An Analysis of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement from a Single Source—Case Study: A Secondary Road in Romania
Abstract
1. Introduction
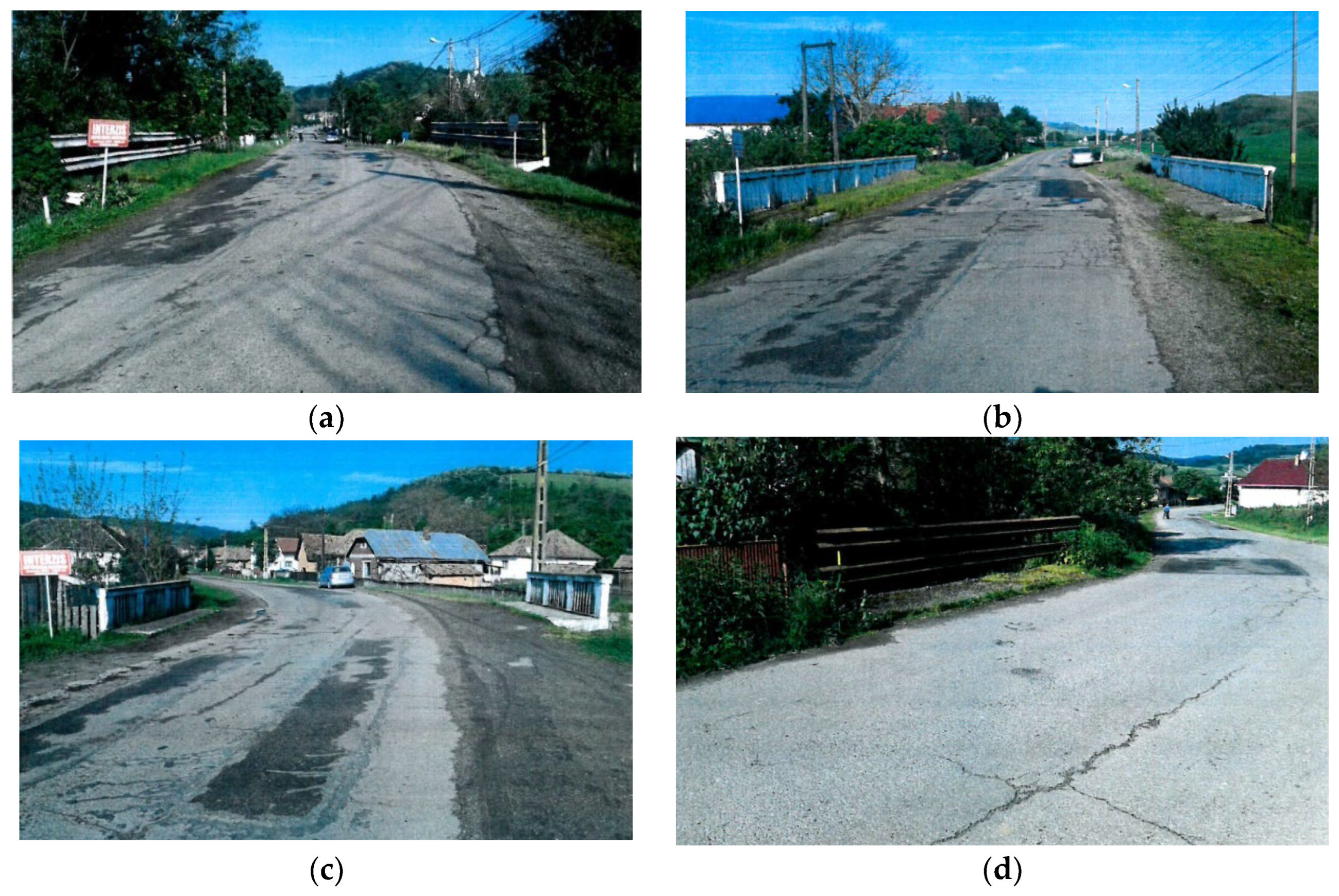
2. Materials
3. Test Methods
4. Results and Discussion
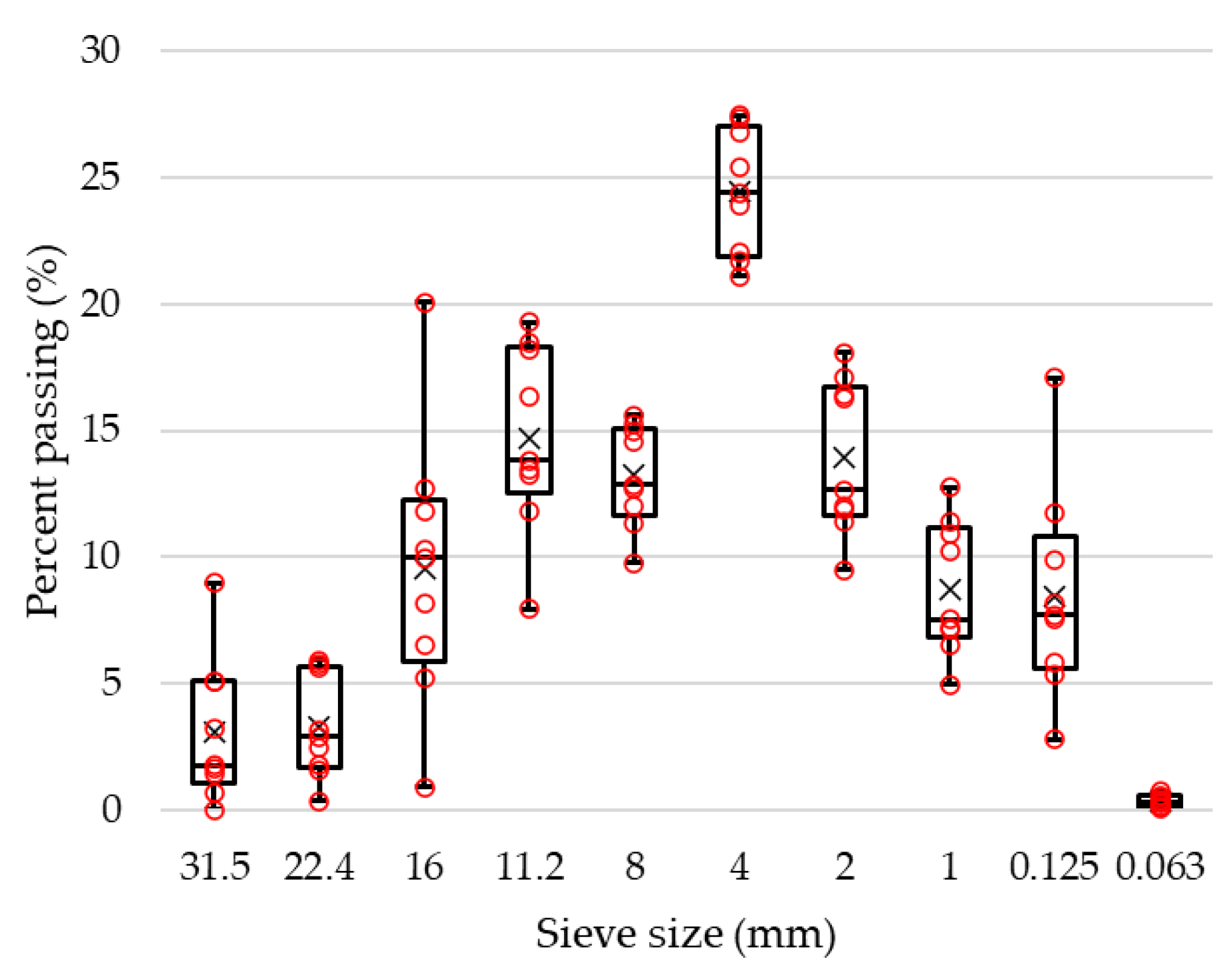
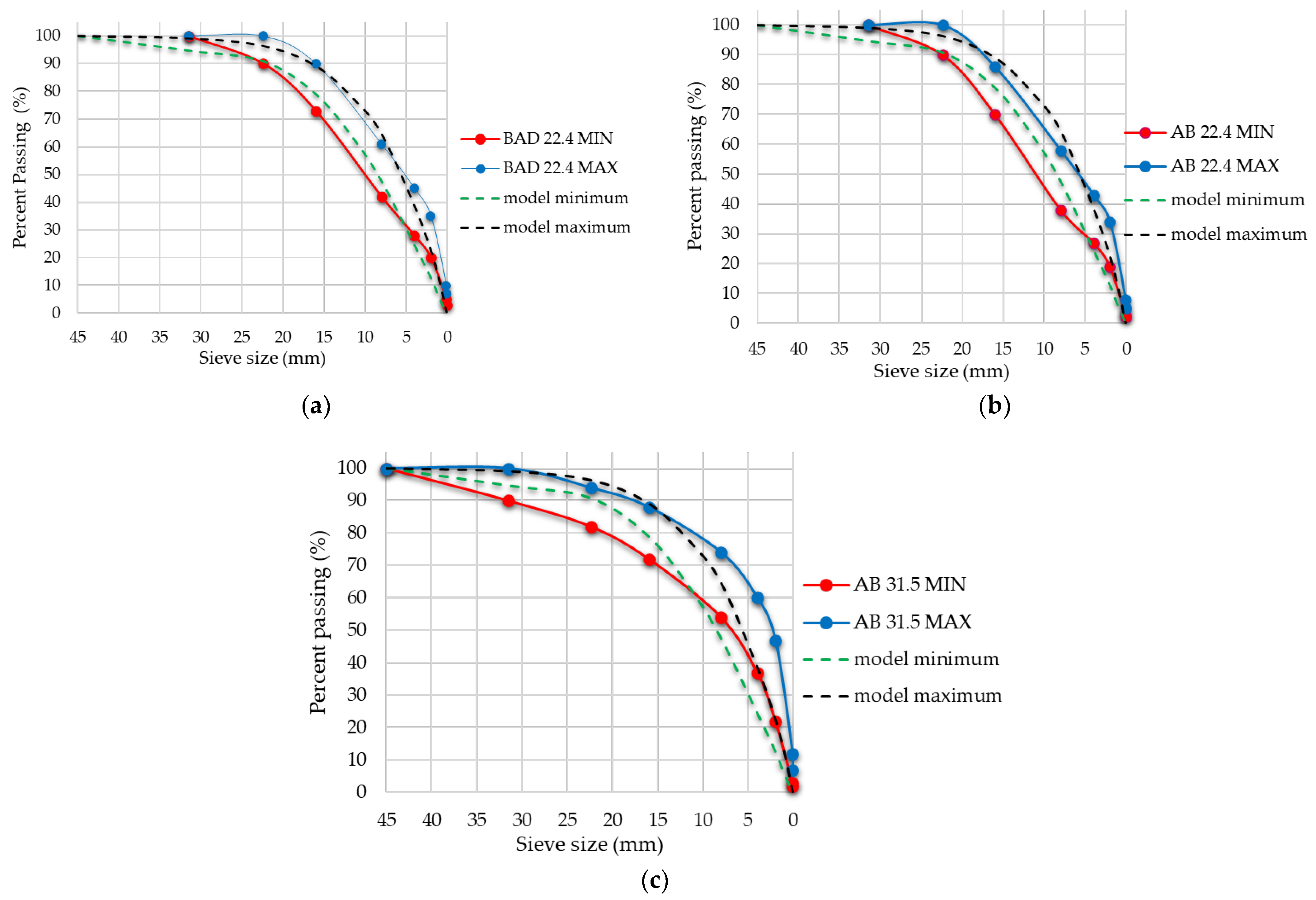
4.1. Properties of RAP Milling before Processing
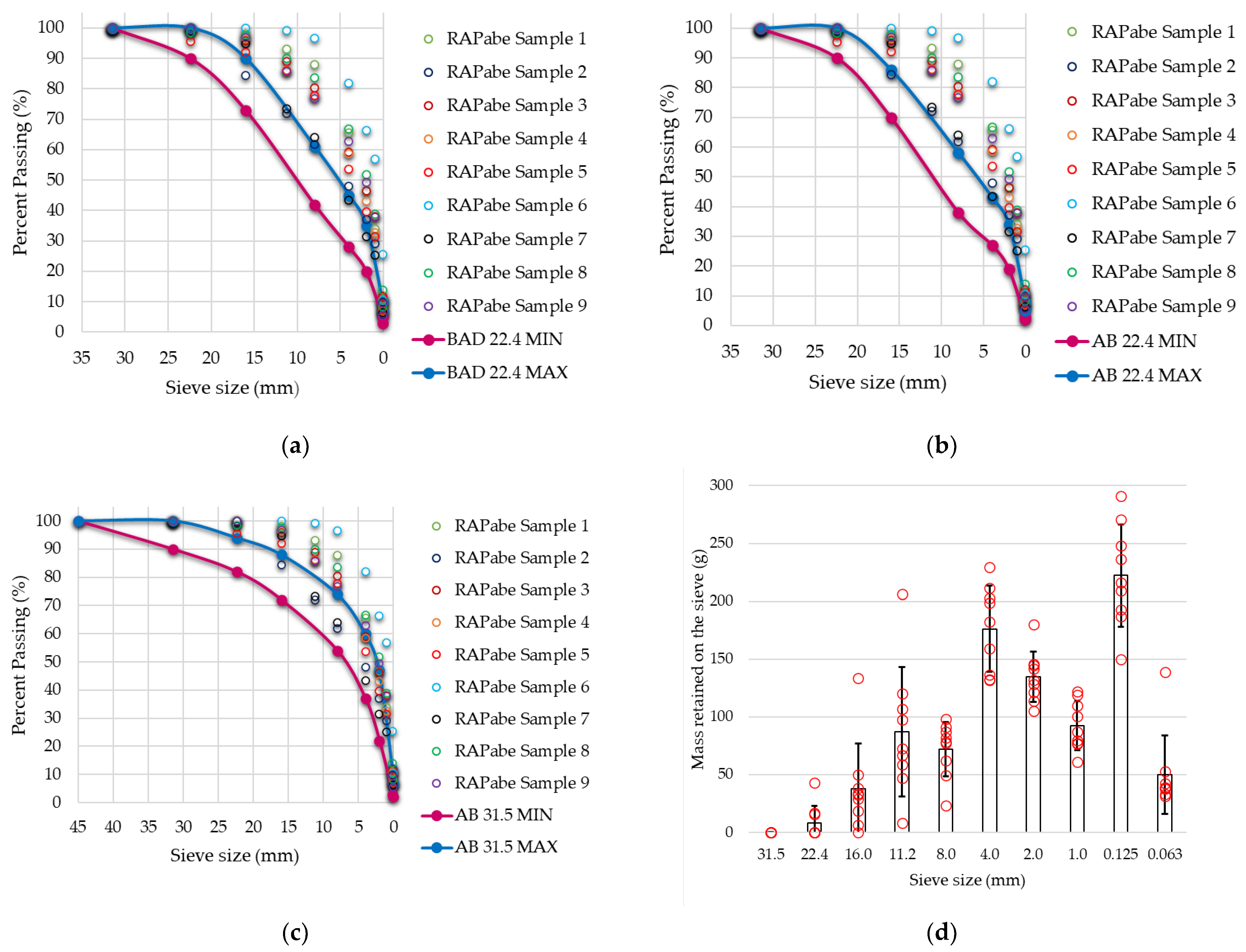
4.2. Properties of RAP Milling after Binder Extraction
4.3. Properties of RAP Milling after Crushing
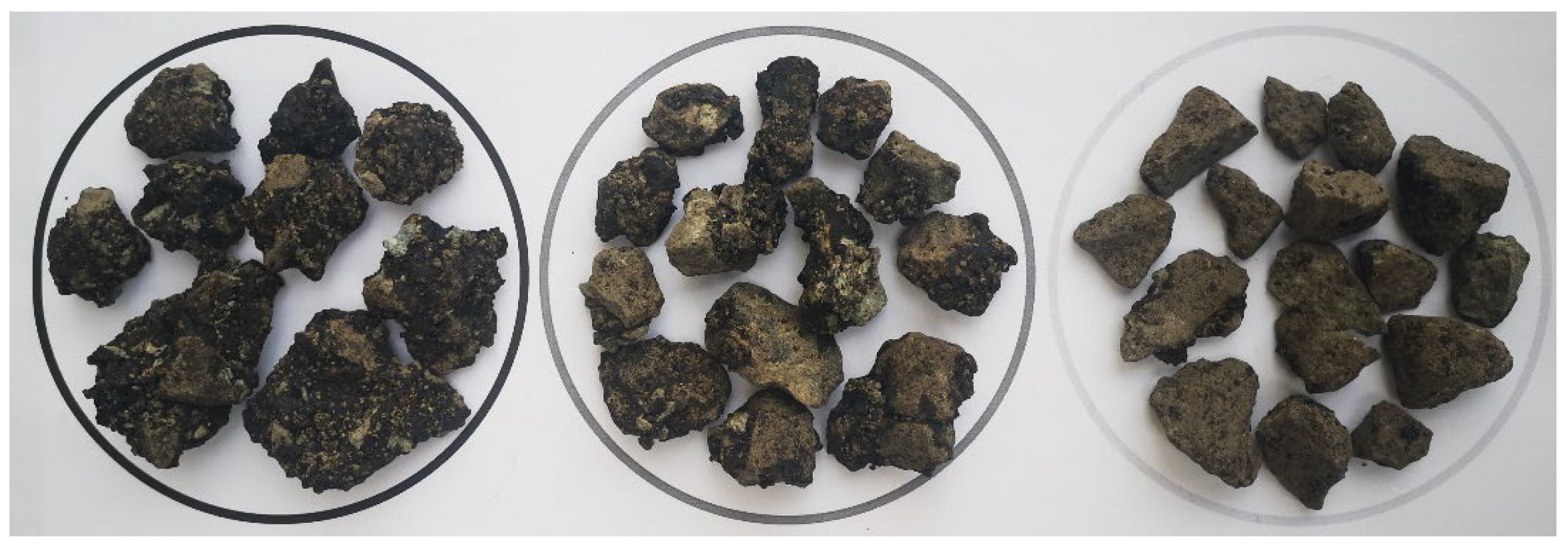
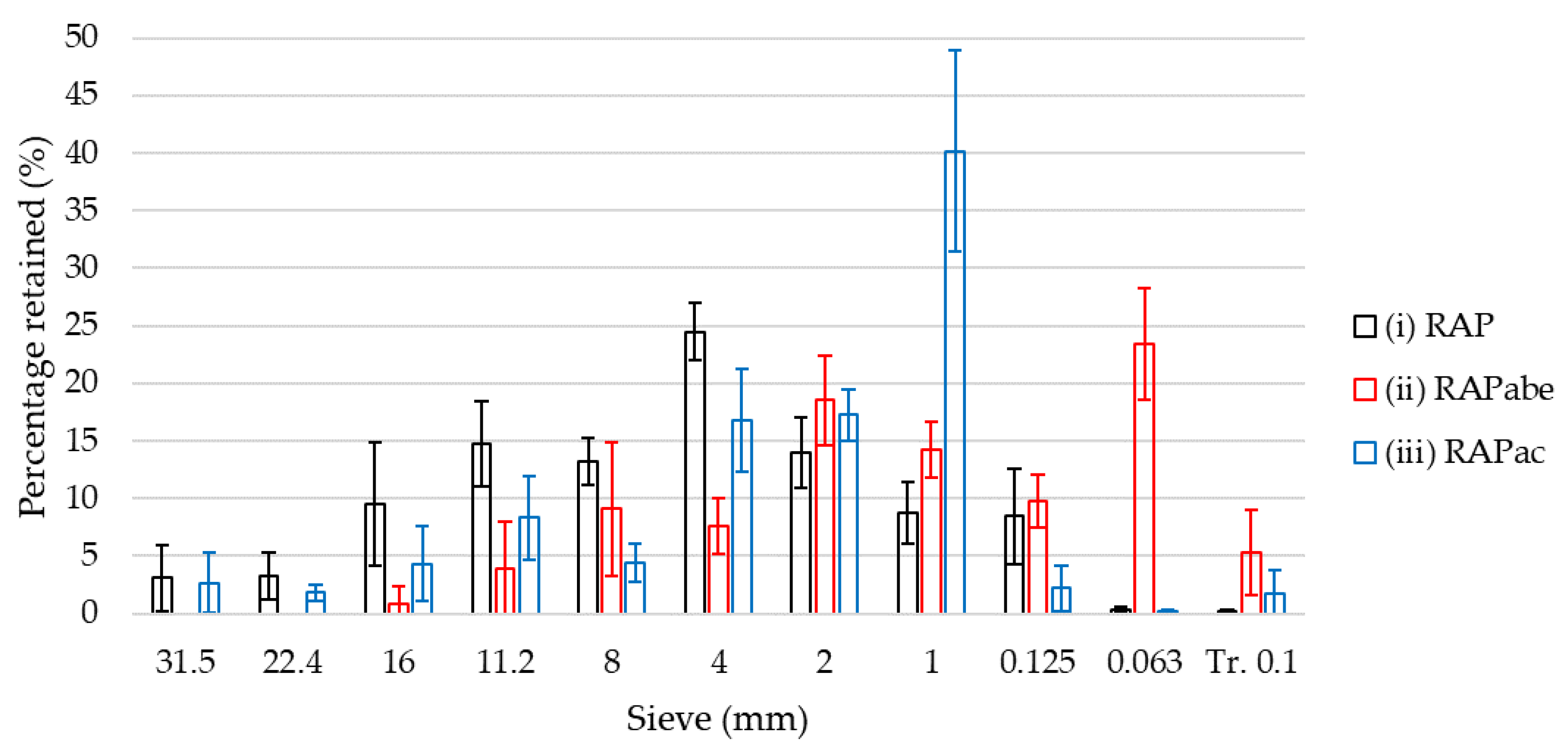
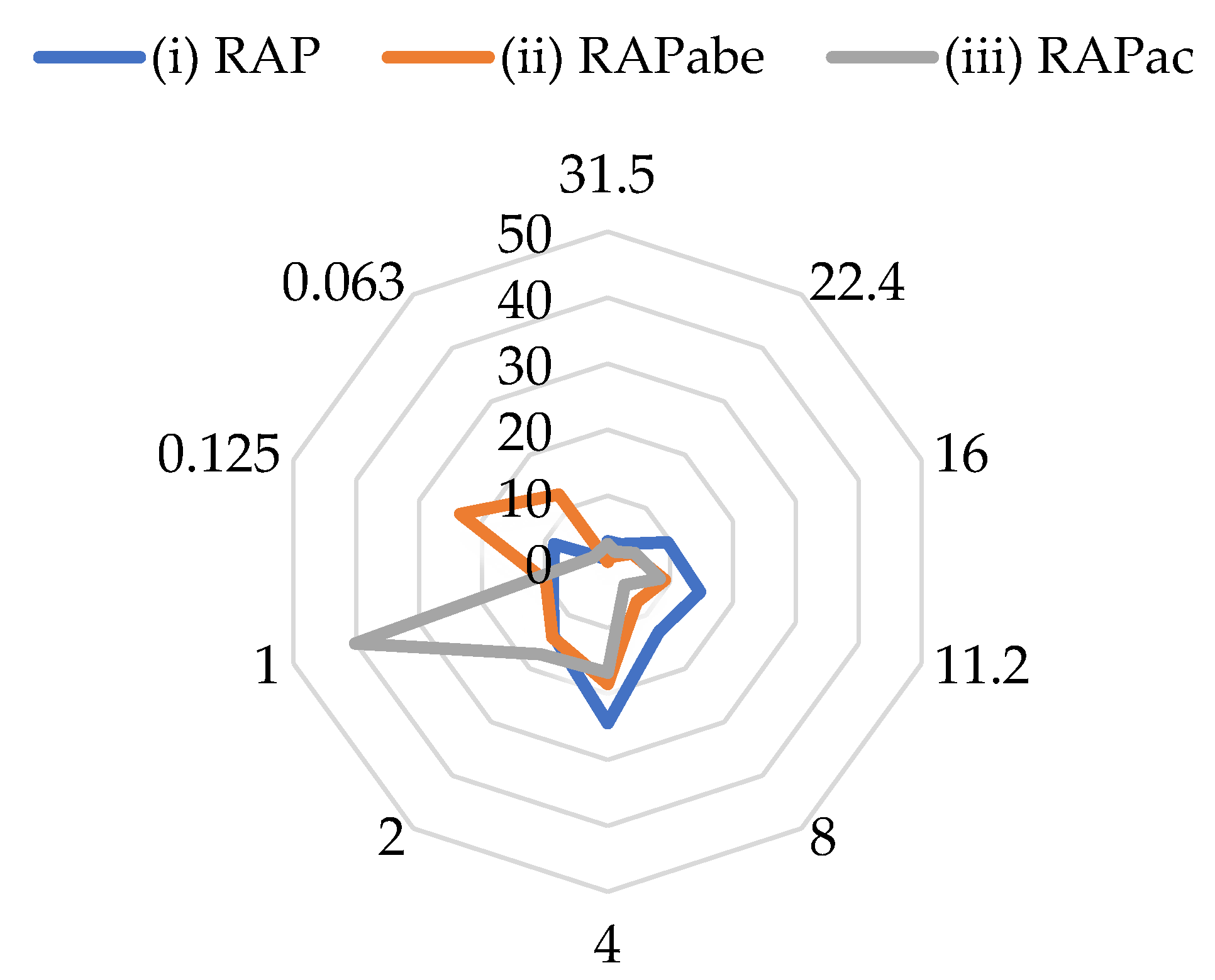
4.4. Cluster Phenomenon
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antunes, V.; Neves, J.; Freire, A.C. Performance assessment of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) in road surface mixtures. Recycling 2021, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.R.; Silva, H.M.; Abreu, L.P.; Pereira, P.A. Effect of different production conditions on the quality of hot recycled asphalt mixtures. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 53, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tao, W.; Gao, J.; Yu, D.; Zhou, J.; He, L.; Yao, Y. Measurement of particle agglomeration and aggregate breakdown of reclaimed asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 296, 123681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chou, Z.; Li, Y.; Ji, J.; Xu, S.F. Effect of blending degree between virgin and aged binder on pavement performance of recycled asphalt mixture with high RAP content. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 2019, 741642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Oga, J.; Haritonovs, V. How to reduce reclaimed asphalt variability A full-scale study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orešković, M.; Bressi, S.; Di Mino, G.; Lo Presti, D. Influence of bio-based additives on RAP clustering and asphalt binder rheology. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on the Bearing Capacity of Roads, Railways and Airfields, Athens, Greece, 28–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, R.; Al-Harthy, A.; Al-Shamsi, K.; Al-Zubeidi, M. Cement stabilization of reclaimed asphalt pavement aggregate for road bases and subbases. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2002, 14, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeux, C.; Salari, S.; Cooper, S., III. Variability of In-Line RAP Crushing vs. Pre-Screened RAP Stockpiles; Tehnical Report (No. FHWA/LA. 17/19-01TA-B); Louisiana Transportation Research Center: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.ltrc.lsu.edu/pdf/2019/19-01TA-B.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2022).
- Zaumanis, M.; Loetscher, D.; Mazor, S.; Stöckli, F.; Poulikakos, L. Impact of milling machine parameters on the properties of reclaimed asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 307, 125114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Yanjun, Q. Effect of reclaimed asphalt pavement on the properties of asphalt binders. Procedia Eng. 2013, 54, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, A.; White, G.; Hosseinpour, M.; Kurumisawa, K.; Hamzah, M.O. Characterization of effects of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) source and content on dynamic modulus of hot mix asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 217, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montañez, J.; Caro, S.; Carrizosa, D.; Calvo, A.; Sanchez, X. Variability of the mechanical properties of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) obtained from different sources. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 116968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Oeser, M. The influence of mixing conditions on the macro-scale homogeneity of asphalt mixtures blended with reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP). Materials 2021, 14, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, V.; Freire, A.C.; Neves, J. A review on the effect of RAP recycling on bituminous mixtures properties and the viability of multi-recycling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Ruan, K.; Tao, W.; Sun, C.; Luo, L. Reducing the variability of multi-source reclaimed asphalt pavement materials: A practice in China. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 122389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yao, Y.; Song, L.; Xu, J.; Yang, J. Determining the maximum permissible content of recycled asphalt pavement stockpile in plant hot-mix recycled asphalt mixtures considering homogeneity: A case study in China. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Statistics Tempo Online. Available online: http://statistici.insse.ro:8077/tempo-online/#/pages/tables/insse-table (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Tegzesiu, S.; Hoda, G. Considerations on the applicability of the design and execution norms governing the recycling of road wearing. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Recycling of the Road Wearing, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 14–15 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- H. G. nr.856/2002 DECISION no. 856 of 16 August 2002, on Waste Management Records and for the Approval of the List of Wastes, Including Hazardous Waste. Available online: https://legislatie.just.ro/Public/DetaliiDocument/38294 (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Burlacu, A.; Peticilă, M.; Răcănel, C.; Obadă, M.; Treiconi, C. Aggregates recycling used on foamed bitumen asphalt layers. In Proceedings of the 14th International Multidisciplinary Scientific Geoconference SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 18–27 June 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimulescu, C.; Burlacu, A. Industrial Waste Materials as Alternative Fillers in Asphalt Mixtures. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, D.; Burlacu, A. Considerations on the benefits of using recyclable materials for road construction. Rom. J. Transp. Infrastruct. 2017, 6, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Răcănel, C.; Burlacu, A. Environment protection by using new technologies for asphalt mixtures. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Road and Rail Infrastructure—CETRA, Split Dalmatia, Croatia, 28–30 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Frank, R. 100% recycled hot mix asphalt: A review and analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 92, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AND 605-2016, Hot Mix Asphalt. Technical Conditions for the Design, Preparation, and Implementation of Asphalt Mixtures. Available online: https://legislatie.just.ro/Public/DetaliiDocumentAfis/197576 (accessed on 4 February 2022).
- Austerman, A.J.; Mogawer, W.S.; Stuart, K.D. Variability of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) properties within a state and its effects on RAP specifications. Transp. Res. Rec. 2020, 2674, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, S.; Pittet, M.; Dumont, A.G.; Partl, M.N. A framework for characterizing RAP clustering in asphalt concrete mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, S.; Dumont, A.G.; Pittet, M. Cluster phenomenon and partial differential aging in RAP mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 99, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Ma, T.; Fang, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W. The evaluation method of particle clustering phenomena in RAP. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, S.; Cavalli, M.C.; Partl, M.N.; Tebaldi, G.; Dumont, A.G.; Poulikakos, L.D. Particle clustering phenomena in hot asphalt mixtures with high content of reclaimed asphalt pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 100, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ma, T.; Fang, Z. Characterization of agglomeration of reclaimed asphalt pavement for cold recycling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 240, 117912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarjono, S.; Hidayati, N. Physical properties of reclaimed asphalt pavement. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 674, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Guo, B. Influence of the particle sizes and densities of RAP on microwave heating efficiency. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Poulikakos, L.D.; Partl, M.N. Performance-based design of asphalt mixtures and review of key parameters. Mater. Des. 2018, 141, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluj County Administration. Feasibility Study—Technical Expertise on the Road. 2016. Available online: https://cjcluj.ro/directia-de-administrare-a-domeniului-public-si-privat/ (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Liu, Q.; Wu, J.; Oeser, M. Micro-and Meso-scale homogeneity of asphalt mixtures with RAP in thermal-non-equilibrium condition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 304, 124609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Su, H. The distribution and performance of reclaimed asphalt pavement materials. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 612, 022080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Fan, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, C.; Gao, W.; Zhan, W. Particle Parameters of Asphalt Pavement Milling Recycling Material. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 766, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun-Or-Rashid, G.M.; Ahmed, B.; Sobhan, M.A.; Rahman, N. Marshall Characteristics of Bituminous Mixes Using Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement. Am. J. Traffic Transport. Eng. 2018, 3, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DD 509-2003, a Revision of Technical Norm DD 509-89 Regarding Recycling of Hot Asphalt Mixtures in Fixed Stations. Available online: https://legislatie.just.ro/Public/DetaliiDocument/53749 (accessed on 4 February 2022).



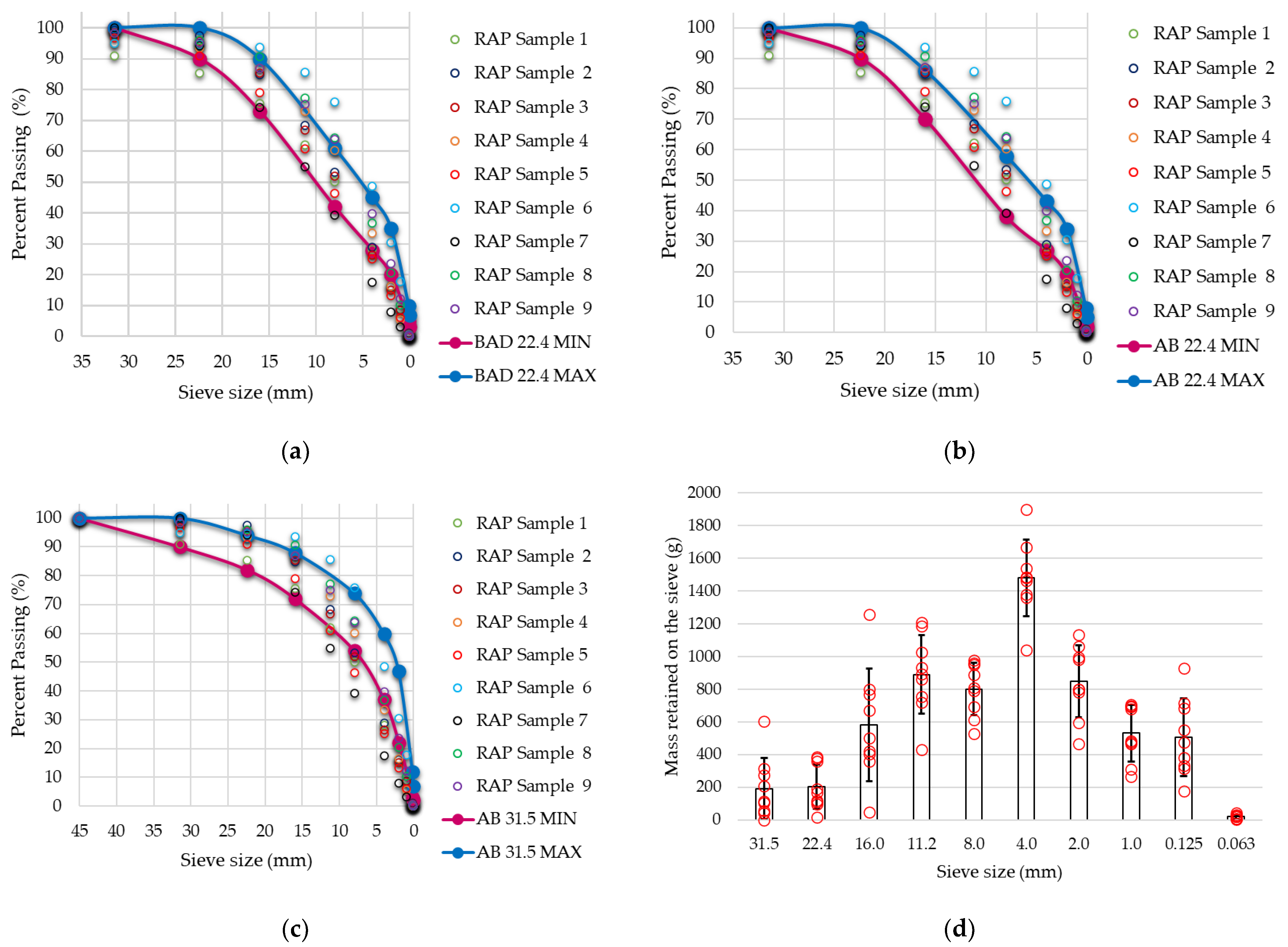
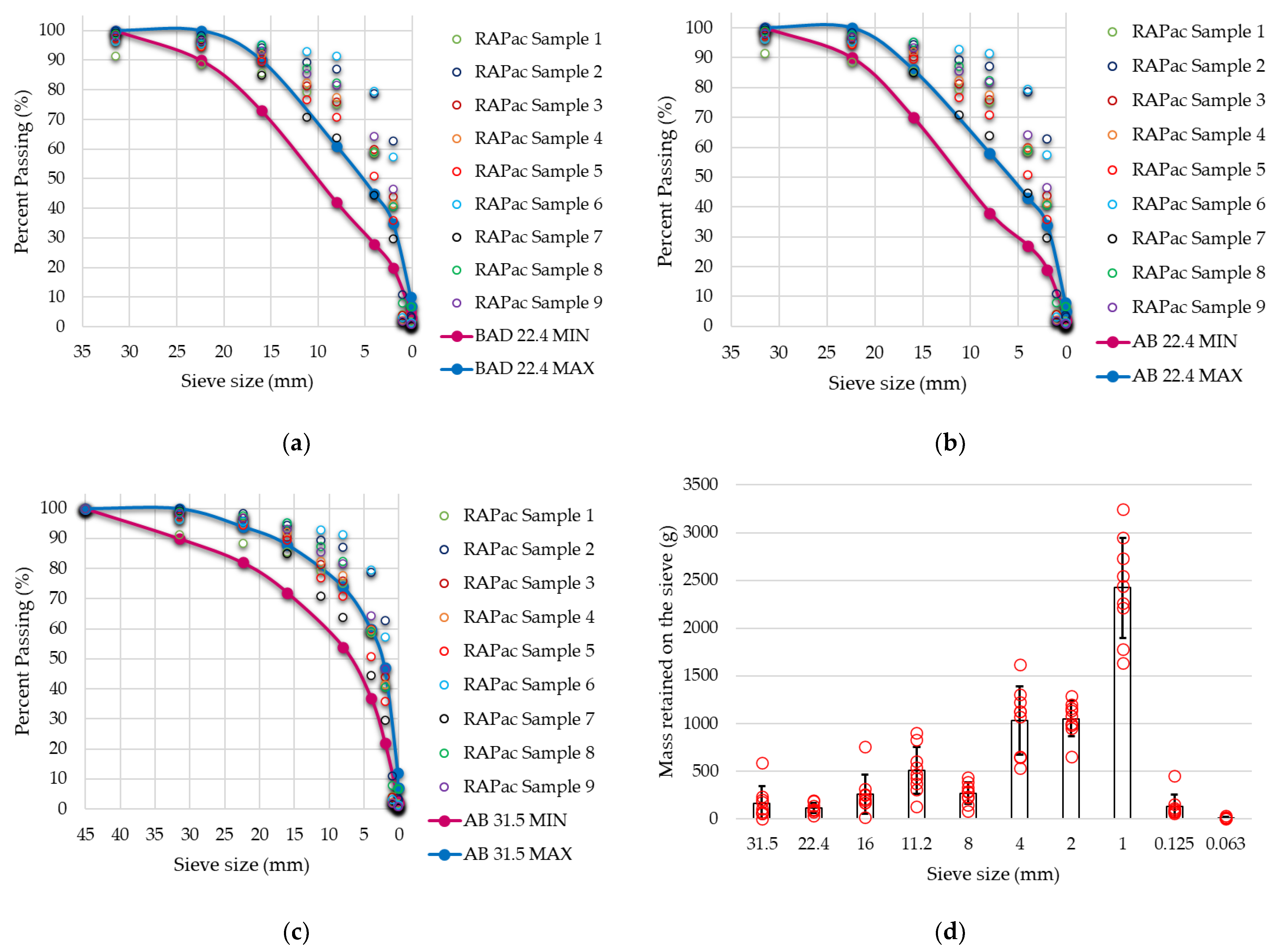
| Binder Content | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | Sample 4 | Sample 5 | Sample 6 | Sample 7 | Sample 8 | Sample 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binder content (%) | 5.29 | 3.55 | 4.79 | 5.16 | 5.09 | 7.44 | 3.68 | 5.33 | 4.51 |
| Sieve (mm) | 31.5 | 22.4 | 16 | 11.2 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0.125 | 0.063 | Avg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 8.98 | 5.62 | 9.99 | 13.27 | 12.01 | 22.05 | 11.92 | 7.21 | 8.19 | 0.44 | - |
| Sample 2 | 0.68 | 1.78 | 12.70 | 16.33 | 15.22 | 24.42 | 12.67 | 7.54 | 7.55 | 0.73 | - |
| Sample 3 | 1.42 | 2.91 | 10.33 | 18.49 | 14.99 | 25.41 | 11.40 | 6.51 | 7.72 | 0.53 | - |
| Sample 4 | 5.07 | 1.59 | 6.52 | 13.82 | 12.72 | 26.81 | 17.10 | 10.93 | 5.33 | 0.08 | - |
| Sample 5 | 3.21 | 5.94 | 11.81 | 18.18 | 14.56 | 21.10 | 12.02 | 7.15 | 5.86 | 0.11 | - |
| Sample 6 | 5.10 | 0.36 | 0.91 | 7.95 | 9.77 | 27.34 | 18.11 | 12.77 | 17.08 | 0.57 | - |
| Sample 7 | 0.00 | 5.78 | 20.07 | 19.29 | 15.61 | 21.71 | 9.50 | 4.95 | 2.81 | 0.14 | - |
| Sample 8 | 1.64 | 2.47 | 5.22 | 13.48 | 12.86 | 27.46 | 16.41 | 10.21 | 9.90 | 0.29 | - |
| Sample 9 | 1.75 | 3.13 | 8.18 | 11.80 | 11.35 | 23.94 | 16.31 | 11.37 | 11.73 | 0.33 | - |
| Mean | 3.10 | 3.28 | 9.52 | 14.74 | 13.23 | 24.47 | 13.94 | 8.74 | 8.47 | 0.36 | 9.08 |
| St dev | 2.84 | 2.04 | 5.37 | 3.68 | 2.00 | 2.47 | 3.05 | 2.64 | 4.14 | 0.23 | 2.59 |
| Cv (%) | 92 | 62 | 56 | 25 | 15 | 10 | 22 | 30 | 49 | 63 | 42 |
| Uniformity | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | Sample 4 | Sample 5 | Sample 6 | Sample 7 | Sample 8 | Sample 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D60 | 10.63 | 9.41 | 9.74 | 7.96 | 11.01 | 5.67 | 12.48 | 7.37 | 7.37 |
| D30 | 4.35 | 4.19 | 4.56 | 3.59 | 4.91 | 1.96 | 6.30 | 3.16 | 2.79 |
| D10 | 1.14 | 1.18 | 1.22 | 1.42 | 1.55 | 0.60 | 2.41 | 0.98 | 0.84 |
| Cu | 9.3 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 5.6 | 7.1 | 9.4 | 5.2 | 7.5 | 8.8 |
| Cc | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sieve (mm) | 31.5 | 22.4 | 16 | 11.2 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0.125 | 0.063 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 96.90 | 93.60 | 84.08 | 69.36 | 56.12 | 31.67 | 17.73 | 8.99 | 0.52 | 0.17 |
| Variance | 8.13 | 12.94 | 43.82 | 89.42 | 122.42 | 84.49 | 41.58 | 18.09 | 0.11 | 0.02 |
| St dev | 2.85 | 3.60 | 6.62 | 9.46 | 11.06 | 9.19 | 6.45 | 4.25 | 0.33 | 0.13 |
| Cv (%) | 3 | 4 | 8 | 14 | 20 | 29 | 36 | 47 | 63 | 79 |
| St error | 0.95 | 1.20 | 2.21 | 3.15 | 3.69 | 3.06 | 2.15 | 1.42 | 0.11 | 0.04 |
| T-stat 95% | 2.31 | 2.31 | 2.31 | 2.31 | 2.31 | 2.31 | 2.31 | 2.31 | 2.31 | 2.31 |
| Confidence interval (%) | 94.70 | 90.83 | 78.98 | 62.07 | 47.60 | 24.59 | 12.77 | 5.71 | 0.27 | 0.06 |
| 99.10 | 96.37 | 89.18 | 76.64 | 64.64 | 38.74 | 22.70 | 12.26 | 0.77 | 0.27 |
| Fraction (mm) | (i) before Processing (%) | (ii) after Binder Extraction (%) | (iii) after Crushing (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Course part (C) | >4 | 68 | 40 | 38 |
| Fine part (F) | ≤4 | 32 | 60 | 62 |
| F/C Ratio | 0.46 | 1.5 | 1.61 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cadar, R.D.; Boitor, R.M.; Dragomir, M.L. An Analysis of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement from a Single Source—Case Study: A Secondary Road in Romania. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7057. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127057
Cadar RD, Boitor RM, Dragomir ML. An Analysis of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement from a Single Source—Case Study: A Secondary Road in Romania. Sustainability. 2022; 14(12):7057. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127057
Chicago/Turabian StyleCadar, Rodica Dorina, Rozalia Melania Boitor, and Mihai Liviu Dragomir. 2022. "An Analysis of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement from a Single Source—Case Study: A Secondary Road in Romania" Sustainability 14, no. 12: 7057. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127057
APA StyleCadar, R. D., Boitor, R. M., & Dragomir, M. L. (2022). An Analysis of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement from a Single Source—Case Study: A Secondary Road in Romania. Sustainability, 14(12), 7057. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127057






