Solution of Multi-Crew Depots Railway Crew Scheduling Problems: The Chinese High-Speed Railway Case
Abstract
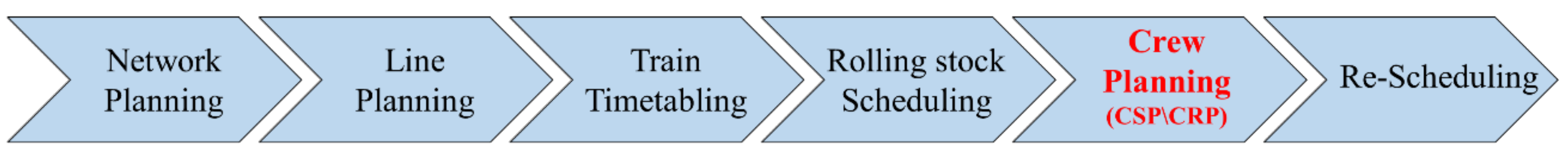
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Base Model Development
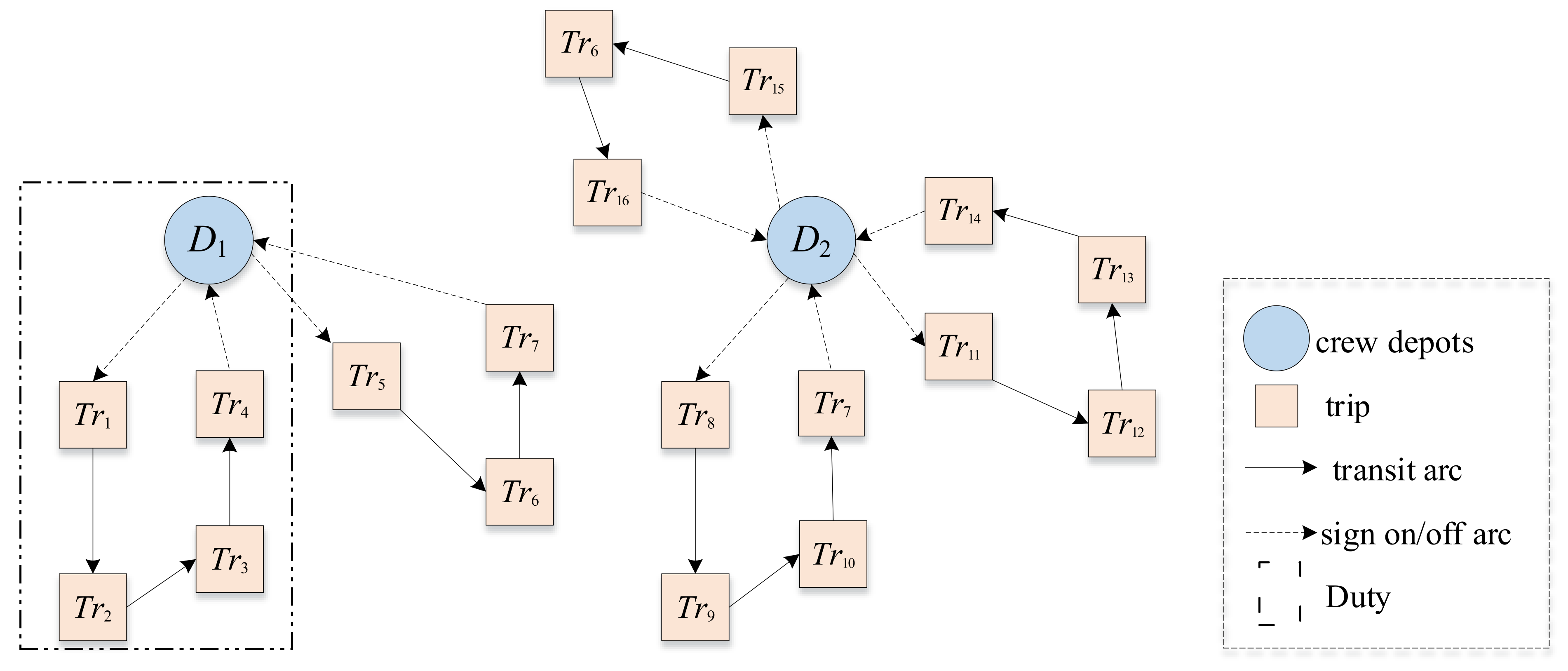
3.1. Problem Description and Assumption
3.2. Parameters, Decision Variables, and Notations
3.3. Mathematical Model
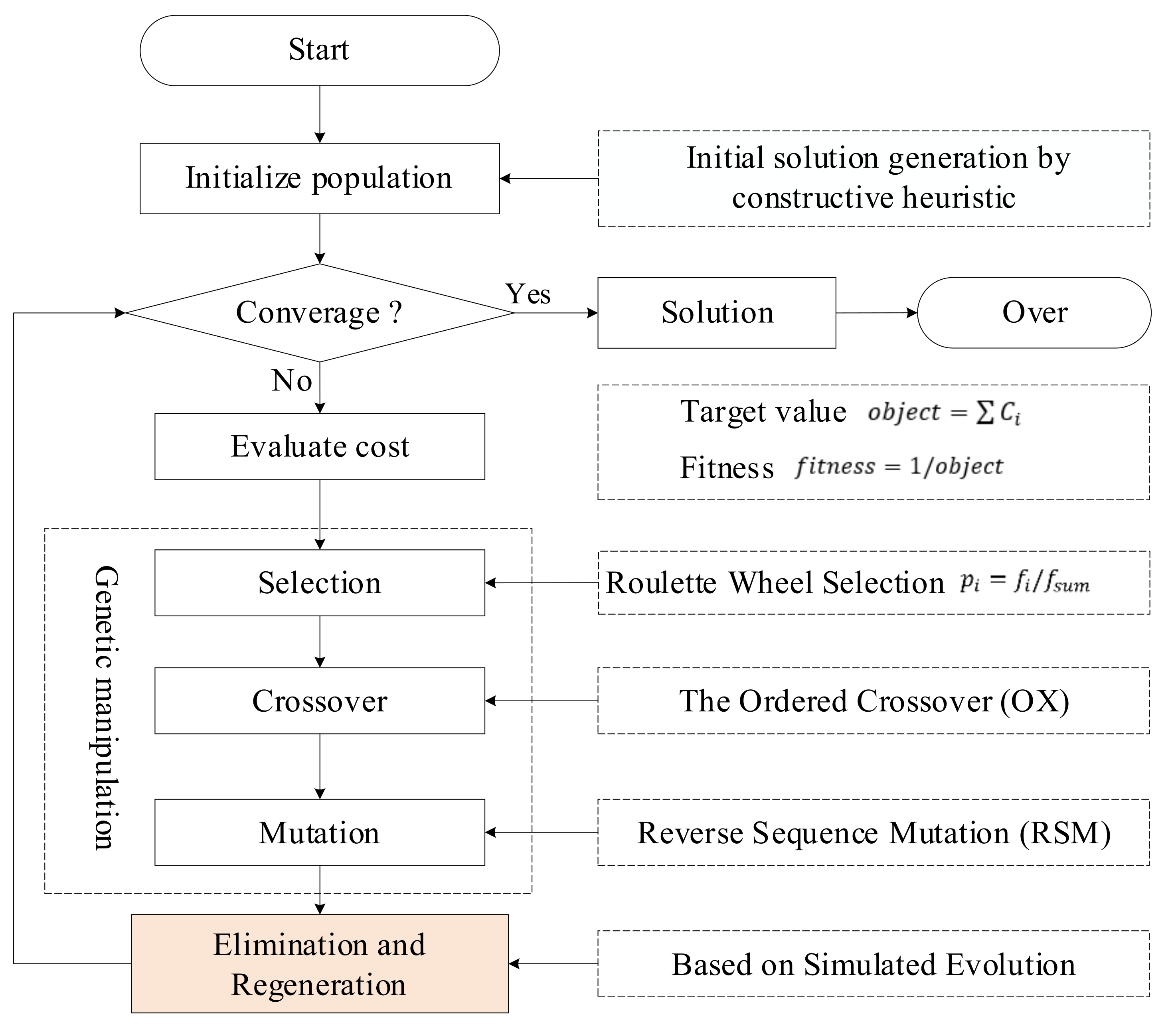
4. Solution Algorithm
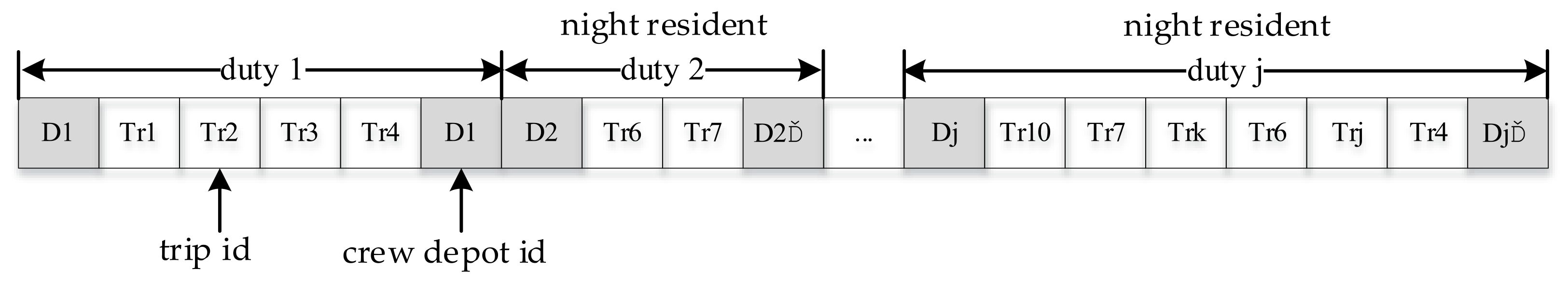
4.1. Representation and Fitness Function
4.2. Initial Population
4.3. Selection
4.4. Crossover
4.5. Mutation
4.6. Elimination and Regeneration
5. Case Study
5.1. Case Description
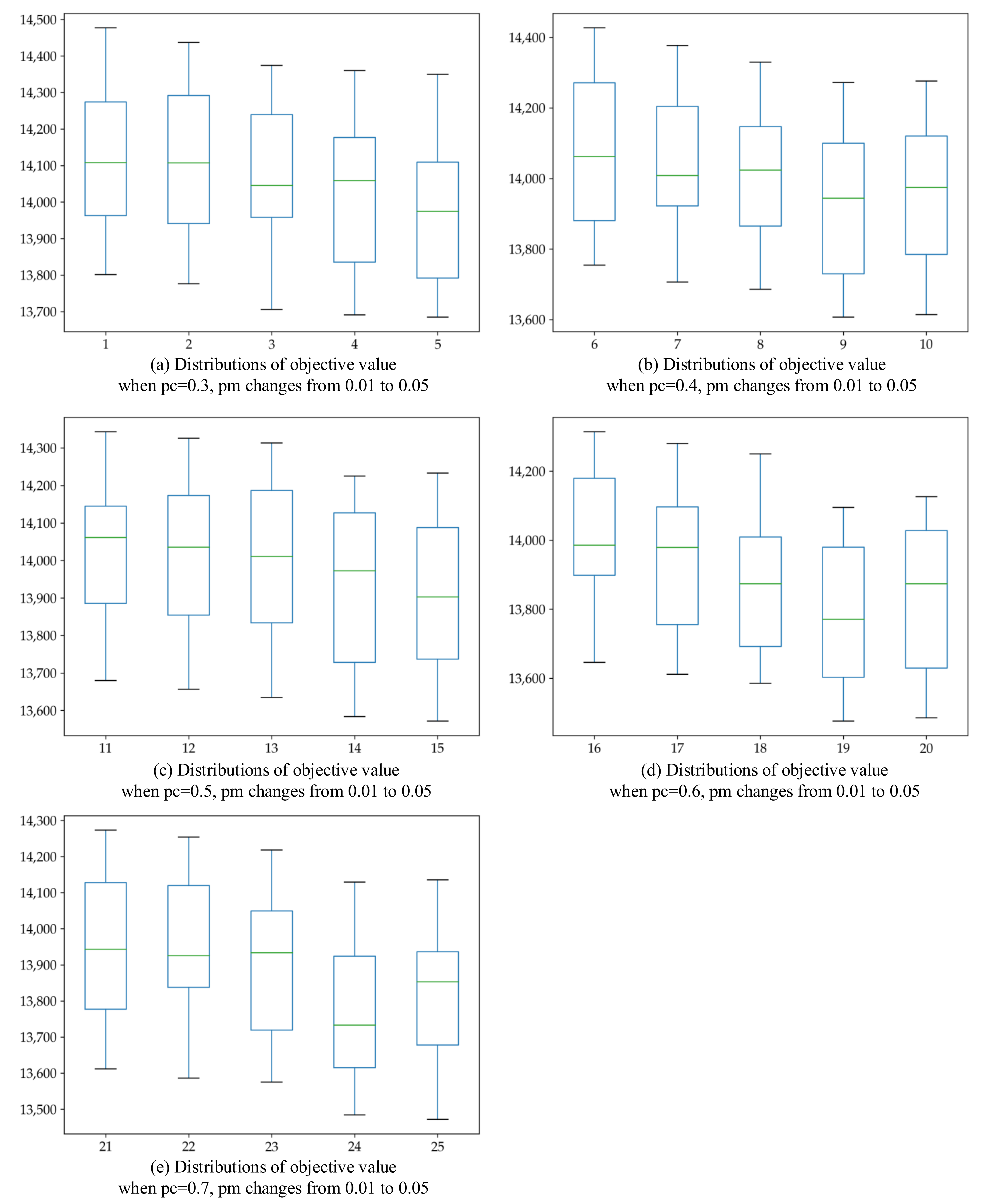
5.2. Parameter Tune and Performance Analysis
5.3. Results, Discussion, and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arabeyre, J.P.; Fearnley, J.; Steiger, F.C.; Teather, W. The Airline Crew Scheduling Problem: A Survey. Transp. Sci. 1969, 3, 140–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraresi, P.; Gallo, G. Network models for vehicle and crew scheduling. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1984, 16, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elms, J.M. The use of computers in bus and crew Scheduling by london buses and its predecessors: A user’s view. from the book computer-aided transit scheduling. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Workshop on Computer-Aided Scheduling of Public Transport, Hamburg, Germany, 28–31 July 1987; pp. 262–271. [Google Scholar]
- Sylvie, L.; Michel, M.; Edouard, O. A new approach for crew pairing problems by column generation with an application to air transportation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1988, 35, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Gershkoff, I. Optimizing Flight Crew Schedules. Interfaces 1989, 19, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.M.; Wren, A. A bus crew scheduling system using a set covering formulation. Transp. Res. Part A: Gen. 1988, 22, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DesRochers, M.; Soumis, F. A Column Generation Approach to the Urban Transit Crew Scheduling Problem. Transp. Sci. 1989, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lourenco, H.R.; Paixao, J.P.; Portugal, R. Multiobjective Metaheuristics for the Bus Driver Scheduling Problem. Transp. Sci. 2001, 35, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, M.; Demirel, N. Çetin A survey of the literature on airline crew scheduling. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 74, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, N.; Karisch, S.E. Airline Crew Rostering: Problem Types, Modeling, and Optimization. Ann. Oper. Res. 2004, 127, 223–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasirzadeh, A.; Saddoune, M.; Soumis, F. Airline crew scheduling: Models, algorithms, and data sets. EURO J. Transp. Logist. 2017, 6, 111–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, T.; Nishi, T.; Voß, S. Two-level decomposition-based matheuristic for airline crew rostering problems with fair working time. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 267, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şafak, Özge; Çavuş, Özlem; Akturk, S. Multi-stage airline scheduling problem with stochastic passenger demand and non-cruise times. Transp. Res. Part B: Methodol. 2018, 114, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Sun, X.; Sun, Y.; Yue, X. Airline crew scheduling: Models and algorithms. Transp. Res. Part E: Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 149, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprara, A.; Toth, P.; Vigo, D.; Fischetti, M. Modeling and Solving the Crew Rostering Problem. Oper. Res. 1998, 46, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgado, E.M.; Martins, J.P. Scheduling and managing crew in the Portuguese railways. Expert Syst. Appl. 1992, 5, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, J.; Hoffmann, K.; Buscher, U. Railway crew scheduling: Models, methods and applications. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 283, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprara, A.; Fischetti, M.; Toth, P.; Vigo, D.; Guida, P.L. Algorithms for railway crew management. Math. Program. 1997, 79, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mingozzi, A.; Boschetti, M.A.; Ricciardelli, S.; Bianco, L. A Set Partitioning Approach to the Crew Scheduling Problem. Oper. Res. 1999, 47, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanczar, P.; Zandi, A. A novel model and solution algorithm to improve crew scheduling in railway transportation: A real world case study. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 154, 107132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, N.; Minashina, I.; Ryabykh, N.; Zakharova, E.; Pashchenko, F. Design and Comparison of Freight Scheduling Algorithms for Intelligent Control Systems. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 98, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaidyanathan, B.; Jha, K.C.; Ahuja, R.K. Multicommodity network flow approach to the railroad crew-scheduling problem. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2007, 51, 325–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caprara, A. Timetabling and assignment problems in railway planning and integer multicommodity flow. Networks 2015, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprara, A.; Kroon, L.; Monaci, M.; Peeters, M.; Toth, P. Passenger Railway Optimization. Handb. Oper. Res. Manag. Sci. 2007, 14, 129–187. [Google Scholar]
- Cadarso, L.; Marín, A. Integration of timetable planning and rolling stock in rapid transit networks. Ann. Oper. Res. 2011, 199, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, L.; Corman, F.; Zhou, X.; Tang, T. Special issue on Integrated optimization models and algorithms in rail planning and control. Transp. Res. Part C: Emerg. Technol. 2018, 88, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, L.; Dollevoet, T.; Huisman, D. Integrating Timetabling and Crew Scheduling at a Freight Railway Operator. Transp. Sci. 2016, 50, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Long, J.; Ding, J. Integrated optimization approach to metro crew scheduling and rostering. Transp. Res. Part C: Emerg. Technol. [CrossRef]
- Huisman, D. A column generation approach for the rail crew re-scheduling problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 180, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veelenturf, L.P.; Potthoff, D.; Huisman, D.; Kroon, L.G. Railway crew rescheduling with retiming. Transp. Res. Part C: Emerg. Technol. 2012, 20, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, D.S.W.; Leung, J.M.Y. Real-time rescheduling and disruption management for public transit. Transp. B: Transp. Dyn. 2017, 6, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaghini, M.; Karimi, M.; Rahbar, M. A set covering approach for multi-depot train driver scheduling. J. Comb. Optim. 2015, 29, 636–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derigs, U.; Malcherek, D.; Schäfer, S. Supporting strategic crew management at passenger railways—model, method and system. Public Transp. 2010, 2, 307–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K.; Buscher, U. Valid inequalities for the arc flow formulation of the railway crew scheduling problem with attendance rates. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 127, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroi, Y.; Nishi, T.; Inuiguchi, M. Improvement of Column Generation Method for Railway Crew Scheduling Problems. IEEJ Trans. Electron. Inf. Syst. 2010, 130, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, S.; Su, X. Rail Crew Scheduling Based on a Pooling Mode for High Speed Passenger Lines. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Logistics Engineering and Intelligent Transportation Systems, Wuhan, China, 26–28 November 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Veelenturf, L.P.; Potthoff, D.; Huisman, D.; Kroon, L.G.; Maróti, G.; Wagelmans, A.P. A Quasi-Robust Optimization Approach for Crew Rescheduling. Transp. Sci. 2016, 50, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jütte, S.; Müller, D.; Thonemann, U.W. Optimizing railway crew schedules with fairness preferences. J. Sched. 2017, 20, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.D., Gelman. Solving large scale crew scheduling problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1997, 97, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shen, Y.; Su, X.; Chen, H. A Crew Scheduling with Chinese Meal Break Rules. J. Transp. Syst. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2013, 13, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y. An estimation of distribution algorithm for public transport driver scheduling. Oper. Res. 2017, 28, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L.; Liang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, S. A column generation-based approach for integrated vehicle and crew scheduling on a single metro line with the fully automatic operation system by partial supervision. Transp. Res. Part E: Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 152, 102406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, J.S.; Scheffler, M.; Tamke, F.; Hoffmann, K.; Buscher, U. An efficient column generation approach for practical railway crew scheduling with attendance rates. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 293, 1113–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel, F.; Luis, C.; Ángel, M. A hybrid model for crew scheduling in rail rapid transit networks. Transp. Res. Part B: Methodol. 2019, 125, 248–265. [Google Scholar]
- Elizondo, R.; Parada, V.; Pradenas, L.; Artigues, C. An evolutionary and constructive approach to a crew scheduling problem in underground passenger transport. J. Heuristics 2009, 16, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwan, R.S.K. Case studies of successful train crew scheduling optimisation. J. Sched. 2011, 14, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K. A Hybrid Solution Approach for Railway Crew Scheduling Problems with Attendance Rates. In Operations Research Proceedings; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fraszczyk, A.; Marinov, M. Sustainable Rail Transport; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, A.; Kuo, A.; Si, X. Real-Time Decision Support for Crew Assignment in Double-Ended Districts for U.S. Freight Railways. Transp. Sci. 2016, 50, 1337–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, H.J. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems: An Introductory Analysis with Applications to Biology, Control, and Artificial Intelligence; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, C.R. Modern Heuristic Techniques for Combinatorial Problems; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Guan, W.; Ma, J.; Liu, T. Improved Genetic Algorithm with Gene Recombination for Bus Crew-Scheduling Problem. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 719409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escobar, Z.A.H.; Gallego, R.R.A.; Romero, L.R.A. Using traditional heuristic algo-algorithms on an initial genetic algo- rithms algorithm population applied to the rithm transmission expansion planning problem. Ing. Investig. 2011, 31, 127–423. [Google Scholar]
- Abdoun, O.; Abouchabaka, J. A Comparative Study of Adaptive Crossover Operators for Genetic Algorithms to Resolve the Traveling Salesman Problem. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1203.3097. [Google Scholar]
- Beasley, J.; Chu, P. A genetic algorithm for the set covering problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1996, 94, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
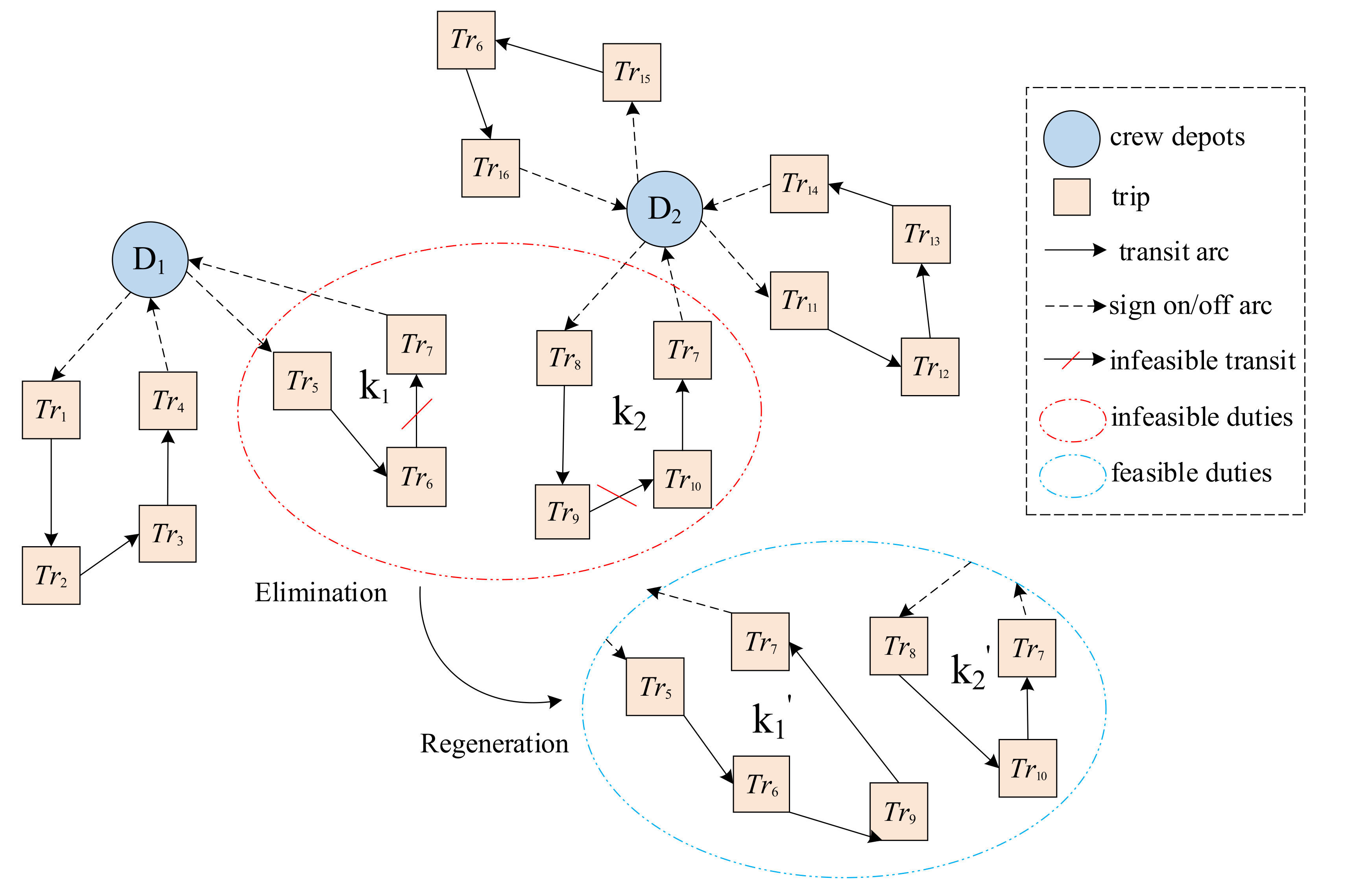
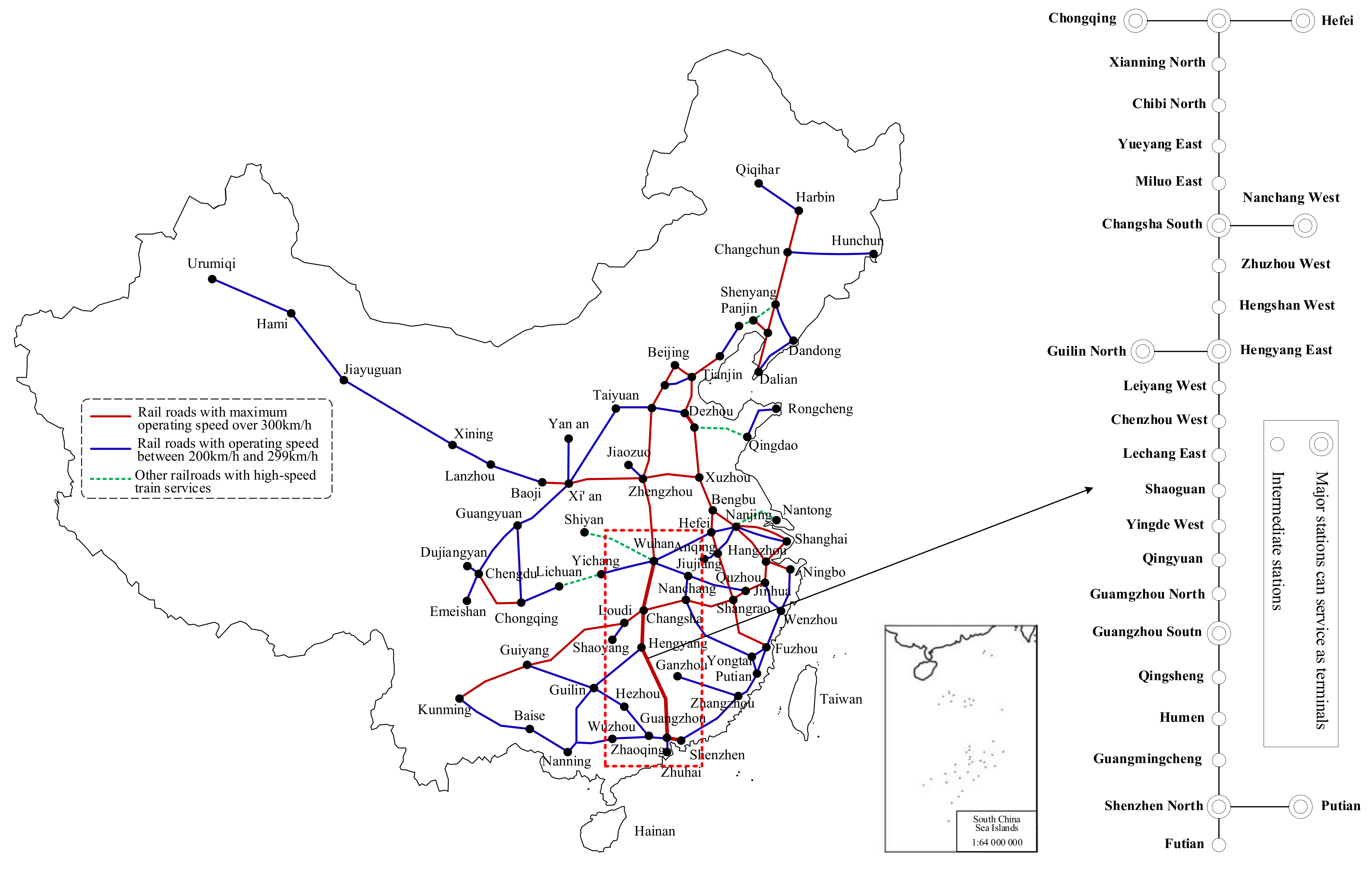


| Notations | Description |
|---|---|
| Sets | |
| Set of complete trips | |
| Parameters | |
| at the origin | |
| at the destination | |
| The duration of the trip i | |
| The minimum time needed for crew units to change the trip | |
| The maximum allowed working time for a crew unit | |
| The required number of crew units of the trip i | |
| The value is equal to 1 if the destination of the trip i is the same as the origin of trip j, 0 otherwise | |
| The transit cost between trip i and trip j | |
| The night resident cost | |
| The duty fixed cost | |
| M | An infinite number to ensure that the constraint is valid |
| Variables | |
| The binary variable, which is equal to 1 if the duty k in crew depot d services trip j after trip i, 0 otherwise | |
| Cumulative work time of duty k in crew depot d | |
| The starting time for duty k in crew depot d to service trip i | |
| The binary variable, which is equal to 1 if trip i is assigned to duty k in crew depot d | |
| Train ID | Departure Station | Arrival Station | Departure Time | Arrival Time | Train Types | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1003 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 07:55 | 12:01 | 11 | 04:06 |
| G1005 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 08:12 | 12:24 | 22 | 04:12 |
| G1007 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 09:30 | 13:37 | 2 | 04:07 |
| G1013 | Wuhan | Shenzhen North | 12:07 | 16:26 | 1 | 04:19 |
| G1015 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 13:45 | 18:16 | 2 | 04:31 |
| G1017 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 14:39 | 18:51 | 2 | 04:12 |
| G1019 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 15:45 | 20:00 | 2 | 04:15 |
| G1021 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 16:58 | 21:22 | 1 | 04:24 |
| G1101 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 06:45 | 11:11 | 1 | 04:26 |
| G1103 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 06:53 | 11:21 | 1 | 04:28 |
| G1105 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 07:37 | 11:31 | 1 | 03:54 |
| G1107 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 08:26 | 13:09 | 2 | 04:43 |
| G1117 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 11:45 | 16:06 | 1 | 04:21 |
| G1123 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 13:58 | 18:23 | 1 | 04:25 |
| G1125 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 15:07 | 19:03 | 1 | 03:56 |
| G1127 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 15:23 | 19:34 | 1 | 04:11 |
| ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ | ⁝ |
| G1129 | Wuhan | Guangzhou South | 15:50 | 19:47 | 1 | 03:57 |
| Operators | ID | Duty | Form | Total Number of Crew Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan Bureau Group Co. Ltd. | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | G1003-G10121 G1005 G1008-G1019 G1101-G1116 G1103-G1140 G1105-G1120-G1133 G1107-G1124 G1007-G1018 | A3 A-A4 A-A A A A A-A A-A | 12 |
| Guangzhou Bureau Group Co. Ltd. | 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | G1002-G1013-G60242 G1004-G1015 G1006-G1017 G6013-G1010-G1021 G1102-G1117-G1134 G1108-G1123 G6101-G1110-G1125-6116 G1112-G1127-G6118 G6105-G1114-G1129-G6120 G1122-G1135 G1014 G6011-G6016-G6001G6026 G6132-G6131-G6110-G6119 G6015-G6018-G6031 G6029-G6034-G6033 G6017-G6020-G6117-G6122 G6021-G6022-G6027 G6012-G6019-G6002-G6025 G6111-G6112 G6103-G6030 | A A-A A-A A A A A A A A A-A A A A-A A A A-A A-A A A | 26 |
| ID | pc | pm | Objective Value | ID | pc | pm | Objective Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.3 | 0.01 | 13,800 | 14 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 13,571 |
| 2 | 0.3 | 0.02 | 13,764 | 15 | 0.5 | 0.05 | 13,560 |
| 3 | 0.3 | 0.03 | 13,700 | 16 | 0.6 | 0.01 | 13,640 |
| 4 | 0.3 | 0.04 | 13,680 | 17 | 0.6 | 0.02 | 13,600 |
| 5 | 0.3 | 0.05 | 13,674 | 18 | 0.6 | 0.03 | 13,574 |
| 6 | 0.4 | 0.01 | 13,750 | 19 | 0.6 | 0.04 | 13,472 |
| 7 | 0.4 | 0.02 | 13,700 | 20 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 13,472 |
| 8 | 0.4 | 0.03 | 13,680 | 21 | 0.7 | 0.01 | 13,600 |
| 9 | 0.4 | 0.04 | 13,605 | 22 | 0.7 | 0.02 | 13,580 |
| 10 | 0.4 | 0.05 | 13,600 | 23 | 0.7 | 0.03 | 13,564 |
| 11 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 13,680 | 24 | 0.7 | 0.04 | 13,472 |
| 12 | 0.5 | 0.02 | 13,650 | 25 | 0.7 | 0.05 | 13,472 |
| 13 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 13,635 | - | - | - | - |
| Experiment ID | Pop size | N | pc | pm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 60 | 0.6 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| 2 | 100 | 60 | 0.6 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| 3 | 100 | 60 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| 4 | 100 | 60 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| 5 | 100 | 60 | 0.6 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| 6 | 100 | 60 | 0.6 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| Algorithm | Best Objective Value | Average Feasible Solution Rate | Average Running Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classical GA | 13,871 | 83% | 41 s |
| Classical PSO | 14,515 | 74% | 24 s |
| Classical TS | 14,017 | 81% | 31 s |
| Improved GA | 13,250 | 100% | 58 s |
| Operators | ID | Duty | Form | Total Number of Crew Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan Bureau Group Co. Ltd. | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | G1101-G1116-G1021 G1103-G1010-G1133 G1105-G1120-G1135 G1003-G1122 G1005-G1124 G1107-G1018 G1007-G1014 | A A A A A-A A-A A-A | 10 |
| Guangzhou Bureau Group Co. Ltd. | 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | G1102 -G1117-G1134 G6132-G6131-G6110-G6119 G6011-G6016-G6001-G6030 G6101-G1110-G1125 G6013-G1112-G1127 G6103-G1012 G1002-G1013-G6024 G6105-G1008-G1019 G6012-G6019-G6022-G6027 G6015-G6034-G6033 G6015-G6018-G6031-G6026 G6029-G6018-G6031 G1004-G1015-G1140-G6116 G1108-G1123-G6120 G6017-G6020-G6117-G6122 G1006-1017-G6118 G1006-1017 G6024-G6110 G6021-6002-6025 G1008-G1019 G1114-G1129 G6111-G6112 | A A A A A A A A A-A A A A A-A A A A A A A-A A A A | 25 |
| Crew Scheduling | Number of crew units | Average Transit Time (min) | Average Duty Time (min) | Average Duty Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| original | 38 | 70.41 | 694.50 | 80.14% |
| improved | 35 | 54.38 | 640.67 | 86.34% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Z. Solution of Multi-Crew Depots Railway Crew Scheduling Problems: The Chinese High-Speed Railway Case. Sustainability 2022, 14, 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010491
Zhao C, Chen J, Zhang X, Cui Z. Solution of Multi-Crew Depots Railway Crew Scheduling Problems: The Chinese High-Speed Railway Case. Sustainability. 2022; 14(1):491. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010491
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Chunxiao, Junhua Chen, Xingchen Zhang, and Zanyang Cui. 2022. "Solution of Multi-Crew Depots Railway Crew Scheduling Problems: The Chinese High-Speed Railway Case" Sustainability 14, no. 1: 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010491
APA StyleZhao, C., Chen, J., Zhang, X., & Cui, Z. (2022). Solution of Multi-Crew Depots Railway Crew Scheduling Problems: The Chinese High-Speed Railway Case. Sustainability, 14(1), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010491





