Influencing Factors of Azerbaijan and China’s Sustainable Tourism Development Strategy under the One Belt One Road Initiative
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Establishment
2.1. Delphi Method
2.1.1. First Round
2.1.2. Second Round
2.1.3. Third Round
2.2. SWOT
2.2.1. Strengths
2.2.2. Weaknesses
2.2.3. Opportunities
2.2.4. Threats
2.3. AHP (Analytic Hierarchy Process)
2.3.1. Building a Hierarchical Analysis Structure
2.3.2. Weight and Consistency Check
2.3.3. Calculation of the Intensity of Factors
2.3.4. Construction of AHP-SWOT Strategic Quadrilateral
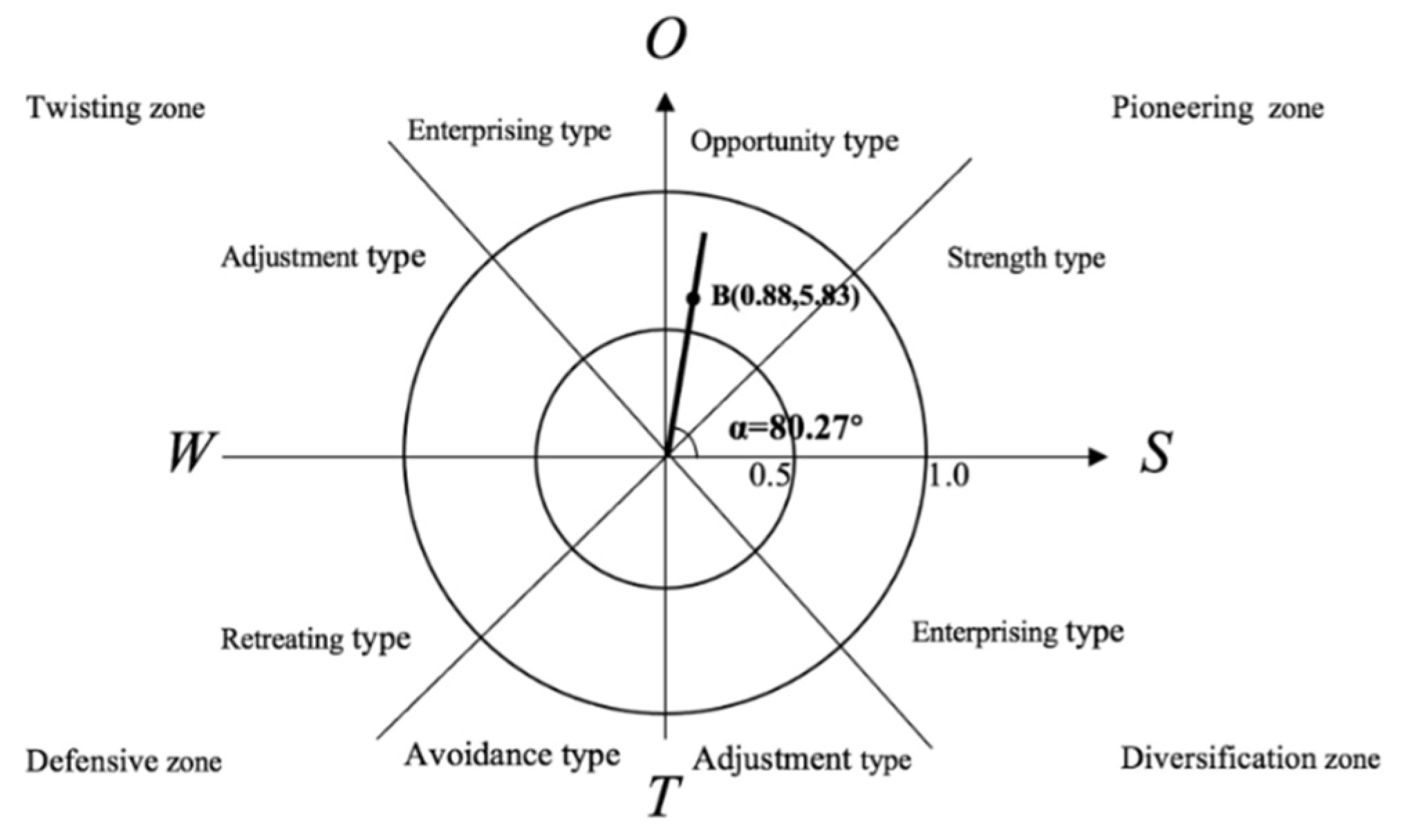
2.3.5. Strategic Vector (θ, ρ)
2.4. Results
3. Discussion
4. Implications and Recommendations
- Seize the opportunities presented by the BRI and implement an innovative strategy comprising the cooperation mechanism.
- 2.
- Emphasize the principles of mutual benefits and common development.
- 3.
- Shaping distinctive cultural brands and expanding the tourism industry chain.
- 4.
- Strengthen interregional multilateral cooperation in tourism
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, A. Building a sustainable ‘Belt and Road’. Horiz. J. Int. Relat. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 7, 212–223. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, M.D. China’s views and comments on the “Belt and Road” initiative. China Leadersh. Monit. 2015, 47, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama, R. “One belt, one road”: China’s new global strategy. J. Contemp. East Asia Stud. 2016, 5, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuchumov, A.; Testina, Y. The Impact of Participation in the Belt and Road Initiative on the Tourist Flows. In New Silk Road: Business Cooperation and Prospective of Economic Development (NSRBCPED 2019); Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, T. One belt, one road, one heritage: Cultural diplomacy and the Silk Road. Diplomat 2016, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, M.N.I.; Hossin, M.A.; Yin, X.; Sarkar, M.K. One belt one road initiative of China: Implication for future of global development. Mod. Econ. 2018, 9, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgiev, G.T. The Chinese “One Belt, One Road” initiative–new opportunities for the European Union and its neighbours in the Black Sea region. KSI Trans. Knowl. Soc. 2015, 8, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Punyaratabandhu, P.; Swaspitchayaskun, J. The political economy of China–Thailand development under the one belt one road initiative: Challenges and opportunities. Chin. Econ. 2018, 51, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; ogly Guliyev, I.S.; Kadirov, F.A.; Eppelbaum, L.V. Geosciences of Azerbaijan; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 1, p. 237. [Google Scholar]
- Mamedov, Z.F. One belt and one road: Participation and role of Azerbaijan in the implementation of the megaproject. In Proceedings of the 55th International Scientific Conference on Economic and Social Development, Baku, Azerbaijan, 18–19 June 2020; Volume 25, pp. 406–412. [Google Scholar]
- Gabusi, G. “Crossing the river by feeling the gold”: The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank and the financial support to the Belt and Road Initiative. China World Econ. 2017, 25, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizade, E.M. Great Silk Road and the” Baku-Tbilisi-Kars” Project. Black Sea Sci. J. Acad. Res. 2015, 22, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chaziza, M. China’s New Silk Road Strategy and the Turkish Middle Corridor Vision. Asian J. Middle East. Islamic Stud. 2021, 15, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeybek, H. What Role for Railways in the Eurasian Supply Chains? In Railway Transportation in South Asia; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 269–292. [Google Scholar]
- Samedova, E.; Abasova, Y. Strategic governance of tourism development in azerbaijan: Practical aspects and a mechanism for improvement. Econ. Soc. Dev. Book Proc. 2020, 3, 521–532. [Google Scholar]
- Tim, W. Heritage diplomacy along the One Belt One Road. Newsletter 2016, 74, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sharon, G.M.K.; Andrei, O. Regional integration in Central Asia: Rediscovering the Silk Road. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2017, 22, 64–66. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, T.T.; Kang, Q.; Pan, B.B.; Yang, Y.S. Synergies of sustainable development goals between China and countries along the Belt and Road initiative. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 39, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menhas, R.; Mahmood, S.; Tanchangya, P.; Safdar, M.N.; Hussain, S. Sustainable development under belt and road initiative: A case study of China-Pakistan economic corridor’s socio-economic impact on Pakistan. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, S.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Mao, Q.; Huang, Y. Resources, environment and economic patterns and sustainable development modes of the Silk Road Economic Belt. J. Resour. Ecol. 2015, 6, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wong, Y.D.; Li, K.X.; Yuen, K.F. Transport research under Belt and Road Initiative: Current trends and future research agenda. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2021, 17, 357–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, E.K. Swot Analysis from a Resource-Based View. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 2001, 9, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Webber, M. From Chinese dam building in Africa to the Belt and Road Initiative: Assembling infrastructure projects and their linkages. Political Geogr. 2020, 77, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurel, M.; Tat, M. SWOT analysis: A theoretical review. J. Int. Soc. Res. 2017, 10, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, W.; Sheila, W. What’s swot in strategic analysis? Strateg. Chang. 1998, 7, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Benzaghta, M.A.; Elwalda, A.; Mousa, M.M.; Erkan, I.; Rahman, M. SWOT analysis applications: An integrative literature review. J. Glob. Bus. Insights 2021, 6, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlados, C. On a correlative and evolutionary SWOT analysis. J. Strategy Manag. 2019, 12, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, G.J.; Castilla, G. OBJECT-based image analysis: Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT). The International Archives of the Photogrammetry. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Cui, F.; Balezentis, T.; Streimikiene, D.; Jin, H. What drives international tourism development in the Belt and Road Initiative? J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2021, 19, 100544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Chenggang, Y.; Hussain, J.; Bano, S.; Nawaz, A. Natural resources, tourism development, and energy-growth-CO2 emission nexus: A simultaneity modeling analysis of BRI countries. Resour. Policy 2020, 68, 101751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Chen, Y.; Long, Y. The structural equivalence of tourism cooperative network in the Belt and Road Initiative Area. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukeshimana, M.C.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Ahmad, M.; Irfan, M. Analysis on barriers to biogas dissemination in Rwanda: AHP approach. Renew. Energy 2021, 163, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sałabun, W.; Wątróbski, J.; Shekhovtsov, A. Are MCDA Methods Benchmarkable? A Comparative Study of TOPSIS, VIKOR, COPRAS, and PROMETHEE II Methods. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ma, C.; Huang, P.; Guo, X. Ecological vulnerability assessment based on AHP-PSR method and analysis of its single parameter sensitivity and spatial autocorrelation for ecological protection—A case of Weifang City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Zeng, G.M.; Chen, G.Q.; Tang, L.; Wang, K.L.; Huang, D.Y. Combining AHP with GIS in synthetic evaluation of eco-environment quality—A case study of Hunan Province, China. Ecol. Model. 2007, 209, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xu, D.; Liu, L. Construction of regional informatization ecological environment based on the entropy weight modified AHP hierarchy model. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2019, 22, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision-making with the AHP: Why is the principal eigenvector necessary. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 145, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making—The analytic hierarchy and network processes (AHP/ANP). J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 2004, 13, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, C.K.; Bai, H. Determining the importance weights for the customer requirements in QFD using a fuzzy AHP with an extent analysis approach. Iie Trans. 2003, 35, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, C.K.; Bai, H. A fuzzy AHP approach to the determination of importance weights of customer requirements in quality function deployment. J. Intell. Manuf. 2002, 13, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catron, J.; Stainback, G.A.; Dwivedi, P.; Lhotka, J.M. Bioenergy development in Kentucky: A SWOT-ANP analysis. For. Policy Econ. 2013, 28, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A.; Raufirad, V.; Rafiaani, P.; Azadi, H. Ecotourism sustainable development strategies using SWOT and QSPM model: A case study of Kaji Namakzar Wetland, South Khorasan Province, Iran. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2015, 16, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsić, S.; Nikolić, D.; Živković, Ž. Hybrid SWOT-ANP-FANP model for prioritization strategies of sustainable development of ecotourism in National Park Djerdap, Serbia. For. Policy Econ. 2017, 80, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marttunen, M.; Lienert, J.; Belton, V. Structuring problems for Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis in practice: A literature review of method combinations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 263, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, W. Integrated analytic hierarchy process and its applications—A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 186, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulecka, J.; Zalazar, E.M. Forest plantations in Paraguay: Historical developments and a critical diagnosis in a SWOT-AHP framework. Land Use Policy 2017, 60, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, H.E.; Dhakal, S.; Mostafa, S.M.G. An assessment of opportunities and challenges for cross-border electricity trade for Bangladesh using SWOT-AHP approach. Energy Policy 2020, 137, 111118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.B.; Agyekum, E.B.; Adadi, P. Agriculture for Sustainable Development: A SWOT-AHP Assessment of Ghana’s Planting for Food and Jobs Initiative. Sustainability 2021, 13, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorlu, K.; Yilmaz, A. Determination of Strategies of Ecotourism in Protected Areas with SWOT-AHP Method: The Case of Aksaray–Ihlara Special Environmental Protection Zone (SEPZ). Coğrafya Derg. 2020, 40, 247–257. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, S.; Marcianò, C. Using an Hybrid AHP-SWOT Method to Build Participatory Ecotourism Development Strategies: The Case Study of the Cupe Valley Natural Reserve in Southern Italy. In International Symposium on New Metropolitan Perspectives; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Barrios, M.; Guilera, G.; Nuño, L.; Gómez-Benito, J. Consensus in the delphi method: What makes a decision change? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 163, 120484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Kale, S.; Chandel, S.; Pal, D.K. Likert scale: Explored and explained. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 7, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazinoory, S.; Abdi, M.; Azadegan-Mehr, M. Swot Methodology: A State-of-the-Art Review for the Past, a Framework for the Future. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2011, 12, 24–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houben, G.; Lenie, K.; Vanhoof, K. A knowledge-based SWOT-analysis system as an instrument for strategic planning in small and medium sized enterprises. Decis. Support Syst. 1999, 26, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reihanian, A.; Mahmood, N.Z.B.; Kahrom, E.; Hin, T.W. Sustainable tourism development strategy by SWOT analysis: Boujagh National Park. Iran. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2012, 4, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmoldt, D.; Kangas, J.; Mendoza, G.A.; Pesonen, M. (Eds.) The Analytic Hierarchy Process in Natural Resource and Environmental Decision Making; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Jin, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Hu, M. Analysis on the Accuracy of Marine Gravity Inversion from the Wide-swath Altimeter Mission. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 4–8 May 2020; p. 12239. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Mohamed, M.; Smarandache, F. An Extension of Neutrosophic AHP–SWOT Analysis for Strategic Planning and Decision-Making. Symmetry 2018, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, H.-H.; Huang, W.-C. Application of a quantification SWOT analytical method. Math. Comput. Model. 2006, 43, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyadi, A.; Bakar, M.A.A.; Hidayat, C. Opportunities and Challenges of Globalisation for ASEAN Destinations through the One Belt One Road Initiative. In Marketing Tourist Destinations in Emerging Economies; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 259–273. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X. A Study on the International Tourism of Jiangxi Province under the Guidance of One Belt, One Road Strategy. Econ. Soc. Changes Facts Trends Forecast 2016, 3, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, U.; Bothra, N. Sino-US trade and trade war. Manag. Econ. Res. J. 2019, 5, 10173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myeong, S.; Jung, Y.; Lee, E. A Study on Determinant Factors in Smart City Development: An Analytic Hierarchy Process Analysis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munda, G. Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis and Sustainable Development. In State of the Art Surveys, 2nd ed.; Greco, S.M., Ehrgott, J.M., Figueira, R., Price, C.C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 233, pp. 1235–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Park, J. A Sustainable Development Strategy for the Uzbekistan Textile Industry: The Results of a SWOT-AHP Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakioglu, G.; Atahan, A.O. AHP integrated TOPSIS and VIKOR methods with Pythagorean fuzzy sets to prioritize risks in self-driving vehicles. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 99, 106948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyoud, S.H.; Fuchs-Hanusch, D. A bibliometric-based survey on AHP and TOPSIS techniques. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 78, 158–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberatore, M.J.; Nydick, R.L. The analytic hierarchy process in medical and health care decision making: A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 189, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Luo, Y. On rank reversal in decision analysis. Math. Comput. Model. 2009, 49, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhifei, L.I.; Chenchen, Z. International Tourism Cooperation Based on “the Belt and Road”: Strategy and Path. Confront. Coop. 1000 Years Pol.-Ger.-Russ. Relat. 2020, 6, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Background | Occupation or Department | Number of People Chosen | Job |
|---|---|---|---|
| Administration institution | Azerbaijan Tourism Board | 2 | Executive in related business |
| Heilongjiang Provincial Bureau of Culture and Tourism | 2 | Executive in related business | |
| Public university | Hunan Normal University | 3 | Professor in related research direction |
| Yunnan University | 2 | Professor in related research direction | |
| Heihe University | 5 | Professor in related research direction | |
| The travel agency | Azerbaijan JT World-Class travel | 3 | Executive in related business |
| China Ctrip travel | 3 | Executive in related business |
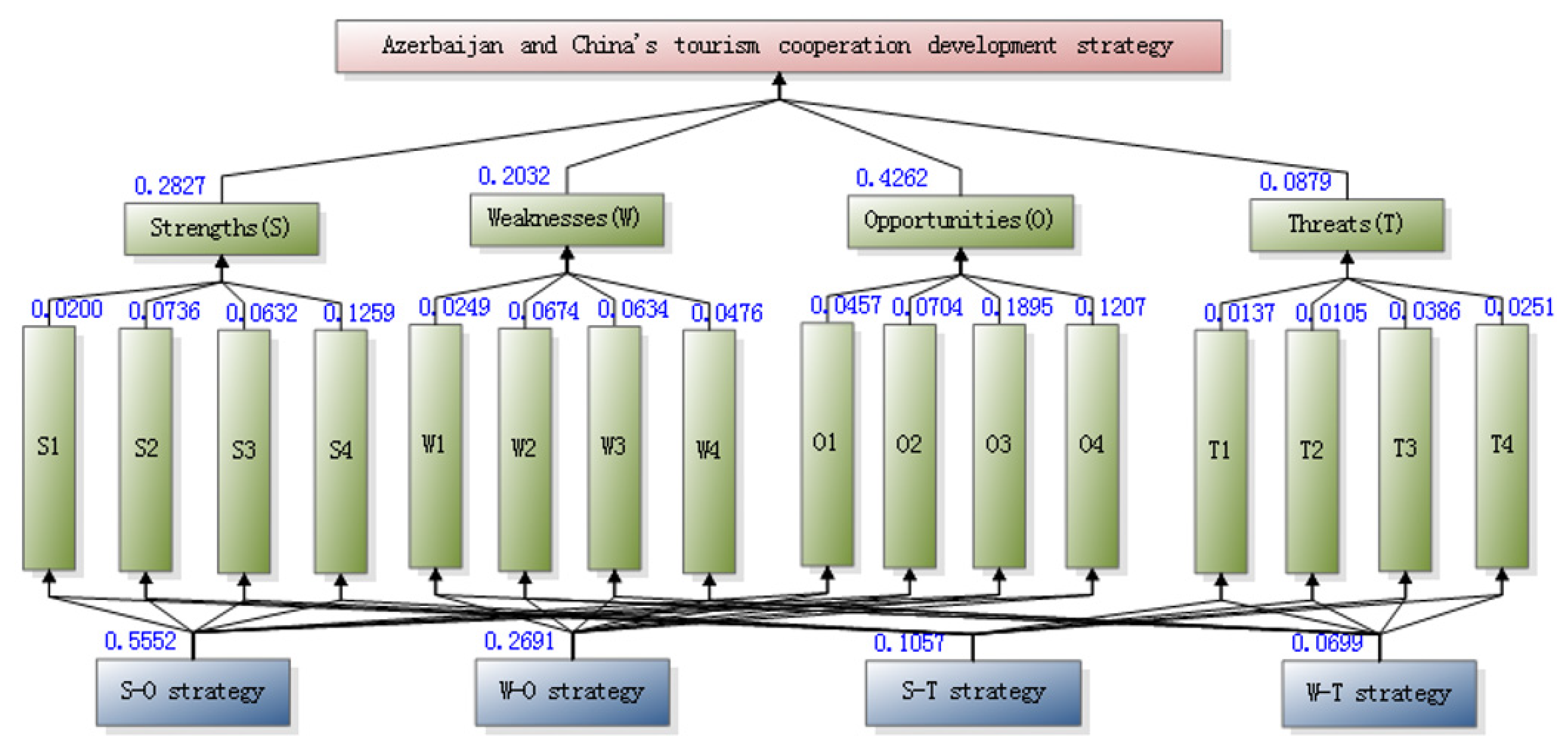
| Factors | Weights | Factors within the Group | CR | λmax | In-Group Weight | Overall Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 0.2827 | S1 | 0.0987 | 4.2635 | 0.0707 | 0.02 |
| S2 | 0.2603 | 0.0736 | ||||
| S3 | 0.2236 | 0.0632 | ||||
| S4 | 0.4453 | 0.1259 | ||||
| W | 0.2032 | W1 | 0.0771 | 4.206 | 0.1225 | 0.0249 |
| W2 | 0.3317 | 0.0674 | ||||
| W3 | 0.312 | 0.0634 | ||||
| W4 | 0.2343 | 0.0476 | ||||
| O | 0.4262 | O1 | 0.0267 | 4.0712 | 0.1072 | 0.0457 |
| O2 | 0.1652 | 0.0704 | ||||
| O3 | 0.4446 | 0.1895 | ||||
| O4 | 0.2832 | 0.1207 | ||||
| T | 0.0879 | T1 | 0.0543 | 4.145 | 0.1559 | 0.0137 |
| T2 | 0.1195 | 0.0105 | ||||
| T3 | 0.4391 | 0.0386 | ||||
| T4 | 0.2856 | 0.0251 |
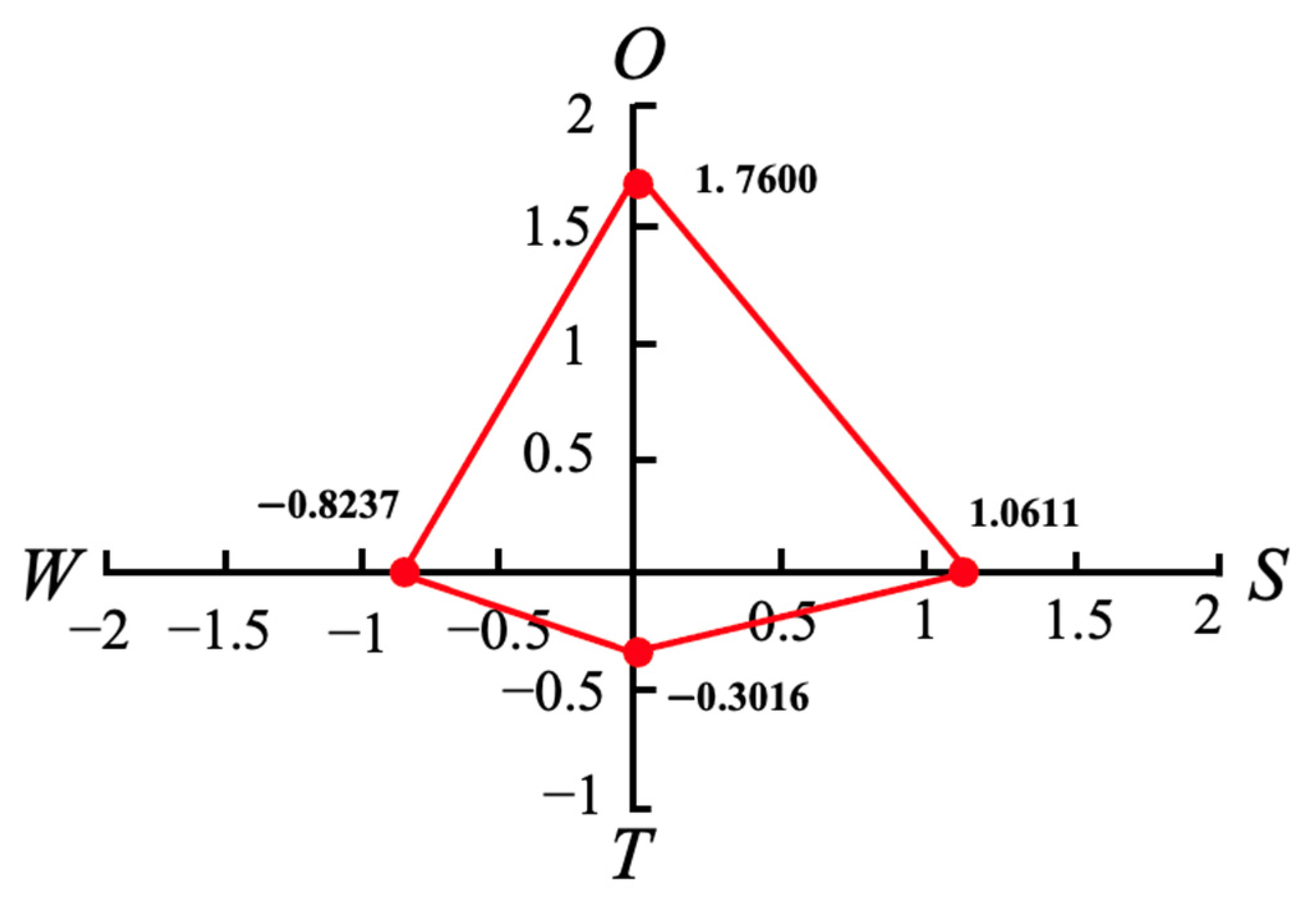
| SWOT Group | Factor Weight | Estimated Strength | Strategic Strength | Total Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths (S) | WS1 = 0.0707 | 4.15 | 0.0830 | ∑Si = 1.0611 |
| WS2 = 0.2603 | 3.70 | 0.2723 | ||
| WS3 = 0.2236 | 3.40 | 0.2148 | ||
| WS4 = 0.4453 | 3.90 | 0.4910 | ||
| Weaknesses (W) | WW1 = 0.1225 | −3.35 | −0.0834 | ∑Wi = −0.8237 |
| WW2 = 0.3317 | −4.15 | −0.2797 | ||
| WW3 = 0.3120 | −4.45 | −0.2821 | ||
| WW4 = 0.2343 | −3.75 | −0.1785 | ||
| Opportunities (O) | WO1 = 0.1072 | 4.55 | 0.2079 | ∑Oi = 1.7600 |
| WO2 = 0.1652 | 4.30 | 0.3027 | ||
| WO3 = 0.4446 | 3.95 | 0.7485 | ||
| WO4 = 0.2832 | 4.15 | 0.5009 | ||
| Threats (T) | WT1 = 0.1559 | −2.80 | −0.0383 | ∑Ti = −0.3016 |
| WT2 = 0.1195 | −3.25 | −0.0341 | ||
| WT3 = 0.4391 | −3.60 | −0.1389 | ||
| WT4 = 0.2856 | −3.60 | −0.0903 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Suk, S. Influencing Factors of Azerbaijan and China’s Sustainable Tourism Development Strategy under the One Belt One Road Initiative. Sustainability 2022, 14, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010187
Liu Y, Suk S. Influencing Factors of Azerbaijan and China’s Sustainable Tourism Development Strategy under the One Belt One Road Initiative. Sustainability. 2022; 14(1):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010187
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yiming, and Sunhee Suk. 2022. "Influencing Factors of Azerbaijan and China’s Sustainable Tourism Development Strategy under the One Belt One Road Initiative" Sustainability 14, no. 1: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010187
APA StyleLiu, Y., & Suk, S. (2022). Influencing Factors of Azerbaijan and China’s Sustainable Tourism Development Strategy under the One Belt One Road Initiative. Sustainability, 14(1), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010187






