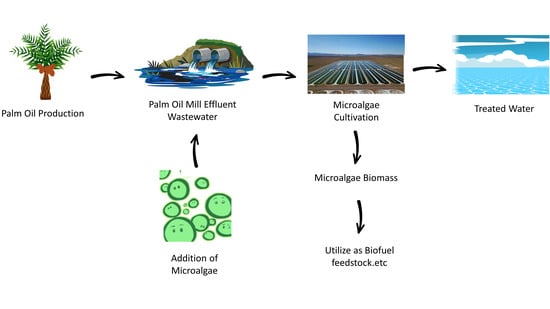
Microalgae Cultivation in Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) Treatment and Biofuel Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Microalgae as a Potential Tool in POME Treatment
2.1. Microalgae Cultivation in POME and Benefits of Treating POME with Microalgae
2.2. Condition of Growth of Microalgae in POME
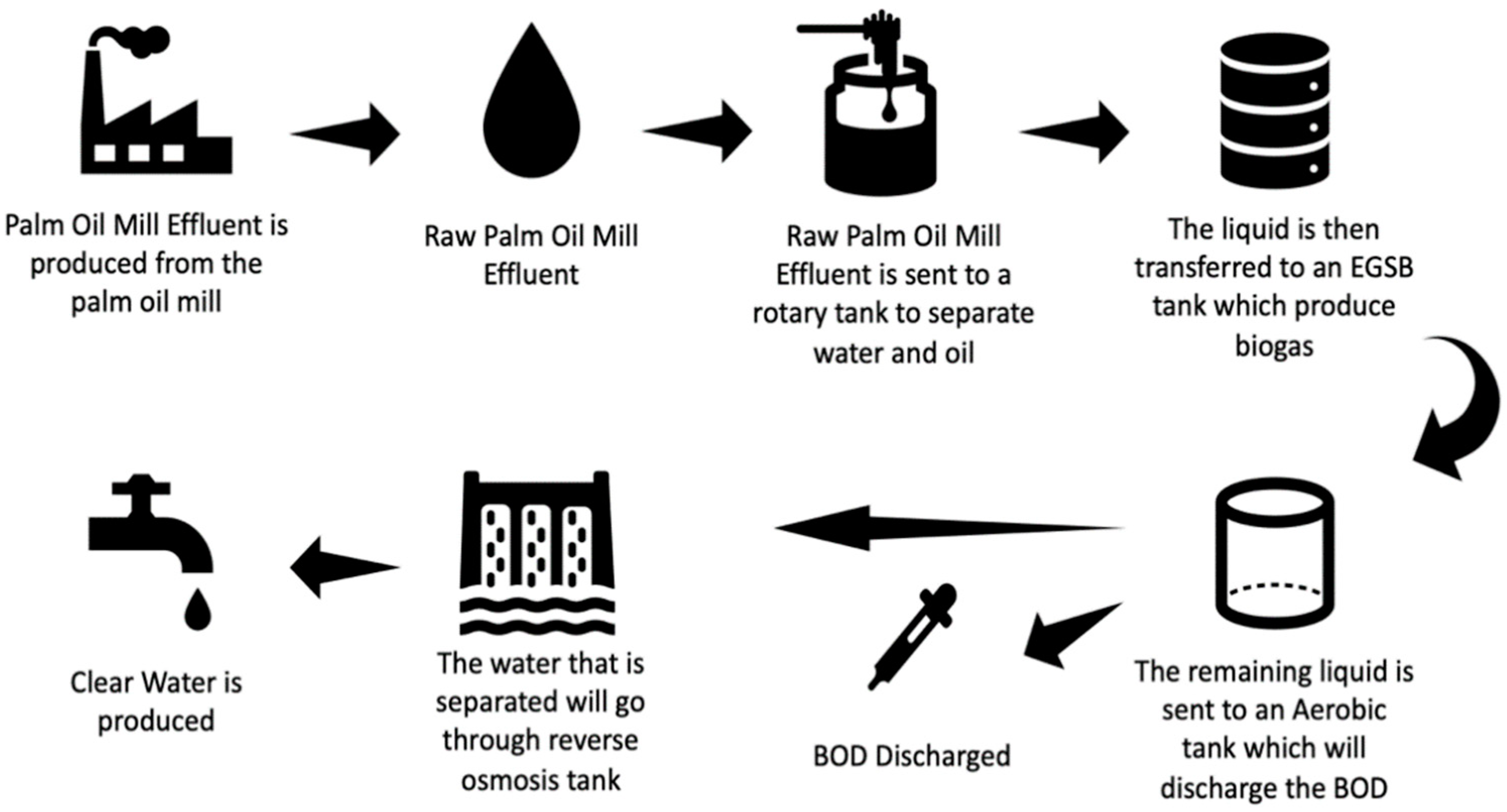
2.3. Pre-Treatment of POME for Microalgae Growth
3. Biofuel Production from POME Treatment Using Microalgae
3.1. Characteristics of Algae for POME Treatment
3.2. Increased Production of Biodiesel Feedstock Using Microalgae from POME Treatment
4. Challenges and Future Perspectives
4.1. Will Microalgae-Based POME Treatment Cause Pollution?
4.2. Impact on Aquatic Organism
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 2018 oleochemicals market size, share & trends analysis report. Focus Surfactants 2019. [CrossRef]
- May, C.Y.; Nesaretnam, K. Research advancements in palm oil nutrition. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyia, C.O.; Uyu, A.M.; Akunna, J.C.; Norulaini, N.A.; Omar, A.K. Increasing the fertilizer value of palm oil mill sludge: Bioaugmentation in nitrification. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.C.; Tan, Y.K.; Wang, C.W. The distribution of chemical constituents between the soluble and the particulate fractions of palm oil mill effluent and its significance on its utilisation/treatment. Agric. Wastes 1984, 11, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.E.; Abdul Wahid, M. Pollutant in palm oil production process. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 2015, 65, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.D.; Lim, J.S. Feasibility of palm oil mill effluent elimination towards sustainable Malaysian palm oil industry. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 111, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garritano, A.N.; de Oliveira Faber, M.; De Sá, L.R.V.; Ferreira-Leitão, V.S. Palm oil mill effluent (POME) as raw material for biohydrogen and methane production via dark fermentation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 92, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, P.E.; Chong, M.F. Development of anaerobic digestion methods for palm oil mill effluent (POME) treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.S.; Tan, W.G.; Halimatul Munawaroh, H.S.; Gupta, V.K.; Ho, S.-H.; Show, P.L. Multifaceted roles of microalgae in the application of wastewater biotreatment: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, F.L.; Korbee, N.; Abdala-Díaz, R.; Álvarez-Gómez, F.; Gómez-Pinchetti, J.L.; Acién, F.G. 6—Growing Algal Biomass Using Wastes; Häder, D.-P., Erzinger, G.S.B.T.-B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 99–117. ISBN 978-0-12-811861-0. [Google Scholar]
- Chisti, Y. Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Buang, A.; Bhat, A.H. Renewable and sustainable bioenergy production from microalgal co-cultivation with palm oil mill effluent (POME): A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 65, 214–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, W.Y.; Show, P.L.; Chang, J.-S.; Ling, T.C.; Juan, J.C. Biosequestration of atmospheric CO2 and flue gas-containing CO2 by microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Show, P.L.; Lau, B.F.; Chang, J.S.; Ling, T.C. New prospects for modified algae in heavy metal adsorption. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, É.C.; Neves, D.B.; Jacob-Lopes, E.; Franco, T.T. Microalgae as feedstock for biodiesel production: Carbon dioxide sequestration, lipid production and biofuel quality. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handler, R.M.; Canter, C.E.; Kalnes, T.N.; Lupton, F.S.; Kholiqov, O.; Shonnard, D.R.; Blowers, P. Evaluation of environmental impacts from microalgae cultivation in open-air raceway ponds: Analysis of the prior literature and investigation of wide variance in predicted impacts. Algal 2012, 1, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydney, E.B.; Sturm, W.; de Carvalho, J.C.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Larroche, C.; Pandey, A.; Soccol, C.R. Potential carbon dioxide fixation by industrially important microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kebelmann, K.; Hornung, A.; Karsten, U.; Griffiths, G. Intermediate pyrolysis and product identification by TGA and Py-GC/MS of green microalgae and their extracted protein and lipid components. Biomass Bioenergy 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Fan, J.; Shen, G. Enhancement of microalgal biomass and lipid productivities by a model of photoautotrophic culture with heterotrophic cells as seed. Bioresour. Technol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wim Brilman, D.W.F.; Withag, J.A.M.; Brem, G.; Kersten, S. Assessment of a dry and a wet route for the production of biofuels from microalgae: Energy balance analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulana, M.; Nur, A.; Ganang, D.H. Enhancement of Biomass Production from Spirulina sp Cultivated in POME Medium. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Chemical and Material Engineering 2012, Semarang, Indonesia, 12–13 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Shuping, Z.; Yulong, W.; Mingde, Y.; Chun, L.; Junmao, T. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of the marine microalgae Dunaliella tertiolecta using thermogravimetric analyzer. Bioresour. Technol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadavalli, R.; Rao, C.S.; Rao, R.S.; Potumarthi, R. Dairy effluent treatment and lipids production by Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Euglena gracilis: Study on open and closed systems. Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Rao, H.; Kumar, A.; Shruthi, M. Eco-friendly approach for treating dairy effluent and lipid estimation using microalgae. Br. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 7, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Show, P.L.; Tang, M.S.Y.; Nagarajan, D.; Ling, T.C.; Ooi, C.-W.; Chang, J.-S. A holistic approach to managing microalgae for biofuel applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.L.; Show, P.L.; Ong, H.C.; Ling, T.C.; Chen, W.-H.; Salleh, M.A.M. Biochar production from microalgae cultivation through pyrolysis as a sustainable carbon sequestration and biorefinery approach. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.L.; Show, P.L.; Ong, H.C.; Ling, T.C.; Chi-Wei Lan, J.; Chen, W.H.; Chang, J.S. Microalgae from wastewater treatment to biochar—Feedstock preparation and conversion technologies. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 150, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, D.F.; Beyer, H.L.; Possingham, H.P.; García-Ulloa, J.; Ghazoul, J.; Schenk, P.M. Freeing land from biofuel production through microalgal cultivation in the Neotropical region. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 94094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, M.M.A.; Buma, A.G.J. Opportunities and challenges of microalgal cultivation on wastewater, with special focus on palm oil mill effluent and the production of high value compounds. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 2079–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, H.; Din, M.F.M.; Keyvanfar, A.; Majid, M.Z.A.; Talaiekhozani, A.; Shafaghat, A.; Lee, C.T.; Shiun, L.J.; Ismail, H.H. Efficiency of Microalgae Chlamydomonas on the Removal of Pollutants from Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME). Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadiyanto, H.; Azimatun Nur, M.M.; Hartanto, G.D. Cultivation of chlorella sp. As biofuel sources in palm oil mill effluent (POME). Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, H.; Md Din, M.F.; Lee, C.T.; Keyvanfar, A.; Shafaghat, A.; Majid, M.Z.A.; Ponraj, M.; Yun, T.X. Lipid production by microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa cultivated in palm oil mill effluent (POME) using hybrid photo bioreactor (HPBR). Desalin. Water Treat. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, M.M.A.; Garcia, G.M.; Boelen, P.; Buma, A.G.J. Influence of photodegradation on the removal of color and phenolic compounds from palm oil mill effluent by Arthrospira platensis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.M.U.; Ahmad, A.; Othman, M.F.; Abdullah, M.A. Effects of palm oil mill effluent media on cell growth and lipid content of Nannochloropsis oculata and Tetraselmis suecica. Int. J. Green Energy 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Din, M.F.M.; Rezania, S.; Khademi, T.; Kumar, A. Palm Oil Mill Effluent as an Environmental Pollutant. In Palm Oil; Waisundara, V., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78923-427-5. [Google Scholar]
- Cheah, W.Y.; Show, P.L.; Juan, J.C.; Chang, J.-S.; Ling, T.C. Microalgae cultivation in palm oil mill effluent (POME) for lipid production and pollutants removal. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 174, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Kamal, S.; Mansor, M.F.; Mohd Jahim, J.; Anuar, N. Effect of pre-treatment palm oil mill effluent POME on biohydrogen production by local isolate Clostridium Butyricum. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 236–238, 2987–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-S.; Law, R.; Chang, C.-C. Biosorption of lead, copper and cadmium by biomass of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PU21. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, S.R.; Chew, K.W.; Show, P.L.; Yap, Y.J.; Ong, H.C.; Ling, T.C.; Chang, J.-S. Analysis of economic and environmental aspects of microalgae biorefinery for biofuels production: A review. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 1700618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.I.; Gonçalves, A.L.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Pires, J.C.M. Experimental and techno-economic study on the use of microalgae for paper industry effluents remediation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Khoiroh, I.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Show, P.L. Techniques of lipid extraction from microalgae for biofuel production: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, W.Y.; Show, P.L.; Yap, Y.J.; Mohd Zaid, H.F.; Lam, M.K.; Lim, J.W.; Ho, Y.-C.; Tao, Y. Enhancing microalga Chlorella sorokiniana CY-1 biomass and lipid production in palm oil mill effluent (POME) using novel-designed photobioreactor. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheah, W.Y.; Show, P.L.; Juan, J.C.; Chang, J.-S.; Ling, T.C. Enhancing biomass and lipid productions of microalgae in palm oil mill effluent using carbon and nutrient supplementation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 164, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.; Sheahan, C.; Fu, P. Metabolic engineering of algae for fourth generation biofuels production. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2451–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-L.; Chai, W.S.; Show, P.L.; Chen, J.-Y.; Chang, Y.-K. Evaluation of dynamic binding performance of C-phycocyanin and allophycocyanin in Spirulina platensis algae by aminated polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 161, 107686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Shahbazian-Yassar, R.; Din, M.F.M.; Khademi, T.; Kumar, A.; Rezania, S. Evaluation of lipid content in microalgae biomass using palm oil mill effluent (Pome). JOM 2017, 69, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Chew, K.W.; Yen, H.-W.; Lim, J.W.; Lam, M.K.; Show, P.L. Cultivation of oily microalgae for the production of third-generation biofuels. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyande, A.K.; Chew, K.W.; Rambabu, K.; Tao, Y.; Chu, D.-T.; Show, P.-L. Microalgae: A potential alternative to health supplementation for humans. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, H.; Yusoff, F.M.; Banerjee, S.; Khatoon, H.; Shariff, M. Availability and utilization of pigments from microalgae. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2209–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, J.D. The promising future of microalgae: Current status, challenges, and optimization of a sustainable and renewable industry for biofuels, feed, and other products. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.W.; Yap, J.Y.; Show, P.L.; Suan, N.H.; Juan, J.C.; Ling, T.C.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Microalgae biorefinery: High value products perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 229, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahman, Y.; Syed, K.; Begum, S.; Roy, P.; Mohtasebi, B. 14—Biofuels: Their Characteristics and Analysis. In Biopolymer-Based Materials, and Bioenergy; Verma, D., Fortunati, E., Jain, S., Zhang, X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Composites Science and Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 277–325. ISBN 978-0-08-102426-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sukumaran, P.; Nulit, R.; Zulkifly, S.; Halimoon, N.; Omar, H.; Ismail, A. Potential of fresh POME as a growth medium in mass production of Arthrospira platensis. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 235–250. [Google Scholar]
- Vairappan, C.S.; Yen, A.M. Palm oil mill effluent (POME) cultured marine microalgae as supplementary diet for rotifer culture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyande, A.K.; Show, P.L.; Guo, R.; Tang, B.; Ogino, C.; Chang, J.-S. Bio-processing of algal bio-refinery: A review on current advances and future perspectives. Bioengineered 2019, 10, 574–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilanovic, D.; Andargatchew, A.; Kroeger, T.; Shelef, G. Freshwater and marine microalgae sequestering of CO2 at different C and N concentrations—Response surface methodology analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.; Vecchi, V.; Barera, S.; Dall’Osto, L. Biomass from microalgae: The potential of domestication towards sustainable biofactories. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zullaikah, S.; Utomo, A.T.; Yasmin, M.; Ong, L.K.; Ju, Y.H. 9—Ecofuel conversion technology of inedible lipid feedstocks to renewable fuel. In Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment; Azad, A., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 237–276. ISBN 978-0-08-102728-8. [Google Scholar]
- Darvehei, P.; Bahri, P.A.; Moheimani, N.R. Model development for the growth of microalgae: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 97, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, I.R. Environmental effects on algal photosynthesis: Temperature. J. Phycol. 1991, 27, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.W.; Chia, S.R.; Show, P.L.; Yap, Y.J.; Ling, T.C.; Chang, J.-S. Effects of water culture medium, cultivation systems and growth modes for microalgae cultivation: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 91, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahrul, H.Z.; Nor, F.J.; Ropandi, M.; Astimar, A.A. A review on the development of palm oil mill effluent (POME) final discharge polishing treatments. J. Oil Palm Res. 2017, 29, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, H.; Din, M.F.M.; Hosseini, S.E.; Ghoshal, S.K.; Ashokkumar, V.; Keyvanfar, A.; Shafaghat, A.; Lee, C.T.; asghar Bavafa, A.; Majid, M.Z.A. Optimum lipid production using agro-industrial wastewater treated microalgae as biofuel substrate. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2016, 18, 2513–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
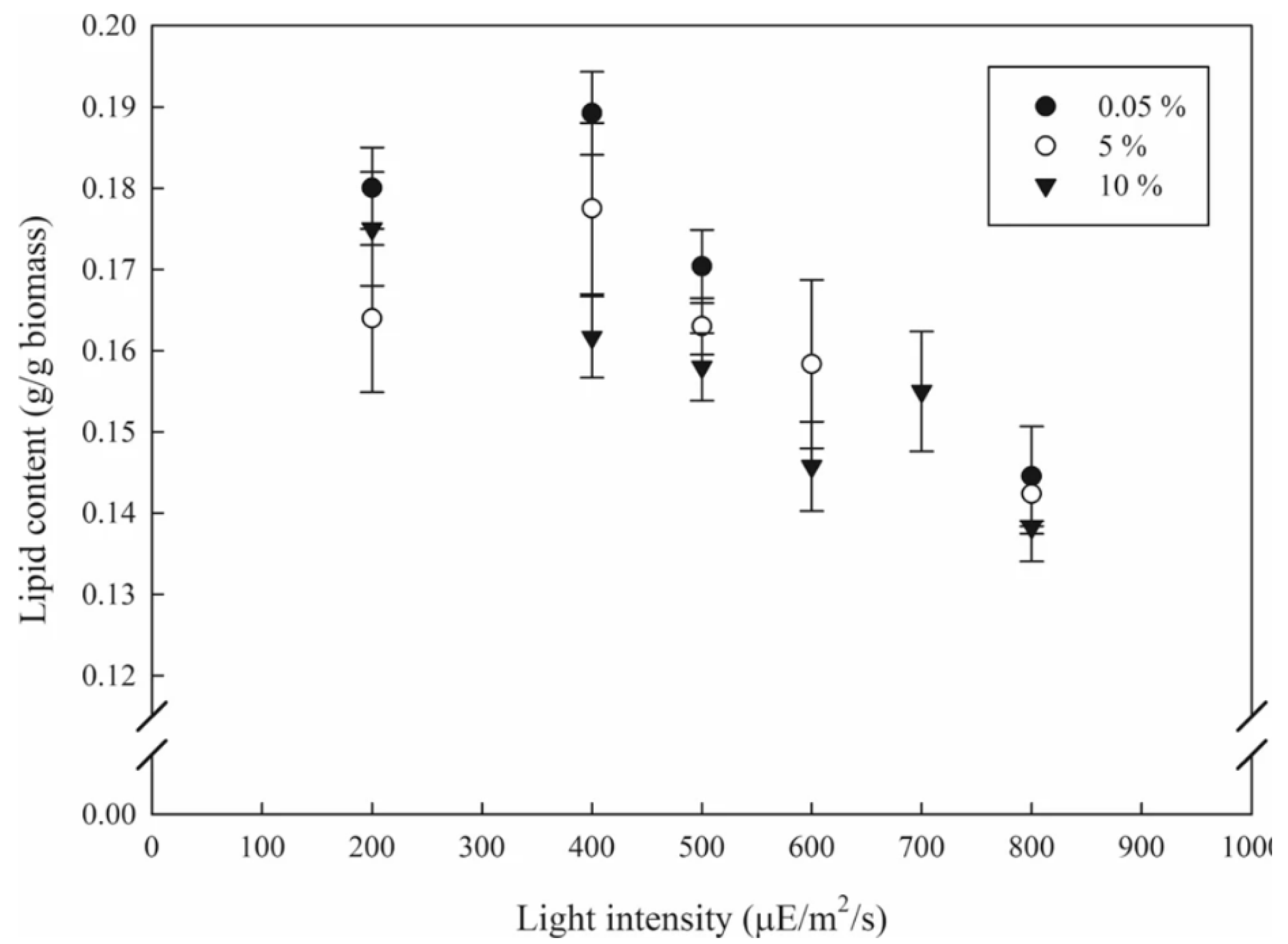
- Bhuyar, P.; Sundararaju, S.; Rahim, M.H.A.; Ramaraj, R.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N. Microalgae cultivation using palm oil mill effluent as growth medium for lipid production with the effect of CO2 supply and light intensity. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsoviti, M.N.; Papapolymerou, G.; Karapanagiotidis, I.T.; Katsoulas, N. Effect of light intensity and quality on growth rate and composition of Chlorella vulgaris. Plants 2020, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Rosenberg, J.N.; Sharif, N.; Betenbaugh, M.J.; Wang, F. Efficient lipid extraction and quantification of fatty acids from algal biomass using accelerated solvent extraction (ASE). RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 29127–29134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Moon, M.; Kwak, M.; Lee, B.; Chang, Y.K. Statistical optimization of light intensity and CO2 concentration for lipid production derived from attached cultivation of green microalga Ettlia sp. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Kim, K.T.; Heo, T.-Y.; Kwon, G.; Lim, C.; Park, J. Inhibition of photosynthetic activity in wastewater-borne microalgal–bacterial consortia under various light conditions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, S.; Thirunavukkarasu, A.R.; Pachiappan, P. Advances in Marine and Brackishwater Aquaculture; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; ISBN 9788132222712. [Google Scholar]
- Takriff, M.S.; Zakaria, M.Z.; Sajab, M.S.; Teow, Y.H. Pre-treatments anaerobic palm oil mill effluent (POME) for microalgae treatment. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.A.; Jahim, J.M.; Anuar, N.; Hassan, O.; Daud, W.R.W.; Mansor, M.F.; Rashid, S.S. Pre-treatment effect of palm oil mill effluent (POME) during hydrogen production by a local isolate Clostridium butryricum. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2011, 2, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Eskicioglu, C.; Marin, J. Microwave, ultrasonic and chemo-mechanical pretreatments for enhancing methane potential of pulp mill wastewater treatment sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7815–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadiyanto, H.; Christwardana, M.; Soetrisnanto, D. Phytoremediations of palm oil mill effluent (POME) by using aquatic plants and microalge for biomass production. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 6, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Luong, T.T.; Lee, D.; Oh, Y.-K.; Lee, T. Reuse of effluent water from a municipal wastewater treatment plant in microalgae cultivation for biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8639–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Pandey, P.K.; Franz, A.K.; Deng, H.; Jeannotte, R. Chlorella vulgaris production enhancement with supplementation of synthetic medium in dairy manure wastewater. AMB Express 2016, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Ahmad, A.; Othman, M.; Abdullah, M. Enhancement of lipid content in Isochrysis Galbana and Pavlova Lutheri using palm oil mill effluent as an alternative medium. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 37, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, G.; Chatzipavlidis, I.; Georgakakis, D. Cultivation of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis in olive-oil mill wastewater treated with sodium hypochlorite. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.; Goswami, S.; Ghosh, A.; Oinam, G.; Tiwari, O.N.; Das, P.; Gayen, K.; Mandal, M.K.; Halder, G.N. Production of biodiesel from microalgae through biological carbon capture: A review. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapie, S.; Jumali, S.S.; Mustaffha, S.; Pebrian, D.E. Analysis of POME discharge quality from different mill in Perak, Malaysia: A case study. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 327, 12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, B.; Alp, M.T.; Sonmez, F.; Kocer, M.A.T.; Canpolat, O. Relationship of Algae to Water Pollution and Waste Water Treatment. In Water Treatment; Elshorbagy, W., Chowdhury, R.K., Eds.; Intech: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Raouf, N.; Al-Homaidan, A.A.; Ibraheem, I.B.M. Microalgae and wastewater treatment. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 19, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Matheickal, J.T.; Yin, P.; Kaewsarn, P. Heavy metal uptake capacities of common marine macro algal biomass. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1534–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.S.; Cheun, J.Y.; Kumar, P.S.; Mubashir, M.; Majeed, Z.; Banat, F.; Ho, S.-H.; Show, P.L. A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. J. Clean. Prod. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambabu, K.; Banat, F.; Pham, Q.M.; Ho, S.-H.; Ren, N.-Q.; Show, P.L. Biological remediation of acid mine drainage: Review of past trends and current outlook. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2020, 2, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambabu, K.; Thanigaivelan, A.; Bharath, G.; Sivarajasekar, N.; Banat, F.; Show, P.L. Biosorption potential of Phoenix dactylifera coir wastes for toxic hexavalent chromium sequestration. Chemosphere 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiewer, S.; Volesky, B. Biosorption by Marine Algae. In Bioremediation; Valdes, J.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 139–169. [Google Scholar]
- Halim, A.; Samsudin, A.; Azmi, A.; Mohd Nawi, M. Nutrients and chemical oxygen demand (COD) removals by microalgae-bacteria co-culture system in palm oil mill effluent (POME). IIUM Eng. J. 2019, 20, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elystia, S.; Muria, S.R.; Anggraini, L. Removal of COD and total nitrogen from palm oil mill effluent in flatphotobioreactor using immobilised microalgae Chlorella sp. Food Res. 2018, 3, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Liu, C.-H.; Lo, Y.-C.; Chang, J.-S. Perspectives on cultivation strategies and photobioreactor designs for photo-fermentative hydrogen production. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8484–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, N.U.R.A.; Loh, S.O.H.K.; Lau, H.L.I.K.N.; Mustafa, E.M.; Vello, V.; Tan, C.Y.A.U.; Phang, S.M.O.I. Cultivation of microalgae in medium containing palm oil mill effluent and its conversion into biofuel. J. Oil Palm Res. 2017, 29, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resdi, R.; Lim, J.S.; Kamyab, H.; Lee, C.T.; Hashim, H.; Mohamad, N.; Ho, W.S. Review of microalgae growth in palm oil mill effluent for lipid production. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2016, 18, 2347–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, N.A.; Ujang, F.A.; Roslan, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Hassan, M.A. The effect of palm oil mill effluent final discharge on the characteristics of Pennisetum purpureum. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, S.; Baioli, F.; Marinello, S. Life cycle assessment of a biofuel production system from algal biomass cultivated in photobioreactors. In Proceedings of the 28th European Biomass Conference and Exhibition, Marseille, France, 27–30 April 2020; pp. 837–844. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.Y.Y.; Yew, G.Y.; Koyande, A.K.; Chew, K.W.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Show, P.L. Green technology for the industrial production of biofuels and bioproducts from microalgae: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1967–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofner, J.; Kamilli, K.A.; Held, A.; Lendl, B.; Zetzsch, C. Halogen-induced organic aerosol (XOA): A study on ultra-fine particle formation and time-resolved chemical characterization. Faraday Discuss. 2013, 165, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.H.; Sturm, B.S.M.; DeNoyelles, F.J.; Billings, S.A. The ecology of algal biodiesel production. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębowski, M.; Zieliński, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Kujawska, N.; Talbierz, S. Microalgae cultivation technologies as an opportunity for bioenergetic system development—Advantages and limitations. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culaba, A.B.; Ubando, A.T.; Ching, P.M.L.; Chen, W.-H.; Chang, J.-S. Biofuel from microalgae: Sustainable pathways. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenntech River Water Quality and Pollution. Available online: https://www.lenntech.com/rivers-pollution-quality.htm (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- Ahmad, A.L.; Chong, M.F.; Bhatia, S.; Ismail, S. Drinking water reclamation from palm oil mill effluent (POME) using membrane technology. Desalination 2006, 191, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, H.; Golomb, D. Carbon Capture and Storage from Fossil Fuel Use. In Encyclopedia of Energy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Karl, D.M.; Beversdorf, L.; Björkman, K.M.; Church, M.J.; Martinez, A.; Delong, E.F. Aerobic production of methane in the sea. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsono, S.S.; Grundmann, P.; Soebronto, S. Anaerobic treatment of palm oil mill effluents: Potential contribution to net energy yield and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from biodiesel production. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 64, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K. Introduction to the Working Group Ⅱ Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Jpn. J. Real Estate Sci. 2015, 29, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Business Specialists The Eight Growth Pressures of Wastewater Treatment: #1 BOD Loading. Available online: https://www.ebsbiowizard.com/eight-growth-pressures-wastewater-treatment-1-bod-loading-3988/ (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- Surya, E.; Hanum, H.; Hanum, C.; Rauf, A.; Hidayat, B.; Harahap, F.S. Effects of Composting on Growth and Uptake of Plant Nutrients and Soil Chemical Properties After Composting with Various Comparison of POME. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 4, 1849–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfahmi, I.; Muliari, M.; Akmal, Y.; Batubara, A.S. Reproductive performance and gonad histopathology of female Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linnaeus 1758) exposed to palm oil mill effluent. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2018, 44, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muliari, M.; Zulfahmi, I.; Akmal, Y.; Karja, N.W.K.; Nisa, C.; Sumon, K.A.; Rahman, M.M. Toxicity of palm oil mill effluent on the early life stages of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, Linnaeus 1758). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 30592–30599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.P.; Nguyen, D.H.; Lim, J.W.; Chang, C.-K.; Leong, H.Y.; Tran, T.N.T.; Vu, T.B.H.; Nguyen, T.T.C.; Show, P.L. Investigation of the relationship between bacteria growth and lipid production cultivating of microalgae Chlorella Vulgaris in seafood wastewater. Energies 2019, 12, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Apandi, N.; Muhamad, M.S.; Radin Mohamed, R.M.S.; Mohamed Sunar, N.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Gani, P.; Rahman, F.A. Optimizing of microalgae Scenedesmus sp. biomass production in wet market wastewater using response surface methodology. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Microalgae | Lipid | Protein | Carbohydrate |
|---|---|---|---|
| B. braunii [17] | 33–86 | 4–40 | 20 |
| C. rheinhardii [18] | 18–22 | 46–48 | 17 |
| C. ellipsoidea [19] | 10–30 | 34–35 | 24–51 |
| C. pyrenoidosa [19] | 8–35 | 31–47 | 20–57 |
| C. vulgaris [20] | 10–50 | 29–58 | 12–17 |
| S. platensis [21] | 4–13 | 42–63 | 8–30 |
| D. tertiolecta [22] | 3–13 | 26–61 | 22 |
| E. gracilis [23] | 11 | 29 | 32 |
| Microalgae Species | Nutrient Reduction (%) | Lipid Production (%) | Growth Rate (1/day) | Biomass Productivity (g/L/d) | Duration (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlamydomonas [30] | 68 | 60 | 1.2 | 0.08 | 7 |
| Chlorella sp. [31] | - | - | 0.066 | 0.058 | 15 |
| S. plantesis [21] | - | - | - | 9.8 | 13 |
| C. pyrenoidosa [32] | 71.16 | 68 | 1.8 | 0.13 | 10 |
| T. suecica [33] | 95 | 27 | - | 0.211 | 7 |
| N. oculata [34] | 93.6 | 39 | - | 0.52 | 7 |
| Source Type | Yield (L oil/ha Year) | Land Required (m2/kg Biodiesel Year) | Biodiesel Production (kg/ha Year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 172 | 66 | 152 |
| Hemp | 363 | 31 | 321 |
| Soybean | 636 | 18 | 562 |
| Jatropha | 741 | 15 | 656 |
| Camelina | 915 | 12 | 809 |
| Rapeseed | 974 | 12 | 862 |
| Sunflower | 1070 | 11 | 946 |
| Castor | 1307 | 9 | 1156 |
| Palm oil | 5366 | 2 | 4747 |
| Microalgae | 58,700–136,900 | 0.1–0.2 | 51,927–121,104 |
| Parameter | Mean | Range |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 4.2 | 3.4–5.2 |
| BOD (mg/L) | 25,000 | 10,250–43,750 |
| COD (mg/L) | 51,000 | 15,000–100,000 |
| Total solids (mg/L) | 40,000 | 11,500–79,000 |
| Suspended solids (mg/L) | 18,000 | 5000–54,000 |
| Volatile solids (mg/L) | 34,000 | 9000–72,000 |
| Oil and grease (mg/L) | 6000 | 130–18,000 |
| Ammoniacal nitrogen (mg/L) | 35 | 4–80 |
| Total nitrogen (mg/L) | 750 | 180–1400 |
| Parameter | Range | Optimum |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 16–27 | 18–24 |
| Salinity (g/L) | 12–40 | 20–24 |
| Light Intensity | 1000–10,000 | 2500–5000 |
| Photoperiod (light:dark) | - | 16:8 (Minimum) 24 h (Maximum) |
| pH | 7–9 | 8.2–8.7 |
| CO2 rate | 1–4% | 1% of volume in air |
| Nutrients | - | N:P (16:1) and Silicon |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Low, S.S.; Bong, K.X.; Mubashir, M.; Cheng, C.K.; Lam, M.K.; Lim, J.W.; Ho, Y.C.; Lee, K.T.; Munawaroh, H.S.H.; Show, P.L. Microalgae Cultivation in Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) Treatment and Biofuel Production. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3247. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063247
Low SS, Bong KX, Mubashir M, Cheng CK, Lam MK, Lim JW, Ho YC, Lee KT, Munawaroh HSH, Show PL. Microalgae Cultivation in Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) Treatment and Biofuel Production. Sustainability. 2021; 13(6):3247. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063247
Chicago/Turabian StyleLow, Sze Shin, Kien Xiang Bong, Muhammad Mubashir, Chin Kui Cheng, Man Kee Lam, Jun Wei Lim, Yeek Chia Ho, Keat Teong Lee, Heli Siti Halimatul Munawaroh, and Pau Loke Show. 2021. "Microalgae Cultivation in Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) Treatment and Biofuel Production" Sustainability 13, no. 6: 3247. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063247
APA StyleLow, S. S., Bong, K. X., Mubashir, M., Cheng, C. K., Lam, M. K., Lim, J. W., Ho, Y. C., Lee, K. T., Munawaroh, H. S. H., & Show, P. L. (2021). Microalgae Cultivation in Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) Treatment and Biofuel Production. Sustainability, 13(6), 3247. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063247