Influence Paths and Spillover Effects of Agricultural Agglomeration on Agricultural Green Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Research Motivation
1.2. Literature Review and Contribution
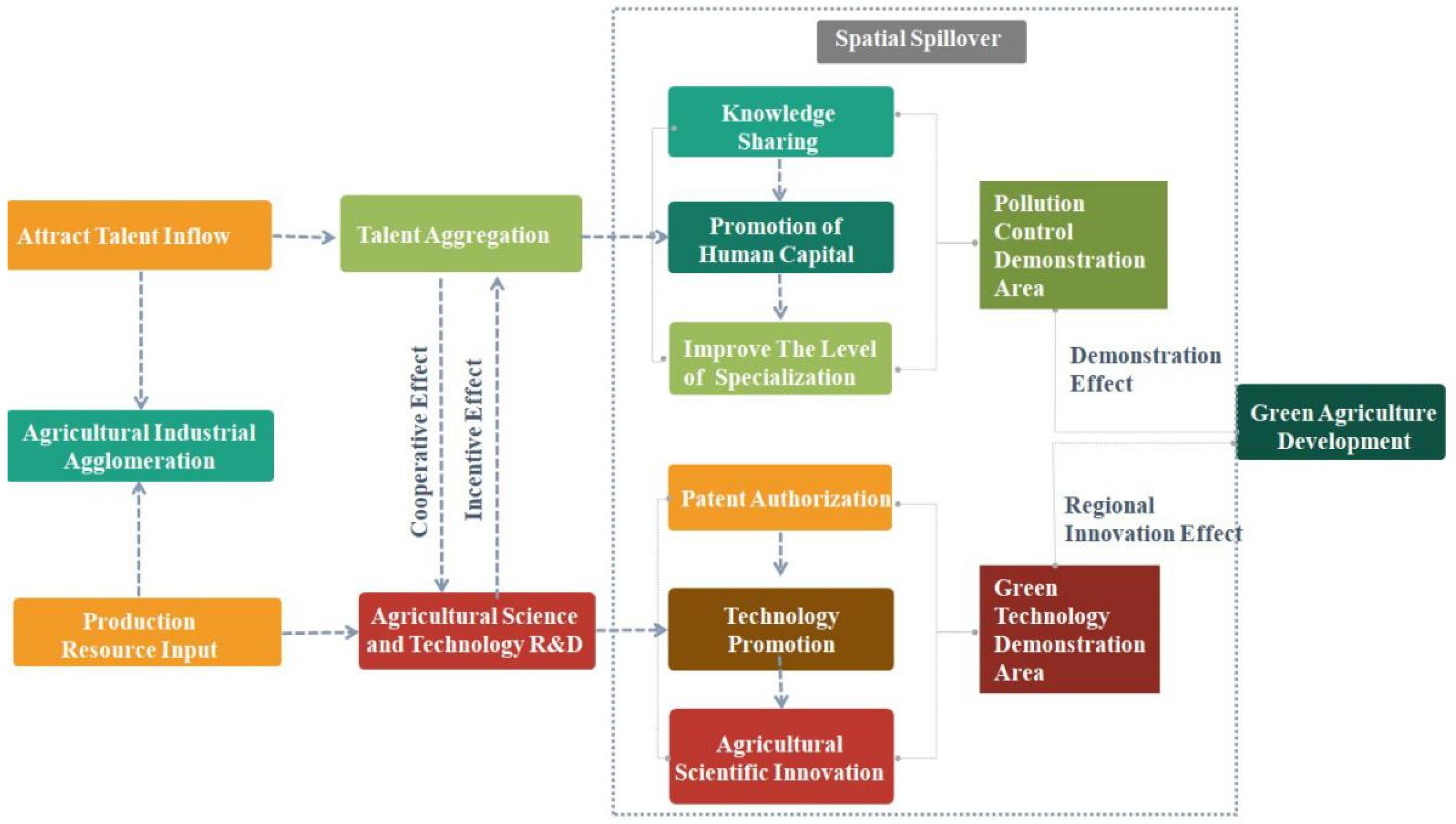
2. Theoretical Analysis
2.1. Positive Effect Mechanism of AIG on AGD
2.2. Negative Effect Mechanism of AIG on AGD
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Base Regression Model
3.2. Spatial Analysis Method
3.3. Mediation Models
3.4. Data Source and Description
4. Empirical Results and Discussion
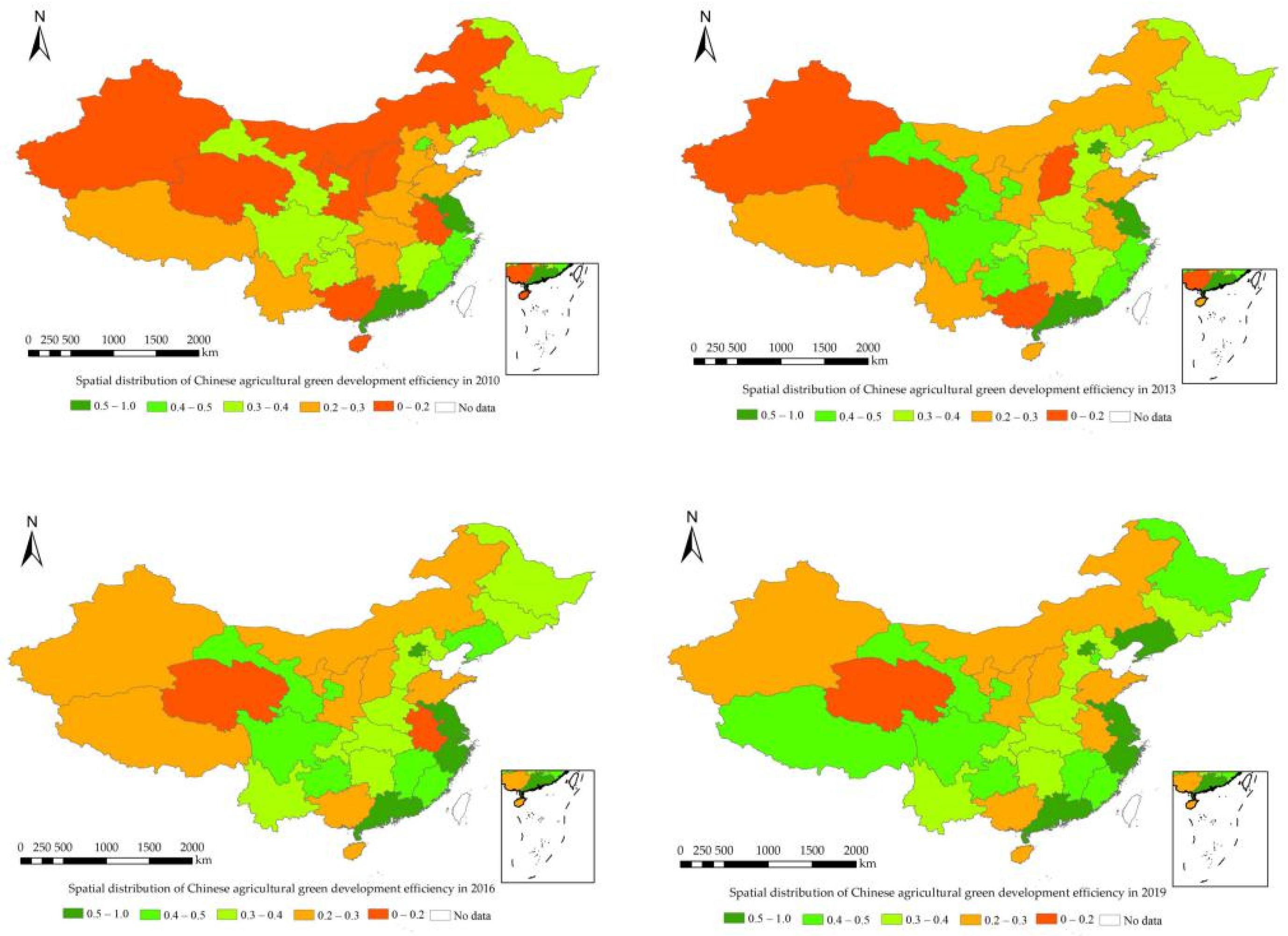
4.1. Calculation of AGD Level
4.2. Spatial Autocorrelation and Estimation Results
4.3. Analysis of Spatial Spillover Results
4.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
5. Test of the Mediation Models
6. Conclusions and Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, W.; Jin, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y. Impact of cultivated land fragmentation on spatial heterogeneity of agricultural agglomeration in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 1571–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, H. Green Agricultural Development Based on Information Communication Technology and the Panel Space Measurement Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Xu, S.; Pan, C. Measurement of the Spatial Complexity and Its Influencing Factors of Agricultural Green Development in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zeng, Y. Impact of Agricultural Industry Agglomeration on Income Growth: Spatial Effects and Clustering Differences. Transform. Bus. Econ. 2020, 19, 486–507. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/353902990 (accessed on 26 October 2021).
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Song, J. Analysis of the Threshold Effect of Agricultural Industrial Agglomeration and Industrial Structure Upgrading on Sustainable Agricultural Development in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tong, L.; Mei, L. The effect of industrial agglomeration on green development efficiency in Northeast China since the revitalization. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, F.; Li, J. A Win–Win Scenario for Agricultural Green Development and Farmers’ Agricultural Income: An Empirical Analysis Based on the EKC Hypothesis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Tong, L.-J.; Li, X.; Li, J.-L.; Sun, Z. Assessment of Spatial Agglomeration of Agricultural Drought Disaster in China from 1978 to 2016. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Coates, K.; Li, X.; Ye, X.; Leipnik, M. Analyzing Agricultural Agglomeration in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanter, D.R.; Musumba, M.; Wood, S.L.R.; Palm, C.; Antle, J.; Balvanera, P.; Dale, V.H.; Havlik, P.; Kline, K.L.; Scholes, R.J.; et al. Evaluating agricultural trade-offs in the age of sustainable development. Agric. Syst. 2018, 163, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, F.; Vergamini, D. Understanding the Spatial Agglomeration of Participation in Agri-Environmental Schemes: The Case of the Tuscany Region. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, Y.; Tan, H.; Hui, S. Ash-related issues during biomass combustion: Alkali-induced slagging, silicate melt-induced slagging (ash fusion), agglomeration, corrosion, ash utilization, and related countermeasures. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2016, 52, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wu, J. Spatial Dependence Evaluation of Agricultural Technical Efficiency—Based on the Stochastic Frontier and Spatial Econometric Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firbank, L.G. Towards the sustainable intensification of agriculture—A systems approach to policy formulation. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergius, M.; Benjaminsen, T.A.; Widgren, M. Green economy, Scandinavian investments and agricultural modernization in Tanzania. J. Peasant Stud. 2018, 45, 825–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Calker, K.J.; Berentsen, P.B.M.; Romero, C.; Giesen, G.W.J.; Huirne, R.B.M. Development and application of a multi-attribute sustainability function for Dutch dairy farming systems. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 57, 640–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Yu, L. Do China’s Modern Agricultural Demonstration Zones work? Evidence from agricultural products processing companies. Appl. Econ. 2022, 2030044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.; Parkhurst, G.; Droppelmann, K.; Benton, T.G. Scaling up pro-environmental agricultural practice using agglomeration payments: Proof of concept from an agent-based model. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 126, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Miao, J.; Zhu, Z. Measuring green total factor productivity of China’s agricultural sector: A three-stage SBM-DEA model with non-point source pollution and CO2 emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apergis, N.; Aye, G.C.; Barros, C.P.; Gupta, R.; Wanke, P. Energy efficiency of selected OECD countries: A slacks based model with undesirable outputs. Energy Econ. 2015, 51, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, W.; Wang, J. Evaluation and Influencing Factors of China’s Agricultural Productivity from the Perspective of Environmental Constraints. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Xia, X. Measurement and spatial convergence analysis of China’s agricultural green development index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19694–19709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y. Influence of Agricultural Mechanization Development on Agricultural Green Transformation in Western China, Based on the ML Index and Spatial Panel Model. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 6351802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, F.; Hao, R.; Wu, L. Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation, Spatial Spillover and Agricultural Green Development—Taking 30 Provinces in China as the Research Object. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, L.H.; Le, T.-H. Eatery, energy, environment and economic system, 1970–2017: Understanding volatility spillover patterns in a global sample. Energy Econ. 2021, 100, 105391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qi, Z.; Pang, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Sun, Y. Analysis on the Agricultural Green Production Efficiency and Driving Factors of Urban Agglomerations in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. Sustainability 2021, 13, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, G.; Deaton, B.J. Agglomeration Effects in Ontario’s Dairy Farming. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2016, 98, 1055–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ge, Z.; Han, S.; Xing, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. Impacts of agricultural industrial agglomeration on China’s agricultural energy efficiency: A spatial econometrics analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Routray, J.K. Operational Indicators for Measuring Agricultural Sustainability in Developing Countries. Environ. Manag. 2003, 32, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, D.-Z.; Zhao, L. Pollution havens and industrial agglomeration. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2009, 58, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, W. The path of improving the value chain flow of agricultural products industry under the effect of technology agglomeration. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2021, 71, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, X. Application and Comparison of Multiple Models on Agricultural Sustainability Assessments: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mishra, A.K.; Zhu, P.; Li, X. Land rental market and agricultural labor productivity in rural China: A mediation analysis. World Dev. 2020, 135, 105089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shi, A.; Wang, X. Carbon emission curbing effects and influencing mechanisms of China’s Emission Trading Scheme: The mediating roles of technique effect, composition effect and allocation effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ren, T.; Wu, H.; Xiao, Y. Housing price, talent movement, and innovation output: Evidence from Chinese cities. Rev. Dev. Econ. 2021, 25, 76–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y. China’s agricultural green total factor productivity based on carbon emission: An analysis of evolution trend and influencing factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorosh, P.; Thurlow, J. Agglomeration, Growth and Regional Equity: An Analysis of Agriculture- versus Urban-led Development in Uganda. J. Afr. Econ. 2012, 21, 94–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adewuyi, A.O. Determinants of import demand for non-renewable energy (petroleum) products: Empirical evidence from Nigeria. Energy Policy 2016, 95, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Tang, A.; Shen, J.; Cui, Z.; Vitousek, P.; Erisman, J.W.; Goulding, K.; Christie, P.; et al. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 2013, 494, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, W.J.; Shen, J. Reducing the environmental footprint of food and farming with Agriculture Green Development. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coluccia, B.; Valente, D.; Fusco, G.; De Leo, F.; Porrini, D. Assessing agricultural eco-efficiency in Italian Regions. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, A.; Salhofer, K.; Scheichel, E. Land tenure, soil conservation, and farm performance: An eco-efficiency analysis of Austrian crop farms. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 180, 106861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.A. The Soil Health Card Scheme in India: Lessons Learned and Challenges for Replication in Other Developing Countries. J. Nat. Resour. Policy Res. 2019, 9, 124–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, P. It’s not just where you farm; it’s whether your neighbor does too. How agglomeration economies are shaping new agricultural landscapes. J. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 18, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type | Variables | Symbols | Definitions | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | The Efficiency of Green Agricultural Development | ADG | Based on the SBM-Undesirable model and considered about undesired output | [3,7,22,24] |
| Core Independent Variable | Agricultural Industrial Agglomeration | AIG | [5,28] | |
| Mediation Variables | Talent Aggregation | TA | Patents Granted Number (Ten Thousand) | [35] |
| Technological innovation | INNO | Undergraduate Students’ Number (Ten Thousand People) | [23,24,31] | |
| The Control Variables | Environmental Protection Investment Rate | EPI | Environmental Protection Financial Investment/Total Government | [3,7,22,36] |
| Industrialization | IND | The Proportion of Industrial Added Value in Its Regional GDP | [3,7,22,36] | |
| Agricultural Financial Investment Rate | GOV | Agricultural Financial Investment/Total Government Expenditure | [3,7,22,36] | |
| Disaster Damage Rate | DR | Disaster Damage Area/Total Sown Area | [3,7,22,36] | |
| Urbanization Rate | URB | Urban Population/Total Population | [3,7,22,36] |
| Variables | Min | Max | Mean | SE | Variables | Min | Max | Mean | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADG | 0.121 | 0.801 | 0.420 | 0.038 | IND | 0.263 | 0.435 | 0.379 | 0.082 |
| AIG | 0.005 | 1.714 | 1.143 | 0.583 | GOV | 0.026 | 0.051 | 0.089 | 0.028 |
| INNO | 2.723 | 8.803 | 6.243 | 1.266 | FR | 0.184 | 0.368 | 0.252 | 0.0636 |
| TA | 0.001 | 0.218 | 0.020 | 0.032 | URB | 0.139 | 0.896 | 0.519 | 0.144 |
| EPI | 0.026 | 0.051 | 0.089 | 0.028 |
| Space Weight Matrix | W1 | W2 | W3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| the efficiency of AGD | 0.331 ** | 0.059 *** | 0.157 * |
| AIG | 0.370 *** | 0.016 ** | 0.158 ** |
| Variable | W1 | W2 | W3 | Variable | W1 | W2 | W3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | ||
| AIG | −0.2813 *** (−0.0920) | −0.0974 (−0.0773) | −0.1438 ** (−0.4902) | W × AIG | −1.1324 *** (−0.3761) | −0.0508 (−0.0833) | −1.0667 ** (−0.4156) |
| AIG2 | 0.1932 * (0.1713) | 0.0803 (0.0539) | 0.0843 (0.0516) | W × AIG2 | 0.2842 ** (0.1838) | 0.2631** (0.1371) | 0.2450 ** (0.1256) |
| EPI | 0.5286 *** (0.5312) | 0.3078 * (0.4530) | 0.2788 * (0.4711) | W × EPI | 0.4491 *** (0.8365) | 0.4027 ** (0.6828) | 0.2056 * (0.4240) |
| IND | −1.1305 *** (−1.0004) | −0.6328 (−0.0679) | −0.8321 * (0.0792) | W × IND | −1.1532 *** (−1.0039) | −1.0073 ** (−0.8951) | −0.8955 ** (−0.6982) |
| GOV | −0.1974 * (−0.1357) | −0.0420 (−0.0836) | −0.2871 * (−0.1896) | W × GOV | −0.0426 (−0.0722) | −0.0313 (−0.0409) | −0.0372 (−0.0420) |
| DR | −0.1774 ** (−2.4091) | −0.0562 (−1.0553) | −0.0079 (−0.0422) | W × DR | −0.3682 *** (−2.1192) | −0.0301 (−0.8256) | −0.0067 (−0.0041) |
| URB | 0.7436 *** (0.3389) | 0.7192 *** (0.3075) | 0.0672 (0.0048) | W × URB | −0.8651 ** (−0.6672) | −0.8934 *** (−0.6792) | −0.6815 ** (−0.5902) |
| λ | −0.2067 *** (0.0892) | −0.1266 ** (0.674) | −0.2098 *** (0.0896) | 0.0067 | 0.0944 | 0.0023 | |
| 34.31 *** | 32.11 *** | 33.96 *** | LM – error | 33.67 *** | 28.16 ** | 31.95 ** | |
| RobustLM – lag | 3.81 ** | 3.54 ** | 3.91 *** | LR_Spatial_error | 3.07 * | 2.93 * | 3.11 * |
| LR_Spatial_lag | 84.29 *** | 85.12 *** | 83.98 *** | RobustLM – error | 83.23 *** | 78.23 ** | 89.04 *** |
| Wald_Spatial_lag | 91.28 *** | 89.77 *** | 90.26 *** | 90.32 *** | 88.54 *** | 90.21 *** | |
| Observations | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 |
| Variable | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | W2 | W3 | W1 | W2 | W3 | W1 | W2 | W3 | |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| AIG | −0.3658 ** (−0.0263) | −0.0394 (−0.0193) | −0.4172 ** (−0.0832) | −0.7694 *** (−0.1944) | −0.0198 (−0.0042) | −0.6911 *** (−0.1859) | −1.1352 *** (−0.3761) | −0.0592 (−0.0833) | −1.1083 *** (−0.4156) |
| AIG2 | 0.1032 (0.0382) | 0.1026 (0.0331) | 0.0672 (0.0084) | 0.1769 ** (0.0527) | 0.1602 ** (0.0502) | 0.1765 ** (0.0520) | 0.2801 *** (0.1824) | 0.2628 *** (0.1326) | 0.2437 *** (0.1231) |
| EPI | 0.4201 *** (0.5425) | 0.3053 ** (0.3892) | 0.2717 ** (0.3085) | 0.2161 * (0.2993) | 0.2121 * (0.2816) | 0.1353 (0.2091) | 0.6362 *** (0.8321) | 0.5174 *** (0.6820) | 0.4071 *** (0.4393) |
| IND | −1.0435 ** (−0.8935) | −0.5592 * (−0.0509) | −0.4930 * (0.0492) | −0.1169 (−0.0037) | −0.5309 * (−0.0503) | −0.5992 * (−0.0547) | −1.1604 *** (−1.0531) | −1.0901 ** (−0.8890) | −1.0922 ** (−0.7102) |
| GOV | −0.0439 * (−0.0961) | −0.0432 * (−0.0878) | −0.0503 * (−0.1062) | −0.0157 (−0.0536) | 0.0138 (0.0382) | 0.0139 (0.0371) | −0.0596 * (−0.0722) | −0.0294 (−0.0382) | −0.0364 (−0.0417) |
| DR | −0.1801 ** (−0.8034) | −0.1921 ** (−0.8476) | −0.0035 (−0.0392) | −0.2292 ** (−1.2034) | −0.2711 ** (−1.2160) | −0.0037 (−0.0021) | −0.4093 *** (−2.1208) | −0.4632 *** (−0.8263) | −0.0072 (−0.0104) |
| URB | 0.7102 *** (0.4910) | 0.4212 ** (0.2015) | 0.7008 *** (0.4722) | −0.3321 ** (−0.1862) | −0.1510 (−0.0582) | −0.3217 ** (−0.1980) | 0.3781 ** (0.1804) | 0.2702 (0.1026) | 0.3791 ** (0.2083) |
| Variable | Eastern | Central | Western | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| AIG | 0.0209 (0.0331) | 0.2311 *** (0.0814) | 0.0412 (0.0309) | 0.2638 *** (0.0817) | 0.0982 (0.0633) | −0.0304 (0.0144) |
| AIG2 | −0.1374 *** (0.0441) | 0.2297 ** (0.0743) | 0.1615 *** (0.0581) | |||
| EPI | 0.0744 * (0.0683) | 0.0637 * (0.0597) | 0.0481 * (0.0361) | 0.0184 * (0.0214) | 0.1149 *** (0.0249) | 0.1045 ** (0.0502) |
| IND | −0.1733 ** (0.0892) | 0.2554 *** (0.0617) | −0.0469 * (0.0791) | −0.2336 *** (0.0569) | 0.1300 (0.1086) | −0.2371 (0.2293) |
| GOV | −0.0913 (0.0800) | 0.0635 (0.0431) | −0.5032 ** (0.0489) | 0.0658 *** (0.0257) | −0.0894 * (0.0539) | −0.0792 (0.1218) |
| DR | 0.0100 (0.0120) | 0.0100 (0.0080) | −0.0258 ** (0.0113) | 0.0037 (0.0010) | −0.0700 *** (0.0182) | −0.0674 * (0.0336) |
| URB | −0.3389 *** (0.1145) | −0.3029 *** (0.0743) | 0.4121 *** (0.0739) | 0.2176 ** (0.0548) | −0.0285 (0.1369) | 0.0073 (0.1422) |
| _cons | −0.5561 * (0.564) | −0.5704 * (0.4912) | 0.2523 (0.4125) | 0.2271 (0.5367) | 0.2340 (0.3742) | −0.0864 (0.5547) |
| R-squared | 0.0905 | 0.1681 | 0.2701 | 0.2194 | 0.2944 | 0.2352 |
| Time Fixation | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Regional Fixation | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 132 | 132 | 99 | 99 | 110 | 110 |
| Variables | ADG | ADG | TA | ADG | ADG | INNO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| AIG | 0.0576 (0.0522) | 0.0643 (0.1148) | 0.1950 ** (0.1793) | 0.0305 (0.0165) | 0.0354 (0.0273) | 0.1433 * (0.0455) |
| EPI | 0.3154 * (8.5297) | 0.4378 ** (7.3908) | 0.5637 *** (8.9144) | 0.3611 * (8.7026) | ||
| IND | 0.3776 *** (0.0576) | −0.0697 (−0.0311) | 0.0728 ** (0.0302) | 0.4525 *** (0.0553) | ||
| FR | 0.3121 (0.4568) | 0.1290 ** (0.0802) | −0.0367 (−0.0141) | 0.6319 *** (0.1153) | ||
| URB | 0.3191 (0.4821) | 0.7290 *** (0.2857) | −0.0363 (−0.1368) | 0.6177 *** (0.1256) | ||
| GOV | 0.0392 (0.3371) | 0.5927 ** (0.2763) | −0.0310 (−0.3389) | 1.1464 *** (0.7833) | ||
| TA | 0.1371 *** (0.0215) | 0.0715 * (0.1902) | ||||
| INNO | 0.2159 *** (0.1069) | 0.3487 *** (0.0718) | ||||
| Constant | 2.0075 *** (0.1327) | −0.1893 (−0.5215) | 0.8756 * (0.4312) | 2.1957 *** (0.1673) | 1.3151 ** (0.6265) | −0.3276 ** (−0.8115) |
| Time Fixation | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES |
| Regional Fixation | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES |
| R-squared | 0.5962 | 0.2464 | 0.2417 | 0.8342 | 0.2740 | 0.2334 |
| N | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 | 341 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, P.; Jin, Z.; Tang, H. Influence Paths and Spillover Effects of Agricultural Agglomeration on Agricultural Green Development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106185
Xu P, Jin Z, Tang H. Influence Paths and Spillover Effects of Agricultural Agglomeration on Agricultural Green Development. Sustainability. 2022; 14(10):6185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106185
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Pei, Zehu Jin, and Huan Tang. 2022. "Influence Paths and Spillover Effects of Agricultural Agglomeration on Agricultural Green Development" Sustainability 14, no. 10: 6185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106185
APA StyleXu, P., Jin, Z., & Tang, H. (2022). Influence Paths and Spillover Effects of Agricultural Agglomeration on Agricultural Green Development. Sustainability, 14(10), 6185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106185





