Testing Convergence of Tourism Development and Exploring Its Influencing Factors: Empirical Evidence from the Greater Bay Area in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Evaluation of Convergence Model
3.2.1. Dimensionless Quantification Processing
3.2.2. Evaluation of Tourism and Cultural Industries
3.2.3. The Coupling-Coordination-Degree Model
3.3. Factoring Determining the Real Convergence
4. Results
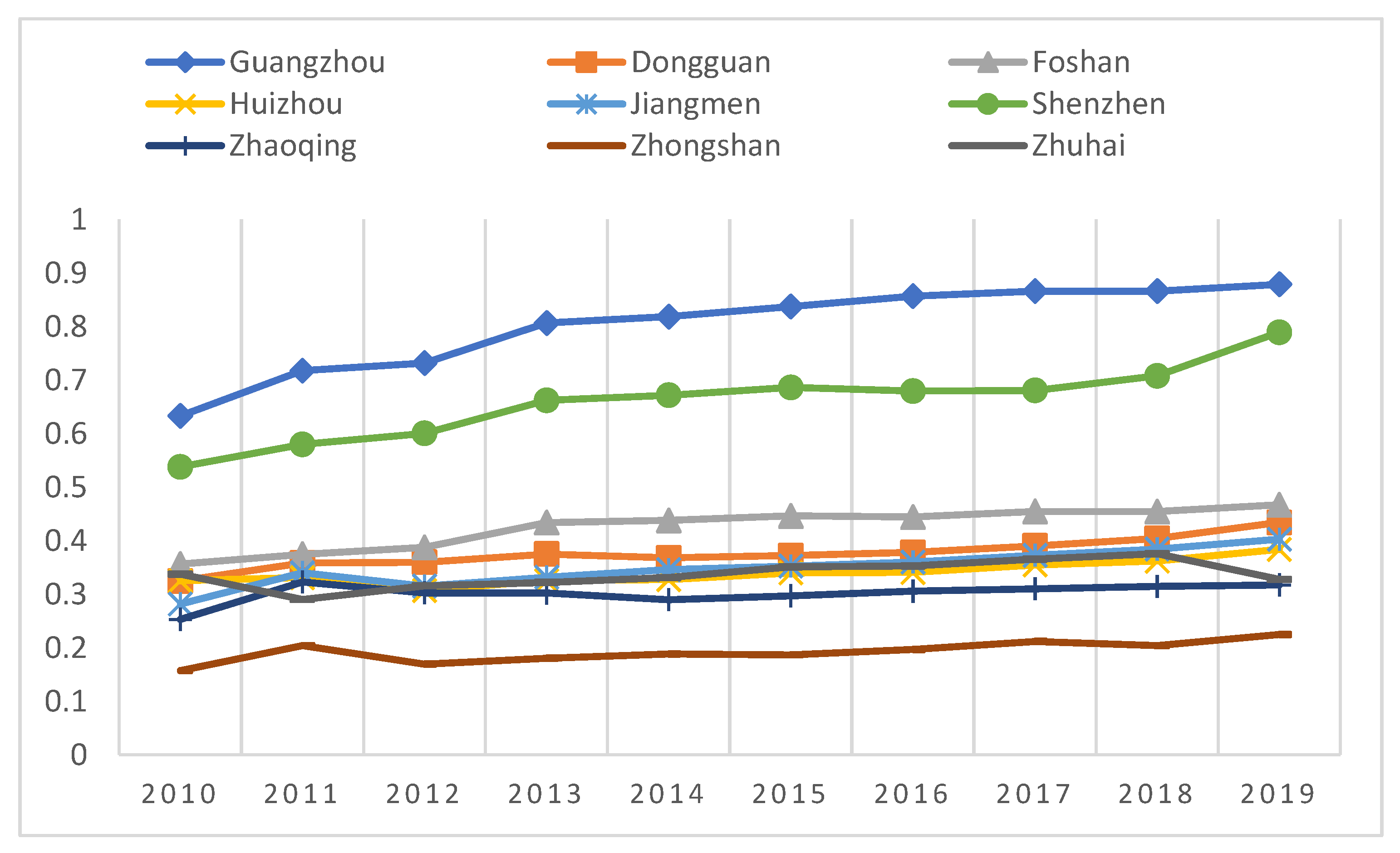
4.1. Comprehensive Development in GBA
4.2. Development Trend of Industrial Integration
4.3. Convergence of Culture and Tourism Sectors in GBA
4.4. Influencing Factors of Convergence
5. Discussions and Conclusions
5.1. Theoretical Contributions
5.2. Managerial Implications
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin, Y. Residents’ perceptions of the impact of cultural tourism on urban development: The case of Gwangju, Korea. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2010, 15, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, R.; Chowdhary, N.; Ranjan, A. Spiritual tourism for psychotherapeutic healing post COVID-19. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2021, 38, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Xu, D.; Xu, L. Spatiotemporal characteristics and impact mechanism of high-quality development of cultural tourism in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loulanski, T.; Loulanski, V. The sustainable integration of cultural heritage and tourism: A meta-study. J. Sustain. Tour. 2011, 19, 837–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.B.; Sotiriadis, M. Exploring and Evaluating the Impact of ICTs on Tourism industry’ Convergence: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Aaron, J.R.; McDowell, W.C.; Lu, D.D. Sustainable Synergies between the Cultural and Tourism Industries: An Efficiency Evaluation Perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bröring, S.; Leker, J. Industry convergence and its implications for the front end of innovation: A problem of absorptive capacity. Creat. Innov. Manag. 2007, 16, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, M.L. Remarks on the economic implications of convergence. Ind. Corp. Chang. 1996, 5, 1079–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Li, Y.F.; Qin, C.; Sun, J.J. How industrial convergence affects regional green development efficiency: A spatial conditional process analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Throsby, D. Cultural capital. J. Cult. Econ. 1999, 23, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, G. Production and consumption of European cultural tourism. Ann. Tour. Res. 1996, 23, 261–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, G. Tourism Trends: The Convergence of Culture and Tourism; Academy for Leisure NHTV University of Applied Sciences: Breda, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Gu, C.; Gu, L.; Zhang, Y. The evaluation of tourism destination competitiveness by TOPSIS & information entropy: A case in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.F.; Li, S.T.; Ji, X.M.; Qing, W.S.; Wang, F.X. Coupling analysis and optimization measures of cultural resources endowment and tourism industry in Shandong. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 207–215. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.L.; Yang, C.Y.; Ming, Q.Z.; Zhang, H.M.; Lu, B.Y. Spatial-Temporal Coordination and driving forces of provincial cultural and tourism industry in China. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 203–213. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guan, D.; Gao, W.; Su, W.; Li, H.; Hokao, K. Modeling and dynamic assessment of urban economy–resource–environment system with a coupled system dynamics–geographic information system model. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Items | Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Tourism Industry | Output | Domestic tourism generated total receipts |
| International tourism generated total receipts | ||
| Number of international tourists | ||
| International tourism income | ||
| Input | Number of luxury hotels | |
| Number of over 4A-grade tourist attractions | ||
| Number of people employed in the travel sector | ||
| Cultural Industry | Output | Total operating income of cultural market |
| Number of visitors to museums | ||
| Number of cultural performance spaces | ||
| Number of audiences of performing arts | ||
| Input | Total spending on culture | |
| Number of individuals working for cultural industry | ||
| Number of mass cultural institutions |
| Classes | Subclasses | Types |
|---|---|---|
| Balanced development index | 0.8 < D ≤ 1 Superior | Superior coordination with culture lagged |
| Superior coordination with tourism and culture | ||
| Superior coordination with tourism lagged | ||
| 0.7 < D ≤ 0.9 Moderate | Moderate coordination with culture lagged | |
| Moderate coordination with tourism and culture | ||
| Moderate coordination with tourism lagged | ||
| 0.6 < D ≤ 0.7 Primary | Primary coordination with culture lagged | |
| Primary coordination with tourism and culture | ||
| Primary coordination with tourism lagged | ||
| Transitional development index | 0.5 < D ≤ 0.6 Barely | Barely coordination with culture hindered |
| Barely coordination with tourism and culture | ||
| Barely coordination with tourism hindered | ||
| 0.4 < D ≤ 0.5 On the verge of disorder | On the verge of disorder with culture lagged | |
| On the verge of disorder with tourism and culture | ||
| On the verge of disorder with tourism lagged | ||
| Unbalanced development index | 0.3 < D ≤ 0.4 Mild disorder | Mild disorder with culture hindered |
| Mild disorder with tourism and culture | ||
| Mild disorder with tourism hindered | ||
| 0.1 < D ≤ 0.3 Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder with culture hindered | |
| Moderate disorder with tourism and culture | ||
| Moderate disorder with tourism hindered | ||
| 0 < D ≤ 0.1 Extreme disorder | Extreme disorder with culture hindered | |
| Extreme disorder with tourism and culture | ||
| Extreme disorder with tourism hindered |
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangzhou | Primary coordination | Moderate coordination | Moderate coordination | Moderate coordination | Moderate coordination | Moderate coordination | Moderate coordination | Moderate coordination | Moderate coordination | Moderate coordination |
| Dongguan | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | On the verge of disorder | On the verge of disorder |
| Foshan | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | On the verge of disorder | On the verge of disorder | On the verge of disorder | On the verge of disorder | On the verge of disorder | On the verge of disorder | On the verge of disorder |
| Huizhou | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Moderate disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder |
| Jiangmen | Moderate disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | On the verge of disorder |
| Shenzhen | Barely coordination | Barely coordination | Primary coordination | Primary coordination | Primary coordination | Primary coordination | Primary coordination | Primary coordination | Moderate coordination | Moderate coordination |
| Zhaoqing | Moderate disorder | Mild disorder | Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder |
| Zhongshan | Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder | Moderate disorder |
| Zhuhai | Mild disorder | Moderate disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder | Mild disorder |
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangzhou | culture lagged | culture lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | culture lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged |
| Dongguan | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged |
| Foshan | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged |
| Huizhou | tourism lagged | culture lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged |
| Jiangmen | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged |
| Shenzhen | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | tourism lagged |
| Zhaoqing | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged |
| Zhongshan | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged |
| Zhuhai | tourism lagged | culture lagged | tourism lagged | tourism lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged | culture lagged |
| Items | Coef. | St. Err. | t-Value | p-Value | [95% Conf.] | [Interval] | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic Development | 0.082 | 0.027 | 2.99 | 0.003 | 0.028 | 0.136 | ** |
| Government Spending | 0.098 | 0.044 | 2.23 | 0.026 | 0.012 | 0.184 | * |
| Urbanization | 0.245 | 0.092 | 2.67 | 0.007 | 0.066 | 0.425 | ** |
| Technological Innovation | 0.164 | 0.043 | 3.79 | 0 | 0.079 | 0.249 | *** |
| Constant | 0.204 | 0.076 | 2.67 | 0.008 | 0.054 | 0.354 | ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Chen, T.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Huang, J. Testing Convergence of Tourism Development and Exploring Its Influencing Factors: Empirical Evidence from the Greater Bay Area in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6616. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116616
Chen H, Chen T, Li L, Chen X, Huang J. Testing Convergence of Tourism Development and Exploring Its Influencing Factors: Empirical Evidence from the Greater Bay Area in China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(11):6616. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116616
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hui, Tianyi Chen, Long Li, Xiaoliang Chen, and Jian Huang. 2022. "Testing Convergence of Tourism Development and Exploring Its Influencing Factors: Empirical Evidence from the Greater Bay Area in China" Sustainability 14, no. 11: 6616. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116616
APA StyleChen, H., Chen, T., Li, L., Chen, X., & Huang, J. (2022). Testing Convergence of Tourism Development and Exploring Its Influencing Factors: Empirical Evidence from the Greater Bay Area in China. Sustainability, 14(11), 6616. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116616





