Abstract
Anchovies are among the largest fish catch worldwide. The anchovy fillet industry generates a huge amount of biowaste (e.g., fish heads, bones, tails) that can be used for the extraction of several potentially valuable bioproducts including omega-3 lipids. Following the extraction of valued fish oil rich in omega-3, vitamin D3 and zeaxanthin from anchovy fillet leftovers using biobased limonene in a fully circular process, the solid residue (anchovy sludge) was used as starting substrate for the production of biogas by anaerobic digestion. In spite of the unbalanced carbon to nitrogen (C/N) ratio, typical of marine biowaste, the anchovy sludge showed a good methane yield (about 280 mLCH4·gVS−1), proving to be an ideal substrate for co-digestion along with other carbon rich wastes and residues. Furthermore, the presence of residual limonene, used as a renewable, not-toxic and edible extraction solvent, does not affect the microbial methanogenesis. The results reported in this study demonstrate that anchovy leftovers after the fish oil extraction process can be efficiently used as a starting co-substrate for the production of biogas in a modern biorefinery.
1. Introduction
The color of a sustainable future is blue and offers an “ocean” of opportunities. The preservation of oceans, seas, rivers and coasts together with the valorization of aquaculture and marine resources is an important part of the circular economy, creating new chances for a sustainable and inclusive growth [1,2,3]. This approach takes form in the new and ambitious concept of the “blue economy”, a paradigm founded on the biomimicry and on the sustainable exploitation of marine and natural resources, which calls for a collective responsibility in preserving the marine environment as one of the key factors of global prosperity [4]. In practice, action for improvement requires the design of innovative production and consumption methods with a far lower environmental impact. Similar efforts are required by the 14th sustainable development goal (“Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development”) of the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development [5,6,7].
In this context, the reuse and valorization of the fish waste is a key process which aims to reduce methane emissions related to unsustainable management (e.g., landfilling) [8]. Furthermore, new economic opportunities for fisheries and the marine/maritime sectors need to be found. Around 35% of the global catch is either lost or wasted every year, whereas about 70% of processed fish turns into by-products (heads, viscera, skin, bones and scales) and is usually disposed of as waste [5]. This biowaste should rather be converted into high value bioproducts and biofuels. While the biorefinery of lignocellulosic biomasses relies, so far, on well-established technologies [9], the complete upgrading of fish waste into biofuels and value-added chemicals can be considered at an embryonic state. Nevertheless, the number of contributions in this field of research are rapidly growing [10,11,12].
Certain fishery by-products are an important source of nutraceuticals and bioactive ingredients [12,13]. Fish by-products are rich in proteins and omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC-PUFAs) [14].
A sufficient daily intake of omega-3 marine essential lipids offers several health benefits to both adults and children and is required for the prevention of many pathologies [15,16]. As a consequence, a significant amount of the global fish catch (22 million tonnes, about 12% of the total) is used for non-food purposes, with about 1 million tonnes of fish oil produced in 2020.
Fish oil, at the industrial scale, is produced with established extractive technologies including wet pressing and extraction, with either organic solvent or supercritical CO2, followed by numerous purification steps [17]. Omega-3 concentrates, for instance, are supplied in the form of synthetic ethyl esters to which natural or synthetic oxidants are usually added to prevent quick oxidation and autooxidation of the double bonds in the LC-PUFA molecular chain. Recently, a new green process for the recovery of a natural oil rich in omega-3, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), vitamin D3 and zeaxantin was developed by the Pagliaro research group, starting from the anchovy processing waste [10]. The method employs citrus-derived d-limonene as a non-toxic and edible extraction solvent in a closed-loop process in which the biobased solvent is fully recovered and recycled after the extraction [18]. The residual product, derived from this new extraction process (anchovy sludge), needs to be valorized in order to close the material cycle.
Anaerobic digestion is widely recognized as one of the most effective biorefinery technologies for the upgrading of different types of organic waste and biomasses into biogas through a series of biochemical reactions (hydrolysis, acidogenesis and methanogenesis) occurring simultaneously in an oxygen-free environment [19,20,21]. Together with biogas (methane: 55–70%; carbon dioxide: 30–45%; others: CO, H2S, NH3, H2O, etc. [22]), a solid–liquid residue, generally known as “digestate”, is produced [23]. The digestate contains macro- and micronutrients, making this by-product suitable as a sustainable replacement for agricultural fertilizers [24,25].
The sustainable production of biogas through anaerobic digestion (AD) of fish processing waste is an emerging field of research. Eiroa et al. tested the digestion of different fish wastes achieving an average methane yield of 260 mLCH4·gVS−1 (where VS stands for volatile solids) for tuna, sardine and needle fish waste, and reaching 350 mLCH4·gVS−1 for mackerel [26]. Nges et al. [27] and Bucker et al. [28] measured a methane yield of 828 mLCH4·gVS−1 and 540 mLCH4·gVS−1 for salmon heads and carp viscera, respectively. When anchovy waste was used as starting substrate for anaerobic digestion, a very low methane yield was registered as a consequence of the excessive accumulation of ammonia [29]. In general, the production of methane, through AD processes, ranges from 200 to 900 mLCH4·gVS−1, depending on the nature of the fish waste [30].
To the best of the authors’ knowledge, studies on the use of fish oil extraction residues in anaerobic digestion are virtually non-existent in the literature. Even if this biowaste is rich in lipids and proteins, the concomitant presence of LC-PUFAs, light metal ions (e.g., Ca2+, Na+, K+, Mg2+) and nitrogen-containing species (i.e., ammonia arisen from protein hydrolysis) can inhibit methanogenesis [31]. Furthermore, the residual limonene from the extraction process (and its dehydrogenation product p-cymene) is a well-known inhibitor of anaerobic digestion, and therefore, it is necessary to verify the suitability of the extraction of the solid residue and its subsequent AD process [32,33,34].
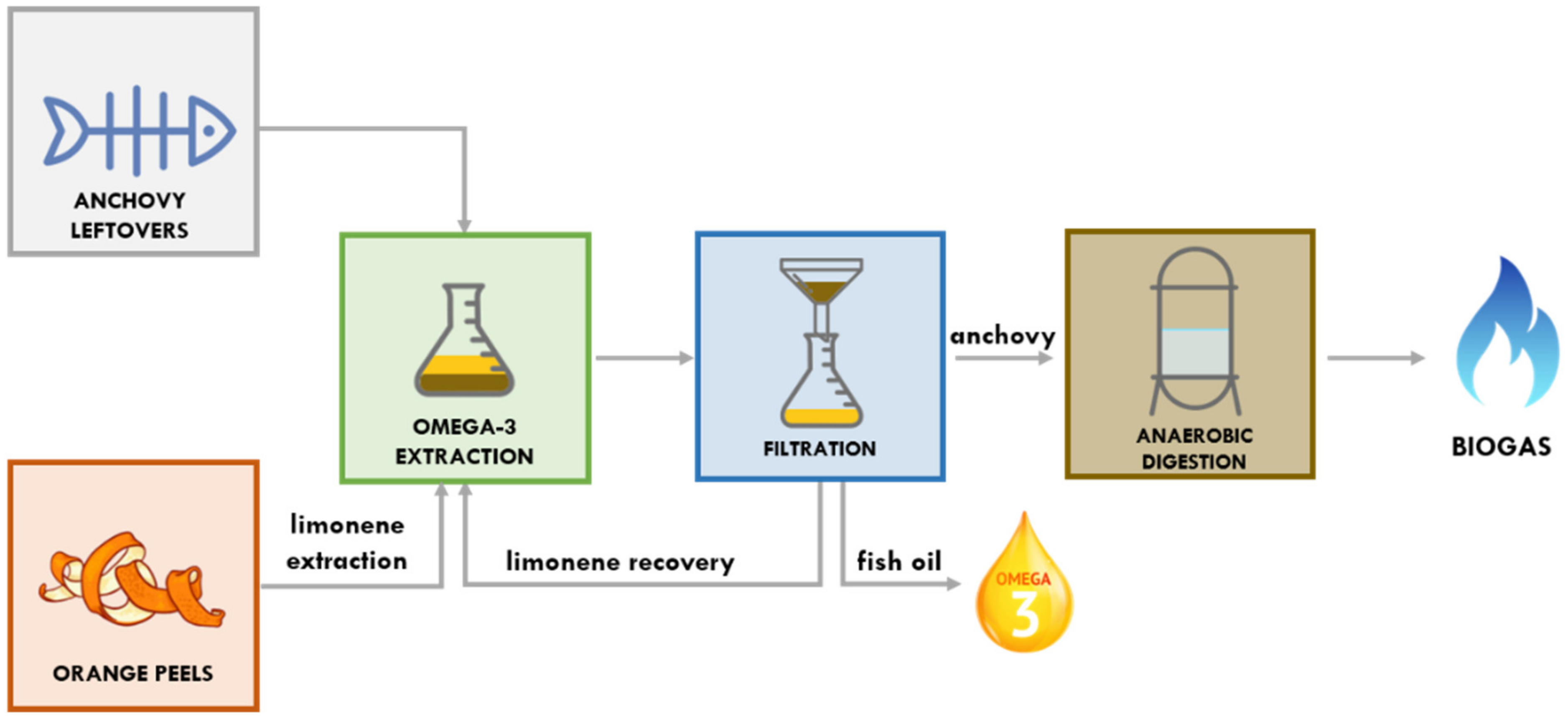
In this study, we present, for the first time, biogas production through the anaerobic digestion of the anchovy sludge residual from the extraction of fish oil, produced from the anchovy processing waste using limonene as a solvent (Figure 1).
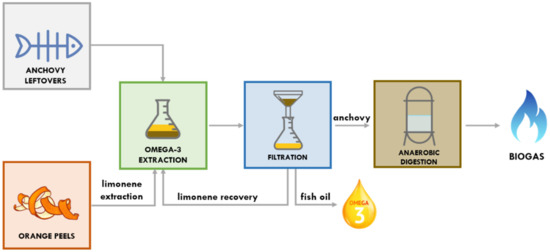
Figure 1.
Biorefinery scheme for anchovy residues.
2. Materials and Methods
All chemicals were purchased from commercial sources (Merck Life Science S.r.l. and Carlo Erba Reagents) and used without any further purification.
The fish oil extraction process was carried out following the procedure previously reported [18]. An electric blender was used to mix and homogenize the frozen anchovy leftovers (300 g) with a first aliquot of d-limonene (150 g) refrigerated at 4 °C. The so-obtained semi-solid grey puree was transferred with a second aliquot of cold d-limonene (150 g) into a glass beaker sealed with aluminum foil and further coated with parafilm. The mixture was magnetically stirred at 700 rpm for 24 h at room temperature with the fish oil obtained by rotavaporing the supernatant at 90 °C (pressure: 40 mbar). The solid anchovy sludge (SAS) was dried in an oven at 70 °C for 3 days and, before use, it was crushed in a ceramic mortar.
The morphological and elemental composition information of the solid anchovy sludge was achieved with a Phenom Pro-X scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with an energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) using the SEM-EDX technique [35].
The analysis of the residual limonene present in the substrate was carried out by mixing 0.3 g of SAS with 3 mL of a toluene solution (as an internal standard) in cyclohexane (0.1 M) for 6 hours [36]. The liquid suspension was then filtered and injected into an offline GC-FID (Agilent 6890 N) equipped with a CP-WAX 52CB column (60 m, i.d. 0.53 mm) according to the analytical procedure reported previously [37,38].
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential thermal analysis (DTA) were performed on a Netzsch instrument under a helium atmosphere from room temperature to 1000 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C/min.
The biochemical methane potential (BMP) consists of measuring volumes of biogas and methane, produced by batches loaded with inoculum, organic substrate (SAS in this case), diluting water and nutrient solutions. The inoculum used in this experiment was a liquid digestate coming from a full-scale anaerobic digestion plant that treats manure and various residues from the agro-industry, located in the Reggio Calabria province (Italy). After the collection, inoculum was sieved to remove undigested materials (e.g., straw) and then stored at 35 °C for few days until the test started. Both the inoculum and the substrate were characterized in terms of pH, total solids (TS) and volatile solids (VS) according to standard methods [39] before the test. Moreover, only the SAS, chemical oxygen demand (COD) and carbon to nitrogen (C/N) ratio were measured by photometric determination (WTW Photolab S12) using specific pre-dosed cuvettes (COD Cell Test 114555) and the elemental analyzer TOC-LCSH (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan), respectively.
The BMP test was carried out according to a method that was extensively used in previous studies (e.g., [40]) and in compliance with the UNI/TS 11703:2018 Italian norm and standardized protocols [41]. The method involves the use of 1.1 L glass bottles (WTW-Germany) as hermetically sealed batches. Each of them has two side necks equipped with perforable septa for biogas collection and a main central neck closed by a stopper. The bottles were placed into a thermostatic cabinet at 35 ± 0.5 °C (mesophilic conditions) and kept under continuous mixing by a magnetic stirrer. Periodically, the generated biogas was withdrawn from the batches, using a 100 mL syringe, and transferred into an alkaline trap (NaOH solution, 3 M) where carbon dioxide was absorbed while the methane caused an increase of the pressure in the trap, which resulted in a displacement of an equal volume of the solution measured in a graduated cylinder. In this way, the percentage of methane in the generated biogas was evaluated.
The BMP test also included blank assays (in duplicates) that were only filled with inoculum in order to measure the non-specific methane production, the internal controls (in duplicates) fed with α-cellulose (CAS 9004-34-6, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) for the validation of the process as required by the UNI/TS 11703:2018 norm, and lastly, the batches (in triplicates) loaded with SAS. Likewise, the inoculum and substrate cellulose were also characterized. In each batch, the volumes of inoculum, diluting water and nutrient solutions, prescribed by the aforementioned norm in order to supply macro- and micronutrients for the bacteria metabolism, were mixed up to a working volume of 350 mL. The solutions were designed as A, B and C, and contained KH2PO4, Na2HPO4 12H2O, NH4Cl (A, 5% of the total working volume), CaCl2 2H2O, MgCl2 6H2O, FeCl2 4H2O (B, 5% of the total working volume) and MnCl2 4H2O, H3BO3, ZnCl2, CuCl2, Na2MoO4 2H2O, CoCl2 6H2O, NiCl2 6H2O, Na2SeO3 (C, 1% of the total working volume). The amounts of cellulose and SAS (2.1 and 2.7 g, respectively) were added in order to reach a substrate to inoculum ratio (on a VS basis) equal to 0.3. Finally, the solids concentration in the batches did not exceed 50 gTS·L−1, as the regulations recommend. Before any test started, the pH of each batch mixture was measured (Table 1).

Table 1.
Experimental reactor settings.
The BMP values of the internal controls and substrate-fed batches were expressed as the volume of produced methane gas under normal conditions (273.15 K and 101.33 kPa) per mass of VS added (mLCH4·gVS−1) and determined by subtracting the average methane production of the blanks (inoculum). In accordance with the regulations, the BMP test was stopped when the daily methane production was lower than 1% of the total cumulated methane volume, determined starting from the test beginning. This evidence emerged on day 34.
The net specific cumulative methane production of the batches fed with SAS were modeled using the modified Gompertz equation, Equation (1) [42]:
where [mL·gVS−1] stands for the specific methane production at time (d), [mL·gVS−1] stands for the methane production at time , [mL·gVS−1·d−1] stands for the maximum methane production rate and [d] stands for the lag phase duration. , and were determined by minimizing the sum of square errors between the model and the experimental average values through the Excel tool “Solver”.
At the end of each test, the digestates were analyzed to determine the pH, TS and VS [39]. Furthermore, resulting from the centrifugation (10.000 rpm per 10 min), the total ammoniacal nitrogen (TAN), the Cl- content using pre-dosed cuvettes (Ammonium Cell Test 114559 and Chloride Cell Test 114730, respectively) and the photometric determination (WTW Photolab S12) in the liquid fraction, the total volatile fatty acids (VFAs) concentration and the volatile organic acids/buffering capacity (FOS/TAC) ratio were determined. In particular, the latter two parameters were determined through a four-point titration method [43] consisting of titrating 20 mL of centrifuged digestate up to pH values of 5.0, 4.4, 4.3 and 4.0 with a 0.1 N sulphuric acid solution. The parameters were calculated by using Equations (2) and (3) [43,44]:
where VFAs and FOS are reported as the acetic acid equivalent (mgHAC·L−1) and TAC as the lime equivalent (mgCaCO3·L−1); and , , and stand for the volumes recorded for acid consumption corresponding to the respective pH values, while and represent the normality of the acid solution (0.1) and the volume in mL of the sample (20), respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
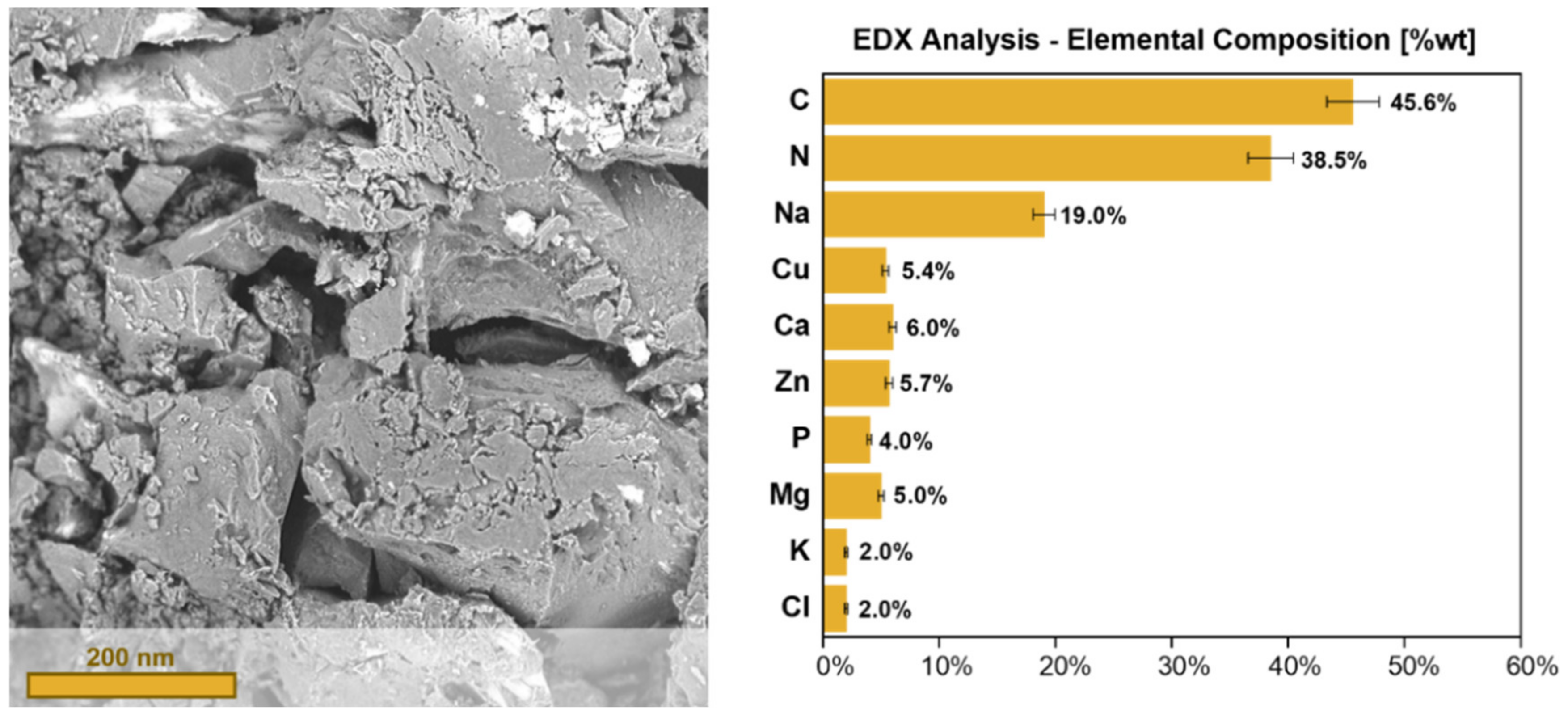
The SEM images clearly show the presence of an irregular and amorphous surface (Figure 2).
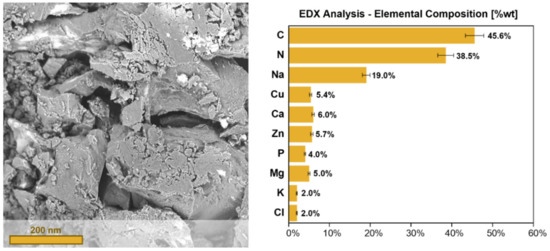
Figure 2.
The scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive X-ray (SEM-EDX) analysis of the solid anchovy sludge.
The EDX analysis revealed the predominant presence of carbon and nitrogen. Other mineral elements including potassium, calcium, magnesium, zinc and copper were also detected. The absence of toxic and/or heavy metal contaminants (such as lead, mercury and cadmium) in the sample is worth noting [45]. This is probably due to the short life span of the small pelagic species present in the Mediterranean sea.
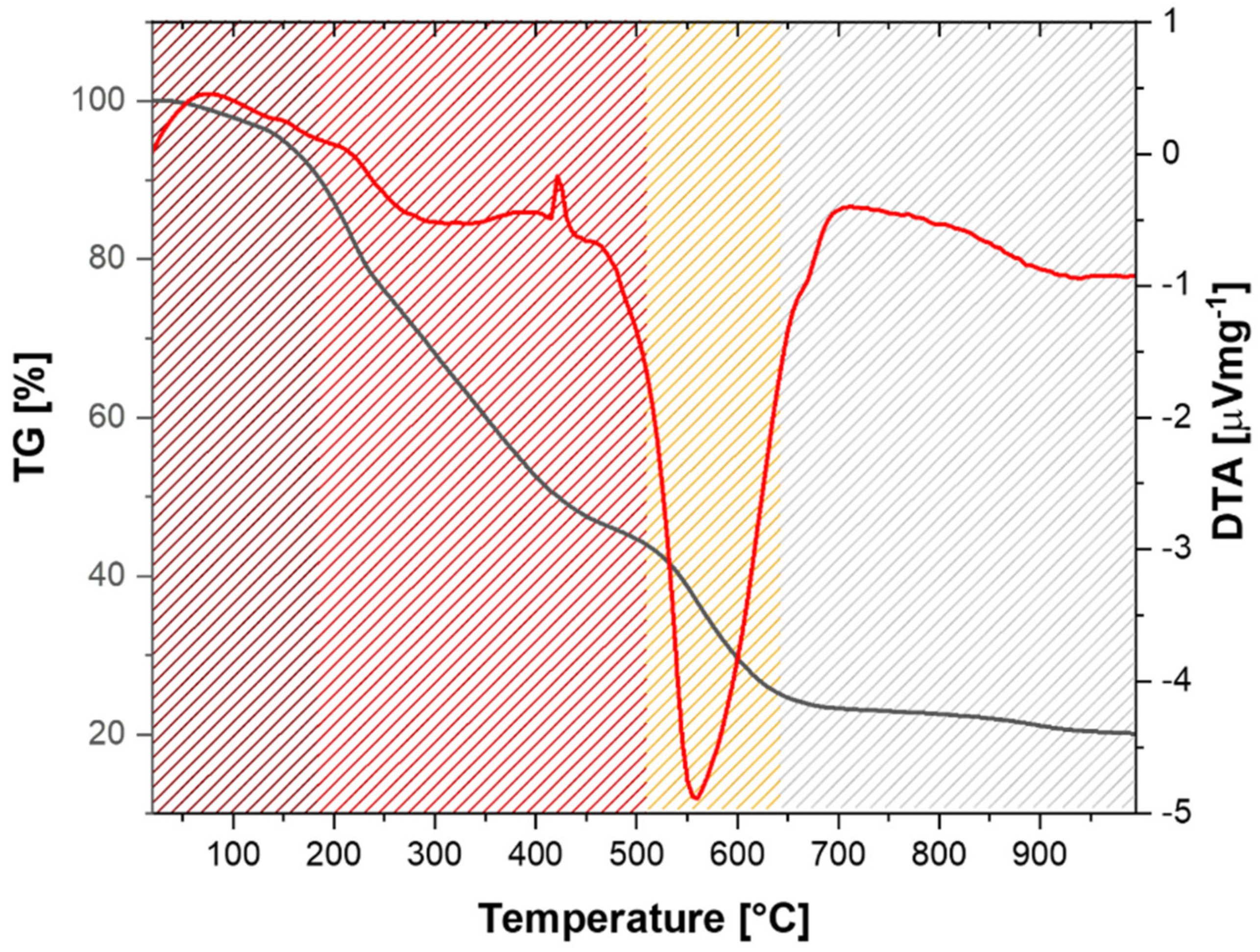
The thermal properties of SAS were determined by TGA and DTA analysis (Figure 3). The first degradation step (25–200 °C), corresponding to a weight loss of about 10%, can be attributed to the residual water and limonene present in the sludge. The next degradation step (200–500 °C), was probably due to degradation of organic materials and proteins, while the last weight loss at a max temperature of about 560 °C was due to combustion of the remained carbon and inorganic phase (including bones and scales) [46].
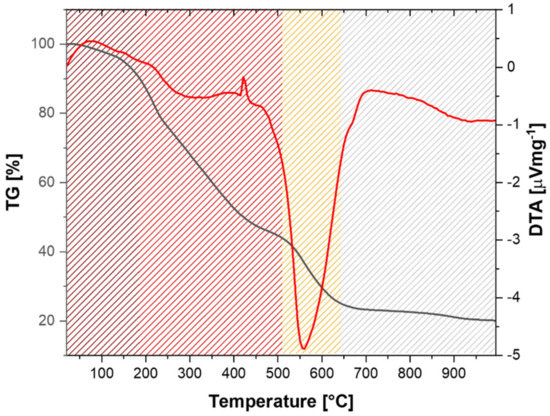
Figure 3.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential thermal analysis (DTA) analysis of the solid anchovy sludge.
The characterization of the inoculum and substrates is summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Characterization of inoculum, cellulose and solid anchovy sludge (SAS).
The solids content of the SAS was quite high due to the drying carried out after the extraction process. The organic matter content, measured as VS and COD, was lower than that expected from other studies, probably because of the extraction process. Furthermore, the high protein content of the fish resulted in a very low C/N ratio. Lastly, since the d-limonene was used as the extraction solvent, its residual presence in the substrate was detected.
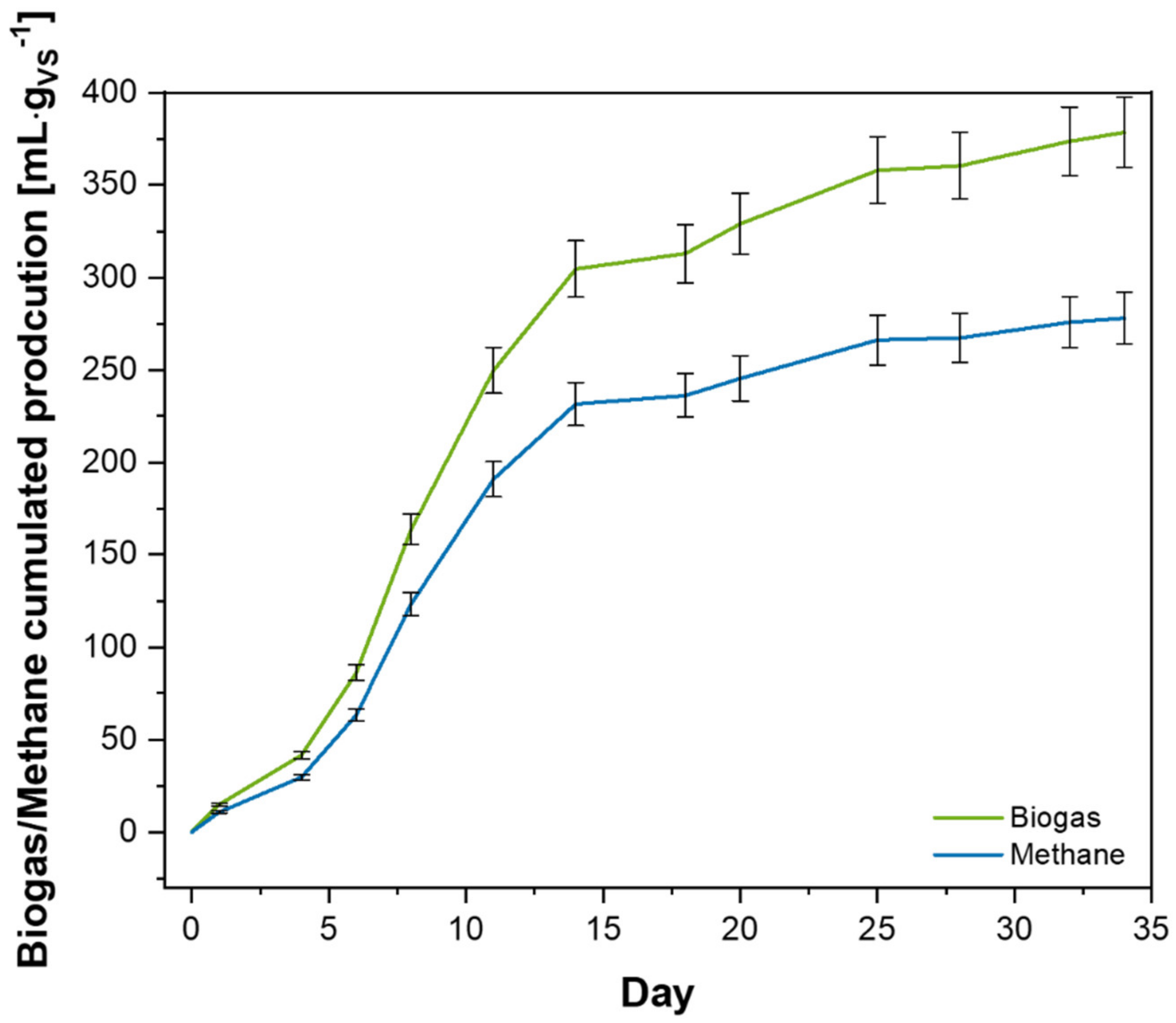
Biogas productions, BMP values and average methane contents for the internal control and SAS-fed batches are summarized in Table 3. The average cumulated biogas and methane production trends of the three replicates fed with the tested substrate are depicted in Figure 4.

Table 3.
Biogas and methane final production and methane content in biogas volumes of control and SAS-fed batches.
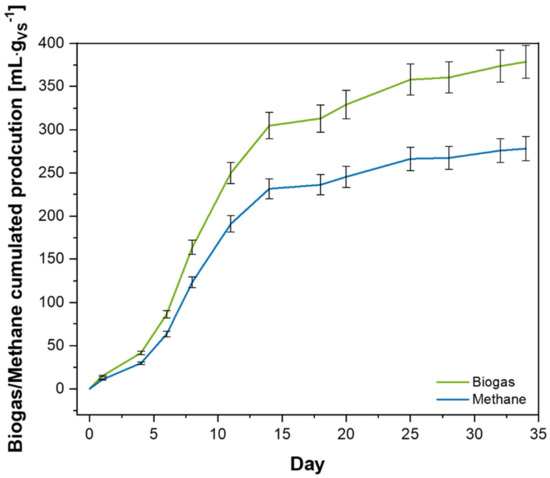
Figure 4.
Cumulated biogas and methane production trends of batches fed with SAS.
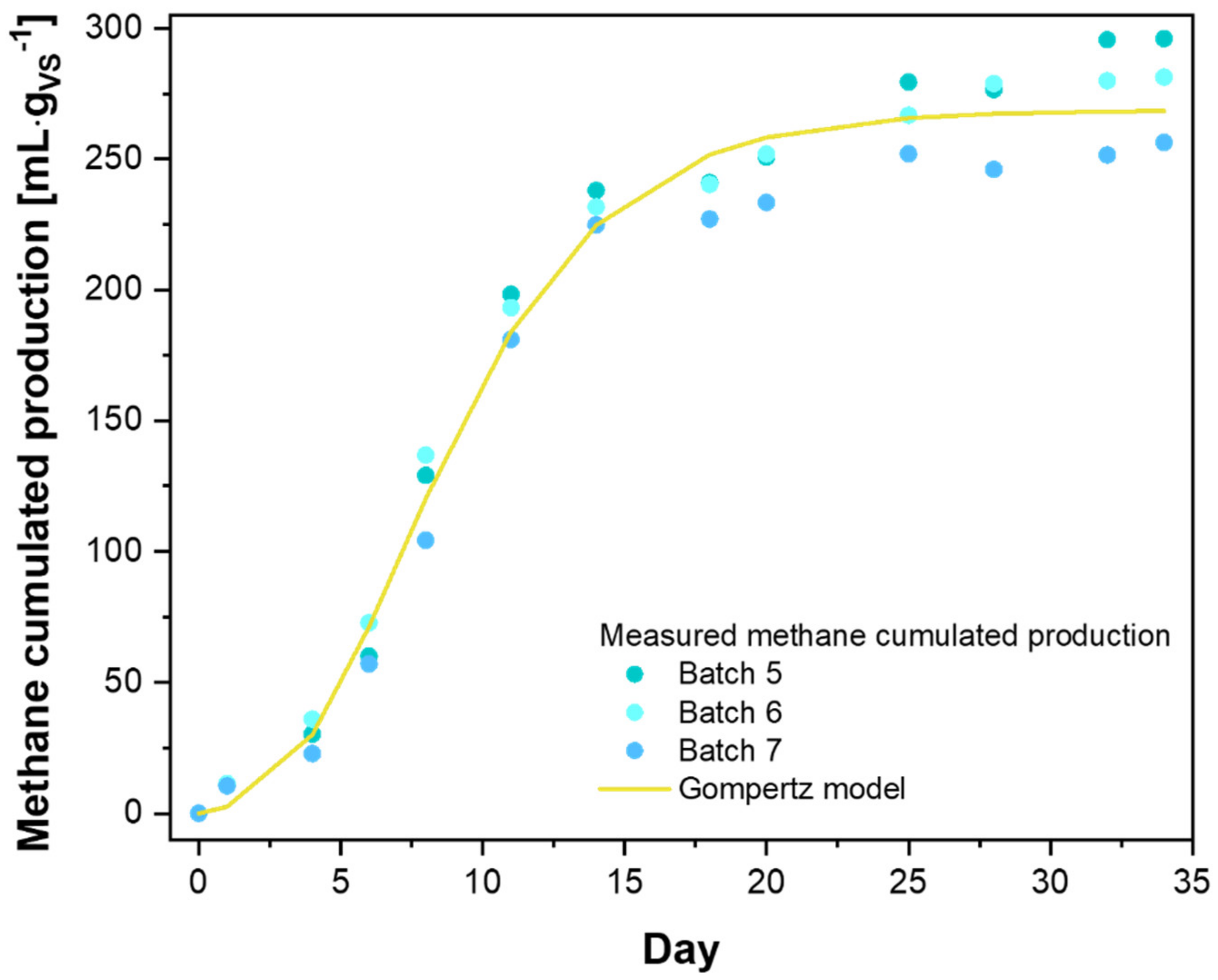
The average cumulated methane production of the substrate batches was modeled with the modified Gompertz equation (Figure 5), and the respective kinetic parameters calculated are summarized in Table 4.
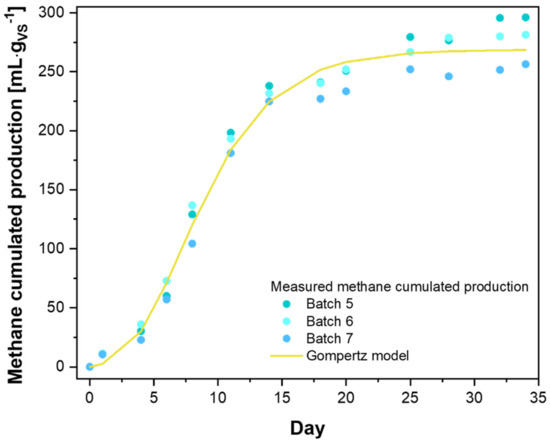
Figure 5.
Simulation of cumulated methane production by the Gompertz model.

Table 4.
Kinetic parameters of the Gompertz equation.
The BMP values of the internal controls met the UNI/TS 11703:2018 requirements of 325 ± 25% mLCH4·gVS−1 and a difference lower than 10% was found. The results support the necessary validation of the BMP test. With regard to the batches fed with SAS, batch 5 showed a slightly higher methane production than the other replicates. However, it is notable that final BMP values of the three batches were quite close to each other, indicating that the respective anaerobic processes were even. Indeed, when evaluating the processes in terms of biogas/methane generation, the digestions also performed similarly in the three replicates. In fact, after a small acclimatation period of a few days, the gas production increased faster up to the 14th day. Then, the batches continued to generate biogas/methane, albeit with a slower rate, until the 34th day when the test was stopped. Moreover, the practically identical methane contents in the biogas volumes confirmed that the anaerobic digestion processes of the three replicates proceeded with similar trends.
The Gompertz interpolating model fits the average of the experimental measurements of the three replicates (r2 > 0.99) well. The ultimate methane production at time ∞ was predicted to be 268.7 mLCH4·gVS−1 in good agreement, although it was slightly lower with the average BMP value at the end of the test. The lag phase duration, found using the Gompertz model of about 3 days, was consistent with the initial low biogas/methane production depicted in Figure 5.
Lastly, in Table 5 the chemical characteristics of the residual digestates are summarized.

Table 5.
Characterization of solid anchovy sludge digestate.
In contrast with the blanks and controls, the pH values of the mixtures of the SAS-fed reactors at the end of the experiment did not vary significantly compared to those measured at the beginning of the test (Table 5). In terms of the TS and VS content, no difference among the different assays was detected. Considering the initial total solids content of each reactor mixture, it can be noticed that in the control and tested substrate-fed reactors the solid matter was consumed by the microbial process, while in the blanks, the solid content changed to a lower extent. The ammonium content was clearly higher in the residual digestates of the reactors loaded with SAS than in the others. This was predictable since the tested substrate showed a low C/N ratio which, in the digestion process, resulted in ammonium accumulation. On the other hand, the determination of the Cl- concentration did not exhibit differences among the different digestates. The total VFAs content was slightly higher in the residual digestates of the tested substrate-fed reactors than in the other assays, while for the FOS/TAC ratios, no differences among the different assays were observed. The very low calculated FOS/TAC ratios suggest that all the organic matter was consumed by microorganisms for each reactor.
The SAS methane yield was consistent with the range observed for fish waste anaerobic digestion (200–900 mLCH4·gVS−1) reported by Ivanovs et al. [30]. Comparing only studies on the anaerobic digestion of fish oil extraction residues, the BMP of our test was lower, by far, than 742 mLCH4·gVS−1 (the residue of salmon heads enzymatically hydrolyzed in Nges et al. [27]) and 426 mLCH4·gVS−1 (residue of carp viscera thermomechanically pre-treated in Bucker et al. [28]). In these studies, as in the present one, nitrogen inhibition was not observed despite the low C/N ratios. This was probably due to the positive inoculum influence. First of all, inoculum can contribute to balancing the substrate nitrogen content, as noticed by Vivekanand et al. [47] and confirmed by Bucker et al. [28]. In the aforementioned studies, the methane yields of fish oil extraction residues were about 10% and 20% lower than those determined by raw fish waste digestion (828 and 541 mLCH4·gVS−1 in Nges et al. [27] and Bucker et al. [28], respectively). This suggests that oil extraction does not severely affect the potential use of fish waste as the substrate in anaerobic digestion. However, further research could be carried out in order to investigate other possible pre-treatments of both fish waste and oil extraction residues. Process conditions very similar to ours were reported by Eiroa et al. [26]. In their study on the anaerobic digestion of four different fish wastes, the methane yield and final TAN content were 285 mLCH4·gVS−1 and 728 mg·L−1 (both on average), respectively. Inhibition was signalized by Morales-Polo et al. [29], where the anaerobic digestion of the anchovy waste generated only 4.6 mLCH4·gVS−1 because of a distinct ammoniacal nitrogen accumulation (TAN concentration of 6.13 g·L−1).
For this reason, it is possible that co-digestion with an additional substrate that has a higher C/N would be beneficial, as already demonstrated for other N-rich substrates (e.g., manure, slaughterhouse waste) [48,49].
Moreover, the residual limonene concentration in the anaerobic mixture was found to be around 40 mg·L−1, well below the level tolerable for a stable AD [32]. However, the initial slow methane production and the peculiar production trend could be due to the adaptation of anaerobic microorganisms to the limonene presence [34].
Finally, it is interesting to highlight the potential impact of this research from a sustainable and an economic point of view. In 2018, the landings of small pelagics in the EU reached 2.06 million tonnes, with anchovies, sardines, herrings and mackerels accounting for the 43% of the total volume. In particular, in the last few years, the EU anchovy landings exceeded 135,000 tonnes, with 91% of the total coming from Spain, Portugal, Italy, Croatia and Greece [50]. Considering that the preparation of anchovy fillets generates about 40% wt. of the leftovers, the environmental benefits that have arisen from their valorization into energy, rather than a landfill disposal, are evident. Moreover, the potential methane production from the residual anchovy sludge appears to be enormous, even after the omega-3 extraction (SAS represents 97% wt. of the total leftovers amount) [18]. Finally, the digestate produced during AD could be beneficially used as amendant/fertilizer in agriculture because of the noticeable nitrogen content and the absence of undesirable compounds (e.g., heavy metals).
4. Conclusions
The full valorization of anchovy fillet processing waste requires converting the residual sludge after the extraction of fish oil rich in omega-3, vitamin D3 and zeaxanthin. In this preliminary report, we used the aforementioned anchovy sludge as a biobased substrate in anaerobic digestion aimed at producing biogas. A good methane yield of about 280 mLCH4·gVS−1 was obtained. The overall process was very stable, thus making the anchovy sludge a suitable substrate for co-digestion with other biomass wastes and residues. Indeed, taking into account the high nitrogen content of the fish waste, we also demonstrated that an optimal carbon to nitrogen ratio (C/N) is advisable in order to maximize biogas production.
Moreover, the residual limonene, used as a green extraction solvent, was found to be in a concentration (40 mg·L−1) lower than that generally reported for the inhibition of the microbial methanogenesis process.
Finally, due to the huge amount of biowaste generated every year from the landing of small pelagics in the EU, a new “blue-biorefinery” scenario can be imagined at a large- scale in the next years for Mediterranean nations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: E.P., M.P. and P.S.C.; writing—original draft preparation: E.P., F.F., R.C. and P.S.C.; writing—review and editing: M.P., P.S.C., D.M.P. and A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable. Page: 10.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Francesco Mauriello for fruitful discussion.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lucarini, M.; Zuorro, A.; Di Lena, G.; Lavecchia, R.; Durazzo, A.; Benedetti, B.; Lombardi-Boccia, G. Sustainable management of secondary raw materials from the marine food-chain: A case-study perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ido, A.; Kaneta, M. Fish oil and fish meal production from urban fisheries biomass in Japan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, Y.; Schmidt, T.G.; Kuntscher, M. Evaluation of food waste prevention measures-the use of fish products in the food service sector. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Blue Economy: 10 Years—100 Innovations—100 Million. Available online: https://www.theblueeconomy.org (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in Action; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations—FAO: New York, NY, USA, 2020; ISBN 9789251326923. [Google Scholar]
- Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda For Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 12–14. [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Our ocean, our Future: Call for Action; General Assembly Resolution; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2017; A/RES/71/3; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrò, P.S.; Gori, M.; Lubello, C. European trends in greenhouse gases emissions from integrated solid waste management. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 2125–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paone, E.; Tabanelli, T.; Mauriello, F. The rise of lignin biorefinery. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliaro, M.; Pizzone, D.M.; Scurria, A.; Lino, C.; Paone, E.; Mauriello, F.; Ciriminna, R. Sustainably Sourced Olive Polyphenols and Omega 3 Marine Lipids: A Synergy Fostering Public Health. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschmeyer, T.; Luque, R.; Selva, M. Upgrading of marine (fish and crustaceans) biowaste for high added-value molecules and bio(nano)-materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4527–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Selva, M.; Issaabadi, Z.; Luque, R. Waste-to-wealth: Biowaste valorization into valuable bio(nano)materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4791–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Li, E.; Irshad, S.; Xiong, Z.; Xiong, H.; Shahbaz, H.M.; Siddique, F. Valorization of fisheries by-products: Challenges and technical concerns to food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K. Seafood Processing By-Products: Trends and Applications; Seaf. Process; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany. [CrossRef]
- Lands, W.E.M. Fish, Omega-3 and Human Health; AOCS press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2005; ISBN 1893997812. [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Health Benefits. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 345–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pike, I.H.; Jackson, A. Fish oil: Production and use now and in the future. Lipid Technol. 2010, 22, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, R.; Scurria, A.; Avellone, G.; Pagliaro, M. A Circular Economy Approach to Fish Oil Extraction. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 5106–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, P.L.; Smith, D.P. Anaerobic wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1986, 20, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatdeenarunat, C.; Nguyen, D.; Surendra, K.C.; Shrestha, S.; Rajendran, K.; Oechsner, H.; Xie, L.; Khanal, S.K. Anaerobic biorefinery: Current status, challenges, and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaseelan, V.N. Anaerobic digestion of biomass for methane production: A review. Biomass Bioenergy 1997, 13, 83–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauser, A.; Deublein, D. Biogas from Waste and Renewables Energy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 9783527327119. [Google Scholar]
- Schievano, A.; Adani, F.; Tamone, F.; D’Imporzano, G.; Scaglia, B.; Genevini, P.L. What is the Digestate? In Anaerobic Digestion: Opportunities for Agriculture and Environment; Adani, F., Schievano, A., Boccasile, G., Eds.; University of Milan: Milan, Italy, 2009; Volume 12, pp. 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Koszel, M.; Lorencowicz, E. Agricultural Use of Biogas Digestate as a Replacement Fertilizers. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 7, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makádi, M.; Tomócsik, A.; Orosz, V. Digestate: A New Nutrient Source—Review. In Biogas; Kumar, S., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2012; Available online: http://www.intechopen.com/books/biogas/digestate-a-new-nutrient-source-r (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Eiroa, M.; Costa, J.C.; Alves, M.M.; Kennes, C.; Veiga, M.C. Evaluation of the biomethane potential of solid fish waste. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nges, I.A.; Mbatia, B.; Björnsson, L. Improved utilization of fish waste by anaerobic digestion following omega-3 fatty acids extraction. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 110, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bücker, F.; Marder, M.; Peiter, M.R.; Lehn, D.N.; Esquerdo, V.M.; Antonio de Almeida Pinto, L.; Konrad, O. Fish waste: An efficient alternative to biogas and methane production in an anaerobic mono-digestion system. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Polo, C.; Cledera-Castro, M.D.M.; Hueso-Kortekaas, K.; Revuelta-Aramburu, M. Anaerobic digestion in wastewater reactors of separated organic fractions from wholesale markets waste. Compositional and batch characterization. Energy and environmental feasibility. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanovs, K.; Spalvins, K.; Blumberga, D. Approach for modelling anaerobic digestion processes of fish waste. Energy Procedia 2018, 147, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, B.; Flotats, X. Effect of limonene on batch anaerobic digestion of citrus peel waste. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 109, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, B.; Flotats, X. Citrus essential oils and their influence on the anaerobic digestion process: An overview. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2063–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, P.S.; Pontoni, L.; Porqueddu, I.; Greco, R.; Pirozzi, F.; Malpei, F. Effect of the concentration of essential oil on orange peel waste biomethanization: Preliminary batch results. Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malara, A.; Paone, E.; Frontera, P.; Bonaccorsi, L.; Panzera, G.; Mauriello, F. Sustainable exploitation of coffee silverskin in water remediation. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, P.S.; Fazzino, F.; Folino, A.; Paone, E.; Komilis, D. Semi-Continuous Anaerobic Digestion of Orange Peel Waste: Effect of Activated Carbon Addition and Alkaline Pretreatment on the Process. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paone, E.; Beneduci, A.; Corrente, G.A.; Malara, A.; Mauriello, F. Hydrogenolysis of aromatic ethers under lignin-first conditions. Mol. Catal. 2020, 497, 111228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumina, B.; Espro, C.; Galvagno, S.; Pietropaolo, R.; Mauriello, F. Bioethanol Production from Unpretreated Cellulose under Neutral Selfsustainable Hydrolysis/Hydrogenolysis Conditions Promoted by the Heterogeneous Pd/Fe3O4 Catalyst. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federatio: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780875530130. [Google Scholar]
- Calabro, P.S.; Panzera, M.F. Biomethane production tests on ensiled orange peel waste. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2017, 35, S130–S136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliger, C.; Alves, M.; Andrade, D.; Angelidaki, I.; Astals, S.; Baier, U.; Bougrier, C.; Buffière, P.; Carballa, M.; De Wilde, V.; et al. Towards a standardization of biomethane potential tests. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso-Bravo, A.; Pérez-Elvira, S.I.; Fdz-Polanco, F. Application of simplified models for anaerobic biodegradability tests. Evaluation of pre-treatment processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebetrau, J.; Pfeiffer, D.; Thrän, D. (Eds.) Collection of Measurement Methods for Biogas—Methods to Determine Parameters for Analysis Purposes and Parameters That Describe Processes in the Biogas Sector; Series of the Funding Programme “Biomass Energy Use”; Deutsches Biomasseforschungszentrum Gemeinnützige GmbH: Leipzig, Germany, 2016; Volume 7, ISSN 2364-897X. Available online: https://www.energetische-biomassenutzung.de/fileadmin/user_upload/Downloads/Ver%C3%B6_entlichungen/07_MMS_Biogas_en_web.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Mézes, L.; Tamas, J.; Borbely, J. Novel approach of the basis of FOS/TAC method. An. Univ. Oradea Fasc. Prot. Mediu. 2011, 17, 713–718. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano-Bilbao, E.; Lozano, G.; Jiménez, S.; Jurado-Ruzafa, A.; Hardisson, A.; Rubio, C.; Weller, D.G.; Paz, S.; Gutiérrez, Á.J. Ontogenic and seasonal variations of metal content in a small pelagic fish (Trachurus picturatus) in northwestern African waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naga, S.M.; El-Maghraby, H.F.; Mahmoud, E.M.; Talaat, M.S.; Ibrhim, A.M. Preparation and characterization of highly porous ceramic scaffolds based on thermally treated fish bone. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 15010–15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekanand, V.; Mulat, D.G.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Horn, S.J. Synergistic effects of anaerobic co-digestion of whey, manure and fish ensilage. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeung, J.H.; Chung, W.J.; Chang, S.W. Evaluation of anaerobic co-digestion to enhance the efficiency of livestock manure anaerobic digestion. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayara, T.; Sánchez, A. A review on anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic wastes: Pretreatments and operational conditions. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The EU Fish Market—EUMOFA. 2020. Available online: https://www.eumofa.eu (accessed on 1 February 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).