Capacity of Marine Microalga Tetraselmis suecica to Biodegrade Phenols in Aqueous Media
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tetraselmis suecica Culture
2.2. Degradation Kinetics
2.3. Determination of Phenolic Compounds
2.4. Determination of COD and Inorganic and Organic Carbon
3. Results
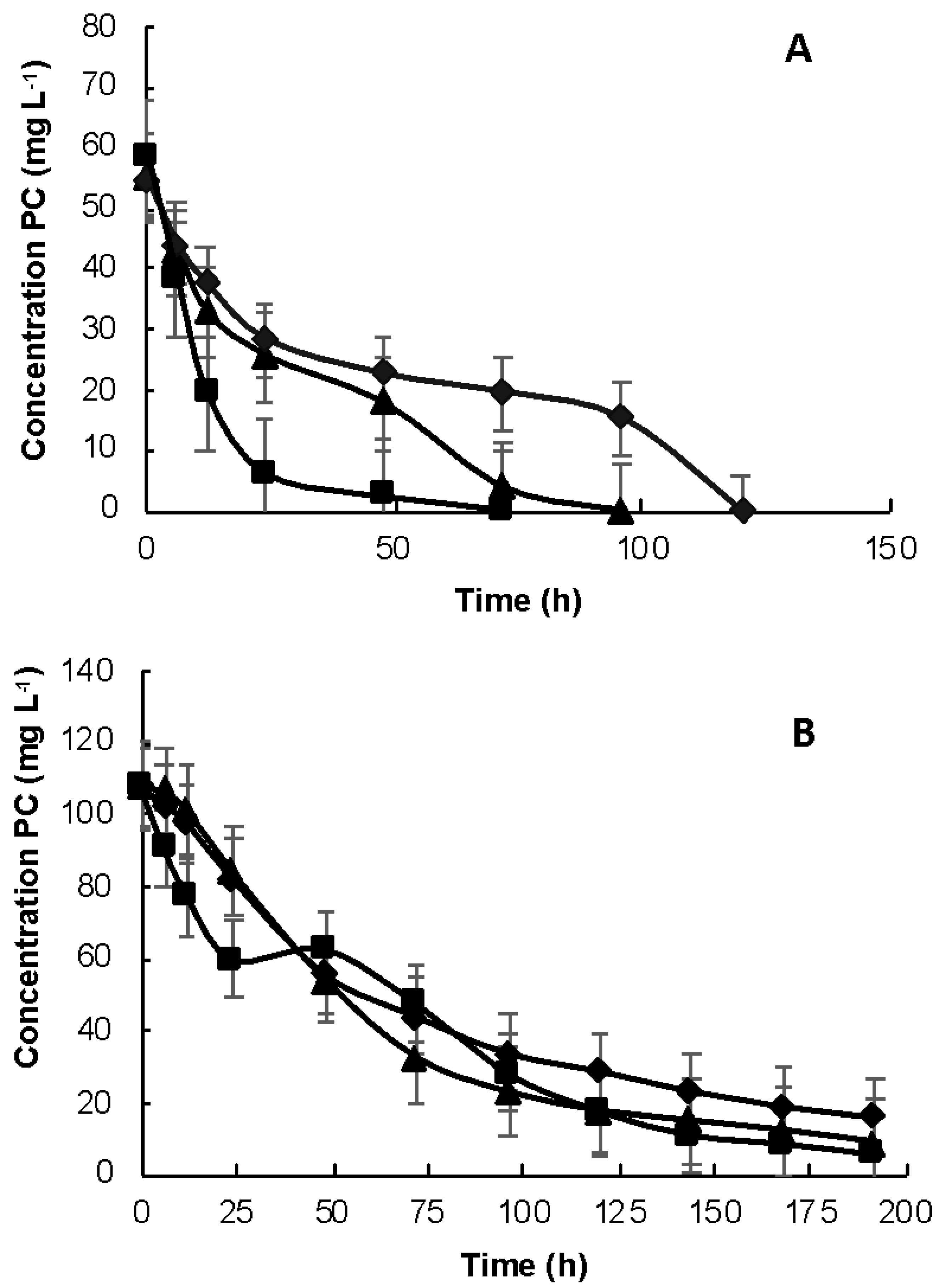
3.1. Kinetic Study of Phenol, p-Cresol and o-Cresol at 50 and 100 mg L−1
3.2. Biotic Removal Kinetics for a Mixture of Phenolic Compounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barik, M.; Das, C.P.; Verma, A.K.; Sahoo, S.; Sahoo, N.K. Metabolic profiling of phenol biodegradation by an indigenous Rhodococcus pyridinivorans strain PDB9T N-1 isolated from paper pulp wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 158, 105168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakthavatsalam, A. A comparative study on growth and degradation behavior of C. pyrenoidosa on synthetic phenol and phenolic wastewater of a coal gasification plant. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103079. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Qiao, K.; Pei, L.; Lv, J.; Xie, S. Using activated carbon prepared from Typha orientalis Presl to remove phenol from aqueous solutions. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surkatti, R.; El-Naas, M. Competitive interference during the biodegradation of cresols. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Raouf, N.; Al-Homaidan, A.; Ibraheem, I. Microalgae and wastewater treatment. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 19, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, B.; Mandal, T.K.; Patra, S. A comprehensive study on Chlorella pyrenoidosa for phenol degradation and its potential applicability as biodiesel feedstock and animal feed. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1382–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazi, A.; Kotzabasis, K. Inductive and resonance effects of substituents adjust the microalgal biodegradation of toxical phenolic compounds. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 135, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, V.; Joseph, A. Acclimation of algal species following exposure to phenol. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1999, 62, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravantinou, A.F.; Theodorakopoulos, M.A.; Manariotis, I.D. Selection of microalgae for wastewater treatment and potential lipids production. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Meng, F.; Cui, H.; Lin, Y.; Wang, G.; Wu, J. Ecotoxicity of phenol and cresols to aquatic organisms: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Ma, H.; Sun, M.; Yin, X.; Feng, Q.; Song, H.; Gai, H. Characterization of cometabolic degradation of p-cresol with phenol as growth substrate by Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayana, K.; Mariano, A.; Vargas, J. A review on microalgae, a versatile source for sustainable energy and materials. Int. J. Energy Res. 2011, 35, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Yang, S.; Guo, B.; Wang, H.; Huo, H.; Zhang, A.; Niu, S. Growth behavior, glucose consumption and phenol removal efficiency of Chlorella vulgaris under the synergistic effects of glucose and phenol. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, C.; De Luca, D.; Amoroso, M.; Benfatto, S.; Maestri, S.; Racioppi, C.; Esposito, F.; Ianora, A. New molecular insights on the response of the green alga Tetraselmis suecica to nitrogen starvation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forootanfar, H.; Shakibaie, M.; Bagherzadeh, Z.; Aghaie-Khozani, M.; Nafissi-Varcheh, N.; Monsef-Esfahani, H.R.; Faramarzi, M.A. The removal of ρ-chlorophenol in aqueous cultures with free and alginate-immobilized cells of the microalga Tetraselmis suecica. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroutsos, D.; Katapodis, P.; Samiotaki, M.; Panayotou, G.; Kekos, D. Detoxification of 2, 4-dichlorophenol by the marine microalga Tetraselmis marina. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, C.-E.; Draga, S.; Măciucă, R.; Niță, R.; Crăciun, N.; Wolff, R. Bisphenol A Effects in Aqueous Environment on Lemna minor. Processes 2021, 9, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregas, J.; Herrero, C.; Cabezas, B.; Abalde, J. Mass culture and biochemical variability of the marine microalga Tetraselmis suecica Kylin (Butch) with high nutrient concentrations. Aquaculture 1985, 49, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Federation, W.E.; Association, A. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Meza-Escalante, E.R.; Texier, A.C.; Cuervo-López, F.; Gomez, J.; Cervantes, F.J. Inhibition of sulfide on the simultaneous removal of nitrate and p-cresol by a denitrifying sludge. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process Environ. Clean Technol. 2008, 83, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanaga, K.; Unno, H. 2.05-Reaction Kinetics and Stoichiometry. In Comprehensive Biotechnology, 2nd ed.; Moo-Young, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, ON, Canada, 2011; pp. 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, F.; Li, H.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Wang, G.; Wu, J. Biodegradation of phenol by Isochrysis galbana screened from eight species of marine microalgae: Growth kinetic models, enzyme analysis and biodegradation pathway. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Blanco, G.; Cuervo-López, F.; Cervantes, F.J.; Beristain-Cardoso, R.; Gómez, J. Nitrite as oxidizing power for p-cresol removal using a denitrifying sludge: Kinetic study. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 2176–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xue, C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y. Strain improvement of Chlorella sp. for phenol biodegradation by adaptive laboratory evolution. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 205, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, P.; Pakshirajan, K.; Saha, P. Biodegradation of phenol and m-cresol in a batch and fed batch operated internal loop airlift bioreactor by indigenous mixed microbial culture predominantly Pseudomonas sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8553–8558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semple, K.T.; Cain, R.B. Biodegradation of phenols by the alga Ochromonas danica. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Compound | 50 mg L−1 | 100 mg L−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qs | RE | qs | RE | |
| Phenol | 1.86 ± 0.22 | 100 ± 0 | 1.12 ± 0.01 | 91.69 ± 0.77 |
| p-cresol | 0.93 ± 0.05 | 100 ± 0 | 1.11 ± 0.05 | 85.20 ± 0.66 |
| o-cresol | 3.27 ± 0.03 | 100 ± 0 | 1.97± 0.31 | 94.50 ± 0.35 |
| Microalga | Phenolic Compound | Conditions | Initial Concentration (mg L−1) | Removal (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetraselmis suecica | phenol, p-cresol, o-cresol (separately) mixture of phenol, p-cresol and o-cresol | 192 h | 50 100 40 (each one in a mixture) | 100 85 Up to 73.6 | This work |
| Chlorella pyrenoidosa | phenol 1 p-cresol 2 | coal gasification effluent, pH 8 | 800 1 400 2 | 97.4 | [2] |
| Chlorella pyrenoidosa | phenol | refinery wastewater | 200 | 100 | [6] |
| Chlorella vulgaris | phenol 1 p-cresol 2 | cometabolic NaHCO3 | 100 1 300 2 | 68.2 1 64 2 | [11] |
| Chlorella vulgaris | phenol | mixotrophic with glucose addition (co-sustrate), 6 days. | Up to 400 | Up to 30 | [13] |
| Tetraselmis suecica | p-chlorophenol | 10-day period in aqueous medium 1. Immobilized in alginate beads 2 | 20 | 67 1 94 2 | [15] |
| Tetraselmis marina | 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) | 6 days glycosidation and malonylation | Not defined | Up to 1 mM | [16] |
| Chlorella sp | phenol | 0.6 g/L−1 initial biomass, 7 days | 500 | 100 | [22] |
| Isochrysis galbana | phenol | 96 h | <100 | 100 | [23] |
| Ochromonas dánica | phenol | heterotrophic growth with 2 mM glucose, 2 days | 94 | 100 | [26] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meza-Escalante, E.R.; Lepe-Martinié, L.; Díaz-Quiroz, C.; Serrano-Palacios, D.; Álvarez-Valencia, L.H.; Rentería-Mexía, A.; Gortáres-Moroyoqui, P.; Ulloa-Mercado, G. Capacity of Marine Microalga Tetraselmis suecica to Biodegrade Phenols in Aqueous Media. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6674. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116674
Meza-Escalante ER, Lepe-Martinié L, Díaz-Quiroz C, Serrano-Palacios D, Álvarez-Valencia LH, Rentería-Mexía A, Gortáres-Moroyoqui P, Ulloa-Mercado G. Capacity of Marine Microalga Tetraselmis suecica to Biodegrade Phenols in Aqueous Media. Sustainability. 2022; 14(11):6674. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116674
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeza-Escalante, Edna R., Larissa Lepe-Martinié, Carlos Díaz-Quiroz, Denisse Serrano-Palacios, Luis H. Álvarez-Valencia, Ana Rentería-Mexía, Pablo Gortáres-Moroyoqui, and Gabriela Ulloa-Mercado. 2022. "Capacity of Marine Microalga Tetraselmis suecica to Biodegrade Phenols in Aqueous Media" Sustainability 14, no. 11: 6674. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116674
APA StyleMeza-Escalante, E. R., Lepe-Martinié, L., Díaz-Quiroz, C., Serrano-Palacios, D., Álvarez-Valencia, L. H., Rentería-Mexía, A., Gortáres-Moroyoqui, P., & Ulloa-Mercado, G. (2022). Capacity of Marine Microalga Tetraselmis suecica to Biodegrade Phenols in Aqueous Media. Sustainability, 14(11), 6674. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116674







