A Study on the Coupled and Coordinated Development of the Logistics Industry, Digitalization, and Ecological Civilization in Chinese Regions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Interactions and Data Sources
2.2. Constructing Indicator System
2.3. Coupling Coordinated Development
2.4. Obstacle Model
3. Results and Discussion
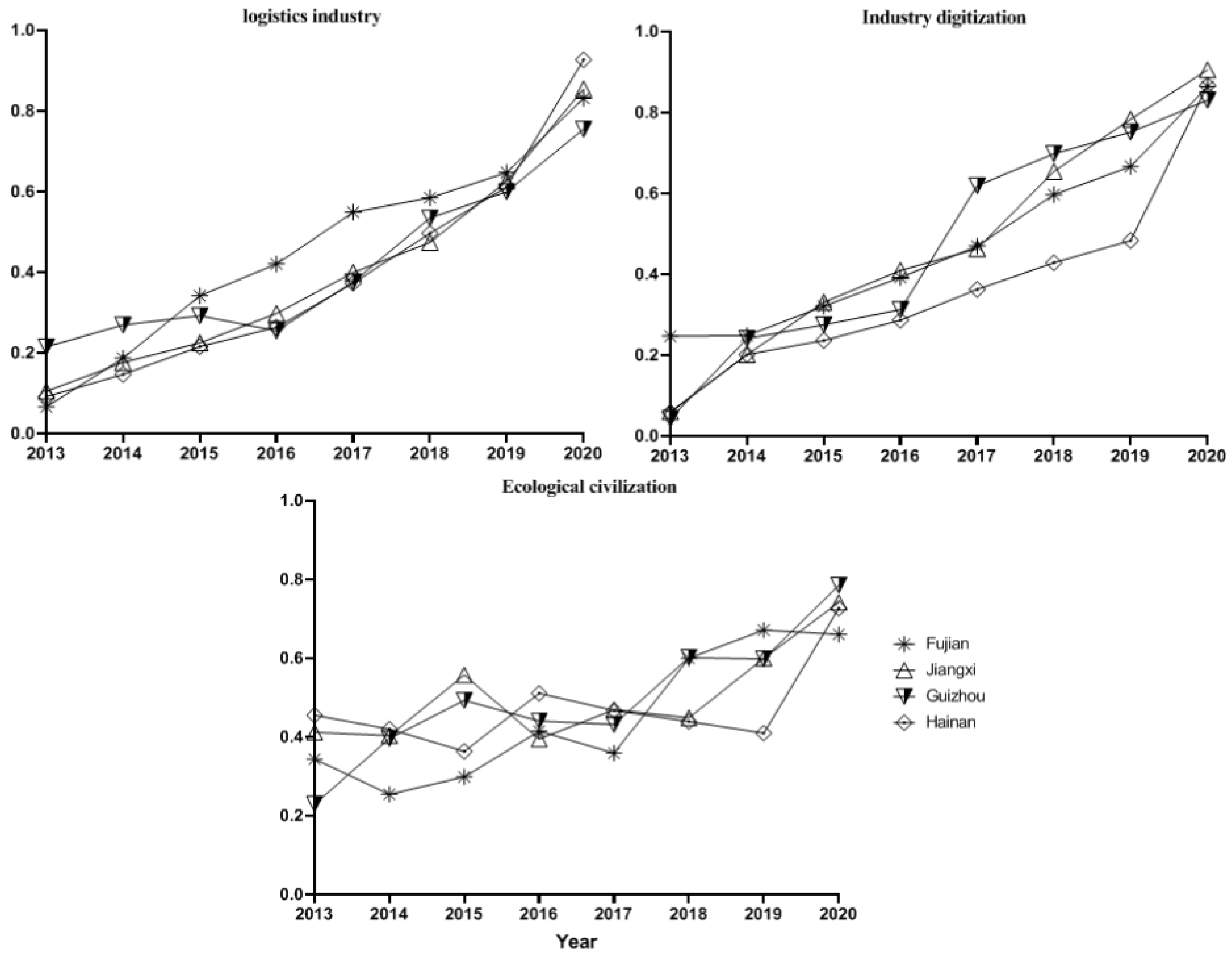
3.1. The Comprehensive Development Status of Three Systems
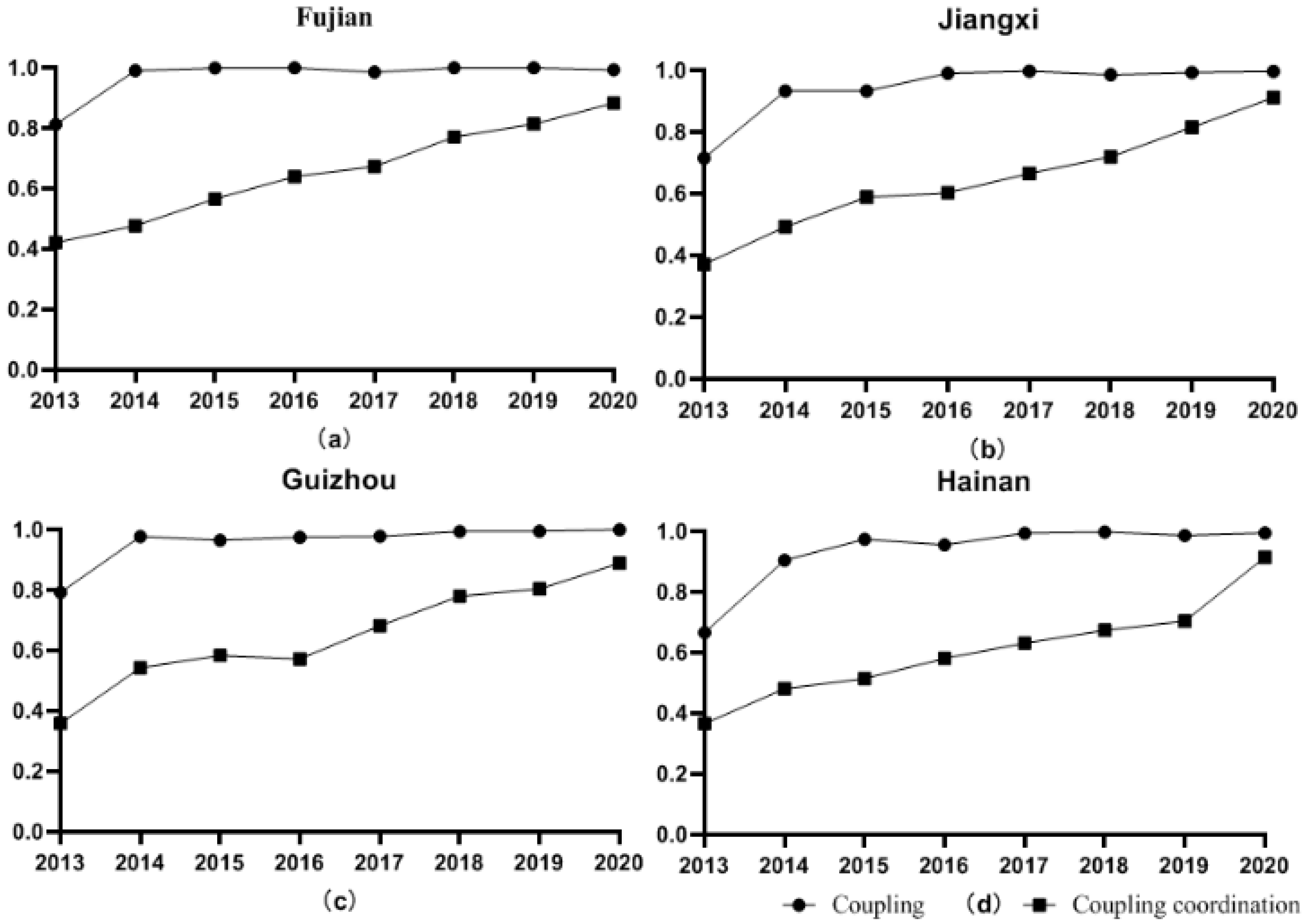
3.2. Coupling Coordination Degree Analysis
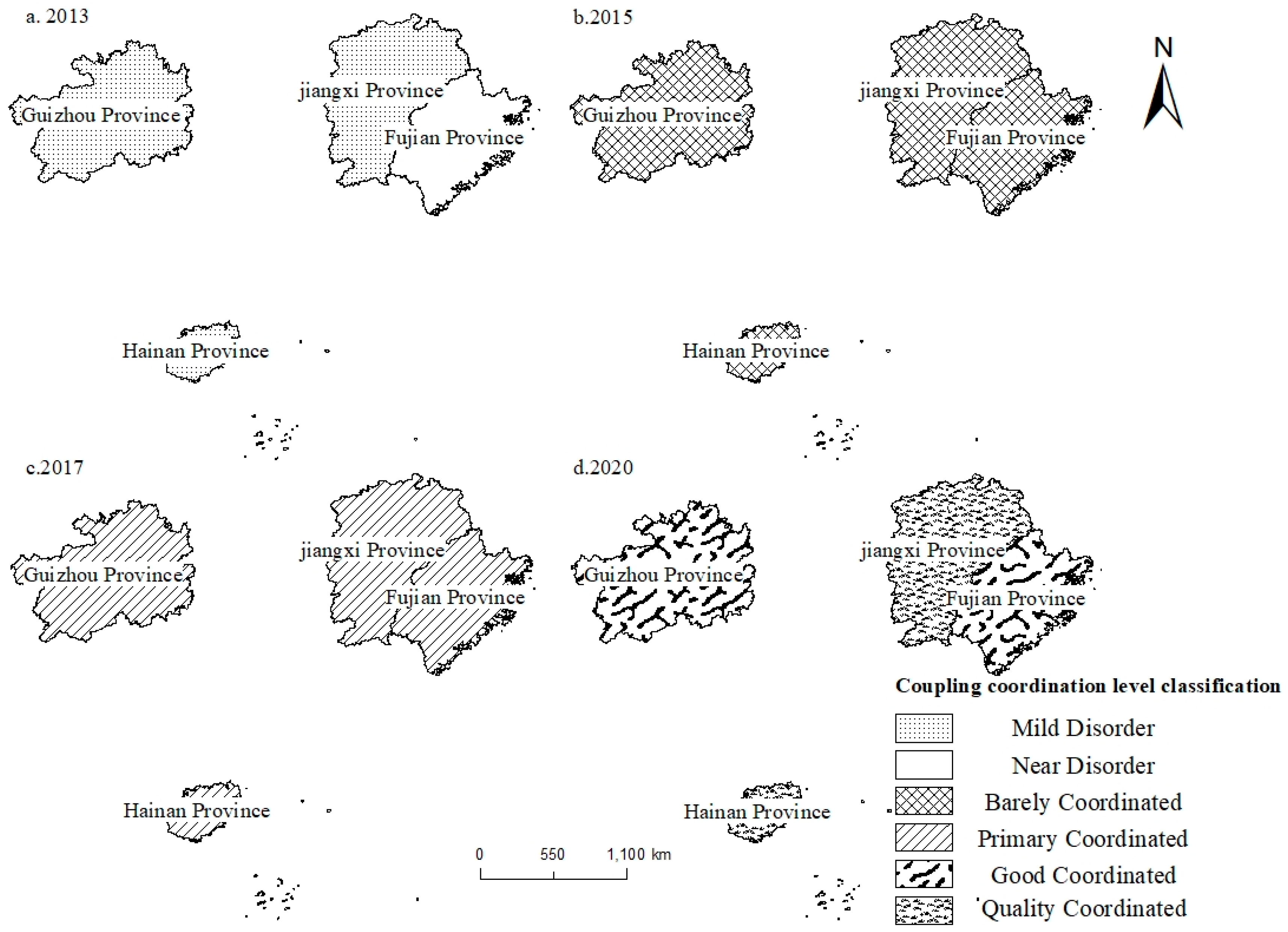
3.3. Coupling Coordination Level
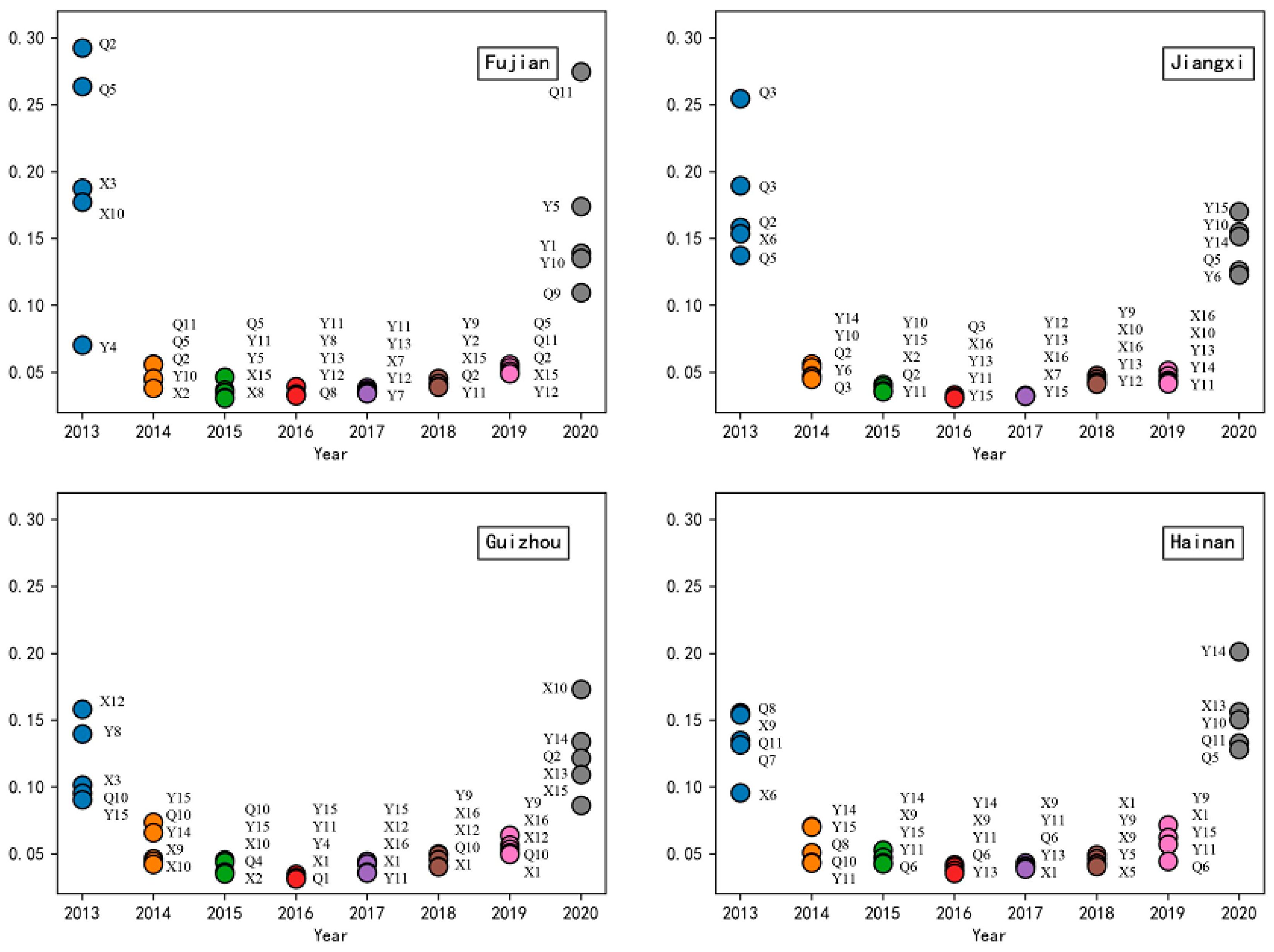
3.4. Obstacle Analysis
3.5. Countermeasures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Chen, X. An evaluation index system of China’s development level of ecological civilization. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.C.; Su, N.; Lun, F. An integrated indicator on regional ecological civilization construction. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buer, S.-V.; Fragapane, G.I.; Strandhagen, J.O. The Data-Driven Process Improvement Cycle: Using Digitalization for Continuous Improvement. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coto-Millán, P.; Fernández, X.L.; Pesquera, M.Á. Impact of logistics on technical efficiency of world production (2007–2012). Netw. Spat. Econ. 2016, 16, 981–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; You, J.; Haiyirete, X.; Zhang, T. Measuring logistics efficiency in China considering technology heterogeneity and carbon emission through a meta-frontier model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpak, N.; Kuzmin, O.; Dvulit, Z.; Sroka, W. Digitalization of the marketing activities of enterprises: Case study. Information 2020, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, L. Research on the efficiency and influencing factors of green logistics in my country’s three major bay area urban agglomerations under the constraint of carbon emissions. Railw. Transp. Econ. 2021, 502, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Frazzon, E.M.; Agostino, Í.R.S.; Broda, E.; Freitag, M. Manufacturing networks in the era of digital production and operations: A so-cio-cyber-physical perspective. Annu. Rev. Control 2020, 49, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.R.; Poist, R.F. Green perspectives and practices: A “comparative logistics” study. Supply Chain. Manag. 2003, 8, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.Y.; Yin, L.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z. Dynamic regulation of natural scenic area system from the perspective of ecological civilization. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2019, 35, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.; Wang, W.; Wu, J. To strengthen the practice of ecological civilization in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarc, R.; Curtis, A.; Kandlbauer, L.; Khodier, K.; Lorber, K.E.; Pomberger, R. Digitalisation and intelligent robotics in value chain of circular economy oriented waste management—A review. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 476–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Li, D.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.; Song, T.; Luo, S. Evaluation of the ecological civilization index of China based on the double benchmark progressive method. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, A.L.; Marks, D.; Sharma, R.; Shekhar, H.; Balmes, C.; Maheng, D.; Arshad, A.; Salehi, P. Assessing the potentials of digitalization as a tool for climate change adaptation and sustainable development in urban centres. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 58, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, W. How to coordinate economic, logistics and ecological environment? evidences from 30 Provinces and Cities in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, S.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Shao, H.; Wang, S. An evaluation method for green logistics system design of agricultural products: A case study in Shandong province, China. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 16878–16887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D. An empirical study of the factors influencing the willingness to implement green coal logistics in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 245, 118932–118958. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, X. Research on the Coupling Coordination Degree of Regional Logistics and Regional Economy. Railw. Transp. Econ. 2012, 383, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Beier, G.; Niehoff, S.; Ziems, T.; Xue, B. Sustainability aspects of a digitalized industry–A comparative study from China and Ger-many. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2017, 4, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Song, X. Analysis of the coupling degree between urbanization and ecological environment in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2005, 1, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, X.; Han, Z. Research on the Coupling Coordination Degree of Logistics Industry and Regional Economy—Taking Suzhou as an Example. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2013, 29, 1137–1140, 1172. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.; Tang, H.; Li, K.; Chu, D. Analysis of Coupling Coordination Degree of Transportation, Logistics Industry and Tourism Development—Taking Wuhan City as an Example. Traffic Inf. Secur. 2021, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- D’Amico, G.; Szopik-Depczyńska, K.; Dembińska, I.; Ioppolo, G. Smart and sustainable logistics of Port cities: A framework for com-prehending enabling factors, domains and goals. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buer, S.-V.; Strandhagen, J.O.; Chan, F.T.S. The link between Industry 4.0 and lean manufacturing: Mapping current research and establishing a research agenda. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 2924–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, S. Comprehensive evaluation and spatial differentiation of China’s ecological civilization con-struction level. East China Econ. Manag. 2015, 29, 52–56, 146. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, F.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Z. How to Evaluate Provincial Ecological Civilization Construction? The Case of Jiangsu Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhou, X.; Huang, C. Research on the coupling and coordination relationship between industrial structure optimization and ecological civilization construction in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. J. Cent. China Norm. Univ. 2020, 54, 555–566. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, W.; Xu, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, R. Evaluation of the logistics development level of the Silk Road Economic Belt based on PCA and RSC. J. East China Jiaotong Univ. 2015, 32, 132–142. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, Z.; Zeng, G.; Shang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhu, F. Evaluation methods and spatial pattern evolution of China’s provincial ecological civilization construction. Econ. Geogr. 2016, 36, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Yin, C. The impact of high-quality development on the level of industrial ecologicalization and regional differences: Based on the dynamic spatial panel Dubin model. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 37, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Qin, W.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Du, Y. Evaluation system and level measurement of marine ecological civilization construction in coastal cities in China. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Markovits-Somogyi, R.; Bokor, Z. Assessing the logistics efficiency of European countries by using the DEA-PC methodology. Transport 2014, 29, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, W.; Yao, W.; Liu, Z. Evaluation of the impact of logistics industry on regional economic vitality from the perspective of national logistics hub construction. Logist. Technol. 2020, 39, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Riezebos, J.; Klingenberg, W.; Hicks, C. Lean Production and Information Technology: Connection or Contradiction? Comput. Ind. 2009, 60, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, C.; Mendes, L. IT in lean-based manufacturing industries: Systematic literature review and research issues. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 7524–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brintrup, A.; Ranasinghe, D.; McFarlane, D. RFID Opportunity Analysis for Leaner Manufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2010, 48, 2745–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.; Yao, W.; Huang, S. Evaluation of Green Logistics Efficiency in Jiangxi Province Based on Three-Stage DEA from the Perspective of High-Quality Development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, Z. Construction and Measurement of my country’s Digital Economy Evaluation System from the Perspective of Supply and Demand. Bus. Econ. Res. 2021, 827, 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Yi, P. Assessment of city sustainability—Coupling coordinated development among economy, society and environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Lin, M.S. Study on the Coupling and Coordination Degree of High-Quality Economic Development and Ecological Environmet in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 11069–11083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Guo, Q. The Interactive Relationships between the Tourism-Transportation-Ecological Environment System of Provinces along the ‘Silk Road Economic Belt’in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Longwu, L.; Zhenbo, W.; Liangkan, C.; Faming, Z. Exploration of coupling effects in the economy—Society—Environment system in urban areas: Case study of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 128, 107858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yu, G.; Qi, Z. Research on the Coordinated Development of Agriculture “Ecology-Economy-Service” in Northwest Arid Areas. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 38, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, J.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Li, P.; Ye, G. Spatiotemporal coupling coordination measurement on islands’ economy-environment-tourism system. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, 212, 105793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J. Tourism-Urbanization-Ecological Environment Coupling Coordination and Development Types—Taking the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region as an Example. J. Shaanxi Norm. Univ. 2016, 44, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Chen, X.; Pang, J.; Wang, N.; Yu, Y. Study on the Coupling and Coordinated Development of Urbanization-Ecological Environment-Tourism Industry—A Case Study of Nine Provinces (Regions and Cities) in the Silk Road Economic Belt. J. Lanzhou Univ. 2018, 54, 762–769. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C. Quantitative Evaluation and Classification System of Coordinated Development of Environment and Econo-my—Taking the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration as an Example. Trop. Geogr. 1999, 2, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
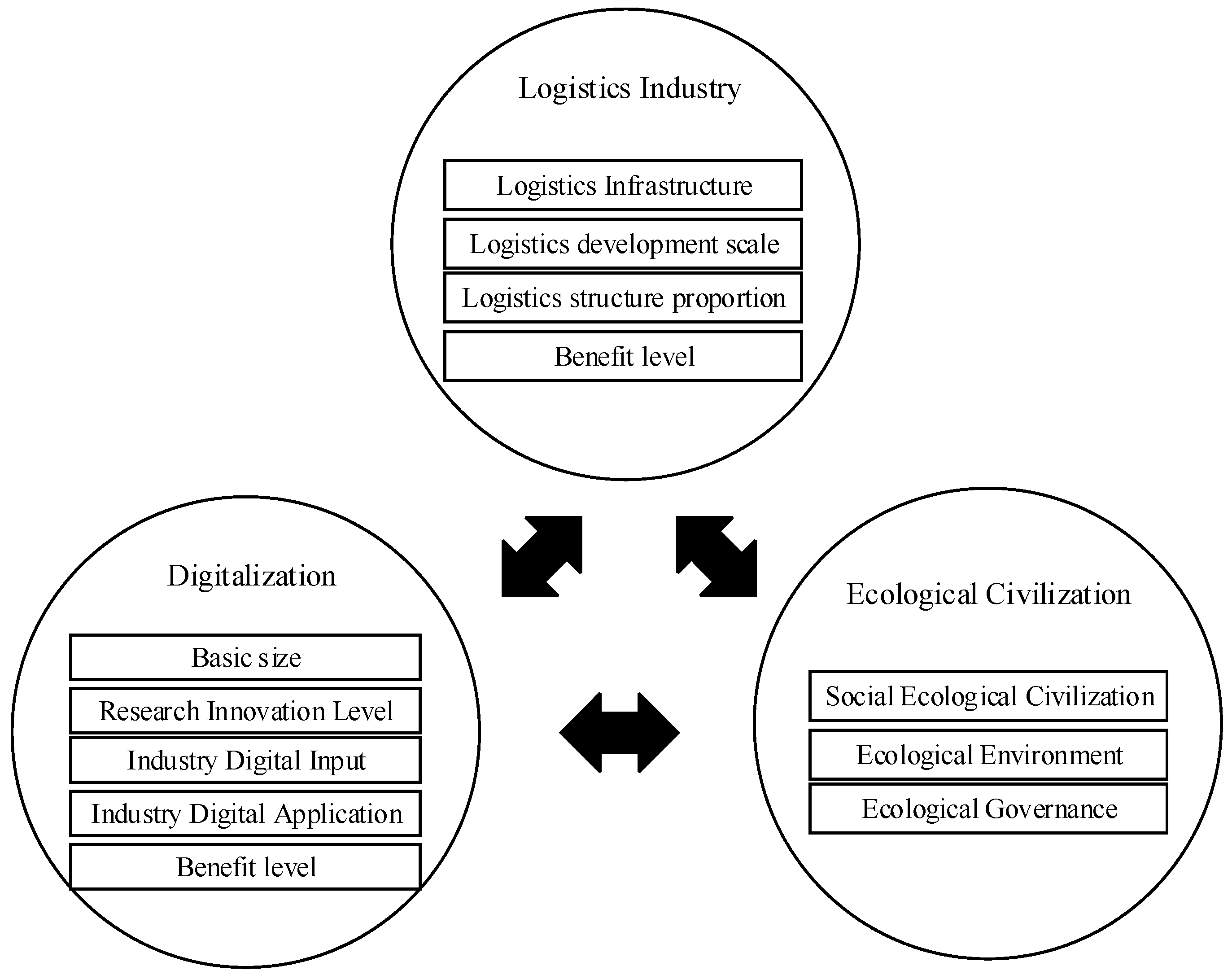
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Unit | Criterion Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ) | Logistics Infrastructure | Number of postal outlets (Y1) | Number | + |
| Truck ownership (Y2) | Vehicles | + | ||
| Transportation route length (Y3) | 10,000 km | + | ||
| Scale of logistics development | Transportation, storage, and post and telecommunications urban unit employment (Y4) | 10,000 people | + | |
| Transportation, storage and postal industry GDP (Y5) | Billions of dollars | + | ||
| Total fixed asset investment in transportation, storage, and postal industry (Y6) | Billions of dollars | + | ||
| Value added of tertiary industry (Y7) | Billions of dollars | + | ||
| Industry Structure | Tertiary industry share (Y8) | % | + | |
| Post and telecommunications business volume (Y9) | Billions of dollars | + | ||
| Transportation, storage, and postal industry GDP share (Y10) | % | + | ||
| Transportation land area (Y11) | Thousands of hectares | + | ||
| Benefit Levels | Express business revenue (Y12) | Billions of dollars | + | |
| Express business volume (Y13) | 10,000 pieces | + | ||
| Freight volume (Y14) | 10,000 t | + | ||
| Freight turnover (Y15) | billion-ton kilometers | + | ||
| ) | Digital Scale | Internet users (X1) | 10,000 households | + |
| Computers per 100 people (X2) | Platform | + | ||
| Cell phone users (X3) | 10,000 households | + | ||
| Cell phone base stations (X4) | Ten thousand | + | ||
| Digital Innovations | Total Patent Applications (X5) | Pieces | + | |
| Total Patent Applications (X6) | 10,000 copies | + | ||
| Internal expenditure on R&D expenses (X7) | Billions of dollars | + | ||
| Digital Governance | Number of computers in use at the end of the year (X8) | Platform | + | |
| Number of corporate owned websites (X9) | Number | + | ||
| E-commerce purchases (X10) | Billions of dollars | + | ||
| Number of enterprises with e-commerce trading activities (X11) | Number | + | ||
| Digital Industries | Websites per 100 companies (X12) | Number | + | |
| A proportion of e-commerce transaction activities (X13) | % | + | ||
| Benefit Levels | Regional GDP (X14) | Billions of dollars | + | |
| E-commerce sales (X15) | Billions of dollars | + | ||
| ) | Socio-Ecological Civilization | Urbanization rate (Q1) | % | + |
| Natural population growth rate (Q2) | ‰ | − | ||
| City Population Density (Q3) | People/km2 | − | ||
| Ecological Environment | Forest cover (Q4) | % | + | |
| Water Resources (Q5) | Billion cubic meters | + | ||
| Urban green space coverage (Q6) | hectares | + | ||
| Ecological Governance | Urban sewage rate (Q7) | % | + | |
| Total energy consumption (Q8) | 10,000 t of standard coal | − | ||
| Total energy production (Q9) | 10,000 t of standard coal | + | ||
| CO2 emissions (Q10) | Tons of CO2 | − | ||
| General industrial solid waste comprehensive utilization rate (Q11) | 10,000 t | + | ||
| Harmless disposal rate of domestic waste (Q12) | % | + |
| Coupling coordination | 0–0.09 | 0.1–0.19 | 0.2–0.29 | 0.3–0.39 | 0.4–0.49 |
| Coordination Levels | Extreme Disorder | Severe Disorder | Moderate Disorder | Mild Disorder | Near Disorder |
| Coupling coordination | 0.5–0.59 | 0.6–0.69 | 0.7–0.79 | 0.8–0.89 | 0.9–1.0 |
| Coordination Levels | Barely coordinated | Primary coordination | Intermediate coordination | Good coordination | Quality coordination |
| Relationship between U1, U2, U3 | Type of System Development | Symbols | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics Priority | Type of logistics industry priority and ecological civilization lagging | IA | |
| Type of logistics industry priority and industry digital lagging | IB | ||
| Industry Digital Priority | Type of industry digital priority and ecological civilization lagging | IIA | |
| Type of industry digital priority and logistics industry lagging | IIB | ||
| Ecological civilization priority type | Type of ecological civilization priority and logistics industry lagging | IIIA | |
| Type of ecological civilization priority and industry digital lagging | IIIB | ||
| Province | Year | U1 | U2 | U3 | D | Contrast | Coordination Level | Coordination Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fujian | 2013 | 0.0662 | 0.2466 | 0.3439 | 0.4216 | Near Disorder | IIIA | |
| 2014 | 0.1868 | 0.2484 | 0.2547 | 0.4772 | Near Disorder | IIIB | ||
| 2015 | 0.3418 | 0.3213 | 0.2988 | 0.5658 | Barely coordinated | IA | ||
| 2016 | 0.4205 | 0.3920 | 0.4145 | 0.6394 | Primary coordination | IB | ||
| 2017 | 0.5489 | 0.4695 | 0.3591 | 0.6726 | Primary coordination | IA | ||
| 2018 | 0.5846 | 0.5970 | 0.5999 | 0.7706 | Intermediate coordination | IIIA | ||
| 2019 | 0.6472 | 0.6666 | 0.6715 | 0.8134 | Good coordination | IIIA | ||
| 2020 | 0.8312 | 0.8639 | 0.6603 | 0.8830 | Good coordination | IIA | ||
| Jiangxi | 2013 | 0.1049 | 0.0604 | 0.4117 | 0.3710 | Mild Disorder | IIIB | |
| 2014 | 0.1763 | 0.2013 | 0.4030 | 0.4927 | Near Disorder | IIIB | ||
| 2015 | 0.2251 | 0.3310 | 0.5570 | 0.5884 | Barely coordinated | IIIA | ||
| 2016 | 0.2981 | 0.4095 | 0.3945 | 0.6032 | Primary coordination | IIB | ||
| 2017 | 0.3994 | 0.4633 | 0.4689 | 0.6653 | Primary coordination | IIIA | ||
| 2018 | 0.4740 | 0.6542 | 0.4488 | 0.7199 | Intermediate coordination | IIA | ||
| 2019 | 0.6261 | 0.7835 | 0.5998 | 0.8155 | Good coordination | IIA | ||
| 2020 | 0.8545 | 0.9051 | 0.7412 | 0.9114 | Quality coordination | IIA | ||
| Guizhou | 2013 | 0.2151 | 0.0433 | 0.2294 | 0.3588 | Mild Disorder | IB | |
| 2014 | 0.2691 | 0.2411 | 0.3962 | 0.5432 | Barely coordinated | IIIB | ||
| 2015 | 0.2922 | 0.2750 | 0.4929 | 0.5839 | Barely coordinated | IIIB | ||
| 2016 | 0.2548 | 0.3127 | 0.4405 | 0.5722 | Barely coordinated | IIIA | ||
| 2017 | 0.3762 | 0.6189 | 0.4318 | 0.6819 | Primary coordination | IIB | ||
| 2018 | 0.5346 | 0.6979 | 0.6016 | 0.7796 | Intermediate coordination | IIB | ||
| 2019 | 0.5998 | 0.7513 | 0.5981 | 0.8037 | Good coordination | IIA | ||
| 2020 | 0.7550 | 0.8301 | 0.7853 | 0.8885 | Good coordination | IIB | ||
| Hainan | 2013 | 0.0916 | 0.0581 | 0.4551 | 0.3665 | Mild Disorder | IIIB | |
| 2014 | 0.1469 | 0.2017 | 0.4198 | 0.4814 | Near Disorder | IIIA | ||
| 2015 | 0.2155 | 0.2364 | 0.3634 | 0.5143 | Barely coordinated | IIIA | ||
| 2016 | 0.2635 | 0.2866 | 0.5109 | 0.5813 | Barely coordinated | IIIA | ||
| 2017 | 0.3734 | 0.3628 | 0.4672 | 0.6313 | Primary coordination | IIIA | ||
| 2018 | 0.4967 | 0.4284 | 0.4393 | 0.6737 | Primary coordination | IB | ||
| 2019 | 0.6118 | 0.4836 | 0.4098 | 0.7035 | Intermediate coordination | IA | ||
| 2020 | 0.9271 | 0.8670 | 0.7267 | 0.9143 | Quality coordination | IA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, W.; Yao, W.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y. A Study on the Coupled and Coordinated Development of the Logistics Industry, Digitalization, and Ecological Civilization in Chinese Regions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6390. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116390
Gan W, Yao W, Huang S, Liu Y. A Study on the Coupled and Coordinated Development of the Logistics Industry, Digitalization, and Ecological Civilization in Chinese Regions. Sustainability. 2022; 14(11):6390. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116390
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Weihua, Wenpei Yao, Shuying Huang, and Yanan Liu. 2022. "A Study on the Coupled and Coordinated Development of the Logistics Industry, Digitalization, and Ecological Civilization in Chinese Regions" Sustainability 14, no. 11: 6390. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116390
APA StyleGan, W., Yao, W., Huang, S., & Liu, Y. (2022). A Study on the Coupled and Coordinated Development of the Logistics Industry, Digitalization, and Ecological Civilization in Chinese Regions. Sustainability, 14(11), 6390. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116390






