Estimating Demand for a New Travel Mode in Boise, Idaho
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sustainable Transportation in Urban Areas
2.1. Sustainable Transportation in University Campuses
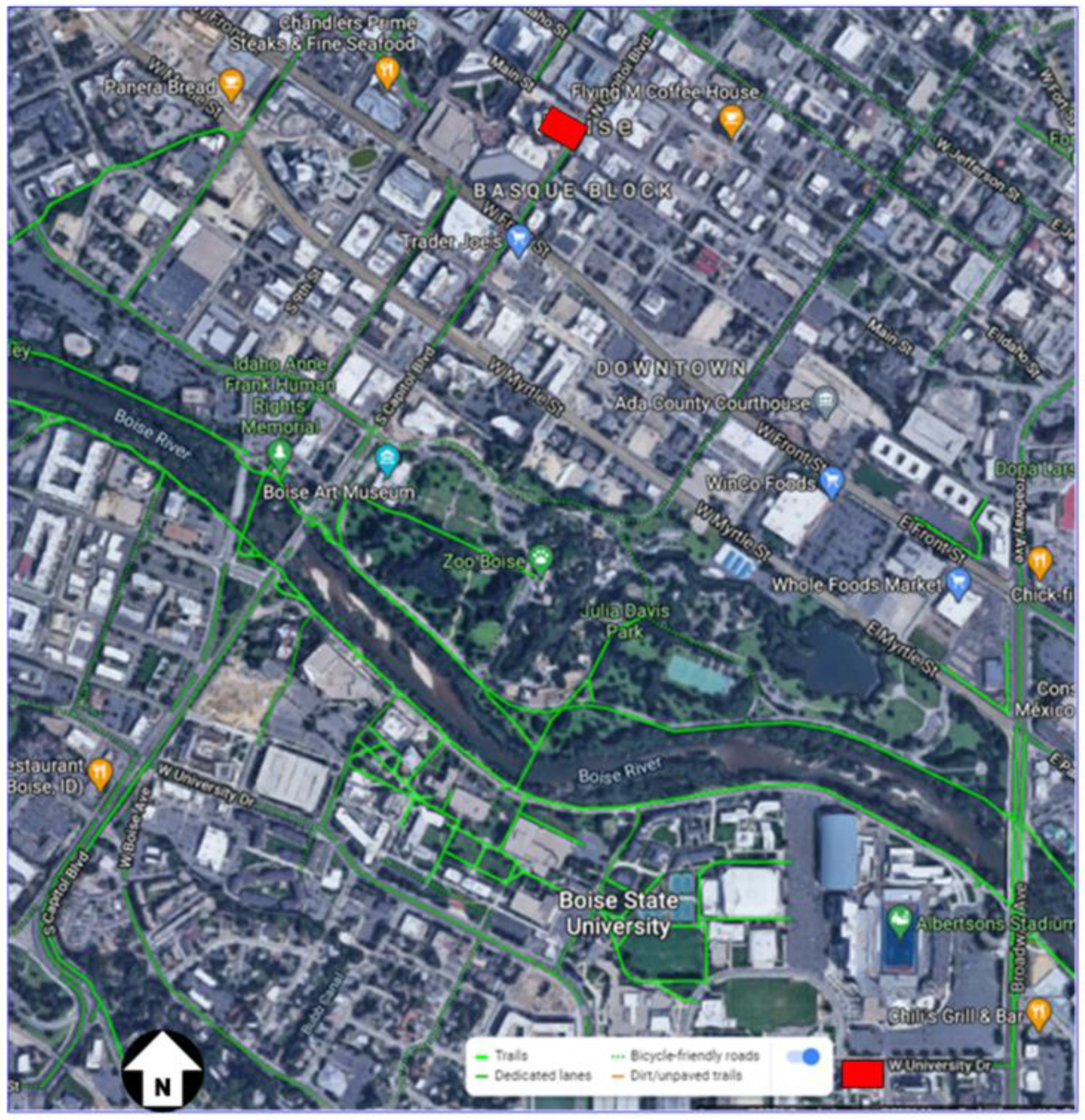
2.2. The Boise State University Case
2.2.1. Current Modes of Travel
Private Car
Shuttle Service
Other Modes
2.2.2. Search for an Alternative Mode
Aerial Tramway
Demand for the Aerial Tramway
3. Research Goal, Objectives, and Paper Structure
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Stated Preference Studies
4.1.1. SP Methods Literature Review
4.1.2. Experiment Design
4.2. Stated Preference Survey
4.2.1. Survey Questionnaire
4.2.2. The Choice Task
4.3. Theoretical Background
5. Results
5.1. Summary Measures
5.2. Statistical Models
5.2.1. The No Downtown Group
5.2.2. The Downtown Group
Model without Interaction Variables
Model with Interaction Variables
6. Discussion
6.1. Models without Interaction Variables (Table 3)
6.2. Models with Interaction Variables (Table 4)
6.3. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Survey Questionnaire
- ▪
- Q1 Dear Respondent: We are conducting a feasibility study to implement an aerial tramway system between the Boise State University campus and downtown Boise. The primary objective of this survey is to assess the willingness of students, faculty, and staff to use the proposed aerial tramway based on specific factors. The factors include efficiency of the aerial tramway, capacity of the carriers, environmental concerns, security vulnerabilities, and terminal locations. Your response will help us to gather accurate, reliable, and relevant information that will assist decision-makers in deciding whether to proceed with the implementation of the system.
- ▪
- Q2 What is your affiliation with Boise State University?
- ○
- Undergraduate student–freshman or sophomore (1)
- ○
- Undergraduate student–junior or senior (2)
- ○
- Graduate student (3)
- ○
- Staff (4)
- ○
- Faculty (5)
- ▪
- Q3 During the preceding 30 days did you travel from the BSU campus to downtown Boise?
- ○
- Yes (1)
- ○
- No (2)
- ▪
- Q4 If an Aerial Tramway were available for a trip between the campus and downtown Boise and you had to make a trip to downtown Boise, would you take the Aerial Tramway for each of the nine combinations of cost and convenience of the Aerial Tramway relative to the most likely mode of travel available to you for the trip. Drag each of the items to one of the two boxes on the right, depending on your choice.
| I would take the Aerial Tramway | I would not take the Aerial Tramway |
| ______ Costlier but more convenient (1) | ______ Costlier but more convenient (1) |
| ______ Costlier but equally convenient (2) | ______ Costlier but equally convenient (2) |
| ______ Costlier and less convenient (3) | ______ Costlier and less convenient (3) |
| ______ Same cost but more convenient (4) | ______ Same cost but more convenient (4) |
| ______ Same cost and convenience (5) | ______ Same cost and convenience (5) |
| ______ Same cost but less convenient (6) | ______ Same cost but less convenient (6) |
| ______ Less costly and more convenient (7) | ______ Less costly and more convenient (7) |
| ______ Less costly but equally convenient (8) | ______ Less costly but equally convenient (8) |
| ______ Less costly and less convenient (9) | ______ Less costly and less convenient (9) |
- ▪
- Q5 Thank you for taking the time to respond to the survey. Your participation will help us to better address the future transportation needs of our community. Go Broncos!
- ▪
- Q6 What mode of travel did you use?
- ○
- Car (1)
- ○
- Shuttle (2)
- ○
- Bicycle (3)
- ○
- Walk (4)
- ▪
- Q7 How many minutes did it take you?
- ▪
- Q8 Compared to other potential modes of travel for this trip, how do you rate your trip in terms of cost?
- ○
- More costly (1)
- ○
- About the same cost (2)
- ○
- Less costly (3)
- ▪
- Q9 Compared to other potential modes of travel for this trip, how do you rate your trip in terms of convenience?
- ○
- More convenient (1)
- ○
- About the same (2)
- ○
- More inconvenient (3)
- ▪
- Q10 If an Aerial Tramway were available for a trip between the campus and downtown Boise and you had to make a trip to downtown Boise, would you take the Aerial Tramway for each of the nine combinations of cost and convenience of the Aerial Tramway relative to your mode of travel. Drag each of the items to one of the two boxes on the right, depending on your choice.
| I would take the Aerial Tramway | I would not take the Aerial Tramway |
| ______ Costlier but more convenient (1) | ______ Costlier but more convenient (1) |
| ______ Costlier but equally convenient (2) | ______ Costlier but equally convenient (2) |
| ______ Costlier and less convenient (3) | ______ Costlier and less convenient (3) |
| ______ Same cost but more convenient (4) | ______ Same cost but more convenient (4) |
| ______ Same cost and convenience (5) | ______ Same cost and convenience (5) |
| ______ Same cost but less convenient (6) | ______ Same cost but less convenient (6) |
| ______ Less costly and more convenient (7) | ______ Less costly and more convenient (7) |
| ______ Less costly but equally convenient (8) | ______ Less costly but equally convenient (8) |
| ______ Less costly and less convenient (9) | ______ Less costly and less convenient (9) |
- ▪
- Q11 How many minutes did it take you (include the time to park your bicycle and walk to your destination)?
- ▪
- Q12 Compared to other potential modes of travel for this trip, how do you rate your trip in terms of cost?
- ○
- More costly (1)
- ○
- About the same cost (2)
- ○
- Less costly (3)
- ▪
- Q13 Compared to other potential modes of travel for this trip, how do you rate your trip in terms of convenience?
- ○
- More convenient (1)
- ○
- About the same (2)
- ○
- More inconvenient (3)
- ▪
- Q14 How many minutes did it take you (include the time to walk to your destination)?
- ▪
- Q15 Compared to other potential modes of travel for this trip, how do you rate your trip in terms of cost (consider factors like wait time)?
- ○
- More costly (1)
- ○
- About the same cost (2)
- ○
- Less costly (3)
- ▪
- Q16 Compared to other potential modes of travel for this trip, how do you rate your trip in terms of convenience (consider factors like parking, traffic congestion, etc.)?
- ○
- More convenient (1)
- ○
- About the same (2)
- ○
- More inconvenient (3)
- ▪
- Q17 How many minutes did it take you (include the time to find parking and walking to your destination)?
- ▪
- Q18 How much did you pay for parking ($)?
- ▪
- Q19 Compared to other potential modes of travel for this trip, how do you rate your trip in terms of cost?
- ○
- More costly (1)
- ○
- About the same cost (2)
- ○
- Less costly (3)
- ▪
- Q20 Compared to other potential modes of travel for this trip, how do you rate your trip in terms of convenience (consider factors like parking, traffic congestion, etc.)
- ○
- More convenient (1)
- ○
- About the same (2)
- ○
- More inconvenient (3)
References
- Poinsatte, F.; Toor, W. Finding a New Way: Campus Transportation for the 21st Century; University of Colorado at Boulder Environmental Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, D.H. Transportation sustainability on a university campus. Int. J. Sustain. High Educ. 2015, 16, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US College Towns with the Best Public Transportation: Commuting Is a Breeze at These 50 Colleges. 2021. Available online: https://www.greatvaluecolleges.net/college-towns-best-public-transportation/ (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Rose, J.; Schellong, D.; Schaetzberger, C.; Hill, J. How E-Scooters Can Win a Place in Urban Transport. 2020. Available online: https://www.bcg.com/publications/2020/e-scooters-can-win-place-in-urban-transport (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Alsaqyani, M. Feasibility of Aerial Tramway at Boise State University; Boise State University: Boise, ID, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- PTV. PTV VISSIM 11 User Manual; PTV: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2018; p. 1219. Available online: http://vision-traffic.ptvgroup.com/en-us/home/ (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- TRB. Highway Capacity Manual: A Guide for Multimodal Mobility Analysis, 6th ed.; TRB: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alshalalfah, B.; Shalaby, A.; Dale, S.; Othman, F.M.Y. Aerial ropeway transportation systems in the urban environment: State of the art. J. Transp. Eng. 2012, 138, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshalalfah, B.; Shalaby, A.; Dale, S. Experiences with Aerial Ropeway Transportation Systems in the Urban Environment. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2014, 140, 04013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J. Cable propelled transit systems—Emirates air line London. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference Automated People Movers and Transit Systems 2013: Half a Century of Automated Transit—Past, Present, and Future, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 21–24 April 2013; pp. 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshalalfah, B.; Shalaby, A.; Dale, S.; Othman, F.M.Y. Improvements and innovations in aerial ropeway transportation technologies: Observations from recent implementations. J. Transp. Eng. 2013, 139, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodship, P. The impact of an urban cable-car transport system on the spatial configuration of an informal settlement. The Case of Medellin. In Proceedings of the 10th International Space Syntax Symposium, London, UK, 13–17 July 2015; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fruehwirth, A.S.; Forte, M.A. The Return of the Cable Car to Oakland. Autom. People Mov. Autom. Transit Syst. 2016, 2016, 26–40. [Google Scholar]
- de Ortuzar, J.D.; Willumsen, L.G. Modelling Transport, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cherchi, E.; Hensher, D.A. Workshop synthesis: Stated preference surveys and experimental design, an audit of the journey so far and future research perspectives. Transp. Res. Procedia 2015, 11, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrik, O.; De Abreu e Silva, J.; Moura, F. Stated preference surveys in transport demand modeling: Disengagement of respondents. Transp. Lett. Int. J. Transp. Res. 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, B.; Cherchi, E.; Sobhani, A. Virtual immersive reality for stated preference travel behavior experiments: A case study of autonomous vehicles on urban roads. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Choudhury, C.F.; Ben-Akiva, M.; Silva, J.A.; Carvalho, D. Stated Preference Survey for New Smart Transport Modes and Services: Design, Pilot Study and New Revision. 2009. Available online: https://its.mit.edu/sites/default/files/documents/wp_trsys_2009_mar_lyang_et_al%282%29.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Rizzi, L.I.; de Ortúzar, J.D. Stated preference in the valuation of interurban road safety. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2003, 35, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, K.; Asgari, H.; Jin, X. Valuation of travel time reliability in freight transportation: A review and meta-analysis of stated preference studies. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2017, 102, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galilea, P.; de Ortúzar, J.D. Valuing noise level reductions in a residential location context. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2005, 10, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, D.; Carnegie, J.; Bilton, P. What does it take for shuttles to succeed? Comparison of stated preferences and reality of shuttle success in New Jersey. Transp. Res. Rec. 2010, 2144, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, J. Applied Logistic Regression, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Agresti, A. Catagorical Data Analysis, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
| Affiliation | No Downtown Trip | Downtown Trip | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faculty | 85 | 276 | 361 |
| Grad | 68 | 128 | 196 |
| Staff | 123 | 377 | 500 |
| UGLD | 53 | 408 | 461 |
| UGUD | 61 | 242 | 303 |
| Total | 390 | 1431 | 1821 |
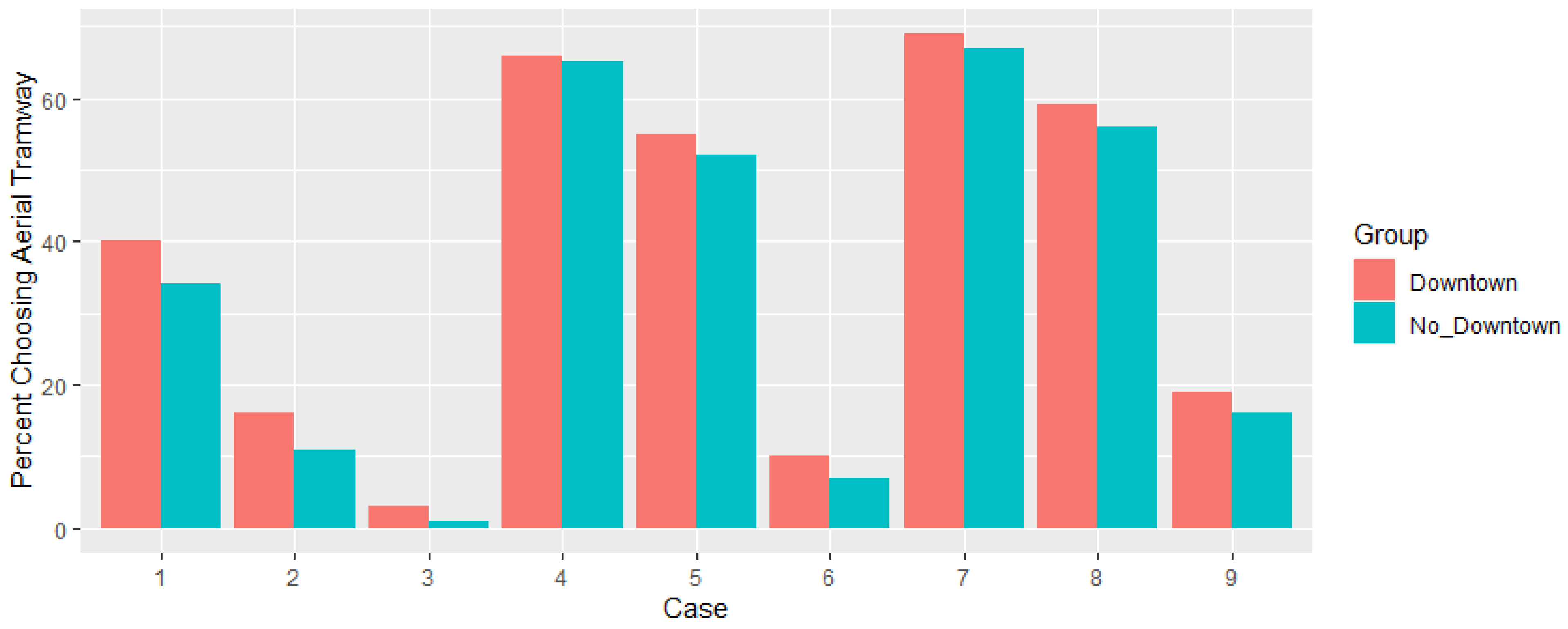
| Case | Number and Percentage Choosing Aerial Tramway | Case Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Downtown Trip | Downtown Trip | ||
| 1 | 132 (34%) | 570 (40%) | Costlier but more convenient |
| 2 | 44 (11%) | 233 (16%) | Costlier but equally convenient |
| 3 | 5 (1%) | 44 (3%) | Costlier and less convenient |
| 4 | 252 (65%) | 972 (68%) | Same cost but more convenient |
| 5 | 203 (52%) | 788 (55%) | Same cost and convenience |
| 6 | 26 (7%) | 137 (10%) | Same cost but less convenient |
| 7 | 262 (67%) | 987 (69%) | Less costly and more convenient |
| 8 | 220 (56%) | 848 (59%) | Less costly but equally convenient |
| 9 | 64 (16%) | 276 (19%) | Less costly and less convenient |
| Coefficients | Estimate | Odds Ratio | Std. Error | z. Value | Pr...z.. | Sign. Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | −0.70 | 0.50 | 0.099 | −7.06 | 1.63E-12 | *** |
| cost_convcase2 | −1.25 | 0.29 | 0.091 | −13.74 | 5.59E-43 | *** |
| cost_convcase3 | −3.07 | 0.05 | 0.163 | −18.85 | 3.07E-79 | *** |
| cost_convcase4 | 1.12 | 3.06 | 0.080 | 14.00 | 1.57E-44 | *** |
| cost_convcase5 | 0.64 | 1.89 | 0.078 | 8.23 | 1.80E-16 | *** |
| cost_convcase6 | −1.88 | 0.15 | 0.106 | −17.68 | 6.50E-70 | *** |
| cost_convcase7 | 1.28 | 3.58 | 0.081 | 15.69 | 1.66E-55 | *** |
| cost_convcase8 | 0.82 | 2.26 | 0.078 | 10.46 | 1.35E-25 | *** |
| cost_convcase9 | −1.05 | 0.35 | 0.087 | −12.00 | 3.74E-33 | *** |
| RoleGrad | 0.25 | 1.29 | 0.088 | 2.86 | 4.22E-03 | ** |
| RoleStaff | 0.16 | 1.17 | 0.065 | 2.40 | 1.65E-02 | * |
| RoleUGLD | 0.07 | 1.07 | 0.064 | 1.07 | 2.83E-01 | |
| RoleUGUD | 0.19 | 1.21 | 0.072 | 2.65 | 7.98E-03 | ** |
| ModeCar | 0.07 | 1.07 | 0.076 | 0.88 | 3.76E-01 | |
| ModeShuttle | 0.10 | 1.10 | 0.095 | 1.01 | 3.12E-01 | |
| ModeWalk | −0.20 | 0.81 | 0.091 | −2.25 | 2.48E-02 | * |
| Travel_time | 0.01 | 1.01 | 0.003 | 4.79 | 1.66E-06 | *** |
| Coefficient | Estimate | Odds Ratio | Std. Error | z. Value | Pr...z.. | Sign. Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | −1.06 | 0.35 | 0.14 | −7.48 | 7.65E-14 | *** |
| cost_convcaseY2 | −1.25 | 0.29 | 0.09 | −13.79 | 3.03E-43 | *** |
| cost_convcaseY3 | −3.08 | 0.05 | 0.16 | −18.90 | 1.09E-79 | *** |
| cost_convcaseY4 | 1.13 | 3.09 | 0.08 | 14.06 | 6.90E-45 | *** |
| cost_convcaseY5 | 0.64 | 1.90 | 0.08 | 8.27 | 1.35E-16 | *** |
| cost_convcaseY6 | −1.89 | 0.15 | 0.11 | −17.73 | 2.52E-70 | *** |
| cost_convcaseY7 | 1.29 | 3.62 | 0.08 | 15.76 | 6.00E-56 | *** |
| cost_convcaseY8 | 0.82 | 2.28 | 0.08 | 10.50 | 8.47E-26 | *** |
| cost_convcaseY9 | −1.05 | 0.35 | 0.09 | −12.04 | 2.31E-33 | *** |
| RoleGrad | 0.63 | 1.87 | 0.25 | 2.51 | 1.21E-02 | * |
| RoleStaff | −0.05 | 0.95 | 0.21 | −0.26 | 7.95E-01 | |
| RoleUGLD | 0.91 | 2.49 | 0.19 | 4.87 | 1.11E-06 | *** |
| RoleUGUD | 1.16 | 3.19 | 0.22 | 5.16 | 2.47E-07 | *** |
| ModeCar | 0.61 | 1.84 | 0.14 | 4.26 | 2.01E-05 | *** |
| ModeShuttle | 0.46 | 1.59 | 0.21 | 2.19 | 2.85E-02 | * |
| ModeWalk | −0.16 | 0.85 | 0.18 | −0.89 | 3.72E-01 | |
| Travel_time | 0.01 | 1.01 | 0.00 | 4.68 | 2.82E-06 | *** |
| RoleGrad:ModeCar | −0.69 | 0.50 | 0.27 | −2.52 | 1.17E-02 | * |
| RoleStaff:ModeCar | 0.06 | 1.07 | 0.23 | 0.28 | 7.79E-01 | |
| RoleUGLD:ModeCar | −1.10 | 0.33 | 0.21 | −5.33 | 9.90E-08 | *** |
| RoleUGUD:ModeCar | −1.23 | 0.29 | 0.24 | −5.07 | 3.95E-07 | *** |
| RoleGrad:ModeShuttle | −0.12 | 0.88 | 0.37 | −0.33 | 7.38E-01 | |
| RoleStaff:ModeShuttle | 0.21 | 1.24 | 0.29 | 0.74 | 4.61E-01 | |
| RoleUGLD:ModeShuttle | −0.83 | 0.44 | 0.27 | −3.02 | 2.51E-03 | ** |
| RoleUGUD:ModeShuttle | −1.19 | 0.30 | 0.32 | −3.71 | 2.07E-04 | *** |
| RoleGrad:ModeWalk | 0.45 | 1.56 | 0.36 | 1.26 | 2.09E-01 | |
| RoleStaff:ModeWalk | 0.65 | 1.91 | 0.27 | 2.35 | 1.86E-02 | * |
| RoleUGLD:ModeWalk | −0.57 | 0.56 | 0.24 | −2.38 | 1.71E-02 | * |
| RoleUGUD:ModeWalk | −0.44 | 0.64 | 0.30 | −1.49 | 1.37E-01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khanal, M. Estimating Demand for a New Travel Mode in Boise, Idaho. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031209
Khanal M. Estimating Demand for a New Travel Mode in Boise, Idaho. Sustainability. 2021; 13(3):1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031209
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhanal, Mandar. 2021. "Estimating Demand for a New Travel Mode in Boise, Idaho" Sustainability 13, no. 3: 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031209
APA StyleKhanal, M. (2021). Estimating Demand for a New Travel Mode in Boise, Idaho. Sustainability, 13(3), 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031209





