Agricultural Heritage: Contrasting National and International Programs in Brazil and Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Brazil
2.1.2. Italy
2.2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Registry, Application, and Administrative Actions
3.2. Dynamic Conservation and Action Plan
3.3. Research, Innovation and Education
3.4. Report, Certification and Rewards
3.5. COVID-19 Response
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Name | Designation | Location | Year of Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black River Traditional Agricultural System | B-NIAHS | Barcelos, Santa Isabel do Rio Negro e São Gabriel da Cachoeira—Amazonas State | 2010 |
| Quebradeiras de Coco-Babaçu Traditional Agricultural System | Cataloged | Lago do Junco—Maranhão | 2017 |
| Vazanteiro Traditional Agricultural System | Cataloged | Matias Cardoso—Minas Gerais State | 2017 |
| Vale do Ribeira Traditional Agricultural System | B-NIAHS | Eldorado—São Paulo State | 2017 |
| Areais da Ribanceira Traditional Agrifood Systems | Cataloged | Imbituba—Santa Catarina State | 2017 |
| Fecho e Fundo de Pasto Traditional Agricultural Systems | Cataloged | Pilão Arcado, Correntina, Campo Alegre de Lourdes, Canudos, Casa Nova, Remanso, Curaçá, Sento Sé, Uauá, Sobradinho, and Juazeiro—Bahia State | 2017 |
| Alto Xingu Traditional Agricultural System | Cataloged | Canarana—Mato Grosso State | 2017 |
| Roça de Toco Traditional Agricultural System | Cataloged | Biguaçu—Santa Catarina State | 2017 |
| Iery Behe Traditional Agricultural System | Cataloged | Novo Airão, Urucará, Presidente Figueiredo—Amazonas State; Rorainópolis, and São João da Baliza—Roraima State | 2017 |
| Arraoil do Bailique Agroforestry System | Catalogued | Macapá—Amapá State | 2017 |
| Gerazeira de Água Boa Agricultural System | Cataloged | Rio Pardo de Minas—Minas Gerais State | 2017 |
| Guarani Boapy Pindó Agroforestry System | Cataloged | Aracruz—Espírito Santo State | 2017 |
| Serra Catarinense Pinion Agroforestry System | Cataloged | Lages, São Joaquim, Painel, Urubici, Bom Retiro, Bocaina do Sul, Correia Pinto, São José do Cerrito, Cerro Negro, Campo Belo do Sul, and Anita Garibaldi—Santa Catarina State | 2017 |
| Sobrado Community Traditional Agricultural System | Cataloged | Rio Pardo de Minas—Minas Gerais State | 2017 |
| Creole Maize Traditional Agricultural System | Cataloged | Pacaraima, Boa Vista—Roraima State | 2017 |
| Alto Jequitinhonha Seed Bank | Cataloged | Turmalina, Minas novas, Chapada do Norte, and Veredinha—Minas Gerais State | 2019 |
| Seara Agrifood Systems | Cataloged | Seara—Santa Catarina State | 2019 |
| Krahò Traditional Agricultural Systems | Cataloged | Itacajá—Tocantins State | 2019 |
| Porto de Moz Agrifood Systems | Cataloged | Porto de Moz—Pará State | 2019 |
| Borborema Family Farming Territories | Cataloged | Borborema—Paraíba State | 2019 |
| Ikioakakwa Traditional Agricultural System | Cataloged | Comodoro—Mato Grosso State | 2019 |
| Fecho de Pasto Traditional Agricultural System | Cataloged | Correntina—Bahia State | 2019 |
| Potreiros Traditional Agricultural System | Cataloged | Vacaria, Monte Alegre dos Campos, Ipê, São Francisco de Paula, and Campestre da Serra—Rio Grande do Sul State | 2019 |
| Southern Espinhaço Mountain Range Traditional Agricultural System | B-NIAHS GIAHS | Diamantina—Minas Gerais State | 2020 |
| Name | Designation | Location | Year of Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sant’Antonio Woods | I-NIAHS | Pestocostanzo—Abruzzo Region | 2012 |
| The Open Fields of Baronia di Carapelle | I-NIAHS | Santo Stefano di Sessanio, Calascio, and Castelvecchio Calvisio—Abruzzo Region | 2012 |
| Terraced Fields and Hills of the Majella | I-NIAHS | Roccamorice, Lettomanoppello, and Abbateggio—Abruzzo Region | 2012 |
| Olive Orchards of Loreto Aprutino | I-NIAHS | Loreto Aprutino—Abruzzo Region | 2012 |
| Fucino Plain at Ortucchio | I-NIAHS | Ortucchio—Abruzzo Region | 2012 |
| Plateaus of Aielli | I-NIAHS | Pizzoli and Barete—Abruzzo Region | 2012 |
| Chestnut Groves of the Vulture-Melfi Area | I-NIAHS | Atella, Barile, Melfi, Rapolla, and Rionero in Vulture—Basilicata Region | 2012 |
| Pastures of the Murgia Materana | I-NIAHS | Matera—Basilicata Region | 2012 |
| Olive Orchards of Ferrandina | I-NIAHS | Ferrandina—Basilicata Region | 2012 |
| Vineyards of Aglianico in the Vulture | I-NIAHS | Rionero in Vulture, Barile, Rapolla, Melfi, Ginestra, Ripacandida, Atella, Maschito, Banzi, Genzano, Forenza, Acerenza, Venosa, Lavello, and Palazzo San Gervasio—Basilicata Region | 2012 |
| Sila Plateaus | I-NIAHS | Spezzano della Sila, Spezzano Piccolo, and Serra Pedace—Calabria Region | 2012 |
| The Grass Fields of Isola Capo Rizzuto | I-NIAHS | Isola Capo Rizzuto—Calabria Region | 2012 |
| Reventino Chestnut Groves | I-NIAHS | Cicala, Serrastretta, Gimigliano, San Pietro Apostolo—Calabria Region | 2012 |
| The Costa Viola | I-NIAHS | Palmi, Seminara, Bagnara, Scilla, and Villa S. Giovanni—Calabria Region | 2012 |
| Monumental Olive Trees at Gioia Tauro | I-NIAHS | Gioia Tauro, Rizziconi, and Taurianova—Calabria Region | 2012 |
| Bergamot Plain | I-NIAHS | Brancaleone—Calabria Region | 2012 |
| The Riviera dei Cedri | I-NIAHS | Diamante and Santa Maria del Cedro—Calabria Region | 2012 |
| Historical Terraced Orchards on Mount Somma | I-NIAHS | Somma Vesuviana— Campania Region | 2012 |
| Mixed Hill Cultures of Lower Irpinia | I-NIAHS | Montemiletto, Taurasi, Torre le Nocelle, and Lapio—Campania Region | 2012 |
| Terraced Lemon Orchards of the Amalfi Coast | I-NIAHS | Minori—Campania Region | 2012 |
| Terraced Hazelnut Groves of the Vallo di Lauro and the Baiano Area | I-NIAHS | Baiano—Campania Region | 2012 |
| Terraced Orchard-Gardens on the Hills of Naples | I-NIAHS | Naples—Campania Region | 2012 |
| Historical Afforestations in the Sele Basin | I-NIAHS | Bagnoli Irpino, Nusco, Lioni, and Caposele—Campania Region | 2012 |
| Vite Maritata of the Phlegraean Volcanic Plain | I-NIAHS | Giugliano in Campania—Campania Region | 2012 |
| Chestnut Groves of the Lavino Area | I-NIAHS | Monte San Pietro and Sasso Marconi—Emilia Romagna Region | 2012 |
| Valli Le Partite Reclamation District | I-NIAHS | Mirandola—Emilia Romagna Region | 2012 |
| Olive Orchards of the Lamone Valley | I-NIAHS | Brisighella—Emilia Romagna Region | 2012 |
| The Partecipanze Centopievesi | I-NIAHS | Pieve di Cento and Cento—Emilia Romagna Region | 2012 |
| The San Vitale Pinewoods | I-NIAHS | Po Delta Park—Emilia Romagna Region | 2012 |
| Diamantina Estate | I-NIAHS | Ferrara—Emilia Romagna Region | 2012 |
| The Hills of Polazzo in the Carso | I-NIAHS | Fogliano Redipuglia, Doberdò del Lago/Obcina Doberdob e Ronchi dei Legionari—Friuli Venezia Giulia | 2012 |
| The Plasencis Countryside | I-NIAHS | Mereto di Tomba and San Vito di Fagagna—Friuli Venezia Giulia Region | 2012 |
| Rosazzo Abbey Hill | I-NIAHS | Manzano and Corno di Rosazzo—Friuli Venezia Giulia Region | 2012 |
| The Ampezzo Forest and the Lumiei Valley | I-NIAHS | Ampezzo, Sauris, and Forni di Sotto—Friuli Venezia Giulia Region | 2012 |
| The Magredi of Vivaro | I-NIAHS | Vivaro and Maniago—Friuli Venezia Giulia Region | 2012 |
| Casette e Prati di Cottanello | I-NIAHS | Cottanello—Lazio Region | 2012 |
| The Chestnut Groves of Canepina | I-NIAHS | Canepina—Lazio Region | 2012 |
| The Farnesiana | I-NIAHS | Allumiere—Lazio Region | 2012 |
| Gorges of the Farfa | I-NIAHS | Sabina area—Lazio Region | 2012 |
| Terraced Olive Orchards of Vallecorsa | I-NIAHS | Vallecorsa—Lazio Region | 2012 |
| Cavaliere Estate | I-NIAHS | Rome (V Municipio) and Guidonia Montecelio—Lazio Region | 2012 |
| Chestnut Groves in the Alta Val Bormida | I-NIAHS | Calizzano, Murialdo, Bardineto, Osiglia and Massimino—Liguria Region | 2012 |
| Wooded Olive Groves of Lucinasco | I-NIAHS | Lucinasco—Liguria Region | 2012 |
| Terraced and Irrigated Chestnut Groves and Vegetable Gardens in Upper Valle Sturla | I-NIAHS | Borzonasca—Liguria Region | 2012 |
| Peri-urban Vegetable Gardens in the Valley of the Entella River | I-NIAHS | Chiavari, Lavagna, Cogorno, Carasco, and San Colombano Certenoli—Liguria Region | 2012 |
| Wooded Meadows and Pastures in the Santo Stefano Cheese Area | I-NIAHS | Santo Stefano d’Aveto—Liguria Region | 2012 |
| Terraced Hazelnut Groves of Tigullio | I-NIAHS | Mezzanego, Borzonasca, Ne, San Colombano Certenoli, and Leivi—Liguria Region | 2012 |
| Low-growing Terraced Vineyards of Tramonti | I-NIAHS UNESCO World Heritage | Cinque Terre National Natural Park, Porto Venere Regional Natural Park, and the Porto Venere-Riomaggiore—Liguria Region | 2012 |
| The baulati Fields of Casalasco | I-NIAHS | Piadena, Calvatone, and Tornata—Lombardia Region | 2012 |
| The Banina Hill | I-NIAHS | San Colombano al Lambro, Graffignana, Inverno, Monteleone, and Miradolo Terme—Lombardia Region | 2012 |
| Morenic Hills of the Lower Garda Lake | I-NIAHS | Ponti sul Mincio, Monzambano, Cavriana, and Solferino—Lombardia Region | 2012 |
| Lemon Houses on the Garda Lake | I-NIAHS | Salò, Gardone Riviera, Toscolano Maderno, Gargnano, Tignale, Tremosine, and Limone—Lombardia Region | 2012 |
| The marcite of the Irrigated Plain | I-NIAHS | Bernate Ticino, Morimondo, Vigevano, Albairate, Buccinasco, Calvignasco, Lacchiarella, Melzo, Noviglio, Peschiera Borromeo, Settala, and Zibido San Giacomo—Lombardia Region | 2012 |
| Bird-catching Sites in Lombardy | I-NIAHS | Colli di Bergamo, Val Seriana, Val Brembana, Val Gandino, and Val Cavallina—Lombardia Region | 2012 |
| Val Muggiasca | I-NIAHS | Vendrogno—Lombardia Region | 2012 |
| Terraced Vineyards of the Valtellina | I-NIAHS | Sondrio, Montagna, Poggiridenti, and Tresivio—Lombardia Region | 2012 |
| The Plateau of Macereto | I-NIAHS | Ussita and Visso—Marche Region | 2012 |
| Hills of Maiolati Spontini | I-NIAHS | Maiolati Spontini, Scisciano, Monte Roberto, and Castelbellino—Marche Region | 2012 |
| Olive Orchards of Coroncina | I-NIAHS | Caldarola—Marche Region | 2012 |
| Piagge of Ascoli Piceno | I-NIAHS | Ascoli Piceno—Marche Region | 2012 |
| Polycultures of Loretello | I-NIAHS | Arcevia—Marche Region | 2012 |
| Sasso Simone and Simoncello | I-NIAHS | Piandimeleto, Frontino, Carpegna, and Pennabilli—Marche Region | 2012 |
| Cereal Farming in Melanico | I-NIAHS | Santa Croce—Molise Region | 2012 |
| La Pista at Campomarino | I-NIAHS | Campomarino—Molise Region | 2012 |
| The Olive Orchards of Venafro | I-NIAHS | Venafro—Molise Region | 2012 |
| The Springs of Monteroduni | I-NIAHS | Monteroduni—Molise Region | 2012 |
| Sheep-Tracks in the Upper Molise | I-NIAHS UNESCO MAB | Collemeluccio and Montedimezzo—Molise Region | 2012 |
| Pastures of Raschera | I-NIAHS | Chiusa di Pesio, Punta Marguareis, Frabosa Soprana, Frabosa Sottana and Magliano Alpi—Piedmont Region | 2012 |
| The Plateau of the Vauda | I-NIAHS | Barbania, Front, Vauda Canavese, San Carlo Canavese, San Francesco al Campo, Lombardore, Rivarossa and Rocca Canavese—Piedmont Region | 2012 |
| The Baraggia Land in the Vercelli and Biella Area | I-NIAHS | Baragge Natural Oriented Reserve—Piedmont Region | 2012 |
| Wood of Sorti della Partecipanza di Trino | I-NIAHS | Trino—Piedmont Region | 2012 |
| The San Michele Farmhouse | I-NIAHS | Bosco Marengo—Piedmont Region | 2012 |
| The Wooded Pastures of Roccaverano | I-NIAHS | Olmo Gentile, Roccaverano, San Giorgio Scarampi and Mombaldone—Piedmont Region | 2012 |
| Historical Polyculture of Valle Uzzone | I-NIAHS | Castelletto Uzzone, Pezzolo Valle Uzzone, Bergolo, Levice and Gottasecca—Piedmont Region | 2012 |
| The Galarei Vineyard | I-NIAHS | Serralunga d’Alba and Diano d’Alba—Piedmont Region | 2012 |
| Monumental Turkish Oak Woods of Valle Ragusa | I-NIAHS | Monte Sant’Angelo—Puglia Region | 2012 |
| The Citrus-Grove Oasis in the Gargano | I-NIAHS | Rodi Garganico, Vico del Gargano, and Ischitella—Puglia Region | 2012 |
| Olive Orchards of the Serre Salentine | I-NIAHS | Alessano—Puglia Region | 2012 |
| The Pastures of the Upper Murgia | I-NIAHS | Gravina and Spinazzola—Puglia Region | 2012 |
| Terraces in the Gargano | I-NIAHS | Mattinata and Monte Sant’Angelo—Puglia Region | 2012 |
| The Itria Valley | I-NIAHS UNESCO WHS | Martina Franca—Puglia Region | 2012 |
| The Vineyards of the Lecce Tavoliere | I-NIAHS | Salice Salentino—Puglia Region | 2012 |
| Olive Groves of Monte Oro | I-NIAHS | Sassari—Sardegna Region | 2012 |
| Rural Landscapes of Asinara | I-NIAHS | Porto Torres—Sardegna Region | 2012 |
| Planted Silvo-pastoral Systems of Monte Minerva | I-NIAHS | Villanova Monteleone, Padria, and Monteleone Rocca Doria—Sardegna Region | 2012 |
| The Citrus Orchards of Conca D’Oro | I-NIAHS | Palermo—Sicilia Region | 2012 |
| The Mixed Orchards of the Valley of the Temples | I-NIAHS UNESCO WHS | Agrigento—Sicilia Region | 2012 |
| The Ficuzza Woods | I-NIAHS | Corleone, Godrano, and Monreale—Sicilia Region | 2012 |
| Enclosed Fields with Carob Trees on the Monti Iblei | I-NIAHS | Ragusa—Sicilia Region | 2012 |
| Manna Ash Woods | I-NIAHS | Pollina, Castelbuono, San Mauro Castelverde—Sicilia Region | 2012 |
| Pantelleria’s “dry-stone” Landscape | I-NIAHS | Trapani—Sicilia Region | 2012 |
| The Pistachio Orchards of Bronte | I-NIAHS | Bronte and Adrano—Sicilia Region | 2012 |
| Polyculture on the Slopes of Etna | I-NIAHS | Maletto, Bronte and Randazzo—Sicilia Region | 2012 |
| The Fir Forest of the Monastery of Vallombrosa | I-NIAHS | Reggello—Toscana Region | 2012 |
| The Biancane of the Val d’Orcia | I-NIAHS | Pienza, Montepulciano, Chianciano and Sarteano—Toscana | 2012 |
| The Monumental Chestnut Groves of the Scesta Valley | I-NIAHS | Bagni di Lucca—Toscana Region | 2012 |
| Hill of Fiesole | I-NIAHS | Fiesole and Florence—Toscana Region | 2012 |
| The Montagnola Senese of Spannocchia | I-NIAHS | Chiusdino—Toscana Region | 2012 |
| Landscape Mosaic of Montalbano | I-NIAHS | Pistoia—Toscana Region | 2012 |
| Silvo-pastoral Landscapes of Moscheta | I-NIAHS | Firenzuola—Toscana Region | 2012 |
| Terraced Vineyards of Lamole | I-NIAHS | Chianti—Toscana Region | 2012 |
| The Fir and Spruce Woods of Val Cadino | I-NIAHS | Valfloriana, Castello-Molina di Fiemme, and Cavalese—Trentino Alto Adige Region | 2012 |
| The vineyards of Val di Cembra | I-NIAHS | Cembra, Lisignago and Giovo—Trentino Alto Adige Region | 2012 |
| Alto Adige | I-NIAHS | N/A | 2012 |
| The Meadows and Wooded Pastures of Salten | I-NIAHS | San Genesio—Trentino Alto Adige Region | 2012 |
| Terraced Vineyards of Santa Maddalena | I-NIAHS | Santa Maddalena—Trentino Alto Adige Region | 2012 |
| The Plestini Plateaus | I-NIAHS | Foligno, and Serravalle di Chienti—Umbria Region | 2012 |
| Spelt Fields at Monteleone di Spoleto | I-NIAHS | Monteleone di Spoleto—Umbria Region | 2012 |
| The Hills of Montefalco | I-NIAHS | Montefalco—Umbria Region | 2012 |
| Plateaus of Castelluccio di Norcia | I-NIAHS | Foligno and Nocera Umbra—Umbria Region | 2012 |
| The Poggi di Baschi | I-NIAHS | Baschi and Montecchio—Umbria Region | 2012 |
| The Rock of Orvieto | I-NIAHS | Terni—Umbria Region | 2012 |
| Stepped Olive Groves | I-NIAHS GIAHS | Spello, Foligno, Trevi, Campello sul Clitunno, and Spoleto—Umbria Region | 2012 |
| High-Mountain Pastures at Dame de Challant | I-NIAHS | Brusson, Gressoney-Saint-Jean, Challand-Saint-Anselme, Challand-Saint-Victor, Issime, and Gaby—Valle D’osta Region | 2012 |
| The “Heroic Viticulture” of the Dora Baltea Area | I-NIAHS | Pont Sant Martin, Donnas, and Bard—Valle D’osta Region | 2012 |
| Plateau of Tretto | I-NIAHS | Tretto—Veneto Region | 2012 |
| The Forest of Cansiglio | I-NIAHS | Farra d’Alpago, Tambre, Cordignano, Sarmede, Fregona, Budoia, Caneva and Polcenigo—Veneto Region | 2012 |
| Wine Hills between Tarzo and Valdobbiadene | I-NIAHS | Tarzo, Refrontolo, Cison di Valmarino, Follina, Pieve di Soligo, Miane, Farra di Soligo, Vidor, and Valdobbiadene—Veneto Region | 2012 |
| The Fief of the Counts of Collalto | I-NIAHS | Susegana—Veneto Region | 2012 |
| The Palù of Quartier Piave | I-NIAHS | Moriago della Battaglia, Sernaglia della Battaglia, Vidor, and Farra di Soligo—Veneto Region | 2012 |
| The Ca’ Tron Farm | I-NIAHS | Roncade—Veneto Region | 2012 |
| The Vineyards of Fonzaso | I-NIAHS | Fonzaso and Arsiè—Veneto Region | 2012 |
| Soave Traditional Vineyards | GIAHS | Soave, Monteforte D’Alpone, Colognola ai Colli and Roncà—Veneto Region | 2018 |
References
- Svizzero, S.; Tisdell, C.A. The Neolithic Revolution and Human Societies: Diverse Origins and Development Paths; Université de La Réunion: Saint-Denis, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- CBD. Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity. Assessment of the Situation Regarding the Principle of “Ensuring that No One is Left Behind”. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/14519SCBDinput_2017HLPF.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- Koohafkan, P.; Altieri, M.A. Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems: A Legacy for the Future; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Van Huylenbroeck, G.; Vandermeulen, V.; Mettepenningen, E.; Verspecht, A. Multifunctionality of Agriculture: A Review of Definitions, Evidence and Instruments. Living Rev. Landsc. Res. 2007, 1, 5–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dela-Cruz, M.J.; Koohafkan, P. Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems: A shared vision of agricultural, ecological and traditional societal sustainability. Resour. Sci. 2009, 31, 905–913. [Google Scholar]
- Van Mil, H.G.; Foegeding, E.A.; Windhab, E.J.; Perrot, N.; Van Der Linden, E. A complex system approach to address world challenges in food and agriculture. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 40, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerer, K.S.; De Haan, S.; Jones, A.D.; Creed-Kanashiro, H.; Tello, M.; Carrasco, M.; Meza, K.; Amaya, F.P.; Cruz-Garcia, G.S.; Olivencia, Y.J.; et al. The biodiversity of food and agriculture (Agrobiodiversity) in the Anthropocene: Research advances and conceptual framework. Anthropocene 2019, 25, 100192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinkwater, L.E.; Friedman, D.; Buck, L. Understanding Agricultural Systems. Systems Research for Agriculture; SARE Outreach: College Park, MD, USA, 2016; Volume 96, ISBN 9781888626162. [Google Scholar]
- Emperaire, L.; Van Velthem, L.; Oliveira, A.G. Patrimônio Cultural Imaterial e Sistema Agrícola: O Manejo da Diversidade Agrícola No Médio Rio Negro (AM). In Proceedings of the 26a Reuniao Brasileira De Antropologia, ABA, Porto Seguro, Brazil, 1–4 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan, P.S. Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS): An Eco-Cultural Landscape Perspective. 2009. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/user_upload/giahs/docs/backgroundpapers_ramakrishnan.pdf (accessed on 7 December 2018).
- Mitchell, N.J.; Barrett, B.F.D. Heritage Values and Agricultural Landscapes: Towards a New Synthesis. Landsc. Res. 2015, 40, 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.M.; Navarro, L.M.; Martins, I.S. Global Biodiversity Change: The Bad, the Good, and the Unknown. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2012, 37, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.-E.; Sørensen, M.; Pedersen, S.M.; Weiner, J. Feeding the world: Genetically modified crops versus agricultural biodiversity. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidt, J.S.; Udry, C. Sistemas Agrícolas Tradicionais no Brasil; Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária (EMBRAPA), Secretaria de Inteligência e Relações Estratégicas, Secretaria de Inovação e Negócios, Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento: Moju, Pará, Brazil, 2019; Volume 3, ISBN 978-85-7035-893-6.
- FAO—Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of the World’s Biodiversity for Food and Agriculture; FAO Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture Assessments: Roma, Italy, 2019; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/CA3129EN/ca3129en.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Hill, R.; Nates-Parra, G.; Quezada-Euán, J.J.G.; Buchori, D.; LeBuhn, G.; Maués, M.M.; Pert, P.L.; Kwapong, P.K.; Saeed, S.; Breslow, S.J.; et al. Biocultural approaches to pollinator conservation. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, C.T.; Lopes, P.F.M.; Campos-Silva, J.V.; Noble, M.M.; Dyball, R.; Peres, C.A.; Young, J. Co-management of culturally important species: A tool to promote biodiversity conservation and human well-being. People Nat. 2020, 2, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, M.C.; McCarter, J.; Mead, A.; Berkes, F.; Stepp, J.R.; Peterson, D.; Tang, R. Defining biocultural approaches to conservation. Trends Ecol. Evolution. 2015, 30, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cámara-Leret, R.; Raes, N.; Roehrdanz, P.; De Fretes, Y.; Heatubun, C.D.; Roeble, L.; Schuiteman, A.; van Welzen, P.C.; Hannah, L. Climate change threatens New Guinea’s biocultural heritage. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaz1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, E.; Martin, G.; Van Wijk, M.; Timsina, J.; Snow, V. Impacts of COVID-19 on agricultural and food systems worldwide and on progress to the sustainable development goals. Agric. Syst. 2020, 183, 102873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Independent Group of Scientists Appointed by the Secretary-General. Global Sustainable Development Report 2019: The Future is Now—Science for Achieving Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda, A.; Doan, D.; Newhouse, D.; Nguyen, M.C.; Uematsu, H.; Azevedo, J.P. A New Profile of the Global Poor. World Dev. 2018, 101, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Poverty Overview: Development News Research Data. 2021. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/poverty/overview#1 (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- FRAC—Food Research and Action Center. Hunger & health: The Impact of Poverty, Food Insecurity, and Poor Nutrition on Health and Well-Being. 2021. Available online: https://frac.org/wp-content/uploads/hunger-health-impact-poverty-food-insecurity-health-well-being.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- FAO—Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAO and Traditional Knowledge: The Linkages with Sustainability, Food Security and Climate Change Impacts. In Gender, Equity and Rural Employment Division, Economic and Social Development Department; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ocelli Pinheiro, R.; Ludwig, T.; Lopes, P. Cultural ecosystem services: Linking landscape and social attributes to ecotourism in protected areas. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 50, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The United Nations. COVID Response: The Impacts of COVID-19 on Indigenous People. Deparment of Economics and Social Affairs. 2020. Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/dpad/wp-content/uploads/sites/45/publication/PB_70.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- GIAHS—Globally Important Heritage Systems. Why Dynamic Conservation of Agricultural Heritage? 2020. Available online: http://www.fao.org/giahs/background/strategy-and-approach/en/ (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- FAO—Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. GIAHS around the World. 2020. Available online: http://www.fao.org/giahs/giahsaroundtheworld/en/ (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- García, M.A.; Yagüe, J.L.; Nicolás, V.L.; Díaz-Puente, J.M. Characterization of Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) in Europe. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Fuller, A.M.; Xu, S.; Min, Q.; Wu, M. Socio-Ecological Adaptation of Agricultural Heritage Systems in Modern China: Three Cases in Qingtian County, Zhejiang Province. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohsaka, R.; Matsuoka, H.; Uchiyama, Y.; Rogel, M. Regional management and biodiversity conservation in GIAHS: Text analysis of municipal strategy and tourism management. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2019, 5, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Yang, L.; Min, Q.; Bai, K.; Li, W. The Significance of Traditional Culture for Agricultural Biodiversity—Experiences from GIAHS. J. Resour. Ecol. 2021, 12, 453–461. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, M. Challenges and Countermeasures for the Sustainable Development of Nationally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems in China. J. Resour. Ecol. 2014, 5, 390–394. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, L.C. Os Vazanteiros do Rio São Francisco: Um Estudo sobre Populações Tradicionais e Territorialidade no Norte de Minas Gerais. Master’s Thesis, UFMG Belo Horizonte, Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). Classificação e Caracterização dos Espaços Rurais e Urbanos do Brasil: Uma Primeira Aproximação. Available online: http://biblioteca.ibge.gov.br/visualizacao/livros/liv100643.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Instituto do Patrimônio Histórico e Artístico Nacional—IPHAN. 2019. Available online: http://portal.iphan.gov.br/noticias/detalhes/5145/livro-sobre-sistemas-agricolas-tradicionais-no-brasil-esta-disponivel-online (accessed on 19 January 2020).
- Barbosa, R.I.; Luz, F.J.F.; Nascimento Filho, H.R.; Maduro, C.B. Pimentas do Gênero Capsicum Cultivadas em Roraima, Amazônia Brasileira. Acta Amaz. 2002, 32, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garnelo, L. Poder, Hierarquia e Reciprocidade: Saúde e Harmonia Entre os Baniwa do Alto Rio Negro; Editora Fiocruz: Manaus, Brazil, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Socioambiental. Pimenta Jiquitaia Baniwa; Organização da Bacia do Icana; Federacao das Organizacoes Indigenas do Rio Negro: São Gabriel da Cachoeira, São Paulo, Brazil, 2016; ISBN 978-85-8226-040-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mauss, M. Ensaio sobre a dádiva. In Sociologia e Antropologia; Mauss, M., Ed.; Ubu Editora: São Paulo, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dayrell, C.A.; Barbosa, R.S.; Costa, J.B.d.A. Dinâmicas produtivas e territoriais no Norte de Minas: O lugar invisível das economias nativas e apontamentos para políticas públicas. Campo. Territ. 2017, 12, 128–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.Q. Environmental Conflicts in The North of Minas Gerais: The Resistance of the Vazanteiros; Revista do Programa de Pós-Graduação em Extensão Rural (UFV): Minas Gerais, Brazil, 2018; ISSN 2359-5116. [Google Scholar]
- Clements, E.A. Agrarian reform, food sovereignty and the MST: Socio-environmental impacts of agrofuels production in the pontal do Paranapanema region of São Paulo State, Brazil. Rev. Nera 2013, 21, 8–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.D. Europe’s First Farmers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Klijn, J. Driving Forces behind Landscape Transformation in Europe, from a Conceptual Approach to Policy Options; The New Dimensions of the European Landscape; Wageningen UR Frontis Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 4, pp. 201–218. [Google Scholar]
- Santucci. The Diversification of Agriculture in Italy: Agritourism and Organic Management. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348478378_The_Diversification_of_Agriculture_in_Italy_Agritourism_and_Organic_Management (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Agnoletti, M. Italian Historical Rural Landscape—Cultural values for the environment and rural development. In Environmental History; ENVHIS: New Delhi, India, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Agnoletti, M.; Emanueli, F.; Corrieri, F.; Venturi, M.; Santoro, A. Monitoring Traditional Rural Landscapes. The Case of Italy. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, M.A.; Koohafkan, P. Globally Important Ingenious Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS): Extent, Significance, and Implications for Development. 2015. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ap021e/ap021e.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- Santoro, A.; Venturi, M.; Agnoletti, M. Agricultural Heritage Systems and Landscape Perception among Tourists. The Case of Lamole, Chianti (Italy). Sustainability 2020, 12, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martellozzo, F.; Amato, F.; Murgante, B.; Clarke, K.C. Modelling the impact of urban growth on agriculture and natural land in Italy to 2030. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 91, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slámová, M.; Belčáková, I. The Role of Small Farm Activities for the Sustainable Management of Agricultural Landscapes: Case Studies from Europe. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Straffelini, E. Agriculture in Hilly and Mountainous Landscapes: Threats, Monitoring and Sustainable Management. Geogr. Sustain. 2020, 1, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieser, A. Why organization theory needs historical analysis—and how this should be performed. Organ. Sci. 1994, 5, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventresca, M.J.; Mohr, J.W. Archival Research Methods. In Blackwell Companion Organizations; Blackwell Publishers Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 805–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szomszor, M.; Adams, J.; Fry, R.; Gebert, C.; Pendlebury, D.A.; Potter, R.W.K.; Rogers, G. Interpreting Bibliometric Data. Front. Res. Metr. Anal. 2021, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchi, L. Políticas Públicas: Conceitos, Esquemas De Análise, Casos Práticos, 1st ed.; Cengage Learning: São Paulo, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Maharjan, K.L.; Gonzalvo, C.M.; Aala, W.F., Jr. Leveraging Japanese Sado Island Farmers’ GIAHS Inclusivity by Understanding Their Perceived Involvement. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. Study Progress of Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (IAHS): A Literature Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.M.; Halpenny, E.A. Communicating the World Heritage brand: Visitor awareness of UNESCO’s World Heritage symbol and the implications for sites, stakeholders and sustainable management. J. Sustain. Tour. 2014, 22, 768–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Ding, L.; Min, Q. The Role of the Important Agricultural Heritage Systems in the Construction of China’s National Park System and the Optimisation of the Protected Area System. J. Resour. Ecol. 2021, 12, 444–452. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Li, H.Y.; Min, Q.W. Value and conservation actors of Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (IAHS) from the perspective of rural households. Resour. Sci. 2020, 42, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Deng, Y. Multi-stakeholder governance of tourism communities in China National Park: Based on trust framework. J. Hubei Univ. Econ. 2018, 16, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, M. Valuing Geodiversity in an ‘Ecosystem Services’ Context. Scott. Geogr. J. 2012, 128, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, S.R.C.; Miyazaki, A.; Yiu, E.; Saito, O. Enhancing Sustainability in Traditional Agriculture: Indicators for Monitoring the Conservation of Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) in Japan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Uchiyama, Y.; Fujihira, Y.; Kohsaka, R. Towards Evidence Based Policy Making in GIAHS: Convention Theory and Effects of GIAHS Registration on the Wholesale and Retail Trade of Traditional and Local Vegetables. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyomura, L. Pandemia da Ignorância Cresce Com o Desmonte do Iphan. 2020. Available online: https://jornal.usp.br/radio-usp/pandemia-da-ignorancia-cresce-com-o-desmonte-do-iphan/ (accessed on 9 September 2020).
- Santos, A. Brazil and the COVID-19 Pandemic. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2017–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.B.; Soares, M.A.; Mucida, D.P. COVID-19 interferes in the disclosure of the first Brazilian GIAHS site. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 81, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floss, M.; Franco, C.M.; Malvezzi, C.; Silva, K.V.; Costa, B.D.R.; Silva, V.X.D.L.; Werreria, N.S.; Duarte, D.R. The COVID-19 pandemic in rural and remote areas: The view of family and community physicians on primary healthcare. Cad. Saúde Pública 2020, 36, e00108920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, A.M.; Leite, M.S.; Langdon, E.J.; Grisotti, M. O desafio da atenção primária na saúde indígena no Brasil. Rev. Panam Salud Pública 2018, 42, e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worley, P. Why we need better rural and remote health, now more than ever. Rural. Remote Health 2020, 20, 5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerini, F.; Dominici, A.; Casini, L. The Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Mass Market Retailing of Wine in Italy. Foods 2021, 10, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unidades de Conservação no Brasil (UCSocioambiental). RESEX Acaú-Goiana. 2018. Available online: https://uc.socioambiental.org/uc/581550 (accessed on 27 February 2020).
- Yang, L.; Liu, M.; Min, Q.; Li, W. Specialization or Diversification? The Situation and Transition of Households’ Livelihood in Agricultural Heritage Systems. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2018, 16, 455–471. [Google Scholar]
- Kajihara, H.; Zhang, S.; You, W.; Min, Q. Concerns and Opportunities around Cultural Heritage in East Asian Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS). Sustainability 2018, 10, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnoletti, M.; Manganelli, S.; Piras, F. COVID-19 and rural landscape: The case of Italy. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 204, 102995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M. Geodiversity: Valuing and Conserving Abiotic Nature; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, M.; Elsevier, B.V. The confused position of the geosciences within the “natural capital” and “ecosystem services” approaches. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 34, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meulen, E.S.; Braat, L.C.; Brils, J.M. Abiotic flows should be inherent part of ecosystem services classification. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrodt, F.; Bailey, J.; Kissling, D.; Rijsdijk, K.F.; Seijmonsbergen, A.C.; van Ree, D.; Hjort, J.; Lawley, R.S.; Williams, C.N.; Anderson, M.G.; et al. To advance sustainable stewardship, we must document not only biodiversity but geodiversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16155–16158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulian, T.; Diazgranados, M.; Pironon, S.; Padulosi, S.; Liu, U.; Davies, L.; Howes, M.J.R.; Borrell, J.S.; Ondo, I.; Oscar, A.; et al. Unlocking plant resources to support food security and promote sustainable agriculture. Plants People Planet 2020, 2, 421–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

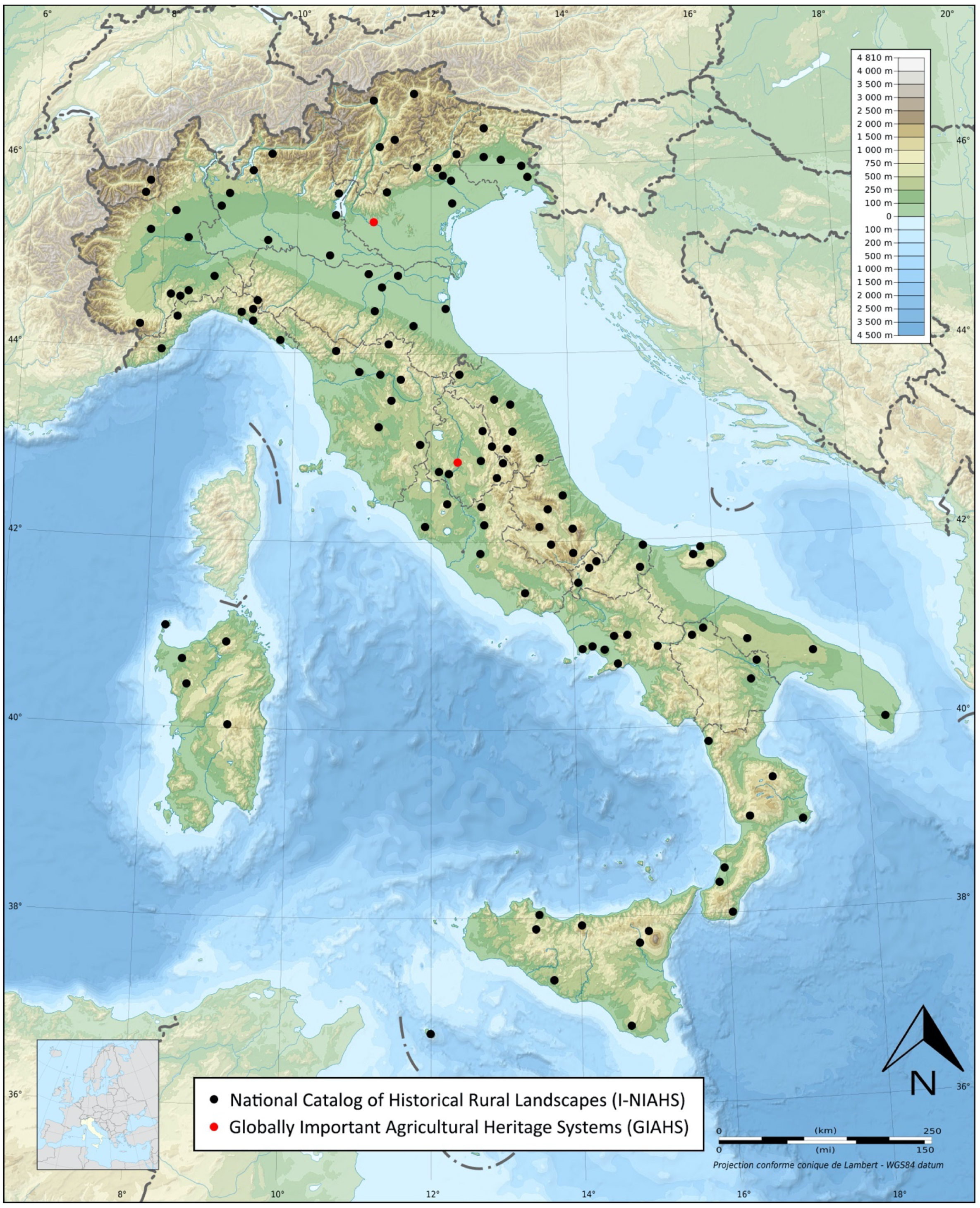
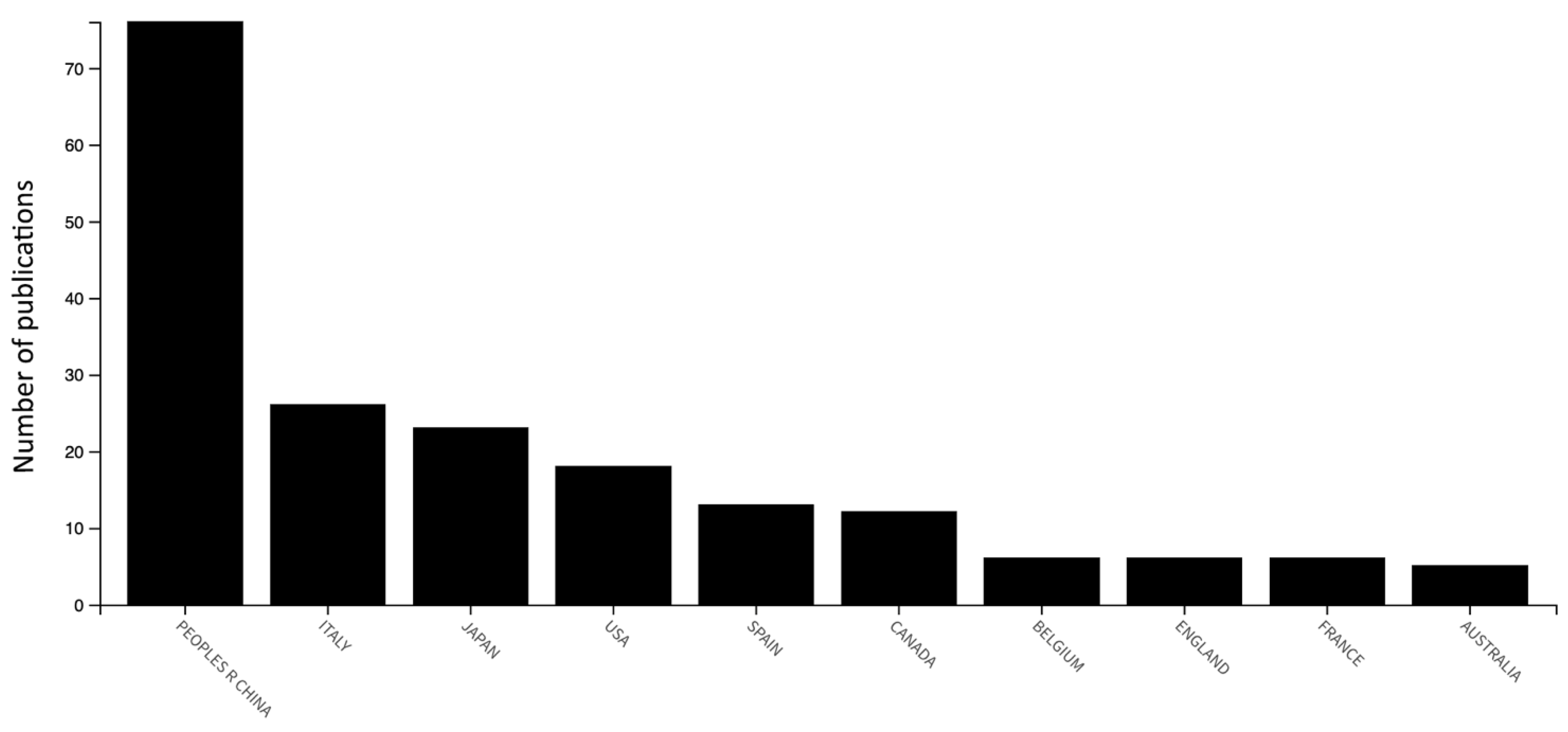
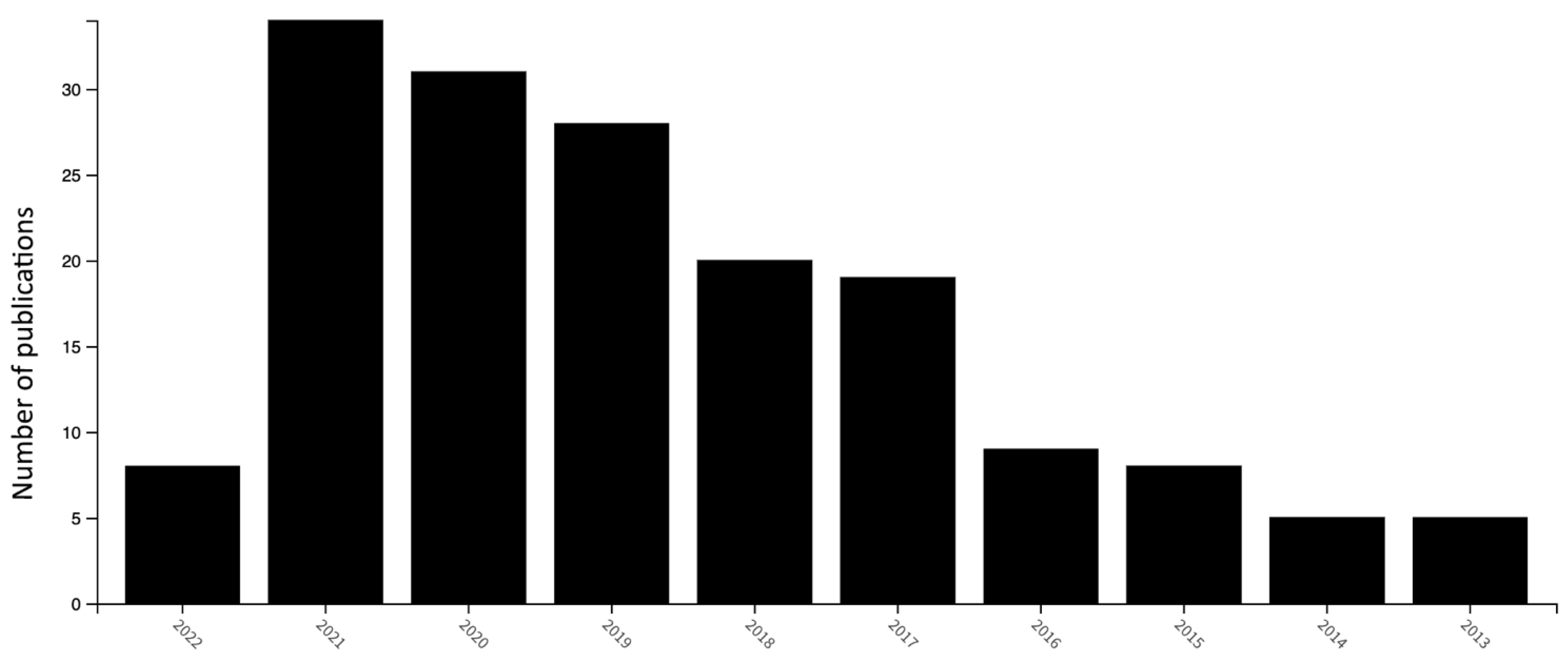

| Name | The Brazilian Traditional Agricultural Systems (B-NIAHS) | The Italian National Register of Historical Rural Landscapes (I-NIAHS) | Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of criteria | 5 | 3 | 5 |
| Start | 2010 | 2012 | 2002 |
| Numbers | 29 * | 123 * | 62 |
| Report | N/A | N/A | Once in 4 years |
| Item | GIAHS | B-NIAHS | I-NIAHS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | No |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | No |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| No | Yes | No |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | No |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | No |
| No | Yes | No |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | No |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | No |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Administrative Actions | Brazil | Italy | GIAHS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Yes | No |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| No | No | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | No | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Yes | Yes | Yes |
| No | Yes | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ocelli Pinheiro, R.; Paula, L.F.A.d.; Giardino, M. Agricultural Heritage: Contrasting National and International Programs in Brazil and Italy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6401. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116401
Ocelli Pinheiro R, Paula LFAd, Giardino M. Agricultural Heritage: Contrasting National and International Programs in Brazil and Italy. Sustainability. 2022; 14(11):6401. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116401
Chicago/Turabian StyleOcelli Pinheiro, Raphael, Luiza F. A. de Paula, and Marco Giardino. 2022. "Agricultural Heritage: Contrasting National and International Programs in Brazil and Italy" Sustainability 14, no. 11: 6401. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116401
APA StyleOcelli Pinheiro, R., Paula, L. F. A. d., & Giardino, M. (2022). Agricultural Heritage: Contrasting National and International Programs in Brazil and Italy. Sustainability, 14(11), 6401. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116401







