Organ. Sci. 2014, 25, 1195–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.C.; Cheng, H.L.; Tseng, C.Y. Reexamining the direct and interactive effect of governance mechanisms upon buyer-supplier cooperative performance. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2014, 43, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Lumineau, F. Revisiting the interplay between contractual and relational governance: A qualitative and meta-analytic investigation. J. Oper. Manag. 2015, 33–34, 15–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.; Zhou, Z.K.; Li, J.J.; Guo, Z. Institutions and opportunism in buyer-supplier exchanges: The moderated mediating effects of contractual and relational governance. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2018, 46, 1014–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiblein, M.J. The choice of organizational governance form and performance: Predictions from transaction cost, resource-based, and real options theories. J. Manag. 2003, 29, 937–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arranz, N.; Fdez de Arroyabe, J.C. Effect of formal contracts, relational norms and trust on performance of joint research and development projects. Br. J. Manag. 2012, 23, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, J.H.; Chu, W.J. The role of trustworthiness in reducing transaction costs and improving performance: Empirical evidence from the United States, Japan, and Korea. Organ. Sci. 2003, 14, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luu, N.; Cadeaux, J.; Ngo, V.L. Governance mechanisms and total relationship value: The interaction effect of information sharing. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2018, 33, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.Z.; Poppo, L.; Yang, Z.L. Relational ties or customized contracts? An examination of alternative governance choices in China. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2008, 39, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidrmuc, J. Trust and transitions: Social capital in a changing world. Sociol. Cas. -Czech Sociol. Rev. 2009, 45, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.C.; Chiu, Y.P. Relationship governance mechanisms and collaborative performance: A relational life-cycle perspective. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2018, 24, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W. Analysis of blockchain ecosystem and suggestions for improvement. J. Inf. Commun. Converg. Eng. 2021, 19, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mungra, Y.; Yadav, P.K. The mediating effect of satisfaction on trust-commitment and relational outcomes in manufacturer-supplier relationship. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2019, 35, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshri, I.; Kotlarsky, J.; Gerbasi, A. Strategic innovation through outsourcing: The role of relational and contractual governance. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2015, 24, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, H.; Zheng, S. Different roles of control mechanisms in buyer-supplier conflict: An empirical study from China. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2017, 65, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Xu, S.; Zeng, X. Design and analysis of knowledge transfer in the process of university-industry collaborative innovation based on social network theory. J. Internet Technol. 2018, 19, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
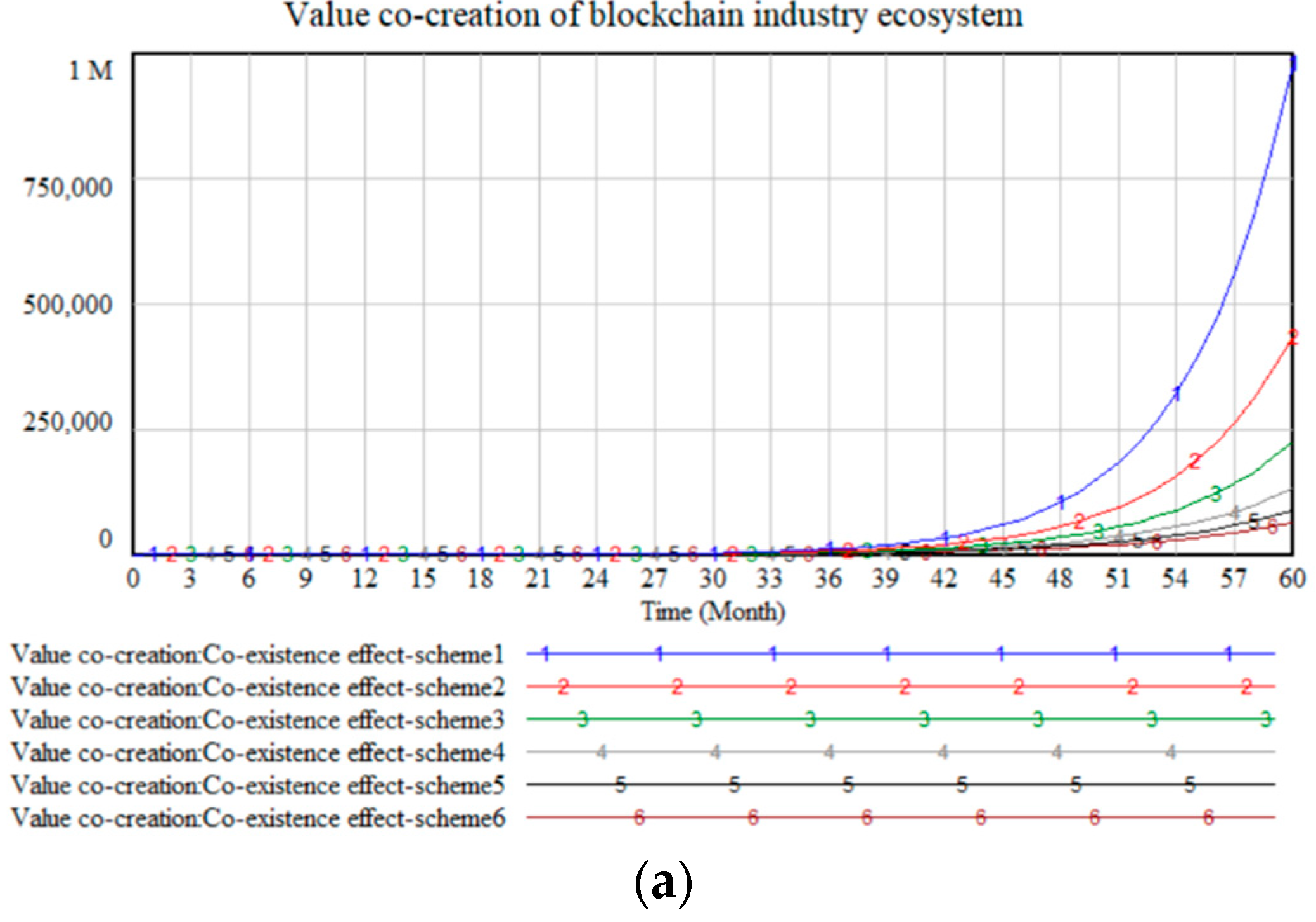
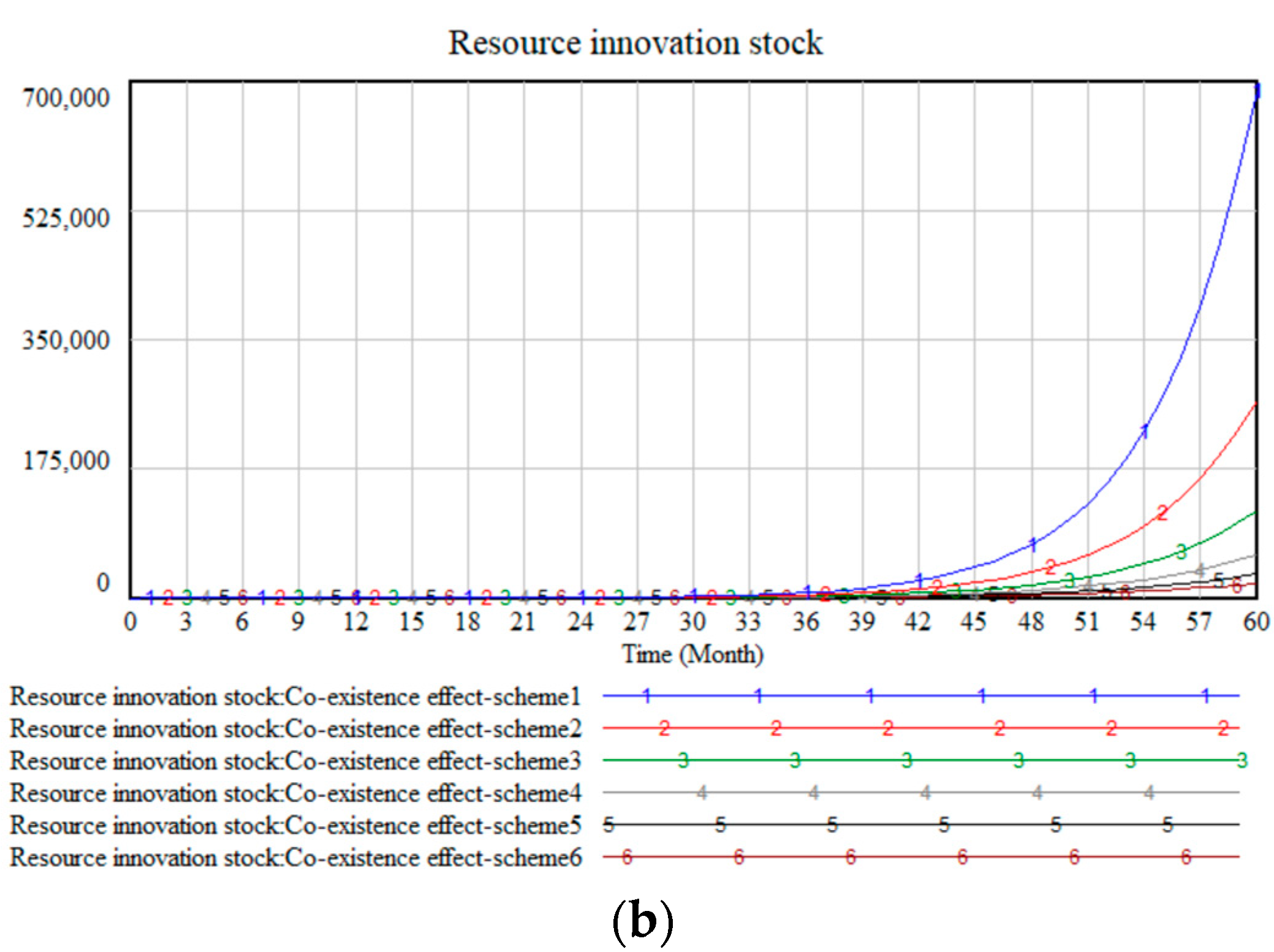
| Variable | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Resource innovation stock | The income of innovation resources obtained through the input of innovation resource and the share of resource [14]. |
| The amount of value loss | Value loss caused by some uncontrollable factors (such as major public emergencies, natural environment, etc.) [26]. |
| The amount of resource inputs | Contribution willingness and input resources of each subject in the industrial ecosystem in the process of industrial innovation [12]. |
| The number of shared resources | Information exchange and resource sharing brought by the interaction between various subjects in the industrial ecosystem [15]. |
| Innovation obstacles | Constraining factors that limit the industrial ecosystem from achieving higher innovation results [7]. |
| Value of blockchain platform | The value generated by the interaction process of enterprises, users and other system subjects in the blockchain platform [5,20]. |
| Relationship quality | The close degree of cooperation and communication among various subjects in the industrial ecosystem [9]. |
| The risk of system | The uncertainty generated by the external environment and the evolution and development of the internal system [14]. |
| Service quality | Users’ perception of platform service and satisfaction during the use of the platform [6,9]. |
| User value | The value generated by users when using the platform. As the number of platform users increases, the influence of the platform will also enhance [8]. |
| Platform attraction | The attractiveness of a platform to enterprises when they make a choice to enter [9]. |
| Contract governance | The rights and responsibilities of each system participant are defined by a formal contract. It is mainly reflected in three aspects: Contract control, contract coordination and contract adaptation [29]. |
| Trust governance | An informal constraint, emphasizing an atmosphere of mutual trust among system participants. It is mainly reflected in two aspects: relationship trust and calculation trust [35]. |
| Adjusted Variables | The Numerical Value | Months | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | ||
| Trust Governance | 0.4 | 33.15 | 226.6 | 1112 | 4641 | 17,720 | 64,339 |
| 0.5 | 33.97 | 239.7 | 1220 | 5304 | 21,207 | 80,944 | |
| 0.6 | 34.99 | 256.7 | 1366 | 6254 | 26,459 | 107,349 | |
| 0.7 | 36.25 | 278.6 | 1565 | 7611 | 34,441 | 150,171 | |
| 0.8 | 37.75 | 306.4 | 1832 | 9568 | 46,800 | 221,677 | |
| 0.9 | 39.54 | 341.5 | 2194 | 12,430 | 66,416 | 345,349 | |
| Contract Governance | 0.3 | 33.15 | 226.6 | 1112 | 4641 | 17,720 | 64,339 |
| 0.4 | 33.43 | 231.0 | 1147 | 4854 | 18,825 | 69,511 | |
| 0.5 | 33.89 | 238.3 | 1208 | 5230 | 20,805 | 78,987 | |
| 0.6 | 34.59 | 249.7 | 1305 | 5847 | 24,172 | 95,650 | |
| 0.7 | 35.60 | 266.7 | 1454 | 6841 | 29,841 | 125,104 | |
| 0.8 | 36.98 | 291.2 | 1682 | 8446 | 39,583 | 179,169 | |
| Adjusted Variables | The Numerical Value | Months | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | ||
| Trust Governance | 0.4 | 16.45 | 94.02 | 412.9 | 1591 | 5742 | 20,064 |
| 0.5 | 17.43 | 106.0 | 494.3 | 2026 | 7785 | 28,957 | |
| 0.6 | 18.67 | 121.8 | 608.1 | 2672 | 11,017 | 43,994 | |
| 0.7 | 20.20 | 142.4 | 766.2 | 3634 | 16,198 | 70,015 | |
| 0.8 | 22.04 | 169.0 | 985.9 | 5082 | 24,677 | 116,428 | |
| 0.9 | 24.24 | 203.2 | 1293.5 | 7296 | 38,904 | 202,086 | |
| Contract Governance | 0.3 | 16.45 | 94.02 | 412.9 | 1591 | 5742 | 20,064 |
| 0.4 | 16.78 | 97.96 | 439.3 | 1730 | 6379 | 22,777 | |
| 0.5 | 17.33 | 104.7 | 485.2 | 1976 | 7544 | 27,880 | |
| 0.6 | 18.18 | 115.2 | 559.7 | 2392 | 9587 | 37,209 | |
| 0.7 | 19.39 | 131.0 | 677.1 | 3082 | 13,174 | 54,562 | |
| 0.8 | 21.08 | 154.2 | 861.0 | 4242 | 19,660 | 88,441 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Xiong, H.; Xu, J. Dynamic Simulation Research on the Effect of Governance Mechanism on Value Co-Creation of Blockchain Industry Ecosystem. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127107
Zhang H, Xiong H, Xu J. Dynamic Simulation Research on the Effect of Governance Mechanism on Value Co-Creation of Blockchain Industry Ecosystem. Sustainability. 2022; 14(12):7107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127107
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hui, Huanhuan Xiong, and Jianxin Xu. 2022. "Dynamic Simulation Research on the Effect of Governance Mechanism on Value Co-Creation of Blockchain Industry Ecosystem" Sustainability 14, no. 12: 7107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127107
APA StyleZhang, H., Xiong, H., & Xu, J. (2022). Dynamic Simulation Research on the Effect of Governance Mechanism on Value Co-Creation of Blockchain Industry Ecosystem. Sustainability, 14(12), 7107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127107





